An Application of Hyperspectral Image Clustering Based on Texture-Aware Superpixel Technique in Deep Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Introducing a superpixel to replace the fixed spatial structure reduces the possibility of foreign objects in the same area and suppresses noise interference to a certain extent;
- The introduction of the ULBP operator increases the texture perception ability of the superpixel algorithm and alleviates the noise interference caused by the lighting conditions during the segmentation process;
- The recognition task of manganese nodules was completed by fusing the superpixel algorithm and clustering algorithm. The average recognition rate was 83.8%.
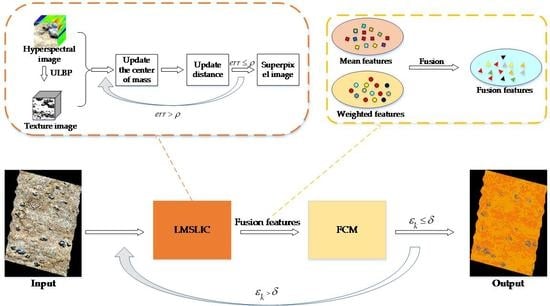
2. Methods
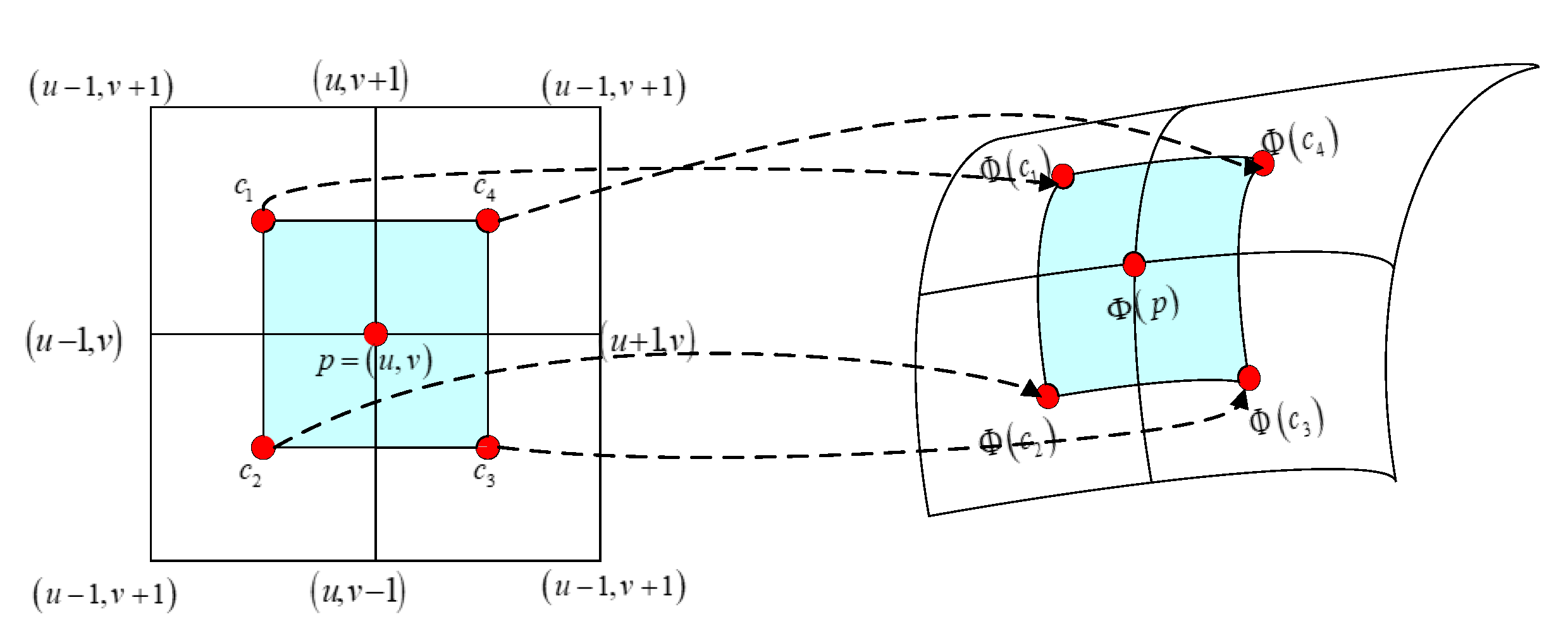
2.1. LMSLIC
2.2. Superpixel Fuzzy Clustering
2.3. Algorithm Process
| Algorithm 1 LMSLIC-FCM |
| Input: Hyperspectral images, , , , , , |
| 1: Obtain |
| 2: Initialize seeds , , , , , calculate and |
| 3: While do |
| 4: While do |
| 5: |
| 6: While do |
| 7: |
| 8: End While |
| 9: |
| 10: While do |
| 11: If then |
| 12: Split huge superpixel |
| 13: End if |
| 14: |
| 15: End while |
| 16: |
| 17: While do |
| 18: |
| 19: If then |
| 20: |
| 21: End if |
| 22: |
| 23: End while |
| 24: |
| 25: While do |
| 26: |
| 27: |
| 28: End while |
| 29: End while |
| 30: |
| 31: End while |
| Output: Classification results |
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Dataset
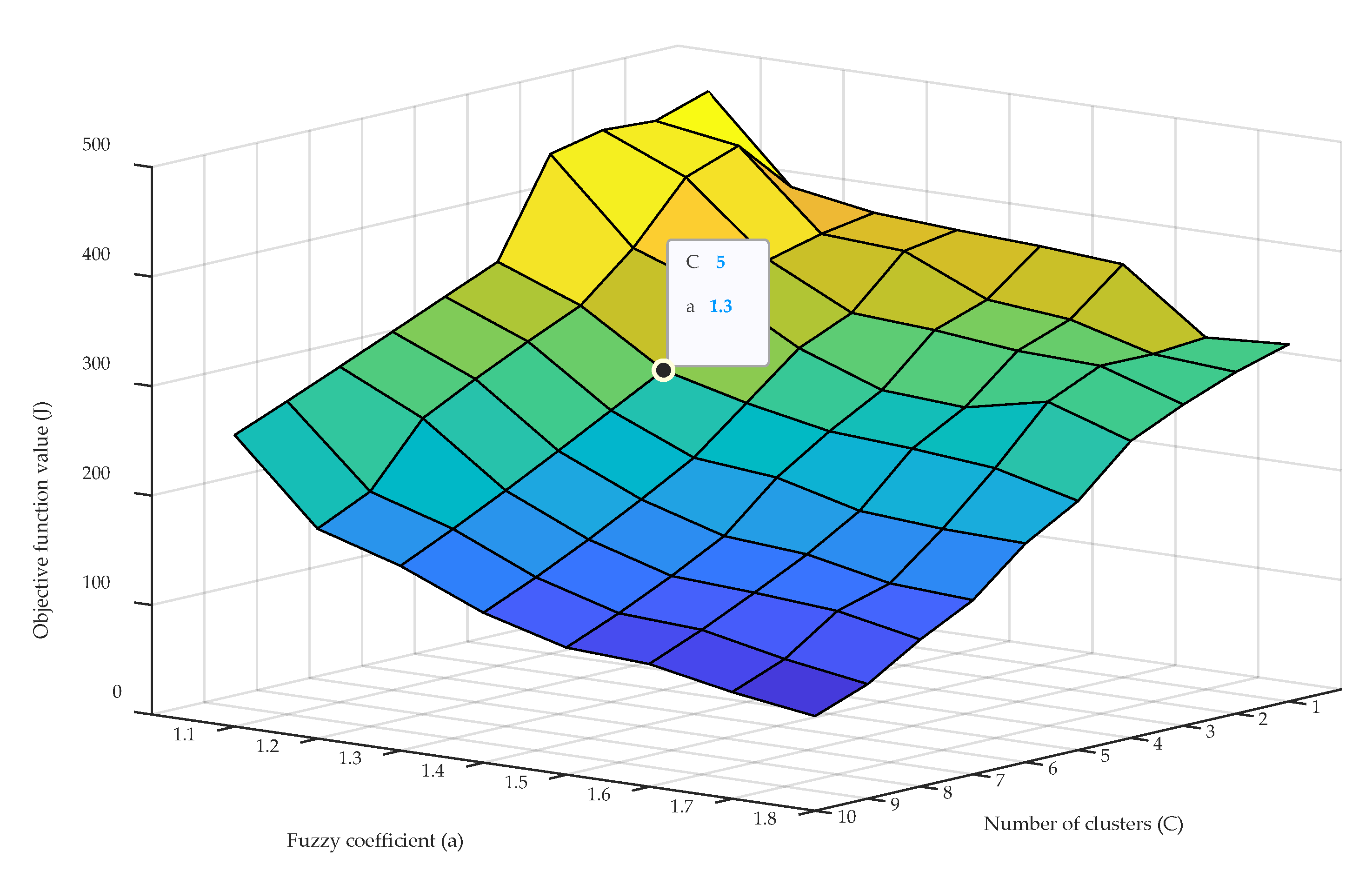
3.2. Experimental Setup
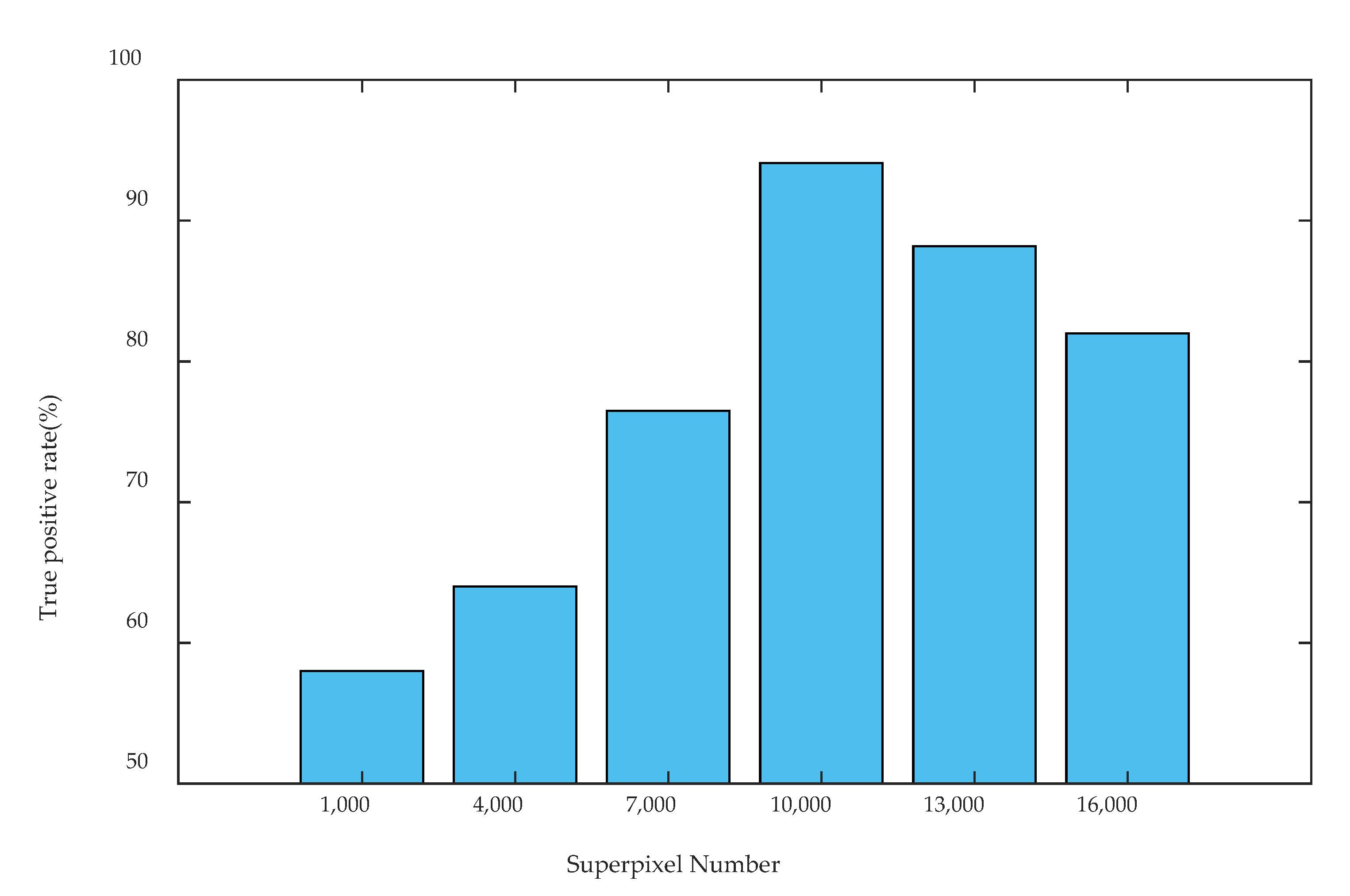
3.3. Superpixel Analysis
3.4. Cluster Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; Hein, J.R.; Dong, Y.; Wang, M.; Ren, X.; Wu, Z.; Li, X.; Chu, F. A possible link between seamount sector-collapse and manganese nodule occurrence in the abyssal plains, NW Pacific Ocean. Ore Geol. Rev. 2021, 138, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.R.; Koschinsky, A.; Kuhn, T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parianos, J.; Lipton, I.; Nimmo, M.J.M. Aspects of estimation and reporting of mineral resources of seabed polymetallic nodules: A contemporaneous case study. Minerals 2021, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucha, J.; Wasilewska-Błaszczyk, M.; Dudek, M. The accuracy of polymetallic nodule resources estimation in the Pacific in the Interoceanmetal area based on samples collected using a box corer. Int. Multidiscip. Sci. GeoConference SGEM 2019, 19, 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; He, G.; Ma, J.; Yu, Z.; Yao, H.; Deng, X.; Liu, F.; Wei, Z. Acoustic quantitative analysis of ferromanganese nodules and cobalt-rich crusts distribution areas using EM122 multibeam backscatter data from deep-sea basin to seamount in Western Pacific Ocean. Deep. Sea Res. Part I: Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 161, 103281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoening, T.; Jones, D.O.; Greinert, J. Compact-morphology-based poly-metallic nodule delineation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasilewska-Błaszczyk, M.; Mucha, J. Possibilities and limitations of the use of seafloor photographs for estimating polymetallic nodule resources—Case study from IOM Area, Pacific Ocean. Minerals 2020, 10, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, A.F. Three decades of hyperspectral remote sensing of the Earth: A personal view. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, S5–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Men, S.; Li, Y.; Ding, Z.; He, J.; Zhao, Z. Underwater hyperspectral imaging technology and its applications for detecting and mapping the seafloor: A review. Sensors 2020, 20, 4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubac, B.; Loisel, H.; Guiselin, N.; Astoreca, R.; Felipe Artigas, L.; Mériaux, X. Hyperspectral and multispectral ocean color inversions to detect Phaeocystis globosa blooms in coastal waters. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2008, 113, C06026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcello, J.; Eugenio, F.; Martín, J.; Marqués, F. Seabed mapping in coastal shallow waters using high resolution multispectral and hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegdan, J.; Ekehaug, S.; Hansen, I.M.; Aas, L.M.S.; Steen, K.J.; Pettersen, R.; Beuchel, F.; Camus, L. Underwater hyperspectral imaging for environmental mapping and monitoring of seabed habitats. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2015-Genova, Genova, Italy, 18–21 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Foglini, F.; Angeletti, L.; Bracchi, V.; Chimienti, G.; Grande, V.; Hansen, I.M.; Meroni, A.N.; Marchese, F.; Mercorella, A.; Prampolini, M. Underwater Hyperspectral Imaging for seafloor and benthic habitat mapping. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for the Sea, Learning to Measure Sea Health Parameters (MetroSea), Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Ødegård, Ø.; Mogstad, A.A.; Johnsen, G.; Sørensen, A.J.; Ludvigsen, M. Underwater hyperspectral imaging: A new tool for marine archaeology. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 3214–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumke, I.; Nornes, S.M.; Purser, A.; Marcon, Y.; Ludvigsen, M.; Ellefmo, S.L.; Johnsen, G.; Søreide, F. First hyperspectral imaging survey of the deep seafloor: High-resolution mapping of manganese nodules. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zheng, E.; Wang, Y.; Gao, F. Recognition of ocean floor manganese nodules by deep kernel fuzzy C-means clustering of hyperspectral images. J. Image Graph. 2021, 26, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Subudhi, S.; Patro, R.N.; Biswal, P.K.; Dell’Acqua, F. A Survey on Superpixel Segmentation as a Preprocessing Step in Hyperspectral Image Analysis. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 5015–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazimali, M.G.; Furxhi, O.; Alahmadi, Y.; Driggers, R. Comparison of illumination sources for imaging systems for different applications. In Proceedings of the Laser Radar Technology and Applications XXIV, Baltimore, MD, USA, 2 May 2019; pp. 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, X. Design of optical system for collimating the light of an LED uniformly. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A-Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2014, 31, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durden, J.M.; Bett, B.J.; Schoening, T.; Morris, K.J.; Nattkemper, T.W.; Ruhl, H.A. Comparison of image annotation data generated by multiple investigators for benthic ecology. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2016, 552, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Li, S. Recent advances on spectral–spatial hyperspectral image classification: An overview and new guidelines. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 56, 1579–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.P.; Prince, S.J.; Warrell, J.; Mohammed, U.; Jones, G. Superpixel lattices. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Bari, Italy, 8–10 October 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Tuzel, O.; Ramalingam, S.; Chellappa, R. Entropy rate superpixel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 2097–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Achanta, R.; Shaji, A.; Smith, K.; Lucchi, A.; Fua, P.; Süsstrunk, S. SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 2274–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Yu, C.-C.; Yu, M.-J.; He, Y. Manifold SLIC: A fast method to compute content-sensitive superpixels. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 651–659. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, B.; Xie, X.; Ma, X.; Ren, G.; Ma, Y. Superpixel-based extended random walker for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3233–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, T.; Ince, T. Sparse representation-based hyperspectral image classification using multiscale superpixels and guided filter. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Bao, W.; Qu, K.; Liang, H. Superpixel-guided preprocessing algorithm for accelerating hyperspectral endmember extraction based on spatial-spectral analysis. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 026514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Tyagi, D.; Sharma, S. Recent advancement of LBP techniques: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computing, Communication and Automation (ICCCA), Greater Noida, India, 29–30 April 2016; pp. 1059–1064. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, J.; Gong, M. Unsupervised hyperspectral band selection by fuzzy clustering with particle swarm optimization. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Lei, C.; Li, F.; Huang, D.; Yang, J. Unsupervised hyperspectral feature selection based on fuzzy C-means and grey wolf optimizer. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 40, 3344–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, K.R.; Khodadadzadeh, M.; Tusa, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Tolosana-Delgado, R.; Gloaguen, R. Hierarchical sparse subspace clustering (HESSC): An automatic approach for hyperspectral image analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zeng, W.; Guan, Q.; Hu, Z. A Sparse topic relaxion and group clustering model for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 4014–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Jia, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Meng, H.; Nandi, A.K. Superpixel-based fast fuzzy C-means clustering for color image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 27, 1753–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumke, I.; Nornes, S. Hyperspectral Imager (UHI) Data Files Acquired on SONNE Cruise SO242/2, ROV Dive SO242/191-1. PANGAEA 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Du, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, L.P. Hyperspectral image classification via a random patches network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 142, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


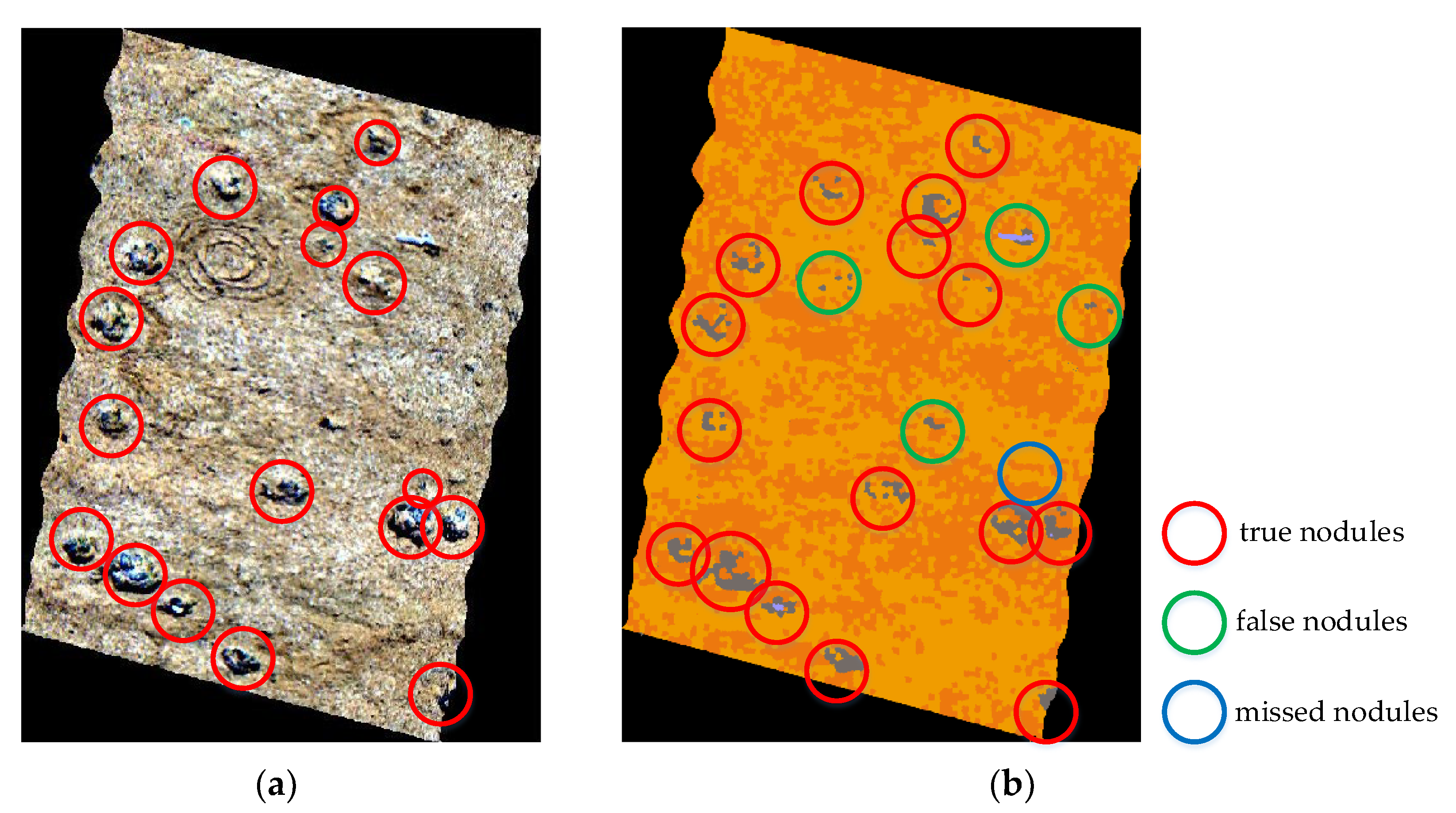
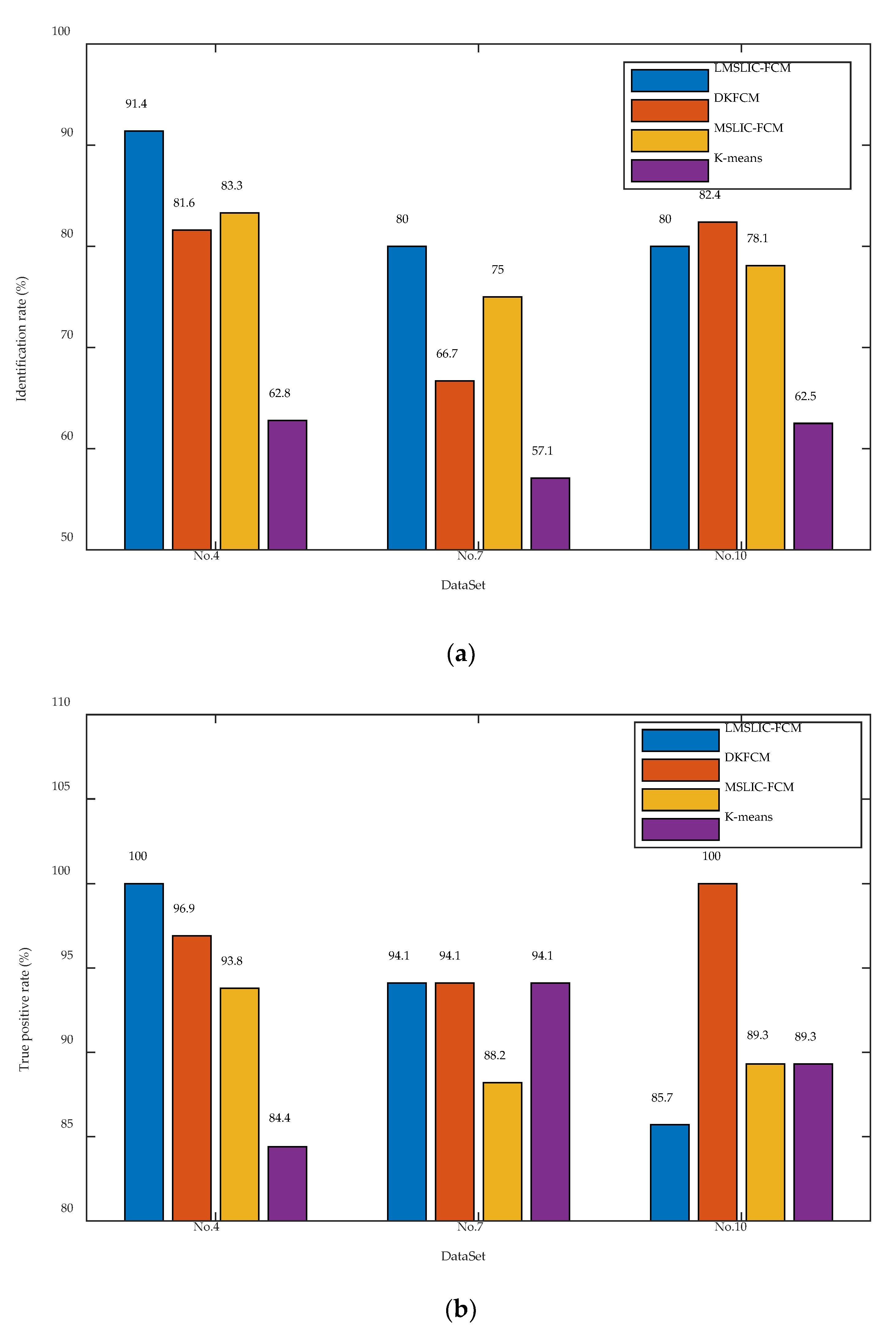

| Track | Manual Count | No. of Identified Nodules | No. of Correct Nodules | No. of False Positives | No. of False Negatives | Identification Rate 1 | True Positive Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMSLIC-FCM | |||||||
| 4 | 32 | 35 | 32 | 3 | 0 | 91.4% | 100% |
| 7 | 17 | 20 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 80.0% | 94.1% |
| 10 | 28 | 30 | 24 | 6 | 4 | 80.0% | 85.7% |
| AVG | 83.8% | 93.3% | |||||
| MSLIC-FCM [25] + [34] | |||||||
| 4 | 32 | 36 | 30 | 6 | 2 | 83.3% | 93.8% |
| 7 | 17 | 20 | 15 | 5 | 2 | 75.0% | 88.2% |
| 10 | 28 | 32 | 25 | 7 | 3 | 78.1% | 89.3% |
| AVG | 78.8% | 90.4% | |||||
| DKFCM [16] | |||||||
| 4 | 32 | 38 | 31 | 7 | 1 | 81.6% | 96.9% |
| 7 | 17 | 24 | 16 | 8 | 1 | 66.7% | 94.1% |
| 10 | 28 | 34 | 28 | 6 | 0 | 82.4% | 100% |
| AVG | 76.9% | 97% | |||||
| K-means | |||||||
| 4 | 32 | 43 | 27 | 16 | 6 | 62.8% | 84.4% |
| 7 | 17 | 28 | 16 | 12 | 1 | 57.1% | 94.1% |
| 10 | 28 | 40 | 25 | 15 | 3 | 62.5% | 89.3% |
| AVG | 60.8% | 89.3% | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, P.; Han, C.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, F.; Yang, Z.; Wu, G. An Application of Hyperspectral Image Clustering Based on Texture-Aware Superpixel Technique in Deep Sea. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195047
Ye P, Han C, Zhang Q, Gao F, Yang Z, Wu G. An Application of Hyperspectral Image Clustering Based on Texture-Aware Superpixel Technique in Deep Sea. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195047
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Panjian, Chenhua Han, Qizhong Zhang, Farong Gao, Zhangyi Yang, and Guanghai Wu. 2022. "An Application of Hyperspectral Image Clustering Based on Texture-Aware Superpixel Technique in Deep Sea" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195047
APA StyleYe, P., Han, C., Zhang, Q., Gao, F., Yang, Z., & Wu, G. (2022). An Application of Hyperspectral Image Clustering Based on Texture-Aware Superpixel Technique in Deep Sea. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 5047. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195047