Abstract
Wildfire is a hazardous natural phenomenon that leads to significant human fatalities, catastrophic environmental damages, and economic losses. Over the past few years, the intensity and frequency of fires have increased worldwide. Studies have been conducted to develop distinctive solutions to minimize forest fires. Systems for distant fire detection and monitoring have been established, showing improvements in data collection and fire characterization. However, wildfires cover vast areas, making other proposed ground systems unsuitable for optimal coverage. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have become the subject of active research in recent years. Deep learning-based image-processing methods demonstrate improved performance in various tasks, including detection and segmentation, which can be utilized to develop modern forest firefighting techniques. In this study, we established a novel two-pathway encoder–decoder-based model to detect and accurately segment wildfires and smoke from the images captured using UAVs in real-time. Our proposed nested decoder uses pre-activated residual blocks and an attention-gating mechanism, thereby improving segmentation accuracy. Moreover, to facilitate robust and generalized training, we prepared a new dataset comprising actual incidences of forest fires and smoke, varying from small to large areas. In terms of practicality, the experimental results reveal that our method significantly outperforms existing detection and segmentation methods, despite being lightweight. In addition, the proposed model is reliable and robust for detecting and segmenting drone camera images from different viewpoints in the presence of wildfire and smoke.
1. Introduction
Fire disasters cause significant harm to human life and property. Therefore, it is critical to establish appropriate, swift, cost-effective, and portable fire-detection systems for the general public. Several studies have been conducted to develop efficient and low-cost fire-detection systems.
The Korean Statistical Information Service reported that approximately 40,300 fire incidences were recorded and identified by the National Fire Agency South Korea in 2019. A result of such fires cost approximately USD 688 million in losses, injuring 2219 people and killing 284 [1].
Wildfires have damaged millions of hectares of land, forest resources, and livestock. They are among the most detrimental and catastrophic natural disasters in the US. According to the National Interagency Fire Center, wildfire summary and statistics reported that approximately 58,985 wildfires occurred in the US in 2021, compared with 58,950 in 2020. In terms of land losses, the wildfires in 2021 consumed approximately 7,125,643 acres compared with 10,122,336 acres in 2020 [2].
Deep learning-based image processing techniques show improved performance in a variety of tasks, including detection [3] and segmentation [4], which can be used to develop wildfire- and smoke-processing techniques. UAVs occupy a central role in important missions owing to their distinct capabilities. The key feature of drones is that they can be automatically controlled by humans or software with sensor technologies and a global positioning system. Recently, distant sensing techniques have been combined with UAVs for the early detection of wildfires. This combination has received global attention and can serve as an alternative to conventional and current wildfire-detection systems. Alternatively, drones with computer-vision-based remote sensing systems are gradually becoming the best option for detecting and monitoring wildfires. They are specifically known for their mobility, speed, safety, and cost-effectiveness [5]. Additionally, they are unique because they adhere to the specific criteria for spectral and spatial-temporal resolution. Such systems can perform prolonged and routine functions that would be impossible for humans. They cover an extended range of gathering and delivering intuitive and accurate information within specific economic resources.
The classification and segmentation of computer-vision-based wildfire and smoke detection systems have increased significantly in recent years [6]. For decades, the primary reason behind such an increase has been the tremendous evolution of deep learning (DL) and machine learning techniques. Computer-vision-based fire-detection systems provide data within a limited period and can easily cover a relatively broad area. Different approaches have been developed to detect wildfires. The approaches are classified based on different attributes (such as motion, texture, and color) used by them for fire detection. It has been demonstrated that DL algorithms are efficient and perform satisfactorily; they provide optimal performance for fire detection and segmentation. However, they exhibit certain drawbacks, such as the false detection of fire pixels and false alarms. DL techniques yield significant results in terms of fire detection. They are specifically employed to study the geometrical features associated with wildfires, such as width, shape, angle, and height. Additionally, they are used to detect the color of wildfires and have achieved promising results in segmenting and classifying wildfires [7,8]. Several studies are being conducted to further investigate the application of DL techniques for wildfires. These methods utilize input images to determine the exact shape of the fire. Such images are captured using traditional visual sensors and yield favorable results. However, the usefulness of such methods for detecting and segmenting forest fires using UAV images has not been confirmed. It is also a matter of concern whether such methods can yield efficient results for multiple problems in forest fires, such as image degradation, background complexity, and small objects.
This paper describes how a proposed encoder–decoder can be used to segment forest fires and smoke using a novel encoder–decoder framework.
In our proposed approach, we have modified EfficientNetv2 [9] with a novel attention gate (AG)-based nested network to construct the segmentation network. The encoder consists of two-path nested CNNs that capture the semantics and contextual information of the input image to generate feature maps. Our novel nested decoder decodes the aggregate feature maps to classify the events and output accurate segmented images. Additionally, we designed the proposed method to be lightweight using depth-wise convolutions, so it can be utilized in real-time. The proposed method was evaluated against several state-of-the-art detection methods on publicly available datasets. The experimental results show the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed method in terms of accuracy and speed.
The aspects of our study are as follows:
1. The proposed two-pathway architecture considers spatial details and categorical semantics separately, such that it can be used for real-time fire and smoke instance segmentation;
2. Pre-activated residual blocks and AGs are used to design a novel nested decoder to improve segmentation accuracy;
3. A new lightweight network based on depth-wise convolutions is proposed to augment the receptive field and capture useful contextual information;
4. The proposed network satisfactorily generalizes the dataset using a combination of datasets and an encoder–decoder network to segment forest fires.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 summarizes previous reviews about the traditional, deep learning, and UAV methods applied to wildfire and smoke studies and article-search strategies; Section 3 presents a detailed description of the detection and segmentation of our model and details the specifics of the drone used in our experiments; Section 4 describes the dataset and experiments and presents the results achieved; subsequently, Section 5 provides a discussion, and Section 6 provides the conclusions.
2. Related works
2.1. Traditional and Deep Learning Methods
Several scholars have contributed to fire-detection development, including vision-sensor-based and conventional fire alarm systems. Fire detection in conventional fire alarm systems requires several environmental sensors, including smoke, heat, and photosensitive sensors [10,11,12]. However, the techniques for conventional fire alarm systems are only effective for fire detection close to the fire, such as when used indoors; however, they fail when used at a long distance, such as outdoors. Moreover, a conventional fire alarm system cannot offer a fire alert or indicate the speed at which the fire is burning. Human intervention is required in conventional fire alarm systems, such as inspecting a fire spot to confirm the presence of a fire in an alert situation. The authors have developed several optical-sensor-based fire-detection techniques [13,14] to overcome these problems. Traditional fire detection (TFD)- and DL-based approaches are the two primary types of vision-based fire-detection systems; TFD is more common. TFD-based approaches function based on digital image processing and pattern recognition techniques. Handcrafted feature extraction in TFD-based approaches is time-consuming and labor-intensive, although these techniques cannot attain high accuracy. The use of CCTV surveillance systems with DL-based approaches is necessary for fire detection, and completely automated characteristics and an extraction method can improve the efficiency and safety of these models.
These models are efficient and dependable owing to the extraction procedure. A comparison between the DL and TFD models reveals that the DL models have higher reliability and lower error rates. Xu et al. [15] proposed a deep neural network to identify forest fire areas in a shot, which was later implemented in a deep neural network. For the smoky saliency map, they merged the salient regions at the pixel and object levels in the CNN model. They established a fire-detection system based on vision transformers and separated a picture into comparably sized patches to reveal a long-range connection. Muksimova et al. [16] developed an attention-guided capsule network-based fire and smoke classification approach that used CCTV to capture outdoor fire/smoke incidents, which plausibly works for single fire and smoke incidents at different outdoor distances. Recent studies have contributed to developing various DL-based fire-detection approaches; all the approaches have achieved excellent accuracy in practical applications. Furthermore, detection accuracy must be improved, and the number of false alarms must be minimized to protect people and prevent property damage. Moreover, these models are computationally demanding and require sophisticated graphics processing units (GPUs) and transputers.
2.2. UAV-Based Fire Segmentation Methods
In recent years, many researchers have addressed the characteristics of remote-sensing images by proposing a high-resolution method [17,18,19]. With deep learning models, it is currently possible to segment fire pixels and determine the exact shape of a flame or smoke from various aerial images. Many modern models, which focus on areal images from drones, implemented domain adaptation [20,21], as a method for enhancing a model’s performance [22] on a target domain with inadequate annotated data [23,24], by applying the knowledge the model has acquired from a related domain with sufficient labeled data. In regards to the classification and segmentation of wildfire, an encoder–decoder U-Net-based method [25] was proposed by [26]. This method received an 87.75% score and proved to be effective in segmenting wildfires, while determining the exact flame shapes by implementing a dropout strategy and the FLAME dataset [26]. Another proposal for smoke and fire segmentation, the VGG16 method, has been introduced [27]. With 93.4% accuracy and a 21.1 s time segmentation for every picture, the VGG16 method proved to be more effective than the previously mentioned models, which used techniques of data augmentation such as crop, flip, rotation, changing brightness/contrast, and adding noises.
Barmpoutis et al. [28] suggested a new sensing system for smoke and fire segmentation, which covered 360 degrees remotely. The RGB 360-degree images that a UAV collects were used in this system. For the smoke and flame region detection, encoder–decoder detectors, two DeepLab V3+s [29], and Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling were implemented. This is followed by the application of an adaptive post-validation to reject regions with specifically identical characteristics of false or positive smoke and/or flames. Experiments, which used different degrees of urban and forest area images, performed better than existing methods such as DeepLabV3+ and reached 94.6%. All these results demonstrated how the proposed method can successfully reduce the rate of false-positive errors and segment both smoke and fire efficiently.
3. Proposed Method
The two-stage architecture based on the segmentation networks of feature extraction networks is shown in Figure 1. The first step is the feature extraction segmentation network, and the second step is the segmentation process. Next, a brief overview of the following research topics is provided: feature extraction (Section 3.1), attention gateway (Section 3.2), parallel branches (Section 3.3), and segmentation network (Section 3.4).
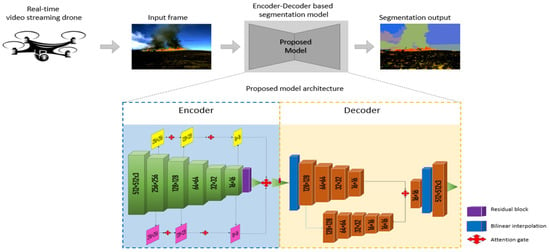
Figure 1.
Overview of proposed architecture for detecting and segmenting objects.
3.1. Feature-Extraction-Network Backbone
The foundation of the proposed method comprises an encoder that uses our recommended two-way feature pyramid network as a transmission mechanism. In every segmentation network, the encoder is the fundamental building element. A powerful encoder must have a large representative capacity. Our goal is to establish a fair balance between the variable count and the computational power in a network’s representational capacity. EfficientNets, a relatively new class of designs, has exceeded existing networks in classification tests, while using fewer number parameters and floating-point operations per second than previous networks. It leverages compound scaling to effectively increase the size, breadth, and resolution of the network over its nodes. Hence, we planned to develop an encoder with a layered decoder on top of this scaled architecture, widely known as the EfficientNetv2 model. EfficientNetv2 was selected because it is the most efficient network in the EfficientNet family that can be trained and tested within a reasonable period, i.e., it includes comparatively fewer parameters, 18 million parameters, which is 7.7 times decreased and has 10 times higher speed than squeeze-and-excitation (SE) models [30].
In most cases, this model may be entirely replaced with any EfficientNet model, if it is selected based on the computing capabilities of available resources and the computational cost. First, we removed the classification head and SE links in the network to adapt EfficientNet to our work. We discovered that the precise modeling of interdependencies across channels of fully convolutional maps, enabled by the SE connections, suppresses feature localization in favor of contextual components in the fully convolutional maps. Adding SE connections to our core would undermine segmentation effectiveness, which necessitates this and the previously mentioned characteristic of a classification network. In addition, we used synchronized in-place activated batch normalization (iABN sync) to substitute for the existing batch normalization layers [31]. Performing multi-GPU training enables different GPU synchronizations across and, thus, yields more accurate gradient figures. Moreover, additional GPU memory is made available by performing in-place operations. The EfficientNet encoder comprised seven blocks, as shown in Figure 1. According to the left to right, each block is denoted as Block 1 through Block 7. The down-sampling parameters of 4 × 4, 8 × 8, 16 × 16, and 32 × 32 are generated from Blocks 2, 3, 5, and 7, respectively. Our two-way feature pyramid network (FPN) receives inputs from the down-sampled outputs of these blocks [32]. The standard FPN, utilized in other segmentation networks, is designed to solve a multiscale feature merge by combining the feature parameters of various resolutions in a nested manner. The 1 × 1 convolution encoder decreases or increases the number of output channels to a specific amount, 256. Next, the lower quality features are up-sampled to a higher resolution before the combination. For example, encoder output aspects from a ×32-bit resolution are shrunk to a ×16-bit resolution and appended to the encoder network output features from a ×16-bit resolution. As a final step of the encoder part, a 3 × 3 convolution layer is applied at each scale to aggregate the fused aspects, which results in learning the C4, C8, C16, and C32 outputs. In this FPN architecture, only a restricted unidirectional flow of information occurs, leading to an inadequate fusion of multiscale characteristics. To minimize this difficulty, by introducing an additional network that collects multiscale features from the bottom to the top to enable a two-way data flow in our proposed bidirectional FPN, two parallel branches are connected.
The 1 × 1 convolution is combined with 256 output filters at each scale to minimize the number of channels in each branch. As shown in pink in our architecture, the descending branch follows the right-to-left aggregation approach of the standard FPN. The lower-resolution encoder output is added to the lower-resolution down-samples from the yellow bottom-to-top branch; this reduces the clarity of the higher-resolution elements by a factor of two. For example, there are several approaches in which encoder output characteristics from the ×8 resolution may be expanded to include elements from the ×4 resolution. In the next step, the outputs from the bottom layer to the up layer and top layer to the down layer per resolution are suitably concatenated and connected through a 3 × 3 convolution layer, which consists of 256 output channels, to receive the results from C4, C8, C16, and C32.
3.2. Attention Gate
AG can be compared to the human vision focus system in terms of performance. The concentration coefficient, , which is in the [0, 1] range, reduces the reactions to unnecessary previous knowledge, while gradually increasing the responses to essential background features’ parameters for the specific activity by automatically concentrating on the region of interest (ROI). AG produces the following result, by combining input feature maps and attentiveness coefficients element by element.
In Equation (1), denotes the feature for class and pixel in layer , and denotes the number of features. For the pixels in the layer, each pixel has an value, where is the amount of feature maps in the layer. Multidimensional concentration coefficients are employed for the several semantic classes, for each AG to learn to concentrate on a portion of the target structure. The AG architecture (red box) is depicted in Figure 1. A gating vector is employed with to establish the focus area for each pixel . It does this by exploiting contextual information to inhibit the lower-level feature response. Instead of using multiplicative concentration [33], additive attention is used to obtain the gating coefficient [34]. The recent is treated as matrix multiplication, making its speed high and more memory-effective than the original. Moreover, experiments have shown additive attention to be more accurate than multiplicative attention. Our network attention is expressed as:
where is the rectified linear unit, and = is a sigmoid activation function. Its characteristics are defined by a set of variables , which includes the following parameters: linear transformations and bias terms . Convolutions of the input tensors are performed channel by channel using channel-wise 1 × 1 × 1 convolutions. It is possible to apply standard backpropagation updates to train the AG parameters.
3.3. Parallel Branches
The encoder portion of the algorithm progressively decreases the input scale of the picture to plot the final feature map. It is necessary to debug a prediction map of a similar scale as the original picture from this reduced feature map because of the decreased feature size. Consequently, we employed layered parallel branches to accomplish our goal, as shown in our architecture. Several parallel branches exist, but the most common type comprises a concatenation of AGs [35], the residual block that was pre-activated, and up-sampling in combination. The encoder output is significantly smaller than the original input picture; therefore, it is extended in the expansion route by utilizing transposed convolutions to compensate for the size difference. These expansion route characteristics are integrated with the contraction path’s characteristics; older approaches such as UNet involve direct concatenation to achieve this combination. UNet architecture has a direct connection that forces aggregation exclusively at the same-scale feature maps of the encoder and decoder subnetworks, imposing an unduly restricted fusion method. With this kind of limitation, we cannot make the network contain local and global information and advanced features.
To our network by including additional parallel branches to the decoder subnetworks, the skip connections are redesigned to aggregate features with different semantic scales, creating a highly flexible feature-fusion technique. However, this is not necessarily the most effective integration method, without considering the relative relevance of high- and low-level properties. The network may become confused because of the cryptic and misleading information that is provided, resulting in incorrect network segmentation. Another vital part of the proposed design is the residual block described below. The residual block comprises a convolution layer and a skip connection, among others. Using this skip link, the low- and high-level data are combined additively, alleviating the vanishing gradient problem in deep networks. During the pre-activation phase of the ResNet architecture [36], LeakyReLU [37] and batch normalization operations are moved before the convolution operation is performed. As shown in Figure 1, the pre-activation residual network resulting from this calculation is expressed as follows:
In Equation (4), and are the input and output of the pre-activation residual block, respectively. Upon summation, the final output of the residual network is represented by. The pre-activation method simplifies network training because it makes the network more responsive. The picture size input into the generator framework is 512 × 512 pixels, as specified by the user. The design utilizes the EfficientNetB4 model, which has been pretrained on ImageNet as an encoder, and a parallel network as a decoder. Figure 1 shows the encoder network, resolution, expansion ratio, kernel size, and number of connections in depth. In the encoder structure, max pooling is used to compress the picture dimension up to 8 × 8 × 448 pixels, followed by a residual network to complete the transformation. On the other side, the decoder comprises a residual network, an AG, and up-sampling, which are concatenated. The dropout values for the bottom two layers of the decoder are 0.25 and 0.1, respectively. To obtain the final prediction map, a 1 × 1 convolution is performed after the decoder, followed by sigmoid activation.
The network can be trained using a combination of loss functions, including dice and binary cross-entropy , to maximize performance. This loss function steered the framework to achieve precise segmentation, significantly improving the segmentation of smoke and fire. The segmentation loss is determined using Equation (5):
where and represent the predictability ground truth labels and predictability map for the forest smoke and fire, respectively. Weights are represented using numbers 1, 2, and 3, which were experimentally structured as 0.4, 0.6, and 1.0 with the experimental results of the validation set. Since the fire segmentation was more challenging than the smoke segmentation, the weights assigned to the fire contribution exceeded those assigned to the smoke contribution. The dice coefficient loss indicates the overlap between the expected output and ground reality. Equation (6) is an example of this loss:
where is the total number of pixels in the image, the binary ground truth mask , and the foretold probability map . The discrepancy between the forecast output probability’s density function and the regression coefficients’ distribution is calculated using the binary cross-entropy function.
This function is expressed as follows by Equation (7), where R(sc) is shown to be the residual block regression coefficient:
3.4. Segmentation Network
Figure 1 depicts how the segmentation head of our proposed network instance functions. Two steps are included in our network. Convolutional networks generate rectangular feature recommendations and an objectless value for the FPN input layer, as shown by the region proposal network (RPN) module in our architecture. Next, the ROI aligns [38] with the used feature concepts to derive features from FPN encodings by directly combining the 14 × 14 spatial information from the channel, which is limited by the proposed feature concept. Subsequently, the collected attributes are input into networks that require feature categorization and mask segmentation, among other techniques. While training the Mask R-CNN instance, loss functions are recommended to train the segmentation component. Two-loss functions are used for the first step of objectivity, estimation loss, and a one-loss function is used for the second step of mask segmentation, classification. A set of optimistic and unfavorable matches are randomly selected such that The abjectness score loss, log, is determined as the logarithmic loss for a proposed .
Here, is the loss of object estimation, is the mask segmentation, and classification loss.
The first approach involves using the objectness score branch of RPN to obtain the objectness score. The second approach requires using the ground truth label to determine the ground truth. To define the positive and negative matches, we used Mask R-CNN (the same method). There are predefined criteria, denoted as and , where is greater than . Geographic features, which are considered low-level information, are processed during the first step. Therefore, a high channel capacity is required for this branch to encode a large amount of spatially precise information. Since the Detail Branch is only concerned with low-level details, we may generate a shallow structure with a short stride for this branch to accommodate this concentration. The central theme of the Detail Branch is to utilize large channels and shallow layers for the spatial features of the scene. Furthermore, the spatial area and number of channels of the feature representation in this branch are significant. Consequently, it is preferable to ignore residual connections, which increase memory access costs and deteriorate the performance of the system. The second stage works in combination with the first stage, and the second stage is intended to capture high-level semantics. This branch has a limited channel capacity; however, the first stage may provide spatial information absent in this branch. Based on our tests, the Semantic Branch had a ratio of (1) channels in the first stage, resulting in a lightweight branch size that is somewhat small. The fast-down sampling approach is used in the second stage to enhance the feature representation and expand the receptive field as rapidly as possible. High-level semantics necessitate the use of a broad receptive field. Thus, the second approach leverages global average pooling (Liu et al., 2015) [39] to integrate the global contextual reaction within the global contextual response.
3.5. Drone
Drones were used to generate a dataset of aerial images of forest fires. For the case studies, we have used a DJI Mavic 3 [40] UAV (Quadcopter). DJI Mavic 3 has a dual-camera setup in a 3-axis gimbal, i.e., a 20 MP wide-angle camera with 4/3” CMOS and a 12 MP telephoto with 1/2” CMOS and 28x hybrid zoom. The camera setups provides a high resolution (e.g., 5.1 K), high frame rate (e.g., 120 fps), and high dynamic range. As a result, it can handle nearly any lighting condition and deliver low-light footage with less noise, which is essential for extreme cases of fire and smoke. Moreover, it provides obstacle avoidance system with auto-tracking of subjects and can cover almost 9.3 miles during aerial maneuvers, which makes it a suitable candidate for the UAV for this study. The specifications for the UAV are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Drone specifications.
4. Experimental Results
First, we present the typical performance measures applied for empirical evaluations and briefly explain the datasets used as a basis for comparison. Thorough quantitative comparisons, benchmarking data, and comprehensive ablation research on the different architectural aspects are presented. Subsequently, the results of our qualitative and visual evaluations of wildfire segmentation are presented for each dataset.
4.1. Implementation Details
Our training setup was based on the PyTorch framework [41], with Tensorflow as the backend; it was trained with the following configuration. The generator network was optimized using the Adam optimizer [42]. We performed experiments on a device with an NVIDIA Geforce RTX 3080 Ti GPU. The test equipment was implemented using an Intel® Core™ i7-11700K 3.60 GHz central processing unit (CPU). The software specifications of the test environment include CUDA 11.1, cuDNN 8.1.1, and Python 3.8.
4.2. Datasets
Several firefighting organizations currently use DL-based fire-detection systems. Generating or locating a large dataset with minimal prejudice is the most challenging task in machine learning research. Ideally, such a dataset would include positive instances with significant feature variations and unfavorable instances comprising standard and complex samples. DL methods require larger datasets for training compared with traditional machine learning methods. Data augmentation methods may be valuable in this situation; however, they must be applied to a sufficiently large dataset to be effective. For example, cancer detection, face recognition, and object recognition are well-developed areas with massive datasets constructed and approved by the community. They are useful in developing and benchmarking new algorithms in their respective fields based on the information included in these datasets. Current widely used fire-detection datasets do not contain other information, such as the smoke area, captured area, vegetation type, prevailing hue, and the intensity of the fire texture. Aerial forest fire images are available in some datasets (for example, the Flames dataset [26]), but they are restricted. In studies on wildfire UAVs, there is a need to generate a dataset to develop algorithms for wildland-fire support systems. The performance of the model is influenced by data preparation, suggesting that some labeling techniques facilitate the recognition and identification of wildfire patterns and features [43]. To mitigate this problem, we collected publicly available wildfire images from the Internet and YouTube videos and compiled them for detection and segmentation. (Our dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/ShakhnozaSh/Wildfire-NET). The new dataset comprised 37,526 images, which were classified for training, validation, and testing. Figure 2 presents an overview of the most critical fire research datasets.
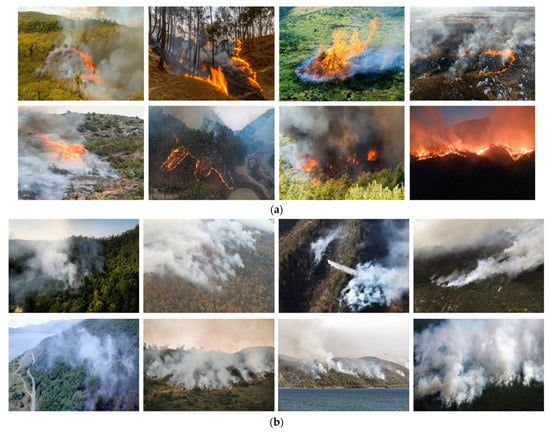

Figure 2.
Description of wildfire datasets: (a) forest fire; (b) forest smoke.
4.3. Training Details
We trained our network using image data with a resolution of 512 × 512 pixels and performed a limited number of random input augmentations, such as data flipping and scaling, within [0.5, 2.0]. EfficientNet values were used to form the backbone of our structure, and the parameters for the iABN sync layers were initialized to 1 to initialize the other layers. We utilized Xavier initialization [44]. There was no set start for the bias, and the Leaky ReLU had an incline of 0.01. In addition, we used Leaky ReLU with an incline of 0.1. To train our method using stochastic gradient descent in the momentum of 0.9, we applied a multistep learning-rate plan that started with base supervised learning. The system was built for specific iterations before decreasing the learning by a factor of 10 at each milestone. Training continued until convergence occurred. Iterations and milestones are denoted as in the following notation: . An Initial warm-up phase was performed in which was linearly increased from 1 3 to in 200 iterations, beginning at 1 3 before commencing the training session. The system was built for an additional 10 epochs with a predetermined learning algorithm of , in addition to freezing the iABN sync layers. For input sizes of 320 × 320 and 512 × 512, we used the ResNet-101 backbone to train our model. The total training time was 3–6 days. For the EfficientNet backbone, the total training time was 5 days with an input size of 512 × 512.
4.4. Process Speediness
As our metrics calculation in the proposed work used Average Precision (AP), AP50mask, and AP75mask and Frames Per Second (FPS), one technique to condense the PR curve into a single value is to use average precision, while the second metric is the FPS metric or the inverse of the Seconds Per Frame metric. The IoU threshold is set at 50% or 75%, respectively, and is referred to as AP50mask and AP75mask. The major metric utilized to assess segmentation performance was the DICE similarity coefficient. For analysis, the mean, median, and standard deviation of DSC were produced. Similar to this, DSC values for the proposed work trial were reported in data tables to show the relationship between the performance of segmentation inside each resolution of images. Based on this comparison, we found that our model outperformed the current best models in terms of inference speed. The interference duration of a single picture was calculated using a batch size of 1 and the total CNN and NMS times for 1000 images divided by 1000, to obtain the inference time of a single image using a batch size of 1. Specifically, we used EfficientNet reduced to the proposed approach and developed two versions: the fast version with an input size of 320 × 320 and the standard version with an input size of 512 × 512. Our model, which is based on PyTorch optimization, can produce accurate results within a short period. The improvements presented in Table 2 are for the case when one-stage detection is combined with our proposed multilevel structure. The resulting speed–accuracy curve is superior to those of existing approaches. In addition, Table A1 provides information on the average and standard deviation based on the resolution of the training image.

Table 2.
Comparison of speed and accuracy with other models.
4.5. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Methods
We begin by evaluating the proposed approach compared to the state-of-the-art methods on our gathered dataset drone wildfire images and videos, to assess its superiority. Since our primary aim was to identify precision and agility, we assessed our results and those of comparable single-model outcomes that have not been subjected to test-time augmentations. The speeds reported in this paper were calculated on a single RTX 3080Ti, indicating that some of the mentioned speeds may be higher than those reported in the corresponding original study. The proposed model exhibits comparable segmentation performance by being 3.8 times faster than the previous best instance-segmentation approach for the COCO platform. When the results of our technique were compared with those of other approaches, we observed a significant difference in effectiveness. The difference in the results between Mask R-CNN and YOLACT-550 at the 50% overlap criterion was 9.5 points; by contrast, it was 6.6 points at the 75% IoU criterion, which is comparable with our qualitative findings. For instance, there was a disparity between the efficiencies of FCIS and Mask R-CNN (AP values of 7.5 and 7.6, respectively). In addition, at the highest, that is, the 95% IoU threshold, the proposed approach outperformed Mask R-CNN by 1.3 AP compared with 1.6. Table 3 includes values for different model configurations, which are presented separately. Furthermore, in addition to our basic picture size model of 512 × 512 pixels, we trained models with 550 × 550 and 700 × 700 pixels, with the anchor sizes adjusted accordingly. Instance segmentation naturally requires larger photographs; decreasing the image size significantly reduces the overall performance. As predicted, increasing the picture size reduces the speed significantly, while simultaneously improving performance. In addition to our backbone network EfficientNet, we tested ResNet-101 to achieve faster results. If faster processing rates are desired, we recommend utilizing ResNet-101 instead of shrinking the picture size, because these setups perform significantly better than the recommended model size of 550, though are somewhat slower. The proposed method performs better and faster than the widely used techniques that exhibit SBD performance.

Table 3.
Quantitative comparison of the proposed method with existing methods in terms of accuracy and runtime.
4.6. Proposed Model Stability
No matter how immobile the objects were, our findings indicate that the proposed model produced more stable video masks than Mask R-CNN and YOLACT. However, we used only static images for training and did not apply any temporal smoothing. Consequently, our masks have a higher standard (few errors may occur in the time in-between frames), and we believe that they are more reliable than the other masks because ours is a one-stage model. The area recommendations provided in the first step of the two-stage approaches significantly impact the masks established in the second stage. By contrast, when using our proposed approach, the models are not impacted even if the model predicts separate packages across frames, resulting in significantly robust masks in terms of temporal stability.
5. Discussion
Previous methods of spotting forest fires have many advantages, including the capacity to recognize flames in shorter amounts of time and with a higher degree of precision. Conversely, anytime there are problems, there will also be obstacles. For instance, when the capture of flames from the perspective of a drone leads to an increased incidence of false positives or when inconspicuous fire sites with a tiny target or a high degree of camouflage are not easily discovered. To be more exact, the improved branch cascades have maps that are the same size throughout both the encoding and decoding stages of the process. The enhanced integration of the pixel location attributes inside the external network is made more accessible. In addition to this, the deep neural network considers the pixel category. As a result, the pixels around the edge of the forest fire targets are changed.
To offer a complete example of the logic behind the model described in this study, our model is compared with the Mask R-CNN and the YOLACT included in the originals, from many vantage points. Table 3’s comparison of convergence shows that, compared to the other three models with the same parameters, our method has a slightly lower total training-loss sample. The visualization result shown in Figure 3 reveals that the segmentation masks our approach generates have the most significant matching degree with the original, unaltered form of the forest fire. The fact that the mask is the item with the most effective degree of resemblance demonstrates this point. When analyzing the edge pixels of forest fires, this has obvious advantages. The quantitative evaluation shown in Table 3 reveals that our method can reach SOTA performance levels in terms of both identification accuracy and segmentation quality. To prove the robustness of our model, the results for the Flame dataset are shown in Figure A1, and additional results are shown in Figure A2. Additionally, because of our model stable structure, it can train from the very beginning to the very end. Consequently, it is feasible to simplify our method and use it on edge devices, assuming that recognition accuracy can be maintained throughout the process.
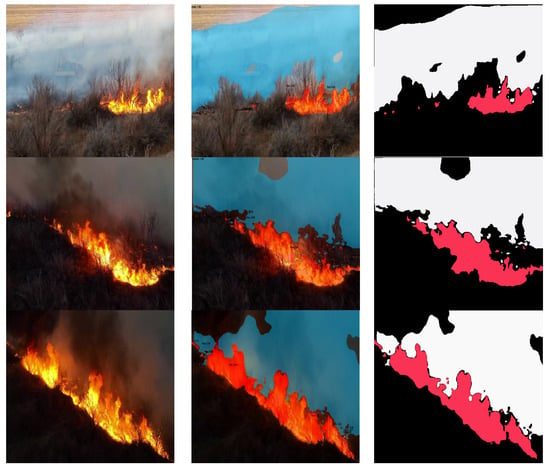
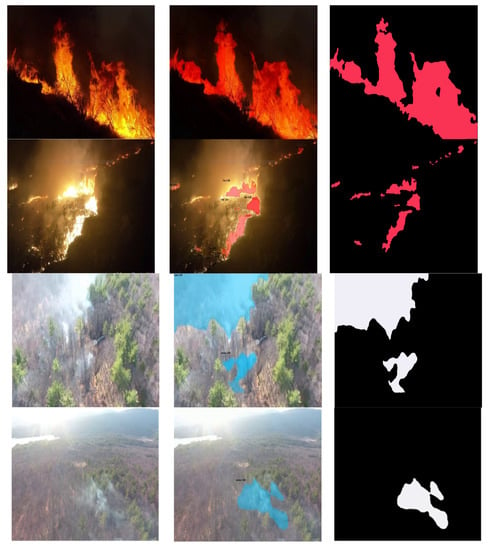



Figure 3.
Description of our model results. We divided our results into three parts: (a) raw images, (b) instance segmentation, and (c) ground truth.
The future goal is to create a robust real-time UAV-assisted wildfire location model that will help firefighters locate a fire at an early stage.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented a lightweight, UAV-image-based wildfire detection and segmentation system by leveraging the advantages of DL. In this proposed approach, we used next contributions: spatial details and categorical semantics, preactivated residual blocks and AG, a new lightweight network, and the satisfactorily generalized dataset. We experimented with the data preparation and model parameters to optimize the AP of wildfire-detection models for wildfire segmentation. The proposed system improves the accuracy and reliability of fire detection for firefighting technology. Moreover, the proposed system can run in real time, thereby making it a potential approach to monitor, control, and minimize the environmental damage caused by wildfires. The experimental results demonstrated the superiority of the proposed system compared to the existing methods, for detecting and segmenting wildfires. The proposed model can be extended to a working prototype in future studies to determine the wildfire level in Figure 3.
Author Contributions
This manuscript was designed and written by S.M. (Shakhnoza Muksimova); S.M. (Shakhnoza Muksimova) conceived the main idea of this study; S.M. (Shakhnoza Muksimova) wrote the program in Python and performed all the experiments; S.M. (Shakhnoza Muksimova) and S.M. (Sevara Mardieva) performed the preprocessing; Y.-I.C. supervised this study and contributed to the analysis and discussion of the algorithm and experimental results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Korea Agency for Technology and Standards in 2022, project numbers are K_G012002073401, K_G012002234001, and by the Gachon University research fund of 2019 (GCU-2019-0794).
Data Availability Statement
This paper used all datasets. We got confirmed used for our publication. And prepared custom dataset can be found at: https://github.com/ShakhnozaSh/Wildfire-NET.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| AG | attention gate |
| AP | average precision |
| CNN | convolution neural network |
| CCTV | closed-circuit television |
| DL | deep learning |
| DSC | standard deviation calculator |
| GPU | graphics processing unit |
| FPN | feature pyramid network |
| FPS | frames per second |
| iABN | in-place activated batch normalization |
| ML | machine learning |
| RGB | red, green, and blue |
| RPN | region proposal network |
| SOTA | state of the art |
| TFD | traditional fire detection |
| UAV | unmanned aerial vehicles |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Additional average and standard deviation based on training image resolution.
Table A1.
Additional average and standard deviation based on training image resolution.
| Image Size | 512 × 512 | 256 × 256 | 128 × 128 | 64 × 64 | 32 × 32 | 28 × 28 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Work: Average and Std. Dev. | 0.928 ± 0.072 | 0.948 ± 0.070 | 0.911 ± 0.069 | 0.902 ± 0.062 | 0.891 ± 0.087 | 0.890 ± 0.088 |
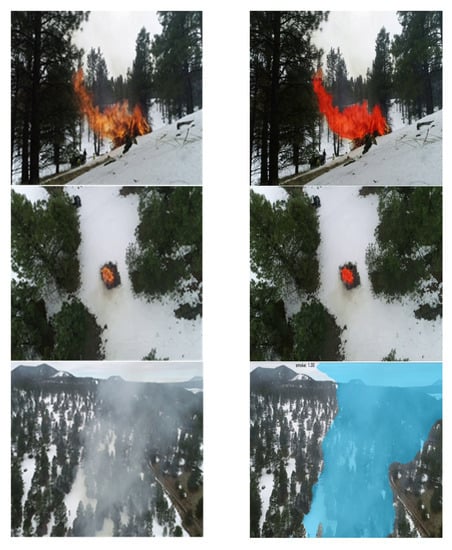



Figure A1.
Results from FLAME dataset.
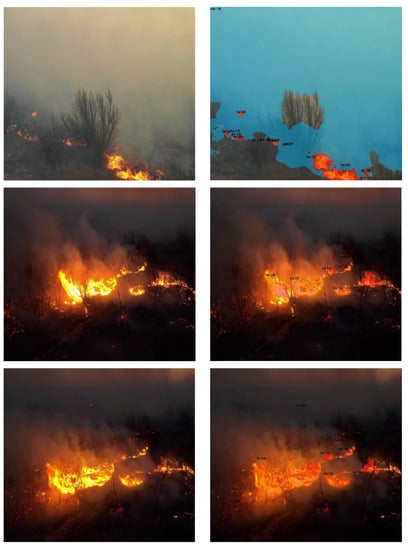

Figure A2.
Our additional results.
References
- Number of Fires, Fire Deaths Fall in 2019 “Yonhap News Agency”. Available online: https://en.yna.co.kr/view/AEN20200106008000315 (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- National Interagency Coordination Center Wildland Fire Summary and Statistics Annual Report 2021. Available online: https://www.predictiveservices.nifc.gov/intelligence/2021_statssumm/annual_report_2021.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2022).
- Zheng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Hu, X.; Huang, Y. Real-Time Detection of Winter Jujubes Based on Improved YOLOX-Nano Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umirzakova, S.; Whangbo, T.K. Detailed feature extraction network-based fine-grained face segmentation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 250, 109036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV). Available online: https://www.kari.re.kr/eng/sub03_02.do (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Frizzi, S.; Kaabi, R.; Bouchouicha, M.; Ginoux, J.-M.; Moreau, E.; Fnaiech, F. Convolutional neural network for video fire and smoke detection. In Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON 2016), Florence, Italy, 23–26 October 2016; pp. 877–882. [Google Scholar]
- Dzigal, D.; Akagic, A.; Buza, E.; Brdjanin, A.; Dardagan, N. Forest Fire Detection based on Color Spaces Combination. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 28–30 November 2019; pp. 595–599. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Ou, X.; Xu, L. A Collaborative Region Detection and Grading Framework for Forest Fire Smoke Using Weakly Supervised Fine Segmentation and Lightweight Faster-RCNN. Forests 2021, 12, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q.V. EfficientNetV2: Smaller Models and Faster Training. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.00298. [Google Scholar]
- Applications for Fire Alarms and Fire Safety. Available online: http://www.vent.co.uk/ fire-alarms/fire-alarm-applications.php (accessed on 5 January 2019).
- Wu, Q.; Cao, J.; Zhou, C.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, S.; Cheng, J.; Pan, G. Intelligent Smoke Alarm System with Wireless Sensor Network Using ZigBee. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2018, 2018, 8235127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Rani, P. Sensor-Based Smart Fire Detection and Fire Alarm System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Chemical Engineering (AdChE) 2020, Dehradun, India, 5–7 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jobert, G.; Fournier, M.; Barritault, P.; Boutami, S.; Auger, J.; Maillard, A.; Michelot, J.; Lienhard, P.; Nicoletti, S.; Duraffourg, L. A Miniaturized Optical Sensor for Fire Smoke Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII (TRANSDUCERS & EUROSENSORS XXXIII), Berlin, Germany, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1144–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, N.; Mushfiq, D.R.; Chowdhury, A.E. Computer Vision and Smoke Sensor Based Fire Detection System. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st International Conference on Advances in Science, Engineering and Robotics Technology (ICASERT), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 3–5 May 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, G.; Wang, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wang, J. Video smoke detection based on deep saliency network. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 105, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muksimova, S.; Umirzakova, S.; Mardieva, S.; Cho, Y.I. Novel Video Surveillance-Based Fire and Smoke Classification Using Attentional Feature Map in Capsule Networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Tao, F.; Liu, X.; Na, J.; Leng, H.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T. RAANet: A Residual ASPP with Attention Framework for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Di, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Jing, W.; Emam, M. SERNet: Squeeze and Excitation Residual Network for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Hu, A.; Xie, Z.; Xie, X.; Tao, L. TE-SAGAN: An Improved Generative Adversarial Network for Remote Sensing Super-Resolution Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjdira, B.; Bazi, Y.; Koubaa, A.; Ouni, K. Unsupervised domain adaptation using generative adversarial networks for semantic segmentation of aerial images. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Tao, D. Category anchor-guided unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation. Adv. Neural Inf. Processing Syst. 2019, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Stan, S.; Rostami, M. Unsupervised model adaptation for continual semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence 2021, Virtually, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 2593–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, F.; Shin, I.; Rameau, F.; Lee, S.; Kweon, I.S. Unsupervised intra-domain adaptation for semantic segmentation through self-supervision. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 3764–3773. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Shen, Z.; Shang, Y.; Yin, J.; Shi, Z. BiFDANet: Unsupervised Bidirectional Domain Adaptation for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsoshoara, A.; Afghah, F.; Razi, A.; Zheng, L.; Peter; Fulé, Z.; Blasch, E. Aerial imagery pile burn detection using deep learning: FLAME Dataset. Comput. Netw. 2021, 193, 108001. [Google Scholar]
- Frizzi, S.; Bouchouicha, M.; Ginoux, J.M.; Moreau, E.; Sayadi, M. Convolutional neural network for smoke and fire semantic segmentation. IET Image Process 2021, 15, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpoutis, P.; Stathaki, T.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Grammalidis, N. Early Fire Detection Based on Aerial 360-Degree Sensors, Deep Convolution Neural Networks and Exploitation of Fire Dynamic Textures. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, R.B.; Lorenzo, P.; Peter, K. In-Place Activated BatchNorm for Memory-Optimized Training of DNNs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; Kaiming, H.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, M.-T.; Pham, H.; Manning, C.D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1508.04025. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Oktay, O.; Schlemper, J.; Folgoc, L.L.; Lee, M.; Heinrich, M.; Misawa, K.; Mori, K.; McDonagh, S.; Hammerla, N.Y.; Kainz, B.; et al. Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.03999. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Identity mappings in deep residual networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 630–645. [Google Scholar]
- Maas, A.L.; Hannun, A.Y.; Ng, A.Y. Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models. In Proceedings of the ICML, Atlanta, GA, USA, 16–21 June 2013; p. 3. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-CNN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Rabinovich, A.; Berg, A.C. ParseNet: Looking Wider to See Better. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.04579. [Google Scholar]
- DJI Mavic 3. Available online: https://www.dji.com/kr/mavic-3 (accessed on 28 June 2022).
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing System, Vancouv, CA, USA, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Zhang, C.J.; Ji, L.; Ran, R.; Wu, H.Y.; Xu, Y.M. Forest fire recognition based on feature extraction from multi-view images. Traitement Du Signal 2021, 38, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier-Initialization. Available online: https://mnsgrg.com/2017/12/21/xavier-initialization/ (accessed on 21 December 2017).
- Wang, Y.; Luo, B.; Shen, J.; Pantic, M. Face mask extraction in video sequence. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact: Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9157–9166. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Kong, T.; Shen, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L. SOLO: Segmenting Objects by Locations. 2019. Available online: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-58523-5_38 (accessed on 4 December 2020).
- Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Kong, T.; Li, L.; Shen, C. SOLOv2: Dynamic, Faster and Stronger. 2020. Available online: https://deepai.org/publication/solov2-dynamic-faster-and-stronger (accessed on 23 March 2020).
- Chen, H.; Sun, K.; Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, Y. Blendmask: Top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8573–8581. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.-Y.; Shvets, M.; Berg, A.C. Retina Mask: Learning to predict masks improves state-of-the-art single-shot detection for free. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.03353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Qi, H.; Dai, J.; Ji, X.; Wei, Y. Fully convolutional instance aware semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, L.; Gong, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, X. Mask scoring r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 6409–6418. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the CVPR, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. Yolact++: Better real-time instance segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).