Abstract
Translational motion compensation is a prerequisite of inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging. Translational motion compensation for datasets with low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is important but challenging. In this work, we proposed a noise-robust translational motion compensation method based on high-order local polynomial transform–generalized scaled Fourier transform (HLPT-GSCFT). We first model the translational motion as a fourth-order polynomial according to order-of-magnitude analysis, and then design HLPT-GSCFT for translation parameter estimation and parametric translational motion compensation. Specifically, HLPT is designed to estimate the acceleration and third-order acceleration of the translational motion and GSCFT is introduced to estimate the second-order acceleration. Both HLPT and GSCFT have a strong ability for cross-term suppression. In addition, we use a minimum weighted entropy algorithm to estimate the velocity of the translational motion, which can improve the noise robustness of the parameter estimation. Experimental results based on a measured dataset prove that the proposed method is effective and noise-robust.
1. Introduction
Translational motion compensation is a pre-step in inverse synthetic aperture radar (ISAR) imaging. In the early days of ISAR imaging, limited by the performance of microelectronic devices, most imaging radars used narrowband tracking–broadband imaging systems. Stretch processing was adopted to perform pulse compression for the echoes. Under this condition, the translational error cannot be modeled because a random phase error is introduced in the echoes. Therefore, early translational motion compensation methods were dedicated to compensating the translation error of each pulse separately. Such methods are called non-parametric translational motion compensation methods and are still widely used today. Specifically, the translational error affects both range profile and phase. Thus, non-parametric methods first align the range profile and then correct the phase. Common range alignment methods include maximum correlation-based range alignment (MCRA) [1] and minimum average range profile entropy (ARPE) [2,3]. Existing phase correction methods involve signal subspace-based methods [4,5,6,7], dominant scatter-based methods [8,9,10] and minimum entropy or maximum contrast methods [11,12,13,14,15]. However, most non-parametric methods struggle to achieve ideal results in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) environments. With the rise of artificial intelligence technology, some scholars have applied neural networks to translational motion compensation. For example, using deep recurrent neural networks for range alignment at low SNR [16] and combining neural networks with compressed sensing to accomplish autofocusing [17,18]. However, such methods require a lot of effort to train.
With the development of microelectronics technology, echoes with coherent translational error can be obtained from modern radar. Under this condition, the translational error can be modeled according to the movement of the target relative to the radar. Currently, most scholars model the translation as a polynomial, and the joint compensation of range profile and phase can be realized by the estimation of translational polynomial parameters. Such methods are called parametric translational motion compensation methods. Since estimating several translational parameters is far easier than estimating hundreds of phase errors, parametric methods are generally more robust. Some scholars draw on the idea of the minimum entropy algorithm in the non-parametric method and propose using the gradient descent algorithm [19,20], or the swarm intelligence algorithms [21,22,23,24,25], to optimize the ISAR image quality to estimate the translational parameters. Other scholars use time–frequency distribution to realize the non-search estimation of translation parameters [26]. However, the accuracy and robustness of parametric translational motion compensation methods need to be further improved. On the one hand, parameter estimation based on image quality of range-Doppler (RD) imaging results easily converges to a local optimum in low SNR, and, on the other, the existing time-frequency transform-based methods, such as the fractional-order Fourier transform based-method [26] and the high-order ambiguous function-based method [27], can only be applied to third-order polynomials, and, therefore, have major limitations.
We propose a noise-robust translational motion compensation method based on high-order local polynomial transform–generalized scaled Fourier transform (HLPT-GSCFT). Through mathematical derivation and order-of-magnitude analysis, we determined that the translational error should be modeled as a fourth-order polynomial. Then we design HLPT-GSCFT to estimate the translational parameters. Specifically, HLPT is designed to estimate the acceleration and the third-order acceleration and GSCFT is used to estimate the jerk. Additionally, we design a minimum weighted entropy algorithm (MWE) to estimate radial velocity. HLPT-GSCFT is robust due to its low degree of nonlinearity. Experimental results of a Yak-42 measured dataset prove that the proposed method is effective and noise-robust.
2. Signal Model
In this section, we derive expressions for the target echoes and detail how we model translational motion as a fourth-order polynomial through order-of-magnitude analysis.
Currently, most imaging radars transmit a wideband linear frequency modulation (LFM) signal
where is the full time, is the pulse width of the transmitted signal, is the carrier frequency, and is the chirp rate. is the rectangular window function, it takes the value of 1 when and 0 in other cases. is the time sequence of a single pulse, which is usually called fast time. is the slow time, where is the number of pulses and is pulse repetition time.
The transmitted signal is reflected by the target and generates an echo. If the total number of scattering centers of the target is N, the echo can be written as
where is the speed of light and is the distance between the radar and the scattering center p.
After pulse compression, (2) can be written as
where is the fast time frequency. According to the basic theory of ISAR imaging [28], can be divided into rotational motion history and translational motion history. When the target moves smoothly, the rotational motion history can be approximated as
where is the rotational angular velocity of the target, is the azimuth coordinate of the scattering center p and is the distance coordinate of the scattering center p. The y-axis of this imaging coordinate system is the radar line of sight direction, and the origin of this coordinate system is the geometric center of the target.
Next, we analyze the translational motion of the target. During ISAR imaging, the motion of the target relative to the radar is shown in Figure 1.
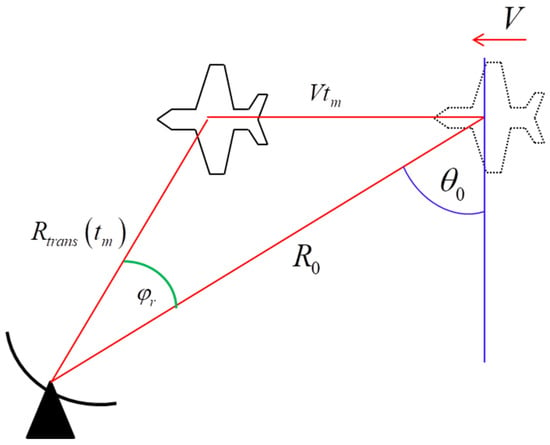
Figure 1.
The motion of the target relative to the radar, where is the initial distance between radar and target, is the translational motion of the target, is the speed of the target and is the initial oblique angle.
According to Figure 1, can be expressed as
Using Taylor series expansion, (5) can be rewritten as
Then we should determine the order of the Taylor series expansion. Obviously, the first-order term of (7) must be preserved. The question is whether the higher-order terms of (7) need to be preserved and if so, to which order. Therefore, we use order-of-magnitude analysis to determine the order of (7). Specifically, the error phase caused by the kth term in (7) can be ignored if it changes by a small amount during the imaging process. According to the Sine Law, can be rewritten as
where is the rotated angle, which is usually taken as 3°–5° [28].
The mapping from to is shown in Figure 2 (set ).
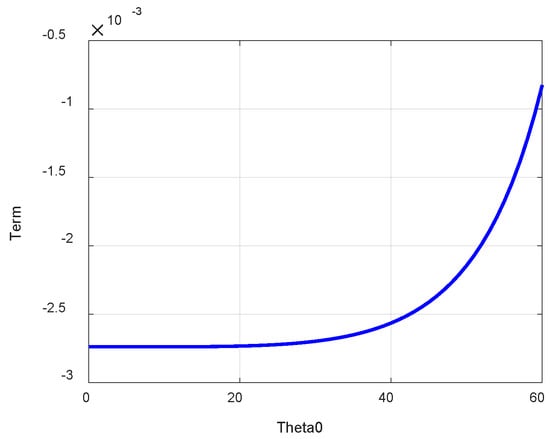
Figure 2.
The mapping from to .
We can find from (8) and Figure 2 that the absolute value of decreases with the increase of or the decrease of . When and , the value of satisfies
Considering that the order of magnitude of is and the order of magnitude of wavelength is , the effect of the squared term in (7) on the phase of the echo cannot be ignored in most cases. In comparison, the maximum of the absolute value of is when and . Therefore, the cubic and the higher terms in (7) can be ignored.
Based on the above analyses, can be written as
It can be found that the model of the translational motion is a fourth-order polynomial, and the echo can be expressed as
3. Translational Parameter Estimation Based on HLPT-GSCFT
To eliminate the translation error, we need to estimate , , and . In this section, we will describe the specific steps of HLPT-GSCFT and display how to estimate and using HLPT and using GSCFT. In addition, we analyze how HLPT-GSCFT suppressed the cross terms.
According to [29,30,31], the local polynomial transform (LPT) can be defined as
where is the delay variable, is the quadratic chirp rate and is the Fourier transform. LPT has the ability to perform non-search estimation on the frequency and quadratic chirp rate of cubic phase signals. Meanwhile, it has a low degree of nonlinearity and strong cross-term suppression ability. Referring to LPT, we propose HLPT.
We define the kernel function of HLPT as
where is the delay constant. The specific expression of can be written as
where is the cross terms of .
Then we perform inverse Fourier transform (IFT) for on , the result of the first part of (15) (we call it “self-terms”) can be expressed as
where is the modified fast time and is the Dirac function.
According to the analyses of Section II, the impact of , and on the range profile is not significant. If we set a small value for , the impact of , and on the range profile will be greatly reduced. Under this condition, the range profile offset caused by , and can be ignored. Therefore, we can approximate that the energy of the self-terms is focused in the range bin corresponding to . Based on the above analysis, we take , the result can be written as
Then we perform LPT for (17) and the result can be expressed as
According to the standing-phase method [28], we can obtain that
It can be found that (19) will reach a maximum only when and . Therefore, the estimation of and can be obtained by peak search as
where and represent the coordinates of the maximum values, respectively
Next, we analyze the ability of HLPT to suppress the cross terms. in (15) has three kinds of components, which can be expressed as
where p, q, r and s are four different scattering centers.
It can be found that ,, and cause migration through resolution cell (MTRC) in . That means only a small part of has the opportunity to participate in LPT after we perform IFT and take . Under this condition, is unable to focus the energy by LPT. Even if and , will not be focused by LPT because the energy only focuses on the range bin corresponding to . Similarly, and will not be focused by LPT. Therefore, HLPT has excellent cross-term suppression ability.
Then we adopt GSCFT to estimate . According to [32,33], GSCFT can be defined as
where represents the zoom factor to avoid spectrum aliasing, is the scaled frequency domain with respect to , and are constant power, is a function of and is an empirical parameter.
We use to construct a compensation function as
Compensating (17) by (26), the result can be written as
Performing GSCFT for (27), we can obtain that
We can take the absolute value of (28) as
Obviously, we can estimate by peak search for (29), and the estimated value of can be written as
4. Translational Motion Compensation
Using , and , we can reconstruct the translational error and compensate for the original echo as
It can be found that the linear translational error has still not been compensated. To ensure the noise robustness of the compensation, we design a minimum weighted entropy algorithm (MWE). The weighted entropy is defined as
where is the ISAR image, and are the sampling number of and , respectively, is the total energy of and is the 2-D Hamming window function.
The linear translational error can be compensated by solving the following optimization
There are many algorithms that can solve one-dimensional optimization problems. Even linear search can successfully solve the problem in (34).
To sum up, the flow chart of translational motion compensation based on HLPT-GSCFT is shown in Figure 3.
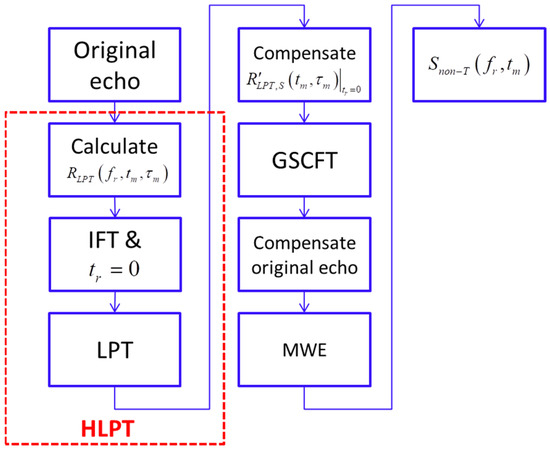
Figure 3.
The flow chart of translational motion compensation based on HLPT-GSCFT.
5. Experiment of Yak-42 Measured Dataset
In this section, we adopt a Yak-42 measured dataset to validate the performance of the proposed method. The shape of the Yak-42 is shown in Figure 4a. A C-band radar records the dataset with a bandwidth of 400 MHz, a PRF of 100 Hz and a carrier frequency of 5.52 GHz. The dataset contains 256 pulses, where each pulse has 256 sampling points. The RD imaging result of the dataset is shown in Figure 4b.
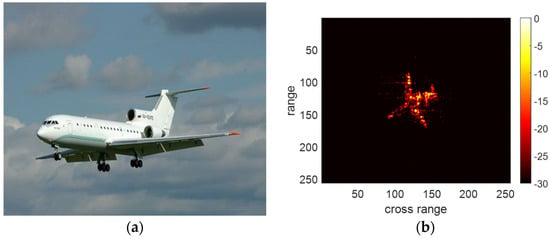
Figure 4.
Yak-42 (a) The shape of the Yak-42. (b) The RD imaging result of the dataset.
Next, we add a translational error for the dataset. We set , and , the expression of the translational motion added in the dataset is the same as (5). The range profile of the dataset after adding the translational error is shown in Figure 5a. According to (12), we can obtain that , , and .
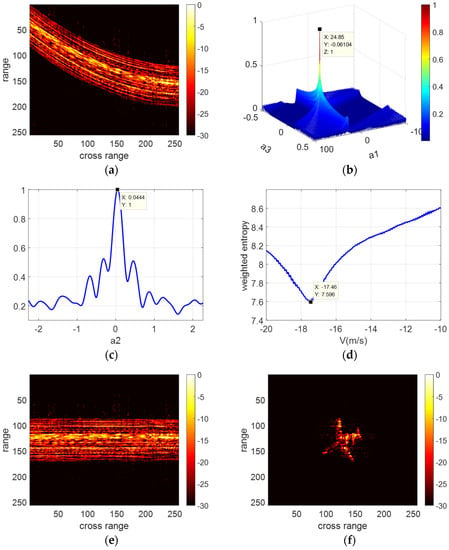
Figure 5.
The range profile of the dataset after adding the translational error and the result of each step. (a) The range profile of the dataset after adding the translational error. (b) The result of HLPT. (c) The result of GSCFT. (d) The result of MWE. (e) The range profile after translational motion compensation. (f) The RD imaging result after translational motion compensation.
We adopt the proposed method to compensate for the Yak-42 dataset. The result of each step is shown in Figure 5b–f.
We found that the range profile with the translational error is significantly bent. In the process of the proposed method, HLPT obtains that and , GSCFT obtains that and MWE obtains that . The relative errors of the translational parameter estimation are 0.2%, 1.5%, 3.2% and 0.2%, respectively. After translational motion compensation by the proposed method, the range profile of the dataset is straight and the RD imaging result is very close to Figure 4b. This proves that the proposed method is able to estimate the translational parameters and compensate for the translational error accurately.
Next, we further validate the effectiveness and the noise robustness of the proposed method by comparing it with other translational motion compensation methods. We adopt particle swarm optimization (PSO) [24] and phase difference–Keystone transform–fractional Fourier transform (PD-KT-FrFT) [26] as a control group. Under the conditions of SNR = 0 dB, −3 dB and −6 dB, the results of the above three methods and the ideal result (Imaging result of the original dataset, illustrated in Figure 4b) are shown in Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8, respectively. Additionally, we provide the entropy of each imaging result in Table 1 to quantify the imaging results. In general, the lower the entropy, the better the image quality.
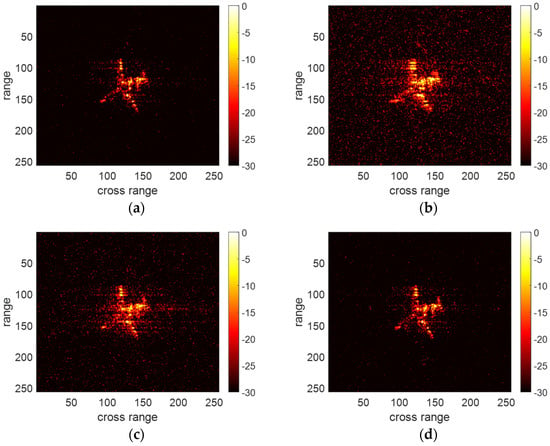
Figure 6.
Translational motion compensation result of different methods under SNR = 0 dB. (a) Ideal result. (b) Result of PSO. (c) Result of PD-KT-FrFT. (d) Result of the proposed method.
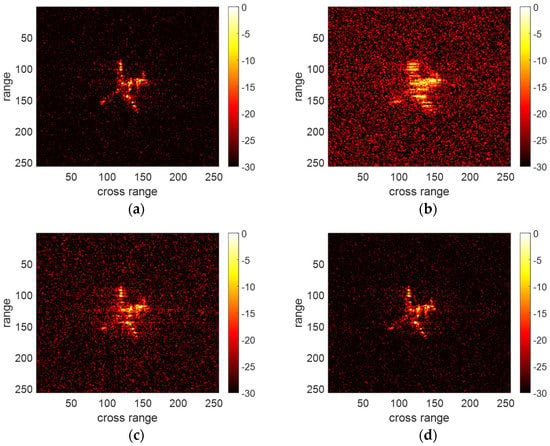
Figure 7.
Translational motion compensation result of different methods under SNR = −3 dB. (a) Ideal result. (b) Result of PSO. (c) Result of PD-KT-FrFT. (d) Result of the proposed method.
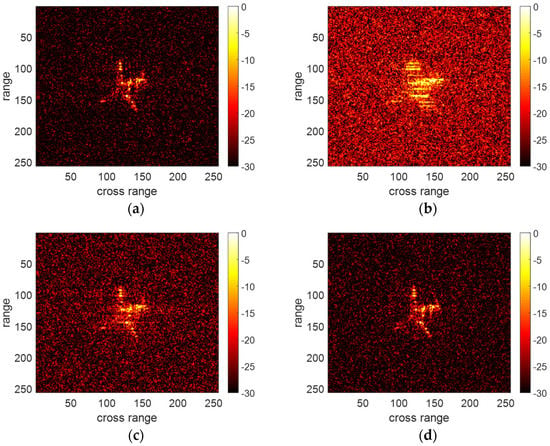
Figure 8.
Translational motion compensation result of different methods under SNR = −6 dB. (a) Ideal result. (b) Result of PSO. (c) Result of PD-KT-FrFT. (d) Result of the proposed method.

Table 1.
The entropy of each imaging result.
The entropy of the results of PSO is higher than that of other methods at different SNRs. Moreover, the results of PSO become increasingly defocused as the SNR decreases. This is because the parameter estimation based on the image quality of RD imaging results is not noise-robust under low SNR. PD-KT-FrFT has better performance and noise robustness than PSO because this method does not depend on the quality of the RD image. However, the results of PD-KT-FrFT still have a certain degree of defocusing because this method is based on the third-order polynomial translation model and is unable to compensate for the translational error caused by . In comparison, the entropy of the results of the proposed method is closest to the ideal results. Moreover, the results of the proposed method are well-focused under different SNRs. Those prove that the proposed method is noise robust than traditional methods.
Finally, we validate the performance of the proposed method under the conditions of extremely low SNR and explore the performance limits of the proposed method. The results of the proposed method under the conditions of SNR = −9, −10, −11 and −12 dB are shown in Figure 9. Additionally, we provide the results of translational parameter estimation in Table 2.
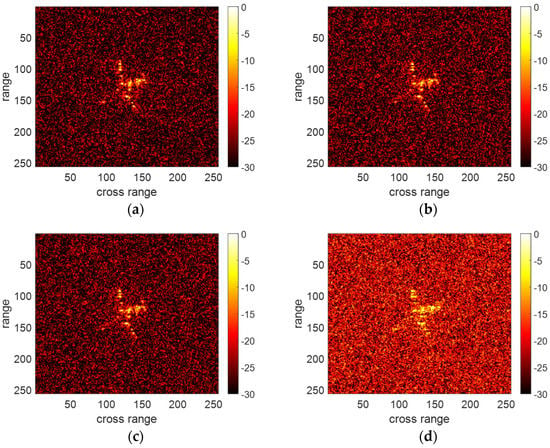
Figure 9.
The results of the proposed method under the conditions of SNR = −9, −10, −11 and −12 dB. (a) SNR = −9 dB. (b) SNR = −10 dB. (c) SNR = −11 dB. (d) SNR = −12 dB.

Table 2.
Result of translational parameter estimation.
The relative errors of the translational parameter estimation are lower than 3.2% when SNR is higher than −11 dB. Each scattering center in Figure 9a,b is well-focused. Under the condition of SNR = −11 dB, the error in translational parameter estimation becomes larger. However, this change is not significant in the final result. Under the condition of SNR = −12 dB, the results of the translational parameter estimation have a significant deviation. This causes a certain degree of defocusing for the result of the proposed method. Therefore, the proposed method is effective and accurate when SNR is higher than −12 dB.
6. Conclusions
This work proposes a noise-robust translational motion compensation method based on HLPT-GSCFT. Specifically, we first model the translational motion as a fourth-order polynomial according to order-of-magnitude analysis and then design HLPT-GSCFT to estimate the translational parameters. In the process of HLPT-GSCFT, HLPT is designed to estimate the acceleration and the third-order acceleration, GSCFT is adopted to estimate the jerk and MWE is designed to estimate the speed. Experimental results based on a Yak-42 measured dataset demonstrate the effectiveness and noise robustness of the proposed method. It must be noted that there are still some shortcomings in the proposed method. On the one hand, as with other parametric translational motion compensation methods, the proposed method is powerless to compensate for random translational errors, and, on the other, the proposed method has limited ability to compensate for sparse aperture echoes. In future research, we hope to extend the proposed method from conventional targets to micro-motion targets for higher-order translational compensation and ISAR imaging.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.H..; methodology, F.L.; software, F.L.; validation, F.L., D.H. and X.G.; formal analysis, C.F.; investigation, F.L.; resources, D.H.; data curation, X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, F.L.; writing—review and editing, C.F.; visualization, F.L.; supervision, D.H.; project administration, C.F.; funding acquisition, D.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China under Grant 2019M661508, Shaanxi Provincial Fund Youth Project of China under Grant 2019JQ-497, and Aviation Science Fund of China under Grant 201920096001 (Funder: Darong Huang).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to the request of the funder.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China under grant 2019M661508, the Shaanxi Provincial Fund Youth Project of China under grant 2019JQ-497 and the Aviation Science Fund of China under grant 201920096001.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, C.C.; Andrews, H.C. Target-motion-induced radar imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1980, 16, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y. Robust ISAR range alignment ia minimizing the entropy of the average range profile. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, T.; Schroth, A. Robust range alignment algorithm via Hough transform in an ISAR imaging system. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 1173–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Bae, J.-H.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Kim, K.-T. ISAR autofocus by minimizing entropy of eigenimages. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2–6 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Cai, J.; Sun, Y.; Xia, X.-G.; Farina, A.; Long, T. Efficient ISAR Phase Autofocus Based on Eigenvalue Decomposition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2195–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, P.; Xing, M.; Sun, G.; Li, Y.; Bao, Z. Minimum Entropy via Subspace for ISAR Autofocus. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 7, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.-J.; Xu, J.; Wang, G.; Xia, X.-G.; Long, T.; Bian, M.-M. An effective ISAR autofocus algorithm based on single eigenvector. In Proceedings of the 2016 CIE International Conference on Radar (RADAR), Guangzhou, China, 10–13 October 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Yeo, T.S.; Bao, Z. Weighted least-squares estimation of phase errors for SAR/ISAR autofocus. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2487–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.; Eichel, P.; Ghiglia, D.; Jakowatz, C. Phase gradient autofocus-a robust tool for high resolution SAR phase correction. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1994, 30, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.; Yeo, T.S. Comments on “Non-iterative quality phase-gradient autofocus (QPGA) algorithm for spotlight SAR imagery”. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Martorella, M.; Chang, S.; Liu, Q.; Ding, Z.; Long, T. Efficient Nonparametric ISAR Autofocus Algorithm Based on Contrast Maximization and Newton’s Method. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 21, 4474–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xing, M.; Yu, H.; Liang, B.; Peng, J.; Sun, G.-C. Motion Compensation/Autofocus in Airborne Synthetic Aperture Radar: A Review. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 10, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, T.M.; Plotnick, D.S. Semiparametric Statistical Stripmap Synthetic Aperture Autofocusing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 2086–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, H.; Liang, B.; Yang, D.-G. Real-Time Processing of Spaceborne SAR Data With Nonlinear Trajectory Based on Variable PRF. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Kong, L.; Cui, G.; Yi, W.; Yang, Y. ISAR imaging of maneuvering target with complex motions based on ACCF–LVD. Digit. Signal Process. 2015, 46, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Kang, L.; Ni, J.; Zhang, Q. Range Alignment in ISAR Imaging Based on Deep Recurrent Neural Network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, X.; Zhou, F. High-Resolution ISAR Imaging and Autofocusing via 2D-ADMM-Net. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, M.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Ran, J. AF-AMPNet: A Deep Learning Approach for Sparse Aperture ISAR Imaging and Autofocusing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xing, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Z. Joint Translational Motion Compensation Method for ISAR Imagery Under Low SNR Condition Using Dynamic Image Sharpness Metric Optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y. Accelerated translational motion compensation with contrast maximization optimization algorithm for inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 13, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Xing, M.; Amin, M.; Sun, G. ISAR Translational Motion Compensation with Simultaneous Range Alignment and Phase Adjustment in Low SNR Environments. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Radar Conference (RadarConf21), Atlanta, GA, USA, 7–14 May 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sheng, J.-L.; Duan, J.; Xing, M.-D.; Qiao, Z.-J.; Bao, Z. Translational motion compensation for ISAR imaging under low SNR by minimum entropy. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2013, 2013, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, D.; Toktas, A. Translational Motion Compensation for ISAR Images Through a Multicriteria Decision Using Surrogate-Based Optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 4365–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Tao, M.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z. Adaptive Translational Motion Compensation Method for ISAR Imaging Under Low SNR Based on Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 5146–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Xu, J.; Peng, Y.N. Parametric inverse synthetic aperture radar manoeuvring target motion compensation based on particle swarm optimizer. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2011, 5, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhan, M.; Liu, H.; Liao, Y.; Liao, G. A Robust Translational Motion Compensation Method for ISAR Imaging Based on Keystone Transform and Fractional Fourier Transform Under Low SNR Environment. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2017, 53, 2140–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Z.; Du, L.; Lu, X.; Ren, K.; Li, L. Ambiguity Function based High-Order Translational Motion Compensation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 1–8, early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Wu, R.; Lan, J.; Bao, Z. Migration Through Resolution Cell Compensation in ISAR Imaging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2004, 1, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubiša, S. Local polynomial Wigner distribution. Signal Process. 1997, 59, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kang, J.; Jiang, Y. ISAR Imaging of Maneuvering Target Based on the Local Polynomial Wigner Distribution and Integrated High-Order Ambiguity Function for Cubic Phase Signal Model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2971–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Feng, C.; Huang, D.; Guo, X. Fast ISAR imaging method for complex manoeuvring target based on local polynomial transform-fast chirp Fourier transform. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2021, 15, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Su, T.; He, X. An ISAR Imaging Algorithm for Nonuniformly Rotating Targets With Low SNR Based on Modified Bilinear Parameter Estimation of Cubic Phase Signal. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 3108–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Su, T.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.H. ISAR Imaging of Nonuniformly Rotating Target Based on a Fast Parameter Estimation Algorithm of Cubic Phase Signal. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4727–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).