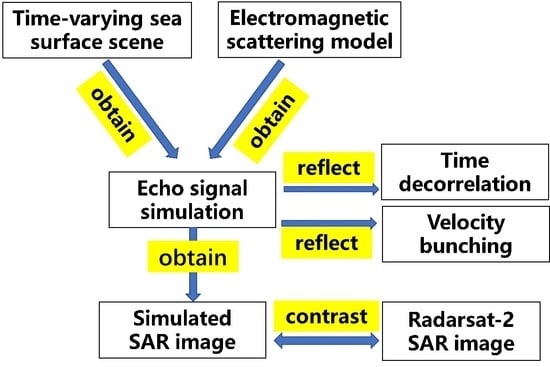
Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modeling of Sea Surface Scene and Electromagnetic Scattering
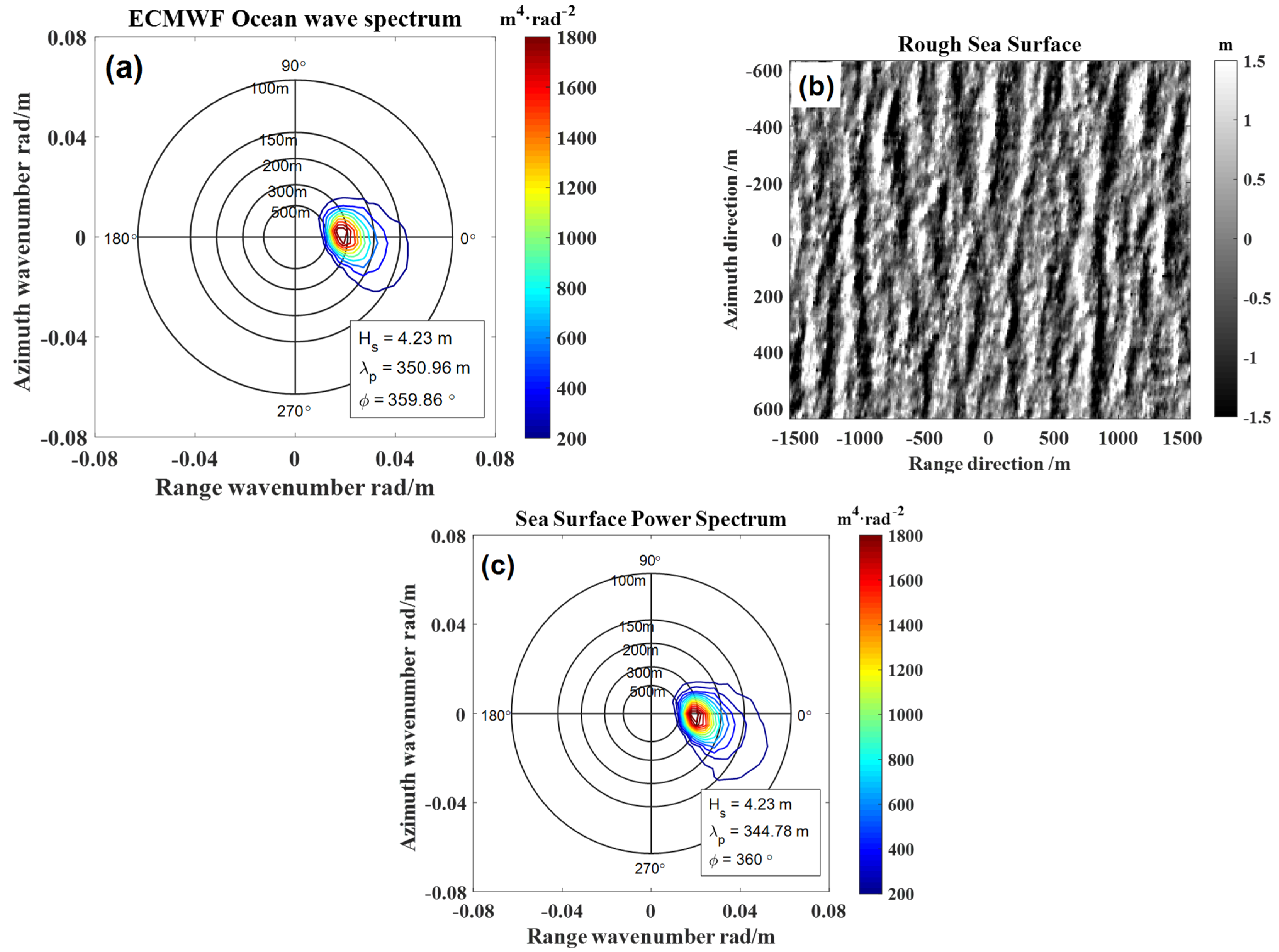
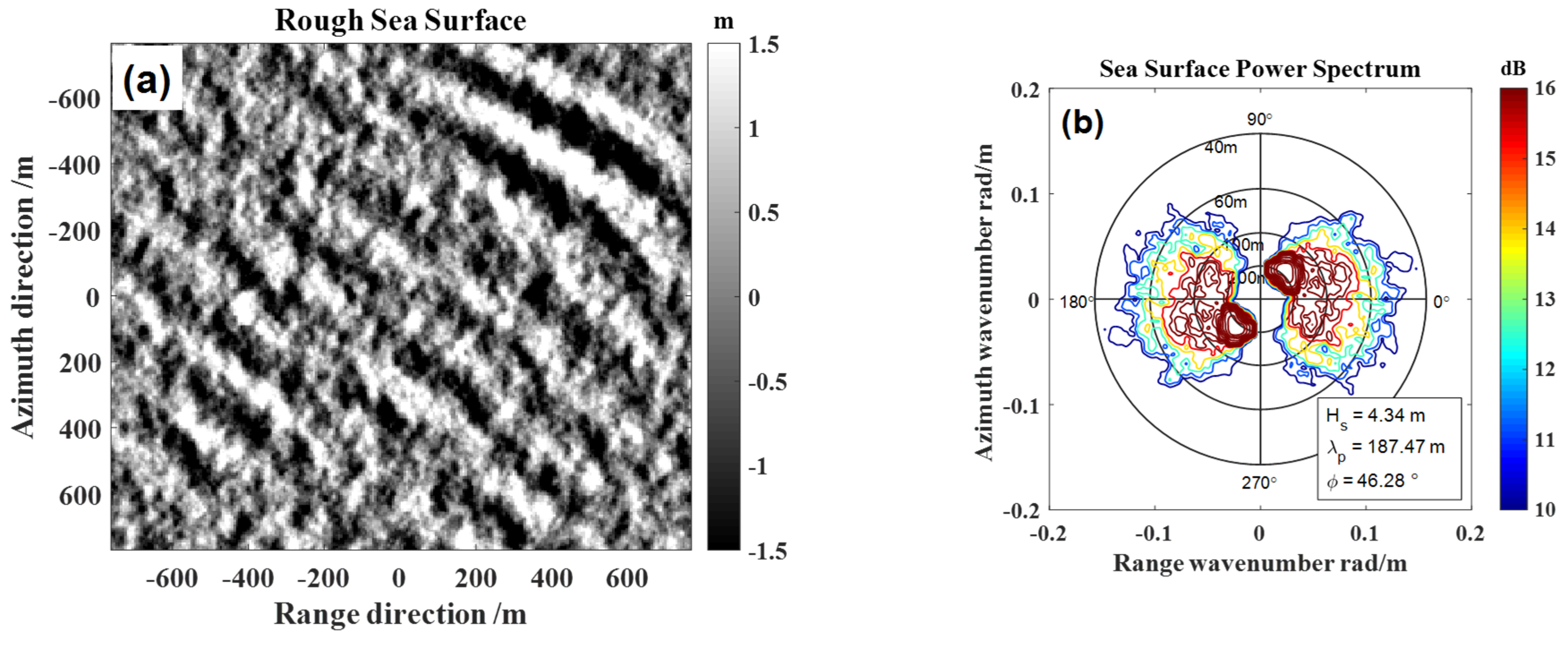
2.1. Modeling of Sea Surface Scene
2.2. Modeling of Electromagnetic Scattering
2.3. The Temporal Decorrelation Analysis
3. SAR Imaging Processing of Time-Varying Sea Surface
- After the fast Fourier transform (FFT) along the range direction, the SAR raw echo signal in range frequency domain can be expressed asThe SAR raw echo signal is multiplied by the range-matched filter in the range frequency domain to remove the second-order phase term of fast time . The range-matched filter is given bywhere is chirp pulse duration, is the range frequency, denotes the rectangular window, and denotes the range FM rate. The echo signal after the range compression is expressed as
- The change of the instantaneous slant range will result in range cell migration, which needs to be corrected. Range cell migration correction is performed after range compression and before azimuth compression. The echo signal and the slant range formula in the range-Doppler (RD) domain are obtained by azimuthal FFT and are given byandwhere is the range migration in the range-Doppler domain. The echo signal is discrete sampling, so the corrected discretized echo signal can be expressed aswhere and are the discretized range time series and the discretized azimuth frequency series, respectively, is the discretized range migration, and is the range sampling rate. The correcting value may be non-integer, so the interpolation operation can be used for the range cell migration correction (RCMC).
- An azimuth matched filter in the range-Doppler domain is used to achieve azimuth compression and can be given byThe 2D time domain complex amplitude of compressed signal is obtained after inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) along the azimuth direction.
4. Verification of Simulation Method
4.1. The Actual SAR Images and the Marine Environment Information
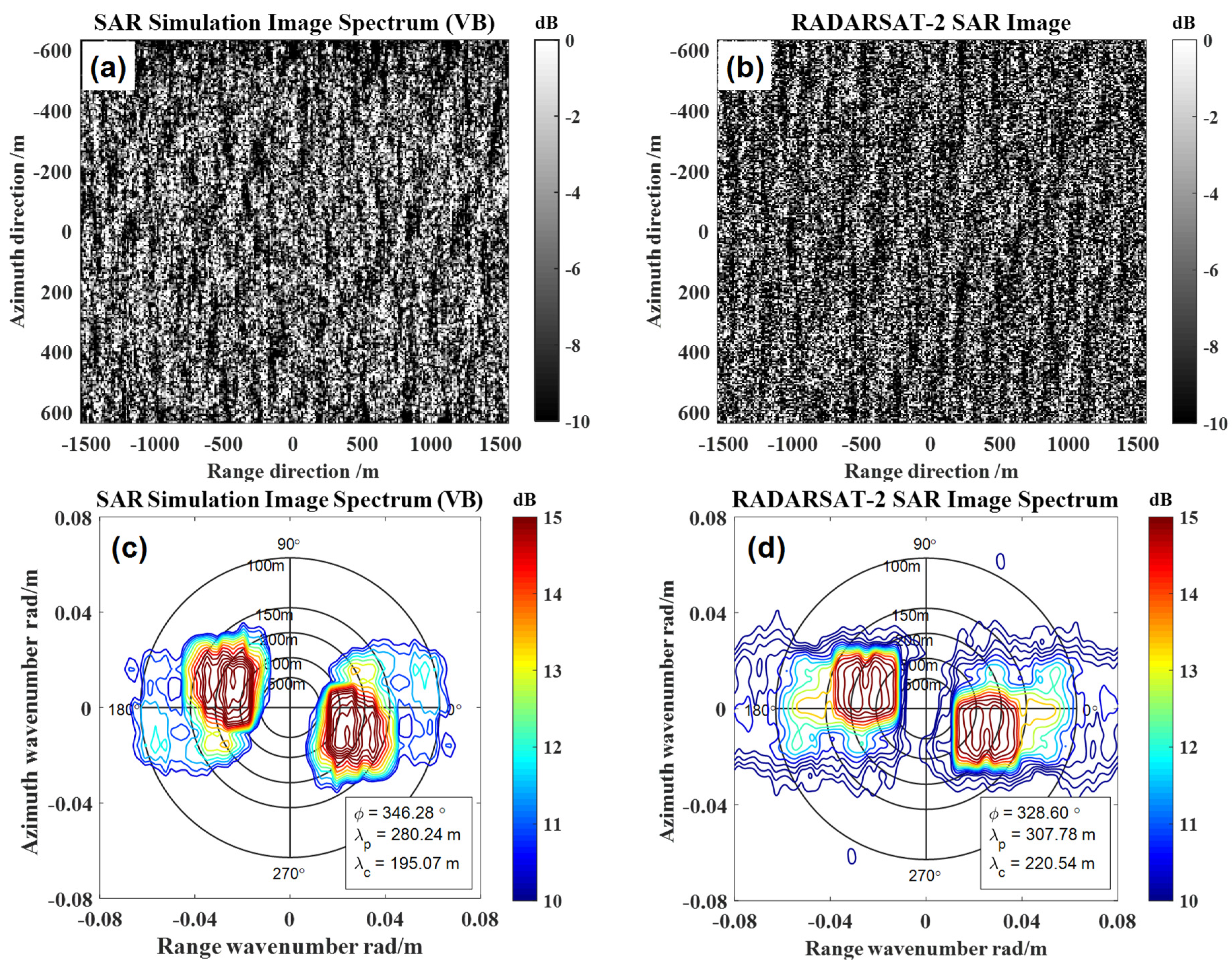
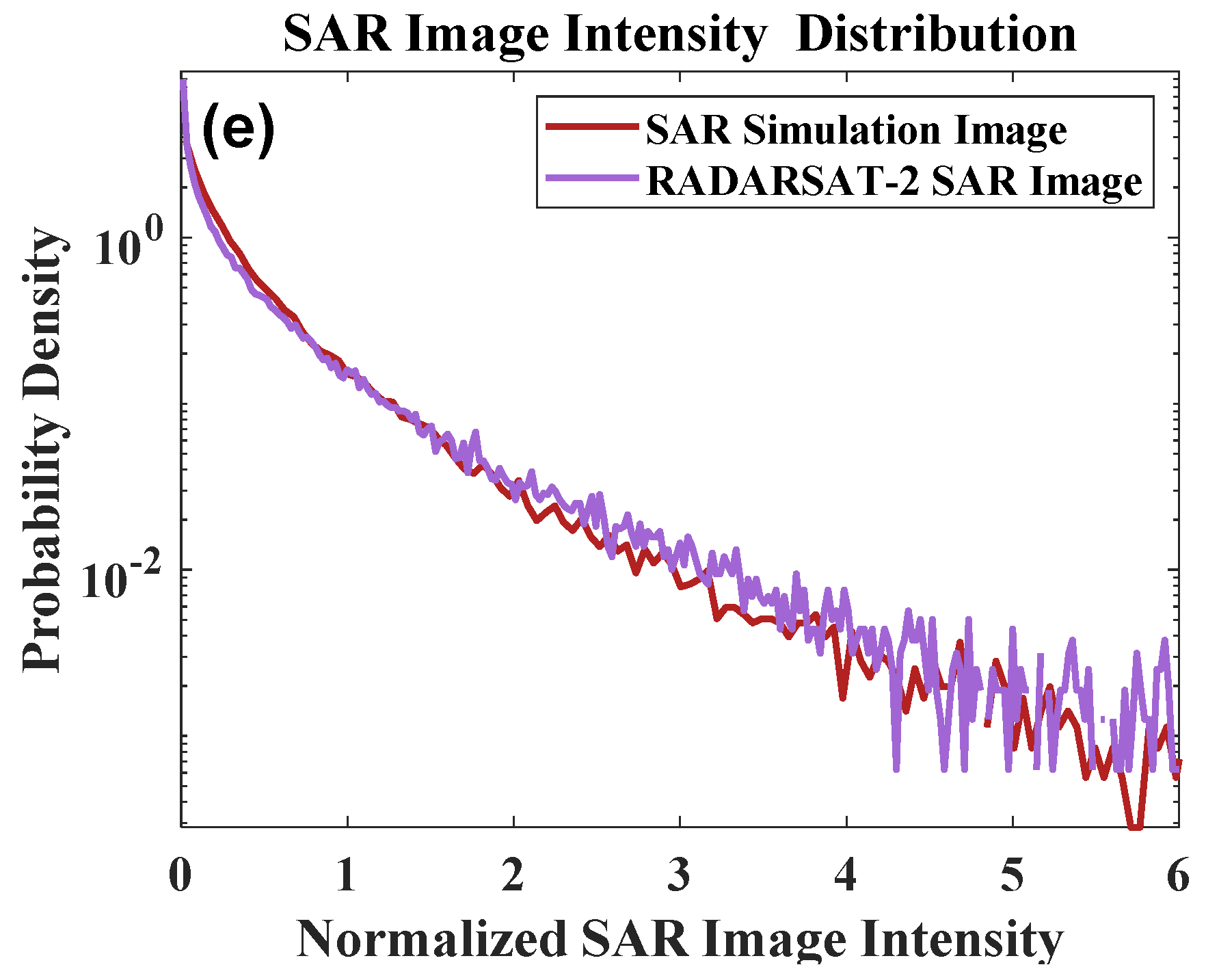
4.2. Contrast Experiment 1 with the Center Incidence Angle 23.27°
4.3. Contrast Experiment 2 with the Center Incidence Angle 33.24°
4.4. Contrast Experiment 3 with the Center Incidence Angle 39.96°
5. Discussion of Simulation Results
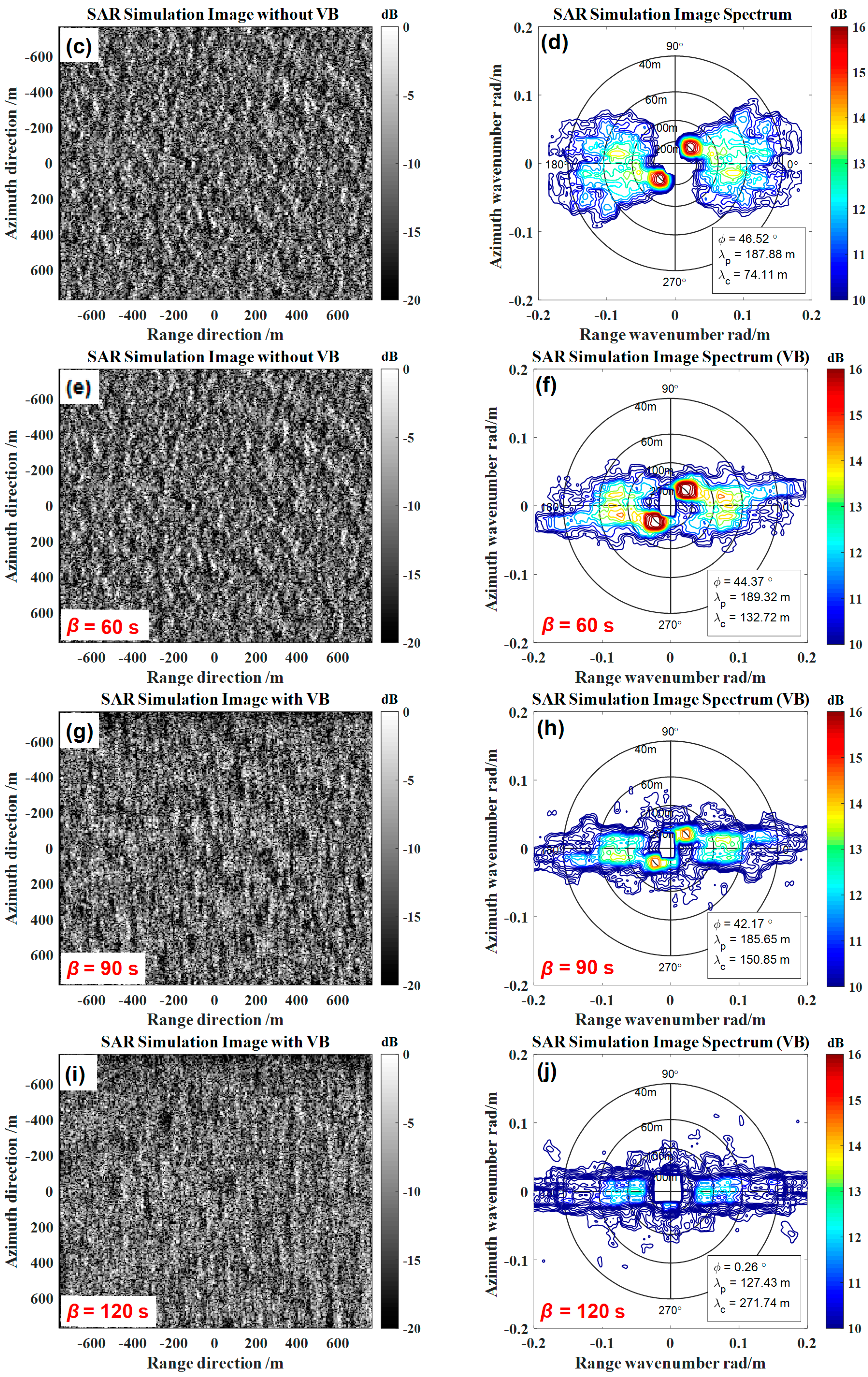
5.1. The Influence of the Velocity Bunching Effect
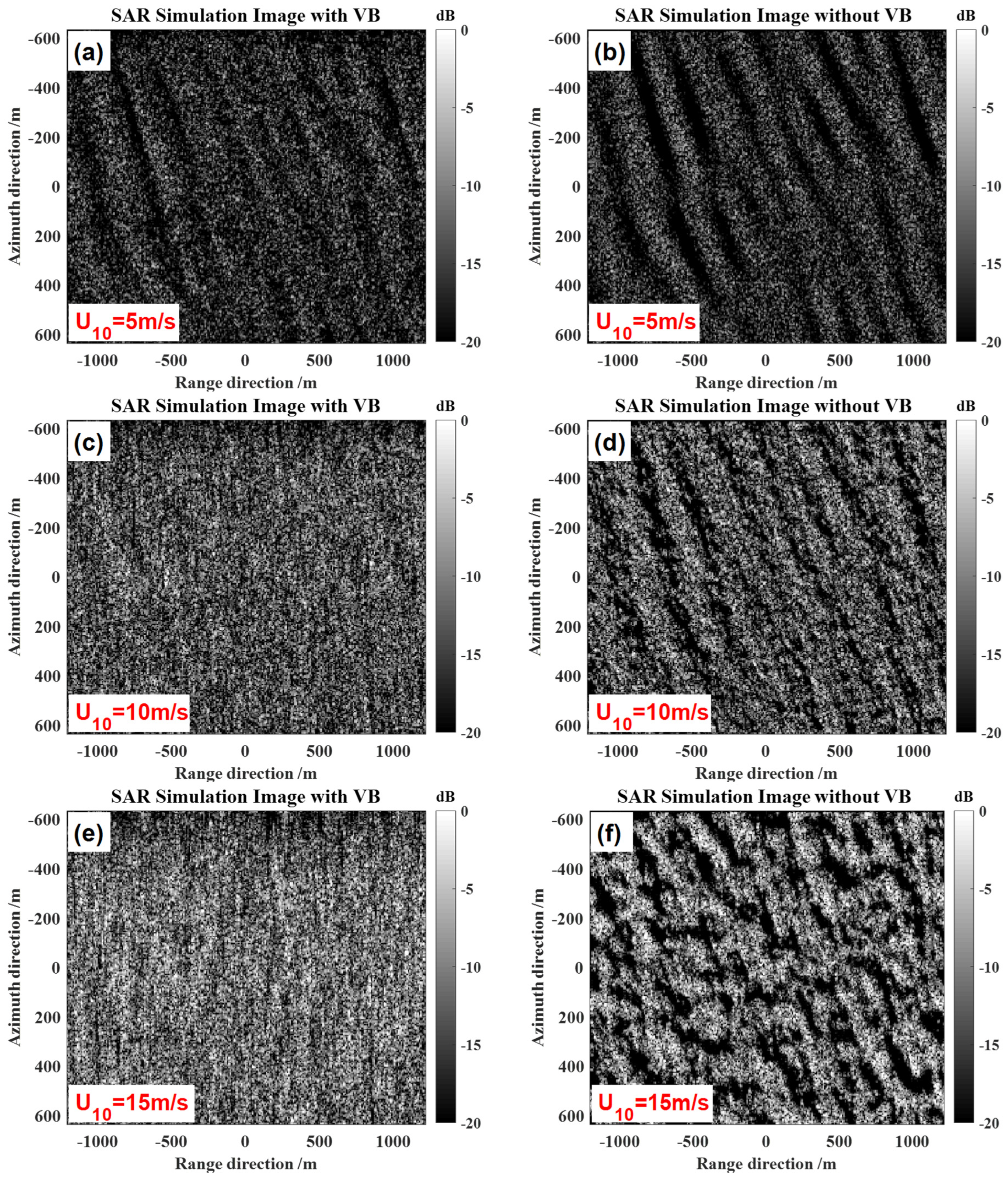
5.2. The Influence of Wind Speed
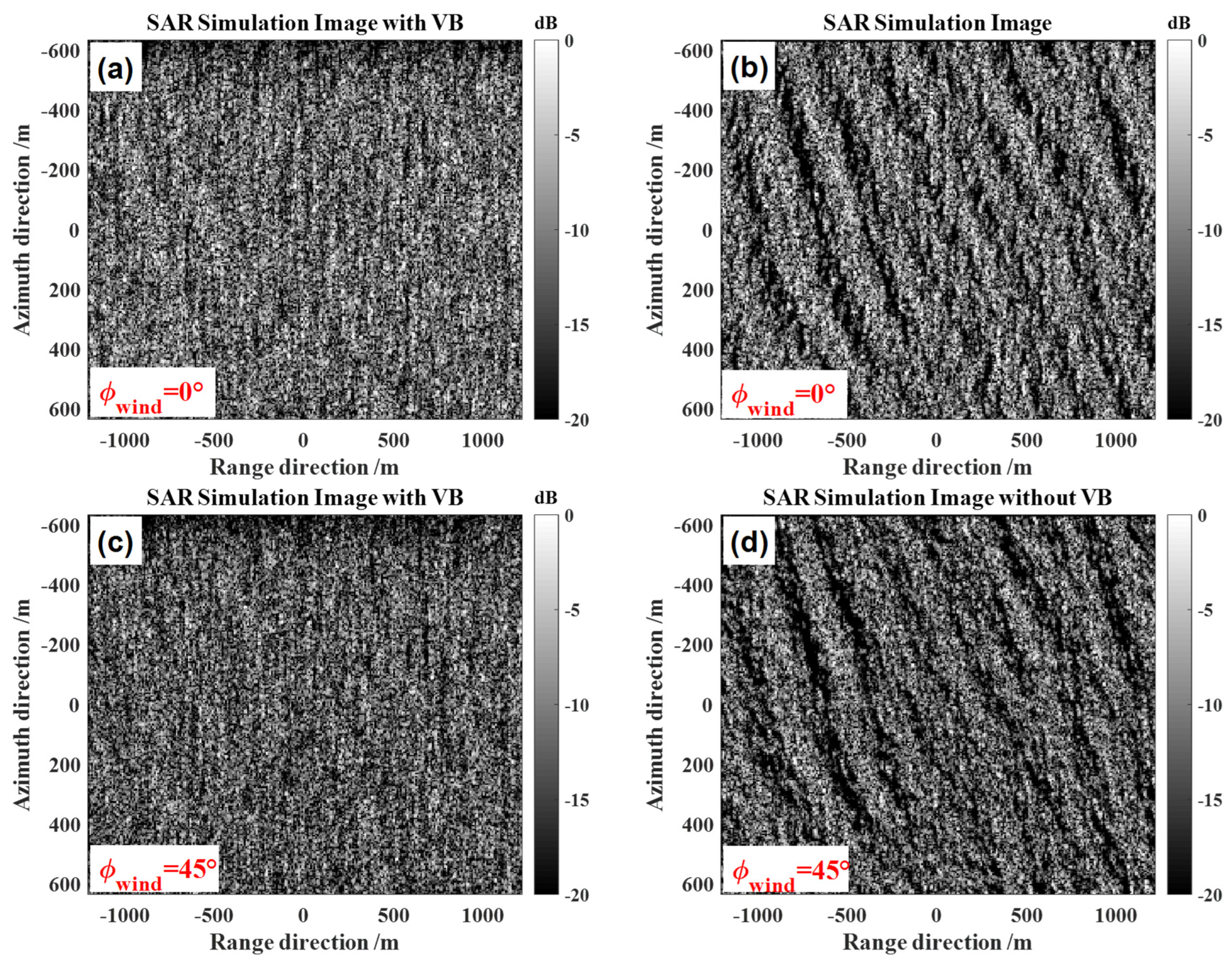
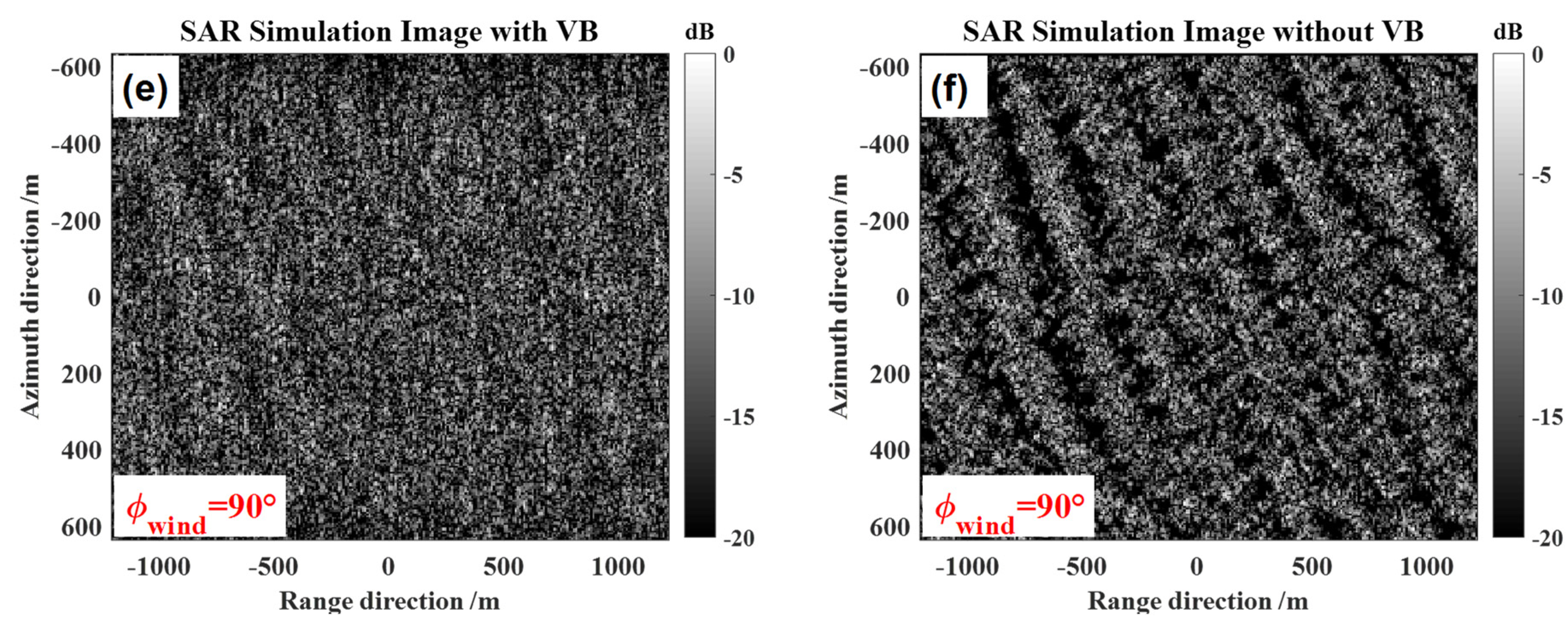
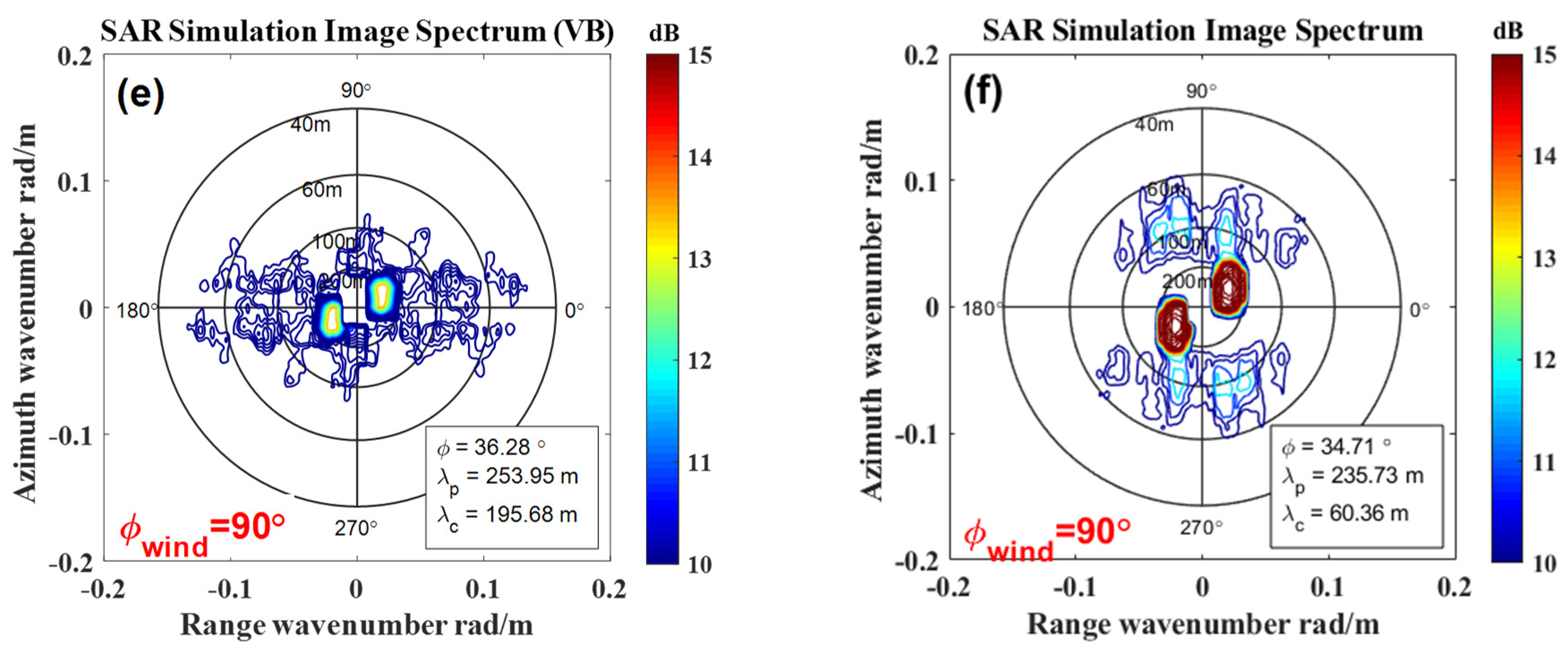
5.3. The Influence of Wind Direction
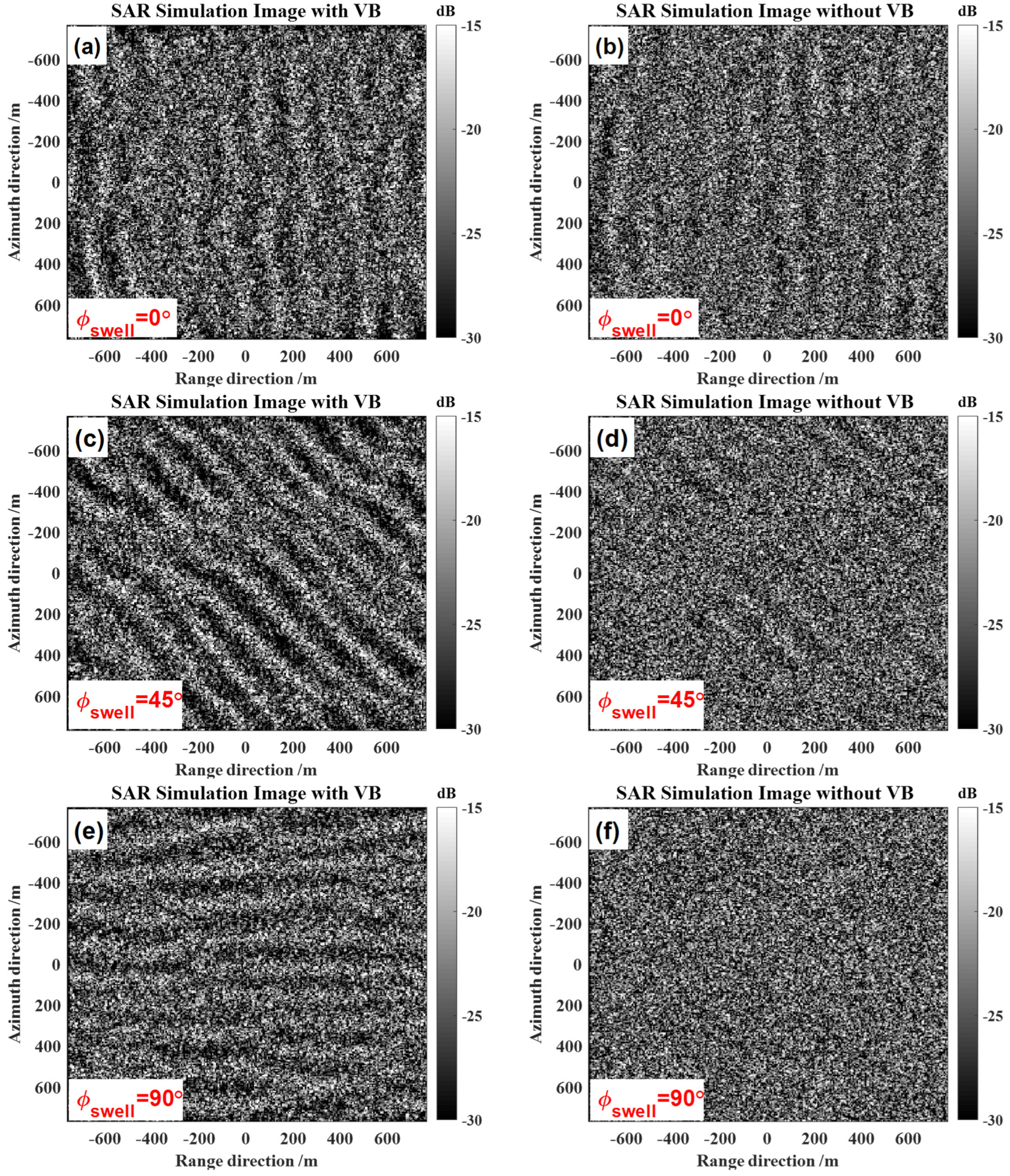
5.4. The Influence of Swell Direction
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alpers, W.; Rufenach, C. The effect of orbital motions on synthetic aperture radar imagery of ocean waves. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1979, 27, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.R.; Ross, D.B.; Rufenach, C.L. On the detectability of ocean surface waves by real and synthetic aperture radar. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 6481–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufenach, C.; Alpers, W. Imaging ocean waves by synthetic aperture radars with long integration times. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1981, 29, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Hasselmann, S. On the nonlinear mapping of an ocean wave spectrum into a synthetic aperture radar image spectrum and its inversion. J. Geophys. Res. 1991, 96, 10713–10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K.; Raney, R.K.; Plant, W.J.; Alpers, W.; Shuchman, R.A.; Lyzenga, D.R.; Rufenach, C.L.; Tucker, M. Theory of synthetic aperture radar ocean imaging: A MARSEN view. J. Geophys. Res. 1985, 90, 4659–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.R.; Bruening, C. On the Relative Importance of Motion-Related Contributions to the SAR Imaging Mechanism of Ocean Surface Waves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, GE-24, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. An analytic representation of the synthetic aperture radar image spectrum for ocean waves. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1988, 93, 13859–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Numerical Simulation of Synthetic Aperture Radar Image Spectra for Ocean Waves. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harger, R. The SAR Image of Short Gravity Waves on a Long Gravity Wave. In Wave Dynamics and Radio Probing of the Ocean Surface; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; pp. 371–392. [Google Scholar]
- Kasilingam, D.; Shemdin, O. Theory for synthetic aperture radar imaging of the ocean surface: With application to the Tower Ocean Wave and Radar Dependence Experiment on focus, resolution, and wave height spectra. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1988, 93, 13837–13848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W. Monte Carlo simulations for studying the relationship between ocean wave and synthetic aperture radar image spectra. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, C.; Alpers, W.; Hasselmann, K. Monte-Carlo simulation studies of the nonlinear imaging of a two dimensional surface wave field by a synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sens. 1990, 11, 1695–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, J.-W.; Koh, I.-S. SAR Image Generation of Ocean Surface Using Time-Divided Velocity Bunching Model. J. Electromagn. Eng. Sci. 2019, 19, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carratelli, E.P.; Dentale, F.; Reale, F.; Missions, E. Numerical Pseudo-Random Simulation of SAR Sea and Wind Response. In Proceedings of the SEASAR, Frascati, Italy, 23–26 January 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Gu, X. Wave Simulation of SAR Signal for Two-Dimensions Sea Surface. In Proceedings of the IEEE Circuits and Systems International Conference on Testing and Diagnosis, Chengdu, China, 28–29 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.; Gu, X.; Yu, T.; Li, J. Simulation of polarization SAR imaging of ocean surface based on the two-scale model. J. EMI 2011, 25, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.; Santos, A.; Violante-Carvalho, N.; Carvalho, L.M.; Brasil-Correa, Y.; Portilla-Yandun, J.; Romeiser, R. A simulator of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) image spectra: The applications on oceanswell waves. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 2981–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guan, W.-T.; Yang, P.-J. The Mono/Bistatic SAR Imaging Simulation of Sea Surface with Breaking Waves Based on a Refined Facet Scattering Field Model. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2021, 2021, 9915688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasilingam, D.; Shemdin, O. Models for synthetic aperture radar imaging of the Ocean: A comparison. J. Geophys. Res. 1990, 951, 16263–16276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harger, R.O. The side-looking radar image of time-variant scenes. Radio Sci. 1980, 15, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Migliaccio, M.; Riccio, D. An ocean SAR simulator based on the distributed surface model. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGARSS ’95. Quantitative Remote Sensing for Science and Applications, Firenze, Italy, 10–14 July 1995; pp. 1361–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti, G.; Migliaccio, M.; Riccio, D. On ocean SAR raw signal simulation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.H.; Cumming, I.G. Processing of Azimuth-Invariant Bistatic SAR Data Using the Range Doppler Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, R.; Runge, H.; Bamler, R.; Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Precision SAR Processing Using Chirp Scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1994, 32, 786–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Neo, Y.L.; Wong, F.H. Interpretations of the omega-K algorithm and comparisons with other algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 1455–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Zhihua, H.; Zhen, D.; Haifeng, H.; Anxi, Y. Spaceborne SAR raw signal simulation of ocean scene. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007; pp. 516–519. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; He, Y. SAR Raw Data Simulation for Ocean Scenes Using Inverse Omega-K Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 6151–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T. Numerical research on clear imaging of azimuth-traveling ocean waves in SAR images. Radio Sci. 2016, 51, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L. Basic Theory and Method of Random Rough Surface Scattering; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Elfouhaily, T.; Chapron, B.; Katsaros, K.; Vandemark, D. A Unified Directional Spectrum for Long and Short Wind-Driven Waves. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 15781–15796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouche, A.; Chapron, B. Global C-Band Envisat, RADARSAT-2 and Sentinel-1 SAR measurements in copolarization and cross-polarization. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 120, 7195–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, W.C.; Wright, J.W. Microwave scattering and the straining of wind-generated waves. Radio Sci. 2016, 10, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpers, W.; Hasselmann, K. The two-frequency microwave technique for measuring ocean wave spectra from an airplane or satellite. Bound. Layer Metereol. 1978, 13, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caponi, E.A.; Crawford, D.R.; Yuen, H.C.; Saffman, P.G. Modulation of radar backscatter from the ocean by a variable surface current. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 12249–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Signal Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithms and Implementation; Publishing House of Electronics Industry: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]

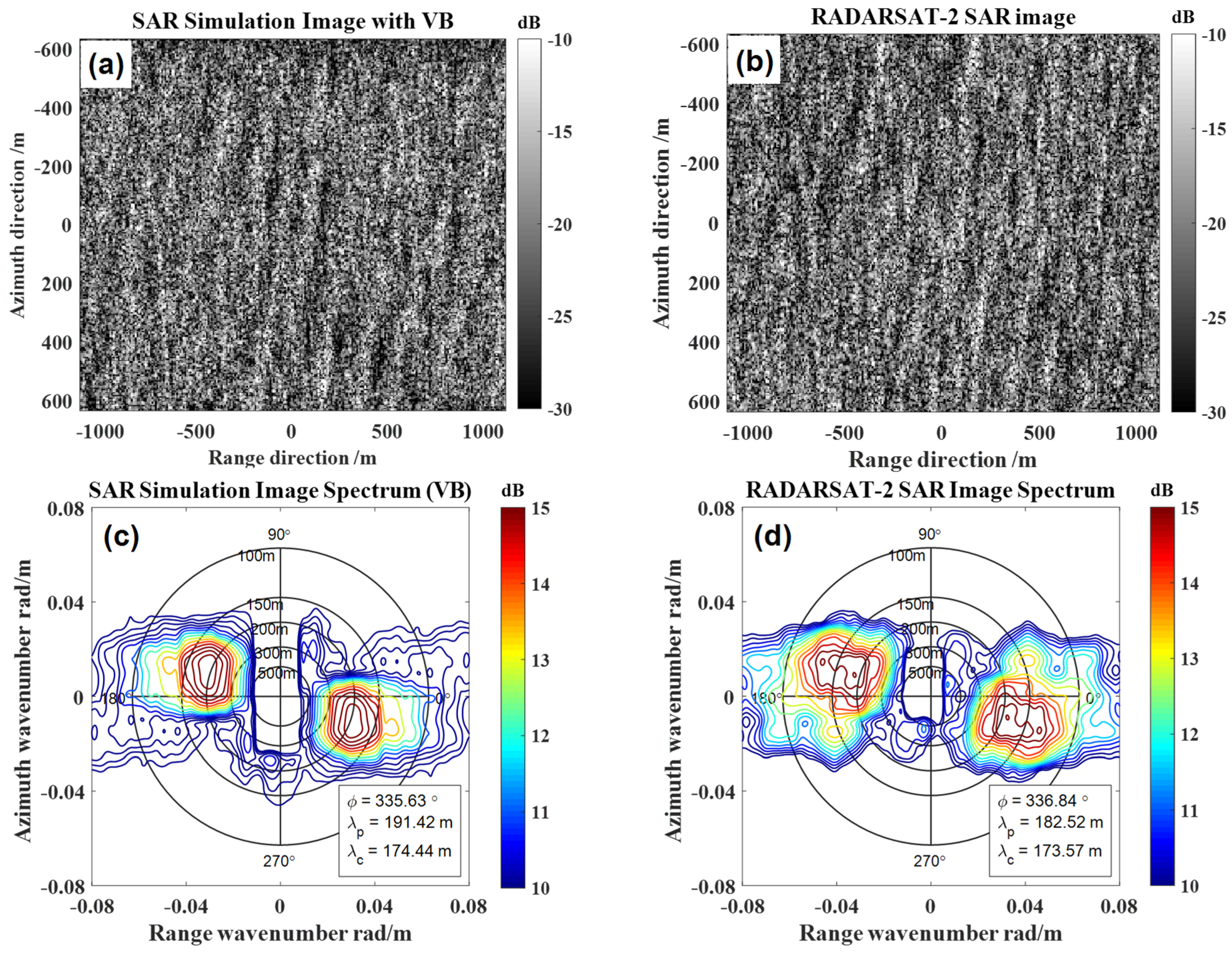
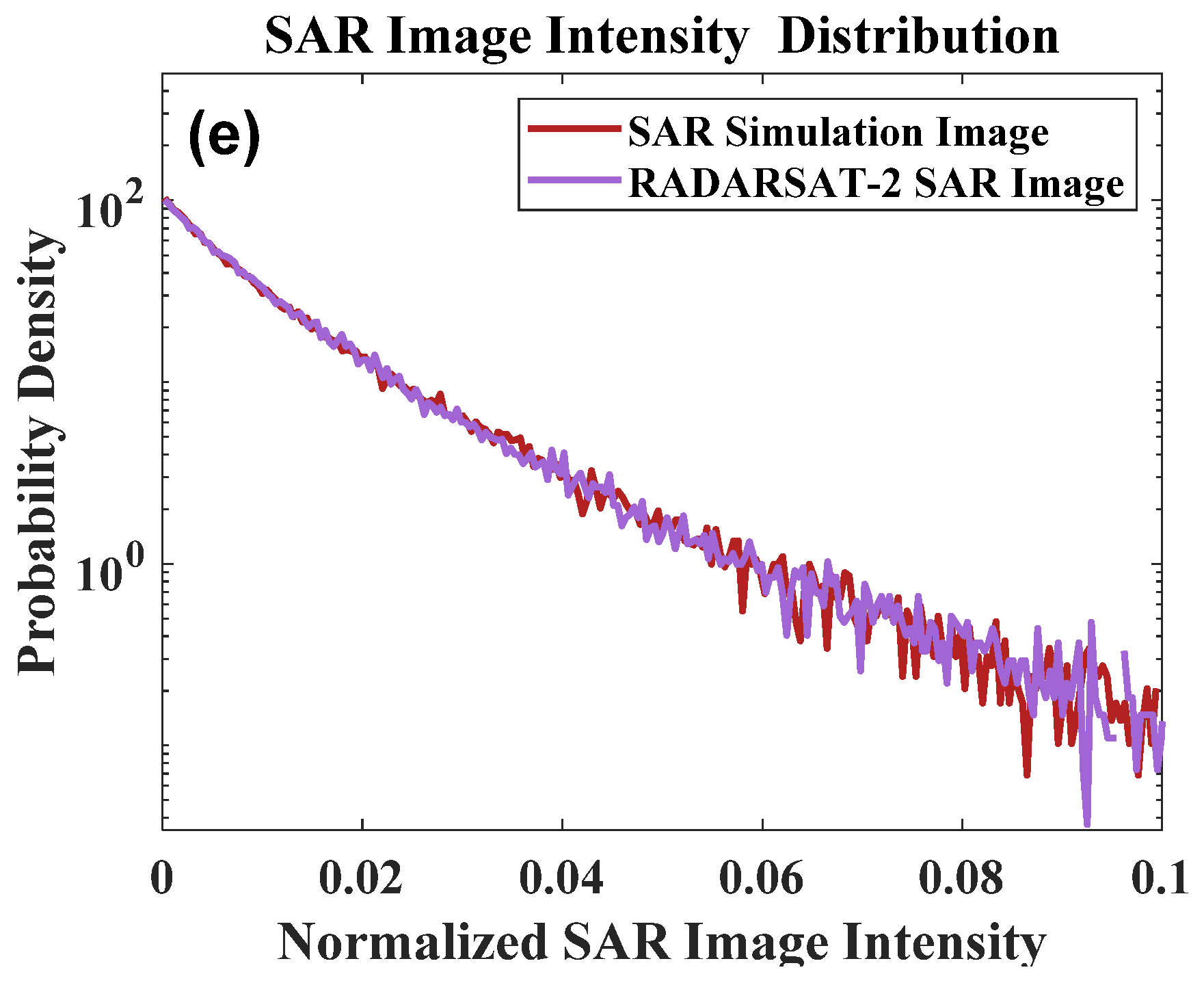

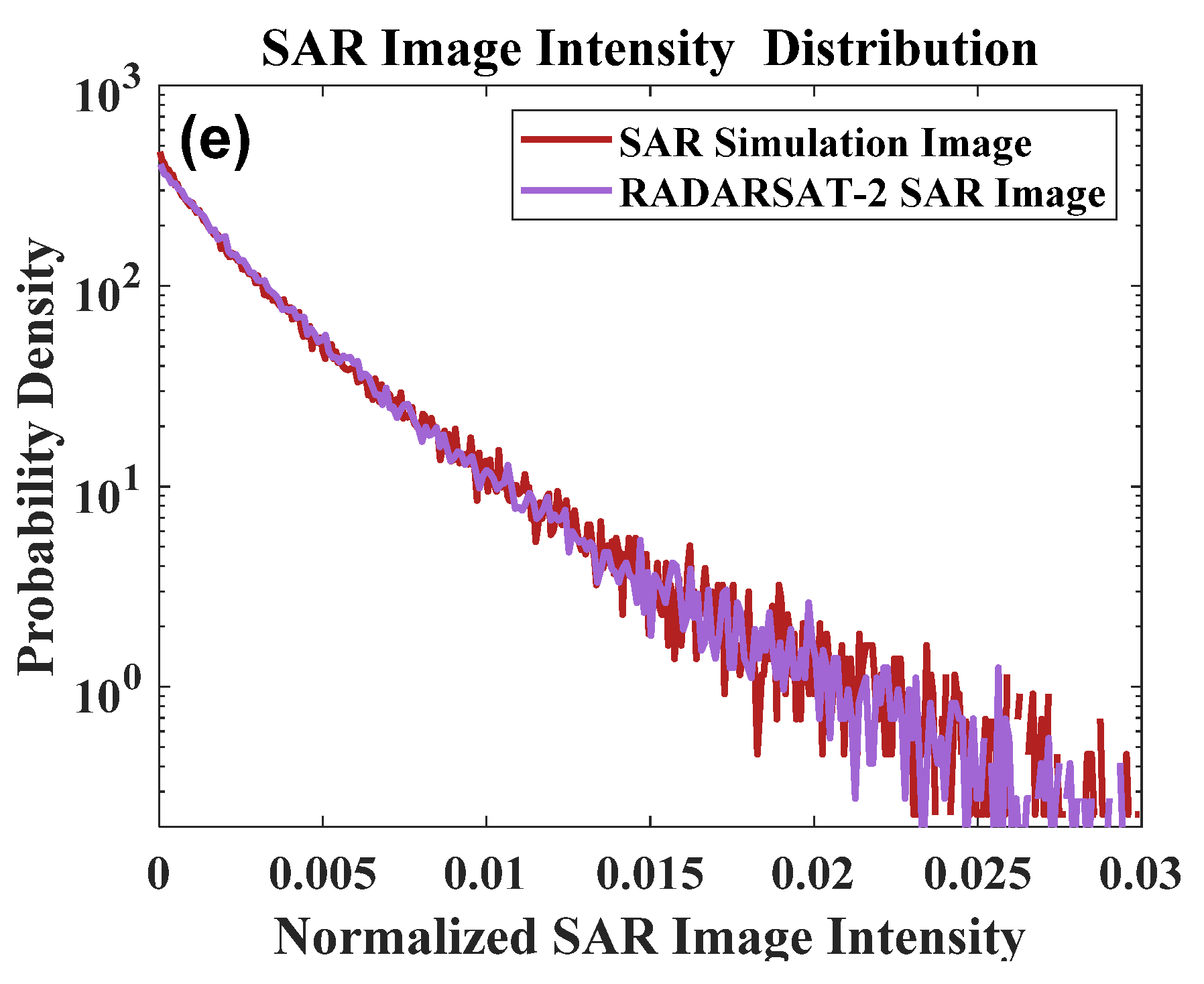
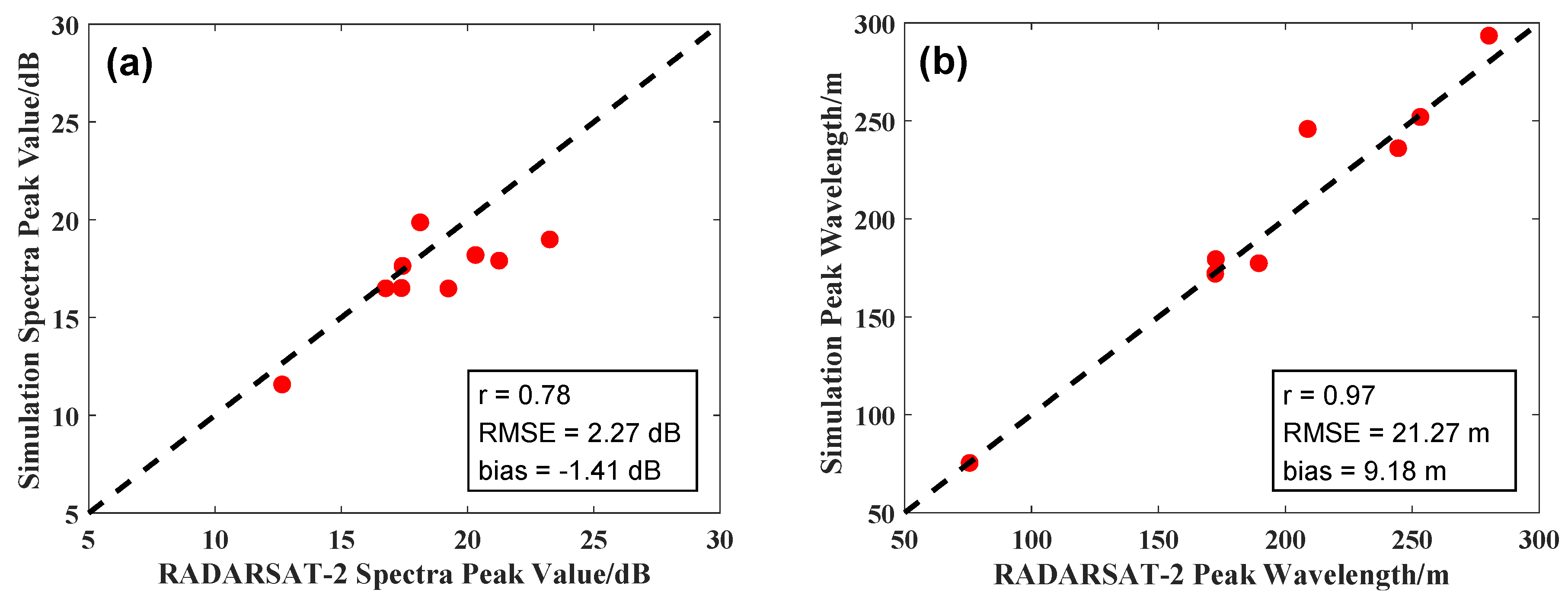




| SAR ID | Acquired Time (UTC) | SAR Image Central Site | Buoy ID | Buoy Wind Direction (Degree) | Buoy Wind Speed (m/s) | Wavelength of the Dominant Wave (m) | Direction of the Dominant Wave (Degree) | SWH (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20090111_ 022504 | 46°04′06″N 131°02′22″W | 46005 | 163 | 9.0 | 362.49 | 360.00 | 4.23 |
| 2 | 20090822_ 143105 | 46°08′05″N 124°30′15″W | 46029 | 3 | 3.0 | 181.41 | 359.56 | 2.08 |
| 3 | 20090225_ 020926 | 35°44′43″N 121°55′42″W | 46028 | 331 | 5.3 | 268.82 | 348.14 | 2.15 |
| 4 | 20090228_ 054758 | 51°07′18″N 178°53′10″W | 46071 | 190 | 4.0 | 172.03 | 2.00 | 3.27 |
| 5 | 20091107_ 152316 | 54°21′23″N 132°23′09″W | 46145 | 295 | 9.1 | 236.33 | 0.56 | 3.77 |
| 6 | 20091208_ 151913 | 54°11′19″N 134°22′30″W | C46205 | 344 | 3.8 | 357.43 | 1.69 | 2.54 |
| 7 | 20090317_ 143915 | 46°07′05″N 124°33′25″W | 46029 | 217 | 7.7 | 179.15 | 359.74 | 3.45 |
| 8 | 20090118_ 143085 | 45°57′43″N 125°39′18″W | 46089 | 3 | 3.7 | 239.49 | 0.82 | 2.72 |
| 9 | 20100515_ 115636 | 28°33′05″N 88°18′34″W | 42040 | 336 | 6.8 | 75.38 | 0.14 | 1.42 |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 5.4 GHz |
| Pulse duration | 21 μs |
| Chirp bandwidth | 30 MHz |
| Azimuth bandwidth | 900 Hz |
| Incident angle | 20–40° |
| Platform velocity | 7.55 km/s |
| Platform altitude | 798 km |
| Azimuth resolution | 4.96 m |
| Slant range resolution | 4.73 m |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 5.4 GHz |
| Pulse duration | 40 μs |
| Chirp bandwidth | 30 MHz |
| Azimuth bandwidth | 1067 Hz |
| Incident angle | 42° |
| Platform velocity | 8 km/s |
| Platform altitude | 36 m, 530 km, 720 km |
| β | 60 s, 90 s, 120 s |
| Azimuth resolution | 6.00 m |
| Range resolution | 5.97 m |
| Scene dimension (Lx × Ly) | 1.53 km × 1.54 m |
| Wind direction | 0° |
| Wind speed | 11 m/s |
| Swell direction | 45° |
| Swell wavelength | 150 m |
| Swell SWH | 3 m |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 5.4 GHz |
| Pulse duration | 21 μs |
| Chirp bandwidth | 30 MHz |
| Azimuth bandwidth | 900 Hz |
| Incident angle | 30° |
| Platform velocity | 7.55 km/s |
| Platform altitude | 700 km |
| β | 120 s |
| Azimuth resolution | 4.96 m |
| Range resolution | 9.47 m |
| Scene dimension | 1.27 km × 2.42 m |
| Wind direction | 60° |
| Wind speed | 5 m/s, 10 m/s, 15 m/s |
| Swell direction | 30° |
| Swell wavelength | 200 m |
| Swell SWH | 2 m |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Wind direction | 0, 45, 90° |
| Wind speed | 10 m/s |
| Swell direction | 30° |
| Swell SWH | 2 m |
| Swell wavelength | 200 m |
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Wind direction | 90° |
| Wind speed | 5 m/s |
| Swell direction | 0, 45, 90° |
| Swell SWH | 2 m |
| Swell wavelength | 200 m |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030439
Li Q, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Bai Y, Zhang Y, Li X. Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(3):439. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030439
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qian, Yanmin Zhang, Yunhua Wang, Yining Bai, Yushi Zhang, and Xin Li. 2022. "Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface" Remote Sensing 14, no. 3: 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030439
APA StyleLi, Q., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Bai, Y., Zhang, Y., & Li, X. (2022). Numerical Simulation of SAR Image for Sea Surface. Remote Sensing, 14(3), 439. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14030439