Internal Geometric Quality Improvement of Optical Remote Sensing Satellite Images with Image Reorientation
Abstract
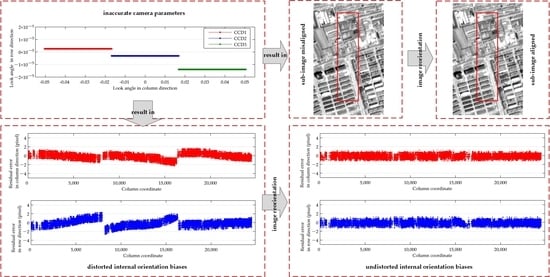
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Sensor Orientation Model
2.2. External Orientation Model
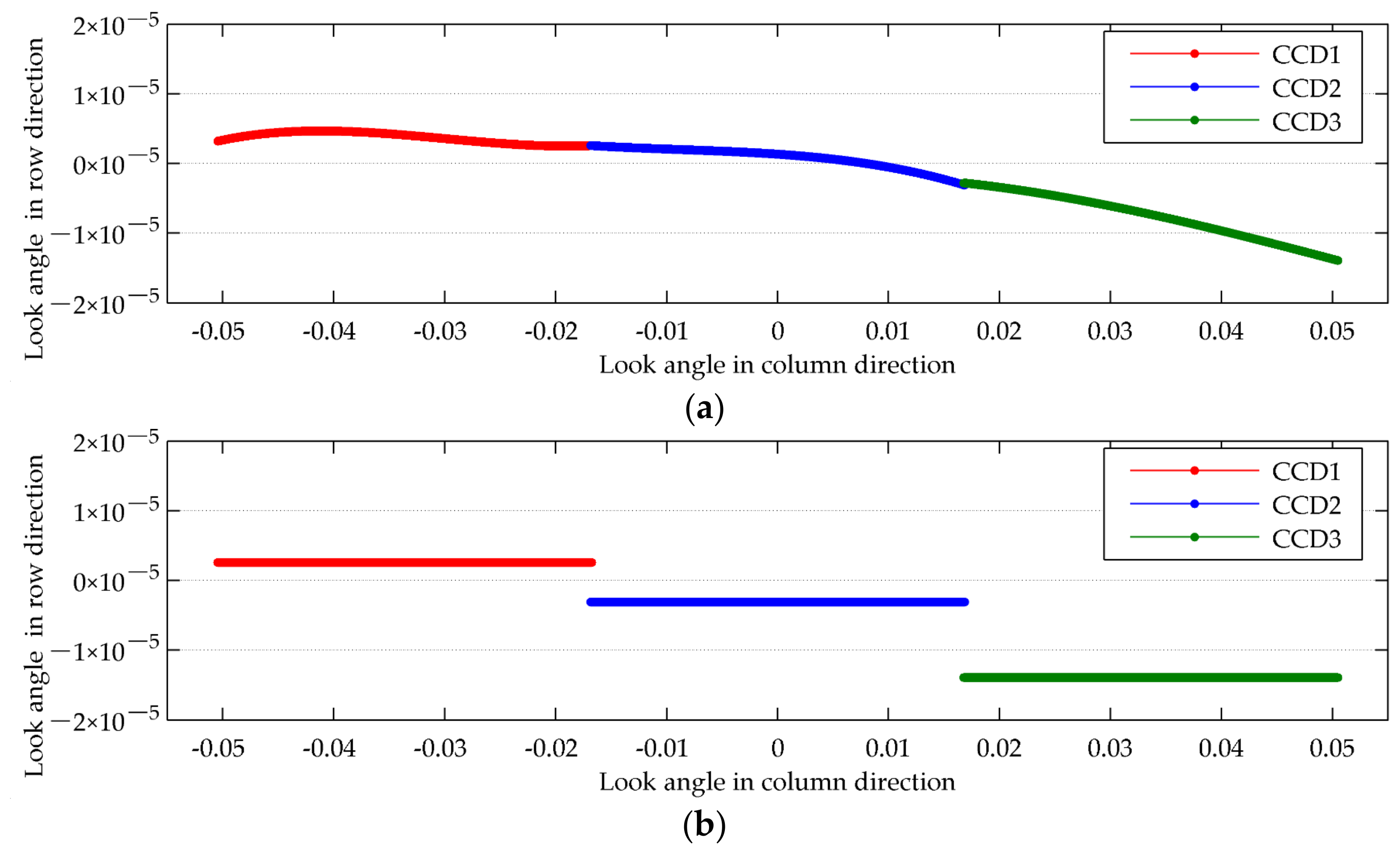
2.3. Internal Orientation Model
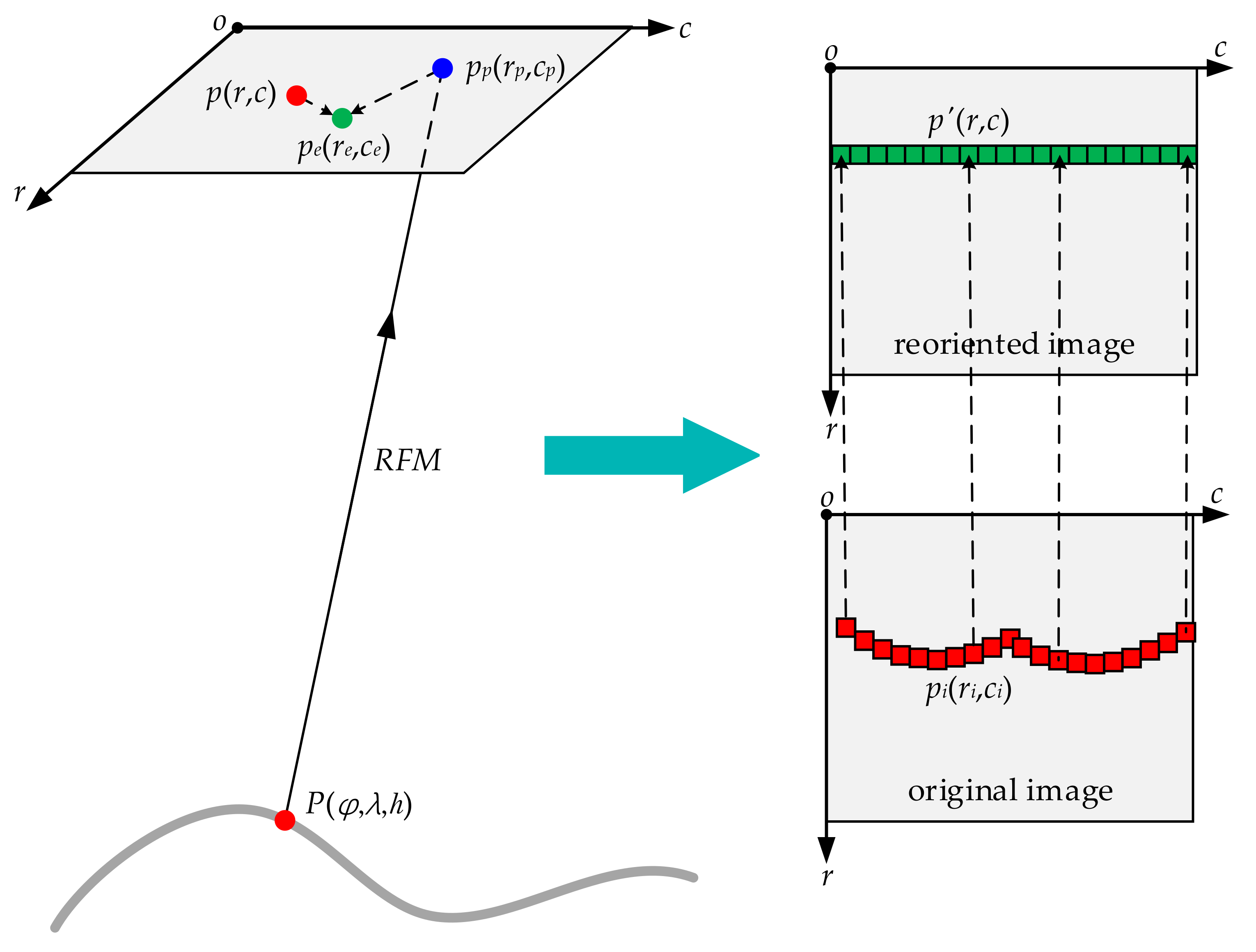
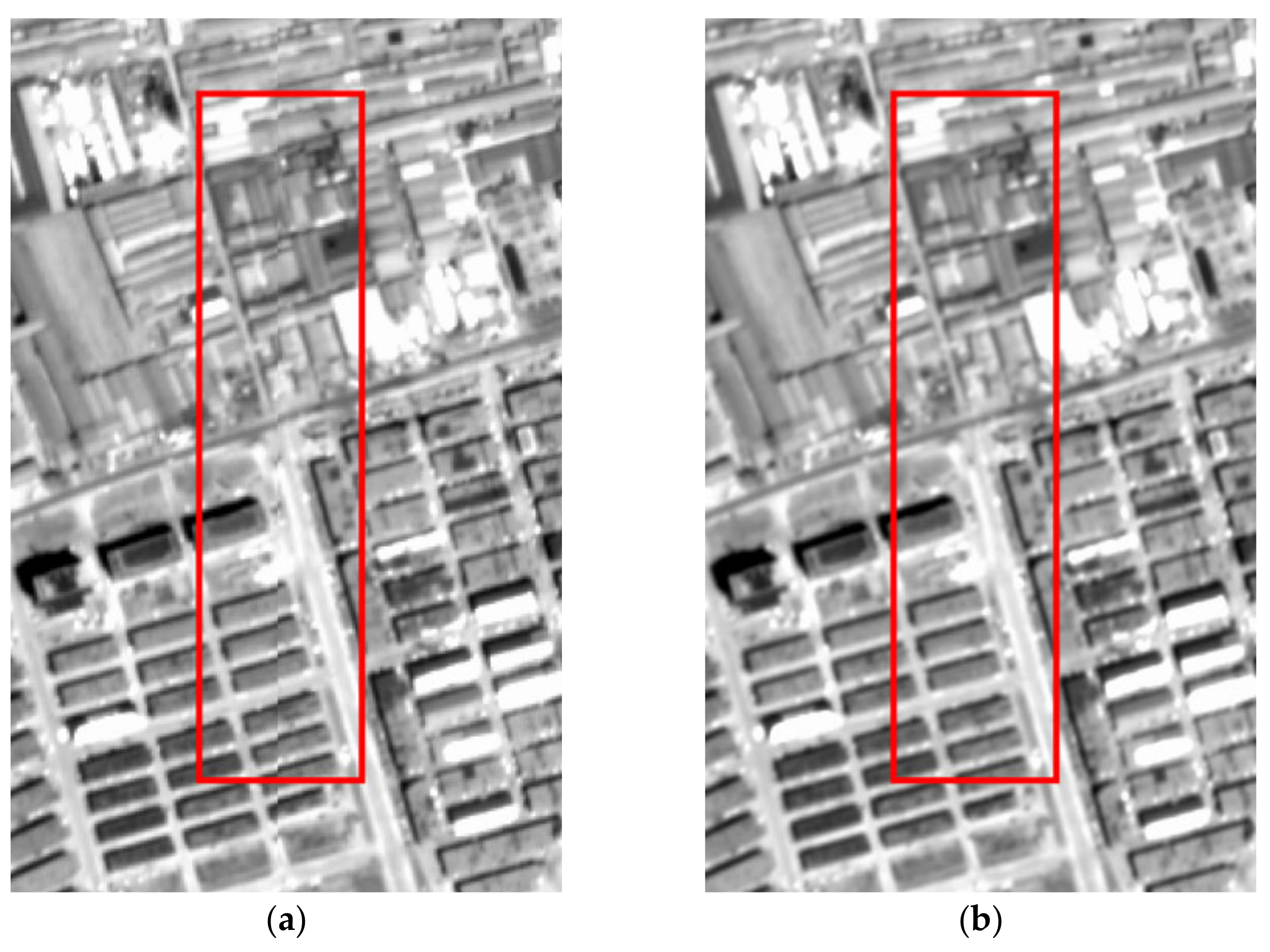
2.4. Image Reorientation
- Dense GCPs in an original image are automatically extracted from the reference DOMs and DEMs by image matching.
- Each ground point p(φ, λ, h) is projected onto the image according to Equation (4), and a projected image point pp(rp, cp) is obtained. With the point pp(rp, cp) and the corresponding point p(r, c), the EO model parameters in Equation (3) are estimated according to the least squares adjustment method.
- With the estimated EO model parameters, EO bias compensation of each projected image point pp(rp, cp) is performed, and an EO-bias-compensated image point pe(re, ce) is obtained. With the point pe(re, ce) and the corresponding point p(r, c), the IO model parameters in Equation (5) are estimated.
- With the estimated IO model parameters, IO bias compensation of each image point p′(r, c) in a reoriented image is performed, and an IO-bias-compensated image point pi(ri, ci) is obtained. According to the image-space coordinates (ri, ci), a grey value is resampled from the original image and assigned to the image point p′(r, c).
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Experimental Datasets
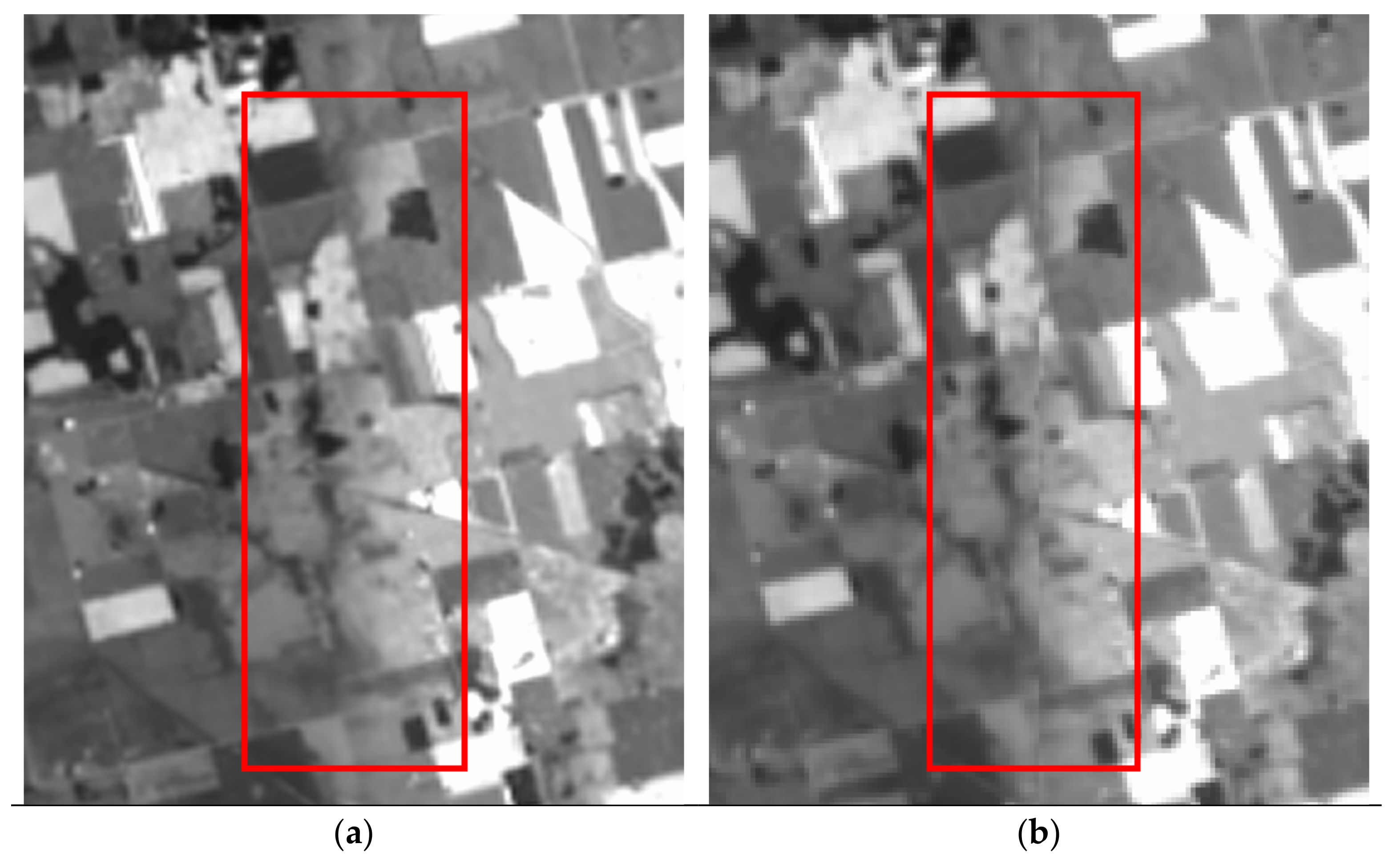
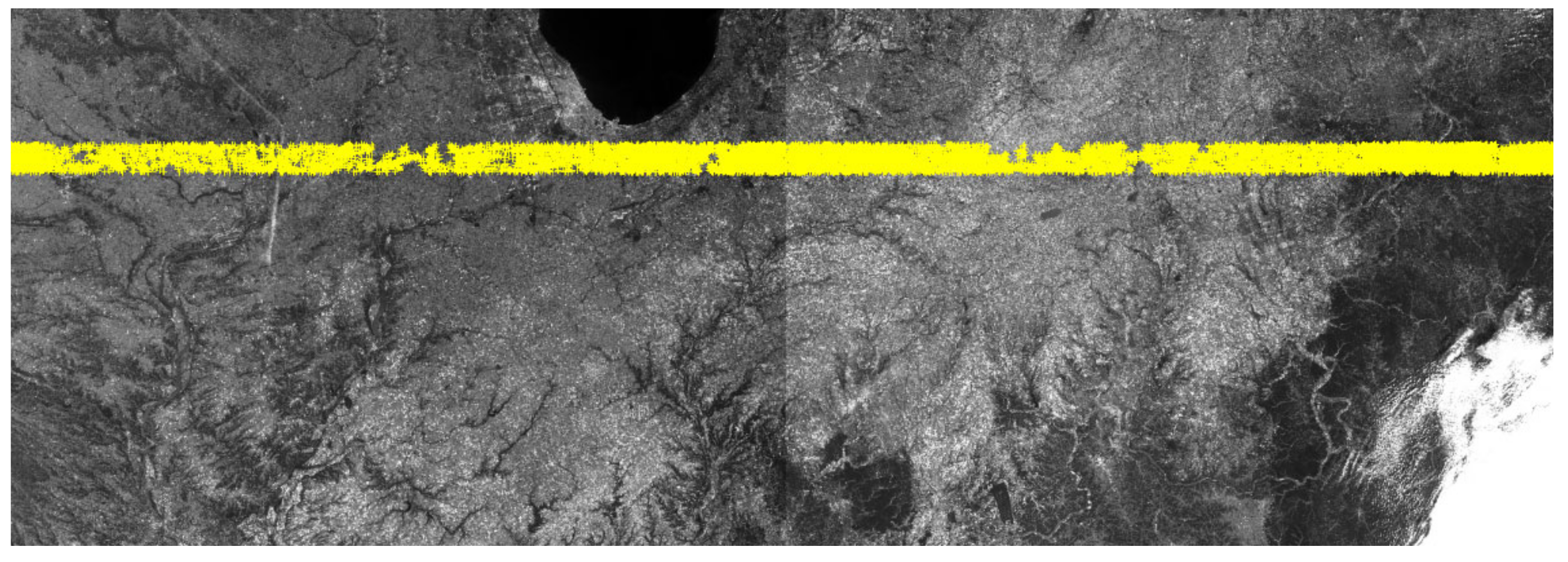
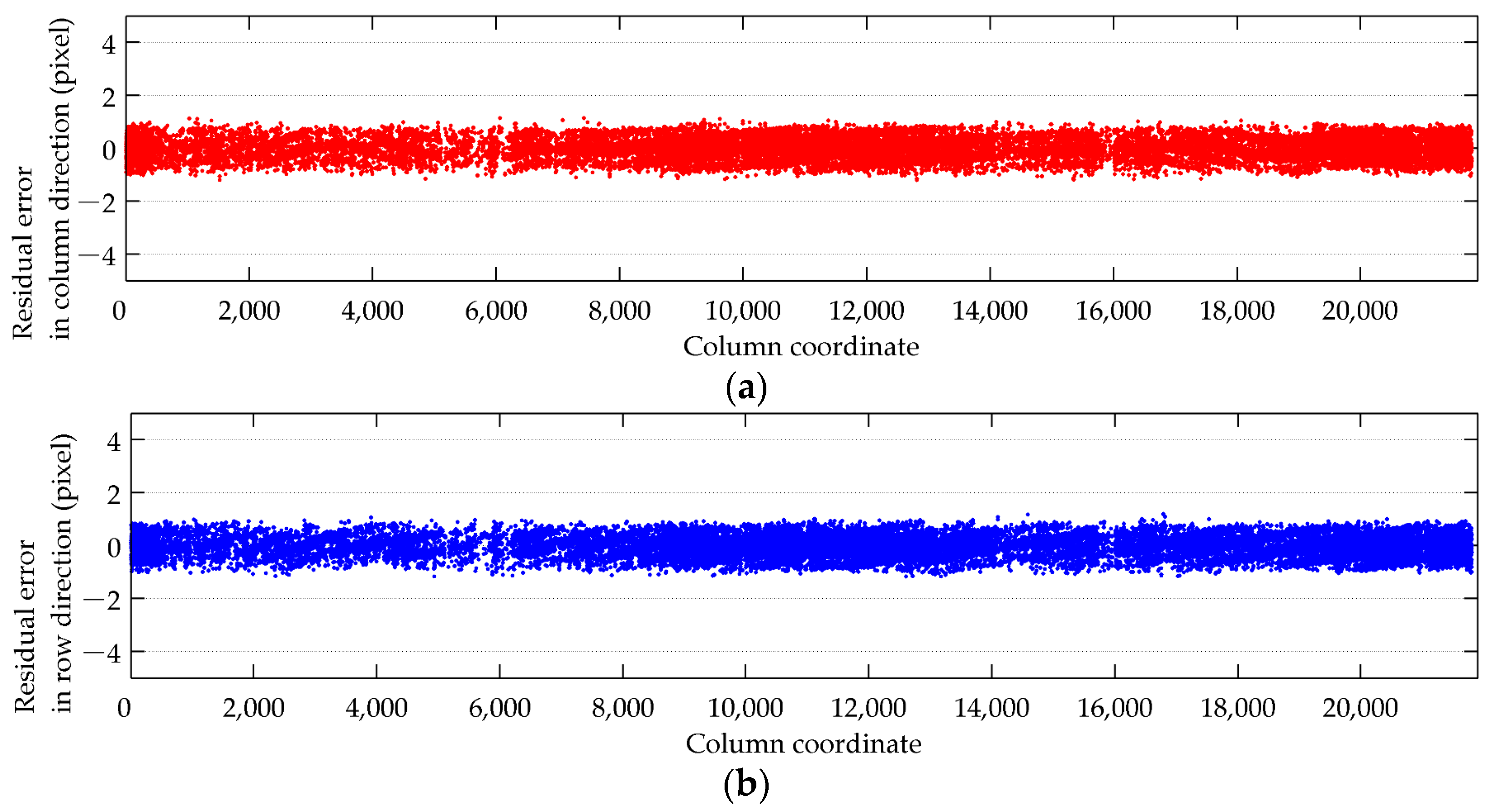
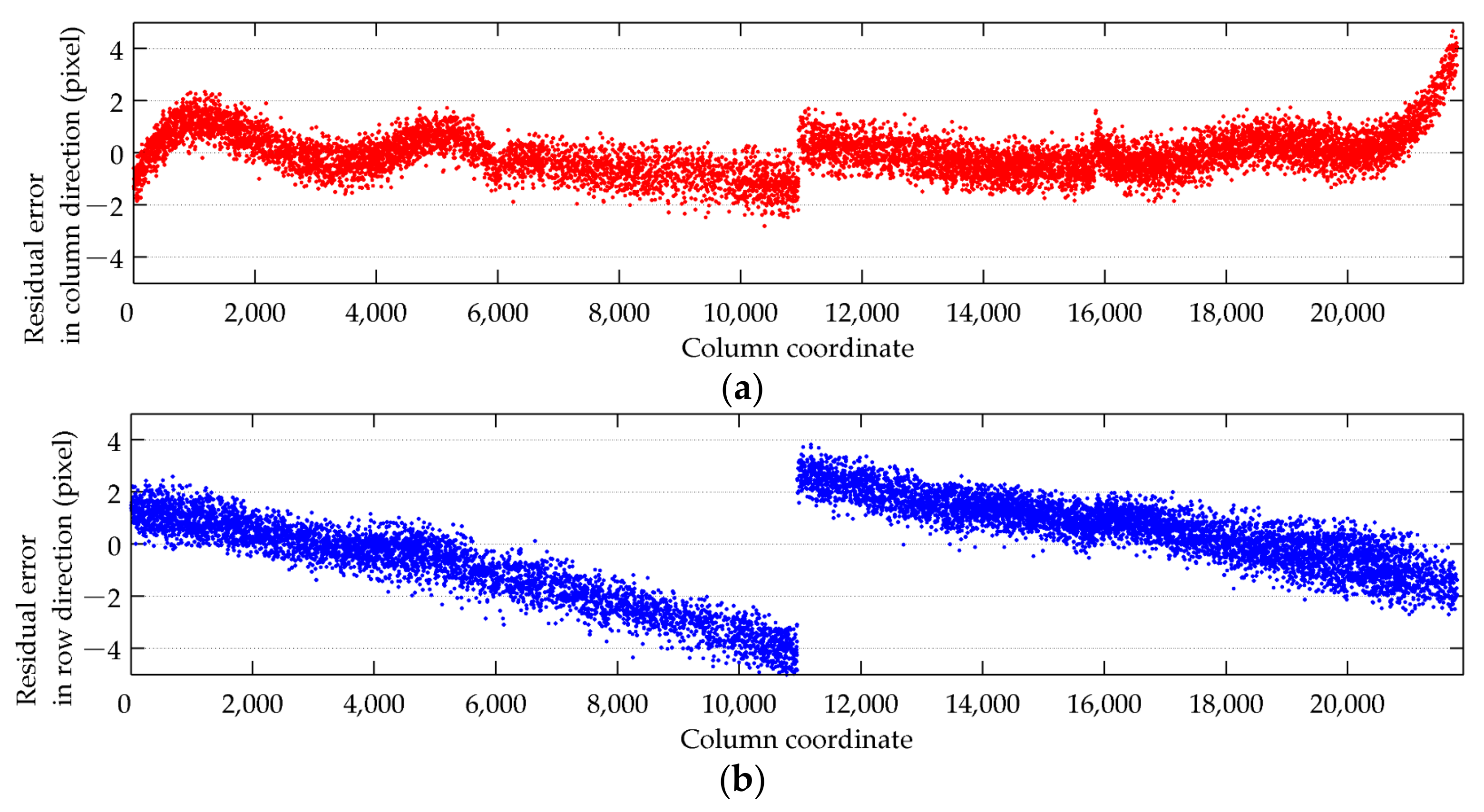
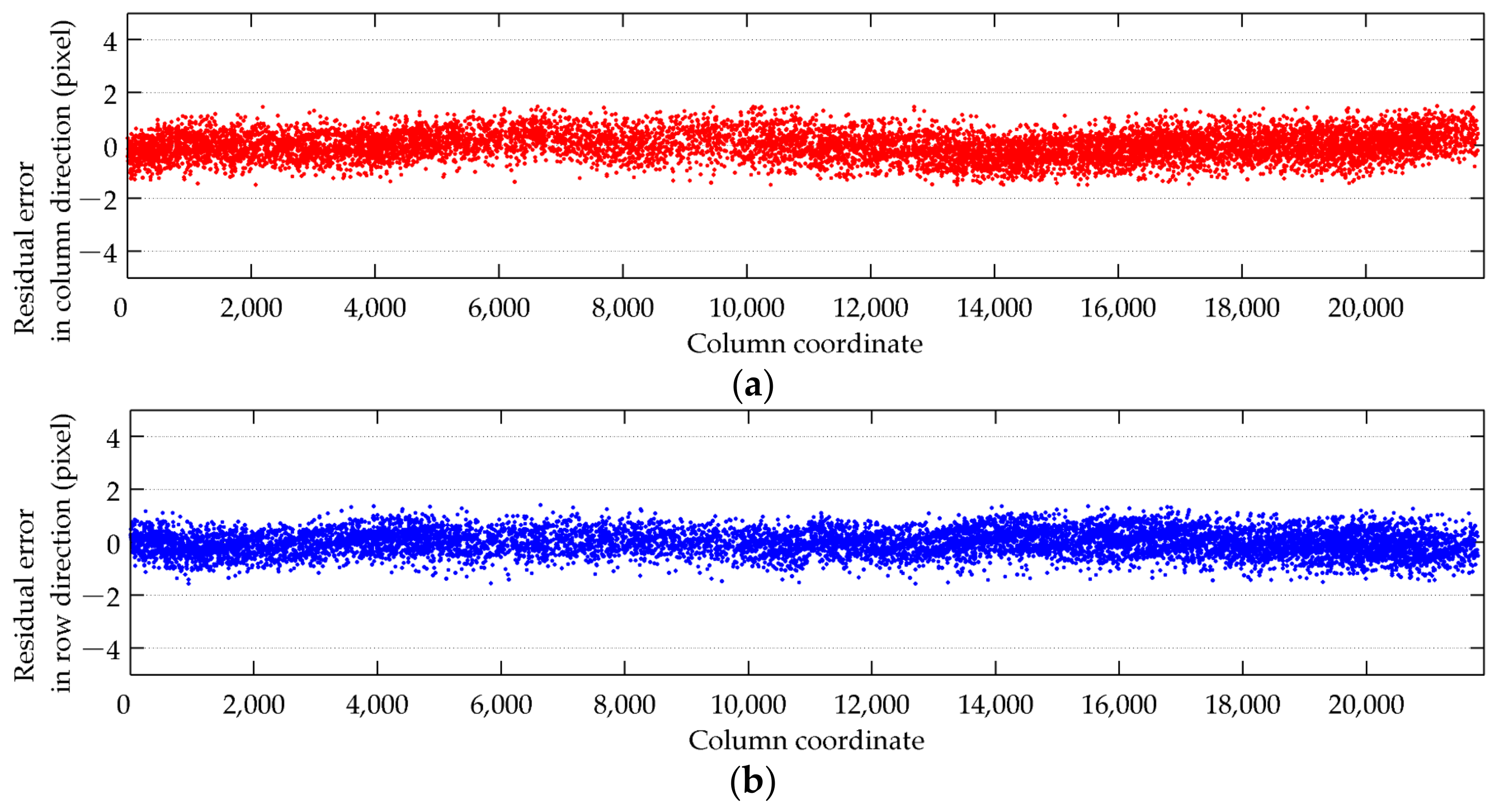
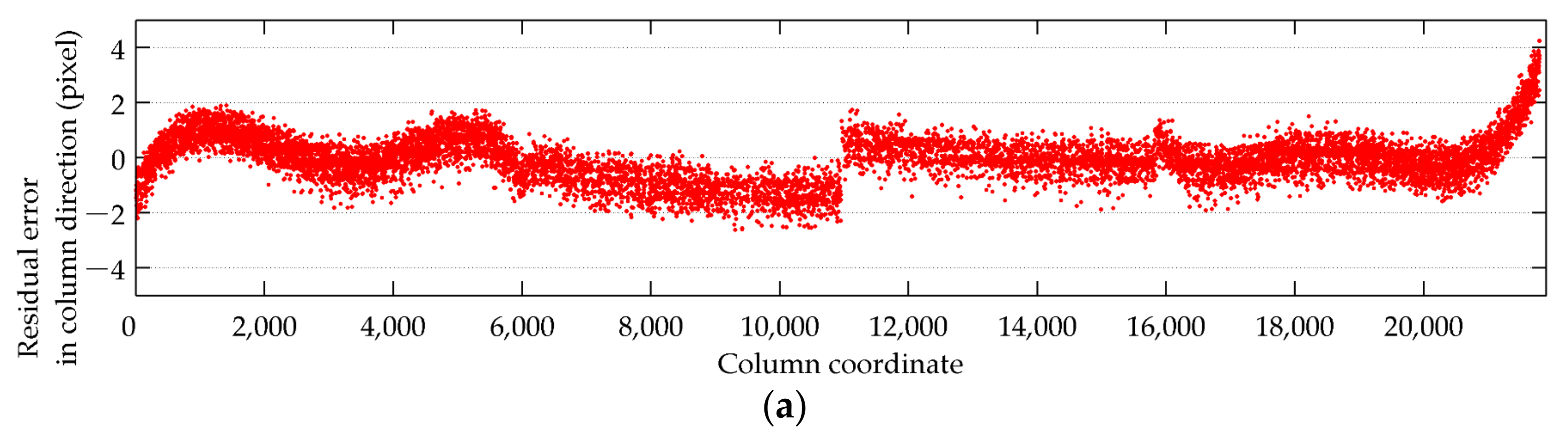
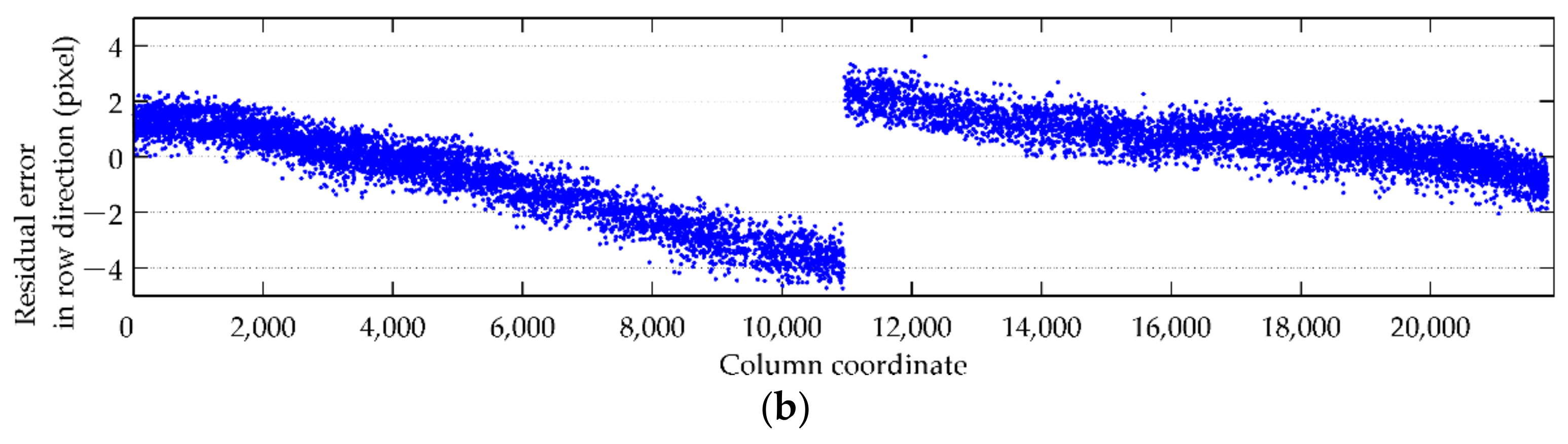
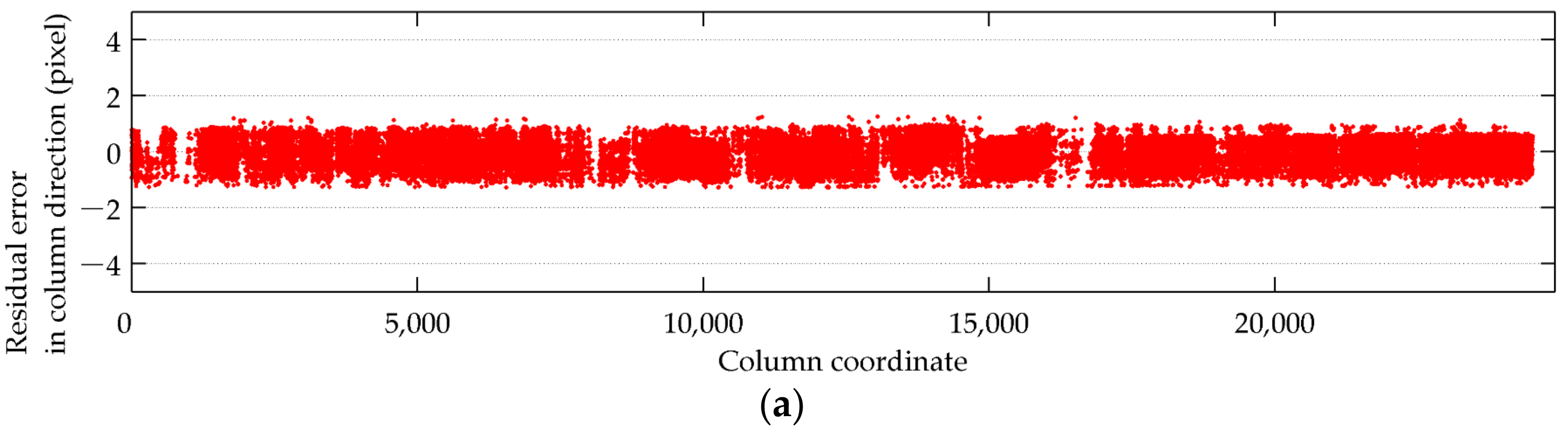
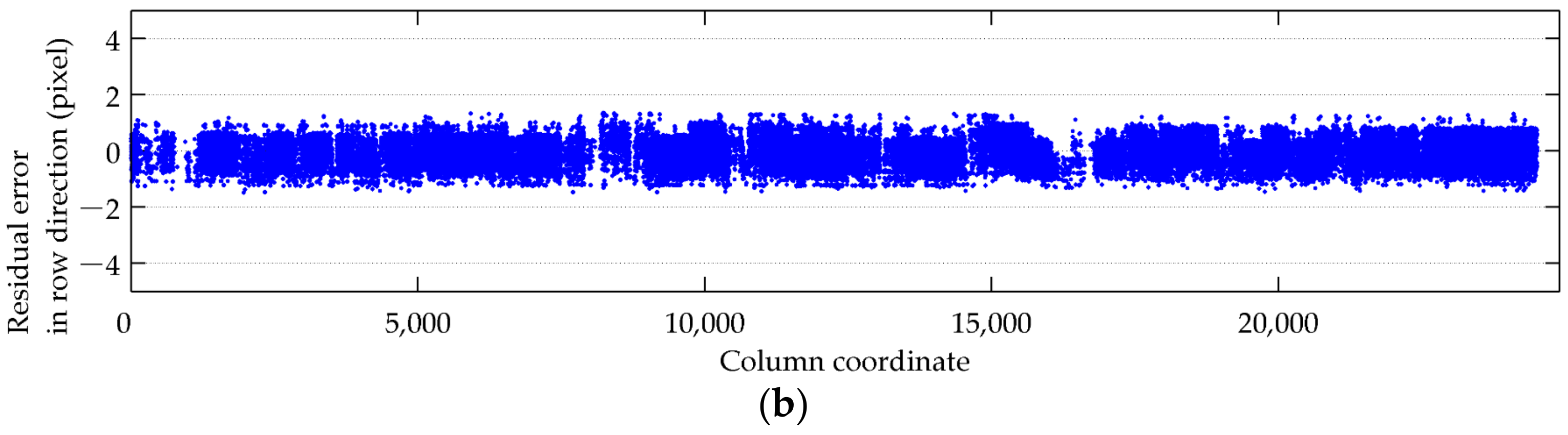
3.2. Internal Geometric Quality Analysis
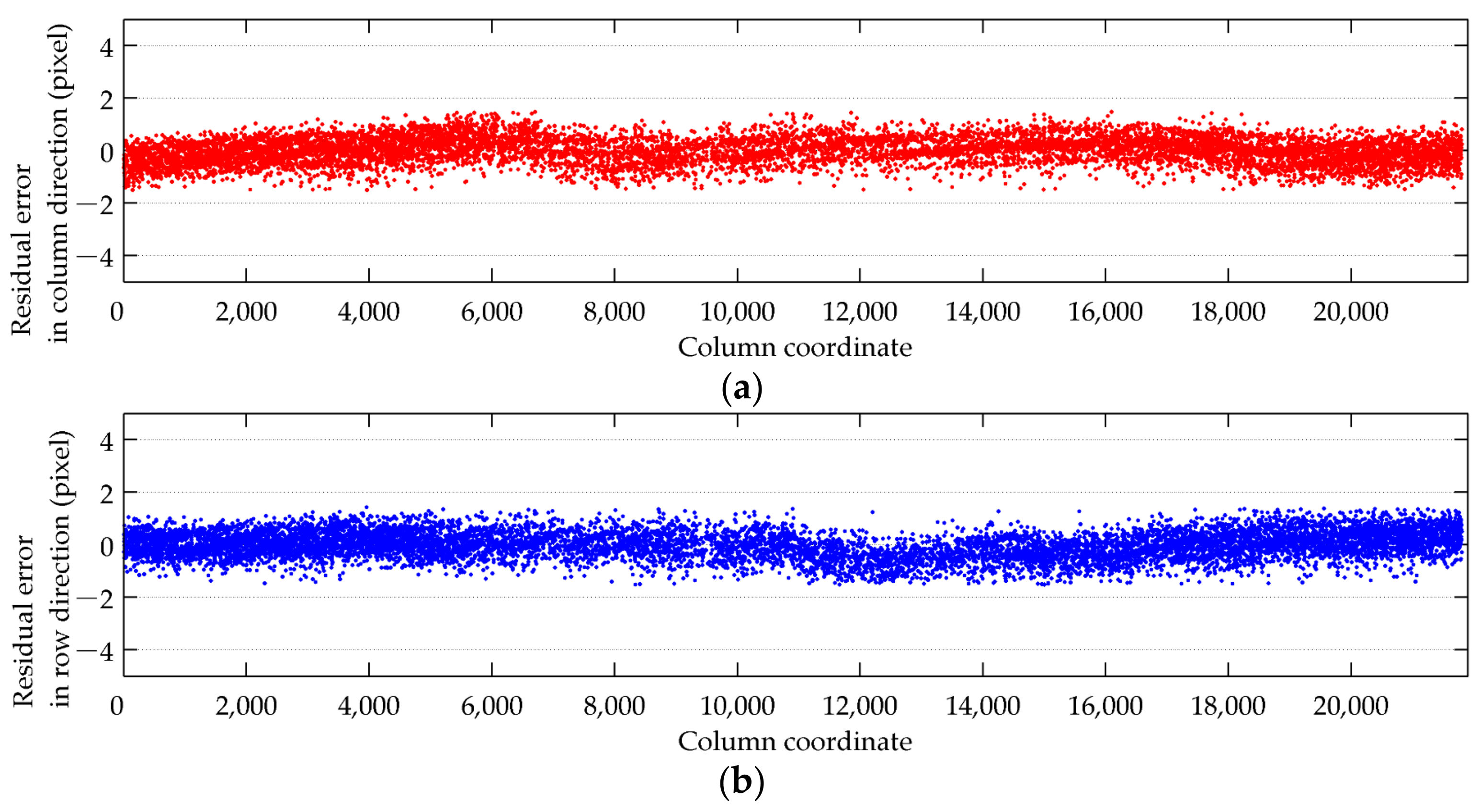
3.3. Performance Analysis of Estimated Internal Orientation Parameters
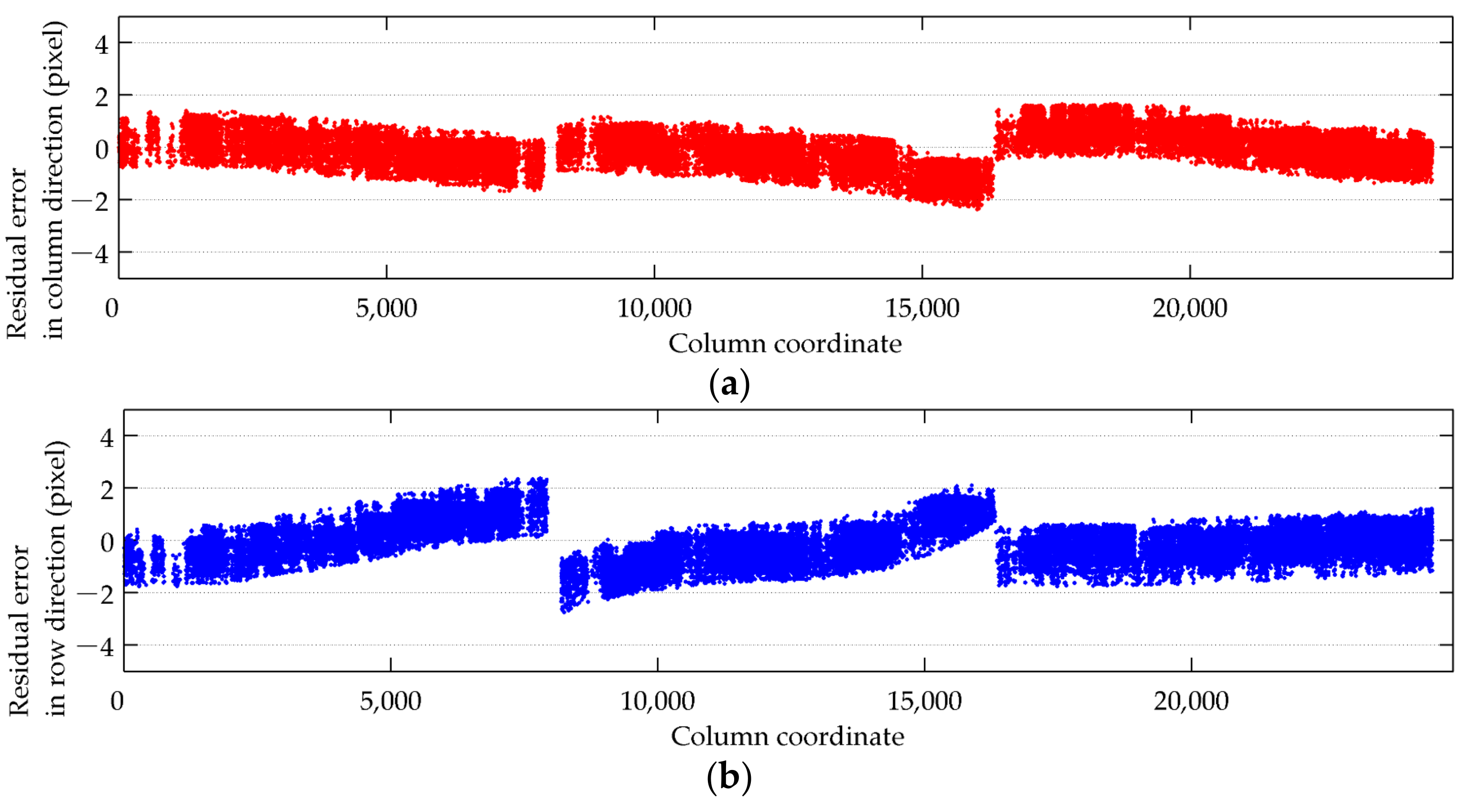
3.4. Experiments with Other Optical Satellite Images
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ORSSIs | optical remote sensing satellite images; |
| EO | external orientation; |
| IO | internal orientation; |
| PSM | physical sensor model; |
| RFM | rational function model; |
| GCPs | ground control points; |
| CCD | charge-coupled device; |
| DOMs | digital orthophoto maps; |
| DEMs | digital elevation models; |
| CZI | coastal zone imager; |
| RPCs | rational polynomial coefficients; |
| LOS | line of sight; |
| GSD | ground sample distance; |
| SRTM | shuttle radar topography mission; |
| RMSEs | root mean square errors. |
References
- Tong, X.; Liu, S.; Weng, Q. Bias-Corrected Rational Polynomial Coefficients for High Accuracy Geo-positioning of QuickBird Stereo Imagery. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Tong, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, P.; Xie, H.; Jin, Y. A Comparison of the Performance of Bias-Corrected RSMs and RFMs for the Geo-Positioning of High-Resolution Satellite Stereo Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 16815–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poli, D. A Rigorous Model for Spaceborne Linear Array Sensors. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aguilar, M.A.; Aguilar, F.J.; Saldaña, M.M.; Fernández, I. Geopositioning Accuracy Assessment of GeoEye-1 Panchromatic and Multispectral Imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2012, 78, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, M.A.; Saldaña, M.M.; Aguilar, F.J. Assessing Geometric Accuracy of the Orthorectification Process from GeoEye-1 and WorldView-2 Panchromatic Images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2013, 21, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xiong, X. Self-Calibration Adjustment of CBERS-02B Long-Strip Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 3847–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, M.; Cheng, Y.; He, L.; Xue, L. An Improved Jitter Detection Method Based on Parallax Observation of Multispectral Sensors for Gaofen-1 02/03/04 Satellites. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Ye, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Jin, Y.; Chen, P.; Xie, H.; Zhang, S. Detection and Estimation of Along-Track Attitude Jitter from ZiYuan-3 Three-Line-Array Images Based on Back-Projection Residuals. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 4272–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, B.; Hu, F.; Zang, X. On-Orbit Geometric Calibration Model and Its Applications for High-Resolution Optical Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4391–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Liu, B.; Li, Q. Correcting Bias in the Rational Polynomial Coefficients of Satellite Imagery Using Thin-Plate Smoothing Splines. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2017, 125, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Li, Q.; Wu, G.; Zhu, J. Bias Compensation for Rational Polynomial Coefficients of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery by Local Polynomial Modeling. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, M. Jitter Compensation of ZiYuan-3 Satellite Imagery Based on Object Point Coincidence. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 6116–6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwind, P.; Schneider, M.; Palubinskas, G.; Storch, T.; Müller, R.; Richter, R. Processors for ALOS Optical Data: Deconvolution, DEM Generation, Orthorectification, and Atmospheric Correction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4074–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, J.; Tadono, T. PRISM On-Orbit Geometric Calibration and DSM Performance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 4060–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, S.; Pan, J.; Zhu, Q. Correction of ZY-3 Image Distortion Caused by Satellite Jitter via Virtual Steady Reimaging Using Attitude Data. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teshima, Y.; Iwasaki, A. Correction of Attitude Fluctuation of Terra Spacecraft Using ASTER/SWIR Imagery with Parallax Observation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Fu, J.; Yuan, X.; Gong, J. Nonlinear Bias Compensation of ZiYuan-3 Satellite Imagery with Cubic Splines. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Li, L.; Liu, S.; Xu, Y.; Ye, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, F.; Xie, H. Detection and Estimation of ZY-3 Three-Line Array Image Distortions Caused by Attitude Oscillation. ISPRS J. Photogram. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 291–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Iwasaki, A.; Xu, G. Attitude Jitter Compensation for Remote Sensing Images Using Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachet, R. SPOT5 In-Flight Commission: Inner Orientation of HRG and HRS Instruments. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inform. 2004, 35, 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Leprince, S.; Musé, P.; Avouac, J.P. In-Flight CCD Distortion Calibration for Pushbroom Satellites Based on Subpixel Correlation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2675–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhadevi, P.V.; Solanki, S.S. In-Flight Geometric Calibration of Different Cameras of IRS-P6 Using a Physical Sensor Model. Photogramm. Rec. 2008, 23, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yuan, X.; Gong, J. In-Orbit Geometric Calibration and Validation of ZY-3 Three-Line Cameras Based on CCD-Detector Look Angles. Photogramm. Rec. 2015, 30, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Guo, B.; Long, X.; Xue, L.; Cheng, Y.; Jin, S.; Zhou, X. On-Orbit Geometric Calibration and Accuracy Verification of GF-6 WFV Camera. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2020, 49, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, M.; Jin, S.; He, L.; Tian, Y. New On-Orbit Geometric Interior Parameters Self-Calibration Approach Based on Three-View Stereoscopic Images from High-Resolution Multi-TDI-CCD Optical Satellites. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7475–7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z. A New Image Mosaicking Approach for the Multiple Camera System of the Optical Remote Sensing Satellite GaoFen1. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.F.; Shin, S.W.; Kim, K.; Kim, C.; Bang, K.I.; Kim, E.M.; Lee, D.C. Comprehensive Analysis of Sensor Modeling Alternatives for High Resolution Imaging Satellites. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, C.S.; Hanley, H.B. Bias-Compensated RPCs for Sensor Orientation of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yuan, X.; Fu, J.; Gong, J. Precise Sensor Orientation of High-Resolution Satellite Imagery with the Strip Constraint. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5313–5323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, S.; Chang, X. Geometric Stitching of a HaiYang-1C Ultra Violet Imager with a Distorted Virtual Camera. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 14109–14116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Jin, S.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z. Image Mosaicking Approach for a Double-Camera System in the GaoFen2 Optical Remote Sensing Satellite Based on the Big Virtual Camera. Sensors 2017, 17, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; He, L.; Wang, Y. A New On-Orbit Geometric Self-Calibration Approach for the High-Resolution Geostationary Optical Satellite GaoFen4. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1670–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CGIAR. SRTM 90m DEM Digital Elevation Database. Available online: https://srtm.csi.cgiar.org/ (accessed on 14 November 2021).
- Cao, J.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, Z. In-Orbit Geometric Calibration of HaiYang-1C Coastal Zone Imager with Multiple Fields. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 18950–18965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Jean, N.; Burke, M.; Lobell, D.; Ermon, S. Transfer Learning from Deep Features for Remote Sensing and Poverty Mapping. In Proceedings of the 13th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 3929–3935. [Google Scholar]
- Pires de Lima, R.; Marfurt, K. Convolutional Neural Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification: Transfer Learning Analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, S.; Guo, X.; Sun, J.; Qiao, S.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y. Landslide Detection from Open Satellite Imagery Using Distant Domain Transfer Learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, M.; Kolouri, S.; Eaton, E.; Kim, K. Deep Transfer Learning for Few-Shot SAR Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, S.; Wei, S.; Lu, M. A Scale Robust Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Building Extraction from Aerial and Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 3308–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


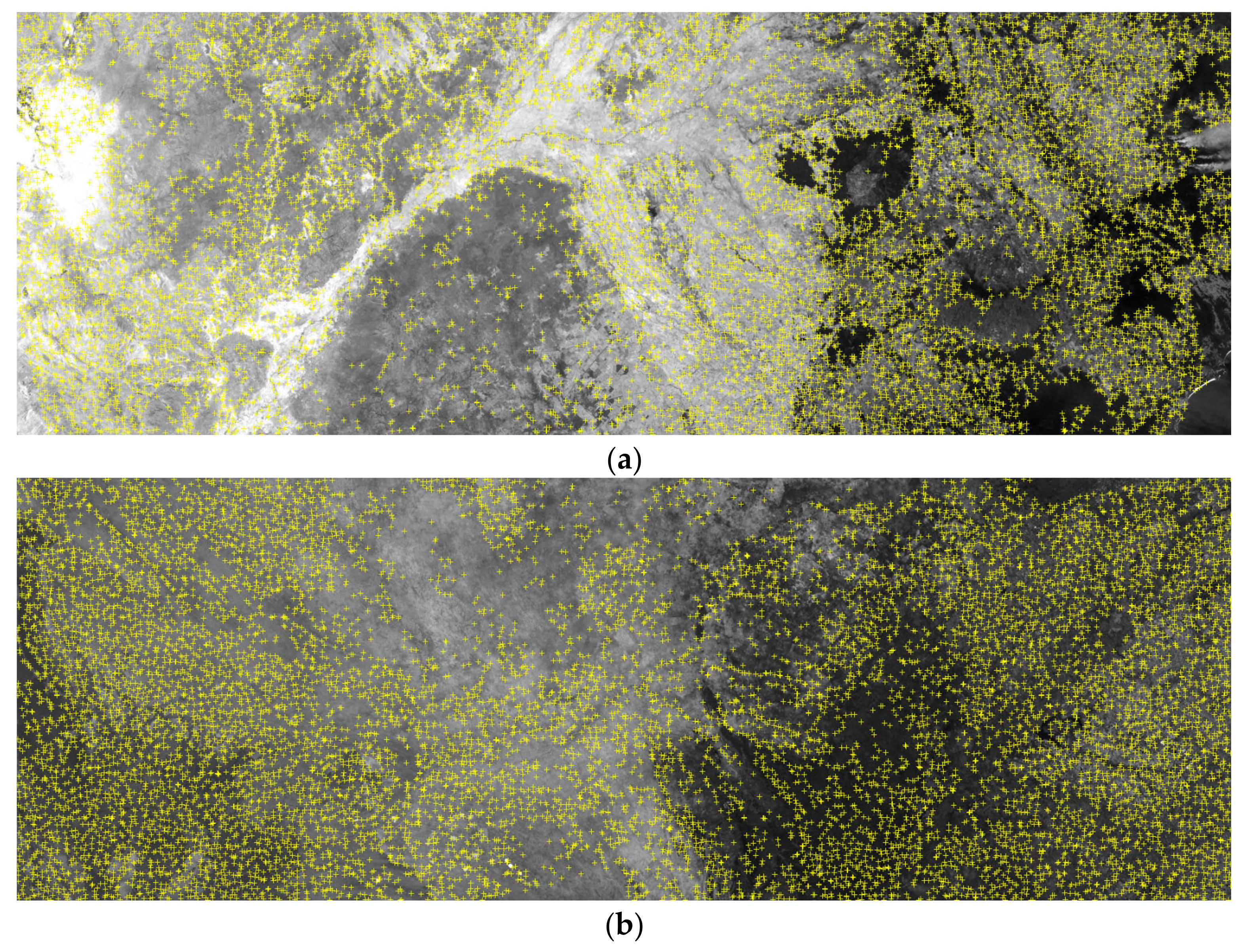

| Image | Acquisition Date | Latitude and Longitude of Scene Center (°) | Terrain Relief (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image 1 | 8 October 2019 | 86.65°W, 40.69°N | 145~435 |
| Image 2 | 7 November 2019 | 147.21°E, 30.52°S | 0~1432 |
| Image 3 | 25 July 2019 | 22.28°E, 26.49°S | 578~2047 |
| Image 4 | 29 July 2019 | 31.09°E, 24.85°S | 0~2295 |
| Image 5 | 19 August 2019 | 45.74°E, 36.35°N | 7~4096 |
| Image 6 | 12 June 2019 | 52.58°E, 31.99°N | 0~4108 |
| Image 7 | 10 December 2019 | 86.17°E, 29.75°N | 589~7772 |
| Image 8 | 9 December 2019 | 105.81°E, 39.68°N | 622~3121 |
| Image 9 | 14 October 2019 | 117.13°E, 48.42°N | 134~2262 |
| Image 10 | 24 September 2019 | 125.26°E, 48.05°N | 50~1655 |
| Image | Experiment | Number of GCPs | Max (Pixel) | RMSE (Pixel) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | c | Planimetry | r | c | Planimetry | |||
| 1 | E1 | 49,480 | −4.479 | 3.757 | 4.803 | 1.937 | 0.903 | 2.137 |
| E2 | 49,432 | 1.198 | −1.197 | 1.550 | 0.378 | 0.376 | 0.533 | |
| Image | Experiment | Number of GCPs | Max (Pixel) | RMSE (Pixel) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | c | Planimetry | r | c | Planimetry | |||
| 2 | S1 | 11,410 | −5.026 | 4.254 | 5.384 | 1.428 | 0.830 | 1.651 |
| S2 | 11,404 | −1.506 | −1.499 | 1.981 | 0.501 | 0.482 | 0.696 | |
| 3 | S1 | 8619 | −4.174 | 2.634 | 4.430 | 0.895 | 1.657 | 1.884 |
| S2 | 8622 | 1.500 | 1.500 | 1.986 | 0.520 | 0.500 | 0.721 | |
| 4 | S1 | 14,579 | −5.040 | 4.506 | 5.623 | 1.718 | 0.880 | 1.930 |
| S2 | 14,585 | −1.495 | −1.486 | 2.016 | 0.487 | 0.437 | 0.655 | |
| 5 | S1 | 14,454 | −4.594 | 4.040 | 5.022 | 1.512 | 0.721 | 1.675 |
| S2 | 14,452 | −1.584 | −1.411 | 2.043 | 0.562 | 0.448 | 0.719 | |
| 6 | S1 | 14,183 | −4.755 | 4.841 | 5.799 | 1.858 | 0.960 | 2.092 |
| S2 | 14,186 | −1.820 | −1.499 | 2.322 | 0.592 | 0.531 | 0.796 | |
| 7 | S1 | 11,894 | −5.380 | 3.747 | 5.601 | 1.657 | 0.785 | 1.834 |
| S2 | 11,888 | −1.701 | −1.676 | 2.179 | 0.540 | 0.559 | 0.778 | |
| 8 | S1 | 12,415 | −5.079 | 4.064 | 5.370 | 1.663 | 0.794 | 1.843 |
| S2 | 12,418 | −1.482 | −1.678 | 2.175 | 0.602 | 0.491 | 0.777 | |
| 9 | S1 | 11,898 | −5.133 | 3.883 | 5.647 | 1.732 | 0.819 | 1.916 |
| S2 | 11,888 | −1.537 | −1.493 | 2.092 | 0.505 | 0.520 | 0.725 | |
| 10 | S1 | 10,504 | −5.846 | 4.669 | 5.846 | 1.560 | 0.812 | 1.759 |
| S2 | 10,507 | −1.566 | 1.495 | 2.141 | 0.458 | 0.505 | 0.682 | |
| Image | Acquisition Date | Latitude and Longitude of Scene Center (°) | Terrain Relief (m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZiYuan-3 02 | 16 April 2019 | 117.866°E, 39.785°N | 1~399 |
| GaoFen-1B | 20 June 2020 | 117.647°E, 37.552°N | 1~124 |
| GaoFen-1D | 5 June 2018 | 117.877°E, 39.654°N | 1~334 |
| Image | Experiment | Number of GCPs | Max (Pixel) | RMSE (Pixel) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | c | Planimetry | r | c | Planimetry | |||
| ZiYuan-3 02 | E1 | 95,525 | −2.746 | −2.361 | 2.930 | 0.738 | 0.615 | 0.961 |
| E2 | 95,537 | −1.481 | −1.273 | 1.922 | 0.428 | 0.416 | 0.597 | |
| GaoFen-1B | E1 | 16,641 | −25.812 | −21.371 | 31.661 | 5.921 | 4.019 | 7.156 |
| E2 | 16,699 | −1.815 | −2.051 | 2.657 | 0.577 | 0.650 | 0.870 | |
| GaoFen-1D | E1 | 53,876 | 3.260 | −3.117 | 4.165 | 1.091 | 1.055 | 1.518 |
| E2 | 53,921 | 2.021 | 2.112 | 2.708 | 0.625 | 0.650 | 0.903 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Zhou, N.; Shang, H.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Z. Internal Geometric Quality Improvement of Optical Remote Sensing Satellite Images with Image Reorientation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030471
Cao J, Zhou N, Shang H, Ye Z, Zhang Z. Internal Geometric Quality Improvement of Optical Remote Sensing Satellite Images with Image Reorientation. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):471. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030471
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jinshan, Nan Zhou, Haixing Shang, Zhiwei Ye, and Zhiqi Zhang. 2022. "Internal Geometric Quality Improvement of Optical Remote Sensing Satellite Images with Image Reorientation" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030471
APA StyleCao, J., Zhou, N., Shang, H., Ye, Z., & Zhang, Z. (2022). Internal Geometric Quality Improvement of Optical Remote Sensing Satellite Images with Image Reorientation. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 471. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030471