LightFGCNet: A Lightweight and Focusing on Global Context Information Semantic Segmentation Network for Remote Sensing Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ●
- We propose the lightweight semantic segmentation network, LightFGCNet, which prioritizes global contextual information by fusing feature information of varying resolutions multiple times.
- ●
- We develop a simple and effective parallel channel spatial attention module (PCSAM), which is a redesigned version of the previously existing channel attention and spatial attention modules that now work together in parallel to reduce noise from multiple fusions.
- ●
- Inspired by the atrous spatial convolution pooling pyramid, we construct a multi-scale fusion module (MSFM), geared towards the needs of the premise of fewer parameters, to extract more multi-scale information and increase context information.
2. Related Work
2.1. Contextual Information
2.2. Attention Mechanism
2.3. Lightweight Model
3. Methodology
3.1. LightFGCNet
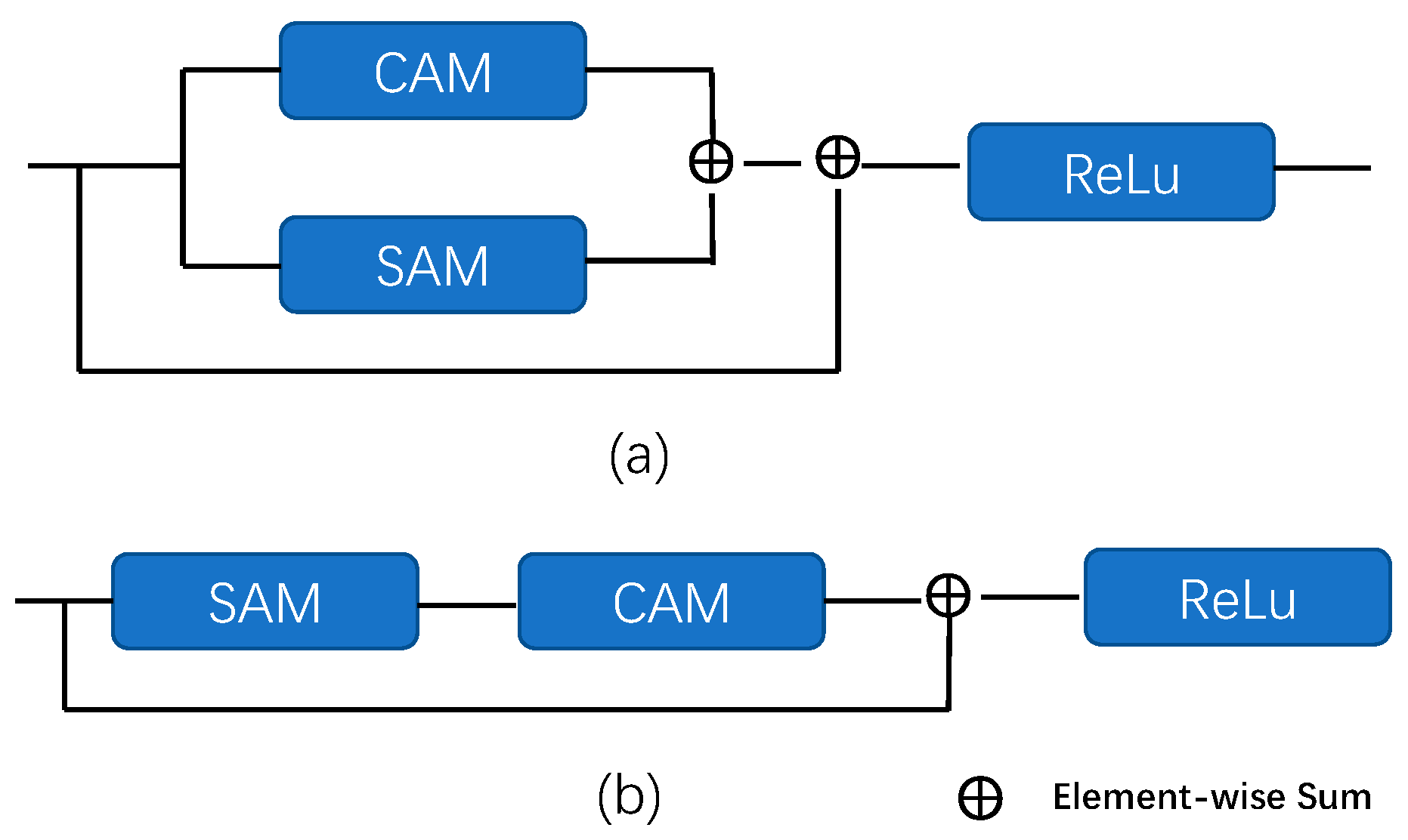
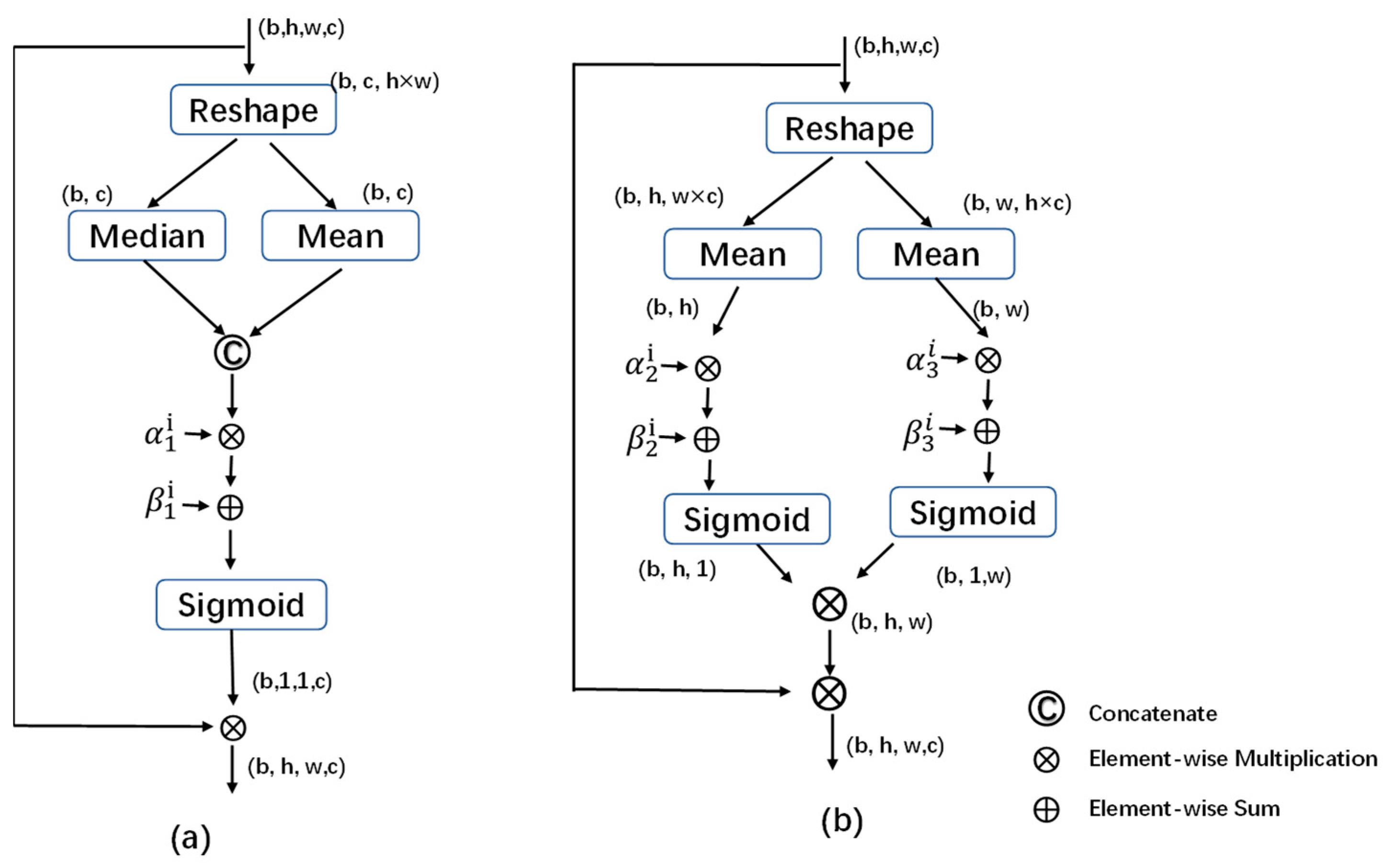
3.2. PCSAM
3.3. MSFM
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Datasets
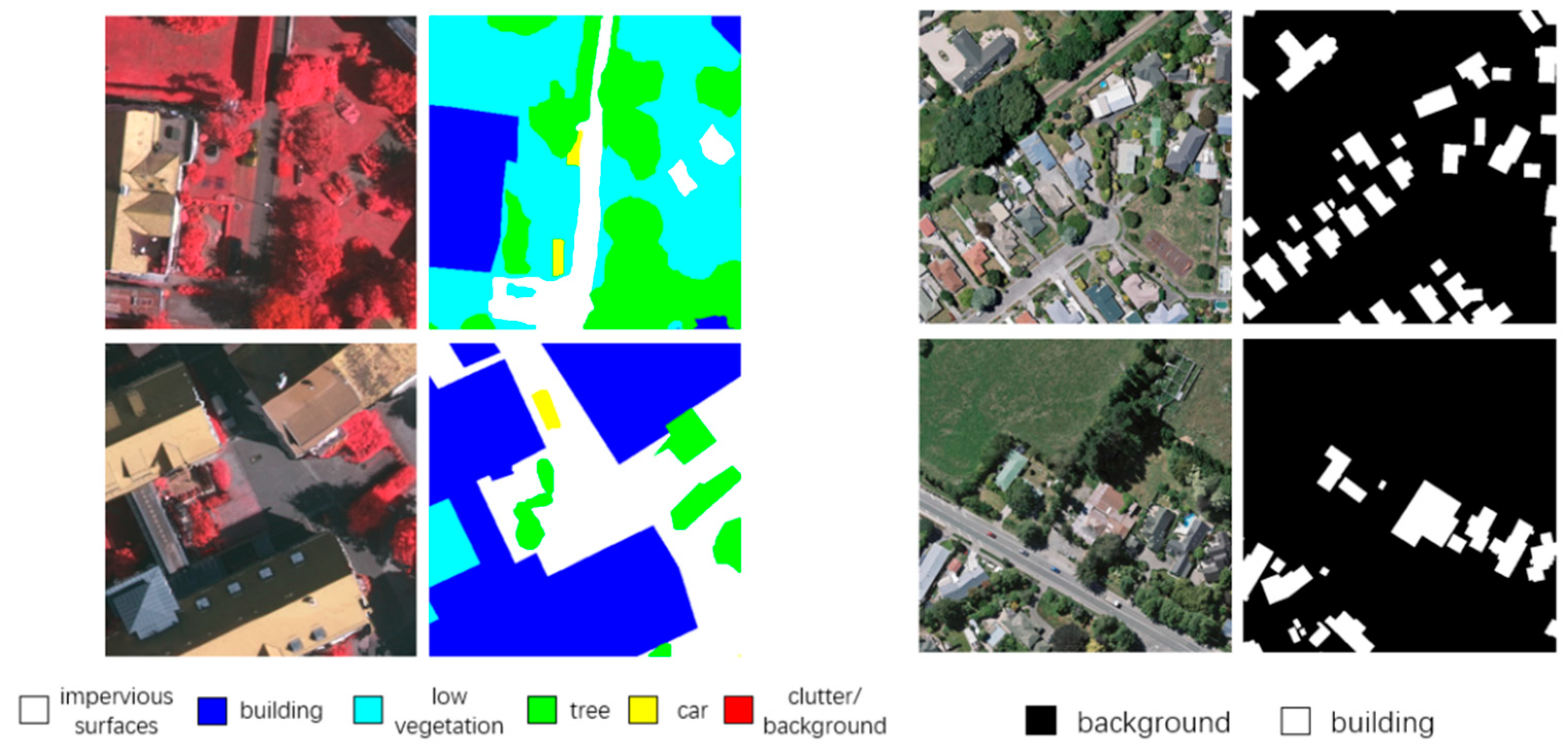
4.1.1. ISPRS Vaihingen Dataset
4.1.2. WHU Building Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Metrics
4.3. Ablation Study
4.3.1. Parallel Channel Spatial Attention Module
4.3.2. Multi-Scale Fusion Module
4.3.3. Channel Number of Basic Block
4.3.4. Comparison of Encoders
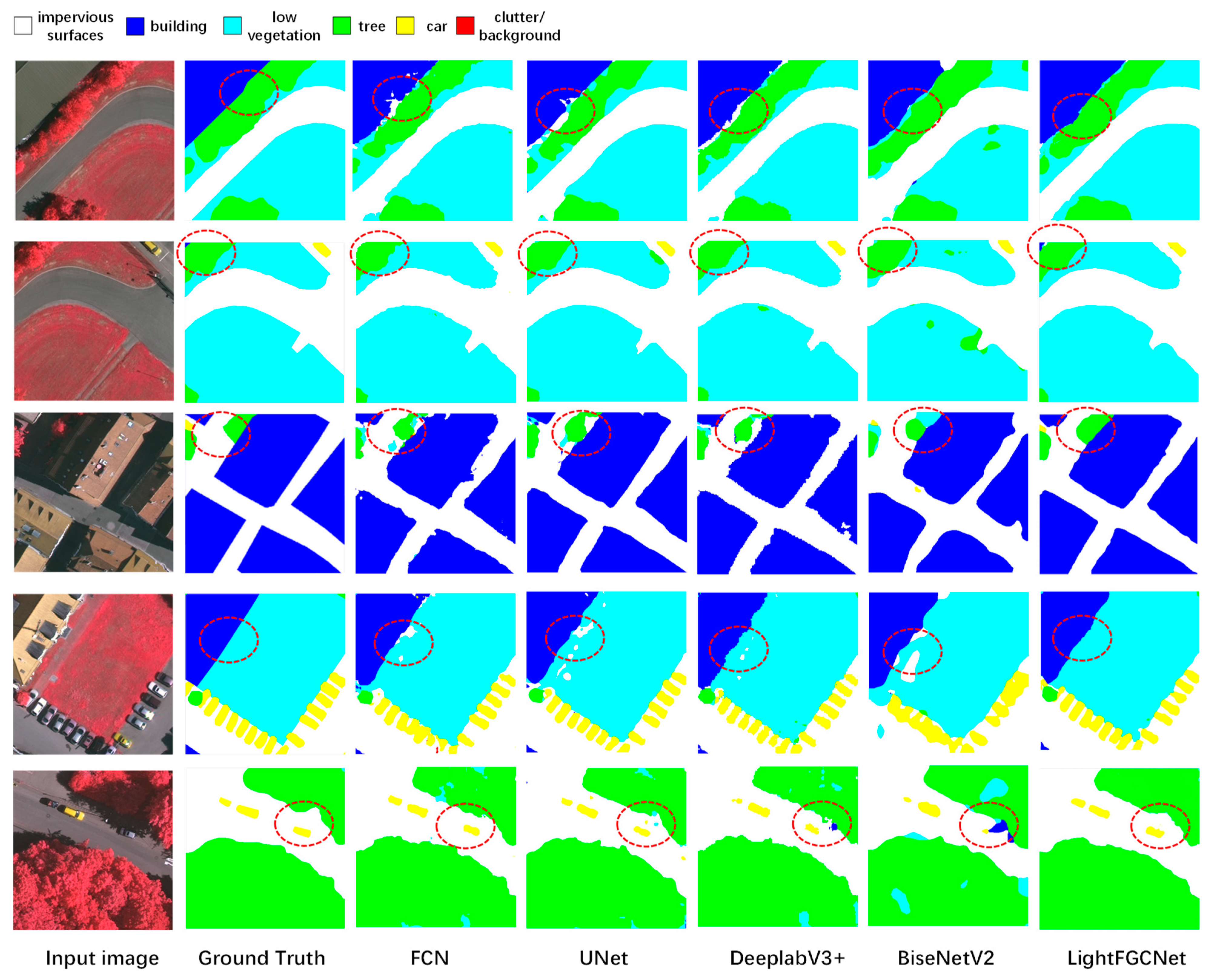
4.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Models
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, T.; Su, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, W.-H. State and parameter estimation of the AquaCrop model for winter wheat using sensitivity informed particle filter. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 180, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets and fully connected crfs. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.7062. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Z.; Li, J. Efficient Transformer for Remote Sensing Image Segmentation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Tang, S.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y. CGNet: A Light-Weight Context Guided Network for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, J. HRCNet: High-Resolution Context Extraction Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Xiao, B.; Liu, D.; Wang, J. Deep High-Resolution Representation Learning for Human Pose Estimation. In Proceedings of the 32nd IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 5686–5696. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.H.; Xu, T.X.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, Z.N.; Jiang, P.T.; Mu, T.J.; Zhang, S.H.; Martin, R.R.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, S.M. Attention mechanisms in computer vision: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 331–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhu, X.; Sun, R.; He, J.; Li, R.; Shen, X.; Yu, B. Tensor Low-Rank Reconstruction for Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00490. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. DenseASPP for Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3684–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2261–2269. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Qian, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhong, X.; Xiao, Z. SRANet: Semantic relation aware network for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2022, 16, 014515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, J.; Loy, C.C.; Lin, D.; Jia, J. PSANet: Point-wise Spatial Attention Network for Scene Parsing. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 270–286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; De Mello, S.; Gu, J.; Zhong, G.; Yang, M.H.; Kautz, J. Learning Affinity via Spatial Propagation Networks. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 1521–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Arnab, A.; Torr, P.H.S. Dynamic Graph Message Passing Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 14–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Liu, X.; Bourennane, S.; Liu, B. Multiscale denoising autoencoder for improvement of target detection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 3002–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, P. Global second-order pooling convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3024–3033. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11531–11539. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. FcaNet: Frequency Channel Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the 18th IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Online, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 763–772. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Zhong, B.; Fu, Y. Image Super-resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 286–301. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Spatial Transformer Networks. In Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015; pp. 2017–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Albanie, S.; Sun, G.; Vedaldi, A. Gather-excite: Exploiting feature context in convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 9423–9433. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Liao, C.; Hu, H.; Mei, X.M.; Li, H.F. MAP-Net: Multiple Attending Path Neural Network for Building Footprint Extraction From Remote Sensed Imagery. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 6169–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Hu, H.; Li, H.F.; Ge, X.M.; Chen, M.; Li, C.N.; Zhu, Q. Joint Learning of Contour and Structure for Boundary-Preserved Building Extraction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.-T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 122–138. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Hou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Rethinking Bottleneck Structure for Efficient Mobile Network Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Edinburgh, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 680–697. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Lu, W.; Cao, J.S.; Xie, G.Q. MKANet: An Efficient Network with Sobel Boundary Loss for Land-Cover Classification of Satellite Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Zhang, H.M.; Song, Y.J. Extraction of Impervious Surface from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on a Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022, 8636973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.B.; Li, R.; Zhang, C.; Fang, S.H.; Duan, C.X.; Meng, X.L.; Atkinson, P.M. UNetFormer: A UNet-like transformer for efficient semantic segmentation of remote sensing urban scene imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 190, 196–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1512.03385. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.G.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, R.S. A Lightweight Network for Building Extraction From Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5614812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Guo, Y.Y.; Bao, T.F.; Fu, C.Q.; Huo, H.; Fang, T. MFALNet: A Multiscale Feature Aggregation Lightweight Network for Semantic Segmentation of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 346–361. [Google Scholar]
- ISPRS Vaihingen Dataset. Available online: https://www.isprs.org/education/benchmarks/UrbanSemLab/2d-sem-label-vaihingen.aspx (accessed on 21 November 2022).
- Ji, S.; Wei, S. Building extraction via convolutional neural networks from an open remote sensing building dataset. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2019, 48, 448–459. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.H.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Gao, C.; Wang, J.; Yu, G.; Shen, C.; Sang, N. BiSeNet V2: Bilateral Network with Guided Aggregation for Real-time Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.02147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, J.; Sun, G.; Li, J.; Deng, M.J.I.G.; Letters, R.S. SMAF-net: Sharing multiscale adversarial feature for high-resolution remote sensing imagery semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 18, 1921–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qiu, K.; Chen, L.; Mei, X.; Hong, L.; Tao, C. SCAttNet: Semantic Segmentation Network With Spatial and Channel Attention Mechanism for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 18, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.C.; Wang, C.Y.; Li, J.H.; Sui, Y. MF-Dfnet: A deep learning method for pixel-wise classification of very high-resolution remote sensing images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 330–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Niu, J. An End-to-End Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling and Skip-Connections Generative Adversarial Segmentation Network for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Aerial Images. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Jing, W.; Song, H.; Chen, G. ESFNet: Efficient Network for Building Extraction From High-Resolution Aerial images. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 54285–54294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.S.; Cai, M.R.; Gu, Y.F.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.X.; Han, Y.X. Cropland encroachment detection via dual attention and multi-loss based building extraction in remote sensing images. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 993961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Z.; Zhang, D.J.; Wu, Y.Q.; Chen, Y.L.; Yan, X.H. A Context Feature Enhancement Network for Building Extraction from High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
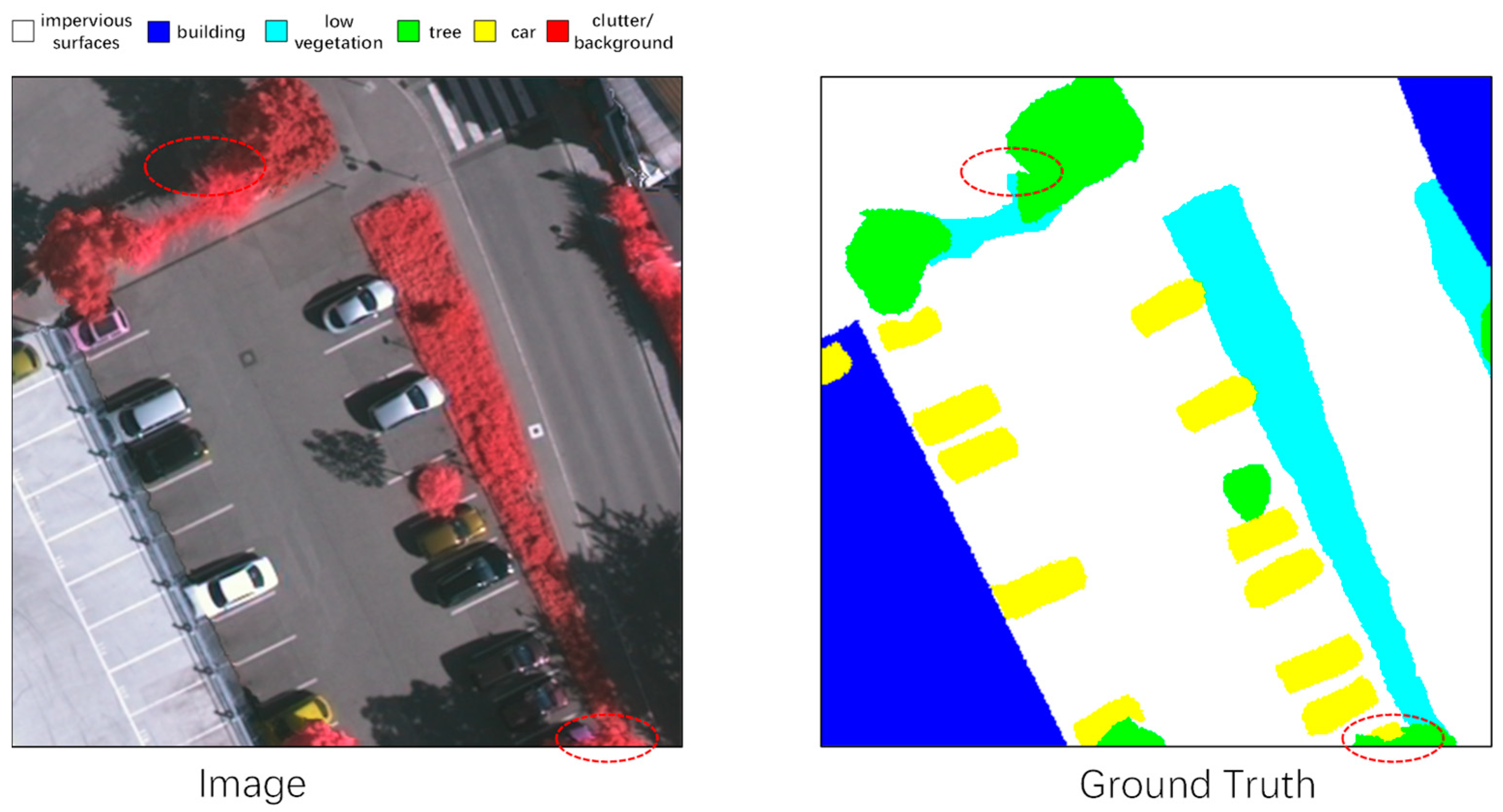




| Method | Mean F1 (%) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|
| LightFGCNet-channel | 81.05 | 84.97 |
| LightFGCNet-spatial | 80.34 | 83.98 |
| LightFGCNet-serial | 81.67 | 85.16 |
| LightFGCNet-parallel | 82.17 | 85.56 |
| Method | Mean F1 (%) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|
| +w/o | 80.86 | 84.49 |
| +ECA | 81.41 | 84.96 |
| +SE | 81.69 | 85.05 |
| +CBAM | 80.84 | 84.78 |
| +PCSAM(ours) | 82.17 | 85.56 |
| Method | Pre_Class F1-Score(%) | Mean F1 (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious Surfaces | Building | Low Vegetation | Tree | Car | ||
| LightFGCNet-w/o | 86.75 | 90.19 | 75.93 | 83.51 | 67.95 | 80.87 |
| LightFGCNet | 87.91 | 91.47 | 77.26 | 84.31 | 69.89 | 82.17 |
| Method | Mean F1 (%) | OA (%) | Parameters (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LightFGCNet-C32 | 80.98 | 84.49 | 1.48 | 10.7 |
| LightFGCNet-C48 | 82.17 | 85.56 | 3.12 | 23.5 |
| LightFGCNet-C64 | 83.16 | 86.47 | 4.71 | 41.3 |
| Encoder | Decoder | Mean F1 (%) | OA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet50 | standard | 76.34 | 82.22 |
| ResNet50 | ours | 81.91 | 85.51 |
| ours | ours | 82.17 | 85.56 |
| Method | Recall (%) | mIoU (%) | OA (%) | Mean F1 (%) | Parameters (M) | FLOPs (G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 83.09 | 68.24 | 84.60 | 80.47 | 12.72 | 72.0 |
| UNet | 83.03 | 69.03 | 84.70 | 81.10 | 8.23 | 67.8 |
| DeeplabV3+ | 83.36 | 68.01 | 84.71 | 80.21 | 14.35 | 79.9 |
| BiseNetV2 | 75.62 | 59.62 | 79.66 | 73.51 | 2.98 | 9.15 |
| SMAF-Net [45] | - | 65.28 | 88.45 | 86.91 | - | - |
| SCAttNet V2 [46] | - | 70.20 | 85.47 | 82.06 | - | - |
| MF-Dfnet [47] | 83.46 | - | 86.2 | 84.36 | 14.34 | - |
| SRANet(50) [17] | - | 66.34 | 86.27 | 77.95 | - | - |
| LightFGCNet-C48 | 84.66 | 70.45 | 85.56 | 82.17 | 3.12 | 23.5 |
| Method | mIoU(%) | Pre_Class F1-Score(%) | Mean F1 (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impervious Surfaces | Building | Low Vegetation | Tree | Car | |||
| FCN | 68.24 | 86.83 | 90.53 | 76.12 | 83.88 | 65.02 | 80.47 |
| UNet | 69.03 | 87.42 | 91.25 | 75.17 | 83.33 | 68.34 | 81.10 |
| DeeplabV3+ | 68.01 | 87.04 | 90.76 | 76.02 | 83.89 | 63.33 | 80.21 |
| BiseNetV2 | 59.62 | 81.96 | 84.73 | 70.41 | 80.89 | 49.56 | 73.51 |
| SMAF-Net [45] | 65.28 | 91.80 | 94.30 | 81.25 | 83.95 | 83.24 | 86.91 |
| SCAttNet V2 [46] | 70.20 | 89.13 | 90.34 | 80.04 | 80.31 | 70.50 | 82.06 |
| MF-DFNet [47] | - | 88.8 | 93.1 | 78.4 | 84.0 | 77.5 | 84.36 |
| SRANet(50) [17] | 66.34 | 88.52 | 92.04 | 78.96 | 85.72 | 79.21 | 77.95 |
| LightFGCNet-C48 | 70.45 | 87.91 | 91.47 | 77.26 | 84.31 | 69.89 | 82.17 |
| Method | Recall (%) | F1 (%) | IoU (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCN | 93.57 | 93.91 | 88.51 |
| UNet | 94.33 | 94.21 | 89.05 |
| DeeplabV3+ | 93.77 | 93.39 | 87.60 |
| BiseNetV2 | 87.44 | 87.31 | 77.47 |
| ASGASN [48] | 95.1 | 94.4 | 89.4 |
| ESFNet [49] | - | - | 85.34 |
| AttsegGAN [50] | - | 94.35 | 89.07 |
| CFENet [51] | - | 92.62 | 87.22 |
| LightFGCNet-C48 | 94.57 | 94.86 | 89.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, M.; Kang, M.; Weise, T.; Wang, X.; Tan, M.; Xu, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C. LightFGCNet: A Lightweight and Focusing on Global Context Information Semantic Segmentation Network for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6193. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246193
Chen Y, Jiang W, Wang M, Kang M, Weise T, Wang X, Tan M, Xu L, Li X, Zhang C. LightFGCNet: A Lightweight and Focusing on Global Context Information Semantic Segmentation Network for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(24):6193. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246193
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yan, Wenxiang Jiang, Mengyuan Wang, Menglei Kang, Thomas Weise, Xiaofeng Wang, Ming Tan, Lixiang Xu, Xinlu Li, and Chen Zhang. 2022. "LightFGCNet: A Lightweight and Focusing on Global Context Information Semantic Segmentation Network for Remote Sensing Imagery" Remote Sensing 14, no. 24: 6193. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246193
APA StyleChen, Y., Jiang, W., Wang, M., Kang, M., Weise, T., Wang, X., Tan, M., Xu, L., Li, X., & Zhang, C. (2022). LightFGCNet: A Lightweight and Focusing on Global Context Information Semantic Segmentation Network for Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sensing, 14(24), 6193. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14246193







