Long-Time Trends in Night Sky Brightness and Ageing of SQM Radiometers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Analysed Data
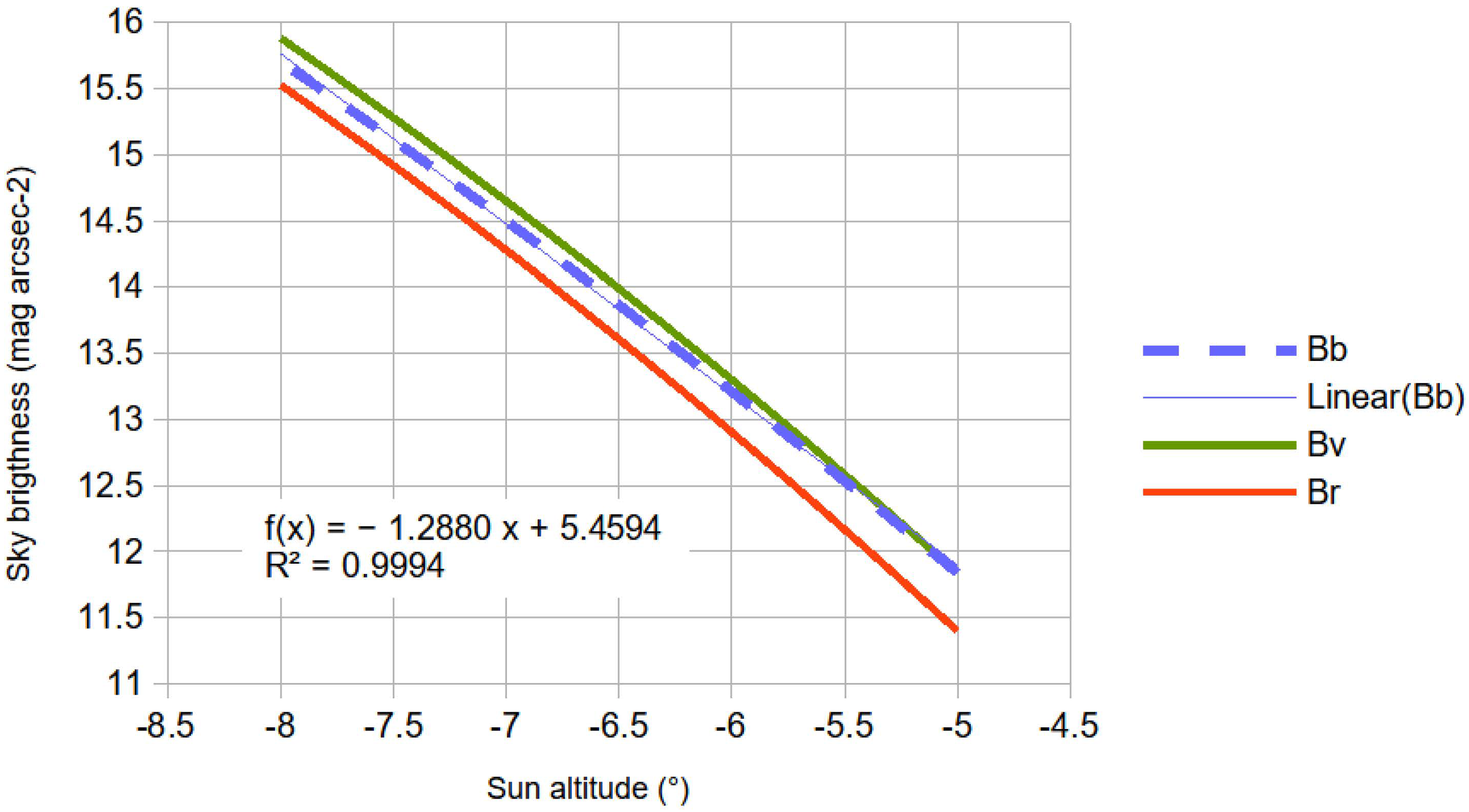
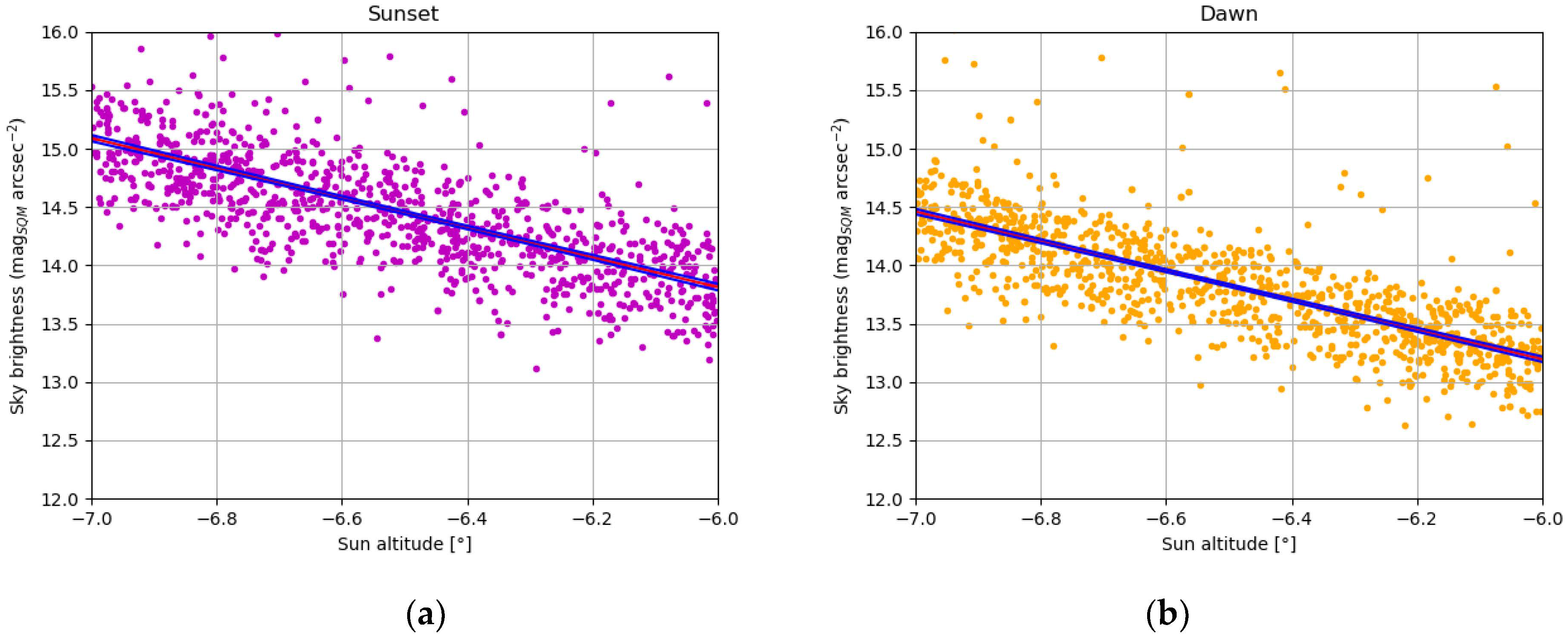
2.2. The Model of Twilight at Sunset and Dawn
- b(t) is the brightness of the sky in defined (reference) meteorological conditions and reference status of the instrument, for example the status after a calibration or at the beginning of a time series;
- m(t) describes the effect of atmospheric conditions different from reference ones, for the latter m = 1;
- r(t) describes the effect of instrument status different from reference one, for the latter r = 1.
| exact local time | |
| exact Sun altitude angle | |
| time shown by the clock in the instrument | |
| time shown by the clock in the instrument corrected for the delay | |
2.3. Approaches to the Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, J.Y.; Waide, P. The world’s appetite for light: Empirical data and trends spanning three centuries and six continents. Leukos 2010, 6, 259–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerbrand, A.K. New Framework of Sustainable Indicators for Outdoor LED (Light Emitting Diodes) Lighting and SSL (Solid State Lighting). Sustainability 2015, 7, 1028–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, R.; Perkins, C.; Tompson, L.; Johnson, S.; Armstrong, B.; Green, J.; Grundy, C.; Wilkinson, P.; Edwards, P. The effect of reduced street lighting on road casualties and crime in England and Wales: Controlled interrupted time series analysis. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2015, 69, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pust, P.; Schmidt, P.J.; Schnick, W. A revolution in lighting. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaston, K.J.; Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Hopkins, J. The ecological impacts of nighttime light pollution: A mechanistic appraisal. Biol. Rev. 2013, 88, 912–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Visser, M.E.; Hölker, F. The biological impacts of artificial light at night: The research challenge. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Cruse, D.; Gaston, K.J. Ecological effects of artificial light at night on wild plants. J. Ecol. 2016, 104, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Holt, L.A. Nature, extent and ecological implications of night-time light from road vehicles. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 55, 2296–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouhant, E.; Gomes, E.; Mondy, N.; Amat, I. Mechanistic, ecological, and evolutionary consequences of artificial light at night for insects: Review and prospective. Entomol. Exp. Et Appl. 2019, 167, 37–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, D.; Frago, E.; Kehoe, R.; Patterson, C.; Gaston, K.J. A meta-analysis of biological impacts of artificial light at night. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Medical Association Press Releases: AMA Adopts Guidance to Reduce Harm from High Intensity Street Lights. Available online: https://www.ama-assn.org/press-center/press-releases/ama-adopts-guidance-reduce-harm-high-intensity-street-lights (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Hatori, M.; Gronfier, C.; Van Gelder, R.N.; Bernstein, P.S.; Carreras, J.; Panda, S.; Marks, F.; Sliney, D.; Hunt, C.E.; Hirota, T.; et al. Global rise of potential health hazards caused by blue light-induced circadian disruption in modern aging societies. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2017, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riegel, K.W. Light pollution: Outdoor lighting is a growing threat to astronomy. Science 1973, 179, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaston, K.J.; Davies, T.W.; Bennie, J.; Hopkins, J. Reducing the ecological consequences of night-time light pollution: Options and developments. J. Appl. Ecol. 2012, 49, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubé, M.; Roby, J. Sky brightness levels before and after the creation of the first International Dark Sky Reserve, Mont-Mégantic Observatory, Québec, Canada. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 139, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänel, A.; Posch, T.; Ribas, S.J.; Aubé, M.; Duriscoe, D.; Jechow, A.; Kollath, Z.; Lolkema, D.E.; Moore, C.; Schmidt, N.; et al. Measuring night sky brightness: Methods and challenges. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 205, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolo, A.; Binotto, R.; Ortolani, S.; Sapienza, S. Measurements of Night Sky Brightness in the Veneto Region of Italy: Sky Quality Meter Network Results and Differential Photometry by Digital Single Lens Reflex. J. Imaging 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bará, S.; Lima, R.C.; Zamorano, J. Monitoring Long-Term Trends in the Anthropogenic Night Sky Brightness. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jechow, A.; Ribas, S.J.; Domingo, R.C.; Hölker, F.; Kolláth, Z.; Kyba, C.C. Tracking the dynamics of skyglow with differential photometry using a digital camera with fisheye lens. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 209, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentin, P.; Bertolo, A.; Cavazzani, S.; Ortolani, S. Calibration of digital compact cameras for sky quality measures. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 255, 107235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barducci, A.; Marcoionni, P.; Pippi, I.; Poggesi, M. Effects of light pollution revealed during a nocturnal aerial survey by two hyperspectral imagers. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 4349–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuechly, H.U.; Kyba, C.C.; Ruhtz, T.; Lindemann, C.; Wolter, C.; Fischer, J.; Hölker, F. Aerial survey and spatial analysis of sources of light pollution in Berlin, Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 126, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.D.; Davies, G.; Fairbrass, A.J.; Matthews, T.J.; Rogers, C.D.; Sadler, J.P. Mapping lightscapes: Spatial patterning of artificial lighting in an urban landscape. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentin, P.; Bettanini, C.; Lorenzini, E.; Aboudan, A.; Colombatti, G.; Ortolani, S.; Bertolo, A. Minlu: An Instrumental Suite for Monitoring Light Pollution from Drones or Airballoons. In Proceedings of the 2018 5th IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Rome, Italy, 20–22 June 2018; pp. 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentin, P.; Bettanini, C.; Bogoni, D. Calibration of an Autonomous Instrument for Monitoring Light Pollution from Drones. Sensors 2019, 19, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouroussis, C.A.; Topalis, F.V. Assessment of outdoor lighting installations and their impact on light pollution using unmanned aircraft systems-The concept of the drone-gonio-photometer. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 253, 107155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, F.; de Miguel, A.S.; Conde, A. Low Cost Multi-Purpose Balloon-Borne Platform for Wide-Field Imaging and Video Observation. In Ground-based and Airborne Telescopes VI. Proceedings of the International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2016; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; p. 99061X. [Google Scholar]
- Bettanini, C.; Fiorentin, P.; Dumitriu, A.; Accatino, F.; Cagnato, E.; Kahol, O.; Ghedin, M.; Celadin, D.; Magro, N.; Bedendo, M.; et al. Design and Test of Autonomous Scientific Payloads for Sounding Balloons. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 7th International Workshop on Metrology for AeroSpace (MetroAeroSpace), Pisa, Italy, 22–24 June 2020; pp. 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W., III; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the Capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Day/Night Band. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Garz, S.; Kuechly, H.; De Miguel, A.S.; Zamorano, J.; Fischer, J.; Hölker, F. High-Resolution Imagery of Earth at Night: New Sources, Opportunities and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-García, R.; García-Gil, M.; Acosta, L.; Bará, S.; Sanchez-de-Miguel, A.; Zamorano, J. Statistical modelling and satellite monitoring of upward light from public lighting. Light. Res. Technol. 2016, 48, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyba, C.C.; Kuester, T.; Sánchez de Miguel, A.; Baugh, K.; Jechow, A.; Hölker, F.; Bennie, J.; Elvidge, C.D.; Gaston, K.J.; Guanter, L. Artificially lit surface of Earth at night increasing in radiance and extent. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzani, S.; Ortolani, S.; Bertolo, A.; Binotto, R.; Fiorentin, P.; Carraro, G.; Zitelli, V. Satellite measurements of artificial light at night: Aerosol effects. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 499, 5075–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinzano, P. Night Sky Photometry with Sky Quality Meter. ISTIL Intern. Rep. 2005, 9, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Pun, C.S.J.; So, C.W. Night-sky Brightness monitoring in Hong Kong: A city-wide light pollution assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2537–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Ruhtz, T.; Fischer, J.; Hölker, F. Red is the new black: How the colour of urban skyglow varies with cloud cover. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 425, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espey, B.; McCauley, J. Initial Irish light pollution measurements and a new Sky Quality Meter-based data logger. Light. Res. Technol. 2014, 46, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, T.; Binder, F.; Puschnig, J. Systematic measurements of the night sky brightness at 26 locations in Eastern Austria. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 211, 144–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyba, C.C.; Tong, K.P.; Bennie, J.; Birriel, I.; Birriel, J.J.; Cool, A.; Danielsen, A.; Davies, T.W.; Peter, N.; Edwards, W.; et al. Worldwide variations in artificial skyglow. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamorano, J.; Garcia, C.; Tapia, C.; Sanchez de Miguel, A.; Pascual, S.; Gallego, J. Star4all night sky brightness photometer. Int. J. Sustain. Light. 2016, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bará, S. Anthropogenic disruption of the night sky darkness in urban and rural areas. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolomei, M.; Olivieri, L.; Bettanini, C.; Cavazzani, S.; Fiorentin, P. Verification of Angular Response of Sky Quality Meter with Quasi-Punctual Light Sources. Sensors 2021, 21, 7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavazzani, S.; Ortolani, S.; Bertolo, A.; Binotto, R.; Fiorentin, P.; Carraro, G.; Saviane, I.; Zitelli, V. Sky Quality Meter and satellite correlation for night cloud-cover analysis at astronomical sites. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 2463–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles, J.; Zamorano, J.; Pascual, S.; Sánchez de Miguel, A.; Gallego, J.; Gaston, K.J. Evolution of Brightness and Color of the Night Sky in Madrid. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnitt, S.; Ruhtz, T.; Fischer, J.; Hölker, F.; Kyba, C.C.M. Temperature stability of the sky quality meter. Sensors 2013, 13, 12166–12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puschnig, J.; Näslund, M.; Schwope, A.; Wallner, S. Correcting sky-quality-meter measurements for ageing effects using twilight as calibrator. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 502, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Duriscoe, D.; Kyba, C.C.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Portnov, B.A.; Rybnikova, N.A.; Furgoni, R. The new world atlas of artificial night sky brightness. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Factbook-CIA Maps. Available online: https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/maps/ (accessed on 20 August 2022).
- Puschnig, J.; Wallner, S.; Schwope, A.; Näslund, M. Long-term trends of light pollution assessed from SQM measurements and an empirical atmospheric model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, stac3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patat, F.; Ugolnikov, O.S.; Postylyakov, O.V. UBVRI twilight sky brightness at ESO-Paranal. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 455, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorentin, P.; Cavazzani, S.; Ortolani, S.; Bertolo, A.; Binotto, R. Instrument assessment and atmospheric phenomena in relation to the night sky brightness time series. Measurement 2022, 191, 110823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
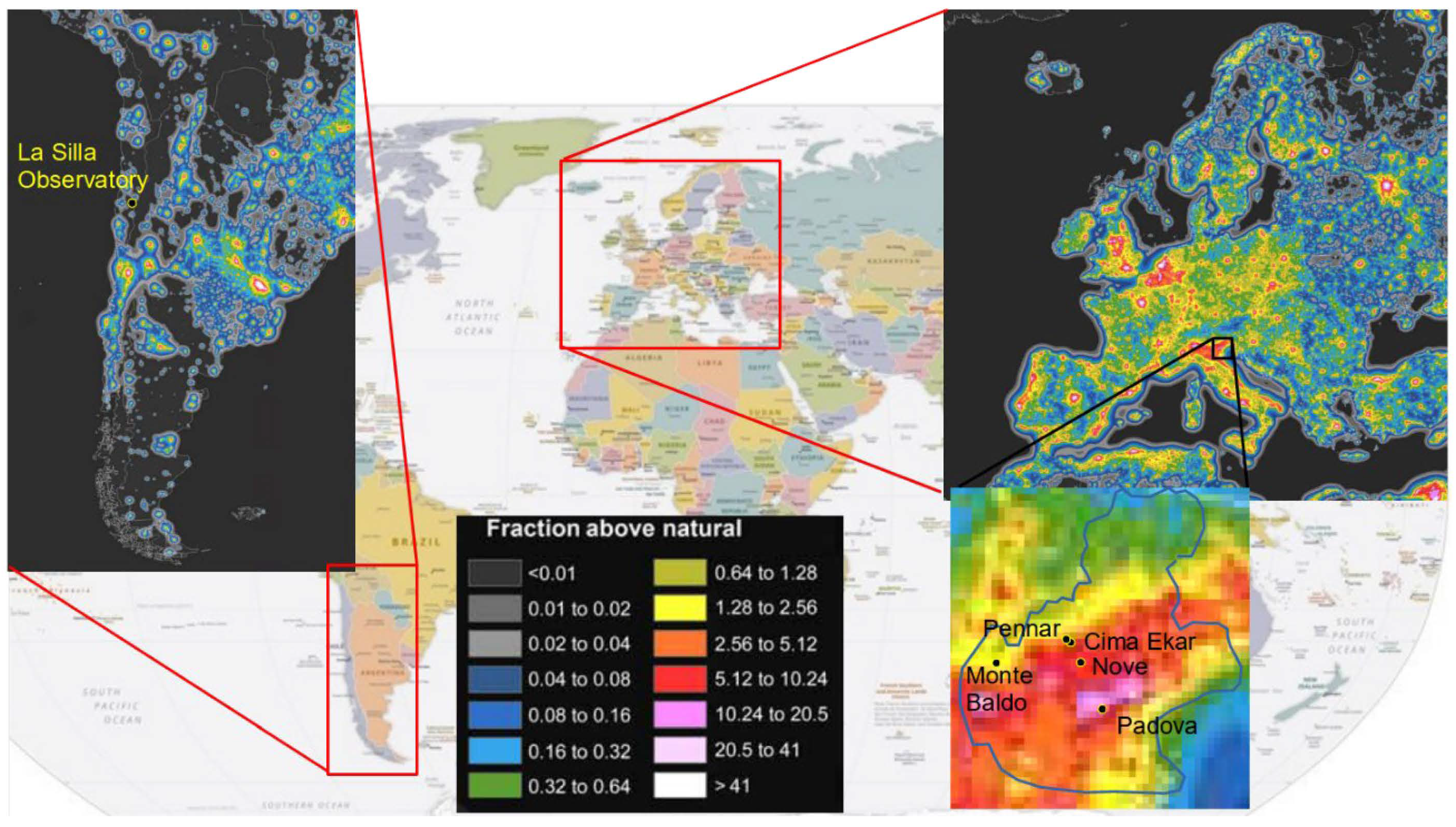
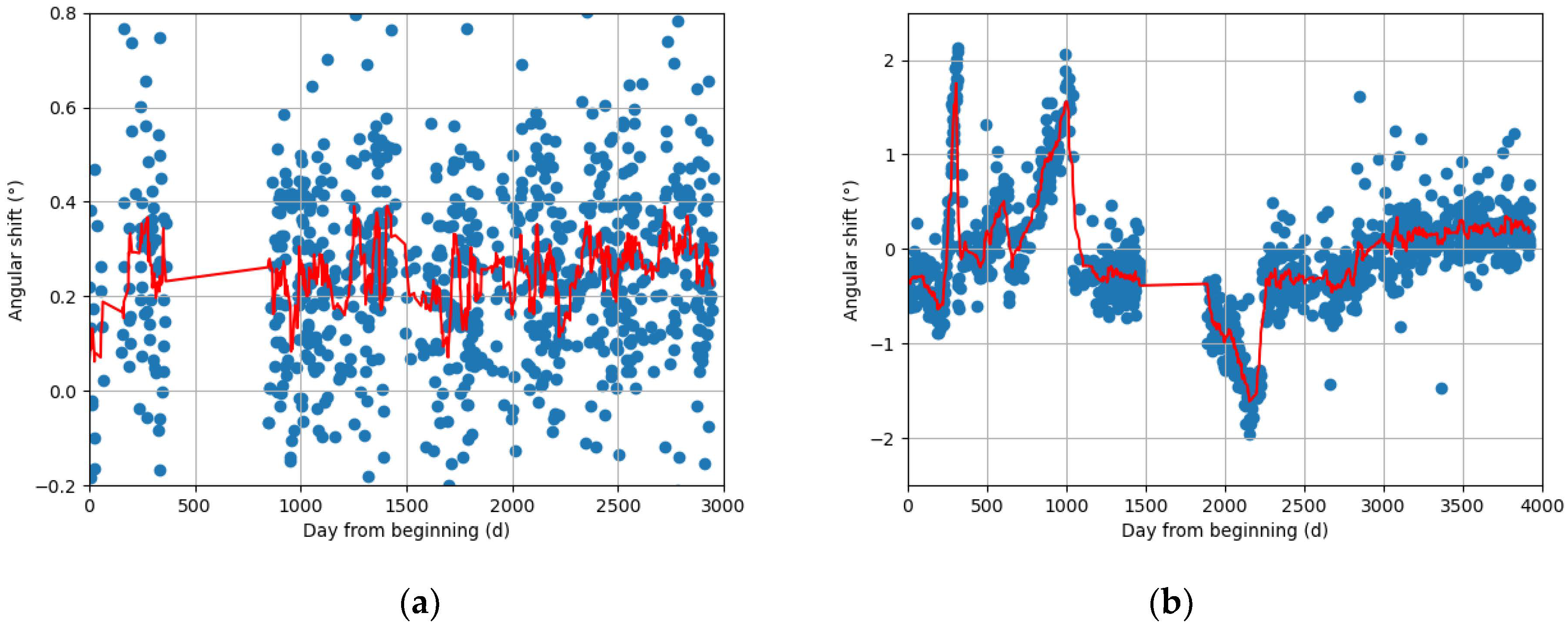


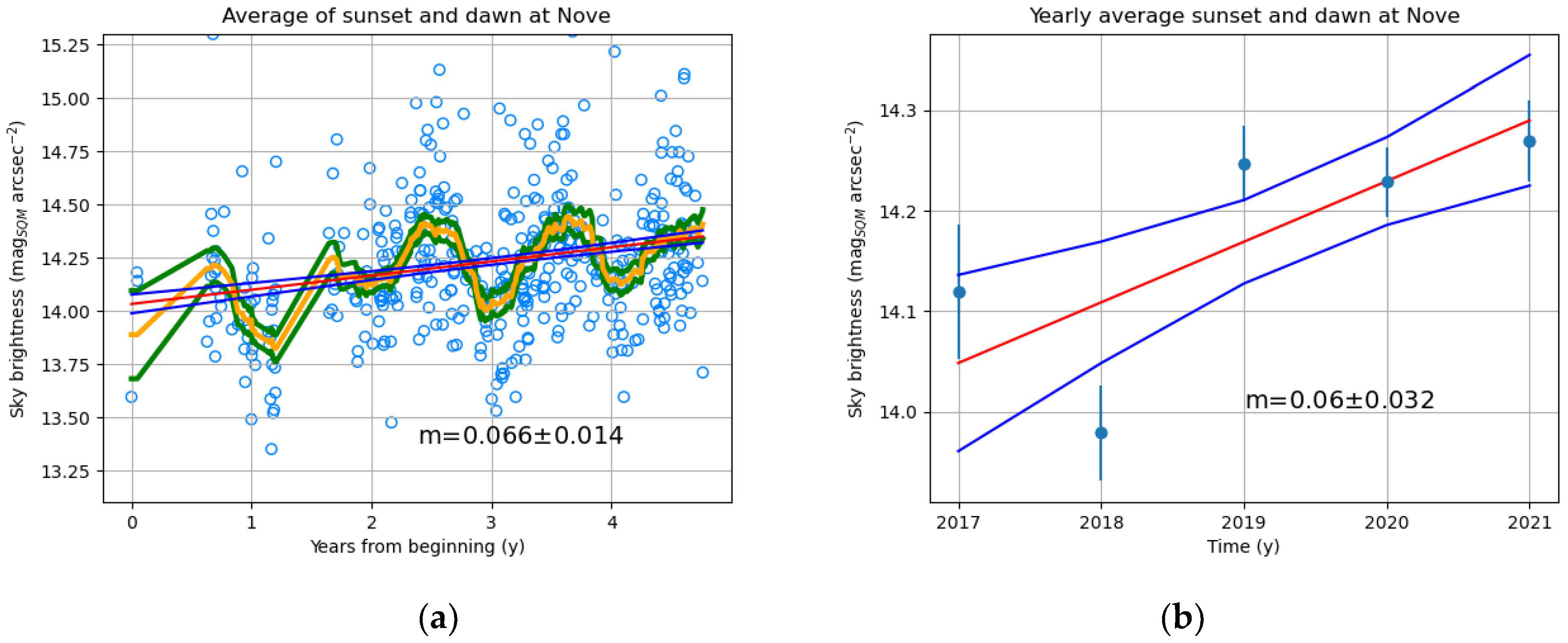
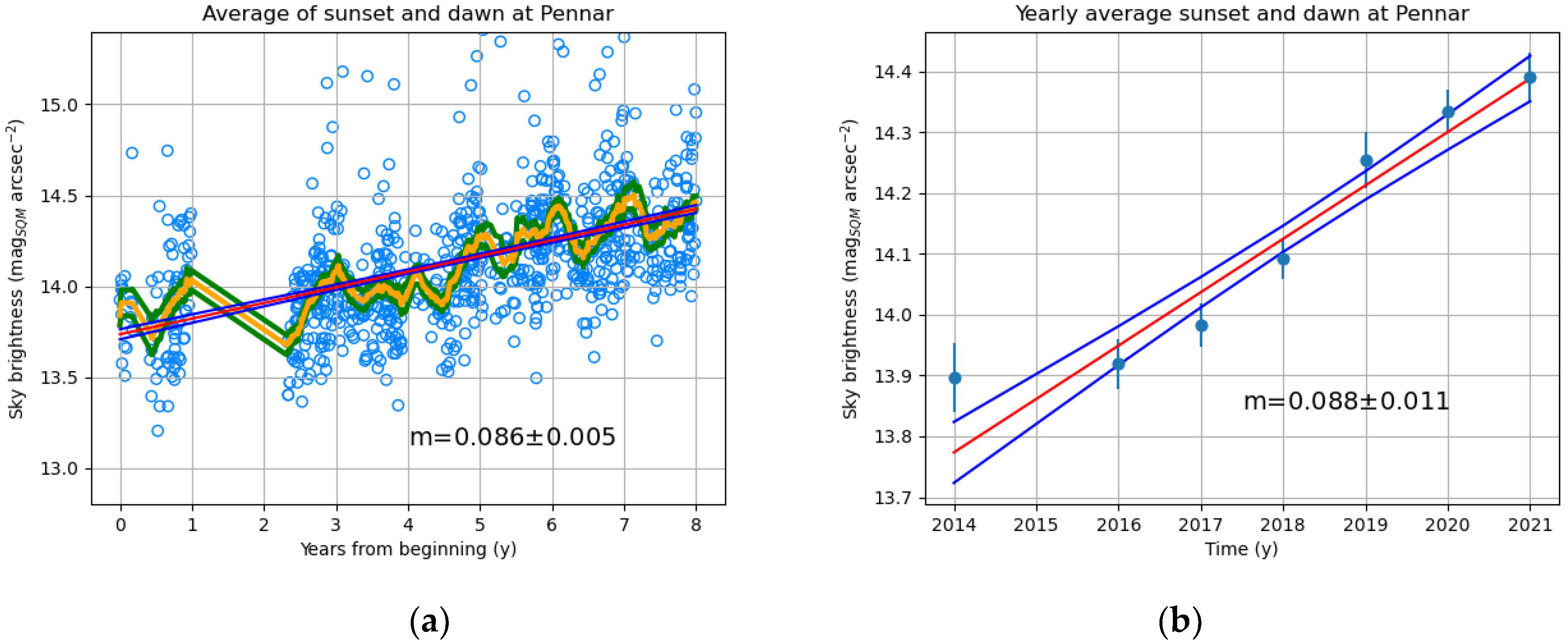
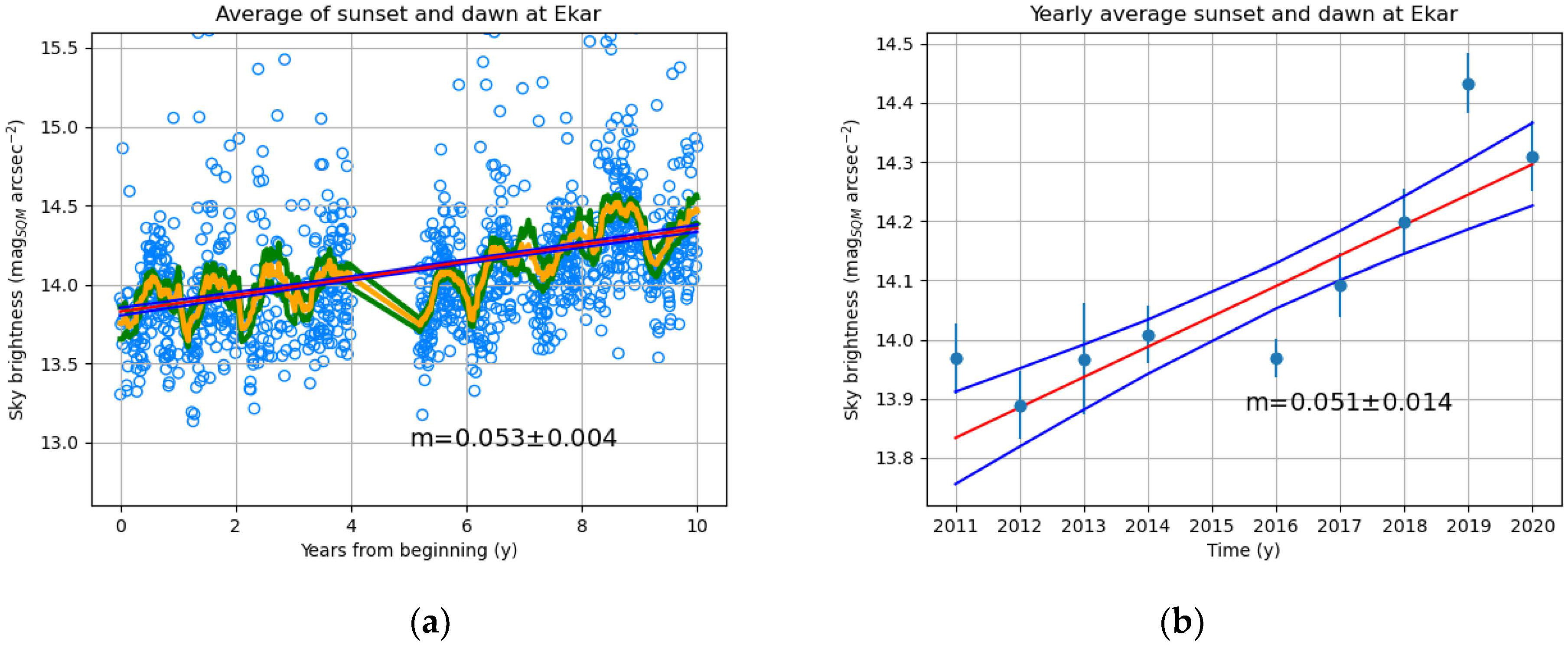

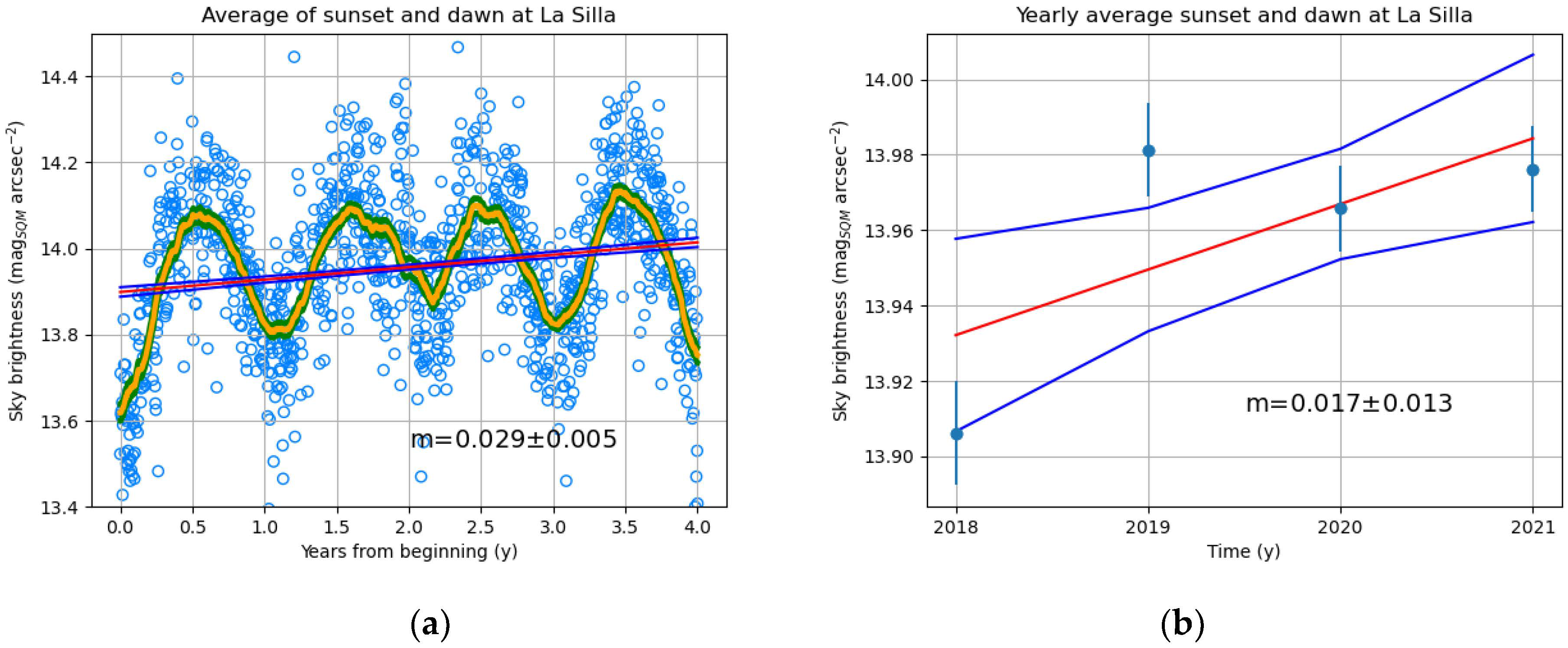
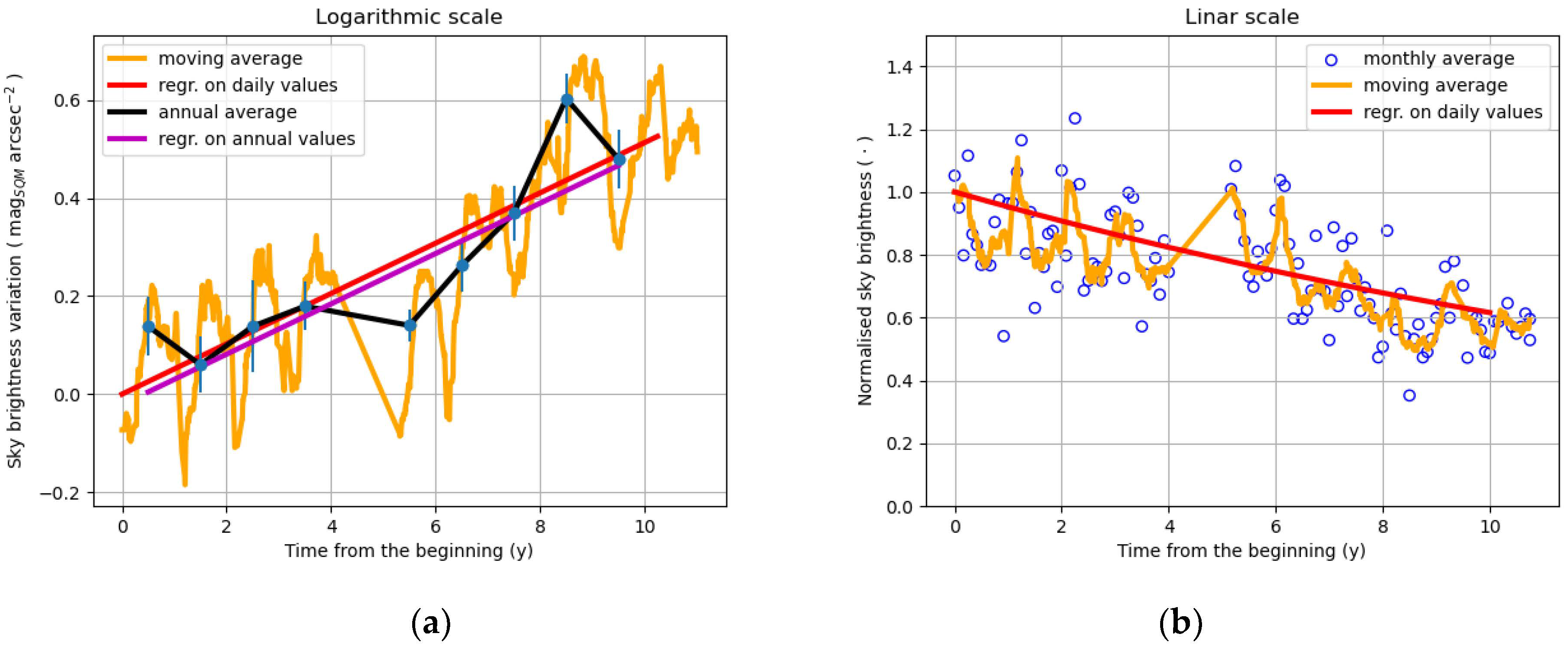

| Site | Altitude (m) |
|---|---|
| Padova (Italia) | 12 |
| Nove (Italia) | 84 |
| Pennar (Italia) | 1050 |
| Ekar (Italia) | 1366 |
| Monte Baldo (Italia) | 2218 |
| La Silla (Chile) | 2400 |
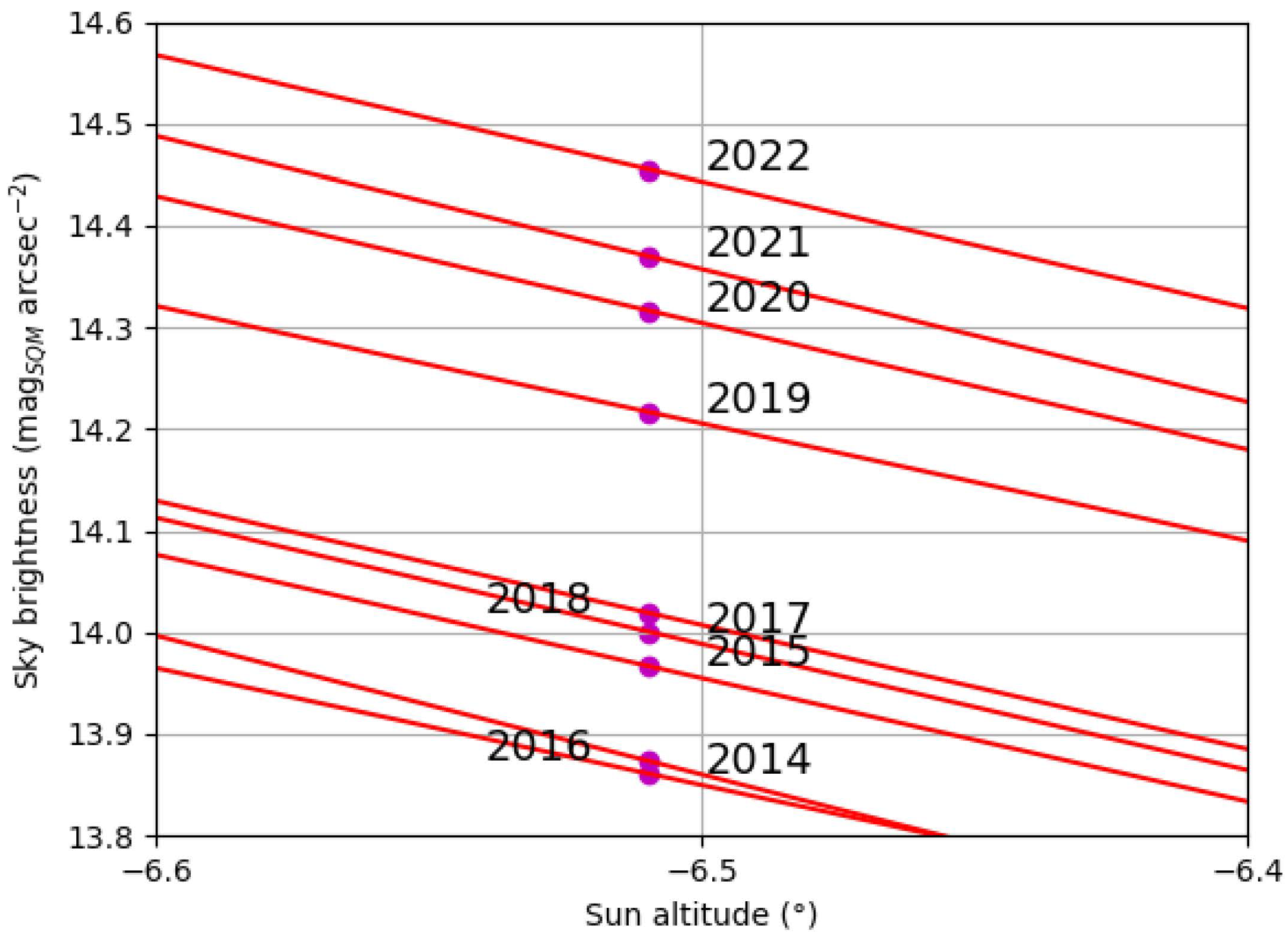
| Site | Working Time (y) | Slope (a) (magSQM arcsec−2 year−1) | Slope (b) (magSQM arcsec−2 year−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Padova (Italia) | 5 | 0.053 ± 0.006 | 0.054 ± 0.013 |
| Nove (Italia) | 5 | 0.068 ± 0.014 | 0.060 ± 0.032 |
| Pennar (Italia) | 8 | 0.086 ± 0.006 | 0.088 ± 0.011 |
| Ekar (Italia) | 10 | 0.053 ± 0.004 | 0.051 ± 0.014 |
| Monte Baldo (Italia) | 7 | 0.086 ± 0.022 | 0.121 ± 0.021 |
| La Silla (Chile) | 4 | 0.029 ± 0.005 | 0.017 ± 0.013 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiorentin, P.; Binotto, R.; Cavazzani, S.; Bertolo, A.; Ortolani, S.; Saviane, I. Long-Time Trends in Night Sky Brightness and Ageing of SQM Radiometers. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225787
Fiorentin P, Binotto R, Cavazzani S, Bertolo A, Ortolani S, Saviane I. Long-Time Trends in Night Sky Brightness and Ageing of SQM Radiometers. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225787
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiorentin, Pietro, Renata Binotto, Stefano Cavazzani, Andrea Bertolo, Sergio Ortolani, and Ivo Saviane. 2022. "Long-Time Trends in Night Sky Brightness and Ageing of SQM Radiometers" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225787
APA StyleFiorentin, P., Binotto, R., Cavazzani, S., Bertolo, A., Ortolani, S., & Saviane, I. (2022). Long-Time Trends in Night Sky Brightness and Ageing of SQM Radiometers. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5787. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225787






