Improving the Performance of Automated Rooftop Extraction through Geospatial Stratified and Optimized Sampling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
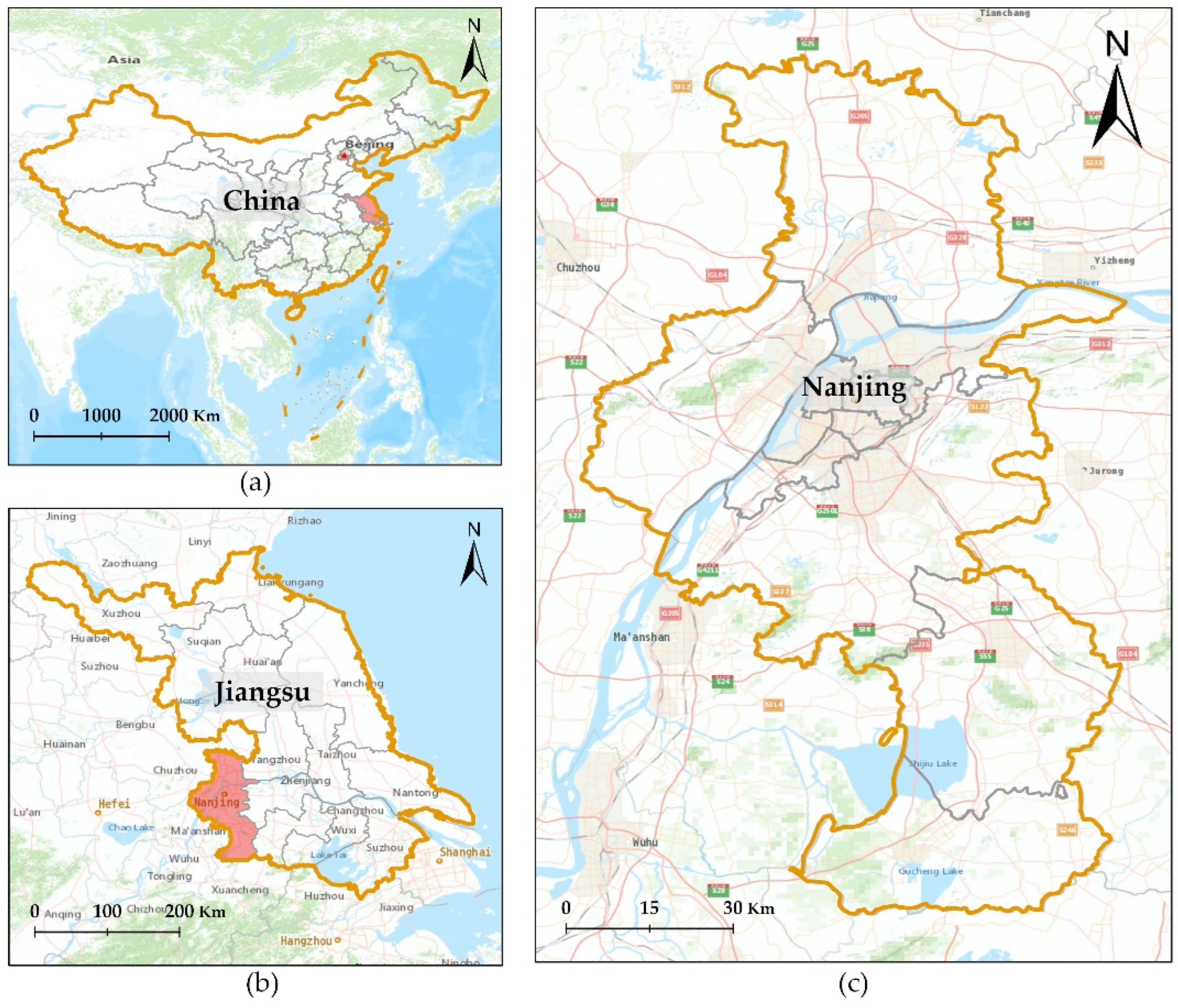
2.1. Study Area
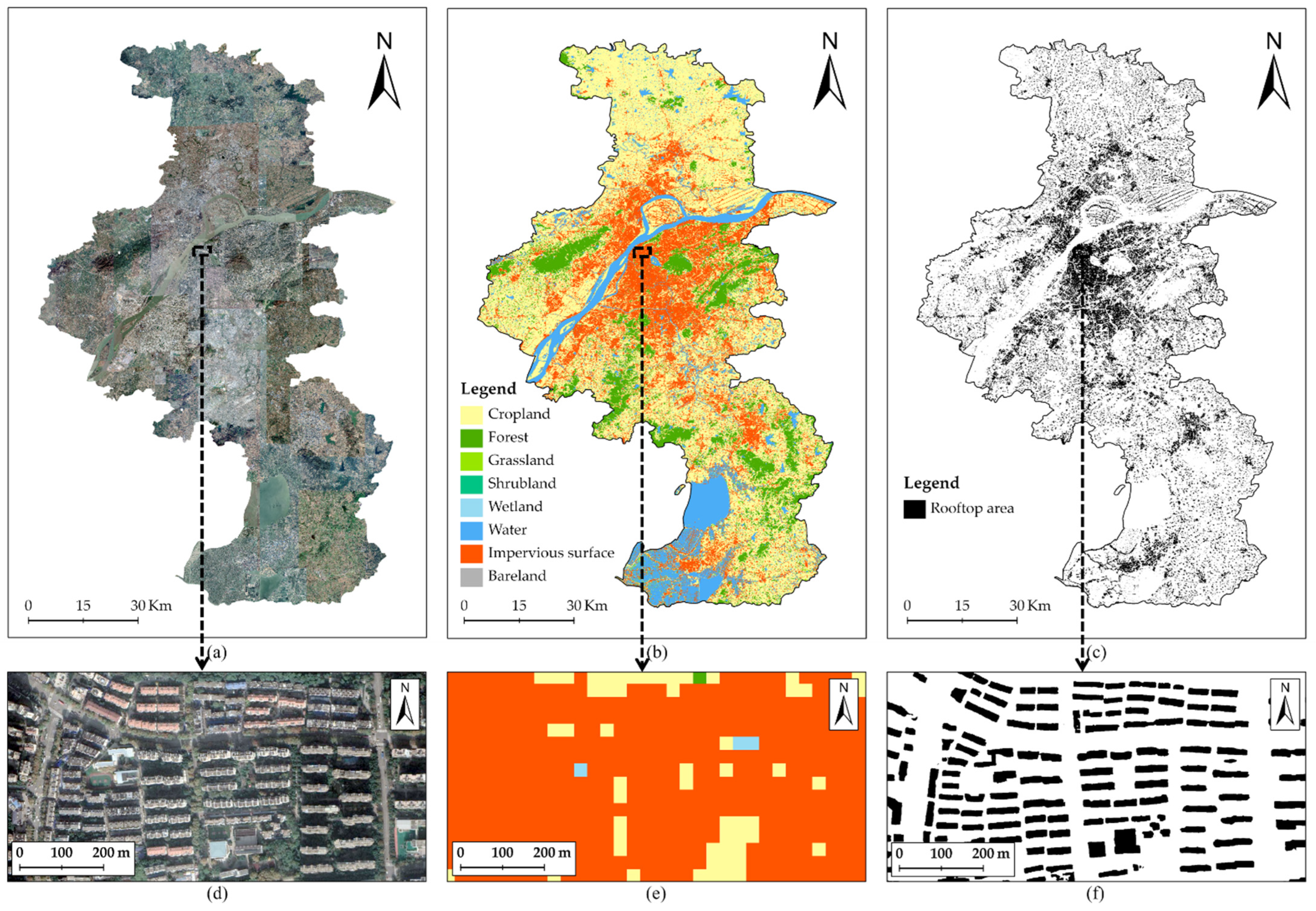
2.2. Dataset
2.2.1. Google Earth Satellite Imagery
2.2.2. Land Cover Data
2.2.3. Vectorized Rooftop Area Data of Nanjing
3. Methodology
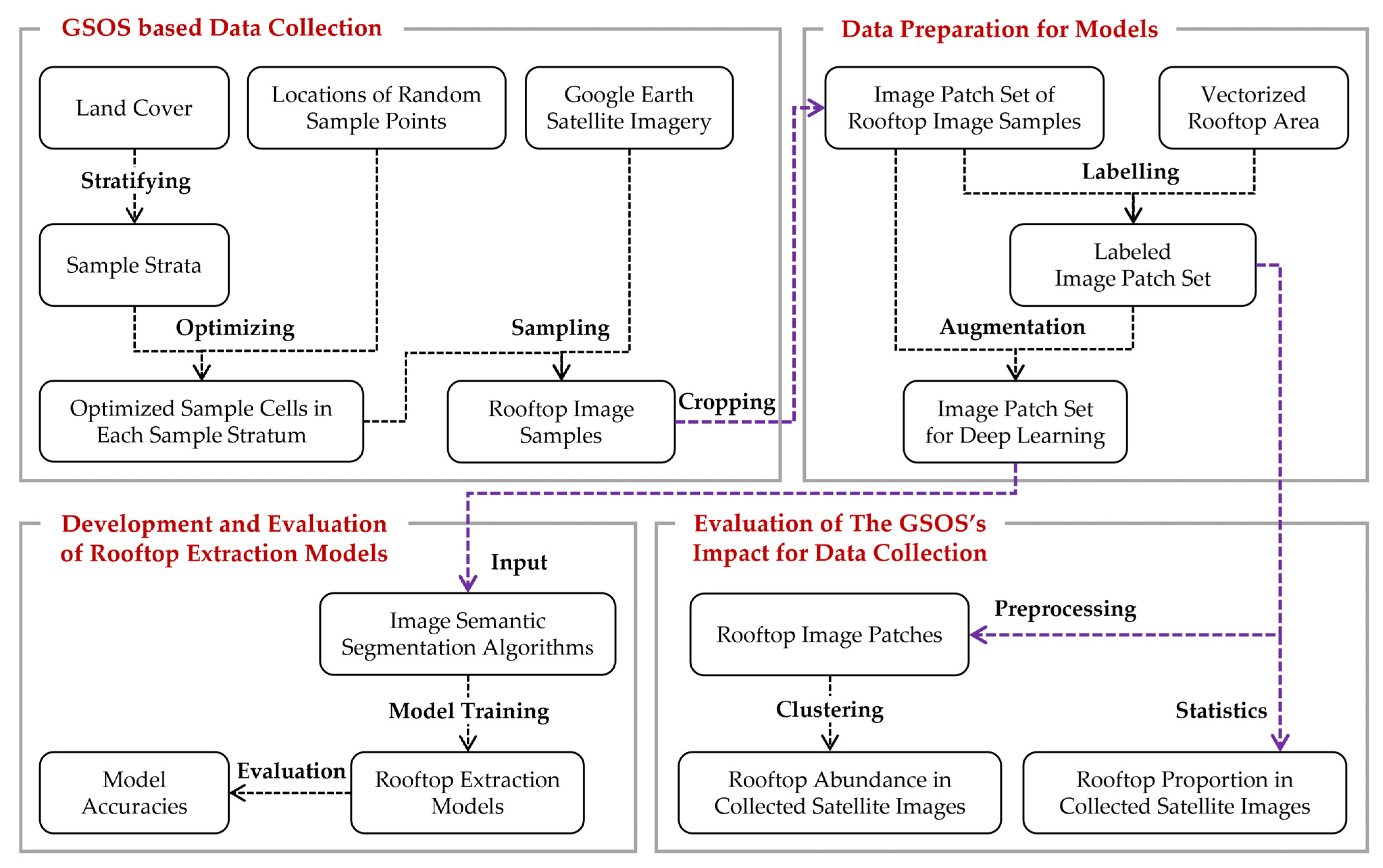
3.1. Research Framework
3.2. Geospatial Stratified and Optimized Sampling
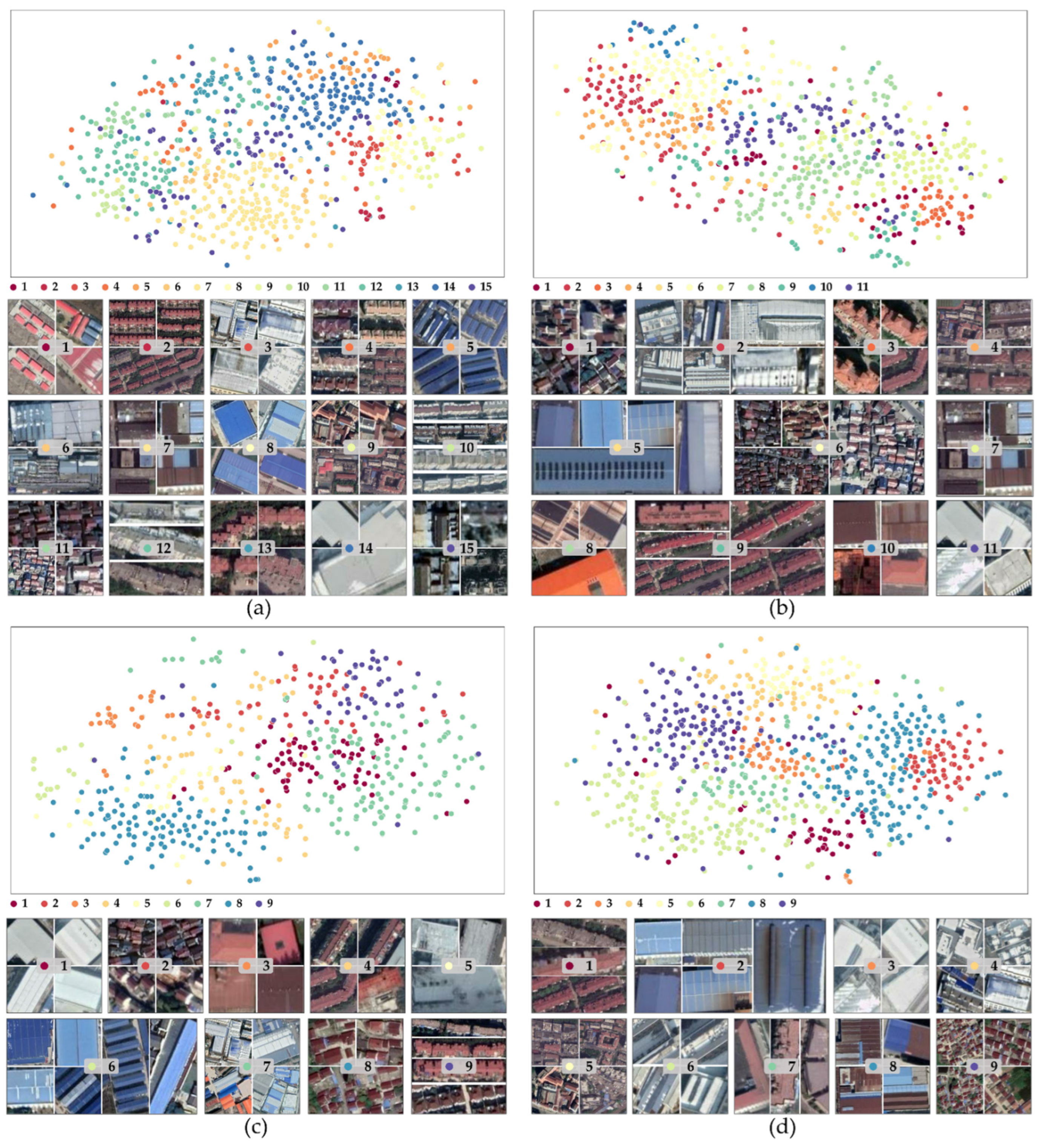
3.2.1. Stratification Considering the Geographical Context
3.2.2. Optimal Sampling Considering the Sample Coverage
3.3. Image Semantic Segmentation
3.4. Evaluation Metrics
4. Results
4.1. Experiment Configuration
4.2. Rooftop Coverage Evaluation
4.2.1. Comparison of Rooftop Proportion
4.2.2. Comparison of Rooftop Abundance
4.3. Rooftop Extraction Model Evaluation
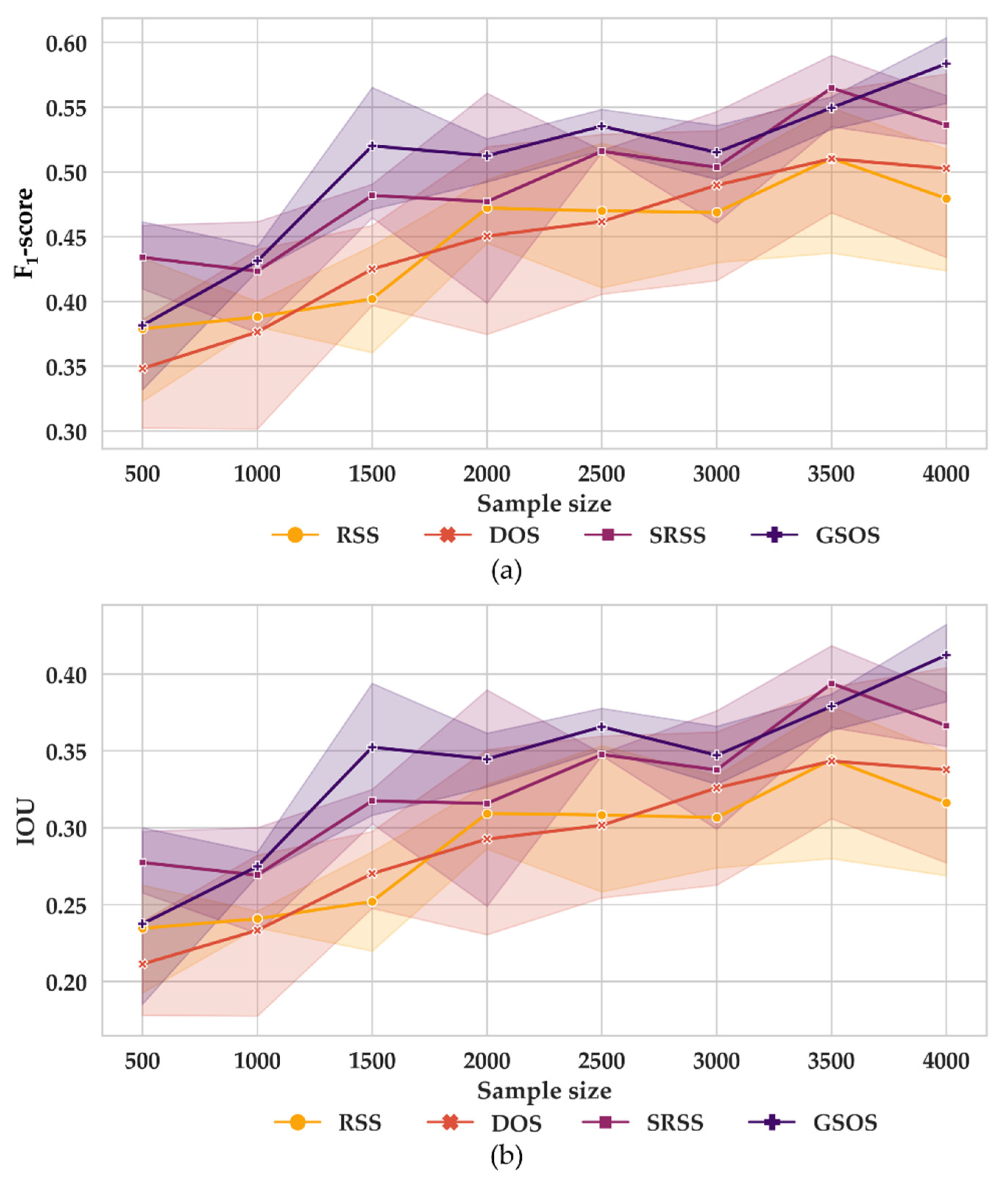
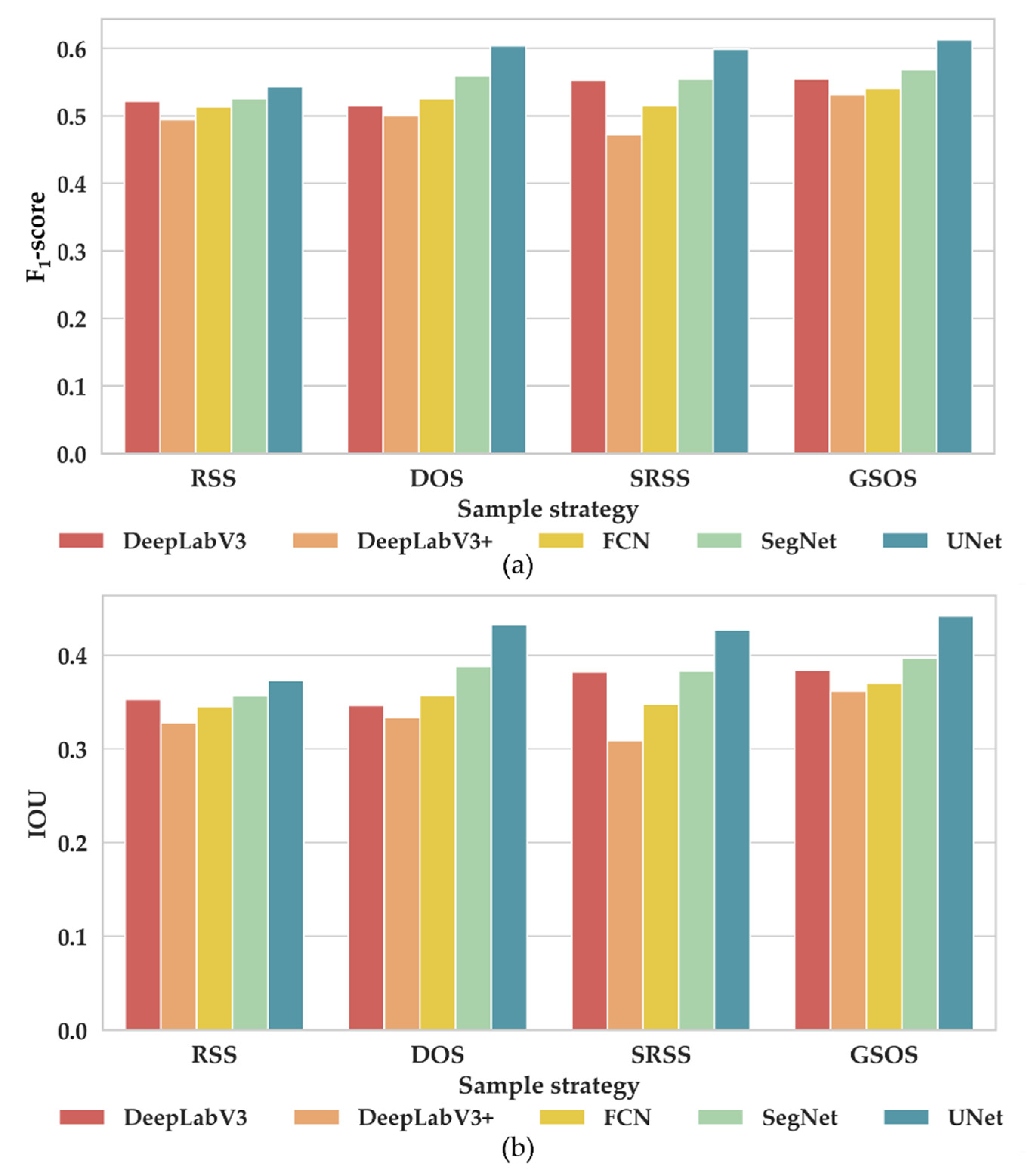
4.3.1. Comparison of the Rooftop Extraction Accuracy
4.3.2. Comparison of Generalizability
5. Discussion
5.1. Uncertainty Analysis
5.2. Potential Improvements of GSOS
- In a study to explore local-scale patterns of urban air pollution, researchers divide cities by landscape and administrative and functional zones to explore urban air NO2 pollution patterns and their causal factors [53].
- On the other hand, varying the spatial simulated annealing optimization objective for different research objectives can also provide a reference for the researchers.
- In a study on lake water quality monitoring, researchers have adopted the mean spatial-temporal error (MSTE) as the optimization objective, with a view to reducing the errors arising from spatial-temporal interpolations [42].
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crompvoets, J.; Bregt, A.; Rajabifard, A.; Williamson, I. Assessing the worldwide developments of national spatial data clearinghouses. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2004, 18, 665–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabifard, A.; Binns, A.; Masser, I.; Williamson, I. The role of sub-national government and the private sector in future spatial data infrastructures. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2006, 20, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Ma, P. Vectorized dataset of roadside noise barriers in China using street view imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2022, 14, 4057–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassar, A.A.A.; Cha, S.H. Review of geographic information systems-based rooftop solar photovoltaic potential estimation approaches at urban scales. Appl. Energy 2021, 291, 116817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernaat, D.E.; de Boer, H.-S.; Dammeier, L.C.; van Vuuren, D.P. The role of residential rooftop photovoltaic in long-term energy and climate scenarios. Appl. Energy 2020, 279, 115705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qian, Z.; Zhong, T.; Chen, M.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, F. Vectorized rooftop area data for 90 cities in China. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslani, M.; Seipel, S. Automatic identification of utilizable rooftop areas in digital surface models for photovoltaics potential assessment. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 118033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Xu, C.; Ma, Z.; Sun, Y. A novel 3D-geographic information system and deep learning integrated approach for high-accuracy building rooftop solar energy potential characterization of high-density cities. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 117985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Shan, M.; Rong, X.; Yang, X. Estimating the spatial distribution of solar photovoltaic power generation potential on different types of rural rooftops using a deep learning network applied to satellite images. Appl. Energy 2022, 315, 119025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, D.; Matuk, O.; Bielecka, E. Polish cadastre modernization with remotely extracted buildings from high-resolution aerial orthoimagery and airborne LiDAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Lü, G.; Yan, J. A city-scale estimation of rooftop solar photovoltaic potential based on deep learning. Appl. Energy 2021, 298, 117132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Fu, K.; Lu, X.; Diao, W.; Sun, H.; Yan, M.; Yu, H.; Sun, X. End-to-end DSM fusion networks for semantic segmentation in high-resolution aerial images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zorzi, S.; Shi, Y.; Fraundorfer, F.; Zhu, X.X. RegGAN: An End-to-End Network for Building Footprint Generation with Boundary Regularization. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.A.A.; Maity, T.; Kole, A. IRU-Net: An Efficient End-to-End Network for Automatic Building Extraction From Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 37811–37828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Bai, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, J.; Ren, P. Multiscale visual attention networks for object detection in VHR remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 16, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Shi, Q.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Ding, H. Scene-driven multitask parallel attention network for building extraction in high-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4287–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Chen, M.; Zhong, T.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Sun, Z.; Lü, G. Deep Roof Refiner: A detail-oriented deep learning network for refined delineation of roof structure lines using satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Zhang, F.; Duarte, F.; Ratti, C. Understanding architecture age and style through deep learning. Cities 2022, 128, 103787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yokoya, N.; Yao, J.; Chanussot, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, B. More diverse means better: Multimodal deep learning meets remote-sensing imagery classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 4340–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Wu, J. Rethinking big data: A review on the data quality and usage issues. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 115, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, B.; Laverdiere, M.; Yang, H.L.; Rose, A. Iterative self-organizing SCEne-LEvel sampling (ISOSCELES) for large-scale building extraction. GIScience Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Yu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z. From data quality to model quality: An exploratory study on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 11th Asia-Pacific Symposium on Internetware, Fukuoka, Japan, 28–29 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.; Minasny, B.; Mendes, W.d.S.; Demattê, J.A.M. The influence of training sample size on the accuracy of deep learning models for the prediction of soil properties with near-infrared spectroscopy data. Soil 2020, 6, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, W.R. A computer movie simulating urban growth in the Detroit region. Econ. Geogr. 1970, 46, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M.F. The validity and usefulness of laws in geographic information science and geography. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 2004, 94, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; He, H.; Yang, K.; Fatholahi, S.N.; Ma, L.; Xu, L.; Li, J. A comparative study of deep learning approaches to rooftop detection in aerial images. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 47, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Garcia, E.A. Learning from imbalanced data. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2009, 21, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Doan, Q.H.; Mai, S.-H.; Do, Q.T.; Thai, D.-K. A cluster-based data splitting method for small sample and class imbalance problems in impact damage classification. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 120, 108628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.D.; Teferra, K.; Hapij, A.; Daddazio, R.P. Refined stratified sampling for efficient Monte Carlo based uncertainty quantification. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2015, 142, 310–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ng, M.K.; Ho, S.-S. ForesTexter: An efficient random forest algorithm for imbalanced text categorization. Knowl. -Based Syst. 2014, 67, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L. FPGA: Fast patch-free global learning framework for fully end-to-end hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5612–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Jiang, C. Strata efficiency and optimization strategy of stratified sampling on spatial population. Prog. Geogr. 2008, 27, 152–160. [Google Scholar]
- Catherine, A.; Troussellier, M.; Bernard, C. Design and application of a stratified sampling strategy to study the regional distribution of cyanobacteria (Ile-de-France, France). Water Res. 2008, 42, 4989–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knotters, M.; Teuling, K.; Reijneveld, A.; Lesschen, J.P.; Kuikman, P. Changes in organic matter contents and carbon stocks in Dutch soils, 1998–2018. Geoderma 2022, 414, 115751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Zuo, S.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, Y.; Ren, Y.; Han, J. Optimal spatial sampling design for monitoring potentially toxic elements pollution on urban green space soil: A spatial simulated annealing and k-means integrated approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clougherty, J.E.; Kheirbek, I.; Eisl, H.M.; Ross, Z.; Pezeshki, G.; Gorczynski, J.E.; Johnson, S.; Markowitz, S.; Kass, D.; Matte, T. Intra-urban spatial variability in wintertime street-level concentrations of multiple combustion-related air pollutants: The New York City Community Air Survey (NYCCAS). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2013, 23, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, S.; Gelatt Jr, C.D.; Vecchi, M.P. Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 1983, 220, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, N.; Fort, M.; Saus, M. Coverage area maximization with parallel simulated annealing. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 202, 117185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Gao, B.; Pan, Y.; Bai, Z.; Gao, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, S. Multi-objective optimization sampling based on Pareto optimality for soil mapping. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Su, B.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, C.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L. Sample design optimization for soil mapping using improved artificial neural networks and simulated annealing. Geoderma 2022, 413, 115749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Hu, M.; Li, X.; Pan, Y. Optimization of the sampling design for multiobjective soil mapping using the multiple path SSA (MP-SSA) method. CATENA 2022, 217, 106479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, L.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Li, T.; Hou, X. Optimal sampling strategy of water quality monitoring at high dynamic lakes: A remote sensing and spatial simulated annealing integrated approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, A.; Ren, Y.; Zuo, S.; Qiu, Y.; Liangbin, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ju, J. Evaluating sample sizes and design for monitoring and characterizing the spatial variations of potentially toxic elements in the soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, F.; Wang, J.; Nemati, A.; Chen, Z.; Pei, H. Mapsegnet: A fully automated model based on the encoder-decoder architecture for indoor map segmentation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 101530–101542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, M. CNN-based encoder-decoder networks for salient object detection: A comprehensive review and recent advances. Inf. Sci. 2021, 546, 835–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. SSDBN: A Single-Side Dual-Branch Network with Encoder–Decoder for Building Extraction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Fu, S.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, F. Object-level semantic segmentation on the high-resolution Gaofen-3 FUSAR-map dataset. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 3107–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, A.A.; Luo, L.; Wang, G.; Yang, E. Pixel-level pavement crack segmentation with encoder-decoder network. Measurement 2021, 184, 109914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, R.; Duan, C.; Zhang, C.; Meng, X.; Fang, S. A novel transformer based semantic segmentation scheme for fine-resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Liu, X.; Tao, F.; Zhou, T. Identification of urban functional areas by coupling satellite images and taxi GPS trajectories. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qian, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhong, T.; Zhu, R.; Lv, G.; Yan, J. Using street view images to identify road noise barriers with ensemble classification model and geospatial analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 78, 103598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Qian, Z.; Lv, G.; Yan, J. Assessment of solar photovoltaic potentials on urban noise barriers using street-view imagery. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Longley, I.; Gao, J.; Kachhara, A.; Salmond, J. A site-optimised multi-scale GIS based land use regression model for simulating local scale patterns in air pollution. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Item | Configuration |
| Optimizer | AdamW |
| Weight decay rate | 0.0005 |
| Learning rate scheduler | Cosine Annealing Warm Restarts |
| Number of iterations for the first restart | 2 |
| The factor increases the number of epochs after a restart | 2 |
| Loss function | BCE&DICE |
| Sample Size | Average Proportion of Rooftops in Image Patches | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RSS | DOS | SRSS | GSOS | |
| 500 | 4.14% | 4.26% | 7.58% | 6.83% |
| 1000 | 3.90% | 2.29% | 7.59% | 6.98% |
| 1500 | 2.31% | 4.17% | 7.86% | 7.14% |
| 2000 | 4.02% | 2.29% | 7.46% | 7.10% |
| 2500 | 4.07% | 2.20% | 7.75% | 7.18% |
| 3000 | 3.88% | 2.38% | 7.52% | 7.05% |
| 3500 | 4.06% | 2.20% | 7.79% | 7.17% |
| 4000 | 4.28% | 2.20% | 7.66% | 7.26% |
| Mean | 3.83% | 2.75% | 7.65% | 7.09% |
| STD | 0.59% | 0.85% | 0.13% | 0.12% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, M.; Qian, Z.; Cao, M.; Wen, Y. Improving the Performance of Automated Rooftop Extraction through Geospatial Stratified and Optimized Sampling. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194961
Sun Z, Zhang Z, Chen M, Qian Z, Cao M, Wen Y. Improving the Performance of Automated Rooftop Extraction through Geospatial Stratified and Optimized Sampling. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194961
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Zhuo, Zhixin Zhang, Min Chen, Zhen Qian, Min Cao, and Yongning Wen. 2022. "Improving the Performance of Automated Rooftop Extraction through Geospatial Stratified and Optimized Sampling" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194961
APA StyleSun, Z., Zhang, Z., Chen, M., Qian, Z., Cao, M., & Wen, Y. (2022). Improving the Performance of Automated Rooftop Extraction through Geospatial Stratified and Optimized Sampling. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4961. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194961







