Abstract
After a coal mine is closed, the coal rock mass could undergo weathering deterioration and strength reduction due to factors such as stress and groundwater, which in turn changes the stress and bearing capacity of the fractured rock mass in the abandoned goaf, leading to secondary or multiple surface deformations in the goaf. Currently, the spatiotemporal evolution pattern of the surface deformation of closed mines remains unclear, and there is no integrated monitoring and prediction model for closed mines. Therefore, this study proposed to construct an integrated monitoring and prediction model for closed mines using small baseline subset (SBAS) interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) and a deep learning-based long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network algorithm to achieve evolution pattern and dynamic prediction of spatiotemporal surface deformation of closed mines. Taking a closed mine in the western part of Xuzhou, China, as an example, based on Sentinel-1A SAR data between 21 December 2015, and 11 January 2021, SBAS InSAR technology was used to obtain the spatiotemporal evolution pattern of the surface during the 5 years after mine closure. The results showed that the ground surface subsided in the early stage of mine closure and then uplifted. In 5 years, the maximum subsidence rate in the study area is −43 mm/a, and the cumulative maximum subsidence is 310 mm; the maximum uplift rate is 29 mm/a, and the cumulative maximum uplift is 135 mm. Moreover, the maximum tilt and curvature are 3.5 mm/m and 0.19 mm/m2, respectively, which are beyond the safety thresholds of buildings; thus, continuous monitoring is necessary. Based on the evolution pattern of surface deformation, the surface deformation prediction model was proposed by integrating SBAS InSAR and an LSTM neural network. The experiment results showed that the LSTM neural network can accurately predict the deformation trend, with a maximum root mean square error (RMSE) of 5.1 mm. Finally, the relationship between the residual surface deformation and time after mine closure was analyzed, and the mechanisms of surface subsidence and uplift were discussed, which provide a theoretical reference for better understanding the surface deformation process of closed mines and the prevention of surface deformation.
1. Introduction
Coal is the world’s main basic energy and important raw material and has great strategic significance for the development of an economy. In recent years, to address climatic and ecological changes and achieve a carbon peak and carbon neutrality, many mines have been closed around the world. Statistics show approximately 500,000 closed mines in the United States by 1993 [1], 50,000 in Australia by July 2011 [2], and 100,000 in the United Kingdom before the early 20th century [3]. According to the annual report issued by the China Coal Industry Association, China has closed 5500 mines and withdrew 1 billion tons of coal production capacity per year between 2016 and 2020 alone [4].
After mine closure, the coal rock mass could undergo weathering deterioration and strength reduction due to various factors, such as stress and groundwater, which changes the stress and bearing capacity of the fractured rock mass in the abandoned goaf, leading to secondary or multiple surface deformations. Since the deformation evolution is long-term and concealed, it poses a potential threat to the safety of surface buildings. In northern France, surface subsidence continues to occur in a mining area more than 20 years after the mine closure [5]. In a Belgian coal mine, the ground surface has uplifted 220 mm during the 20 years since the mine closure [6]. In an abandoned mining area in southwest Poland, residual deformation continues to be noticeable 15 years after the mine closure [7]. For the room-and-pillar mines in the United States, due to pillar failures, the ground experiences sudden subsidence, causing damage to buildings [8]. In addition, earthquakes and groundwater cause the surrounding rock and coal pillars to collapse in the brown coal mines in Miyagi and Iwate prefectures, Japan, leading to ground collapse [9]. Therefore, an effective, integrated monitoring and prediction model should be established for closed mines to protect nearby property and the surrounding environment.
Traditional methods, such as global positioning system (GPS) and leveling measurements, have high accuracy, yet they have disadvantages, such as high cost, heavy workload, and incomplete monitoring [10]. In addition, the methods are not able to retrospectively obtain evolution data of deformations that have occurred. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) technology has great advantages compared to the traditional methods, such as all-weather, high-precision, and large-scale coverage [11,12]. Traditional InSAR technology is prone to influences of temporal and spatial baselines. The most recent advanced InSAR technology can analyze time-series SAR images and extract high-coherence points for mathematical modeling to obtain deformation time series data. For instance, permanent scatterers InSAR (PS InSAR) [13,14] and small baseline subsets InSAR (SBAS InSAR) [15] can not only suppress the influence of spatiotemporal decorrelation and atmospheric noise in the interferogram but also achieve millimeter-level or even submillimeter-level monitoring accuracy, which provide new methods for surface deformation monitoring in mining areas [16,17,18]. Based on 10 Envisat satellite images, Zhao et al. [19] used the SBAS InSAR technology to monitor the surface deformation of the Datong mining area in Shanxi, China, and found that the surface deformation was caused jointly by mining, groundwater extraction, and the construction of a new economic zone. Fan et al. [20] used temporally coherent point InSAR (TCP InSAR) to monitor the surface subsidence of the Yuyang mining area in Shaanxi, China, and found that the maximum subsidence rate is 162 mm/a and the cumulative subsidence is 86 mm. In addition, based on 56 Sentinel-1A images, Dang et al. [21] used the PS InSAR technology to monitor the surface subsidence between 2015 and 2019 caused by underground mining in Quang Ninh, Vietnam, and found that the average subsidence rate reached 14.5 mm/a.
Most existing studies have focused on surface deformation monitoring during mining, while few studies have been performed on the deformation after mine closure. Thus, the surface deformation characteristics after mine closure remain unclear. In addition, in existing studies, the InSAR technology is only used as a data acquisition method for surface subsidence monitoring, and an integrated monitoring-prediction model is lacking. In fact, monitoring and prediction are inseparable in the prevention of geological disasters in mines. Only by integrating mine subsidence monitoring and prediction can the surface deformation and the future deformation characteristics be understood in time to provide a reasonable basis for the decision-making of the mine management.
With the rapid development of artificial intelligence (AI), deep learning methods have been widely used in computer vision [22], machine translation [23], and language recognition [24]. The deep learning network is a multilayer perceptron that contains multiple hidden layers. A deep nonlinear network structure is obtained through sample learning to achieve the approximation of complex functions. For complex data, deep learning can achieve distributed data representation by combining low-level features and abstracting high-level features, thereby illustrating the essential data characteristics. The deep learning technology provides a new solution for surface deformation prediction in mining areas. Typical neural networks mainly include back-propagation (BP) neural networks [25] and recurrent neural networks (RNN) [26], but a weak predictor such as BP neural network which is frequently trapped in a local minimum and the problem of vanishing gradient is faced by RNN. Long short-term memory (LSTM) [27] is an advanced RNN, a sequential network, that allows information to persist. It is capable of handling the vanishing gradient problem faced by RNN.
Therefore, this study used SBAS InSAR and an LSTM neural network algorithm to build an integrated monitoring and prediction model for closed mines. Specifically, the SBAS InSAR technology was used to obtain the temporal and spatial evolution of the ground surface after the mine closure. Then, based on the SBAS InSAR deformation time series data, the LSTM neural network was used to construct a dynamic prediction model for surface deformation. Finally, the accuracy of the prediction results was assessed, and the surface deformation mechanism was analyzed. The study results provide the evolution pattern and dynamic prediction of spatiotemporal surface deformation of closed mines and corresponding surface deformation mechanism, which can help better understand the surface deformation process of closed mines and the prevention of surface deformation.
2. Methods
2.1. Principles of SBAS InSAR
Assuming that N + 1 SAR images are arranged in time series t0, t1, …, tn, one of the master images is selected to register the other images. Based on the spatiotemporal baseline threshold, interferometric pairs are combined to obtain M multilook differential interferograms. The value of M satisfies the following condition [15]:
For the K-th differential interferogram generated at , the interferometric phase value of any pixel (x, r) is the following:
In Equation (2), we have implicitly assumed that the phase signal is unwrapped and the topographic phase component is removed. (x, r) are the coordinates of the pixel in the azimuth and range directions. are the deformation phase values at relative to t0. λ is the radar wavelength, and d and are the deformations in the line of sight (LOS) relative to the initial moment t0.
In all interferograms, the master image sequence in chronological order is , the slave image sequence in chronological order is , and , k = 1, 2, …, M. Then, the observation equation of the phase composition of the interferogram is the following:
where is the k-th differential interferometric phase, and are the deformation phases of the master image IEK and slave image ISK at time t, respectively.
From Equation (1), there are a total of M interferometric pairs. Hence, Equation (3) can be rewritten as follows:
where A is an M × N coefficient matrix, the coefficient of the master image is 1, the coefficient of the slave image is −1, and the values of remaining images are 0. is the phase matrix to be obtained. is the phase matrix of the differential interferogram. Taking the image value obtained at t0 as the reference, there are N unknowns in Equation (4).
When the rank of matrix A is N, and M ≥ N, the least-squares method can be used to calculate the optimal estimated value of Equation (4), as follows:
If the matrix A is rank deficient, that is, M < N, is a singular matrix. The singular value decomposition method can be used to find the minimum norm solution, and then the surface deformation in the LOS direction can be obtained.
According to field observations, there was no obvious horizontal movement of the land surface, the deformation in the LOS direction can be directly projected to the vertical direction without considering the horizontal displacement [28], as follows:
where W is the land vertical displacement, is the deformation in the LOS direction, and θ is the incident angle of the satellite.
2.2. Principles of LSTM
The LSTM network is an improved RNN, which effectively solves the problem of gradient explosion or vanishing gradient in traditional RNNs due to their inability to transmit long-term information [29,30]. LSTM introduces the cell state to store the current state information and transmits the information to the next LSTM unit at the next moment. In addition, a gating mechanism is introduced, that is, the input gate, forget gate, and output gate are used to control the path of information transmission. First, the input gate determines the information added to the cell state to generate a new state. Then, the forget gate determines the information discarded from the cell state. Finally, the output gate determines the output value [31]. The gates in the LSTM network are controlled by a nonlinear activation function, whose value is between (0, 1), indicating the proportion of information that is allowed to pass through [32]. The equations are as follows:
where i, f, and o are the input gate, forget gate, and output gate, respectively, are the corresponding weight matrices, respectively, and are the corresponding bias matrices, respectively. is the external state at the previous moment, and σ is the sigmoid function.
Figure 1 shows the structure of the LSTM recurrent unit. The calculation process is as follows: (i) calculate three “gates” and candidate state based on the external state at the previous moment and the input at the current moment; (ii) update the memory unit based on the forget gate and the input gate ; (iii) based on the output gate , transfer the internal state information to the external state and output after the external state is processed through the activation function. The calculation equations are as follows:
where are the corresponding weight matrices. are the corresponding bias matrices. is the external state at the current moment. is the output at the current moment. are sigmoid and hyperbolic tangent functions, respectively.
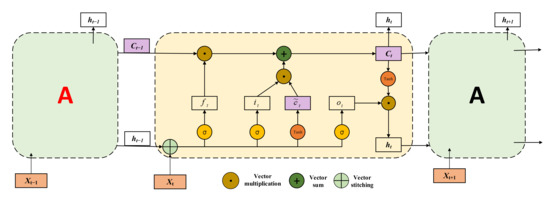
Figure 1.
Structure of the LSTM recurrent unit. The red A is the cell state at the previous moment Xt−1, the black A represents the cell state at the next moment Xt+1, and the middle cell is the cell state at the current moment Xt.
2.3. Time Series Prediction Model Combining SBAS InSAR Monitoring Results and LSTM
A series of time-related discrete data is obtained through SBAS InSAR technology. According to the principle of time series analysis, the discrete data constitute a nonlinear time series , where n represents the number of items being monitored. In subsidence prediction using LSTM, the key is to reconstruct the data and establish the functional relationship between the observation data and the subsequent data. To predict the surface deformation data , the previous observations can be used as the training data to construct a function , where , and P is the dimension of the input space vector. The prediction model is composed of four parts, i.e., data preprocessing, network training, model testing and parameter optimization, and output of prediction results. The specific steps are as follows:
Step 1: Data preprocessing. Perform cubic spline interpolation on the deformation monitoring data obtained by SBAS InSAR to transform the deformation data into a time series of equal time interval . Then, the interpolated time series is normalized using the standard deviation normalization method, and the dataset is obtained.
Step 2: Network training. Assuming that there are R sample points, the first S points are used as the training set , the remaining R-S samples are used as the test set, and the input and output of the training set Ytr can be expressed as follows:
The Adam optimization algorithm [33] is used to update the network weights, and the model parameters are initialized, including the number of iterations, the number of hidden units, the learning rate, and the number of hidden layers. Next, the training set is taken as the input to the fully connected layer. Then, the loss function image is used to determine the rationality of the initial parameters.
Step 3: Model testing and parameter optimization. In the test, 90% of the samples are used as the training set and the remaining 10% are used as the test set. The parameters that have a large impact on the performance of the model, i.e., the number of iterations, the number of hidden units, the learning rate, and the number of hidden layers are selected for optimization. Orthogonal experiments are designed to optimize the parameters of the LSTM model [17,34].
Step 4: Output of prediction results. Based on the optimal parameters obtained in Step 3, the surface deformation is predicted, and the prediction result is output. Figure 2 shows the flowchart of the integrated monitoring–prediction model proposed in this study.

Figure 2.
Flowchart of the integrated SBAS InSAR-LSTM model.
3. Case Study
3.1. Study Area
Xuzhou is located in the northwest of Jiangsu Province, China (Figure 3a). Xuzhou has a history of coal mining for more than 120 years, with the highest annual coal output reaching approximately 25 million tons. While coal mining has brought considerable economic benefits to Xuzhou, it has also caused approximately 23,333 hectares of land to collapse, resulting in the relocation of villages and towns, abandonment of crop fields, damage to infrastructure, and deterioration of the ecological environment. Under the influence of multiple factors, such as coal resource exhaustion and the overcapacity reduction policy, many coal mines in Xuzhou have been closed in rapid succession. In this case, the study area includes three mines: the Jiahe Mine, the Zhangxiaolou Mine, and the Pangzhuang Mine (Figure 3b). The Zhangxiaolou Mine is approximately 5.0 km from east to west and approximately 3.4 km from north to south and was closed in December 2015. The Jiahe Mine is approximately 5.5 km from east to west and 4.5 km from north to south and was closed in December 2015. The Pangzhuang Mine is approximately 6.1 km from east to west and 3 km from north to south and was closed in December 2012. The total area is approximately 60 km2. Fan et al. [35] used the InSAR technology and probability integration method to obtain the surface deformation pattern during coal mining in the area. Unfortunately, Fan et al. did not monitor the surface deformation after the mine closures. Zheng et al. [36] performed surface deformation monitoring in the area using the Stanford Method for Persistent Scatterers (StaMPS) technique. However, only the deformation in the LOS direction was obtained, which cannot fully reflect the surface deformation characteristics. Moreover, Zheng et al. did not include a prediction of surface deformation in the area. Therefore, this study attempted to use SBAS InSAR technology to obtain the multidimensional spatiotemporal evolution data of the land surface after the mine closures. Then, based on the deformation time series data, the LSTM neural network was used to construct an integrated surface deformation monitoring/prediction model.
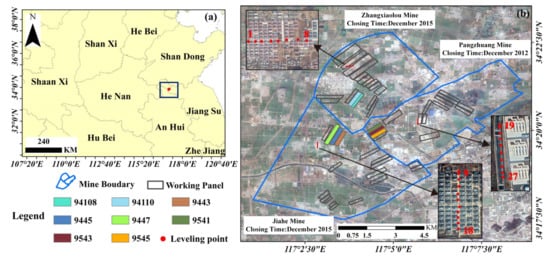
Figure 3.
Study area. (a) Location of the study area, (b) distribution of the working panels. The quadrilaterals of different colors represent different working panels. The blue line is the mine boundary, and the red dots are second-order leveling monitoring points.
3.2. Data
This study collected 135 SAR images between 21 December 2015, and 11 January 2021, in the study area. The imaging mode is Interferometric Wide (IW) swath, the polarization mode is VV, and the incident angle is approximately 39.5°. The spatial resolutions of the images in the range and azimuth directions are 5 m and 20 m, respectively. The specific parameters are shown in Table 1. The date in bold in Table 1 is the acquisition time of the common master image. The revisit time of most Sentinel-1A SAR images is 12 days; some images with a revisit time longer than 12 days are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
SAR image parameters.
In addition, the digital elevation model (DEM) data used in this study are the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 1 data from National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), with a spatial resolution of 30 m × 30 m (http://gdex.cr.usgs.gov/gdex/ (accessed on 20 October 2021))). The orbit data are the precise orbital ephemeris data provided by the European Space Agency (ESA, https://s1qc.asf.alaska.edu/aux_poeorb/ (accessed on 20 January 2022))), and the positioning accuracy is within 5 cm. External DEM data and precision orbit data were used to eliminate terrain errors and orbit errors, respectively.
The vertical baseline and temporal baseline thresholds used for interferometric pair combinations are 200 m and 72 days, respectively, and 581 available interferometric pairs were generated. Figure 4 shows the distribution of the interferometric pairs. First, differential interferometry was performed on the 581 interferometric pairs to obtain the differential interferograms. Then, the minimum cost flow method [37] was used to perform phase unwrapping, and control points with stable land surfaces were selected for orbit refinement and re-elimination of curved earth phase trend. Finally, a spatial-temporal filtering operation was used to mitigate the effect of atmospheric artifacts, and the SVD method [38] was used to calculate the average annual deformation rate (Figure 5).

Figure 4.
SAR image spatiotemporal baseline diagram. The red dot is the common master image, and the green dots are the slave images.
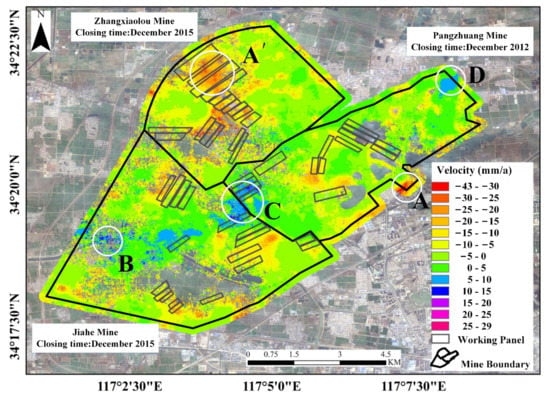
Figure 5.
Average annual deformation rate in the LOS direction between 21 December 2015, and 11 January 2021.
3.3. Analysis of Deformation Monitoring Results
Figure 5 shows that between 21 December 2015, and 11 January 2021, the maximum surface subsidence rate in the study area is −43 mm/a, as indicated by the white circle A at the southeast corner of the Pangzhuang Mine, and the maximum uplift rate is 29 mm/a, as indicated by the white circle B in the southwest part of the Jiahe Mine. The main uplift area is located at the junction of the Jiahe Mine and the Pangzhuang Mine (white circle C). Additionally, surface uplift is observed in the white circle D in the northeast corner of the Pangzhuang Mine. Figure 5 shows that surface subsidence is dominant in the mining area, and the uplift is only found in a small area, which might be related to the short closure time. In addition, there is severe subsidence in the northwestern part of the Zhangxiaolou Mine, which is related to the time of closure and the mining intensity (white circle A′).
To quantify the pattern of surface deformation after mine closure, time-dimension integration was performed on the deformation rate to obtain the cumulative surface deformation in each mine (Figure 6). As the overall surface deformation in the study area is relatively small, the image time interval used in this study was set to approximately 150 days, and 12 cumulative deformation maps were obtained. Figure 6a shows that within 150 days (from 21 December 2015 to 23 May 2016) of mine closure, area E in the northwest of the Jiahe Mine starts to subside, the land surface maintains good stability in the Zhangxiaolou Mine, and area A in the southeast part of the Pangzhuang Mine experiences subsidence. On 11 January 2021 (Figure 6l), the maximum cumulative subsidence at the southeast parts of the Pangzhuang Mine, the Jiahe Mine, and the Zhangxiaolou Mine are −310 mm, −281 mm, and −164 mm, respectively. It is worth noting that beginning 12 August 2016 (Figure 6d), the area D in the northwest corner of the Pangzhuang Mine, and area C at the junction of the Jiahe Mine and the Pangzhuang Mine start to rise, and the maximum uplift reaches 41 mm and 135 mm on 11 January 2021 (Figure 6l).

Figure 6.
Vertical deformation time series between 21 December 2015 and 11 January 2021. A represents the maximum surface subsidence rate area at the Pangzhuang Mine, C is the main uplift area at the junction of the Jiahe Mine and the Pangzhuang Mine, D represents the surface uplift area at the Pangzhuang Mine, E area starts to subside within 150 days (from 21 December 2015 to 23 May 2016) of mine closure at the Jiahe Mine.
The residual surface deformation after the mine closure mainly includes vertical displacement and deformation (e.g., subsidence, uplift, tilt, and curvature displacement) and horizontal displacement and deformation. According to field observations, there was no obvious horizontal movement of the land surface. Therefore, only the impact of tilt and curvature displacement on surface buildings was evaluated. To obtain the continuous deformation field of tilt and curvature, the vertical deformation field in Figure 6 was interpolated, and then the tilt and curvature value of each point was calculated according to the mining subsidence theory [39] (Figure 7 and Figure 8), as follows:
where is the tilt between points 2 and 3 (mm/m). are the subsidence at points 2 and 3, respectively. is the horizontal distance between points 2 and 3 (m).

Figure 7.
Distribution of tilt in each mine between 21 December 2015 and 11 January 2021. Red stars represent the points that need to be focused on.

Figure 8.
Distribution of curvature in each mine between 21 December 2015, and 11 January 2021.
Since the curvature is the first derivative of the tilt, the curvature is as follows:
where is the curvature of the surface points 2, 3, and 4 (mm/m2). is the average tilt between points 3 and 4 (mm/m). is the horizontal distance between points 3 and 4 (m).
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show that the curvature and tilt of each mine increase with time. Between 21 December 2015, and 6 August 2018, the curvature and tilt of each mine are within the allowable range in the ground deformation (i = 3 mm/m, K = 0.2 mm/m2) [40], indicating that the surface is in a stable state. Between 11 December 2015 and 11 November 2018, the tilt of an area in the Jiahe Mine exceeds 3 mm/m, as indicated by the red star in Figure 7g; areas with similar tilt were not found in the other two mines. Between 21 December 2015 and 3 July 2021, the tilt of an area in the Zhangxiaolou Mine exceeds 3 mm/m, as indicated by the red stars in Figure 7k,l. Figure 8 indicates that from 21 December 2015 to 11 January 2021, the curvature deformation value of each mining area was lower than 0.2 mm/m2, indicating that it is currently in a relatively stable state. In order to ensure the safety of surface buildings, it is necessary to continue monitoring.
Next, the maximum surface deformation points between 24 December 2015 and 11 January 2021, were extracted from Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8 to analyze the dynamic deformation pattern (Figure 9a–f). Figure 9a shows that the maximum uplift point of the Zhangxiaolou Mine first subsides and then elevates rapidly. The uplift increase slows after 26 July 2017, and the maximum uplift reaches 96 mm. In comparison, the uplifts in the Jiahe Mine and the Pangzhuang Mine are more stable, and the maximum uplifts are 135 mm and 104 mm, respectively. As shown in Figure 9b, before 2 April 2017, the surface subsidence rate in the Jiahe Mine is high, while after 2 April 2017, the subsidence rate slows, and the maximum subsidence is −295 mm. In the Zhangxiaolou Mine and the Pangzhuang Mine, the subsidence is continuous, although the rate slows after 2020; the maximum subsidence values are −275 mm and −258 mm, respectively. The results indicate that the land surface tends to stabilize over time after the mine closure, and there is no longer any violent deformation.

Figure 9.
Time series results at the maximum deformation points of each mine. (a) Maximum uplift, (b) maximum subsidence, (c,d) maximum tilt, and (e,f) maximum curvature. The dotted line represents the turning points of deformation trend.
Figure 9c,d show the maximum tilt curves of each mine. The tilt of all three mines changes slowly in the beginning. Since the beginning 15 January 2018, the tilt deformation accelerates. After 16 April 2019, the tilt curve becomes stable. The maximum tilts of the Jiahe Mine, the Zhangxiaolou Mine, and the Pangzhuang Mine are 3.2 mm/m, 3.5 mm/m, and −2.9 mm/m, respectively. The maximum tilt curve shows that the uneven surface deformation after the mine closure causes a tilt greater than the allowable range specified in the ground deformation. Thus, continuous monitoring is required to prevent the occurrence of hazardous events. Figure 9e,f show the maximum curvature of each mine. The maximum curvatures of the Jiahe Mine, the Zhangxiaolou Mine, and the Pangzhuang Mine are 0.18 mm/m2, 0.19 mm/m2, and 0.17 mm/m2, respectively. The change in the curvature is similar to that of the tilt curve, and the maximum curvature is within the allowable deformation range, indicating a relatively stable state.
3.4. Data Accuracy Verification
To verify the reliability of the SBAS InSAR method, cross-validation was performed using the PS InSAR method. Figure 10a is the annual average deformation rate in the LOS direction obtained by PS InSAR. Figure 10a shows that the range of the average annual deformation rate in the PS InSAR method is −41 mm/a to −32 mm/a, and that of SBAS InSAR is −43 mm/a to −29 mm/a. The maximum difference between the two methods is 3 mm/a, suggesting a good consistency. In addition, 13,544 common points were selected on the deformation maps of the two methods, and the results of numerical fitting are shown in Figure 10b. Figure 10b shows that the root mean square error (RMSE) between SBAS InSAR and PS InSAR is 1.4 mm/a, and the correlation coefficient is 0.81, indicating a high degree of consistency. In terms of the density of monitoring points, SBAS InSAR is superior to PS InSAR.

Figure 10.
(a) PS InSAR average annual deformation rate in LOS direction between 21 December 2015 and 11 January 2021, (b) fitting of 13,544 common points of the deformation rate obtained by PS InSAR and SBAS InSAR.
To further verify the accuracy of the SBAS InSAR results, the LOS deformation obtained by SBAS InSAR was converted to vertical subsidence, and the subsidence at the leveling points in Figure 3 were compared with the leveling data. Figure 11a shows that the leveling data and SBAS InSAR monitoring results are consistent in terms of the deformation trend, and the maximum absolute error is 1.2 mm. Figure 11b shows that the correlation coefficient between the leveling data and the InSAR fitting result is 0.91, and the corresponding RMSE is 0.3 mm. The above results suggest that the accuracy of the SBAS InSAR results can meet actual requirements.

Figure 11.
Comparison between SBAS InSAR results and leveling data. (a) Comparison of different periods: 18 November 2020, through 18 December 2020, and 18 December 2020, through 11 January 2021, (b) fitting of SBAS InSAR results and leveling data. Note that leveling data was collected by Trimble DiNi03 electronic level with an accuracy of ±0.3 mm per kilometer round trip.
3.5. Subsidence Prediction Based on SBAS InSAR Results
From SBAS InSAR, deformation data were obtained in 135 periods between 24 December 2015, and 11 January 2021. Since the time interval of certain images is not 12 days, the cubic spline interpolation method [41] was used during data preprocessing to obtain data in 155 periods. The first 90% of the deformation data (from 21 December 2015 to 3 July 2020) were used as the training dataset, and the remaining 10% (from 15 July 2020 to 11 January 2021) were taken as the test dataset.
Orthogonal tests [17,34] were designed to obtain the optimal parameters of the LSTM neural network, including the number of iterations, the number of hidden units, the learning rate, and the number of hidden layers. The orthogonal table was designed as L16 (44), that is, there are four types of influencing factors (the number of iterations, the number of hidden units, the learning rate, and the number of hidden layers), and four levels for each factor (A, B, C, and D). The specific parameter settings are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Factors and levels used in the orthogonal test design.
Thirty discrete points were randomly selected for the orthogonal tests. To verify the accuracy of the model and eliminate random errors, the average of multiple tests was used as the final result. The 16 parameter combinations are shown in Table 3. Based on the average RMSE of the model prediction results and the running time, combination number 12 was determined to be the optimal combination, specifically, the number of iterations is 100, the hidden unit is 200, the learning rate is 0.0025, and the number of hidden layers is 2.

Table 3.
Optimal parameter combination obtained in the orthogonal test. Bold fonts represent the selected optimal parameters.
Based on the optimal parameter combination, all vertical deformation points in Figure 6 (258,029 points) were extracted, and the LSTM neural network was used for deformation prediction. The prediction step is 12 days, and the prediction for 15 periods (from 27 July 2020 to 11 January 2021) was obtained. A prediction diagram was plotted every 36 days, and the results are shown in Figure 12a–e. The LSTM neural network can accurately predict the deformation trend, with a small error (the maximum RMSE is 5.1 mm). To compare the reliability of different prediction methods, the LSTM was compared with the BP neural network and the support vector regression (SVR) [42] prediction algorithm. Figure 12f–j show the prediction results of the BP neural network and Figure 12k–o show the prediction results of SVR algorithm. Figure 12f–o show that both the BP and SVR algorithms can accurately predict the deformation trend. However, the prediction error of BP increases over time, and the RMSE increases from 6.7 mm to 15.3 mm; the prediction error of SVR also increases with time, but its performance is better than BP, and the maximum RMSE is 10.5 mm. Compared with BP and SVR, the results of LSTM are the best, and the RMSE is only 5.1 mm, which is close to that of SBAS InSAR. LSTM can avoid large fluctuations in the prediction results of some points, and the result is robust. Thus, LSTM can meet the requirement of long-term time-series predictions.

Figure 12.
Comparison of different prediction models. (a–e) Prediction results of LSTM; (f–j) prediction results of BP; (k–o) prediction results of SVR. The time points for the above predictions are 20 August 2020, 25 September 2020, 31 October 2020, 6 December 2020, and 11 January 2021.
Figure 13a–l show the residual error of different prediction models. Figure 13a–e show the prediction residual error of the LSTM neural network, Figure 13f–j show the prediction residual error of the BP neural network, and Figure 13k–o show the prediction residual error of the SVR algorithm. The prediction residual errors of BP and SVR are relatively large, and the maximum residual errors are 116 mm and 127 mm, respectively. In comparison, the overall residual error of the LSTM neural network is small; its maximum residual error is 54 mm.

Figure 13.
Residual errors of different models. (a–e) Residual errors of LSTM; (f–j) residual errors of BP; (k–o) residual errors of SVR. The time points for the above predictions are 20 August 2020, 25 September 2020, 31 October 2020, 6 December 2020, and 11 January 2021.
4. Discussion
To study the relationship between the residual deformation and time after mine closure, the #9541, #9543, and #9545 working panels in the Pangzhuang Mine, the #9443, #9445, and #9447 working panels in the Jiahe Mine, and the #94110 and #94108 working panels in the Zhangxiaolou Mine in Figure 3 were selected. The mine closure time and geological conditions of each working panel are shown in Table 4. The maximum uplift or maximum subsidence of each working panel were obtained, and the residual deformation over time was calculated, as shown in Figure 14. The maximum residual uplift in the working panels in the Pangzhuang Mine is in a power function relationship with time and the #9541, #9543, and #9545 working panels are in the stage of continuous uplift and have not reached stability yet (Figure 14a–c). Hence, continuous monitoring is needed. The maximum residual subsidence of the #94110 and #94108 working panels in the Zhangxiaolou Mine is a logarithmic relationship with time (Figure 14d–h). The maximum residual deformation of the #9443, #9445, and #9447 working panels in the Jiahe Mine is a logarithmic relationship with time in the subsidence stage, but a power function relationship in the uplift stage (Figure 14e–g). Based on the mine closure time, the #94110 and #94108 working panels in the Zhangxiaolou Mine experience subsidence during the six-year period between mine closure and 2021; the #9541, #9543, and #9545 working panels in the Jiahe Mine are elevated between 24 December 2015, and 11 January 2021; the #9443, #9445, and #9447 working panels in the Pangzhuang Mine are in a subsidence state during the 8.8 years, 10.7 years, and 8.9 years after the mine closure day (24 December 2015), respectively, and there is an uplift trend.

Table 4.
Mining termination time and geological conditions of each working panel.

Figure 14.
The relationship between cumulative subsidence or uplift of each working panel and the mining termination time. (a–c) The relationship between cumulative uplift and mining termination time, (d–h) the relationship between cumulative subsidence and mining termination time, and (e–g) the relationship between first subsidence and uplift and mining termination time.
The above analysis shows that the land surfaces above the working panels experience a changing process from subsidence to uplift after the mine closure. The mechanism of this process can be explained as follows: Due to coal mining activities, the overlying strata can be divided into caving zone, fractured zone, and continuous bending zone [39,43,44] from bottom to top (Figure 15a). The gaps between rocks in the caving zone are relatively large, which is conducive to the passage of water and sediment. The stratum in the fractured zone is connected, which easily leads to water diversion and accumulation. The bent zone has an overall layered structure and generally can be isolated from water. In the initial stage after mine closure, due to the influence of the overlying strata and gravity, the caving zone and fractured zone are compressed until a force equilibrium is reached. During this process, the land surface could subside (Figure 15a,b). The underground drainage facility is withdrawn after the mine closure, resulting in an increase in the groundwater level that causes the increase in the pore pressure of the fractured rock mass and the decrease in effective stress. As a result, the fractured rock mass could rebound, causing deformation and expansion of solid particles, i.e., an increase in the volume of the rock mass, thus, the land surface uplifts (Figure 15c).
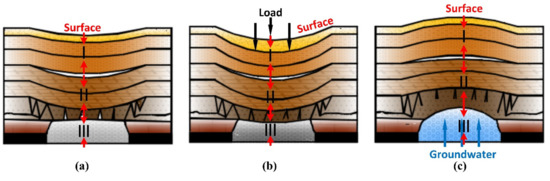
Figure 15.
Schematic diagram of changes in overlying strata and surface. I, II, and III are the bent zone, fractured zone, and caving zone, respectively. (a) The original condition of the three zones formed by coal mining, (b) changes in the overlying strata and the surface under load, (c) changes in the overlying strata and the surface under the influence of groundwater.
5. Conclusions
This study constructed an integrated monitoring and prediction model for the closed mine area based on SBAS InSAR and a deep learning-based LSTM neural network. The proposed model can obtain the spatiotemporal evolution pattern and deformation characteristics of the land surface after the mine closure; additionally, the proposed model can predict the future deformation trends and pattern of the surface. This study solves the problems as follows: (i) surface deformation characteristics and mechanisms after mine closure remain unclear, and (ii) there is no integrated monitoring and prediction model for closed mines.
Taking three closed mines in the western part of Xuzhou, China, as an example, based on 135 Sentinel-1A SAR data between 21 December 2015, and 11 January 2021, the SBAS InSAR technology was used to obtain the spatiotemporal evolution of the land surface within 5 years after mine closure. The results showed that the land surface subsides in the early stage after the mine closure, and then uplifts in the later stage. In the 5 years after mine closure, the maximum subsidence rate is −43 mm/a and the cumulative maximum subsidence is −310 mm; the maximum uplift rate is 29 mm/a and the cumulative maximum uplift is 135 mm. The maximum tilt and curvature are 3.5 mm/m and 0.19 mm/m2, respectively. The tilt in some areas exceeds the safety threshold of buildings, indicating that the surface deformation may damage the buildings and structures on the surface; therefore, continuous monitoring is necessary.
A surface deformation prediction model was proposed by integrating SBAS InSAR results with an LSTM neural network. The results showed that the LSTM neural network can accurately predict the deformation trend, and the overall error is small, with a maximum RMSE of 5.1 mm. Finally, the relationship between the residual deformation and time after mine closure was analyzed, and the mechanisms of the subsidence and uplift were discussed. The results provide theoretical references for understanding the process of surface deformation and for prevention and control of surface deformation after mine closure.
This study only focused on the closed longwall mining areas, without considering the influence of other mining methods on surface deformation. In addition, only one type of SAR data was used in this study. Different mining methods and different geological mining conditions and the fusion of SAR data of different wavebands and different resolutions are the focuses of subsequent research.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.C., X.Z. and Z.L.; methodology, X.Z. and Z.L.; software, H.Y.; validation, H.Y., L.Q. and J.Y.; formal analysis, H.Y.; investigation, J.K. and Y.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, H.Y. and B.C.; writing—review and editing, B.C., X.Z. and Z.L.; visualization, H.Y.; supervision, B.C., X.Z. and Z.L.; project administration, B.C. and Z.L.; funding acquisition, B.C., X.Z., J.K., Y.Y. and Z.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (reference numbers 52074133, 41901303 and 41907240), Key Laboratory of Land Satellite Remote Sensing Application, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People’s Republic of China (reference number KLSMNR-202203), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (reference number 2019M663601), the Key Research and Development Program of Xuzhou (Social Development, reference number KC20180), the Shaanxi Province Science and Technology Innovation team (reference number 2021TD-51), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (reference numbers 300102260301 and 300102261108), and by the European Space Agency through the ESA-MOST DRAGON-5 project (reference number 59339), the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX20_2362).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to confidentiality.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the provision of the Sentinel-1 data by ESA and DEM data by NASA.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fields, S. The earth’s open wounds: Abandoned and orphaned mines. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, A154–A161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unger, C.; Lechner, A.M.; Glenn, V.; Edraki, M.; Mulligan, D.R. Mapping and Prioritising Rehabilitation of Abandoned Mines in Australia. In Proceedings of the Life of Mine 2012, Maximising Mine Rehabilitation Outcomes, AusIMM/CMLR, Brisbane, Australia, 2012; The Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (AusIMM): Carlton North, VIC, Australia, 2012; pp. 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Inventory of Closed Mining Waste Facilities (Updated January 2014). Available online: http://publications.environment-agency.gov.uk/ (accessed on 20 November 2017).
- Yan, L. How to transform abandoned coal mines into new ones? China Coal J. 2021, 8, 5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guéguen, Y.; Deffontaines, B.; Fruneau, B.; Al Heib, M.; de Michele, M.; Raucoules, D.; Guise, Y.; Planchenault, J. Monitoring residual mining subsidence of Nord/Pas-de-Calais coal basin from differential and Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (Northern France). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca, M.C.; Hooper, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F. Surface deformation induced by water influx in the abandoned coal mines in Limburg, The Netherlands observed by satellite radar interferometry. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 88, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blachowski, J.; Kopeć, A.; Milczarek, W.; Owczarz, K. Evolution of Secondary Deformations Captured by Satellite Radar Interferometry: Case Study of an Abandoned Coal Basin in SW Poland. Sustainability 2019, 11, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zipf, R.K.; Mark, C. Design methods to control violent pillar failures in room-and-pillar mines. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sect. A-Min. Ind. 1997, 106, A124–A132. [Google Scholar]
- Aydan, O. Crustal stress changes and characteristics of damage to geo-engineering structures induced by the Great East Japan Earthquake of 2011. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2015, 74, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Hao, M. Large-scale deformation monitoring in mining area by D-InSAR and 3D laser scanning technology integration. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2013, 23, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, K.G.; Richard, M.G.; Howard, A.Z. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Galloway, D.; Bell, J.W.; Zebker, H.A.; Laczniak, R.J. Sensing the ups and downs of Las Vegas: InSAR reveals structural control of land subsidence and aquifer-system deformation. Geology 1999, 27, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Fairbairn, D.; Kang, J.; Hu, J.; Liang, L. Three-dimensional time-varying large surface displacements in coal exploiting areas revealed through integration of SAR pixel offset measurements and mining subsidence model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Mei, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, H. Retrieving Three-Dimensional Large Surface Displacements in Coal Mining Areas by Combining SAR Pixel Offset Measurements with an Improved Mining Subsidence Model. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Deng, K.; Fan, H.; Yu, Y. Combining SAR interferometric phase and intensity information for monitoring of large gradient deformation in coal mining area. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 48, 701–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, C.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Zou, W. Integration of MODIS data and Short Baseline Subset (SBAS) technique for land subsidence monitoring in Datong, China. J. Geodyn. 2011, 52, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Xu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Du, S. Using temporarily coherent point interferometric synthetic aperture radar for land subsidence monitoring in a mining region of western China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 26003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.K.; Nguyen, T.D.; Dao, N.H.; Duong, T.L.; Dinh, X.V.; Weber, C. Land subsidence induced by underground coal mining at Quang Ninh, Vietnam: Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar observation using Sentinel-1 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3563–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, N.; Yan, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Shen, C. Multi-label learning based deep transfer neural network for facial attribute classification. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 80, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcheggiani, D.; Titov, I. Encoding Sentences with Graph Convolutional Networks for Semantic Role Labeling. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–11 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.-R.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N.; et al. Deep Neural Networks for Acoustic Modeling in Speech Recognition: The Shared Views of Four Research Groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D.E.; Hinton, G.E.; Williams, R.J. Learning representations by back-propagating errors. Nature 1986, 323, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelenbe, E. Learning in the Recurrent Random Neural Network. Neural Comput. 1993, 5, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysis; Kluwer Academic: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Continual Prediction Using LSTM with Forget Gates; Springer: London, UK, 1999; pp. 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Gradient Flow in Recurrent Nets: The Difficulty of Learning Long-Term Dependencies; Wiley-IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, X.; Niu, Y. Hourly day-ahead solar irradiance prediction using weather forecasts by LSTM. Energy 2018, 148, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Cao, H. Prediction for Tourism Flow based on LSTM Neural Network. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 129, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi, G. Off-line and on-line quality control systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Quality, Tokyo, Japan, 6–12 September 1978; Volume 4, pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.D.; Cheng, D.; Deng, K.Z.; Chen, B.Q.; Zhu, C.G. Subsidence monitoring using D-InSAR and probability integral prediction modelling in deep mining areas. Surv. Rev. 2015, 47, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, H.; Deng, K.; Du, S.; Wang, L. Analysis of Pre- and Post-Mine Closure Surface Deformations in Western Xuzhou Coalfield From 2006 to 2018. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 124158–124172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Loan, C. Matrix Computations: Matrix Computations; The Johns Hopkins University Press: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1996; pp. 49–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kratzsch, H. Mining Subsidence Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; pp. 62–89. [Google Scholar]
- State Bureau of Coal Industry. Regulations of Coal Pillar Design and Extraction for Buildings, Water Bodies Railways, Main Shafts and Roadways; Coal e Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- McKinley, S.; Levine, M. Cubic spline interpolation. Coll. Redw. 1998, 45, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palchik, V. Formation of fractured zones in overburden due to longwall mining. Environ. Earth Sci. 2003, 44, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.S.; Ma, W.M.; Zhong, W.L. Surface Subsidence Engineering; Society for Mining Metallurgy: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).