High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Notations
2.2. Tensor CPD Method and Linear Radon Transform
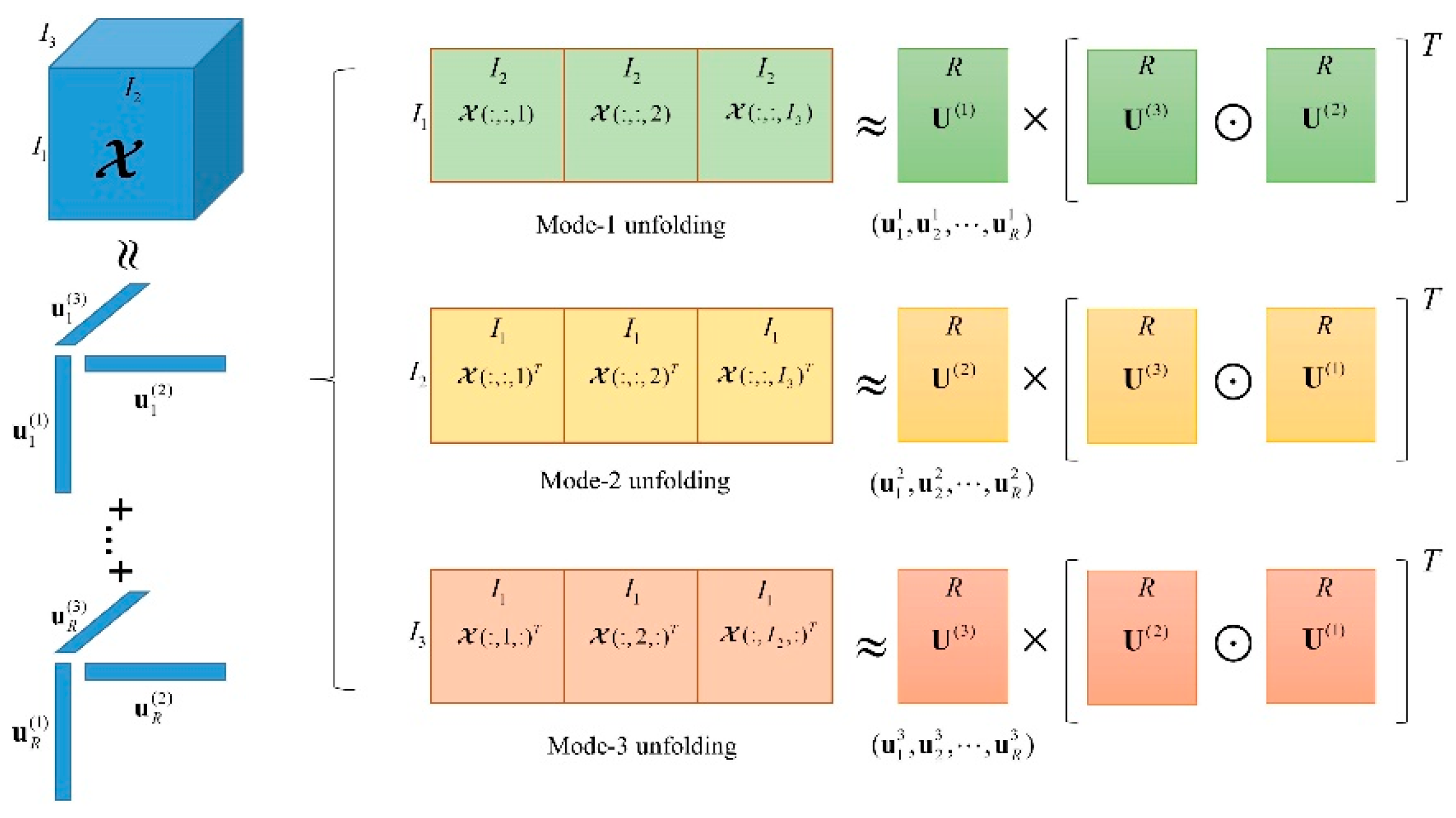
2.2.1. Tensor CPD Method
2.2.2. Linear Radon Transform
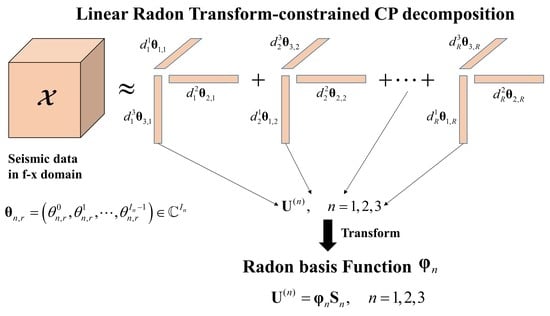
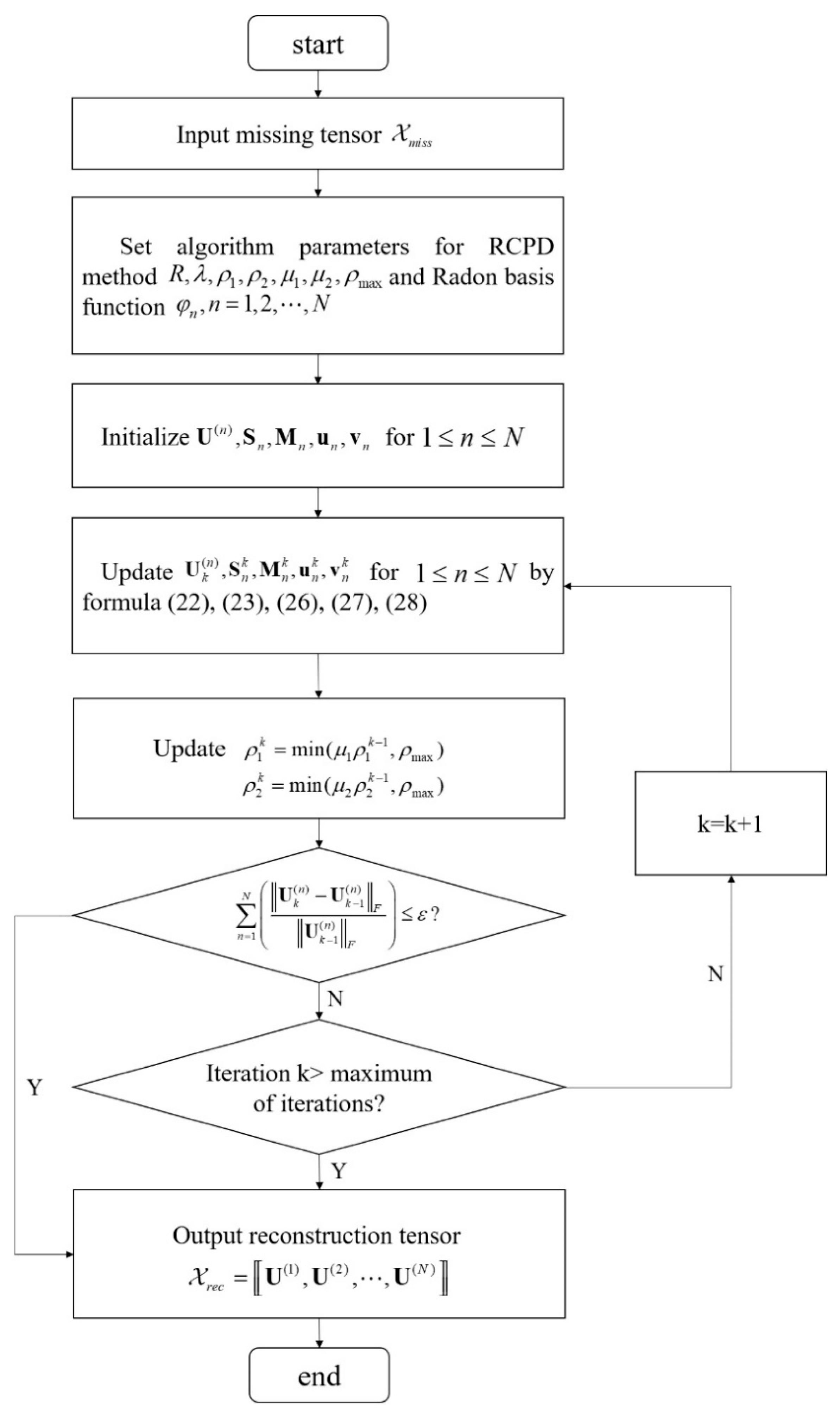
2.3. Linear Radon Transform–Constrained CPD for Tensor Completion
- 1.
- Update .
- 2.
- Update .
- 3.
- Update .
- 4.
- Update .
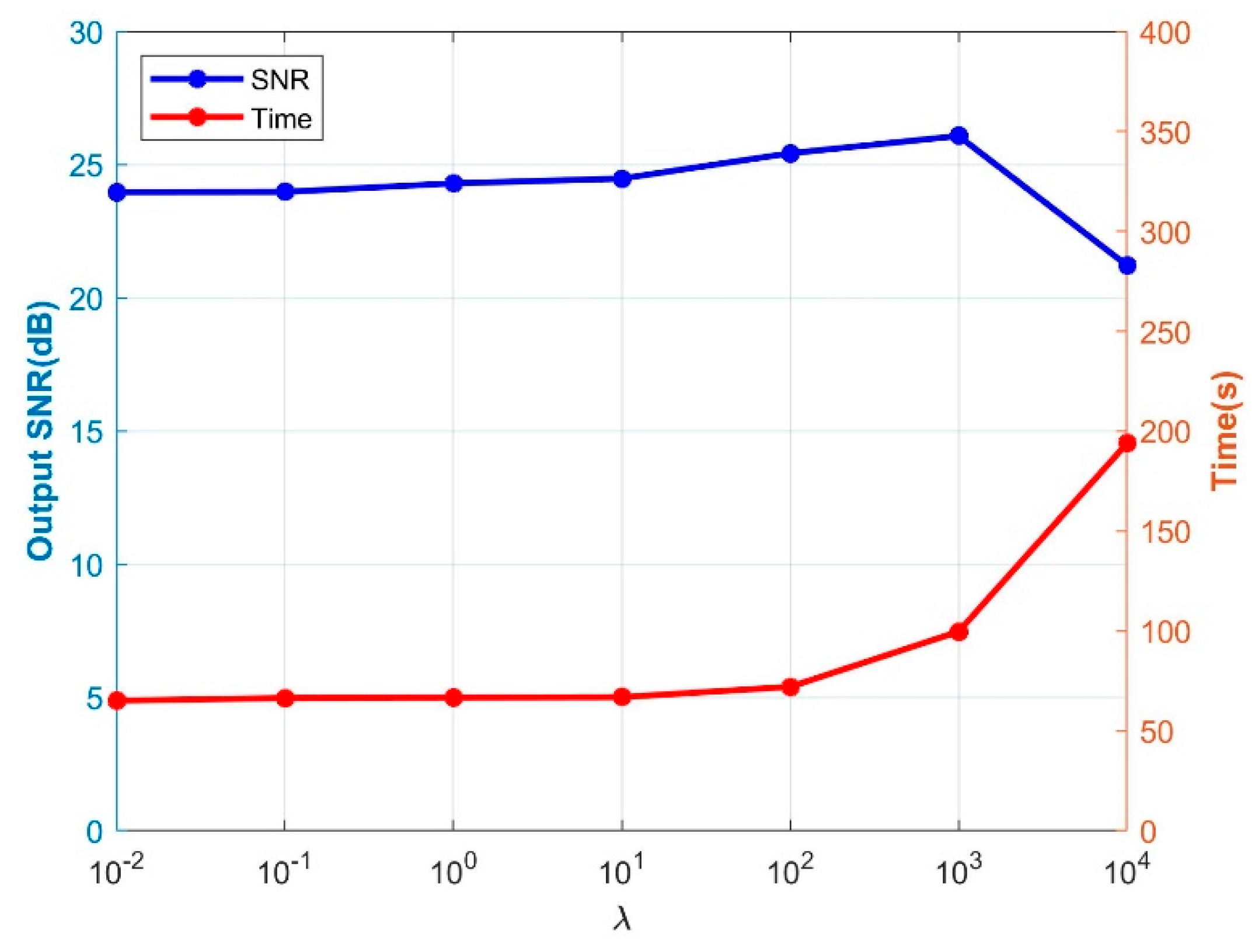
3. Results
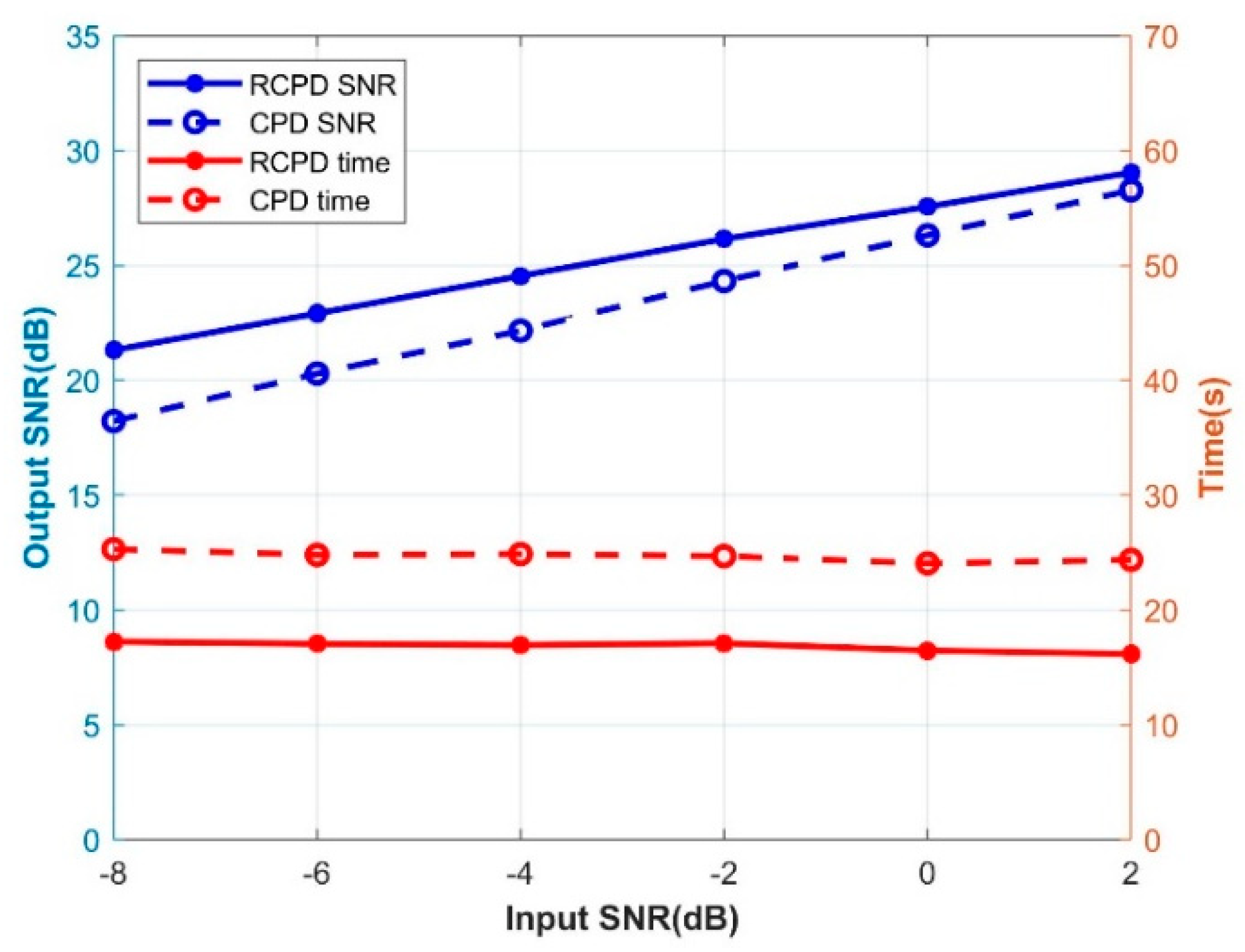
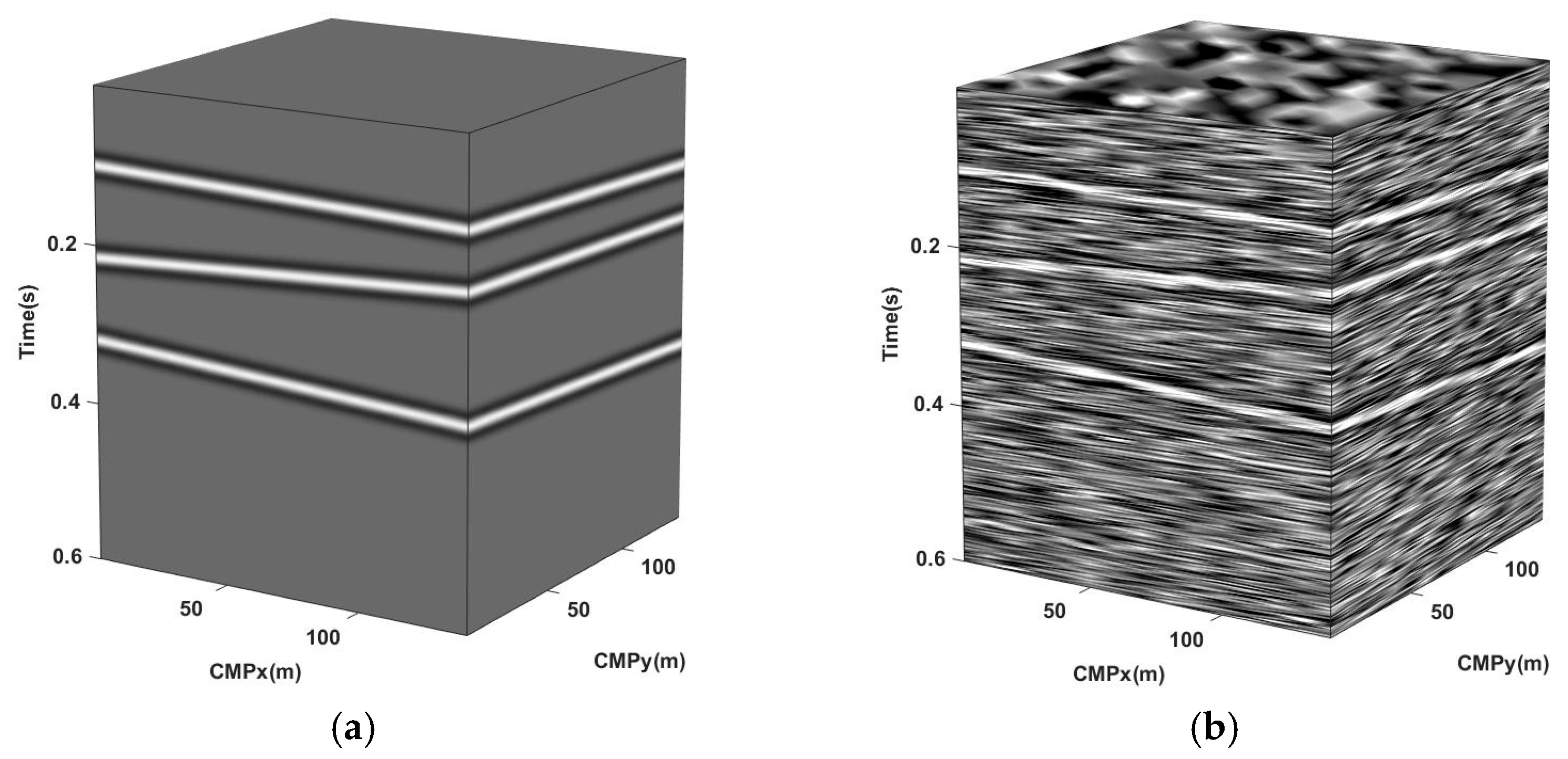
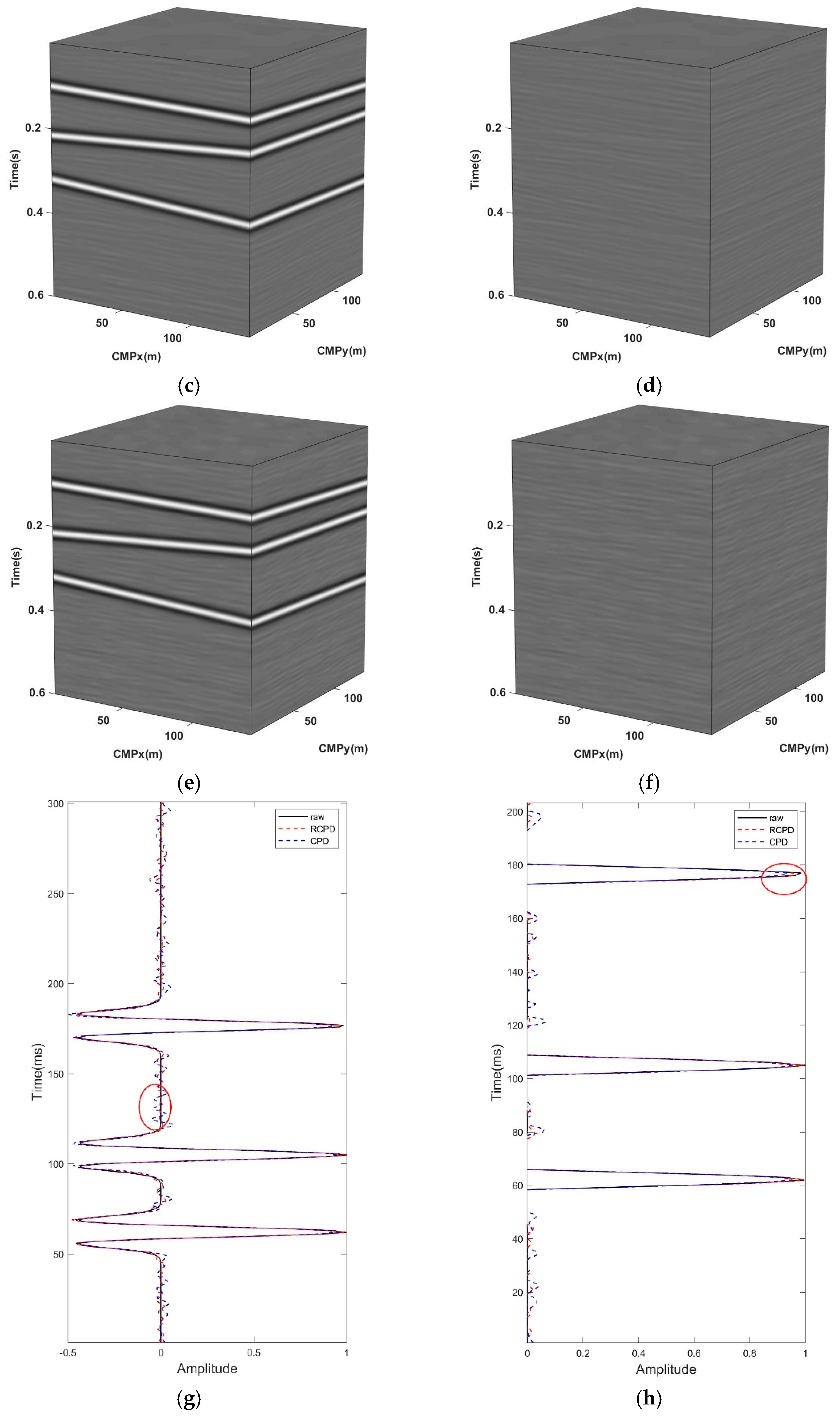
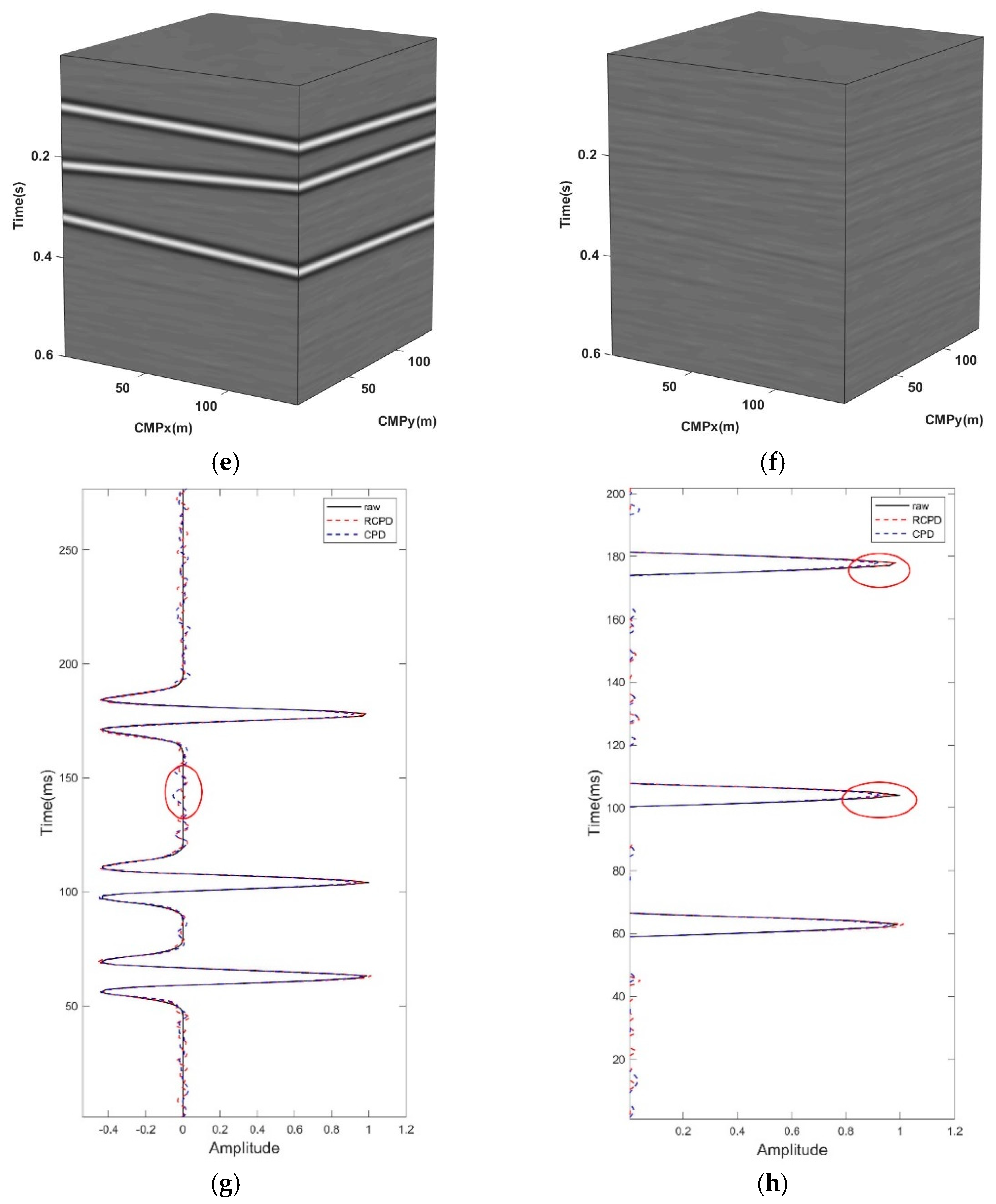
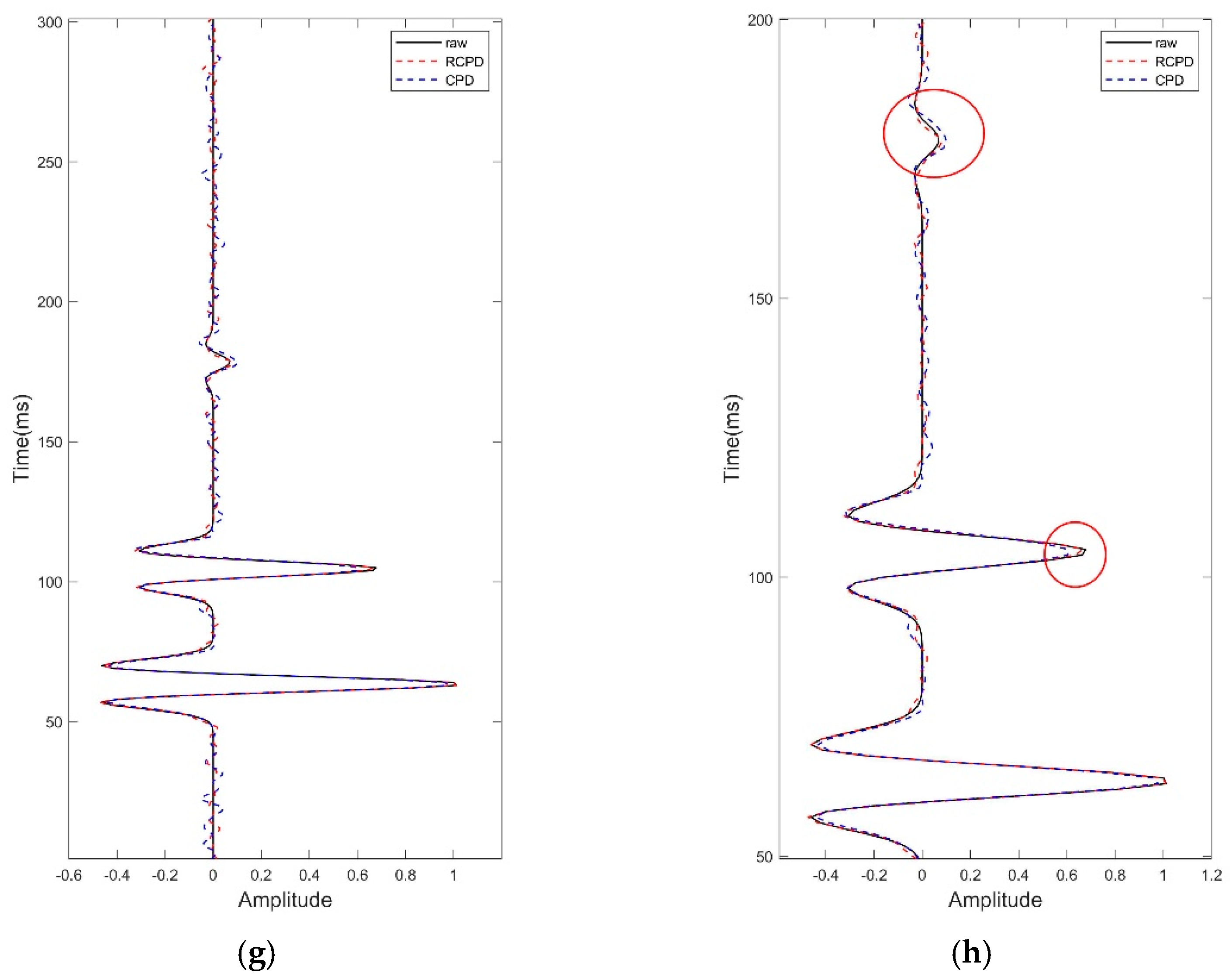
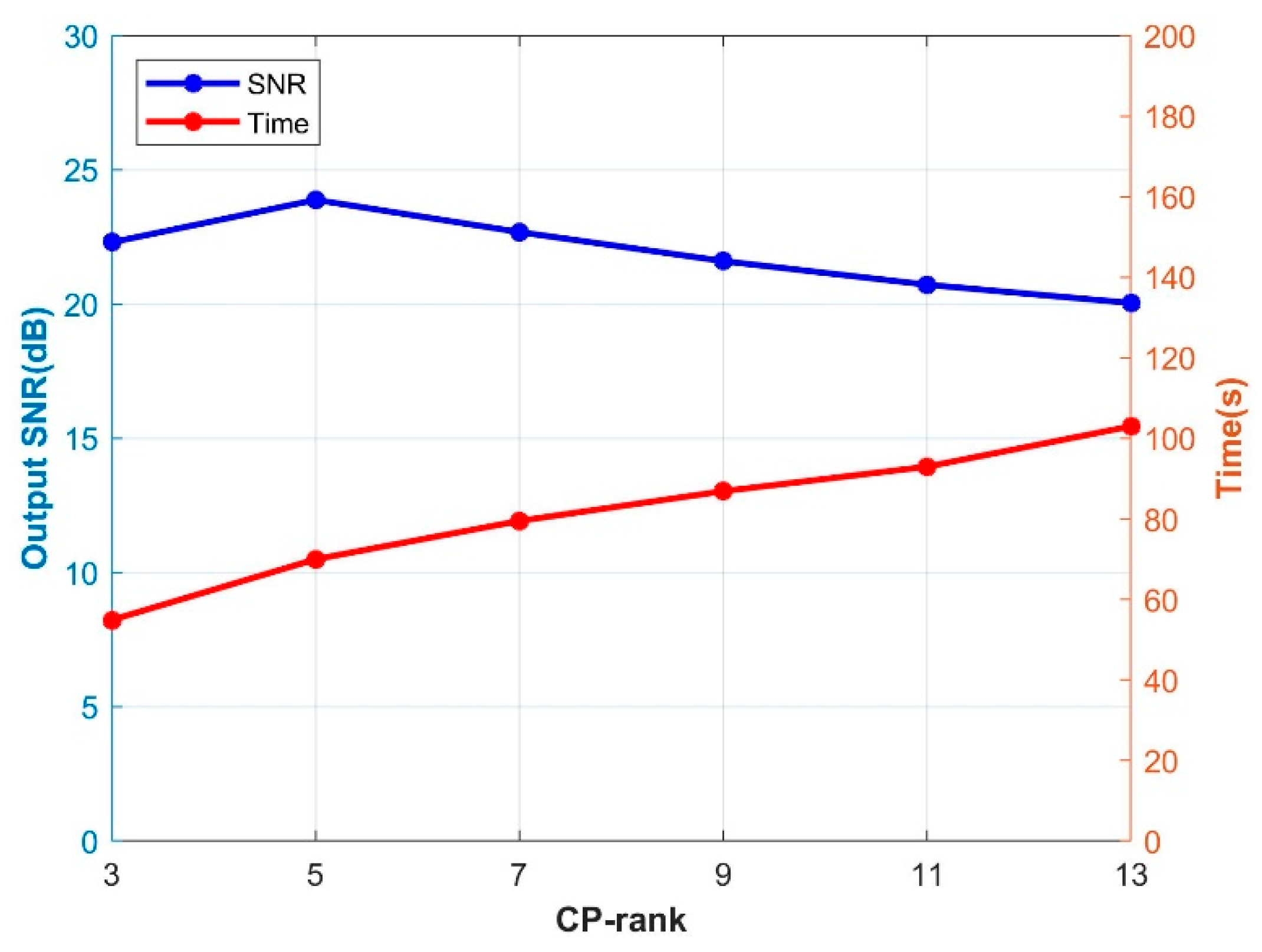
3.1. Synthesis Data Experiment
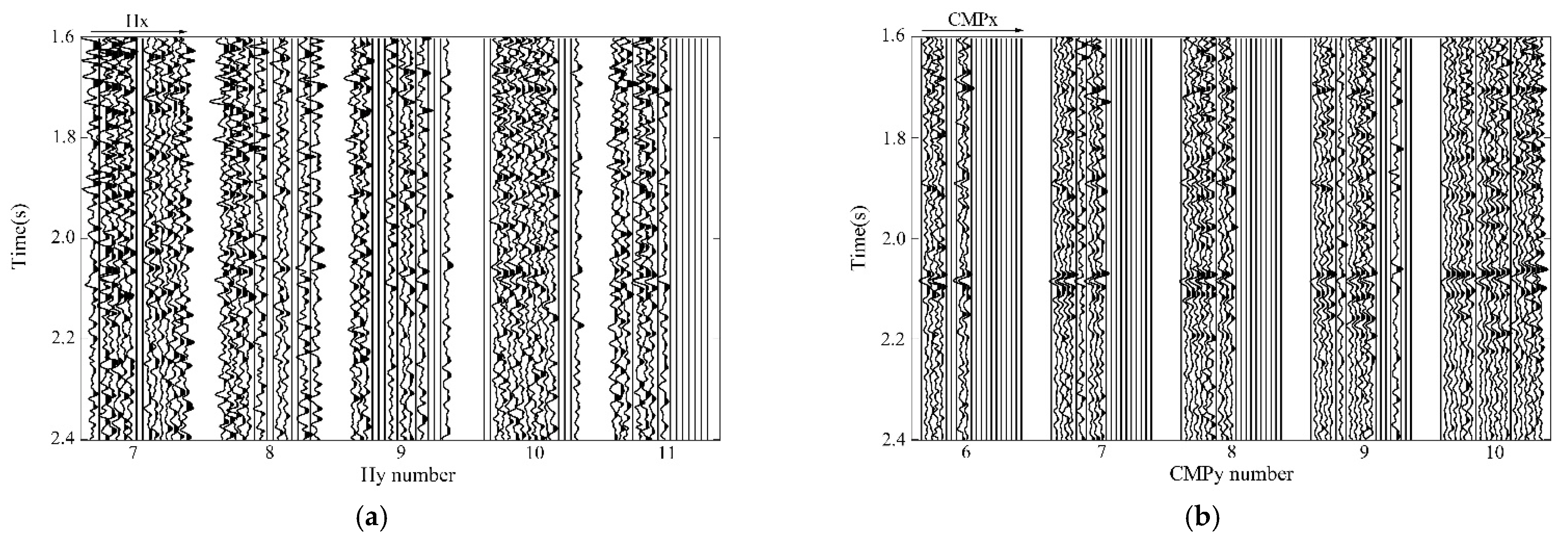
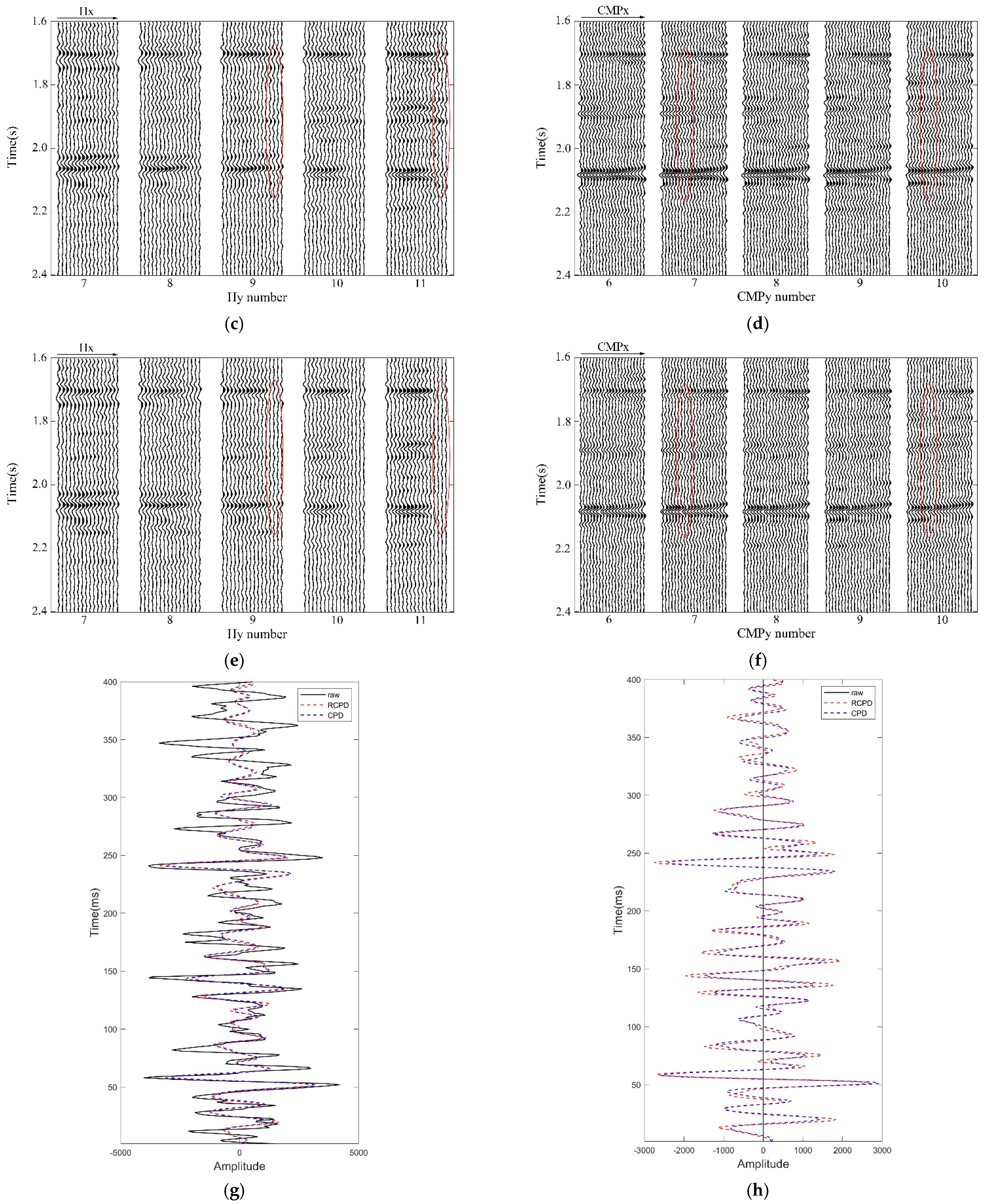
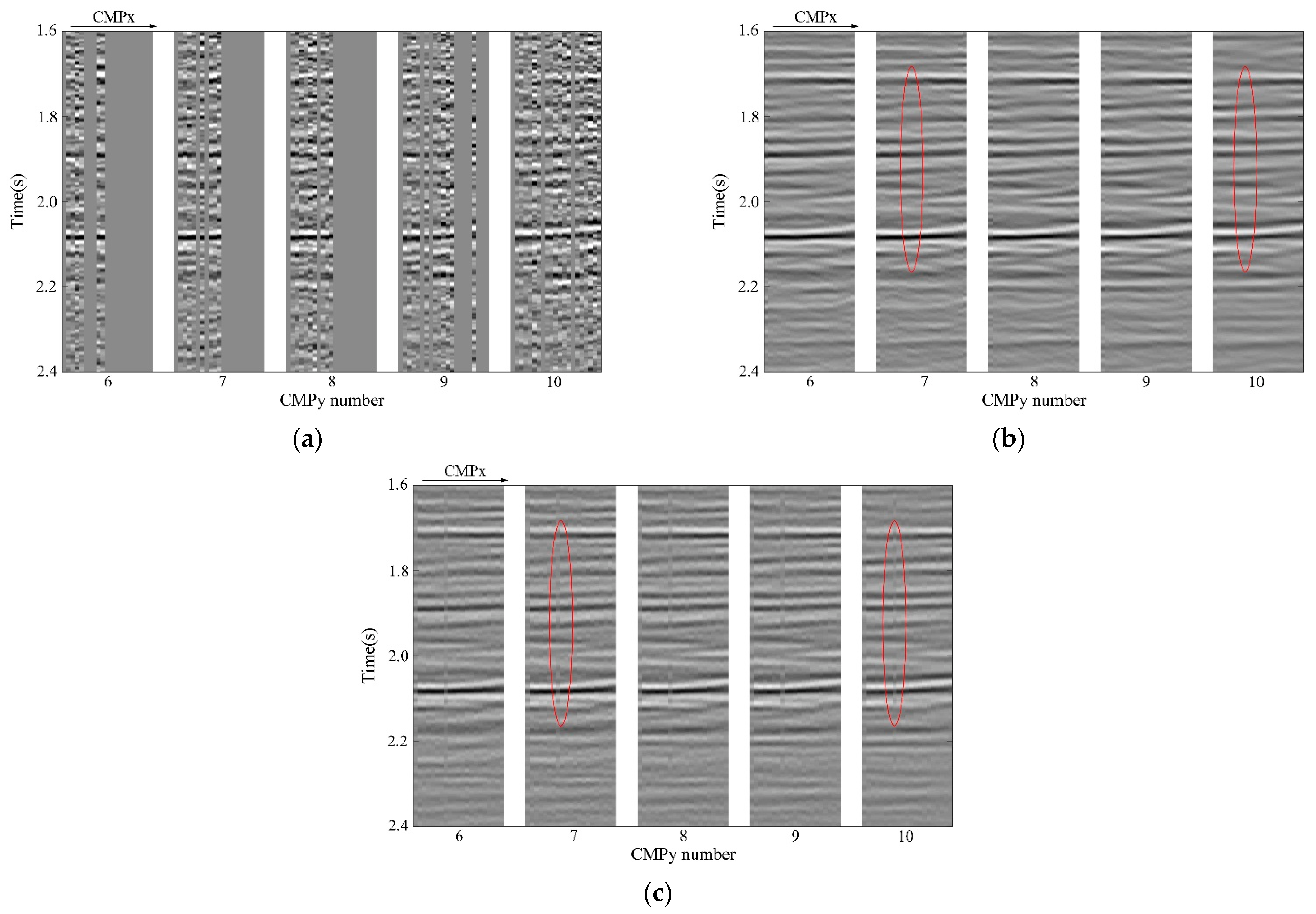
3.2. Field Data Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Abma, R.; Claerbout, J. Lateral prediction for noise attenuation by t-x and f-x techniques. Geophysics 1995, 60, 1887–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbostel, S.C. Spatial prediction filtering in the t-x and f-x domains. Geophysics 1991, 56, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulunay, N. FXDECON and complex wiener prediction filter. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 1986; pp. 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H. High-dimensional center filtering method based on block matching. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2019; pp. 4580–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza, V.E.; Sacchi, M.D. Multifrequency singular spectrum analysis. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2009; pp. 3193–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropeza, V.E.; Sacchi, M.D. A randomized SVD for Multichannel Singular Spectrum Analysis (MSSA) noise attenuation. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 3539–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Gan, S. Damped multichannel singular spectrum analysis for 3D random noise attenuation. Geophysics 2016, 81, V261–V270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trickett, S.R. F-xy eigenimage noise suppression. Geophysics 2003, 68, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolda, T.G.; Bader, B.W. Tensor Decompositions and Applications. SIAM Rev. 2009, 51, 455–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, A.; Mandic, D.; Phan, A.-H.; Caiafa, C.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, Q.; Lathauwer, L. Tensor Decompositions for Signal Processing Applications From Two-way to Multiway Component Analysis. Signal Process. Mag. IEEE 2014, 32, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilmer, M.E.; Martin, C.D. Factorization strategies for third-order tensors. Linear Algebra Appl. 2011, 435, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, N.; Sacchi, M.D. A tensor higher-order singular value decomposition for prestack seismic data noise reduction and interpolation. Geophysics 2012, 77, V113–V122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreimer, N.; Stanton, A.; Sacchi, M.D. Tensor completion based on nuclear norm minimization for 5D seismic data reconstruction. Geophysics 2013, 78, V273–V284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ely, G.; Aeron, S.; Hao, N.; Kilmer, M.E. 5D seismic data completion and denoising using a novel class of tensor decompositions. Geophysics 2015, 80, V83–V95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, F.L. The Expression of a Tensor or a Polyadic as a Sum of Products. J. Math. Phys. 1927, 6, 164–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harshman, R.A. Foundations of the PARAFAC procedure: Models and conditions for an “explanatory” multi-model factor analysis. UCLA Work. Pap. Phon. 1970, 16, 1–84. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.D.; Chang, J.-J. Analysis of individual differences in multidimensional scaling via an n-way generalization of “Eckart-Young” decomposition. Psychometrika 1970, 35, 283–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Sacchi, M. Incoherent noise attenuation via randomized CP decomposition. In 2017 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 5006–5010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, B. Vandermonde constrained CANDECOMP/PARAFAC tensor decomposition for high-dimensional seismic data reconstruction. Geophysics 2022, 87, V533–V544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Ulrych, T.J. Physical Wavelet Frame Denoising. Geophysics 2003, 68, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, H. Comparisons of wavelets, contourlets and curvelets in seismic denoising. J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, T.S.; Bisset, D. The Radon transform and its properties. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trad, D.; Ulrych, T.; Sacchi, M. Latest views of the sparse Radon transform. Geophysics 2003, 68, 386–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H. High-Resolution Linear Radon Transformation with L0-norm Constraint. In Proceedings of the Beijing 2014 International Geophysical Conference & Exposition, Beijing, China, 21–24 April 2014; pp. 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, W.; Geng, J. A Robust and Efficient Sparse Time-Invariant Radon Transform in the Mixed Time–Frequency Domain. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7558–7566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.J.; Böniger, U.; Verschuur, D.J. Non-linear primary-multiple separation with directional curvelet frames. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 170, 781–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, F.; Hennenfent, G. Non-parametric seismic data recovery with Curvelet frames. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.-X.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Geophysical data sparse reconstruction based on L0-norm minimization. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 10, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Zhang, C.; Han, X. 2-D TFPF based on Contourlet transform for seismic random noise attenuation. J. Appl. Geophys. 2016, 129, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehui, K.; Peng, Z. Seismic random noise attenuation using shearlet and total generalized variation. J. Geophys. Eng. 2015, 12, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, X. AVO-preserving data reconstruction by 3D high-order sparse-parabolic Radon transform. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts; OnePetro: Richardson, TX, USA, 2017; pp. 4338–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, W.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, J.; Xu, J.; Zhu, G.; Tang, W. 3D high-order sparse radon transform with L1–2 minimization for multiple attenuation. Geophys. Prospect. 2022, 70, 655–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boe, T.H. Enhancement of large faults with a windowed 3D Radon transform filter. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2012; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2012; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, Z.; Qu, Y. The 3D conical Radon transform for seismic signal processing. Geophysics 2022, 87, V481–V504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radon, J.; Parks, P.; Clark, C. On the determination of functions from their integral values along certain manifolds. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 5, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, B.; Neal, P.; Eric, C.; Borja, P.; Jonathan, E. Distributed Optimization and Statistical Learning via the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. Found. Trends® Mach. Learn. 2011, 3, 1–122. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.-J.; So, H.C. Outlier-Robust Matrix Completion via Lp-Minimization. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2017, 66, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioucas-Dias, J.M.; Figueiredo, M.A.T. A New TwIST: Two-Step Iterative Shrinkage/Thresholding Algorithms for Image Restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2992–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Cai, J.F.; Guo, D.; Tang, G.; Chen, Z.; Qu, X. Vandermonde Factorization of Hankel Matrix for Complex Exponential Signal Recovery—Application in Fast NMR Spectroscopy. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 5520–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, K. High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275
Ouyang Z, Zhang L, Wang H, Yang K. High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Zhiyuan, Liqi Zhang, Huazhong Wang, and Kai Yang. 2022. "High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275
APA StyleOuyang, Z., Zhang, L., Wang, H., & Yang, K. (2022). High-Dimensional Seismic Data Reconstruction Based on Linear Radon Transform–Constrained Tensor CANDECOM/PARAFAC Decomposition. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6275. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246275