RSEI or MRSEI? Comment on Jia et al. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Comparison of RSEI with MRSEI
2.1. RSEI
2.2. MRSEI
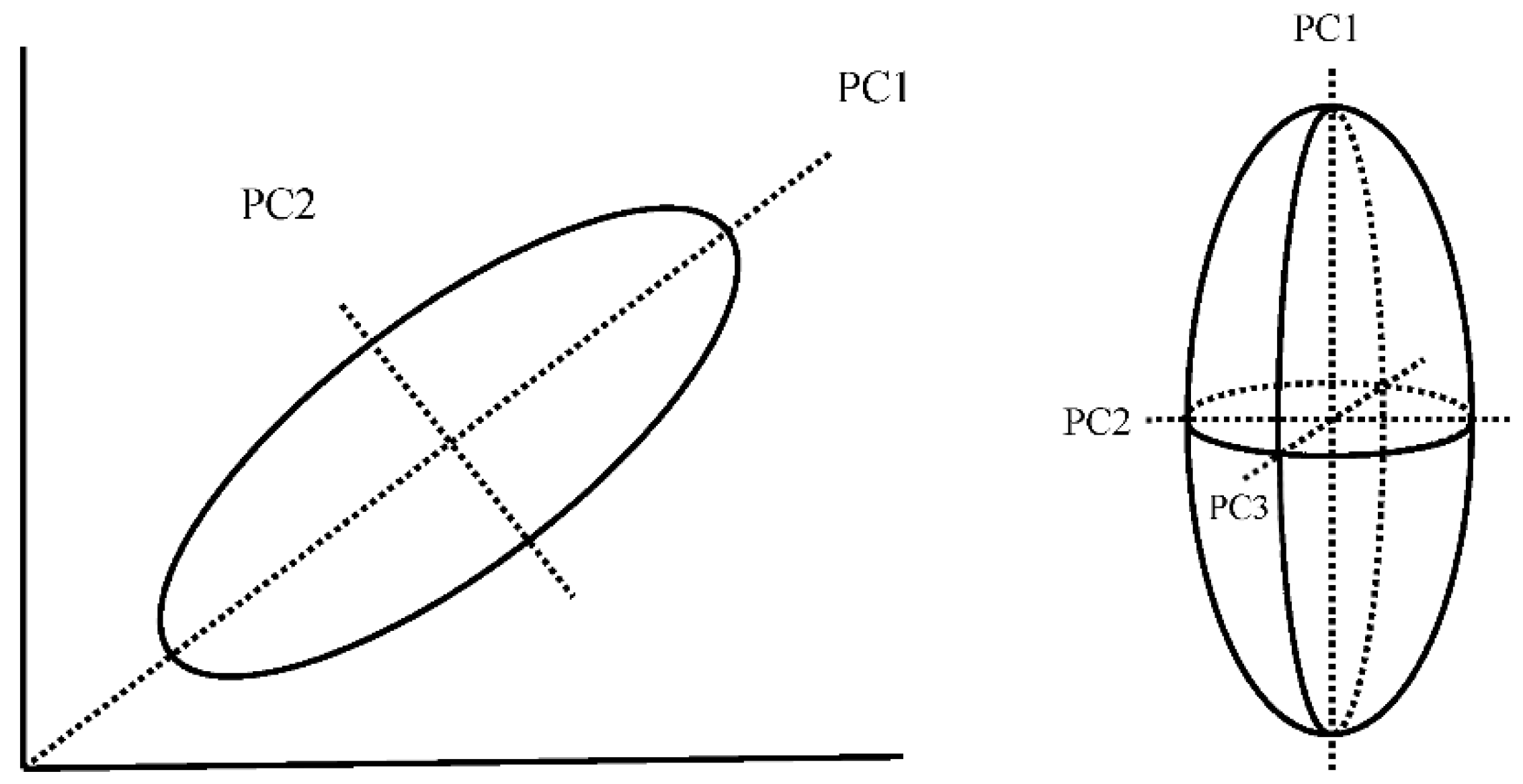
2.3. Principal Component Transformation
3. Case of the Qaidam Basin
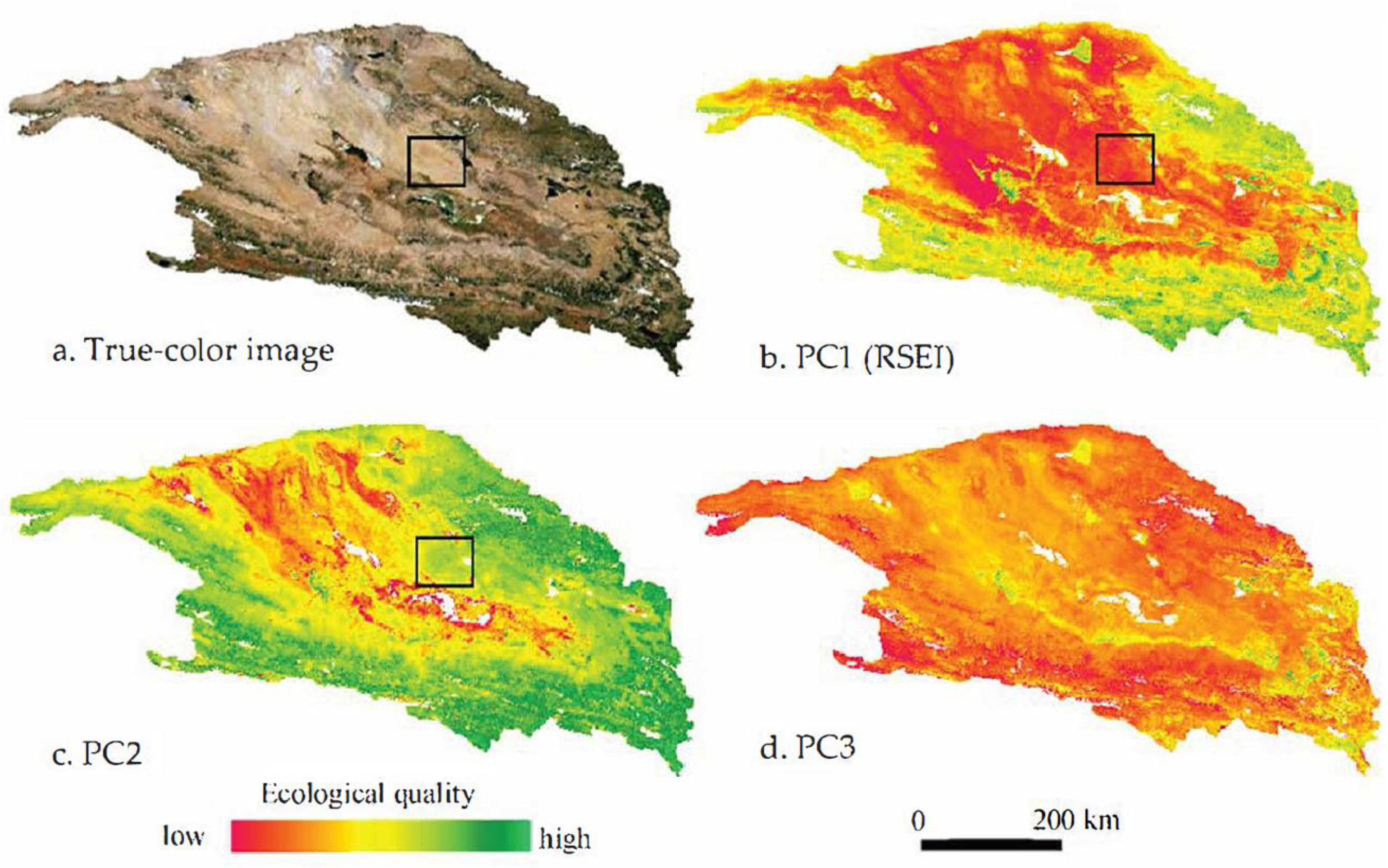
3.1. Characteristics of PCs 1, 2, and 3
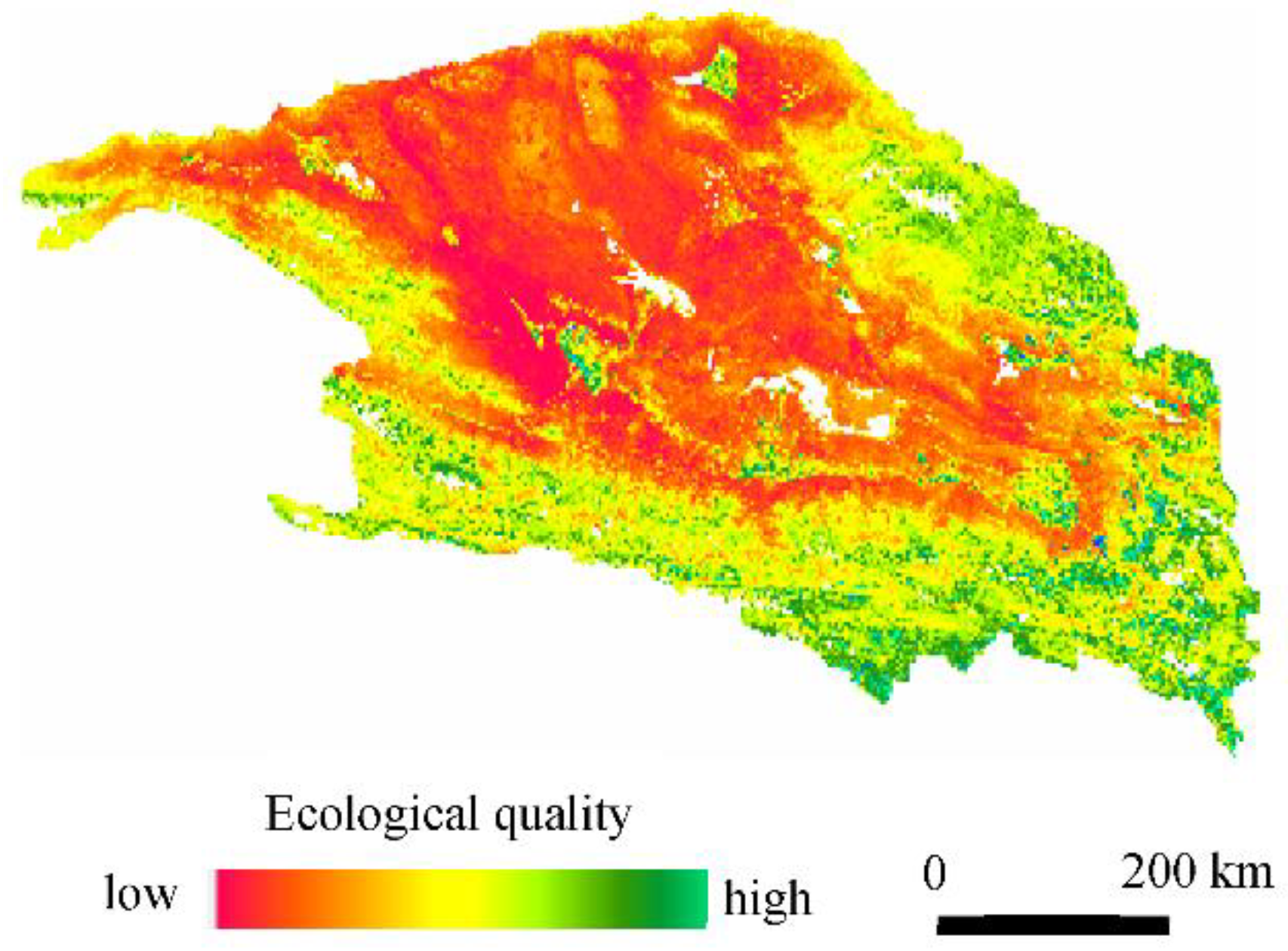
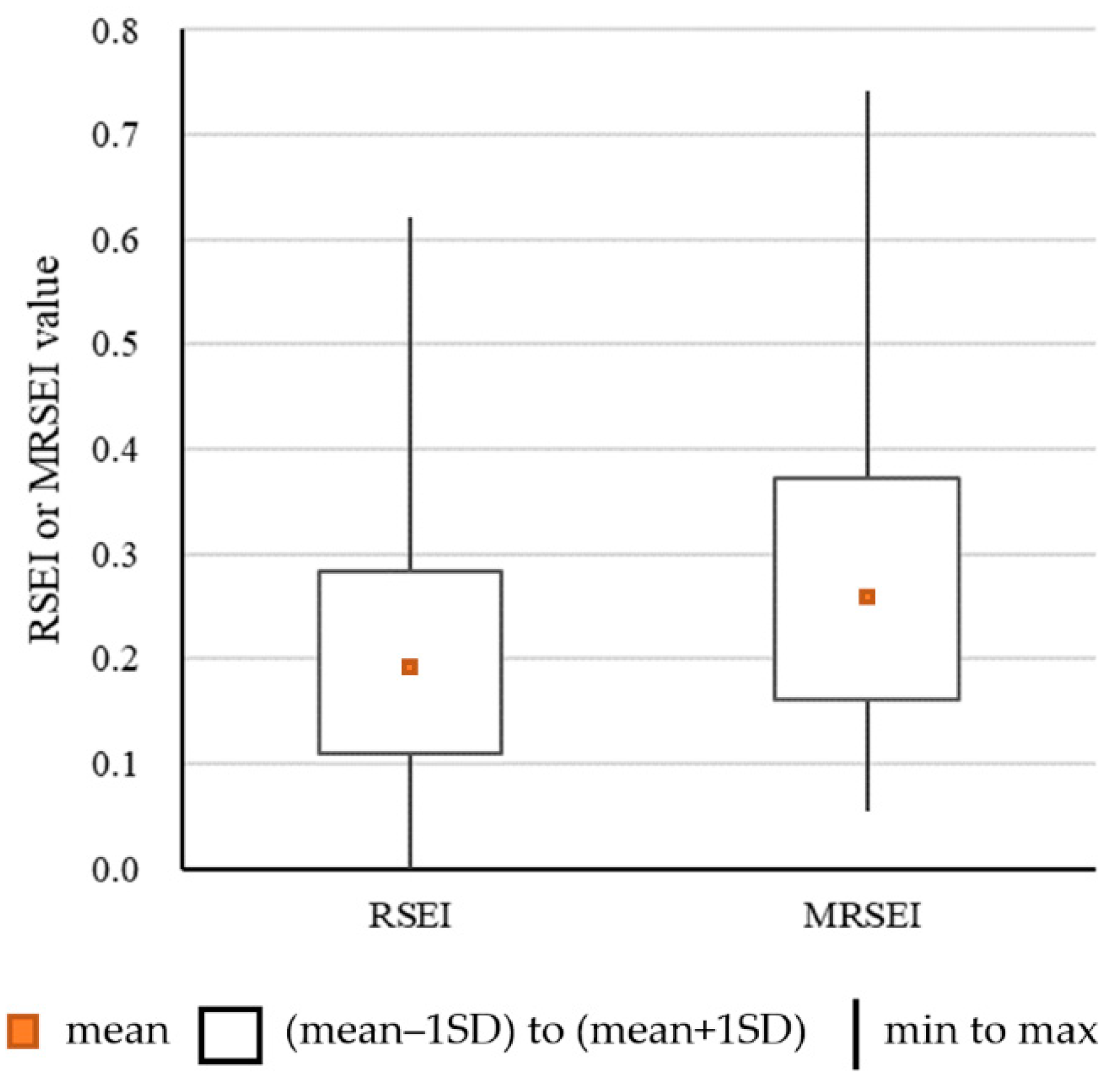
3.2. Quantitative Comparison between RSEI and MRSEI
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jia, H.; Yan, C.; Xing, X. Evaluation of eco-environmental quality in Qaidam Basin based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Xu, W.; Lu, N.; Huang, S.; Wu, C.; Wang, L.; Dai, F.; Kou, W. Assessment of spatial–temporal changes of ecological environment quality based on RSEI and GEE: A case study in Erhai Lake Basin, Yunnan province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firozjaei, M.K.; Kiavarz, M.; Homaee, M.; Arsanjani, J.J.; Alavipanah, S.K. A novel method to quantify urban surface ecological poorness zone: A case study of several European cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, S. Dynamic monitoring of eco-environmental quality in arid desert area by remote sensing: Taking the Gurbantunggut Desert China as an example. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 30, 877–883. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, F.; Li, M. Assessing land cover and ecological quality changes under the new-type urbanization from multi-source remote sensing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing index for assessment of regional ecological changes. China Environ. Sci. 2013, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Q.; Wang, M.Y.; Shi, T.T.; Guan, H.D.; Fang, C.Y.; Lin, Z.L. Prediction of ecological effects of potential population and impervious surface increases using a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI). Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilt, J.H.; Unfried, T.M.; Roca, B. Using objective and subjective measures of neighborhood greenness and accessible destinations for understanding walking trips and BMI in Seattle, Washington. Am. J. Health Promot. 2007, 21, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts, A.M.; Harris, R.J.; Phan, T.; Livesley, S.J.; Williams, N.S.G.; Tapper, N.J. Thermal infrared remote sensing of urban heat: Hotspots, vegetation, and an assessment of techniques for use in urban planning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.W.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring Vegetation Systems in the Great Plains with ERTS. In Proceedings of the 3rd ERTS Symposium, Washington, DC, USA, 10–14 December 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Crist, E.P. A TM tasseled cap equivalent transformation for reflectance factor data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1985, 17, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, M.H.A.; Zhang, L.F.; Shuai, T.; Tong, Q.X. Derivation of a tasselled cap transformation based on Landsat 8 at-satellite reflectance. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.S.; Rogers, A.S.; Townshend, J.R.G.; Lawrence, W.T.; Dorn, K.; Eldred, K.; Stutzer, D.; Lindsay, F.; Rizzo, E. Developing a Model for Determining Coastal Marsh “Health”. In Proceedings of the 3rd Thematic Conference on Remote Sensing for Marine and Coastal Environments, Seattle, WA, USA, 18–20 September 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, P.; Ma, M.; Zhou, X.; Liao, T.; Wu, S. Effects of long-term and large-scale ecology projects on forest dynamics in Yangtze River Basin, China. Forest Ecol. Manag. 2021, 496, 119463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.A.; Baral, P.; Yaragal, S.; Pradhan, B. Bulk processing of multi-temporal Modis data, statistical analyses and machine learning algorithms to understand climate variables in the Indian Himalayan region. Sensors 2021, 21, 7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, R.; Ojeda, N.; Azócar, J.; Venegas, C.; Inostroza, L. Application of NDVI for identify potentiality of the urban forest for the design of a green corridors system in intermediary cities of Latin America: Case study, Temuco, Chile. Urban For. Urban Green. 2020, 55, 126821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. A remote sensing urban ecological index and its application. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7853–7862. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Z.W.; Niu, R. Detecting ecological spatial-temporal changes by remote sensing ecological index with local adaptability. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.K.; Amoushahi, S.; Gholipour, M. Spatiotemporal ecological quality assessment of metropolitan cities: A case study of central Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.T.; Xu, H.Q. Assessing fractional vegetation cover changes and ecological quality of the Wuyi Mountain National Nature Reserve based on remote sensing spatial information. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 533–542. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Guan, H.D.; Shi, T.T.; Hu, X.S. Detecting ecological changes with a remote sensing based ecological index (RSEI) produced time series and change vector analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, S.; Alavipanah, S.K.; Konyushkova, M.; Mijani, N.; Fathololomi, S.; Firozjaei, M.K.; Homaee, M.; Hamzeh, S.; Kakroodi, A.A. A Remotely sensed assessment of surface ecological change over the Gomishan Wetland. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.Q.; Zhang, F.; He, Y.F.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.C.; Arikena, M. Assessment of spatial and temporal variation of ecological environment quality in Ebinur Lake Wetland National Nature Reserve, Xinjiang, China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q.; Zhang, H. Ecological response to urban expansion in an island city: Xiamen, southeastern China. Sci. Geogr. Sinica 2015, 35, 867–872. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Yang, M.H.; Hou, Y.T.; Zhao, Y.N.; Xue, X.Z. Spatiotemporal evolution of island ecological quality under different urban densities: A comparative analysis of Xiamen and Kinmen Islands, southeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 124, 107438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Airiken, M.; Zhang, F.; Chan, N.W.; Kung, H. Assessment of spatial and temporal ecological environment quality under land use change of urban agglomeration in the North Slope of Tianshan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12282–12299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.M.; Xue, L. Dynamic monitoring and analysis of ecological environment in Weinan City, Northwest China based on RSEI model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 27, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Sun, C.J.; Sun, J.L.; Chen, W.; Li, X.G. Ecological security characteristics of main irrigated agricultural areas on the Loess Plateau based on remote sensing information. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, X.R.; Hu, Z.Q.; Zhu, Q.; Ruan, M.Y. Research on temporal and spatial resolution and the driving forces of ecological environment quality in coal mining areas considering topographic correction. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.M.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuju, D.R.; Paull, D.J.; Griffin, A.L. Change detection techniques based on multispectral images for investigating land cover dynamics. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meer, F.D.; van der Werff, H.M.A.; van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A.; Hecker, C.A.; Bakker, W.H.; Noomen, M.F.; van der Meijde, M.; Carranza, E.J.M.; de Smeth, J.B.; Woldai, T. Multi- and hyperspectral geologic remote sensing: A review. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2012, 14, 112–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crósta, A.P.; De Souza Filho, C.R.; Azevedo, F.; Brodie, C. Targeting key alteration minerals in epithermal deposits in Patagonia, Argentina, using ASTER imagery and principal component analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4233–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargi, H. Principal components analysis for borate mapping. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of Normalised Difference Water Index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
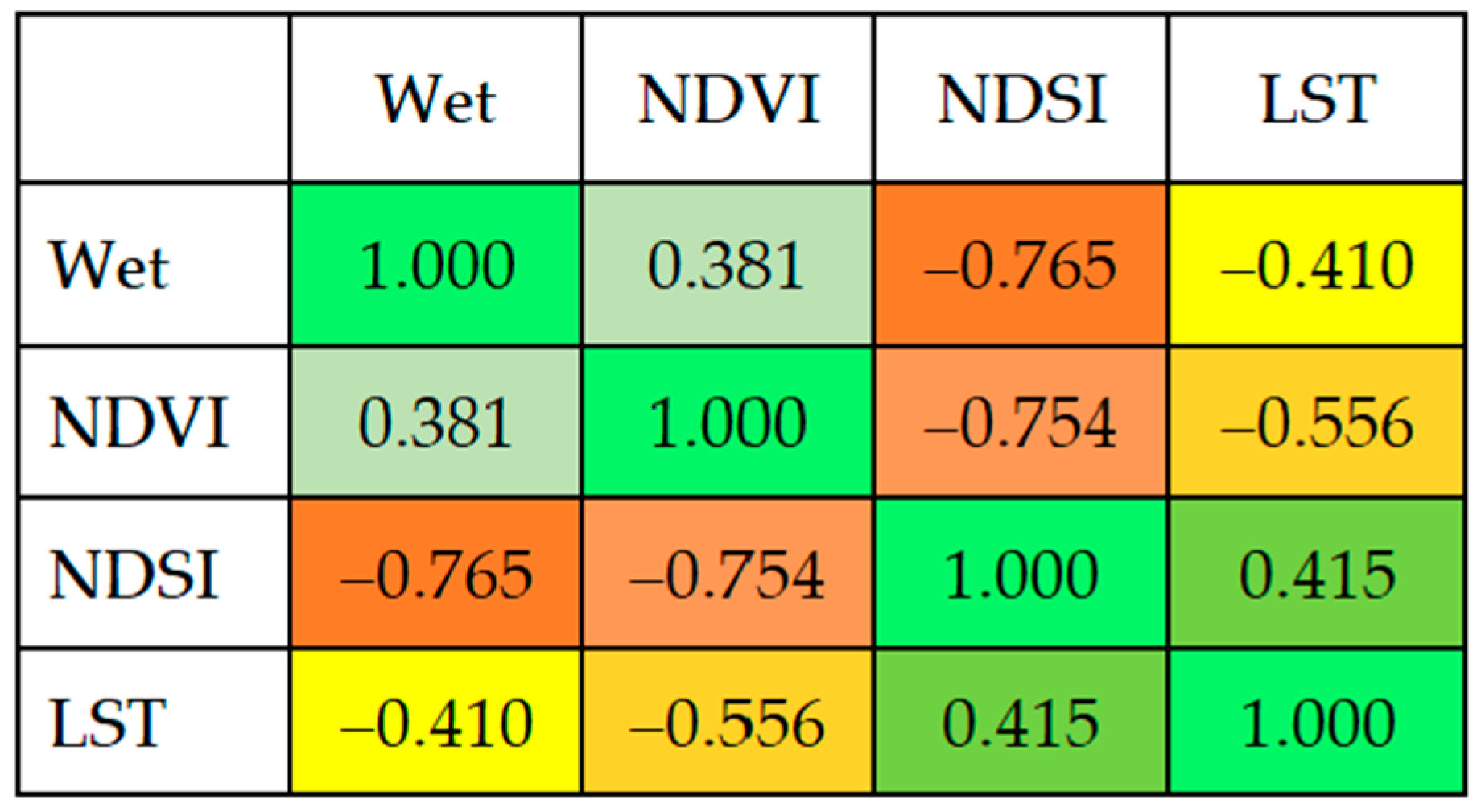
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wet (wetness) | 0.3852 | –0.4742 | 0.1806 | 0.7708 |
| NDVI (greenness) | 0.1958 | 0.6937 | 0.6716 | 0.1716 |
| NDSI (dryness) | –0.4714 | 0.4329 | –0.4659 | 0.6110 |
| LST (heat) | –0.7688 | –0.3263 | 0.5472 | 0.0553 |
| Eigenvalue | 0.0180 | 0.0068 | 0.0044 | 0.0004 |
| Proportional eigenvalue | 0.61 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, H.; Duan, W.; Deng, W.; Lin, M. RSEI or MRSEI? Comment on Jia et al. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215307
Xu H, Duan W, Deng W, Lin M. RSEI or MRSEI? Comment on Jia et al. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(21):5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215307
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Hanqiu, Weifang Duan, Wenhui Deng, and Mengjing Lin. 2022. "RSEI or MRSEI? Comment on Jia et al. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543" Remote Sensing 14, no. 21: 5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215307
APA StyleXu, H., Duan, W., Deng, W., & Lin, M. (2022). RSEI or MRSEI? Comment on Jia et al. Evaluation of Eco-Environmental Quality in Qaidam Basin Based on the Ecological Index (MRSEI) and GEE. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4543. Remote Sensing, 14(21), 5307. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14215307






