High-Resolution Mapping of Seaweed Aquaculture along the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Google Earth Engine (2016–2022)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area, Data, and Materials
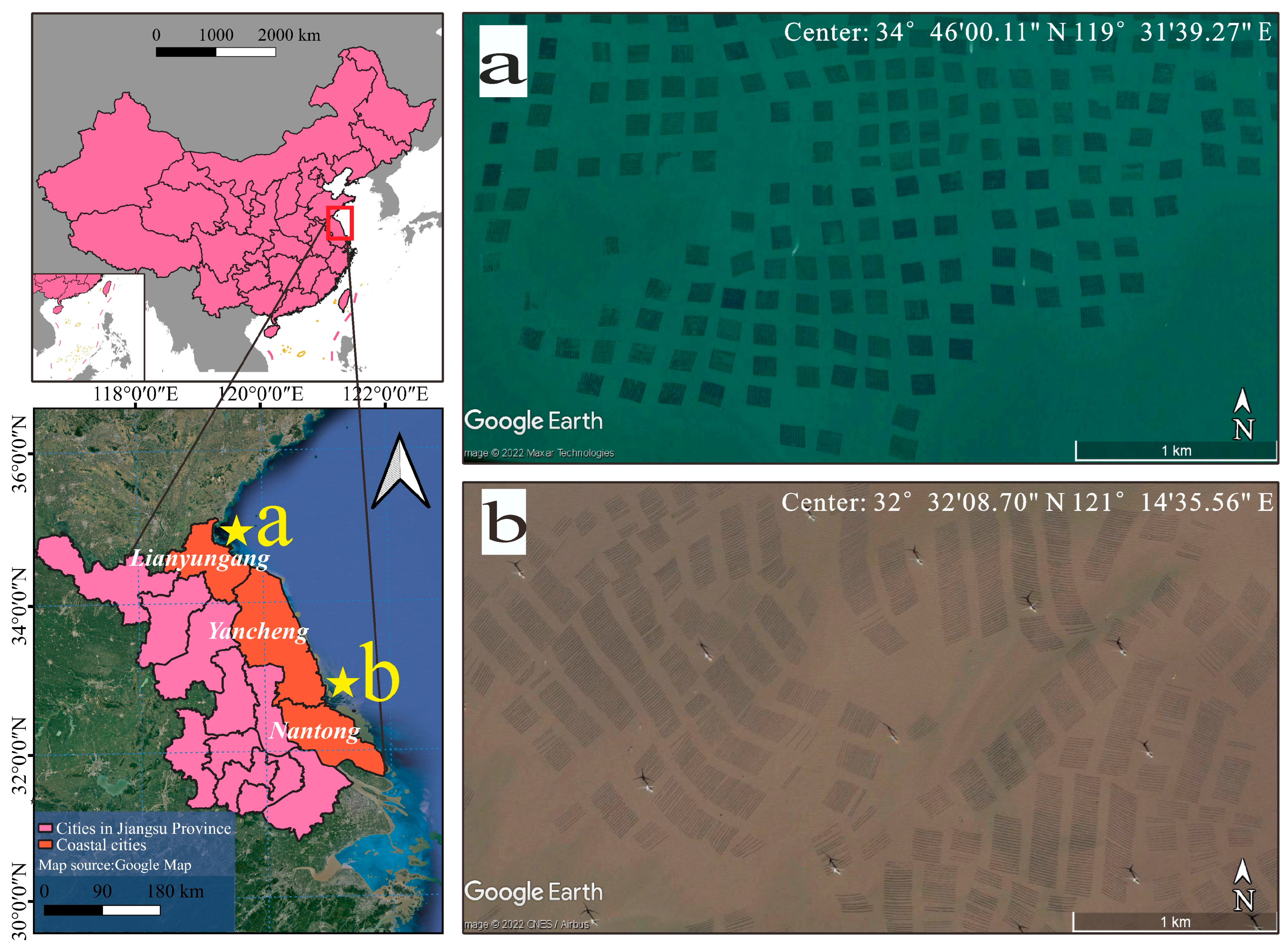
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Materials
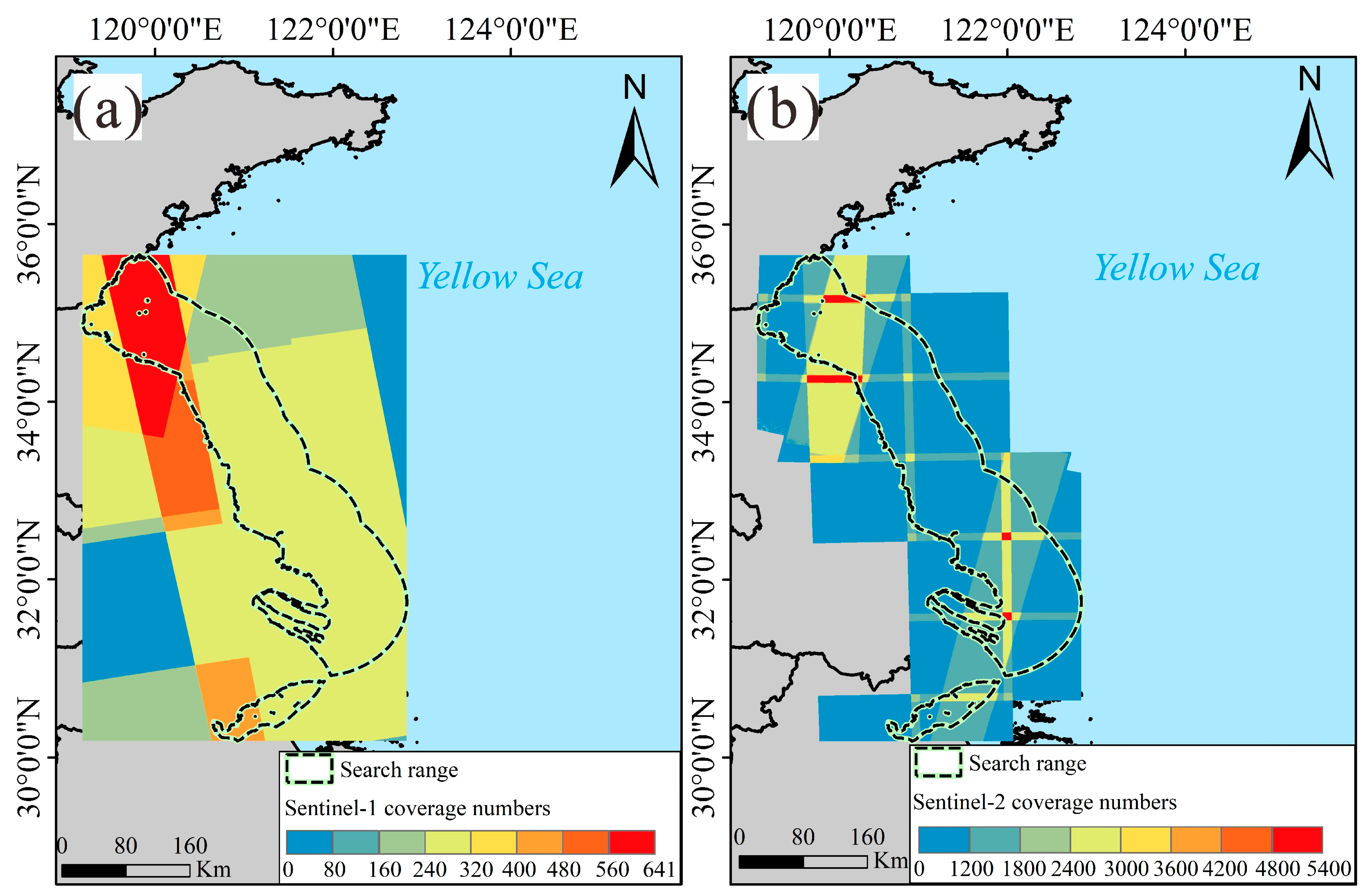
2.2.1. Satellite Datasets
2.2.2. Data from Government Statistics and Reports
3. Methods
3.1. Image Pre-Processing
3.1.1. MISC-OA Marine Mask Extraction
3.1.2. Sentinel Image Pre-Processing
3.2. Feature Selection and Extraction
3.3. Classification with Random Forest
3.4. Post-Classification
3.4.1. Integrated Updating
3.4.2. Fill and Smooth Edges
3.4.3. Remove Noise and Debris
3.4.4. Remove Offshore Wind Power
3.5. Convex Hull Algorithm
3.6. Validation
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Accuracy Assessment
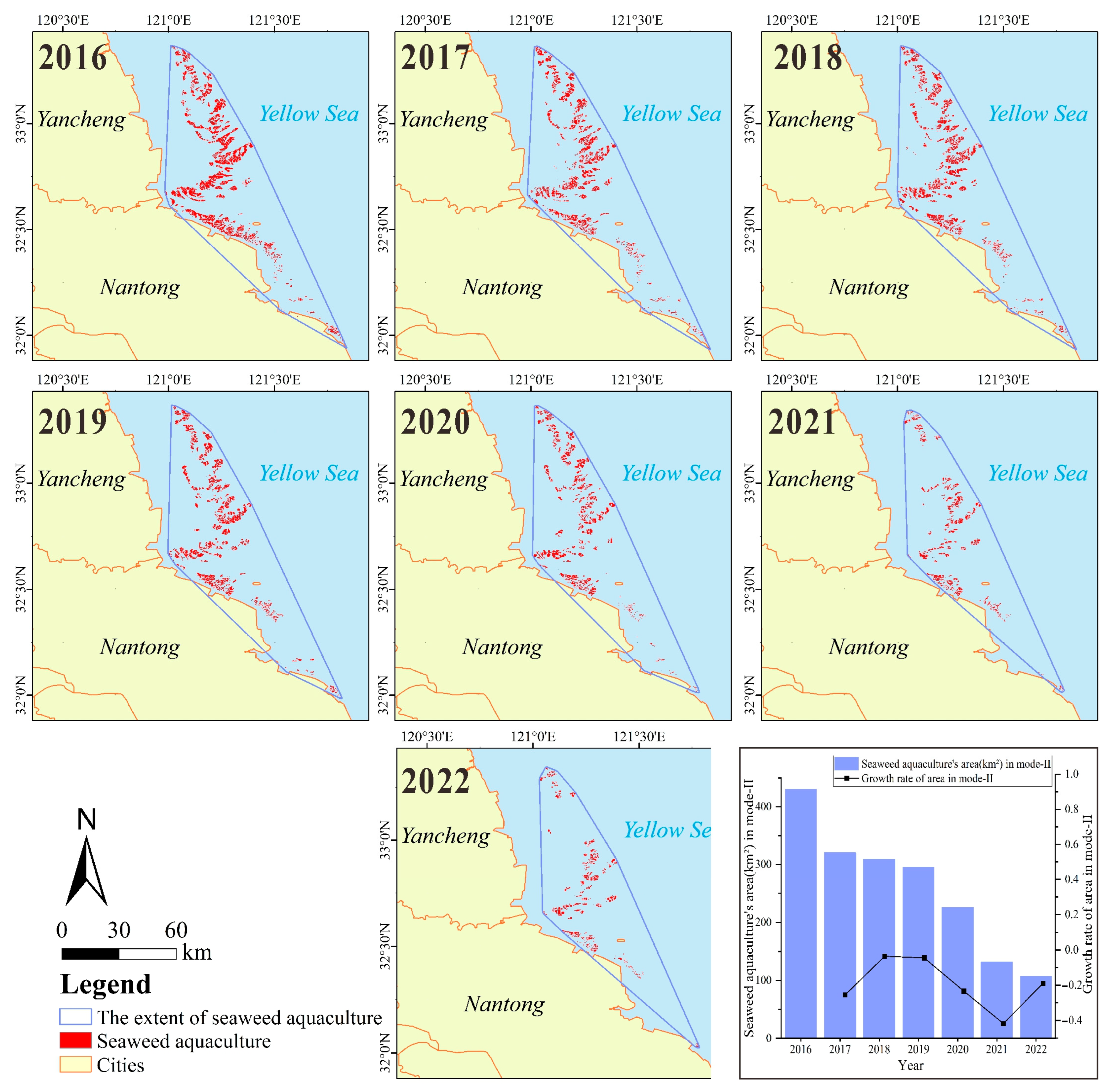
4.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamics in Seaweed Aquaculture
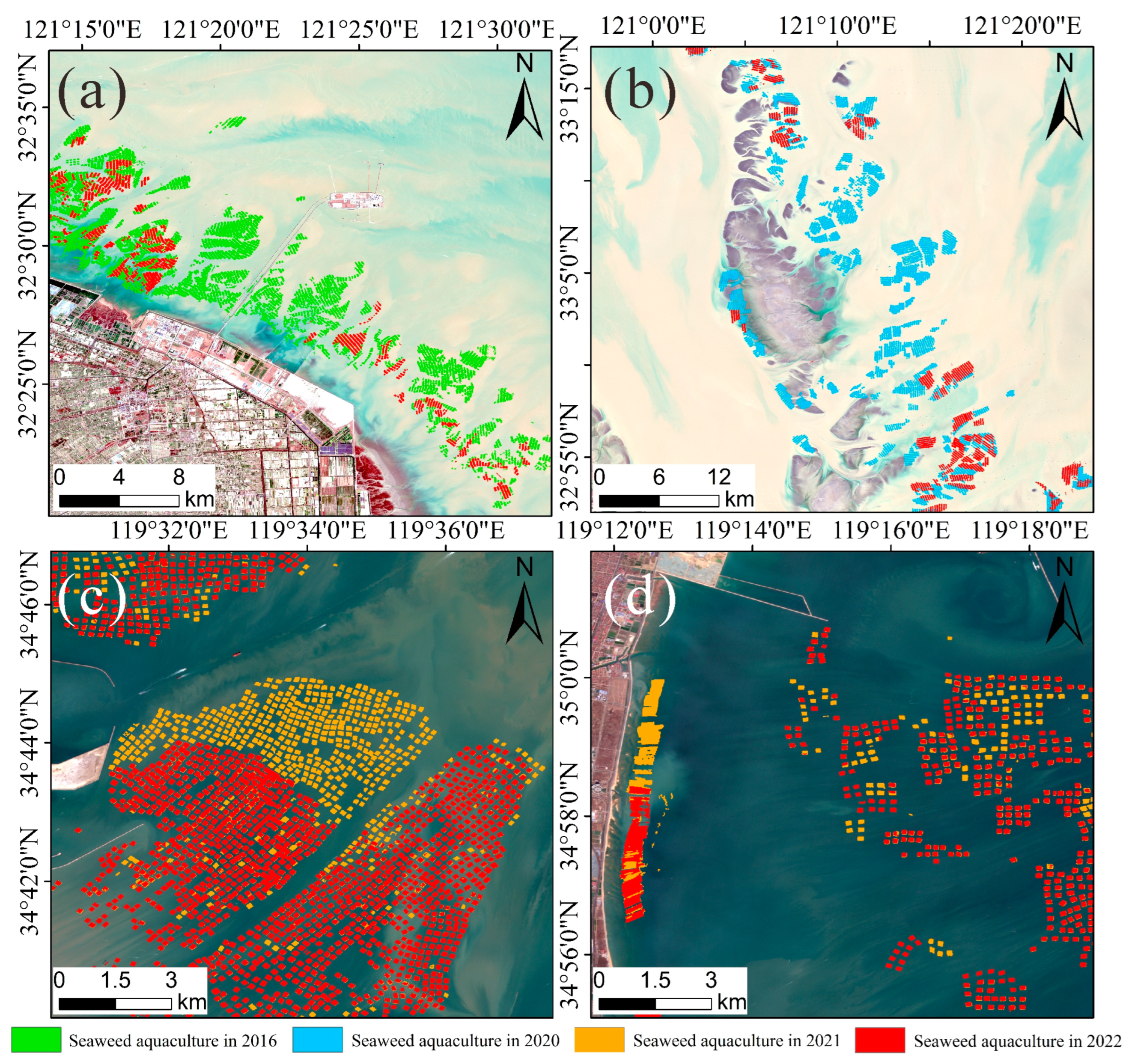
4.3. Spatial Distribution of Diverse Modes of Seaweed Aquaculture
4.4. Analysis of Unsustainable Development of Seaweed Aquaculture
5. Discussion
5.1. Model Performance and Data Accuracy
5.2. Development and Impact of Seaweed Aquaculture
5.3. Recent Policy Restrictions on Seaweed Aaquaculture
5.4. Applicability and Limitations of Research Methods
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, H. Global impacts of COVID-19 on sustainable ocean development. Innovation 2022, 3, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, M.L.; Critchley, A.T.; Mouritsen, O.G. A role for dietary macroalgae in the amelioration of certain risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease. Phycologia 2019, 54, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M. Algae as Nutrition, Medicine and Cosmetic: The Forgotten History, Present Status and Future Trends. World J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 6, 1934–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M.; Bruhn, A.; Krause-Jensen, D. A seaweed aquaculture imperative to meet global sustainability targets. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 5, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimmer, M.A.; Larson, S.; Lapong, I.; Purnomo, A.H.; Pong-Masak, P.R.; Swanepoel, L.; Paul, N.A. Seaweed Aquaculture in Indonesia Contributes to Social and Economic Aspects of Livelihoods and Community Wellbeing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Poza, S.; Leandro, A.; Cotas, C.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Goncalves, A.M.M. The Evolution Road of Seaweed Aquaculture: Cultivation Technologies and the Industry 4.0. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Yao, L.; Liu, J.; Tong, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, S.; Fu, M.; Zhuang, M.; He, P.; et al. Prevention strategies for green tides at source in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 178, 113646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhu, A.; Chen, R. China’s algal bloom suffocates marine life. Science 2021, 373, 751–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W. Monitoring and Tracking the Green Tide in the Yellow Sea With Satellite Imagery and Trajectory Model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 5172–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.U.; Hasan, O.; Rahman, M.M.; Akter, M.; Rahman, M.S.; Sarker, S. Seaweeds for the sustainable blue economy development: A study from the south east coast of Bangladesh. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The First Wetland Inventory Map of Newfoundland at a Spatial Resolution of 10 m Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, X.; He, S.; Li, S.; Zheng, W.; Luo, W. Study on Spatial Expansion Model of Laver Cultivation Area in Jiangsu Offshore. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2021, 40, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; An, D.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Chen, J. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.D.; Zaidi, A.Z.; Abdullah, M. Performance Evaluation of Newly Proposed Seaweed Enhancing Index (SEI). Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Fei, D.; Shao, G.; Lu, Y.; Chu, J. Extracting Raft Aquaculture Areas from Remote Sens. Images via an Improved U-Net with a PSE Structure. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Xu, Q.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Automatic Raft Labeling for Remote Sens. Images via Dual-Scale Homogeneous Convolutional Neural Network. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teluguntla, P.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Oliphant, A.; Xiong, J.; Gumma, M.K.; Congalton, R.G.; Yadav, K.; Huete, A. A 30-m landsat-derived cropland extent product of Australia and China using random forest machine learning algorithm on Google Earth Engine cloud computing platform. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, R. High-resolution mapping of water photovoltaic development in China through satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, J.; Yan, B.; Ni, J.; Yang, L. The History, Status Quo and Development Trend of Pyropia Yezoensis Industry of China. Mar. Econ. China 2018, 3, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, S.; Jia, M.; Ma, Y. Monitoring coastal reclamation changes across Jiangsu Province during 1984–2019 using landsat data. Mar. Policy 2022, 136, 104887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, S.; Mao, H.; Shan, C. Thoughts on the ecological control methods of prolifera in the semi-floating raft type seaweed cultivation area in the northern Jiangsu shoal. Aquaculture 2021, 42, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Guo, X.; Chen, R. Automatic extraction of aquaculture ponds based on Google Earth Engine. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2020, 198, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sentinel-1 Algorithms. Available online: https://developers.google.com/earthengine/guides/sentinel1 (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ji, Y.; Chen, J.; Deng, Y.; Chen, J.; Jie, Y. Combining Segmentation Network and Nonsubsampled Contourlet Transform for Automatic Marine Raft Aquaculture Area Extraction from Sentinel-1 Images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidal Flat Planning for Aquaculture Waters in Jiangsu Province (2020–2030). Available online: http://coa.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2022/1/25/art_11977_10330806.html (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- China Fisheries Statistical Yearbook. Available online: https://www.cafs.ac.cn/info/1397/37342.htm (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Jiangsu Province Marine Disaster Bulletin. Available online: http://zrzy.jiangsu.gov.cn/gtxxgk/nrglIndex.action?classID=8a908254409a391f01409a4c2f31000d (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- China Marine Disaster Bulletin. Available online: http://gi.mnr.gov.cn/202205/t20220507_2735508.html (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Ren, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Rapid, robust, and automated mapping of tidal flats in China using time series Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jia, M.; Zhang, R.; Ren, Y.; Wen, X. Incorporating the Plant Phenological Trajectory into Mangrove Species Mapping with Dense Time Series Sentinel-2 Imagery and the Google Earth Engine Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, J.; Kang, Z.; Liu, Q. Research progress in the ecological consequences of Ulva prolifera green tides in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2021, 40, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Lewis, P.E.; Gomez-Dans, J.L.; Wu, Q. A Sensor Invariant Atmospheric Correction: Sentinel-2/MSI and Landsat 8/OLI. Available online: https://eartharxiv.org/repository/view/1034/ (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Sun, Z.; Luo, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xue, K.; Lu, L. Nation-Scale Mapping of Coastal Aquaculture Ponds with Sentinel-1 SAR Data Using Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Liu, H.; Batchily, K.; Van Leeuwen, W. A Comparison of Vegetation Indices over a Global Set of TM Images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 59, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Huete, A. A feedback based modification of the NDVI to minimize canopy background and atmospheric noise. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Justice, C.; Liu, H. Development of vegetation and soil indices for MODIS-EOS. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1994, 49, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obata, K.; Miura, T.; Yoshioka, H.; Huete, A.; Vargas, M. Spectral Cross-Calibration of VIIRS Enhanced Vegetation Index with MODIS: A Case Study Using Year-Long Global Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.; He, K.; Lin, S.; Zuo, Y.; Chen, X. Comparison of forest and shrublands in potentially afforested areas based on remote sensing and field surveys. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2022, 42, 7362–7371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejatian, A.; Makian, M.; Gheibi, M.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M. A novel viewpoint to the green city concept based on vegetation area changes and contributions to healthy days: A case study of Mashhad, Iran. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Z.; Zou, J.; Xing, Q. A Spectral-Mixing Model for Estimating Sub-Pixel Coverage of Sea-Surface Floating Macroalgae. Atmosphere-Ocean 2018, 56, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.S.; Kearney, M.S. Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh Thematic Mapper scenes using spectral indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 25, 2317–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, N.; Dong, J.; Huang, J.; Du, G.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Yang, T.; Di, Y.; Xiao, X. The 10-m crop type maps in Northeast China during 2017–2019. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, C.; Valero, S.; Inglada, J.; Champion, N.; Dedieu, G. Assessing the robustness of Random Forests to map land cover with high resolution satellite image time series over large areas. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Xi, Y.; Xiao, X.; Doughty, R.B.; Liu, M.; Jia, M.; et al. Rapid expansion of coastal aquaculture ponds in China from Landsat observations during 1984–2016. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 82, 101902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Niu, J.; Sui, Z.; Shan, T.; Wang, T.; Tang, X.; Liang, Z.; Pang, S. Overview and Prospects of China Economic Seaweed Cultivation Technology. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiangsu Province’s “14th Five-Year” Marine Economic Development Plan. Available online: http://zrzy.jiangsu.gov.cn/gggs/2021/08/1310014567860.html (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Hu, Z.M.; Shan, T.F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.S.; Critchley, A.T.; Choi, H.G.; Yotsukura, N.; Liu, F.L.; Duan, D.L. Kelp aquaculture in China: A retrospective and future prospects. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 1324–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tens of Thousands of Acres of Seaweed Severely Damaged by Sea Ice. Available online: http://pic.people.com.cn/n1/2016/0125/c1016-28081828.html (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Zhuang, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, S.; He, P. Golden seaweed tides accumulated in Pyropia aquaculture areas are becoming a normal phenomenon in the Yellow Sea of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detailed Explanation of Marine Disasters in Jiangsu in 2017: Golden Tide Landed on the Coast and Flooded. Available online: http://www.hycfw.com/Article/211801 (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Notice on the Release of Provincial Subsidy Funds for the Prevention and Control of Prolifera Green Tide in 2021. Available online: http://czt.jiangsu.gov.cn/art/2021/8/17/art_77309_9977448.html (accessed on 8 May 2022).
- Gimpel, A.; Stelzenmüller, V.; Grote, B.; Buck, B.H.; Floeter, J.; Núñez-Riboni, I.; Pogoda, B.; Temming, A. A GIS modelling framework to evaluate marine spatial planning scenarios: Co-location of offshore wind farms and aquaculture in the German EEZ. Mar. Policy 2015, 55, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opinions of the General Office of the Jiangsu Provincial Government on Accelerating the Promotion of High-Quality Development of Fisheries. Available online: http://www.js.gov.cn/art/2020/6/17/art_64797_9217205.html (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Hadi, A.A.; Wicaksono, P. Accuracy assessment of relative and absolute water column correction methods for benthic habitat mapping in Parang Island. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart and Innovative Agriculture, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 4–5 November 2020. [Google Scholar]



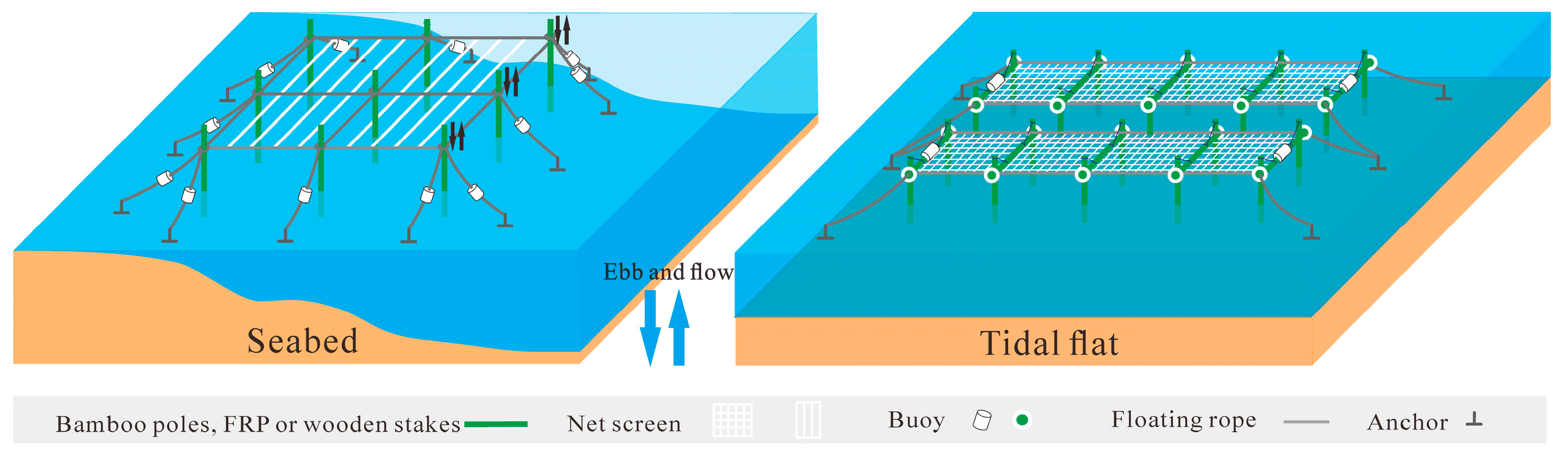
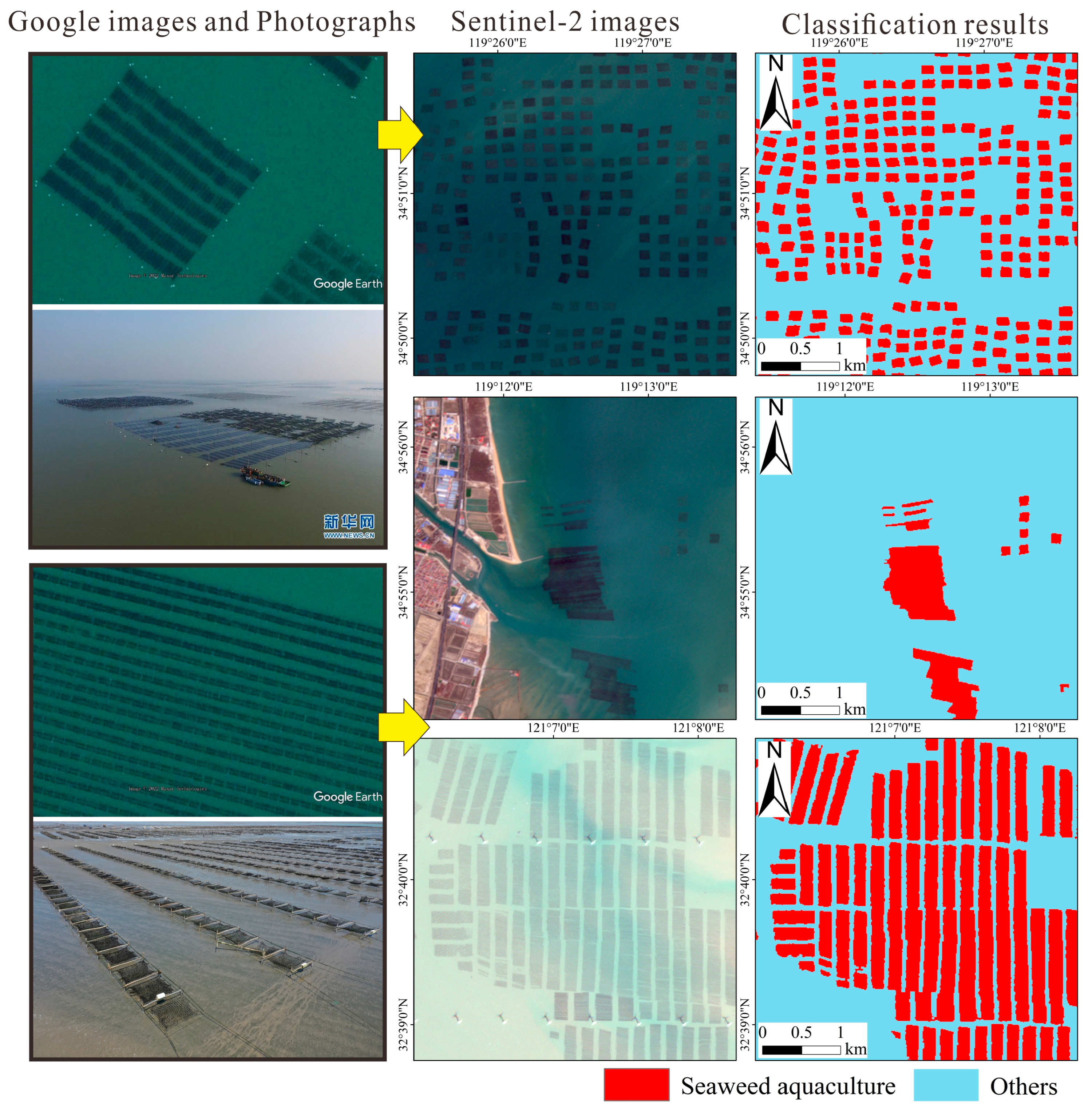
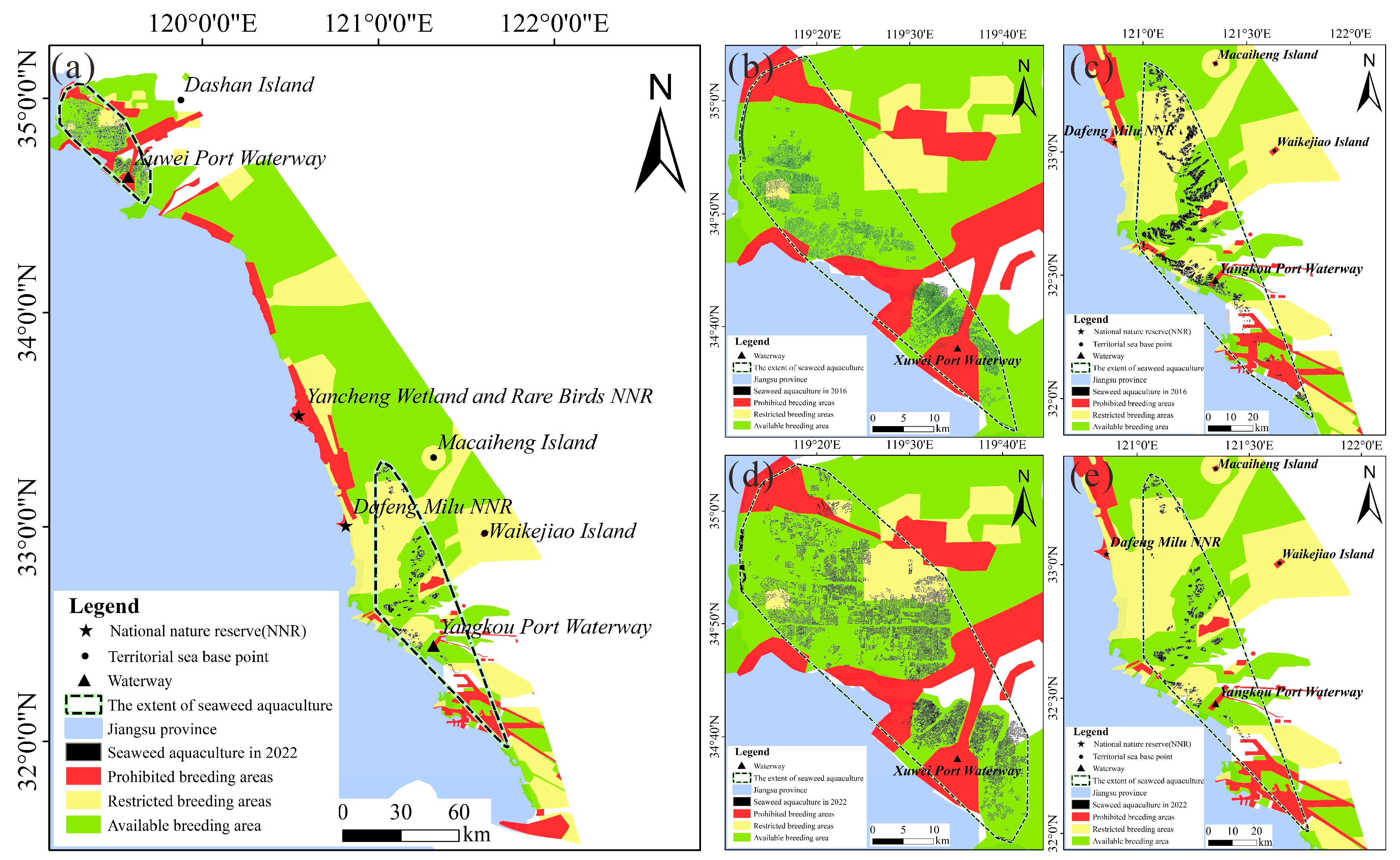
| Satellite Sensor | Format or Level | Spatial Resolution (m) | Time Resolution (Day) | Duration of This Study (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 SAR | IW/Level-1 | 10 | 6 | 2016–2022 |
| Sentinel-2 MSI | L1-C/L2-A | 10 | 5 | 2016–2022 |
| Feature Type | Formulation/Band |
|---|---|
| Spectrum | Sentinel-2 (B1-B5, B8, B8A, B11, B12) |
| Radar | Sentinel-1 (VV + VH) |
| Water indices | |
| Vegetation indices | |
| Soil index |
| Time/Breeding Mode | Mode-I | Mode-II | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall Accuracy | Kappa | Overall Accuracy | Kappa | |
| 2016 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.89 |
| 2017 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.95 | 0.89 |
| 2018 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.98 | 0.96 |
| 2019 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.88 | 0.74 |
| 2020 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.95 | 0.90 |
| 2021 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.91 |
| 2022 | 0.97 | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Jia, N.; Chen, R.; Guo, X.; Ge, J.; Zhou, F. High-Resolution Mapping of Seaweed Aquaculture along the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Google Earth Engine (2016–2022). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246202
Cheng J, Jia N, Chen R, Guo X, Ge J, Zhou F. High-Resolution Mapping of Seaweed Aquaculture along the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Google Earth Engine (2016–2022). Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246202
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jie, Nan Jia, Ruishan Chen, Xiaona Guo, Jianzhong Ge, and Fucang Zhou. 2022. "High-Resolution Mapping of Seaweed Aquaculture along the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Google Earth Engine (2016–2022)" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246202
APA StyleCheng, J., Jia, N., Chen, R., Guo, X., Ge, J., & Zhou, F. (2022). High-Resolution Mapping of Seaweed Aquaculture along the Jiangsu Coast of China Using Google Earth Engine (2016–2022). Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6202. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246202







