A Recursive Hull and Signal-Based Building Footprint Generation from Airborne LiDAR Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
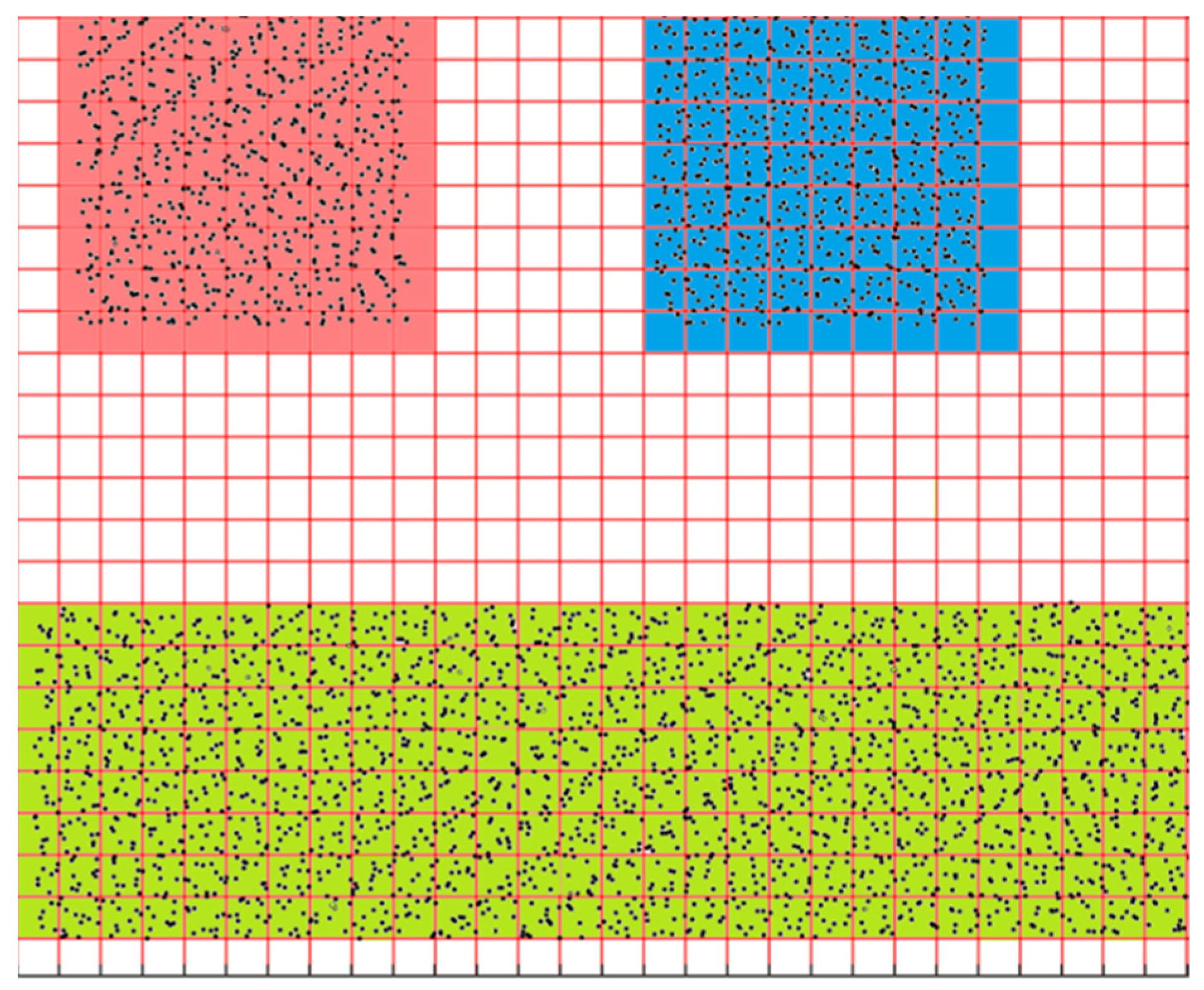
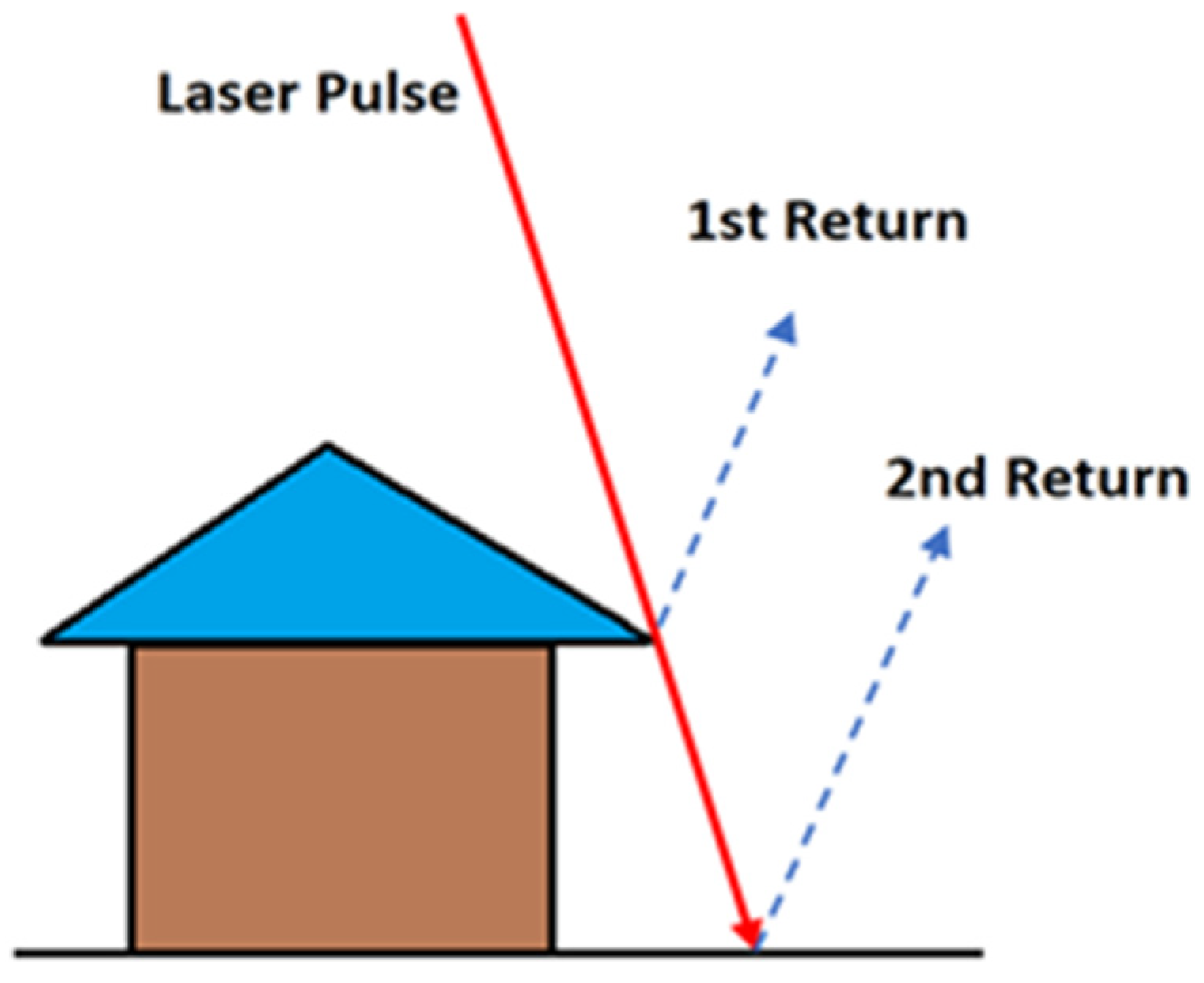
3.1. Data Pre-Processing
3.2. Initial Building Outline Generation
3.2.1. Extraction of Outermost Points
3.2.2. Recursive Convex Hull Algorithm
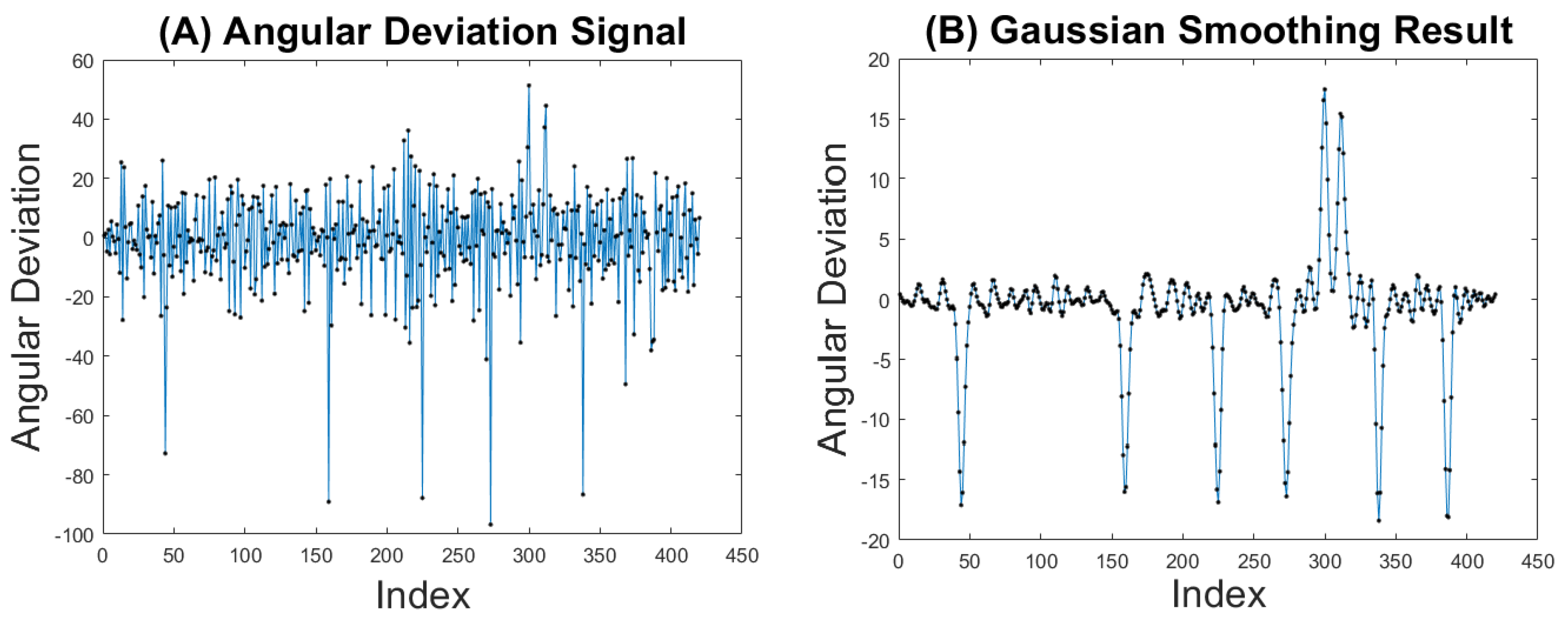
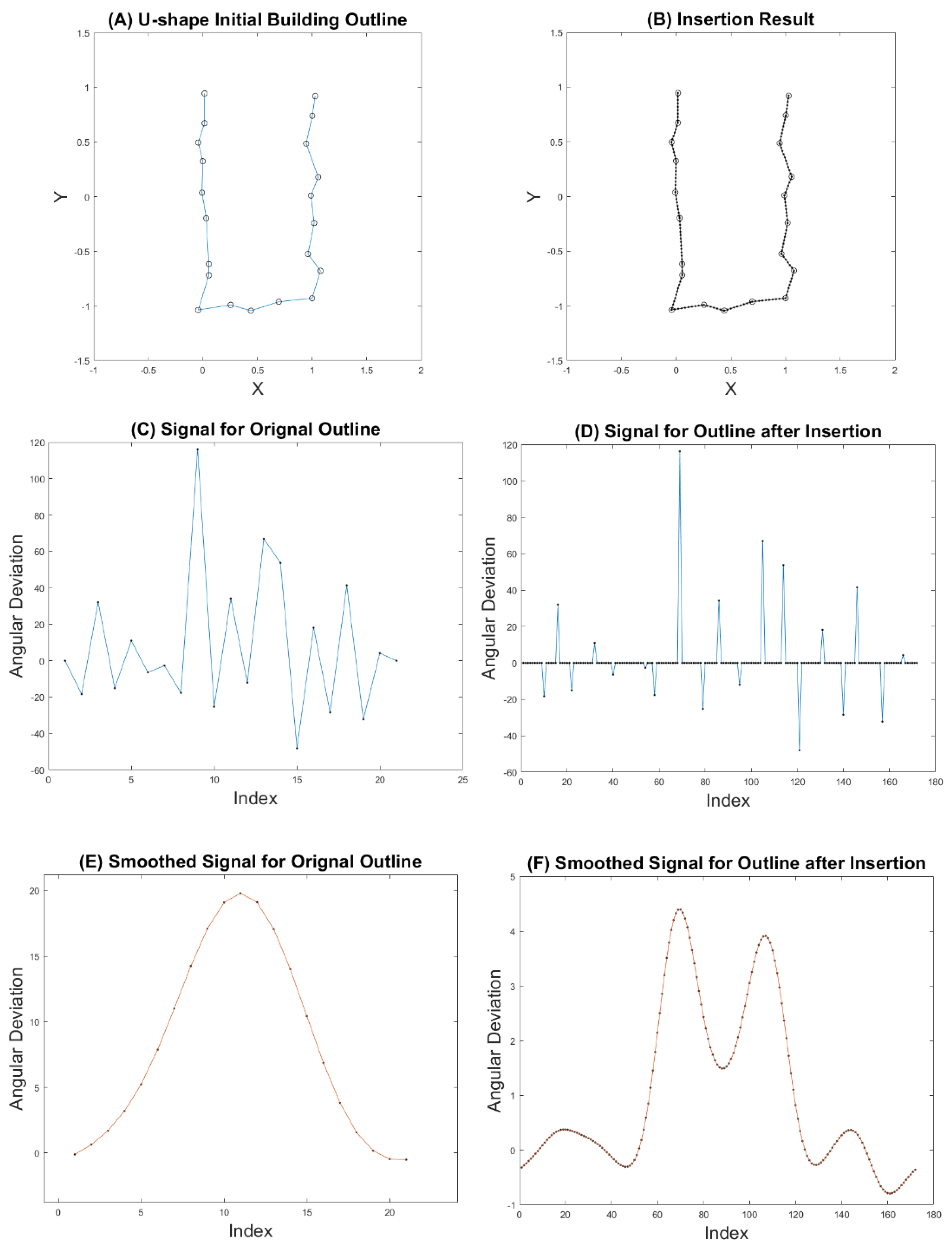
3.3. Signal Based Regularization
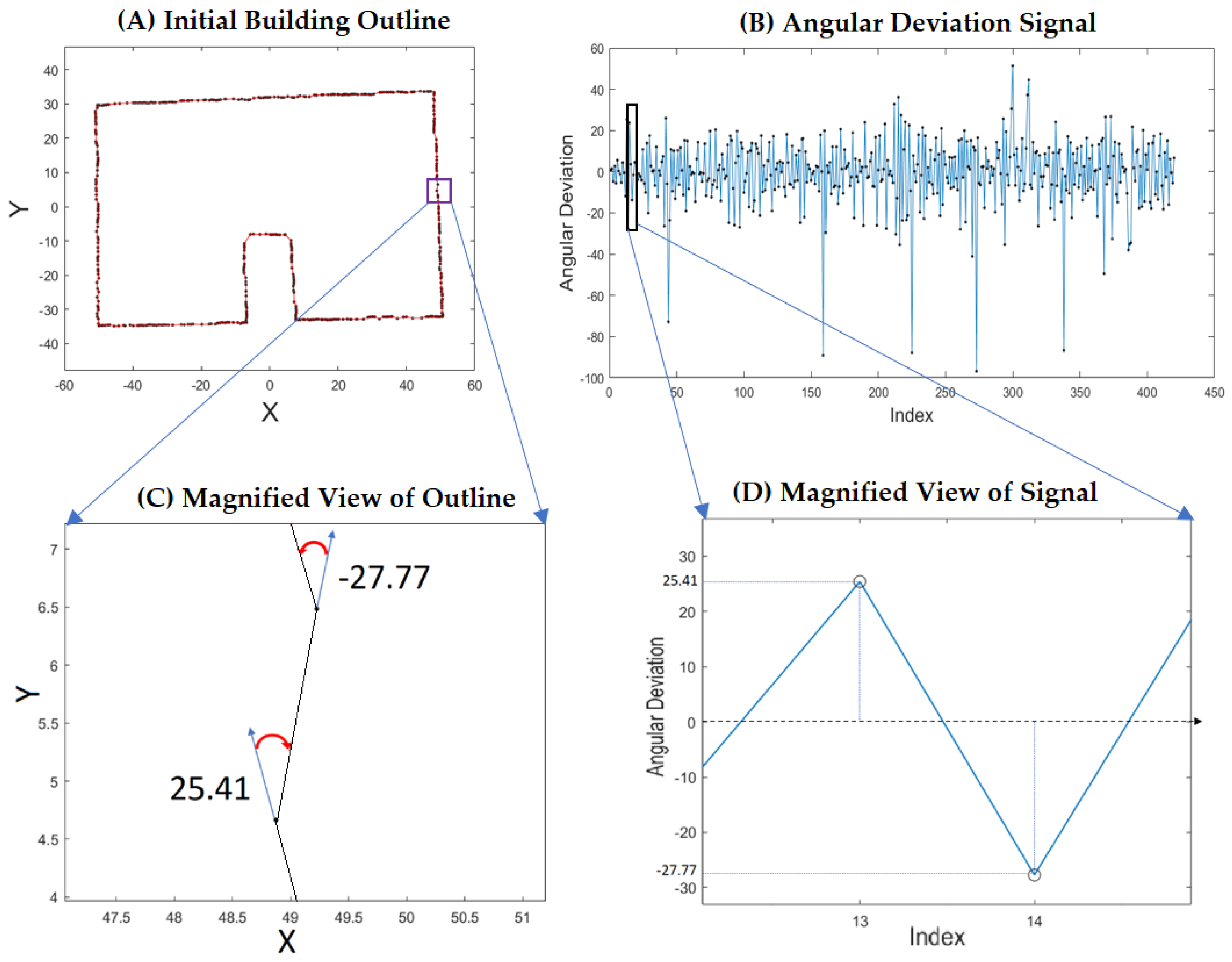
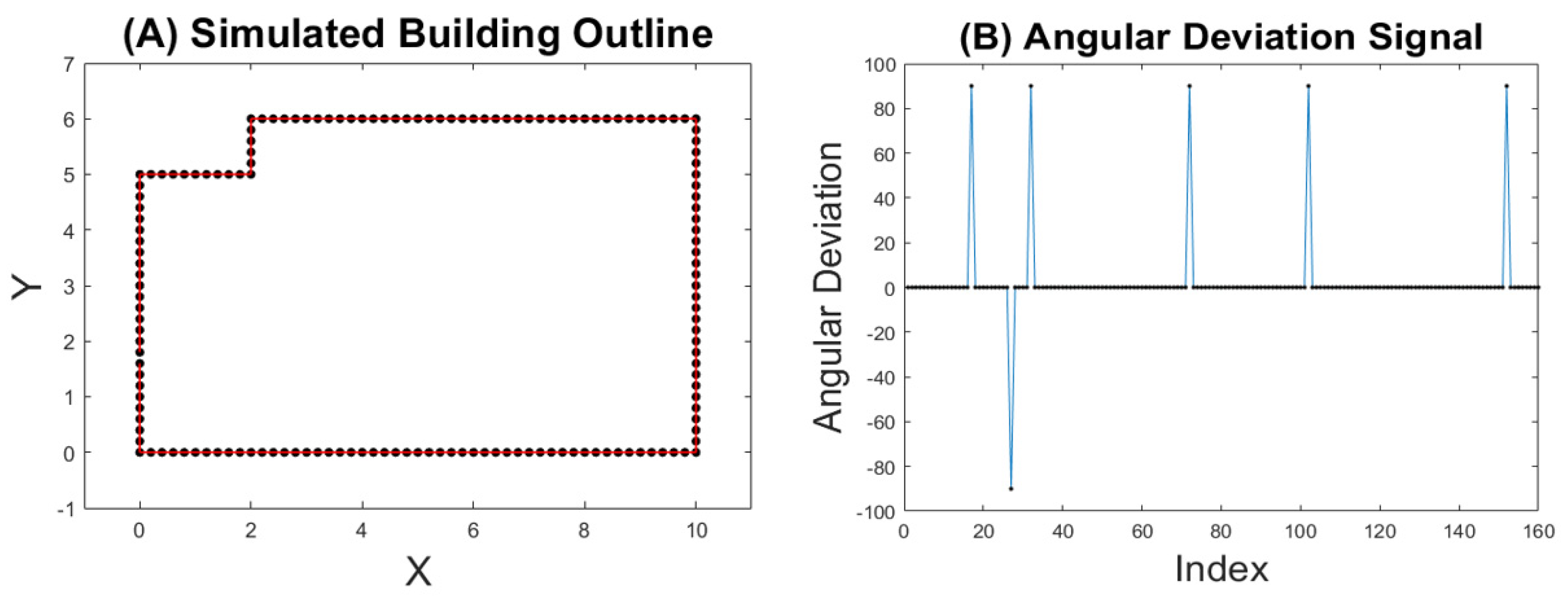
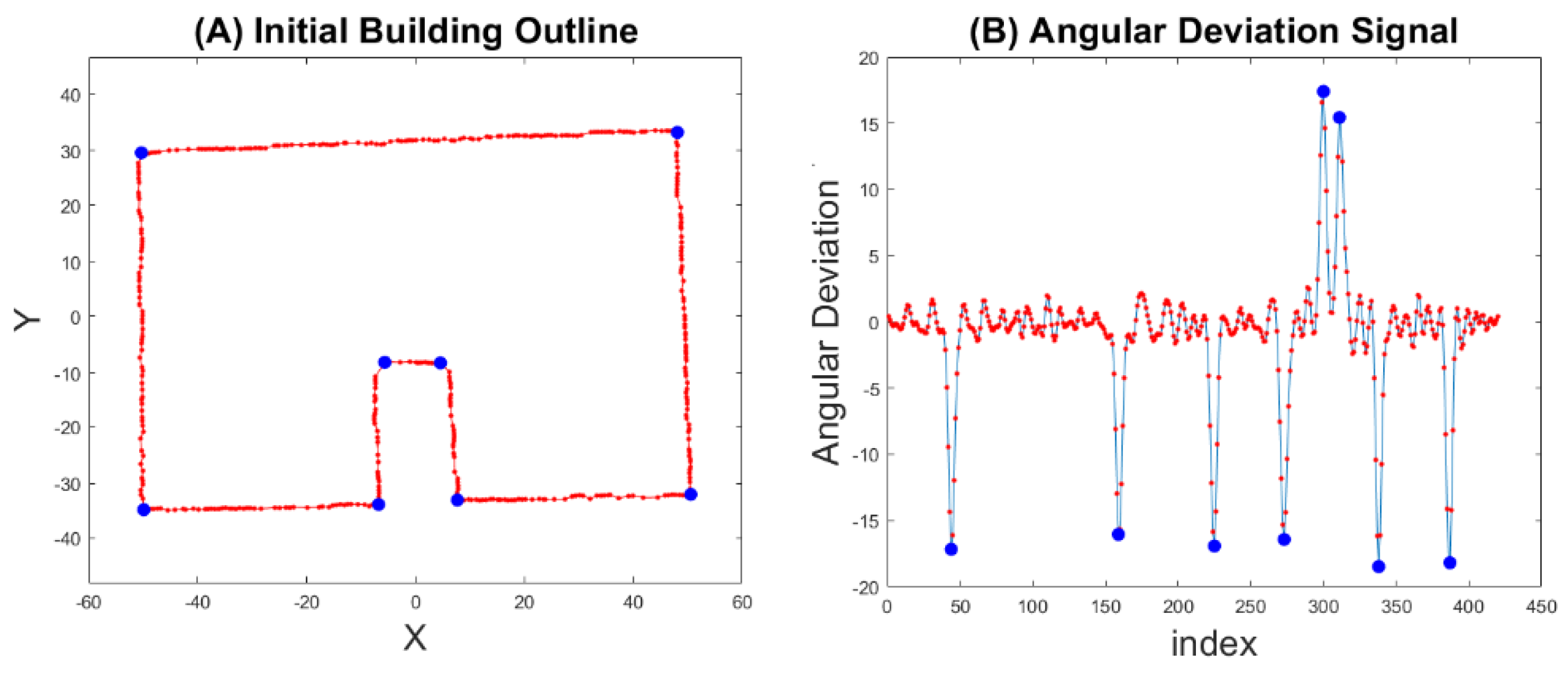
3.3.1. Transforming Initial Building Outline to Discrete Signal
3.3.2. Denoising
3.3.3. Identifying Building Corner
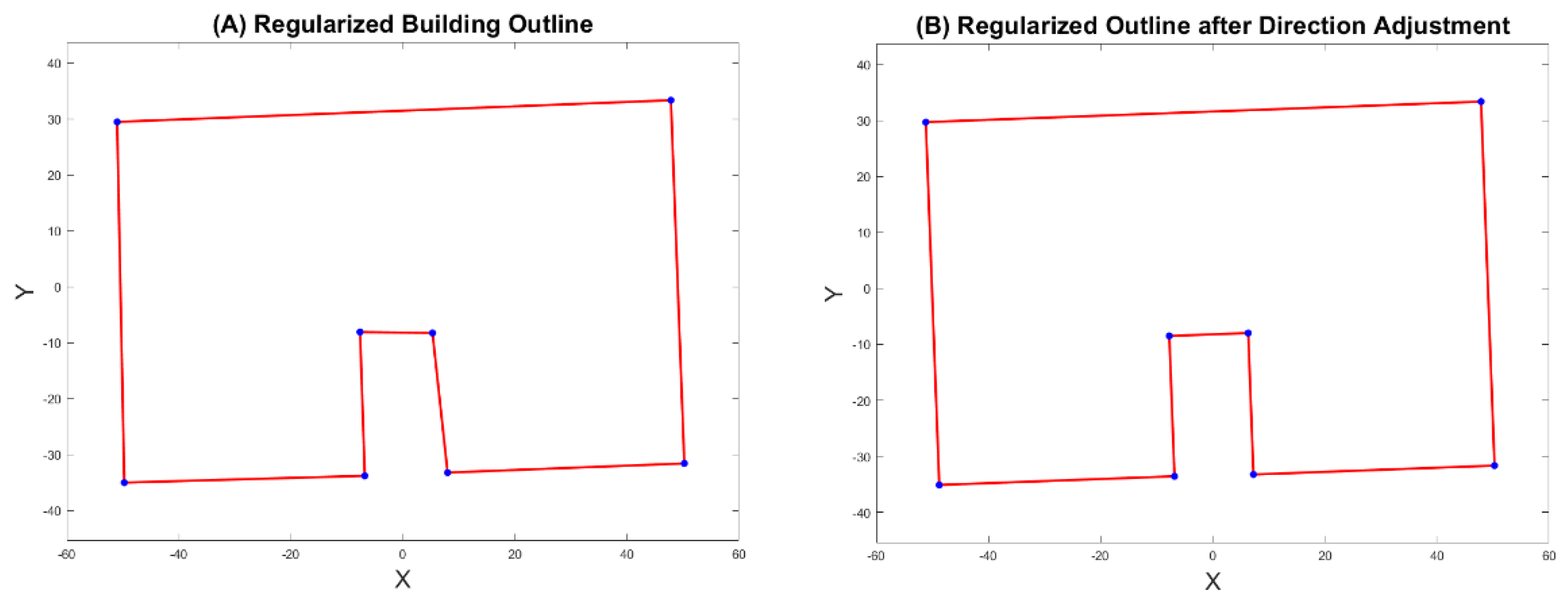
3.3.4. Reconstructing Building Footprint
4. Experiment Results
4.1. Test Dataset
4.2. Parameter Setting
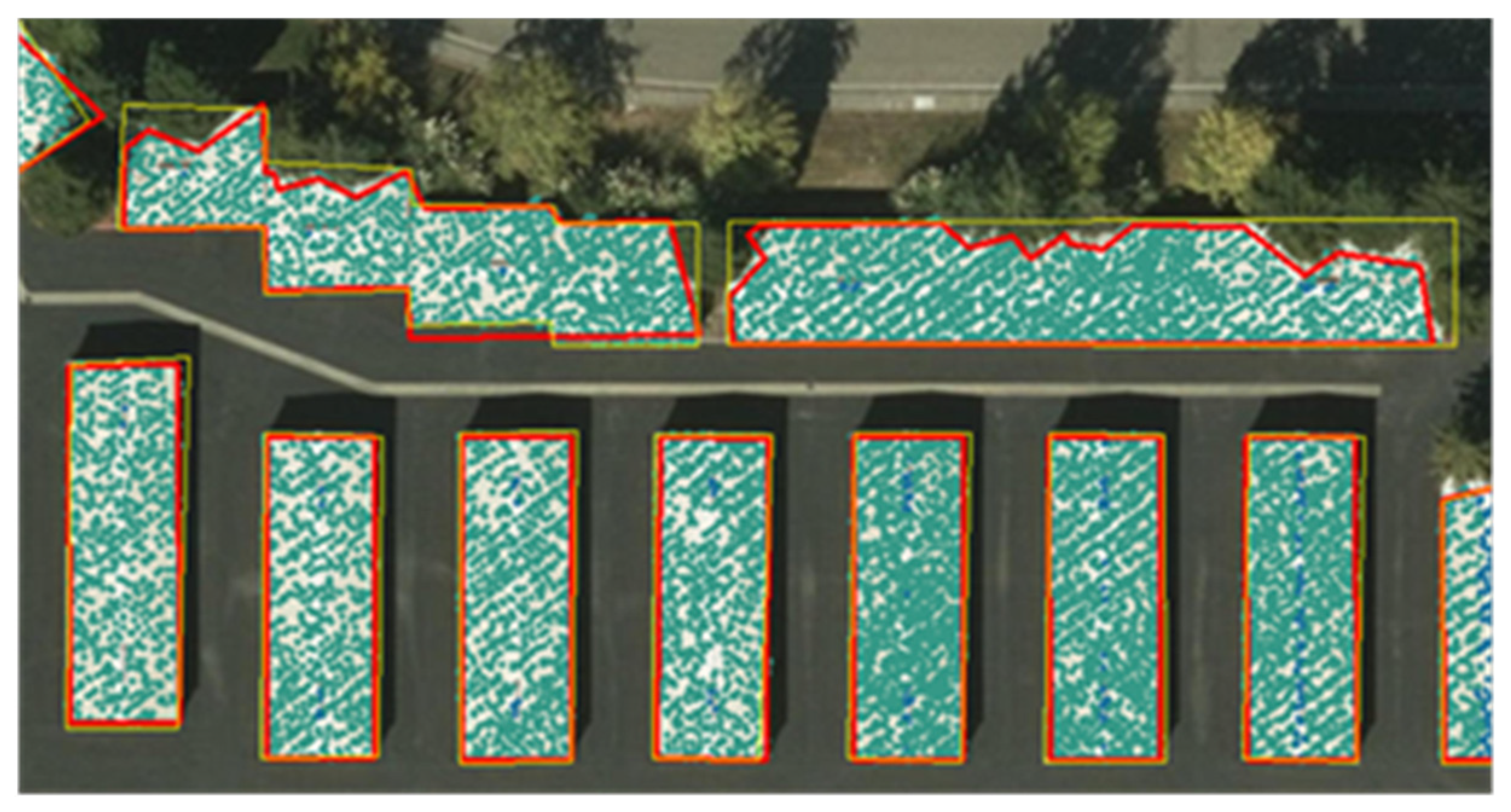
4.3. Result and Evaluation
- Intersection over Union (IoU).
- 2.
- Corner Distance (CD).
- 3.
- Corner Complexity Difference (CCD).
- 4.
- Corner Correspondence Rate
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shufelt, J.A.; McKeown, D.M. Fusion of monocular cues to detect man-made structures in aerial imagery. CVGIP Image Underst. 1993, 57, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Yan, J.; Chen, S.C. Automatic construction of building footprints from airborne LIDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröger, G.; Kolbe, T.H.; Nagel, C.; Häfele, K.H. OGC City Geography Markup Language (CityGML) Encoding Standard 2.0.0; Open Geospatial Consortium: Arlington, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Biljecki, F.; Ledoux, H.; Stoter, J. An improved LOD specification for 3D building models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 59, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Peethambaran, J.; Chen, D. Lidar point clouds to 3-D urban models: A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 606–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, D.M., Jr.; McGlone, J.C.; Ford, S.J.; Cochran, S.D.; Shufelt, J.A. Automated Cartographic Feature Attribution Using Panchromatic and Hyperspectral Imagery. In Proceedings of the DARPA Image Understanding Workshop, Monterey, CA, USA, 20–23 November 1998; pp. 517–536. [Google Scholar]
- Rüther, H.; Martine, H.M.; Mtalo, E.G. Application of snakes and dynamic programming optimisation technique in modeling of buildings in informal settlement areas. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2002, 56, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, C.B.; Dobkin, D.P.; Huhdanpaa, H. The quickhull algorithm for convex hulls. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. (TOMS) 1996, 22, 469–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. Cartogr. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Geovisualization 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, A.; Shan, J. Building boundary tracing and regularization from airborne LiDAR point clouds. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, R.A. Computing the shape hull of points in the plane. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computing Society Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Processing, Troy, NY, USA, 6–8 June 1977; pp. 231–241. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, M.; Habib, A. Interpolation of lidar data and automatic building extraction. In Proceedings of the ACSM-ASPRS Annual Conference, Washington, DC, USA, 19–26 April 2002; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 432–441. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Schenk, T. Building extraction and reconstruction from lidar data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 958–964. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Neumann, U. Fast and extensible building modeling from airborne LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Irvine, CA, USA, 5–7 November 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Edelsbrunner, H.; Kirkpatrick, D.; Seidel, R. On the shape of a set of points in the plane. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1983, 29, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, B.; Kada, M.; Wichmann, A. Automatic extraction and regularization of building outlines from airborne lidar point clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, XLI-B3, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthy, A.; Bethel, J. Heuristic filtering and 3D feature extraction from LIDAR data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2002, 34, 29–34. [Google Scholar]
- Widyaningrum, E.; Gorte, B.; Lindenbergh, R. Automatic building outline extraction from ALS point clouds by ordered points aided hough transform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fraser, C.S. An energy minimization approach to automated extraction of regular building footprints from airborne LiDAR data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2014, 2, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jwa, Y.; Sohn, G.; Tao, V.; Cho, W. An implicit geometric regularization of 3d building shape using airborne lidar data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. XXXVI 2008, 5, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, O.; Lodha, S.K.; Helmbold, D.P. A bayesian approach to building footprint extraction from aerial lidar data. In Proceedings of the Third International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization, and Transmission (3DPVT’06), Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 14–16 June 2006; pp. 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Awrangjeb, M. Using point cloud data to identify, trace, and regularize the outlines of buildings. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 551–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Wan, Y.C.; Yao, F. A method of 3d building boundary extraction from airborne lidar points cloud. In Proceedings of the 2010 Symposium on Photonics and Optoelectronics, Chengdu, China, 19–21 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ester, M.; Kriegel, H.P.; Sander, J.; Xu, X. A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise. Inkdd 1996, 96, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Stout, M.; Bacardit, J.; Hirst, J.D.; Krasnogor, N. Prediction of recursive convex hull class assignments for protein residues. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dubayah, R.; Hurtt, G. UMD-NASA Carbon Mapping/Sonoma County Vegetation Mapping and LiDAR Program, Distributed by OpenTopography. 2014. Available online: https://doi.org/10.5069/G9G73BM1 (accessed on 21 October 2018). [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Sohn, G.; Jung, J.; Gerke, M.; Baillard, C.; Benitez, S.; Breitkopf, U. The ISPRS benchmark on urban object classification and 3D building reconstruction. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. I-3 2012, 1, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




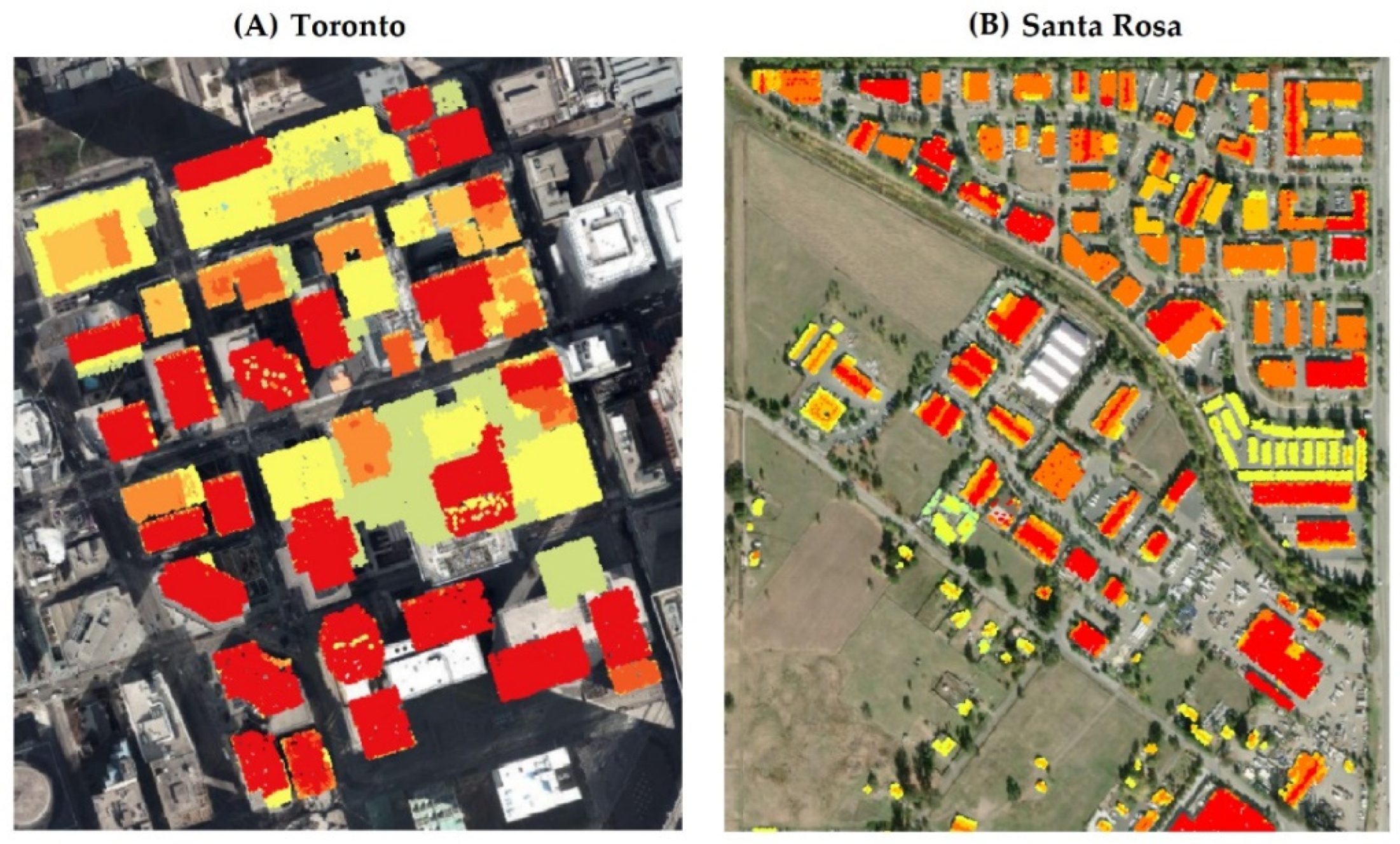
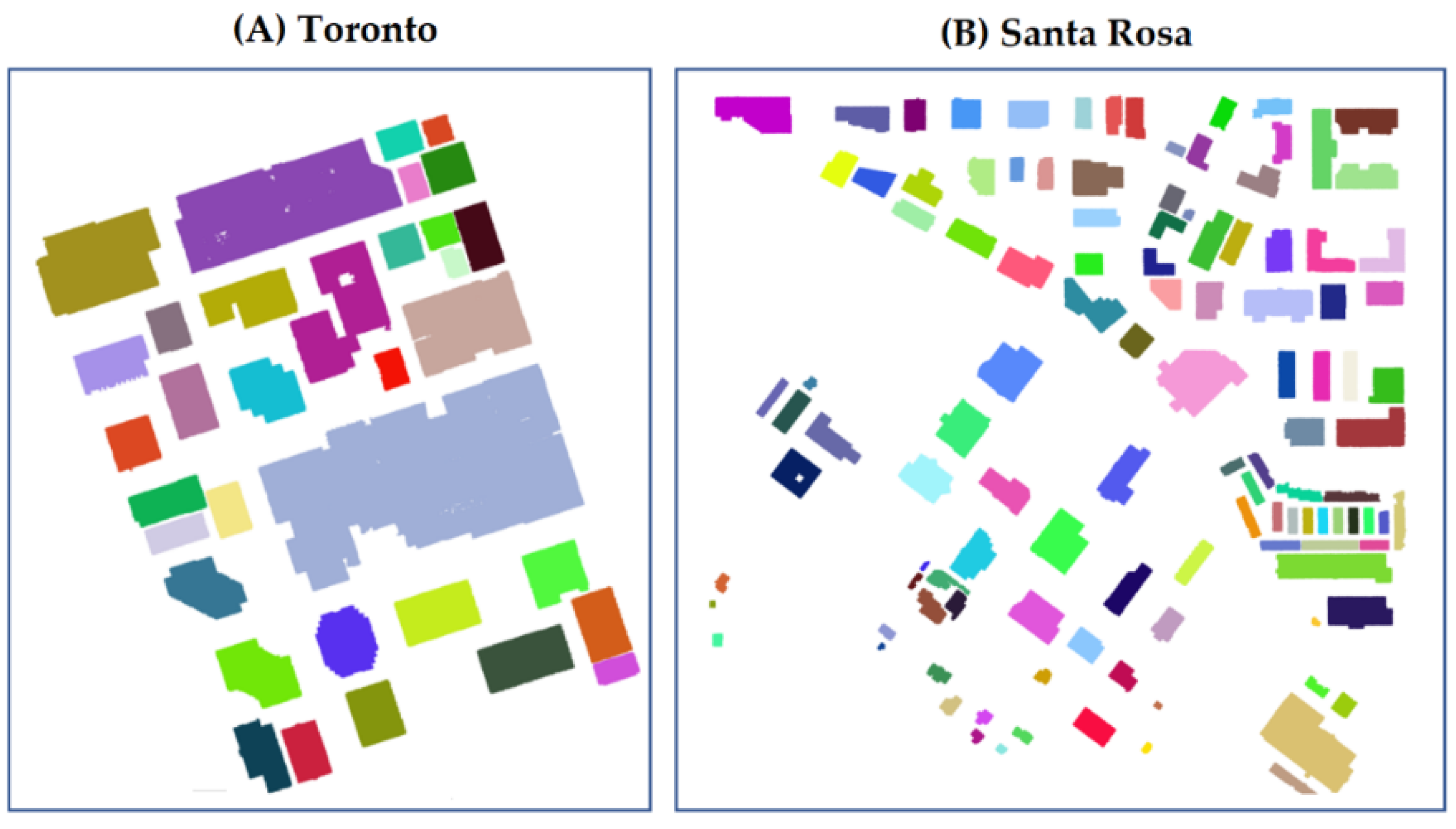




| Area | Point Density | Building Number |
|---|---|---|
| Santa Rosa | 115 | |
| Toronto | 34 |
| Area | sd | len | ε |
|---|---|---|---|
| Santa Rosa | 1 | 36 | 0.25 |
| Toronto | 1 | 24 | 0.2 |
| Algorithm | Signal-Based Method | Douglas–Peucker | Principal-Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | 90.37% | 90.19% | 90.29 % |
| CD | 1.382 m | 1.797 m | 1.531 m |
| CCD | 6.82 % | 89.73% | 216.40% |
| CCR | 77.82% | 52.54% | 36.68% |
| Algorithm | Signal-Based Method | Douglas–Peucker | Principal-Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| IoU | 96.08% | 95.24% | 96.01% |
| CD | 0.592 m | 0.922 m | 0.823 m |
| CCD | 5.49% | 22.12% | 55.79% |
| CCR | 88.21% | 66.99% | 81.58% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Qiu, F.; Shi, F.; Tang, Y. A Recursive Hull and Signal-Based Building Footprint Generation from Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225892
Li X, Qiu F, Shi F, Tang Y. A Recursive Hull and Signal-Based Building Footprint Generation from Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225892
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiao, Fang Qiu, Fan Shi, and Yunwei Tang. 2022. "A Recursive Hull and Signal-Based Building Footprint Generation from Airborne LiDAR Data" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225892
APA StyleLi, X., Qiu, F., Shi, F., & Tang, Y. (2022). A Recursive Hull and Signal-Based Building Footprint Generation from Airborne LiDAR Data. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5892. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225892






