Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Reclamation in the Antaibao Open-Pit Mine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
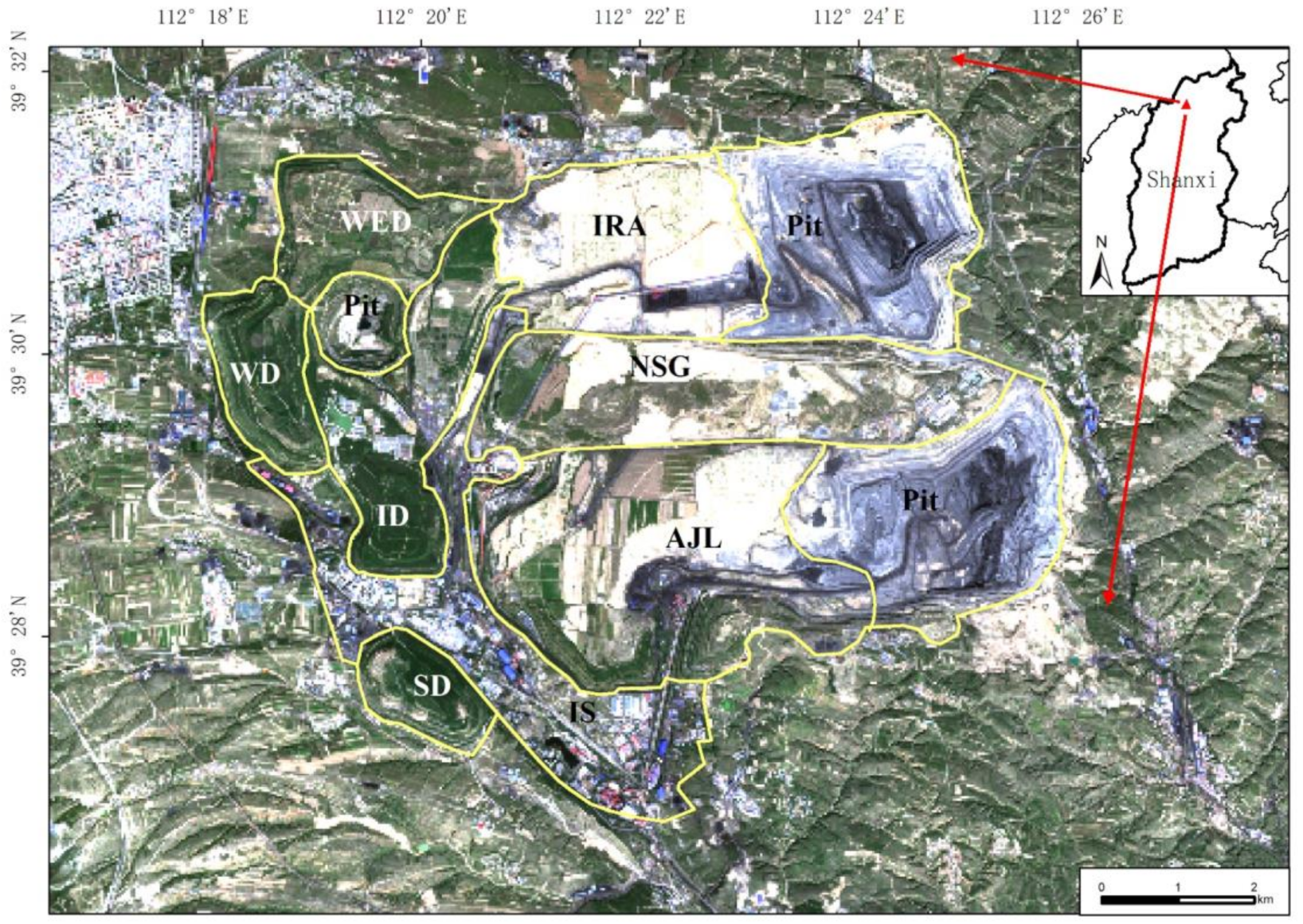
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Preprocessing and Calculation of NDVI
2.3.2. Remote Sensing Interactive Interpretation
2.3.3. Unary Regression Analysis
2.3.4. Sen+Mann–Kendall Trend Analysis
2.3.5. Mann–Kendall Mutation Test
3. Results
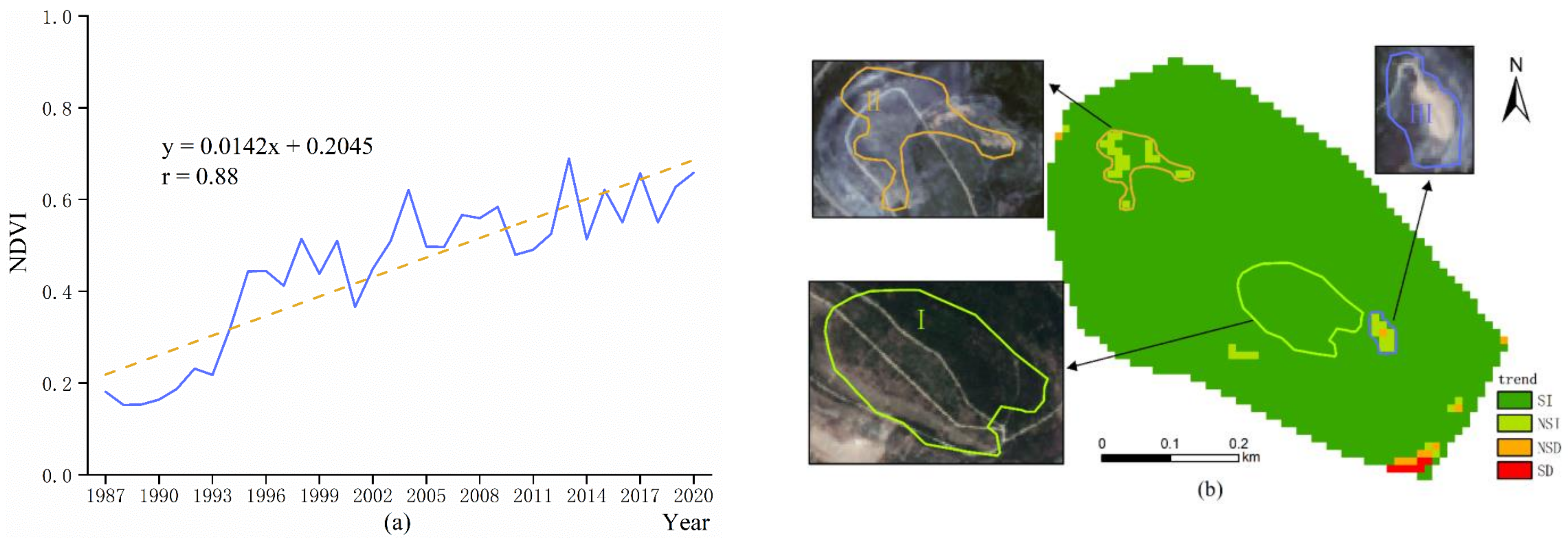
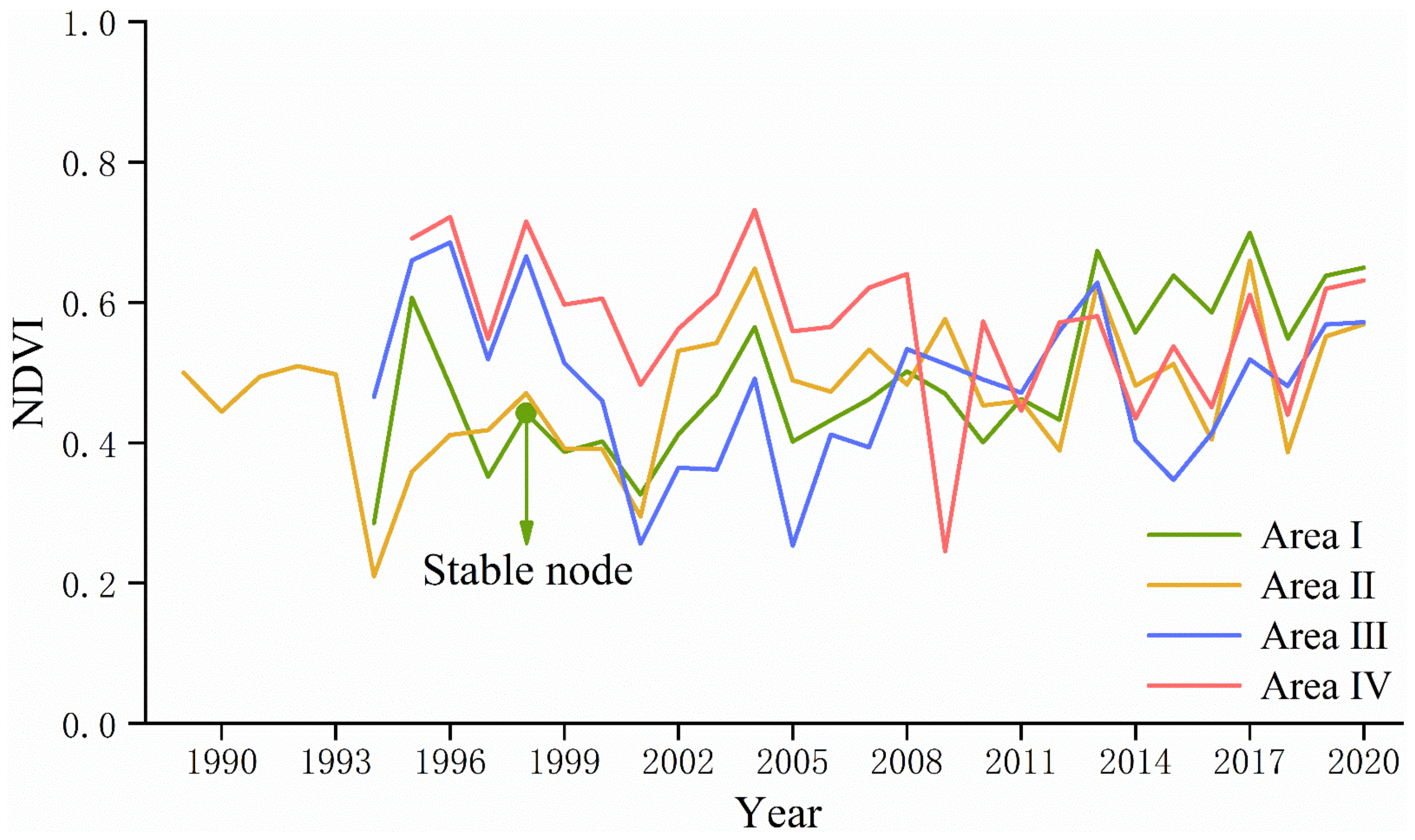
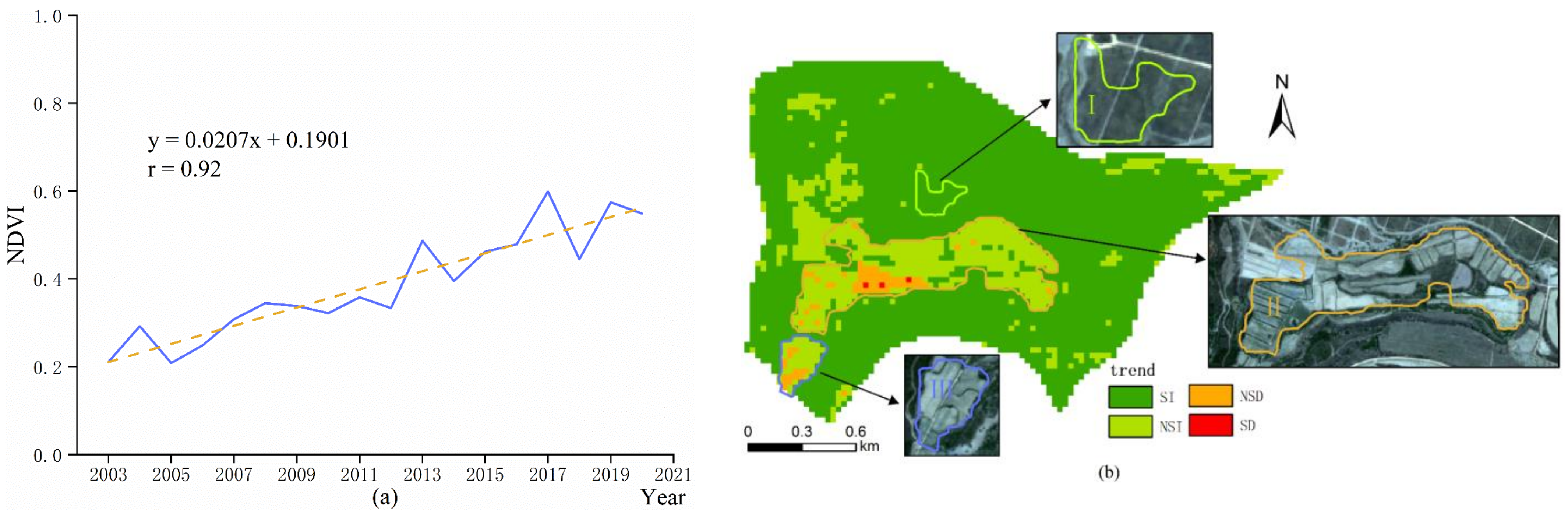
3.1. Monitoring Results in the South Dump
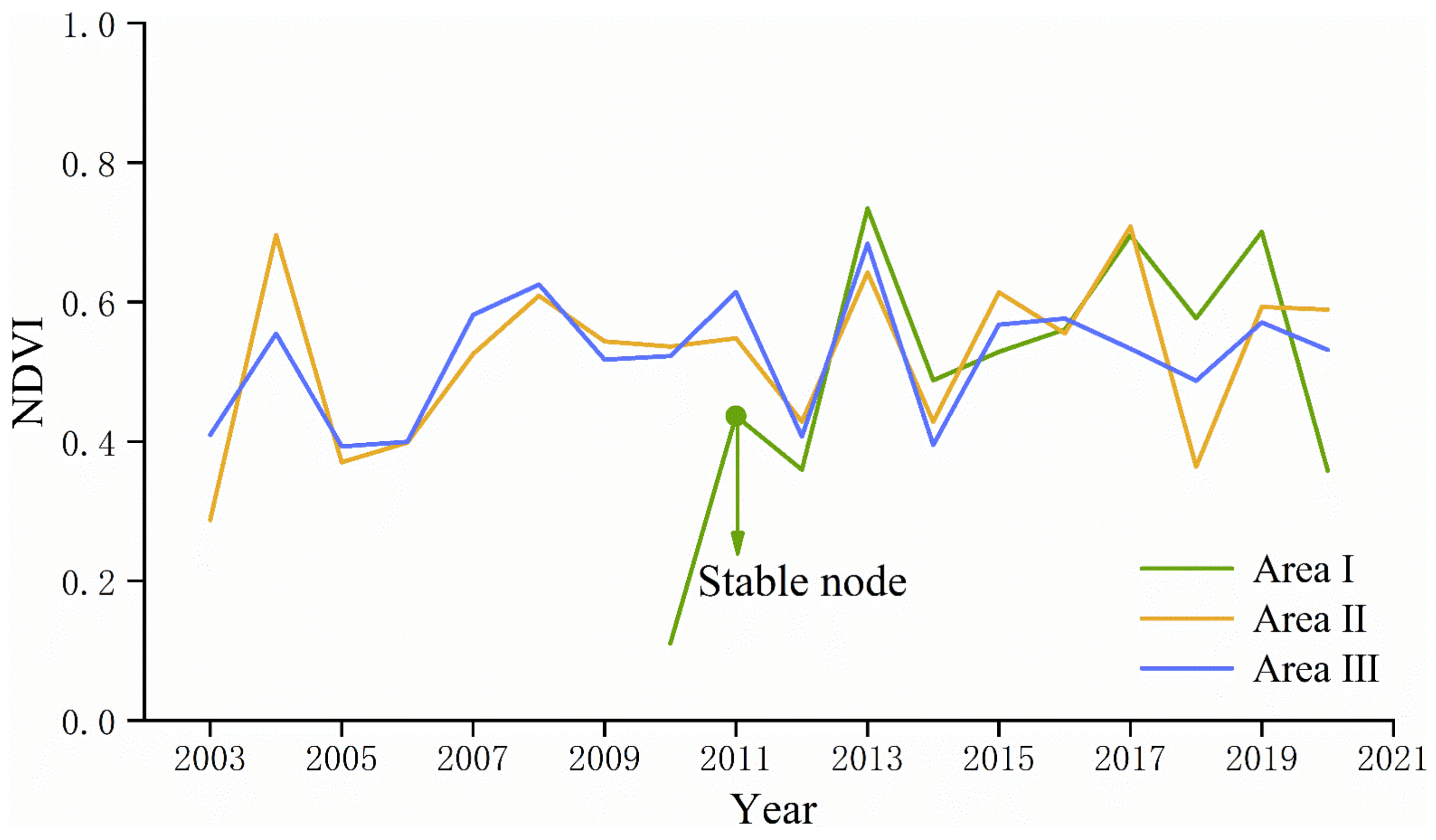
3.2. Monitoring Results in the West Dump
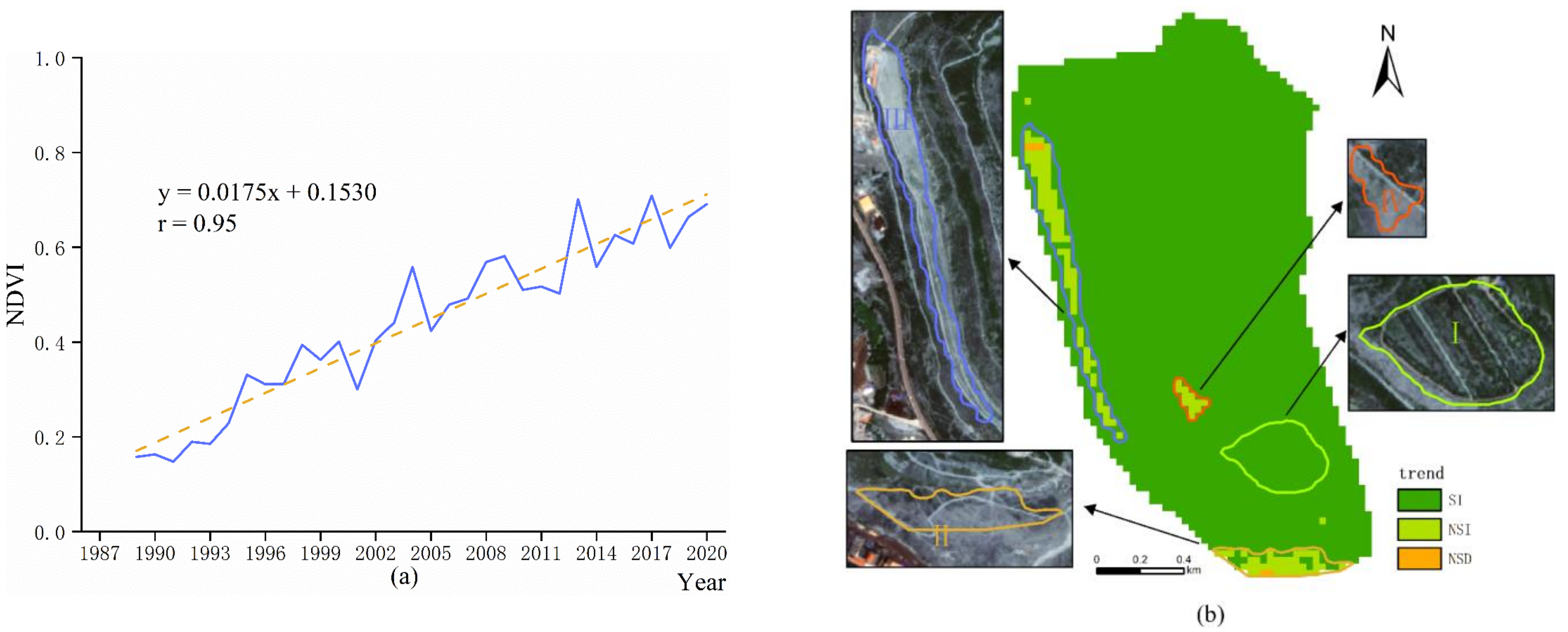
3.3. Monitoring Results in the West Expansion Dump
3.4. Monitoring Results in the Inner Dump
4. Discussion
4.1. The Influence of Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Cangue on Vegetation
4.2. The Influence of Terrain on Vegetation
4.3. The Role of Vegetation in Soil Erosion
4.4. Limitations of Interactive Interpretation
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- After regreening, NDVI values all showed increasing trends within a short period. Moreover, due to the distinction in the reclamation mode, the growth trends of regreening vegetation in each dump showed certain regularity. The main performance is: the earlier the regreening time, the more areas that are covered by significantly improved vegetation. In this study: 97.31% (the proportion of significantly improved vegetation in the south dump) > 95.58% (the proportion in the west dump) > 86.56% (the proportion in the inner dump) > 79.89% (the proportion in the west expansion dump).
- (2)
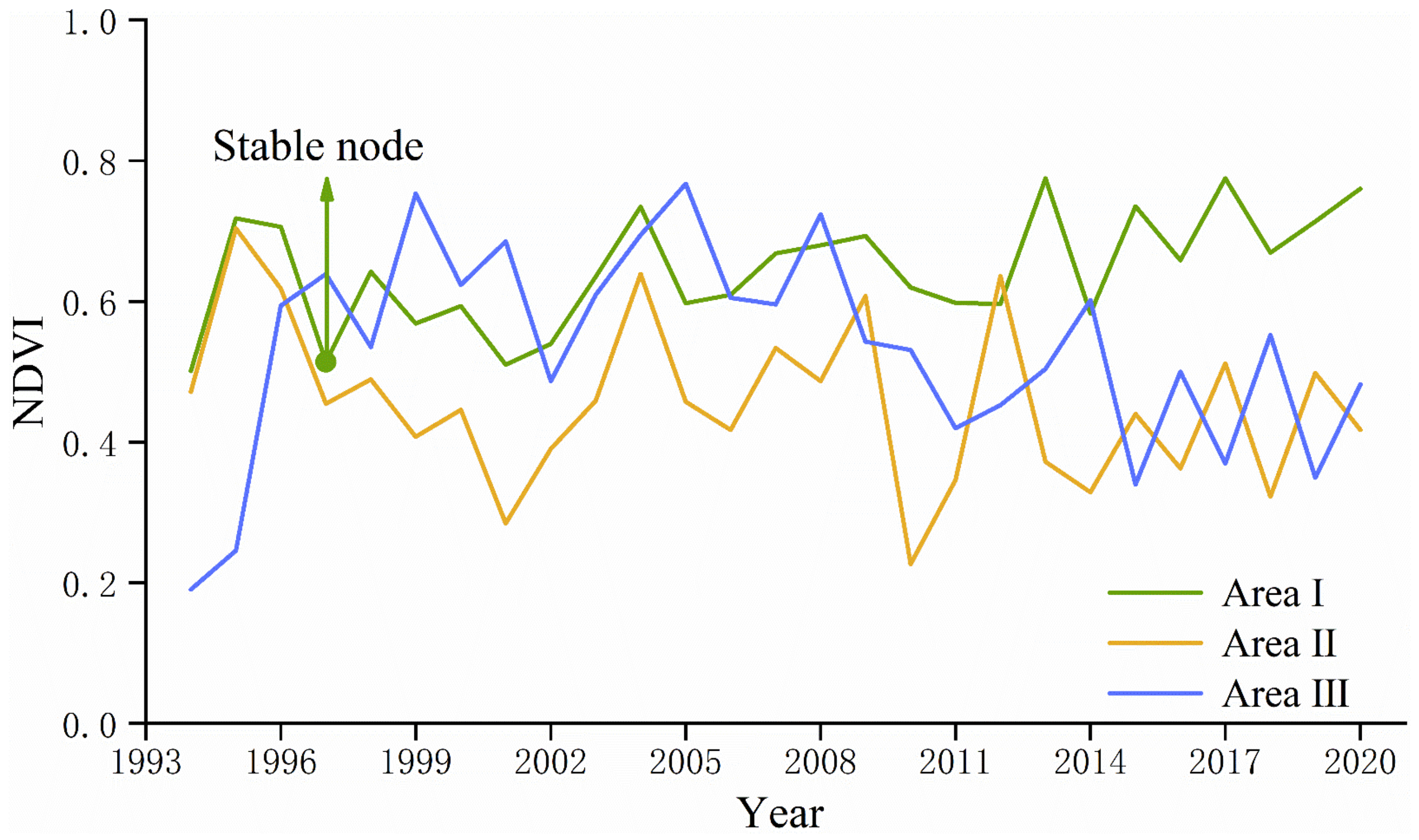
- Different types of regreening vegetation have different time points for reaching stability. In this study, by extracting the “typical area” with significantly increasing trends in NDVI values for the Mann–Kendall mutation test, it takes about three years for wood, shrub, and a mix of grass, and shrub and wood to reach stability, but only one year for grass.
- (3)
- The degraded areas in the mining area were expansive and repetitive. Repeatability means that the degraded area was very likely to degrade once more after the second revival. For example, area III in the west dump was damaged in 2000 and 2013, respectively. Expansion means that the degraded area may extend to the surroundings in the next degradation, similar to area III in the south dump.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, G.A.S. Coal and climate change. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim. Chang. 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D. Current status, challenges and policy recommendations regarding the sustainable development of mining areas in China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2014, 5, 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Qin, Q.; Bai, Z. Characterizing the effects of opencast coal-mining and land reclamation on soil macropore distribution characteristics using 3D CT scanning. CATENA 2018, 171, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Niu, S.; Bai, Z. The reclaimed coal mine ecosystem diverges from the surrounding ecosystem and reaches a new self-sustaining state after 20–23 years of succession in the Loess Plateau area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 727, 138739. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, Y. Optimization scheme on internal and external dump in Xinjiang south open-pit coal mine. Opencast Min. Technol. 2015, 1, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Keesstra, S.; Nunes, J.; Novara, A.; Finger, D.; Avelar, D.; Kalantari, Z.; Cerdà, A. The superior effect of nature based solutions in land management for enhancing ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keesstra, S.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Azorin-Molina, C.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; Cerdà, A. Effects of soil management techniques on soil water erosion in apricot orchards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Zimmermann, N.E. Predictive habitat distribution models in ecology. Ecol. Model. 2000, 135, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Bai, Y.; Lei, S.; Deng, K. Time-series SBAS pixel offset tracking method for monitoring three-dimensional deformation in a mining area. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 118787–118798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Song, W.; Gu, H.; Li, F. Progress in the remote sensing monitoring of the ecological environment in mining areas. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, K.; Robertson, C.; Braun, D.; Greig, C. U-Net convolutional neural network models for detecting and quantifying placer mining disturbances at watershed scales. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 104, 102510. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. A new index for delineating built-up land features in satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 4269–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Wu, J.; Lu, S.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, X.; Song, L. Soil and soil environmental quality monitoring in China: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, F.; Sheykhi, V.; Salari, M.; Bagheri, A. Soil quality assessment using GIS-based chemometric approach and pollution indices: Nakhlak mining district, Central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Zha, Y. Hyperspectral sensing of heavy metals in soil and vegetation: Feasibility and challenges. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 136, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doña, C.; Chang, N.-B.; Caselles, V.; Sánchez, J.M.; Camacho, A.; Delegido, J.; Vannah, B.W. Integrated satellite data fusion and mining for monitoring lake water quality status of the Albufera de Valencia in Spain. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 416–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, D.; Zhang, L.; Jiao, Q.; Li, Q. Application of hyperspectral remote sensing for environment monitoring in mining areas. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padró, J.-C.; Carabassa, V.; Balagué, J.; Brotons, L.; Alcañiz, J.M.; Pons, X. Monitoring opencast mine restorations using Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1602–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Xie, M.M.; Li, H.T.; Feng, Q.Q.; Zhang, C.; Bai, Z.K. Monitoring ecosystem restoration of multiple surface coal mine sites in China via LANDSAT images using the Google Earth Engine. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2936–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Bai, Z.; Cao, Y. Identification of land reclamation stages based on succession characteristics of rehabilitated vegetation in the Pingshuo opencast coal mine. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, K.Z.; Wang, M.J.; Karthikeyan, R. Basin-scale spatial soil erosion variability: Pingshuo opencast mine site in Shanxi Province, Loess Plateau of China. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Li, S. Measurement and prediction of land use conflict in an opencast mining area. Resour. Policy 2021, 71, 101999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Yun, W. Land reclamation in mining area and reutilization of reclaimed land: Taking Pingshuo mining area as an example. Resour. Ind. 2008, 5, 32–37. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Ye, B.; Bai, Z.; Hui, J. Comparison of the vegetation index of reclamation mining areas calculated by multi-source remote sensing data. Land 2022, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S. Spatiotemporal Variation of Dump Reclamation Disturbance Index and Influencing Factors. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Loveland, T.R.; Dwyer, J.L. Landsat: Building a strong future. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. Science of landsat analysis ready data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W. Consistency evaluation of landsat-7 and landsat-8 for improved monitoring of colored dissolved organic matter in complex water. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, Z.; Qin, Q.; Ye, X. A framework of generating land surface reflectance of China early landsat MSS images by visibility data and its evaluation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1802. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Su, B. Significant remote sensing vegetation indices: A review of developments and applications. J. Sens. 2017, 2017, 1353691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y. Extraction of vegetation information from visible unmanned aerial vehicle images. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Mahlein, A.-K.; Oerke, E.-C.; Steiner, U.; Dehne, H.-W. Recent advances in sensing plant diseases for precision crop protection. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2012, 133, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring vegetation systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. NASA Spec. Publ. 1974, 351, 309. [Google Scholar]
- Vanmaercke, M.; Poesen, J.; Maetens, W.; de Vente, J.; Verstraeten, G. Sediment yield as a desertification risk indicator. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1715–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Lei, Y.; Li, C.; Manevski, K.; Shen, Y. Using NDVI percentiles to monitor real-time crop growth. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 162, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León-Tavares, J.; Roujean, J.-L.; Smets, B.; Wolters, E.; Toté, C.; Swinnen, E. Correction of directional effects in VEGETATION NDVI time-series. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, D.; Guo, L. Mapping abandoned farmland in China using time series MODIS NDVI. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142651. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Xia, H.; Jiao, W. Extraction of natural wetland information in Heilongjiang Province based on Sentinel-2A satellite data. Geomat. Spat. Inf. Technol. 2022, 45, 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q. The Research on Non-Linear Regression Analysis Methods. Master’s Thesis, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Achite, M.; Caloiero, T.; Toubal, A.K. Rainfall and runoff trend analysis in the Wadi Mina Basin (Northern Algeria) using non-parametric tests and the ITA method. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militino, A.F.; Moradi, M.; Ugarte, M.D. On the performances of trend and change-point detection methods for remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R. A nonparametric trend test for seasonal data with serial dependence. Water Resour. Res. 1984, 20, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.N.; Sah, S.; Das, B.; Potekar, S.; Chaudhary, A.; Pathak, H. Innovative trend analysis of spatio-temporal variations of rainfall in India during 1901–2019. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2021, 145, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Danandeh Mehr, A.; Azad, N. Trend analysis of hydroclimatological variables in Urmia lake basin using hybrid wavelet Mann–Kendall and Şen tests. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEN P, K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s Tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Soh, L.-K.; Samal, A.; Chen, X.-H. Trend analysis of streamflow drought events in Nebraska. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burn, D.H.; Hag Elnur, M.A. Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J. Hydrol. 2002, 255, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Gong, H.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Gao, M.; Sun, Y. Analysis of the Spatiotemporal variation in land subsidence on the Beijing Plain, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; He, Z. Temperature change characteristics in Gansu Province of China. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 728. [Google Scholar]
- Nádudvari, Á. Thermal mapping of self-heating zones on coal waste dumps in Upper Silesia (Poland)—A case study. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2014, 128–129, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Shao, H.; Liao, Q.; Fan, Y. Experimental study of the effects of stacking modes on the spontaneous combustion of coal gangue. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 123, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Di, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Repairing effects of sulfate-reducing bacteria on the dissolved pollutant of coal gangue based on leaching experiments. Energy Sources Part A 2020, 1–14, 1556–7036. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.F.; Wang, L.A.; Huang, C. Environmental effects of coal gangue and its utilization. Energy Sources Part A 2016, 38, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, K.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y. Estimate of sulfur, arsenic, mercury, fluorine emissions due to spontaneous combustion of coal gangue: An important part of Chinese emission inventories. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, M.; Hu, Z.; Duan, X.; Zhou, T.; Nie, X. Using UAV and field measurement technology to monitor the impact of coal gangue pile temperature on vegetation ecological construction. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Reading, L. Effects of surface coal mining and land reclamation on soil properties: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2019, 191, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Cao, Y.; Bai, Z.; Qin, Q. Effects of soil and topographic factors on vegetation restoration in opencast coal mine dumps located in a loess area. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Lv, C. Effects of vegetation on runoff and soil erosion on reclaimed land in an opencast coal-mine dump in a loess area. Catena 2015, 128, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X. Study on the Relationship among Dump Slope Aspect and the Vegetation Coverage of Large Opencast Coal Mine in Loess Plateau—A Case Study in West Dump in AnTaibao Coal Mine. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.-L.; Tao, Z.-G.; He, M.-C.; Pang, S.-H.; Li, M.-N.; Xu, H.-T. Stability analysis of open-pit gold mine slopes and optimization of mining scheme in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 2997–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X. Re-Established Vegetation Response to Climate Factorson Surface Mined Land. Ph.D. Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Bai, Z.; Chen, W. Ecological reclamation effect of mining dump in Loess area. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 31, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhao, T.; Xie, B.; Cao, F.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y. Simulation of topographic reconstruction of abandoned mine based on sub-watershed natural geomorphology. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 236–244. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Bai, Z.; Sun, H. Do reconstructed landforms have multifractal characteristics? A case study at an opencast coalmine dump in the loess area of China. CATENA 2021, 196, 104925. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Wang, H.; Fu, B.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. Effects of plant diversity on soil erosion for different vegetation patterns. CATENA 2016, 147, 632–637. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Fang, H. Quantitative analysis of driving factors in soil erosion using geographic detectors in Qiantang River catchment, Southeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 134–147. [Google Scholar]
- Keesstra, S.; Nunes, J.P.; Saco, P.; Parsons, T.; Poeppl, R.; Masselink, R.; Cerdà, A. The way forward: Can connectivity be useful to design better measuring and modelling schemes for water and sediment dynamics? Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 1557–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Franch-Pardo, I.; Novara, A.; Sannigrahi, S.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. Examining the effectiveness of catch crops as a nature-based solution to mitigate surface soil and water losses as an environmental regional concern. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 6, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J. Characteristics of soil and water erosion on the slopes with different vegetation patterns in red soil region of Southern China. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 95–99. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Yang, Q.; Tang, D.; Kang, X.; Huang, W. Geochemistry of sulfur and elements in coals from the Antaibao surface mine, Pingshuo, Shanxi Province, China. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2001, 46, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, Y. One more time: Ecosystem restoration and rehabilitation of mining areas. China Land Sci. 2018, 32, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Wang, J. On methods and experiences of land cover information interpretation based on high resolution images in national geographic conditions monitoring. Stand. Surv. Mapp. 2015, 31, 5–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pengra, B.W.; Stehman, S.V.; Horton, J.A.; Dockter, D.J.; Schroeder, T.A.; Yang, Z.; Cohen, W.B.; Healey, S.P.; Loveland, T.R. Quality control and assessment of interpreter consistency of annual land cover reference data in an operational national monitoring program. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 238, 111261. [Google Scholar]
- Tarko, A.; Tsendbazar, N.E.; de Bruin, S.; Bregt, A.K. Influence of image availability and change processes on consistency of land transformation interpretations. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 86, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Khandelwal, A.; Gerber, J.; Carlson, K.; West, P.; Kumar, V. Learning large-scale plantation mapping from imperfect annotators. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (IEEE BigData 2016), Washington, DC, USA, 5–8 December 2016; pp. 1192–1201. [Google Scholar]



| Sensor Type | Spatial Resolution (m) | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Landsat 4/5 TM | 30 × 30 | 1986–2011 |
| HJ1B CCD2 | 30 × 30 | 2012 |
| Landsat 8 OLI | 30 × 30 | 2013–2020 |
| Trend Features | ||
|---|---|---|
| > 0 | > 1.96 | Significant Increase |
| < 1.96 | Not Significant Increase | |
| = 0 | Any value | No Change |
| < 0 | < 1.96 | Not Significant Decrease |
| > 1.96 | Significant Decrease |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Ye, B.; Bai, Z.; Feng, Y. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Reclamation in the Antaibao Open-Pit Mine. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225634
Hu J, Ye B, Bai Z, Feng Y. Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Reclamation in the Antaibao Open-Pit Mine. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(22):5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225634
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jiameng, Baoying Ye, Zhongke Bai, and Yu Feng. 2022. "Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Reclamation in the Antaibao Open-Pit Mine" Remote Sensing 14, no. 22: 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225634
APA StyleHu, J., Ye, B., Bai, Z., & Feng, Y. (2022). Remote Sensing Monitoring of Vegetation Reclamation in the Antaibao Open-Pit Mine. Remote Sensing, 14(22), 5634. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14225634







