Automatic Extraction of Discontinuity Traces from 3D Rock Mass Point Clouds Considering the Influence of Light Shadows and Color Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
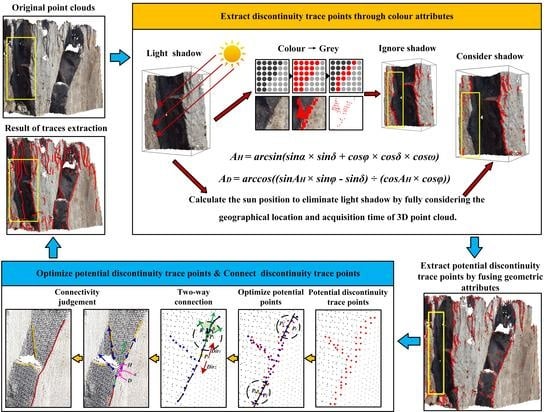
2. Methodology
- Acquire 3D point clouds.
- Extract the potential discontinuity trace points from the color attributes of the 3D point clouds.
- Extract potential discontinuity trace points from the geometric attributes of the 3D point clouds.
- Use a local line normalization smoothing technique to optimize the potential discontinuity trace points.
- Use an algorithm for establishing the two-way connections of a local vector buffer to connect the discontinuity trace points and determine the connectivity of the discontinuity traces at the same time. Finally, obtain the discontinuity traces of the rock mass’s surface.
- Calculate the area density and the average trace length of the rock mass.
2.1. Description of the Datasets
2.1.1. Example Case and Case B
2.1.2. Case A
2.1.3. Case C
2.2. Extraction of Potential Discontinuity Trace Points
2.2.1. Extracting Potential Discontinuity Trace Points from the Color Attributes
2.2.2. Extracting the Potential Discontinuity Trace Points from the Geometric Attributes
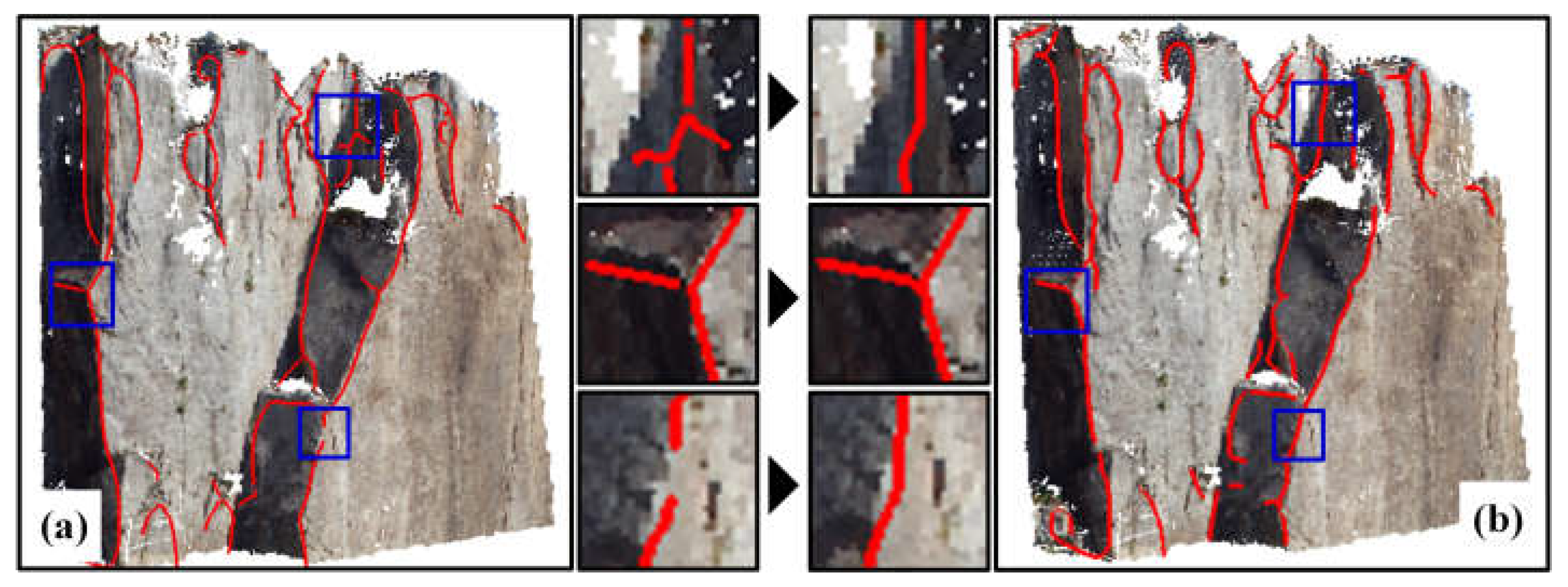
2.3. Optimization of Potential Discontinuity Trace Points
2.4. Connecting the Discontinuity Trace Points
2.5. Calculation of the Area Density
3. Case Studies
3.1. Case A: Overall Process Analysis and Comparison
3.2. Case B: Comparison of the Results of the Proposed Method with Those of Existing Methods
3.3. Case C: Comparison of the Results of the Proposed Method with Those of Existing Methods
3.4. Calculation of the Area Density and the Average Discontinuity Trace Length
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, J.T.; Wu, L.X.; Zhang, M.M.; Liu, S.J.; Sun, X.Y. Towards automatic discontinuity trace extraction from rock mass point cloud without triangulation. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2018, 112, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, L.X.; Liu, S.J.; Yang, T.H.; Zhu, W.C.; Zhang, Z.R. A geometry- and texture-based automatic discontinuity trace extraction method for rock mass point cloud. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2019, 124, 104132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lan, Z.G.; Ma, Z.F.; Tan, C.; Que, J.S.; Wang, F.Y.; Cao, C. Determination of statistical discontinuity persistence for a rock mass characterized by non-persistent fractures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2020, 126, 104177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, A.J.; Abelian, A.; Tomas, R. Discontinuity spacing analysis in rock masses using 3D point clouds. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.F.; Cao, B.; Tang, H.M. Rock Discontinuities Identification from 3D Point Clouds Using Artificial Neural Network. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2022, 55, 1705–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, P.N.; Wu, L.X.; Zhou, W.H.; Yu, Y.N. Towards semi-automatic rock mass discontinuity orientation and set analysis from 3D point clouds. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 103, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lato, M.; Kemeny, J.; Harrap, R.M.; Bevan, G. Rock bench: Establishing a common repository and standards for assessing rockmass characteristics using LiDAR and photogrammetry. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 50, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Kemeny, J.; Jiang, Q.H.; Pan, Z.W. Automatic extraction of blocks from 3D point clouds of fractured rock. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 109, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, L.; Walton, G.; Kromer, R. Classification methods for point clouds in rock slope monitoring: A novel machine learning approach and comparative analysis. Eng. Geol. 2019, 263, 105326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, A.J.; Tomas, R.; Abellan, A. Characterization of rock slopes through slope mass rating using 3D point clouds. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2016, 84, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Ni, P.P.; Guo, M.D. Spatial characterization of joint planes and stability analysis of tunnel blocks. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 38, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.; Sarkar, K.; Singh, A.K.; Chawla, S. Preliminary slope stability analysis and discontinuities driven susceptibility zonation along a crucial highway corridor in higher Himalaya, India. J. Mt. Sci. 2020, 17, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Ruan, Y.K. Estimation of mean trace length by setting scanlines in rectangular sampling window. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2016, 84, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menegoni, N.; Giordan, D.; Perotti, C.; Tannant, D.D. Detection and geometric characterization of rock mass discontinuities using a 3D high-resolution digital outcrop model generated from RPAS imagery—Ormea rock slope, Italy. Eng. Geol. 2019, 252, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbit, P.R.; Durkin, P.R.; Hugenholtz, C.H.; Hubbard, S.M.; Kucharczyk, M. 3-D stratigraphic mapping using a digital outcrop model derived from UAV images and structure-from-motion photogrammetry. Geosphere 2018, 14, 2469–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesley, J.T.; Leier, A.L.; White, S.; Torres, R. Using unmanned aerial vehicles and structure-from-motion photogrammetry to characterize sedimentary outcrops: An example from the Morrison Formation, Utah, USA. Sediment. Geol. 2017, 354, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncella, R.; Forlani, G.; Remondino, F. Photogrammetry for geological applications: Automatic retrieval of discontinuity orientation in rock slopes. Conf. Videometrics VIII 2005, 5665, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Corradetti, A.; McCaffrey, K.; De Paola, N.; Tavani, S. Evaluating roughness scaling properties of natural active fault surfaces by means of multi-view photogrammetry. Tectonophysics 2017, 717, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigli, G.; Casagli, N. Semi-automatic extraction of rock mass structural data from high resolution LIDAR point clouds. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.E.; Shakoor, A.; Watts, C.F. Comparing discontinuity orientation data collected by terrestrial LiDAR and transit compass methods. Eng. Geol. 2014, 181, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudal, P.; Grenon, M.; Turmel, D.; Locat, J. Analysis of a Large Rock Slope Failure on the East Wall of the LAB Chrysotile Mine in Canada: LiDAR Monitoring and Displacement Analyses. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2017, 50, 807–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Palma, B.; Ruocco, A.; Parise, M. Discontinuity Characterization of Rock Masses through Terrestrial Laser Scanner and Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Techniques Aimed at Slope Stability Assessment. Appl. Sci.-Basel 2020, 10, 2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Xiao, A.C.; Wu, L.; Mao, L.G. Automatic fracture detection based on Terrestrial Laser Scanning data: A new method and case study. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 106, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Tong, L.H.; Li, M.C.; Liu, Y.X. Semi-Automatic Registration of Airborne and Terrestrial Laser Scanning Data Using Building Corner Matching with Boundaries as Reliability Check. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6260–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battulwar, R.; Zare-Naghadehi, M.; Emami, E.; Sattarvand, J. A state-of-the-art review of automated extraction of rock mass discontinuity characteristics using three-dimensional surface models. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 13, 920–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeny, J.; Post, R. Estimating three-dimensional rock discontinuity orientation from digital images of fracture traces. Comput. Geosci. 2003, 29, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemy, F.; Hadjigeorgiou, J. Discontinuity trace map construction using photographs of rock exposures. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2003, 40, 903–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umili, G.; Ferrero, A.; Einstein, H.H. A new method for automatic discontinuity traces sampling on rock mass 3D model. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 51, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.H.; Wu, F.Q.; Saroglou, C. Automatic identification and characterization of discontinuities in rock masses from 3D point clouds. Eng. Geol. 2019, 265, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.F.; Tang, H.M.; Xia, D.; Wang, L.Q.; Zhao, B.B.; Teaway, J.W.; Chen, H.Z.; Zhou, T. Automated measurements of discontinuity geometric properties from a 3D-point cloud based on a modified region growing algorithm. Eng. Geol. 2018, 242, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhu, H.H. A new method for automated discontinuity trace mapping on rock mass 3D surface model. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 89, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.S.; Wu, W.; Zhu, H.H.; Zhang, L.Y.; Li, X.J.; Zhang, H. A modified method of discontinuity trace mapping using three-dimensional point clouds of rock mass surfaces. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 12, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, W.; Burge, M.J. Digital Image Processing; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 387–388. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. Threshold selection method from gray-level historams. Ieee Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




















| Case | Area Density of the Rock Mass | Average Discontinuity Trace Length/m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing Method | Proposed Method | Existing Method | Proposed Method | |
| Case A | 2.0159 | 2.1904 | 0.5116 | 0.7561 |
| Case B | 0.6764 | 0.9872 | 1.7891 | 2.1875 |
| Case C | 4.2605 | 4.6567 | 0.1366 | 0.1895 |
| Parameter | Meaning | Value Range | Best Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| search radius | r– | 6r | |
| direction threshold | 0–90 | 25 | |
| connection radius | r– | 15r | |
| direction offset | 0–90 | 45 | |
| spatial offset | r– | 2r |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Mao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, W.; Yang, T. Automatic Extraction of Discontinuity Traces from 3D Rock Mass Point Clouds Considering the Influence of Light Shadows and Color Change. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215314
Guo J, Zhang Z, Mao Y, Liu S, Zhu W, Yang T. Automatic Extraction of Discontinuity Traces from 3D Rock Mass Point Clouds Considering the Influence of Light Shadows and Color Change. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215314
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jiateng, Zirui Zhang, Yachun Mao, Shanjun Liu, Wancheng Zhu, and Tianhong Yang. 2022. "Automatic Extraction of Discontinuity Traces from 3D Rock Mass Point Clouds Considering the Influence of Light Shadows and Color Change" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215314
APA StyleGuo, J., Zhang, Z., Mao, Y., Liu, S., Zhu, W., & Yang, T. (2022). Automatic Extraction of Discontinuity Traces from 3D Rock Mass Point Clouds Considering the Influence of Light Shadows and Color Change. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5314. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215314