A Multi-Channel Descriptor for LiDAR-Based Loop Closure Detection and Its Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The method for CMCD: A novel CMCD method is proposed to resolve the lack of point clouds in the discriminative power of scene description. It enhances the discriminative power of descriptors and mitigates the effect of abnormal pixel values in a single channel on subsequent feature screening by synthesizing the distance, height, and intensity features of point clouds.
- The feature extraction algorithm DTORB: The feature extraction algorithm DTORB is designed to get rid of the subjective tendency of the constant threshold ORB algorithm in extracting descriptor features. A dynamic threshold is designed to screen features via the objective global and local distributions of point clouds to ensure high-quality features can still be extracted from the three-channel images generated using point clouds. Meanwhile, the rotation-invariance property of ORB features guarantees DTORB features are also rotation-invariant.
- A rotation-invariant similarity measurement method is developed to figure out the similarity score between descriptors by calculating the Hamming distance between matched features. Its theoretical basis is also visualized.
- A comprehensive evaluation of our solution is made over the KITTI odometry sequences with a 64-beam LiDAR and the campus datasets of Jilin University collected by a 32-beam LiDAR, and the results demonstrate the validity of our proposed LCD method.
2. Related Work
2.1. Vision-Based LCD
2.2. LiDAR-Based LCD
3. Methods
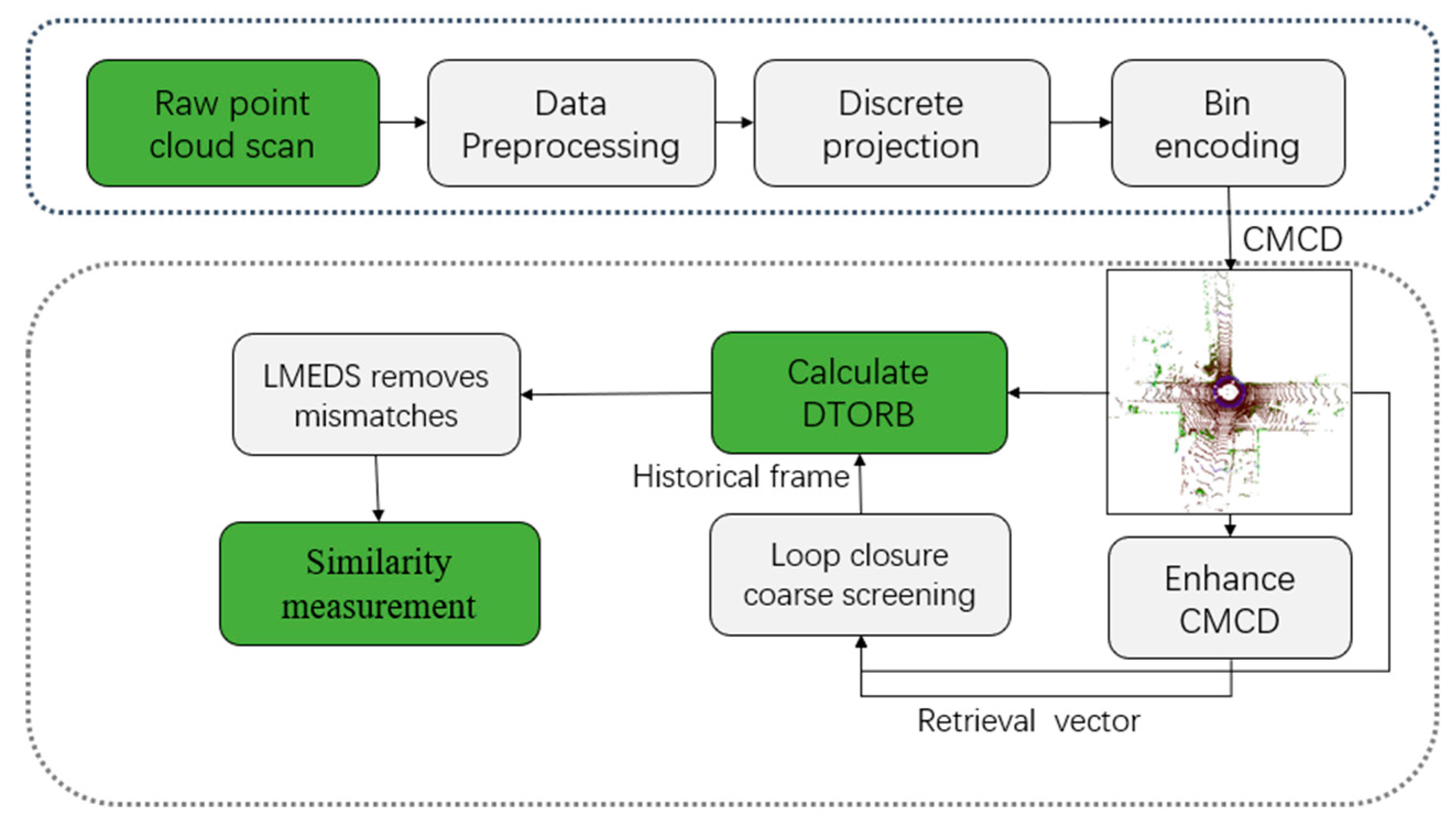
3.1. System Overview
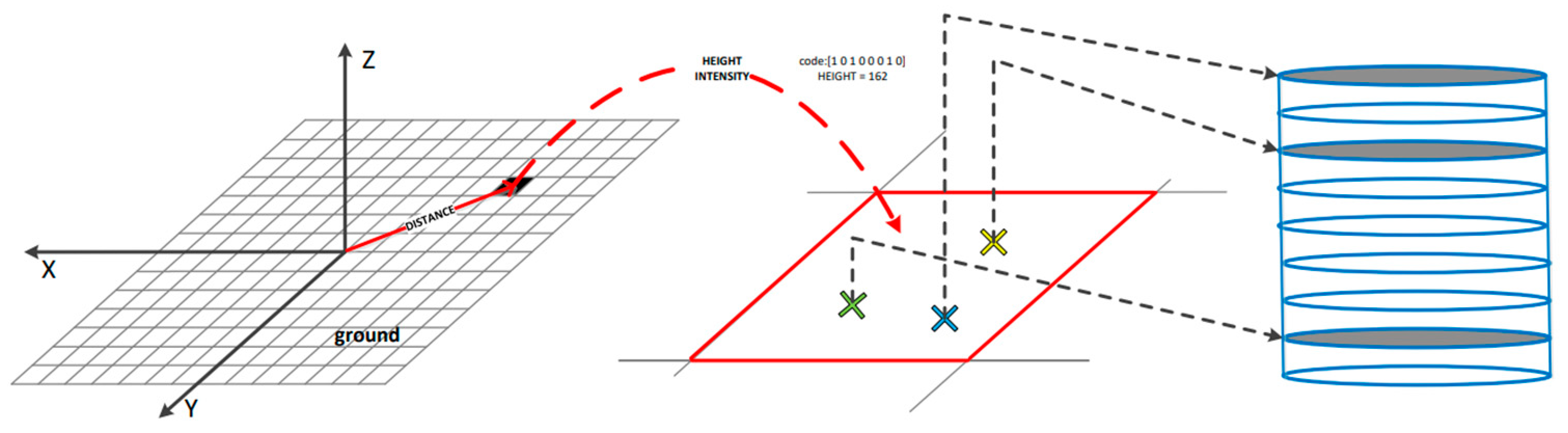
3.2. Construction of Multi-Channel Descriptors
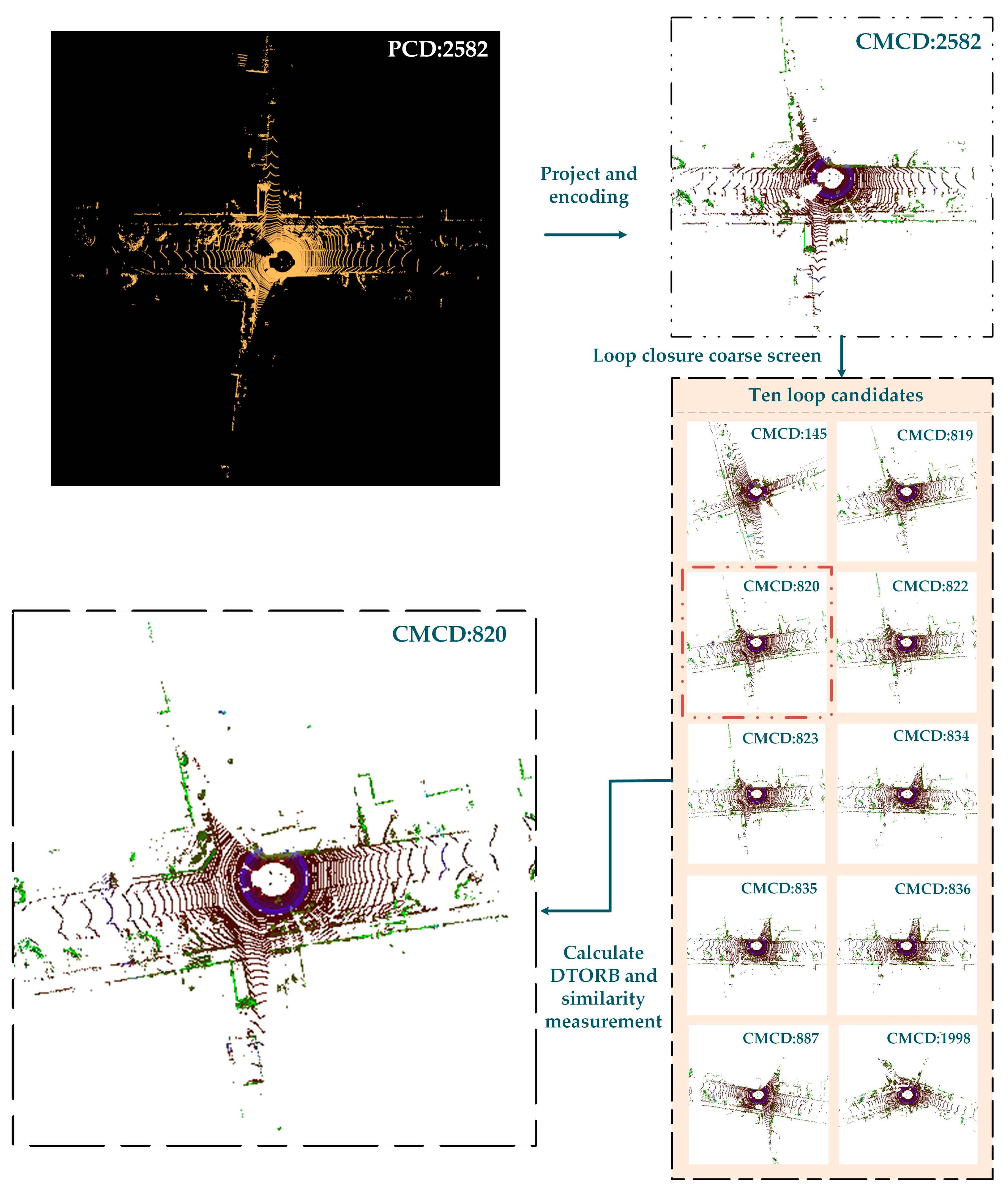
3.3. Selection of Loop Candidates
3.4. DTORB Feature Extraction Algorithm
3.5. Similarity Measurement
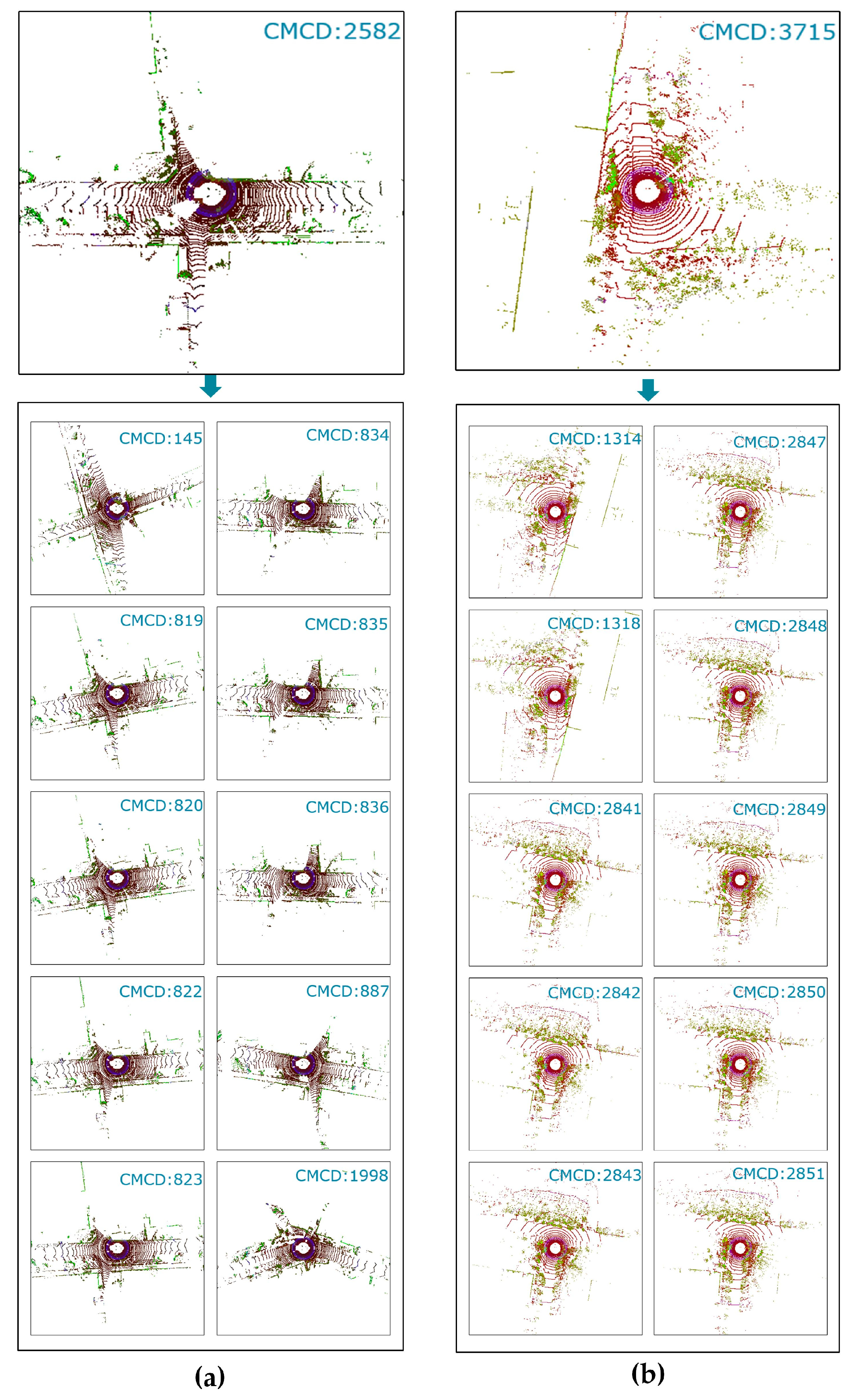
4. Results
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Experimental Settings
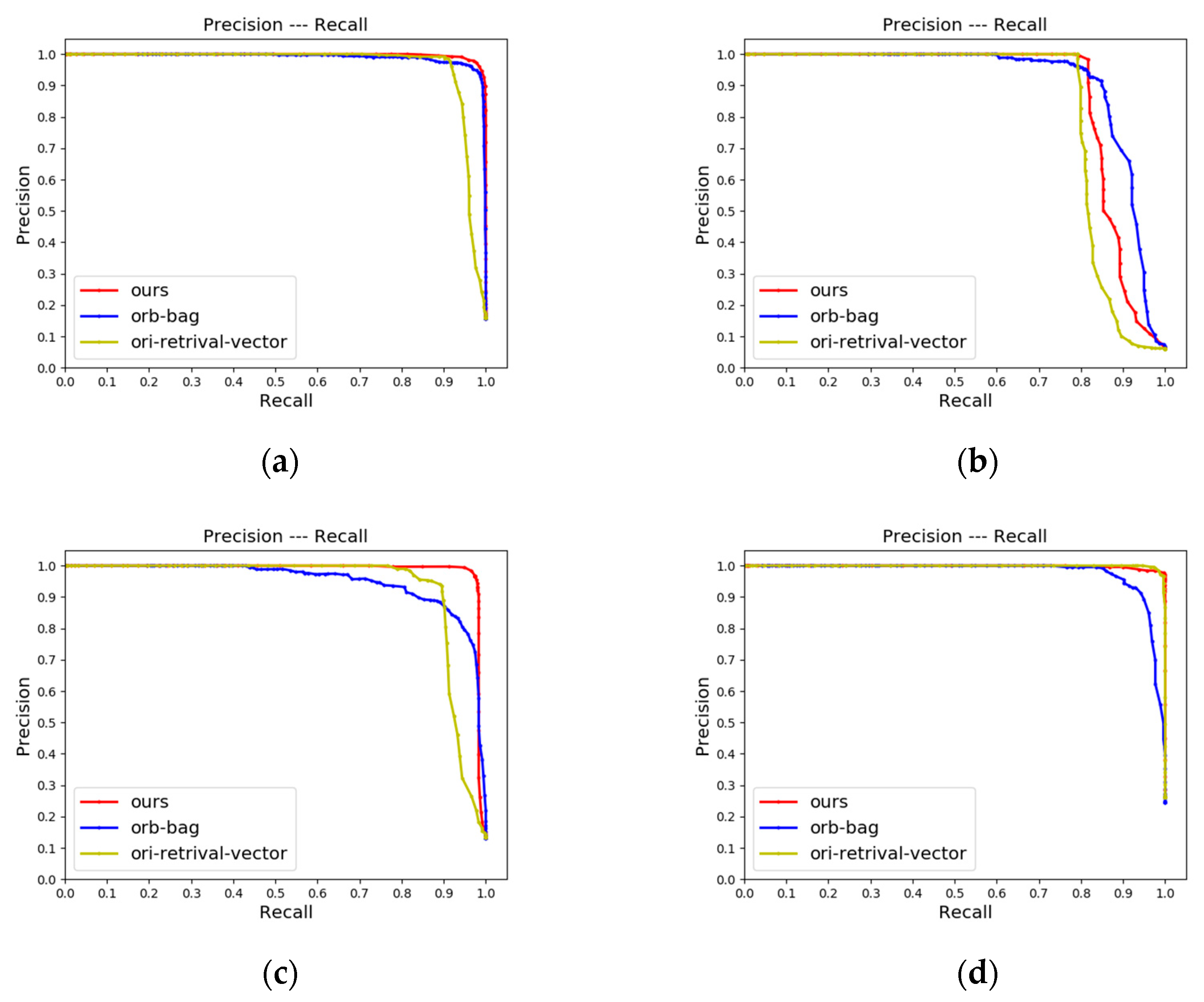
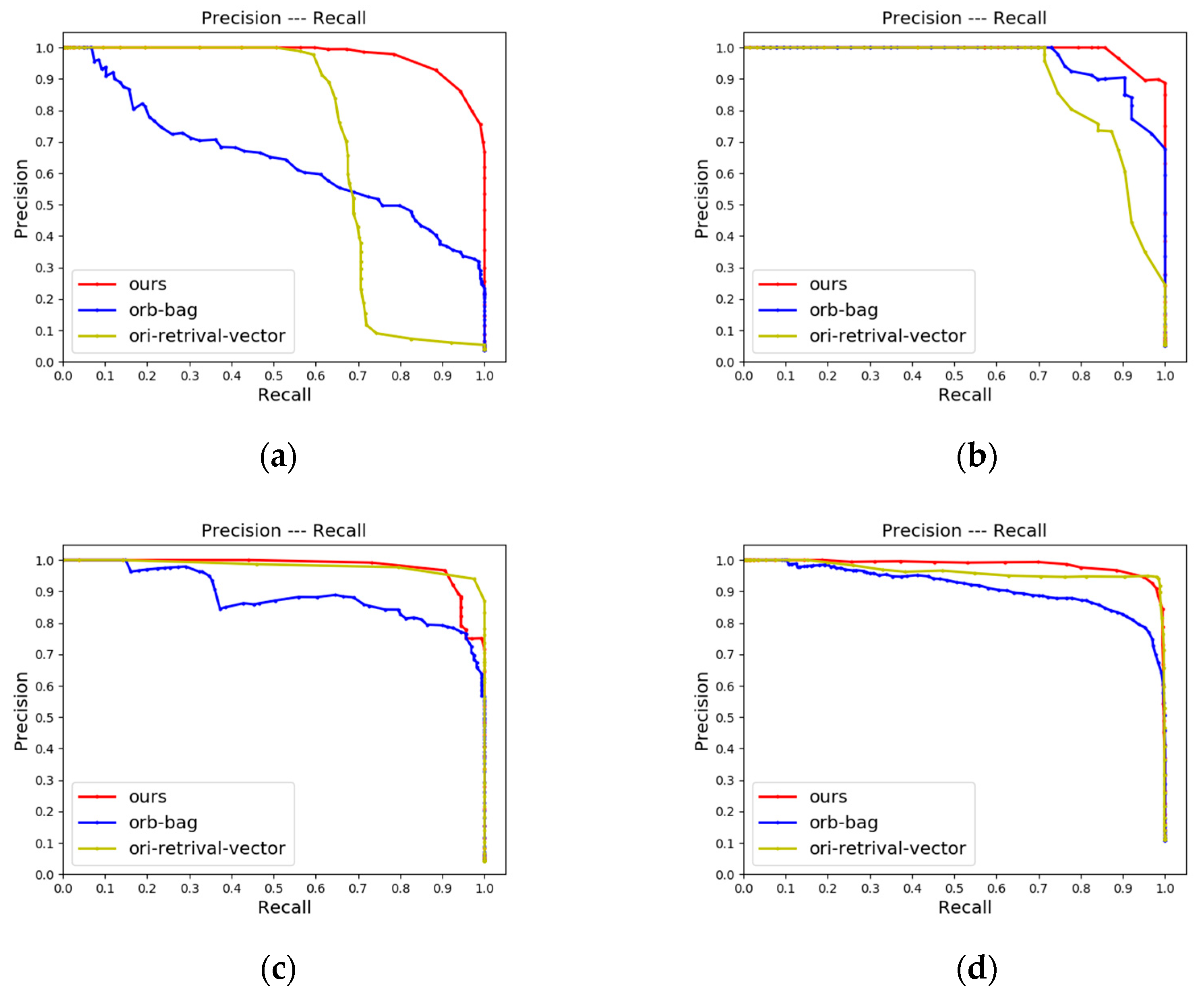
4.2.1. LCD Performance
4.2.2. Place Recognition Performance
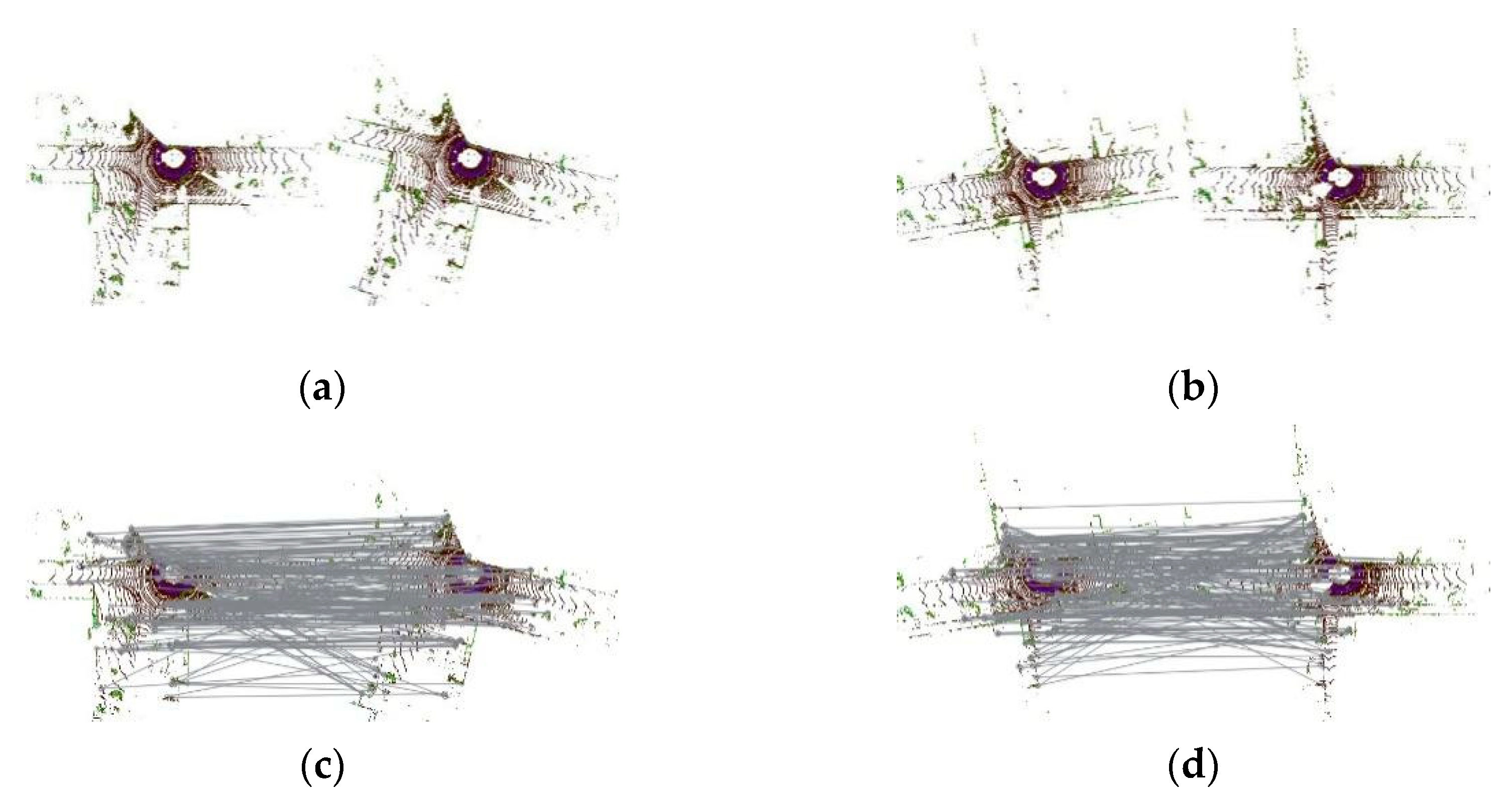
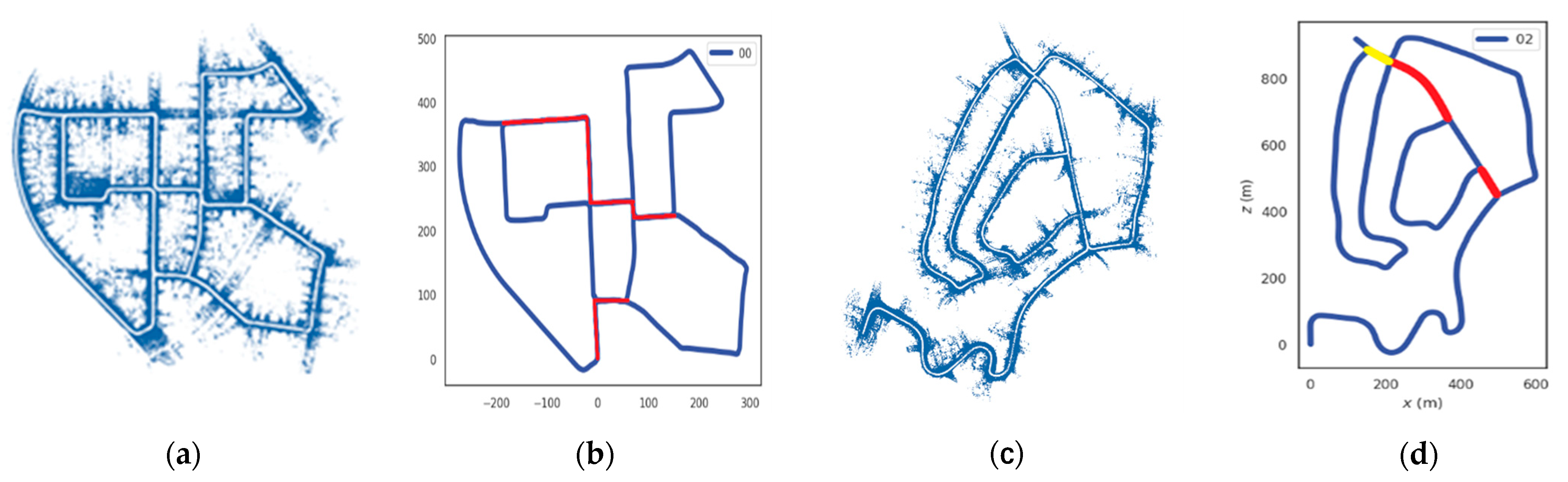
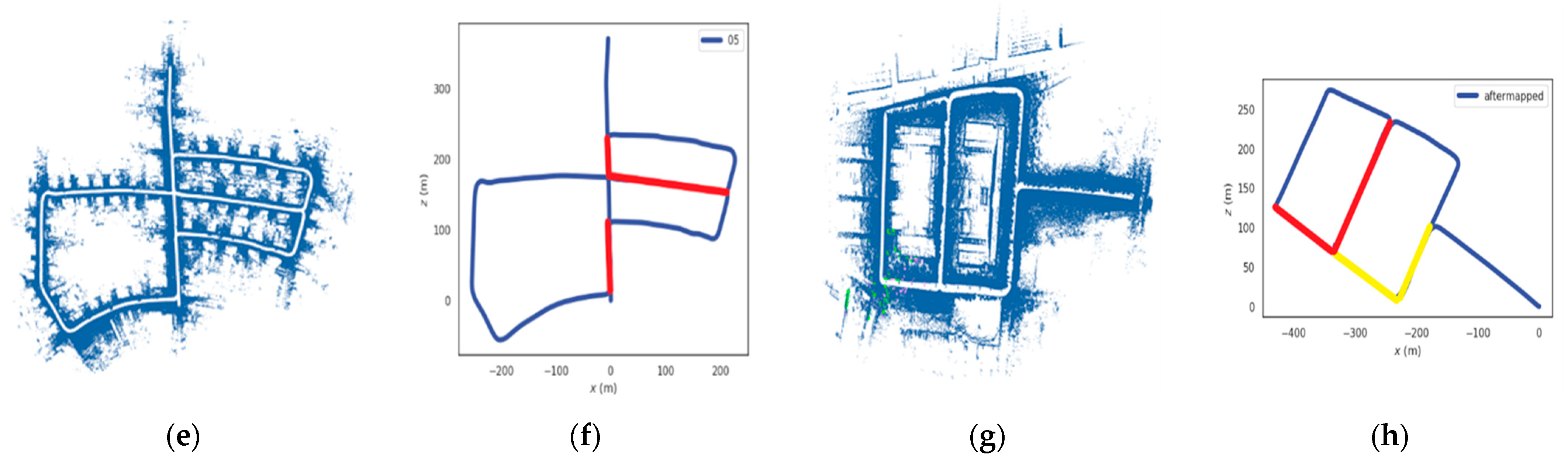
4.2.3. Improvement of the Mapping
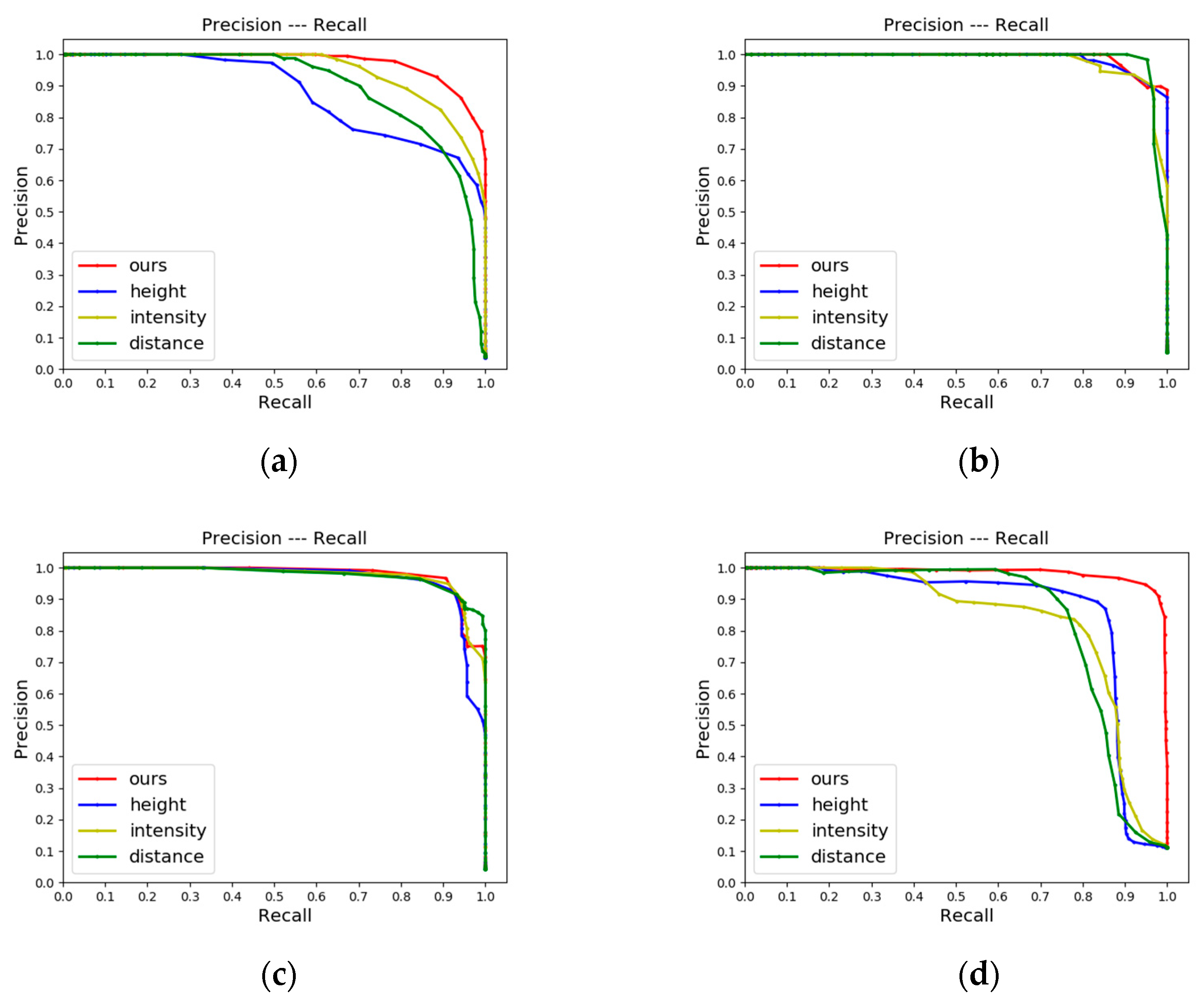
4.2.4. Ablation Experiments
4.2.5. Analysis of Computation Time
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, B.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J. A Survey of Simultaneous Localization and Mapping. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.05214. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Singh, S. LOAM: Lidar odometry and mapping in real-time. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Berkeley, CA, USA, 12–16 July 2014; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B. Lego-loam: Lightweight and ground-optimized lidar odometry and mapping on variable terrain. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4758–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Meyers, D.; Wang, W.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. Lio-sam: Tightly-coupled lidar inertial odometry via smoothing and mapping. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 5135–5142. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, C.; Xue, W.; Li, Q. A LiDAR/Visual SLAM Backend with Loop Closure Detection and Graph Optimization. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, C.; Luo, B.; Zhang, C. DV-LOAM: Direct visual lidar odometry and mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derpanis, K.G. Overview of the RANSAC Algorithm. Image Rochester NY 2010, 4, 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Kim, A. Scan context: Egocentric spatial descriptor for place recognition within 3d point cloud map. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 4802–4809. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.; Choi, S.; Kim, A. Scan context++: Structural place recognition robust to rotation and lateral variations in urban environments. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2021, 38, 1856–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Englot, B.; Duarte, F.; Ratti, C.; Rus, D. Robust place recognition using an imaging lidar. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 5469–5475. [Google Scholar]
- Sivic, J.; Zisserman, A. Video Google: A text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; pp. 1470–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Cummins, M.; Newman, P. FAB-MAP: Probabilistic localization and mapping in the space of appearance. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2008, 27, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, H.; Tuytelaars, T.; Gool, L.V. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 404–417. [Google Scholar]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. Fast relocalisation and loop closing in keyframe-based SLAM. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014; pp. 846–853. [Google Scholar]
- Gálvez-López, D.; Tardos, J.D. Bags of binary words for fast place recognition in image sequences. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlkinger, W.; Vincze, M. Ensemble of shape functions for 3d object classification. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Karon Beach, Thailand, 7–11 December 2011; pp. 2987–2992. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, R.B.; Blodow, N.; Beetz, M. Fast point feature histograms (FPFH) for 3D registration. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Kobe, Japan, 12–17 May 2009; pp. 3212–3217. [Google Scholar]
- Bosse, M.; Zlot, R.; Flick, P. Zebedee: Design of a spring-mounted 3-d range sensor with application to mobile mapping. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 1104–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, R.; Dugas, D.; Stumm, E.; Nieto, J.; Siegwart, R.; Cadena, C. Segmatch: Segment based place recognition in 3d point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 5266–5272. [Google Scholar]
- Uy, M.A.; Lee, G.H. Pointnetvlad: Deep point cloud based retrieval for large-scale place recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4470–4479. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 652–660. [Google Scholar]
- Arandjelovic, R.; Gronat, P.; Torii, A.; Pajdla, T.; Sivic, J. NetVLAD: CNN architecture for weakly supervised place recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 5297–5307. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H. M2DP: A novel 3D point cloud descriptor and its application in loop closure detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Daejeon, Korea, 9–14 October 2016; pp. 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Xie, L. Intensity scan context: Coding intensity and geometry relations for loop closure detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Paris, France, 31 May–31 August 2020; pp. 2095–2101. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xu, C.-Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Yang, J.; Kong, H. Lidar iris for loop-closure detection. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 5769–5775. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Cao, S.-Y.; Han, B.; Shen, H.-L.; Li, J. BVMatch: Lidar-Based Place Recognition Using Bird’s-Eye View Images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 6076–6083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Läbe, T.; Milioto, A.; Röhling, T.; Vysotska, O.; Haag, A.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. OverlapNet: Loop closing for LiDAR-based SLAM. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.11344. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, W.; Li, D.; Xu, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, T. An advanced k nearest neighbor classification algorithm based on KD-tree. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference of Safety Produce Informatization (IICSPI), Chongqing, China, 10–12 December 2018; pp. 902–905. [Google Scholar]
- Shlens, J. A tutorial on principal component analysis. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.1100. [Google Scholar]
- Rosten, E.; Drummond, T. Machine learning for high-speed corner detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 430–443. [Google Scholar]
- Calonder, M.; Lepetit, V.; Strecha, C.; Fua, P. Brief: Binary robust independent elementary features. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 778–792. [Google Scholar]
- Meer, P.; Mintz, D.; Rosenfeld, A.; Kim, D.Y. Robust regression methods for computer vision: A review. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 1991, 6, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Code of SC Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/gisbi-kim/scancontext (accessed on 24 September 2021).
- The Code of ISC Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/wh200720041/iscloam (accessed on 13 March 2021).
- The Code of M2DP Algorithm. Available online: https://github.com/gloryhry/M2DP-CPP (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- The Code of ESF Algorithm. Available online: http://pointclouds.org/documentation/classpcl_1_1_e_s_f_estimation.html (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision meets robotics: The kitti dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Wei, J.; Li, R.; Cheng, J. LeGO-LOAM-SC: An Improved Simultaneous Localization and Mapping Method Fusing LeGO-LOAM and Scan Context for Underground Coalmine. Sensors 2022, 22, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinkiewicz, S.; Levoy, M. Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Dellaert, F. Factor Graphs and GTSAM: A Hands-On Introduction; Georgia Institute of Technology: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]


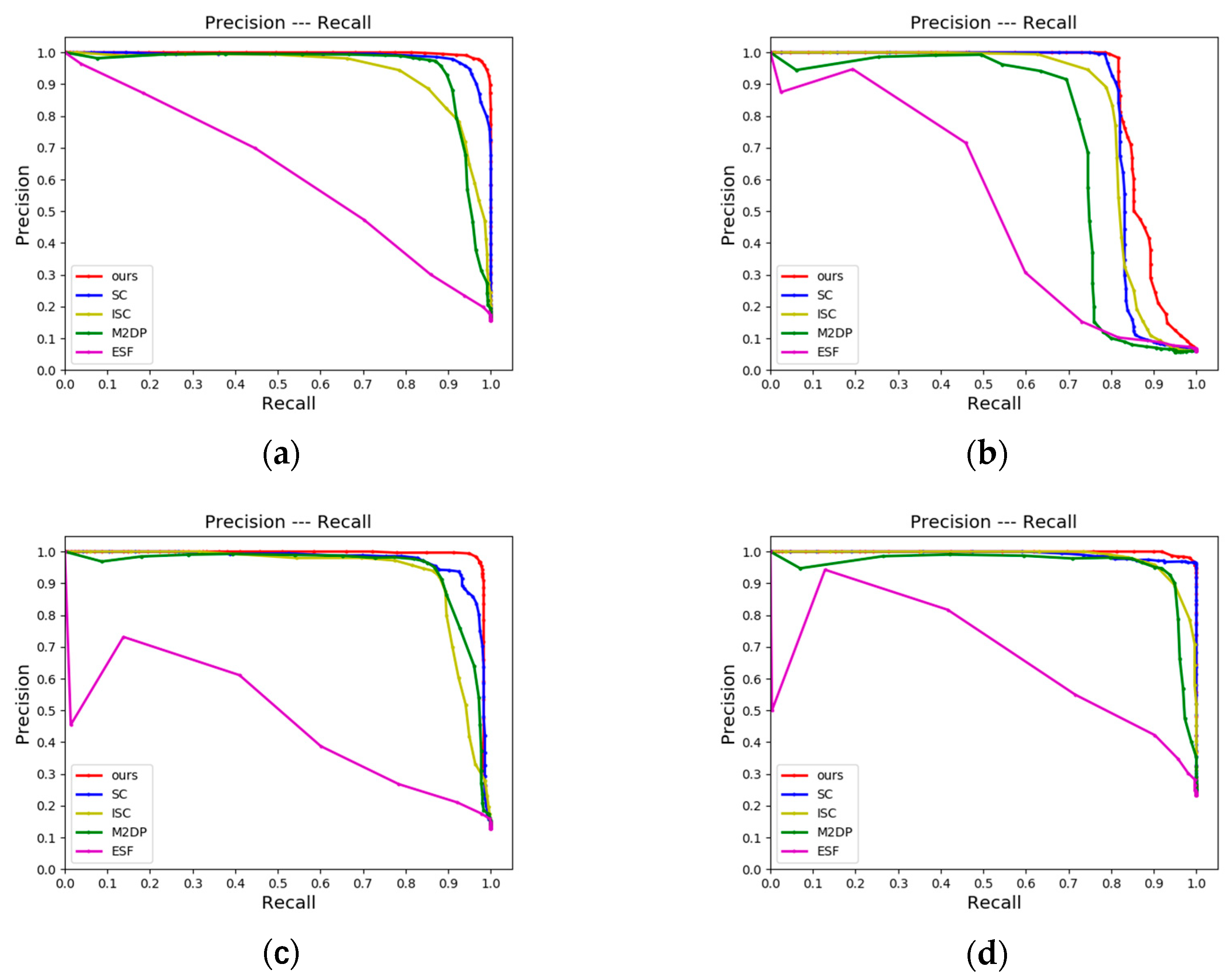
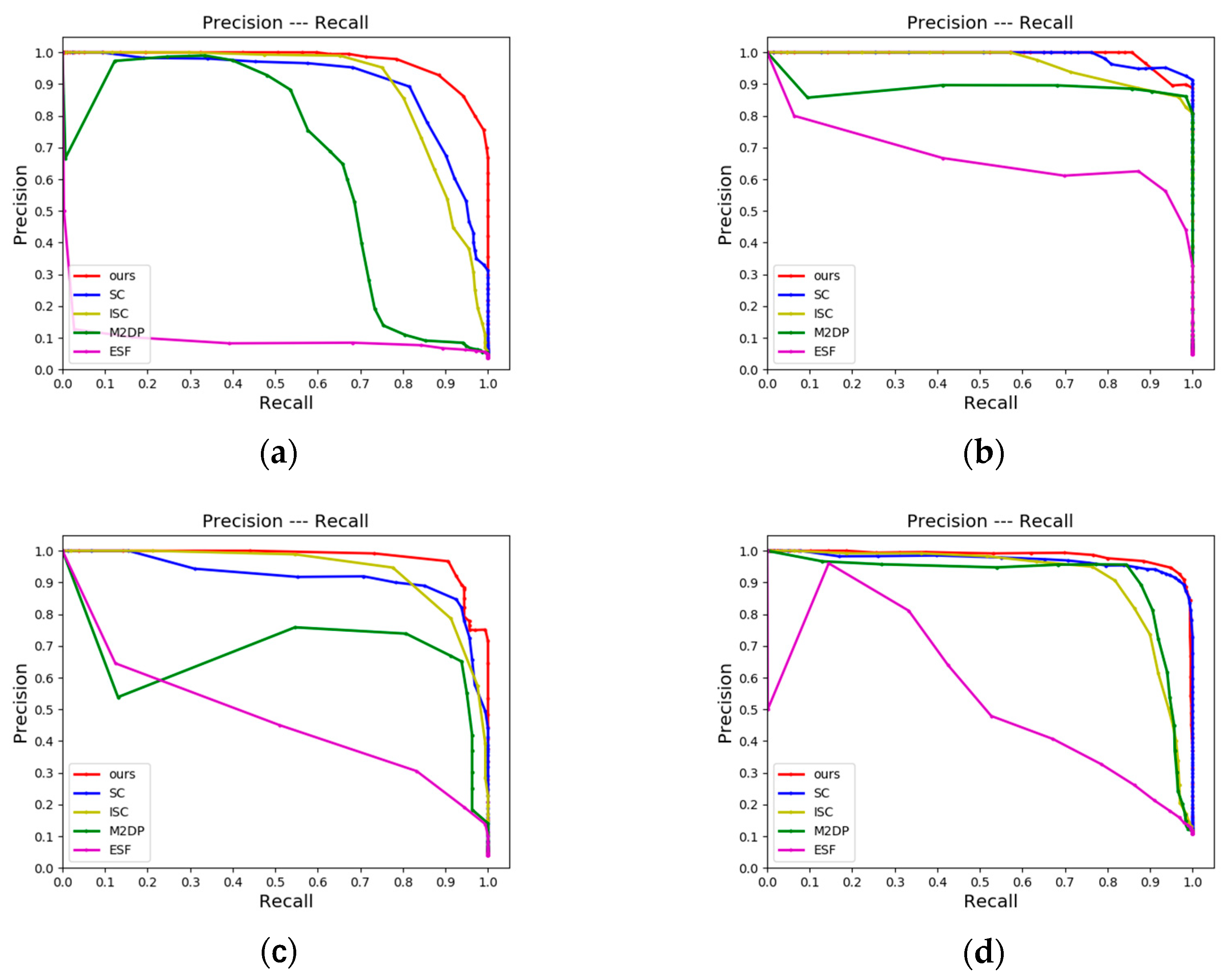

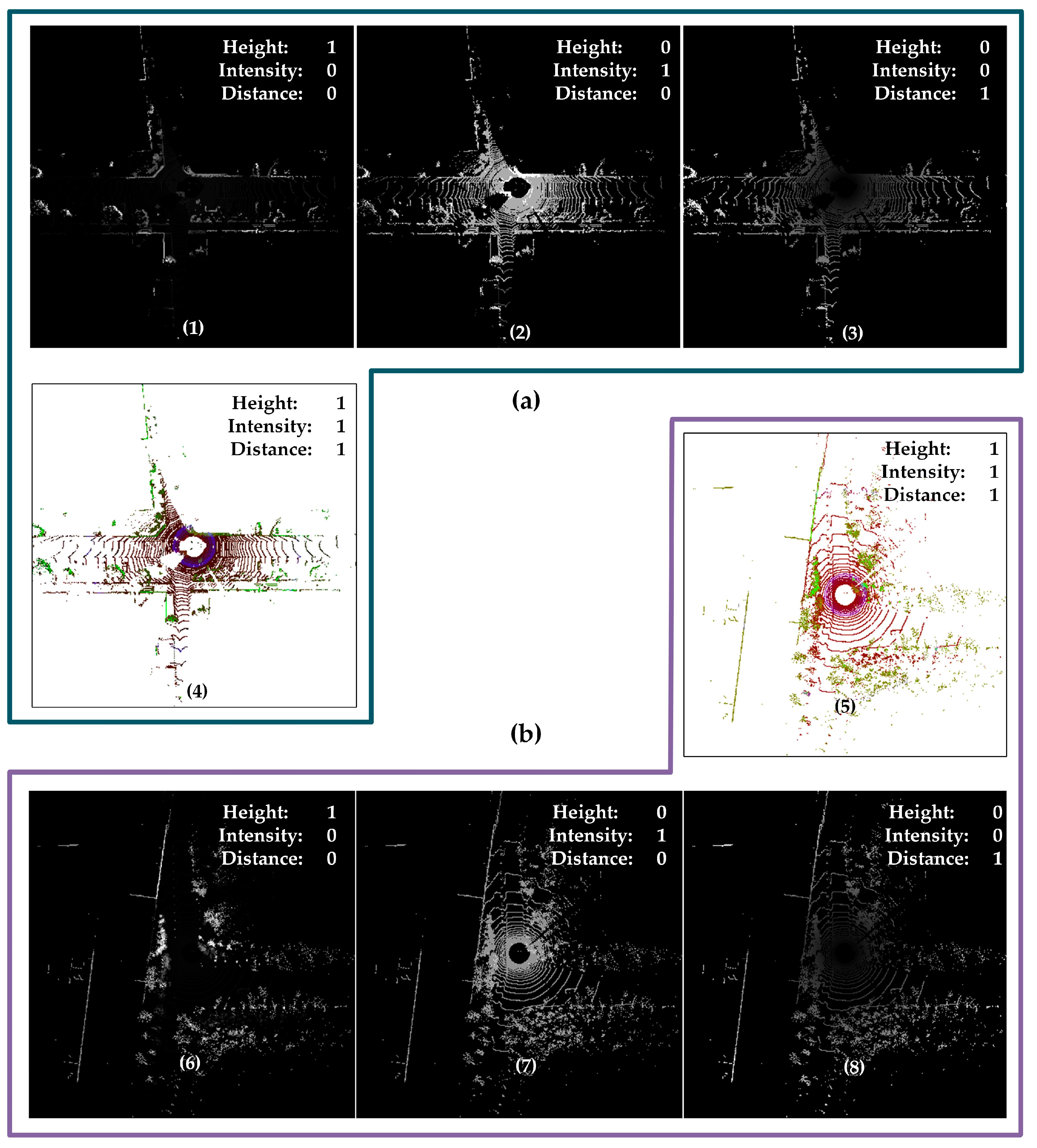

| Methods | KITTI-00 | KITTI-02 | KITTI-05 | KITTI-06 | jlu00 | jlu01 | jlu02 | jlu03 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC | 0.9493/0.8719 | 0.8776/0.8746 | 0.9189/0.8326 | 0.9809/0.8957 | 0.8520/0.7407 | 0.9545/0.8809 | 0.8843/0.6776 | 0.9366/0.5396 |
| ISC | 0.8693/0.7141 | 0.8365/0.7935 | 0.8825/0.7564 | 0.9298/0.8677 | 0.8397/0.6485 | 0.9104/0.7857 | 0.8532/0.6056 | 0.8596/0.5321 |
| M2DP | 0.9188/0.7809 | 0.7902/0.5722 | 0.8892/0.5844 | 0.9328/0.6737 | 0.6667/0.4333 | 0.9185/0.7286 | 0.7717/0.3692 | 0.8970/0.4833 |
| ESF | 0.5653/0.4821 | 0.5589/0.4375 | 0.4795/0.2273 | 0.6216/0.45 | 0.1500/0.25 | 0.7285/0.53 | 0.4781/0.3226 | 0.5108/0.25 |
| Ours | 0.9754/0.8969 | 0.8950/0.8560 | 0.9729/0.8989 | 0.9827/0.9001 | 0.9056/0.7986 | 0.9403/0.8786 | 0.9359/0.7205 | 0.9478/0.5933 |
| Methods | Avg KITTI Execution Time (s/Query) | Avg JLU Execution Time (s/Query) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KITTI-00 | KITTI-02 | KITTI-05 | KITTI-06 | jlu00 | jlu01 | jlu02 | jlu03 | |
| SC | 0.0867 | 0.0861 | 0.0885 | 0.0846 | 0.0583 | 0.0558 | 0.0658 | 0.0732 |
| ISC | 0.0697 | 0.0687 | 0.0678 | 0.0656 | 0.0537 | 0.0513 | 0.0580 | 0.0605 |
| M2DP | 0.3655 | 0.3873 | 0.3869 | 0.3827 | 0.3974 | 0.3554 | 0.3739 | 0.3538 |
| ESF | 0.0728 | 0.0784 | 0.0785 | 0.0664 | 0.0724 | 0.0574 | 0.0541 | 0.0655 |
| Ours | 0.0603 | 0. 0601 | 0.0589 | 0.0525 | 0.0587 | 0.0483 | 0.0539 | 0.0598 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, G.; Wei, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hou, M.; Liu, Z. A Multi-Channel Descriptor for LiDAR-Based Loop Closure Detection and Its Application. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225877
Wang G, Wei X, Chen Y, Zhang T, Hou M, Liu Z. A Multi-Channel Descriptor for LiDAR-Based Loop Closure Detection and Its Application. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225877
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Gang, Xiaomeng Wei, Yu Chen, Tongzhou Zhang, Minghui Hou, and Zhaohan Liu. 2022. "A Multi-Channel Descriptor for LiDAR-Based Loop Closure Detection and Its Application" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225877
APA StyleWang, G., Wei, X., Chen, Y., Zhang, T., Hou, M., & Liu, Z. (2022). A Multi-Channel Descriptor for LiDAR-Based Loop Closure Detection and Its Application. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5877. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225877











