A New Magnetic Target Localization Method Based on Two-Point Magnetic Gradient Tensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Magnetic Gradient Tensor and Tensor Invariants
2.2. Localization Principle of the NTPT Method
3. Simulations
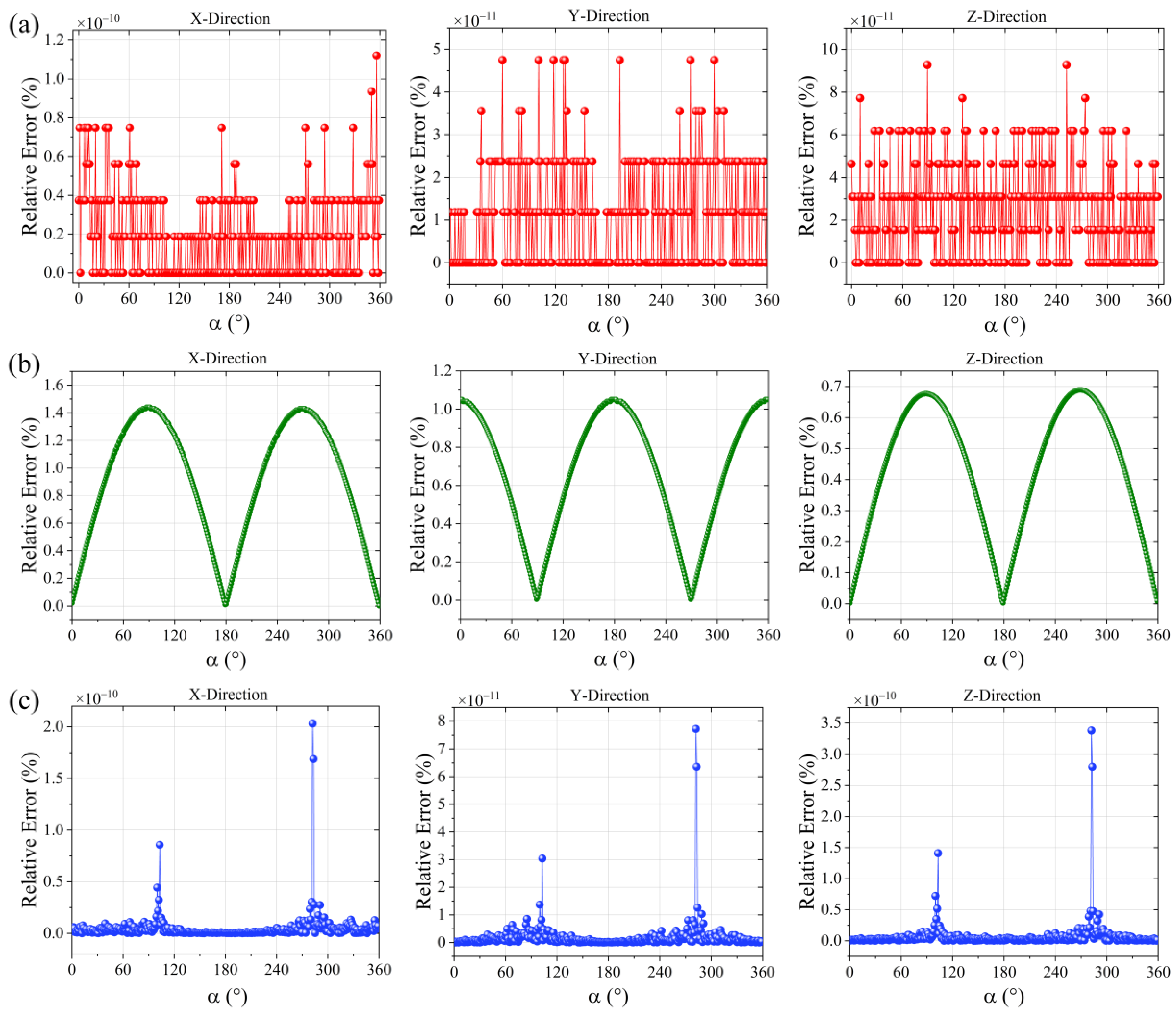
3.1. Without the Influence of the Noise
3.2. With the Influence of the Noise
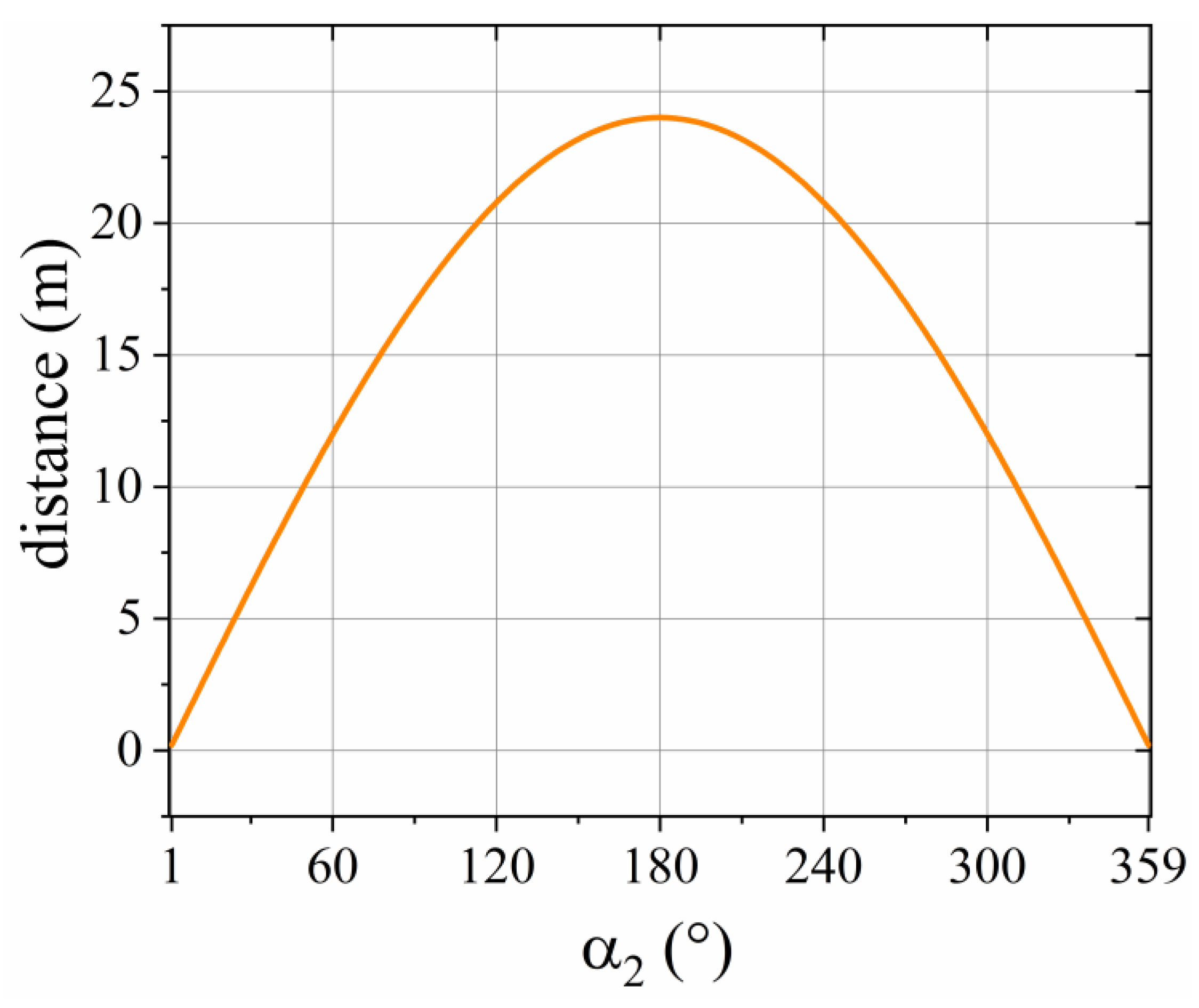
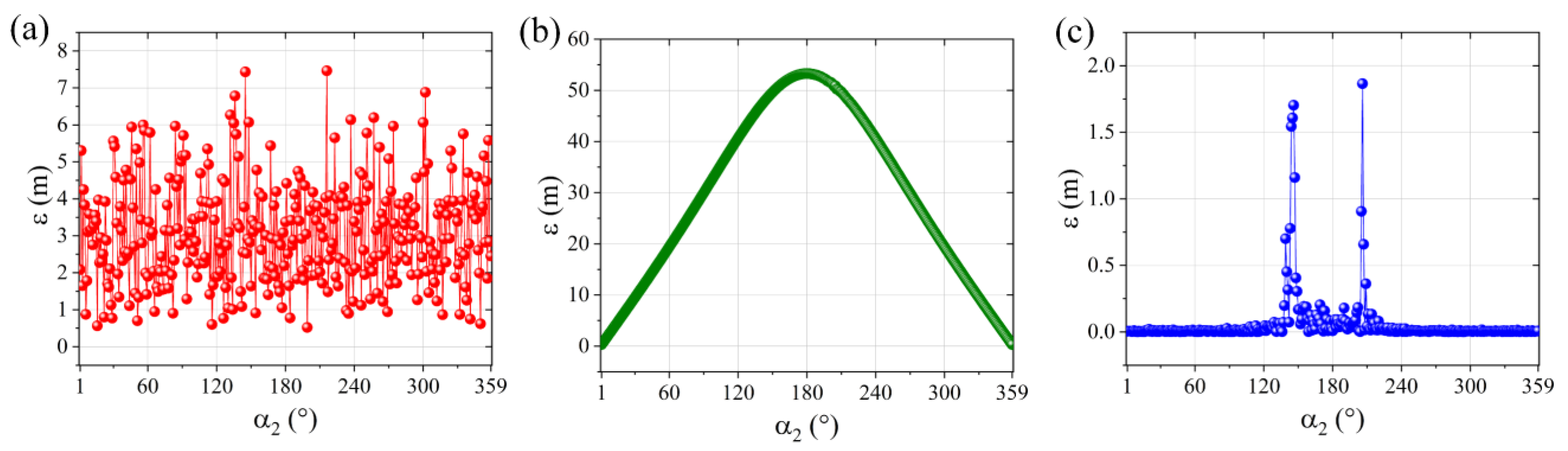
3.3. Influence of Distance between Observation Points
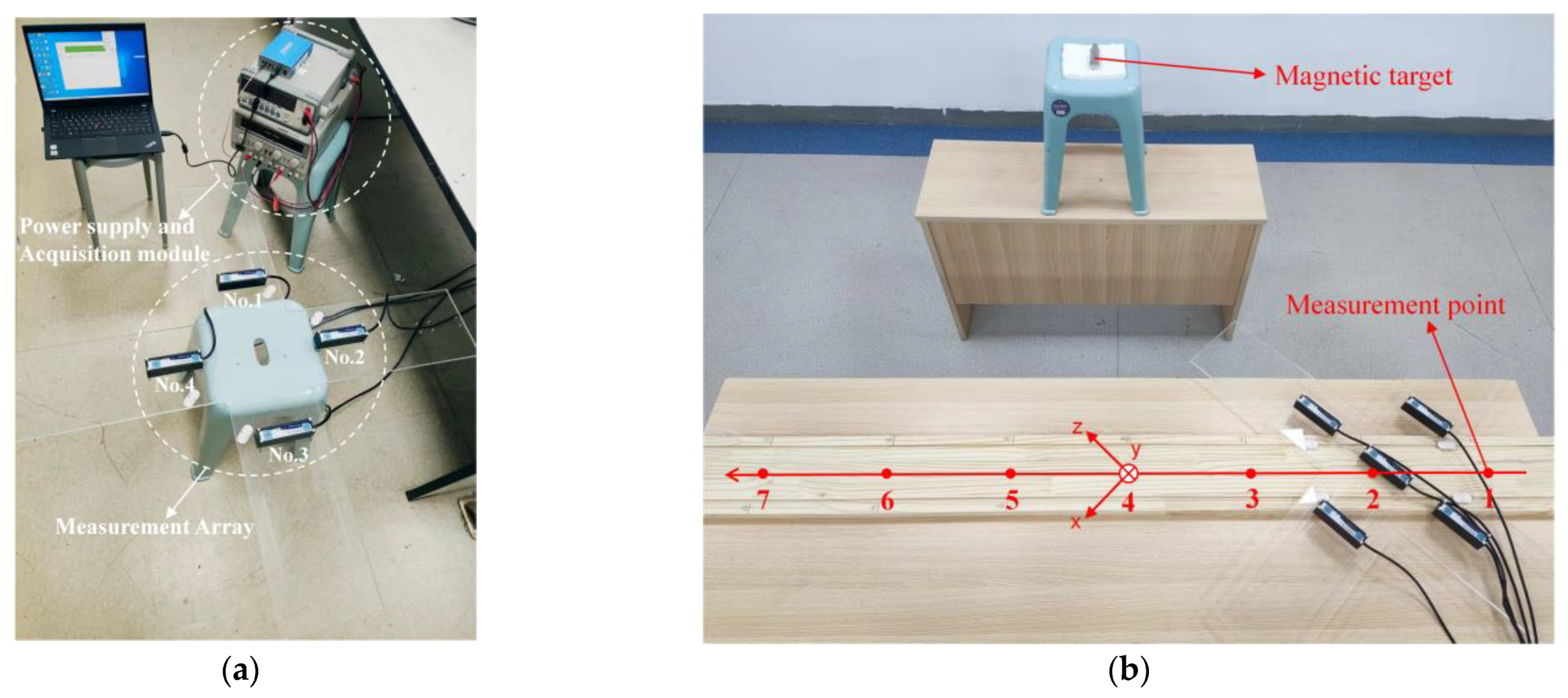
4. Experiments and Result Analysis
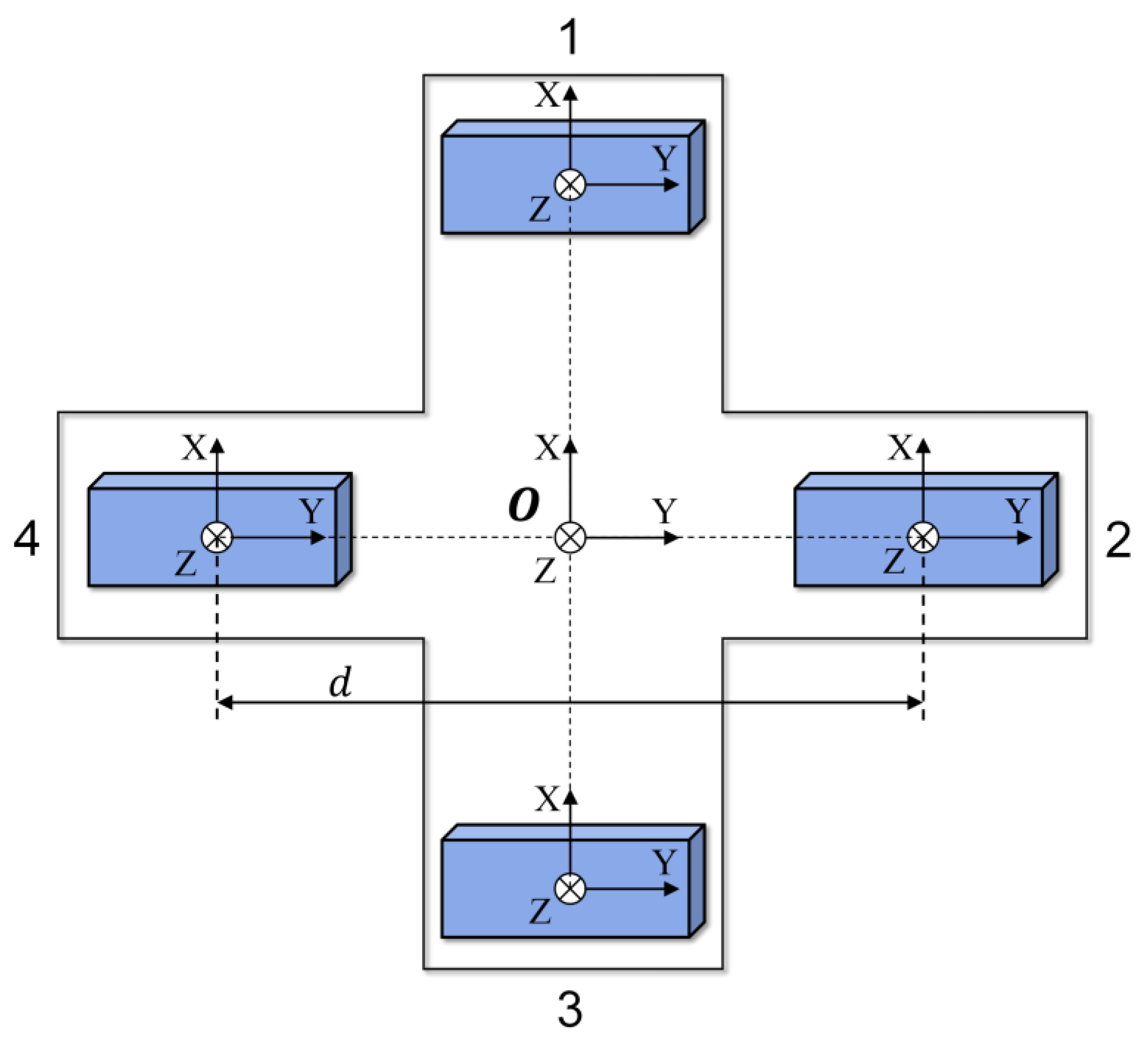
4.1. Magnetic Gradient Tensor Measurement Array Model
4.2. Experimental Verification and Result Analysis
4.2.1. Localization with Adjacent Measurement Points
4.2.2. Localization with Variational Observation Point Distances
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, H.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Qin, J.; Wang, T. Magnetic Anomaly Detection and Localization Using Orthogonal Basis of Magnetic Tensor Contraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5944–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, N.; Chang, M.; Xu, L. Research on the Model and the Location Method of Ship Shaft-Rate Magnetic Field Based on Rotating Magnetic Dipole. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 162999–163005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Tang, J.; Ren, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, X.; Zhao, T. Multiple Underwater Objects Localization With Magnetic Gradiometry. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wu, L.H.; Sun, F. Underwater Continuous Localization Based on Magnetic Dipole Target Using Magnetic Gradient Tensor and Draft Depth. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.; Oeschger, J. Generalized magnetic gradient contraction based method for detection, localization and discrimination of underwater mines and unexploded ordnance. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2005 MTS/IEEE, Washington, DC, USA, 17–23 September 2005; pp. 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Luan, X. Accurate Measurement of Characteristic Response for Unexploded Ordnance With Transient Electromagnetic System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, S.; Luo, C. Underground Target Localization Based on Improved Magnetic Gradient Tensor With Towed Transient Electromagnetic Sensor Array. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 25025–25033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.; Clark, D.; Leslie, K.; Bick, M.; Tilbrook, D.; Foley, C. GETMAG–a SQUID Magnetic Tensor Gradiometer for Mineral and Oil Exploration. Explor. Geophys. 2004, 35, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, L.; Wang, T. High-Precision Joint Magnetization Vector Inversion Method of Airborne Magnetic and Gradient Data with Structure and Data Double Constraints. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, A.Y.; Park, J.W. Repolarization Heterogeneity of Magnetocardiography Predicts Long-Term Prognosis in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 1305–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primin, M.A.; Nedayvoda, I.V. Non-Contact Analysis of Magnetic Fields of Biological Objects: Algorithms for Data Recording and Processing. Cybern. Syst. Anal. 2020, 56, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.W.; Clark, D.A. The magnetic gradient tensor: Its properties and uses in source characterization. Lead. Edge 2006, 25, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, W. Dipole tracking with a gradiometer. Nav. Ship Res. Dev. Lab. Informal Rep. NSRDL/PC 1972, 3493. [Google Scholar]
- Wynn, W.; Frahm, C.; Carroll, P.; Clark, R.; Wellhoner, J.; Wynn, M. Advanced superconducting gradiometer/magnetometer arrays and a novel signal processing technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1975, 11, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, H. Analysis of the magnetic gradient tensor. Tech. Memo. 1985, 8, 5–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nara, T.; Suzuki, S.; Ando, S. A Closed-Form Formula for Magnetic Dipole Localization by Measurement of Its Magnetic Field and Spatial Gradients. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2006, 42, 3291–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.; Wei, Z.; Xie, Y. A closed-form formula for magnetic dipole localization by measurement of its magnetic field vector and magnetic gradient tensor. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 499, 166274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Nara, T.; Ando, S.; Kojima, F.; Kobayashi, F.; Nakamoto, H. A Truncated Singular Value Decomposition approach for locating a magnetic dipole with Euler’s equation. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2016, 52, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.; Lee, K.; Oeschger, J. Improved magnetic STAR methods for real-time, point-by-point localization of unexploded ordnance and buried mines. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2008, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 15–18 September 2008; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegert, R.F. Magnetic STAR technology for real-time localization and classification of unexploded ordnance and buried mines. In Proceedings of the Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XIV, Orlando, FL, USA, 13–17 April 2009; pp. 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Li, P.; Wei, Z.; Liu, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, L. Magnetic dipole localization and magnetic moment estimation method based on normalized source strength. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 502, 166450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, G.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, H.; Li, Z. Magnetic dipole localization based on magnetic gradient tensor data at a single point. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Y.; Leslie, K.; Clark, D. Multiple-Order Magnetic Gradient Tensors for Localization of a Magnetic Dipole. IEEE Magn. Lett. 2017, 8, 6506605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ren, G.; Li, Z.; Li, Q. A third-order magnetic gradient tensor optimization algorithm based on the second-order improved central difference method. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 065302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, M.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, H. Estimating Locations and Moments of Multiple Dipole-Like Magnetic Sources From Magnetic Gradient Tensor Data Using Differential Evolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobely, T.E.; Salem, A. Position detection of unexploded ordnance from airborne magnetic anomaly data using 3-D self organized feature map. In Proceedings of the Fifth IEEE International Symposium on Signal Processing and Information Technology, Athens, Greece, 18–21 December 2005; pp. 322–327. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, P.; Zhang, N.; Lin, C.; Chang, M.; Xu, L. Two-point magnetic field positioning algorithm based on rotating magnetic dipole. Measurement 2021, 174, 109059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Li, X.H.; Zeng, X.N. Online magnetic target location method based on the magnetic gradient tensor of two points. Chin. J. Geophys. 2017, 60, 3995–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, C.; Ge, J.; Dong, H.; Liu, Z. Magnetic Dipole Two-Point Tensor Positioning Based on Magnetic Moment Constraints. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Gu, H.; Chang, M.; Fang, L.; Lin, P.; Lin, C. Magnetic Target Linear Location Method Using Two-Point Gradient Full Tensor. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.L.; Shen, W.B.; Yang, M.; Kuhn, M.; Ran, J. First-Order Derivatives of Principal and Main Invariants of Magnetic Gradient Tensor of a Uniformly Magnetized Tesseroid and Spherical Shell. Surv. Geophys. 2022, 43, 1233–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Pan, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, L.; Li, L. Improvement and omnidirectional analysis of magnetic gradient tensor invariants method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 7603–7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beiki, M.; Clark, D.A.; Austin, J.R.; Foss, C.A. Estimating source location using normalized magnetic source strength calculated from magnetic gradient tensor data. Geophysics 2012, 77, J23–J37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiao, C.; Gao, J.; Zhou, G. Experiment research of magnetic dipole model applicability for a magnetic object. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2010, 18, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.A. New methods for interpretation of magnetic vector and gradient tensor data I: Eigenvector analysis and the normalised source strength. Explor. Geophys. 2012, 43, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, N.; Fang, L.; Chen, H.; Lin, P.; Lin, C.; Wang, J. Simulation Analysis of Magnetic Gradient Full-Tensor Measurement System. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 6688364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Error | x | y | z | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | ||||
| NTPT (%) | 0.034% | 0.013% | 0.05% | |
| XTPT (%) | 0.95% | 0.71% | 0.56% | |
| NSPT (%) | 8.24% | 5.69% | 6.72% | |
| Sets | NTPT (%) | XTPT (%) | NSPT (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | x | y | z | x | y | z | |
| 1 | 9.31 | 3.24 | 16.13 | 12.32 | 2.14 | 14.38 | 24.32 | 26.85 | 32.07 |
| 2 | 1.69 | 11.13 | 5.60 | 14.59 | 5.11 | 14.41 | 14.78 | 20.02 | 35.68 |
| 3 | 6.40 | 7.26 | 10.82 | 5.17 | 17.53 | 16.09 | 20.95 | 37.44 | 34.89 |
| 4 | 11.68 | 4.93 | 6.45 | 3.67 | 16.39 | 15.42 | 30.57 | 42.05 | 31.96 |
| 5 | 10.97 | 14.06 | 11.89 | 9.61 | 5.60 | 10.24 | 32.94 | 39.40 | 14.93 |
| 6 | 13.01 | 0.15 | 9.62 | 9.34 | 0.13 | 12.37 | 28.94 | 22.00 | 44.31 |
| 7 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 26.49 | 17.06 | 25.63 |
| Mean | 8.84 | 6.80 | 10.09 | 9.12 | 7.82 | 13.82 | 25.57 | 29.26 | 31.35 |
| Sets | Distance (cm) | NTPT (%) | XTPT (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | x | y | z | ||
| 1 | 30 | 9.31 | 3.24 | 16.13 | 12.32 | 2.14 | 14.38 |
| 2 | 60 | 14.55 | 3.39 | 13.56 | 15.96 | 5.14 | 23.41 |
| 3 | 90 | 4.09 | 6.90 | 13.17 | 13.34 | 13.55 | 34.86 |
| 4 | 120 | 10.92 | 2.80 | 10.19 | 7.75 | 41.71 | 53.99 |
| 5 | 150 | 9.43 | 1.82 | 8.63 | 7.13 | 86.65 | 93.04 |
| 6 | 180 | 3.62 | 4.56 | 4.57 | 21.64 | 141.98 | 152.97 |
| Mean | - | 8.65 | 3.78 | 11.04 | 13.02 | 48.53 | 62.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, W. A New Magnetic Target Localization Method Based on Two-Point Magnetic Gradient Tensor. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236088
Liu G, Zhang Y, Wang C, Li Q, Li F, Liu W. A New Magnetic Target Localization Method Based on Two-Point Magnetic Gradient Tensor. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(23):6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236088
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Gaigai, Yingzi Zhang, Chen Wang, Qiang Li, Fei Li, and Wenyi Liu. 2022. "A New Magnetic Target Localization Method Based on Two-Point Magnetic Gradient Tensor" Remote Sensing 14, no. 23: 6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236088
APA StyleLiu, G., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., Li, Q., Li, F., & Liu, W. (2022). A New Magnetic Target Localization Method Based on Two-Point Magnetic Gradient Tensor. Remote Sensing, 14(23), 6088. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14236088







