Spatiotemporal Variation in Vegetation Growth Status and Its Response to Climate in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
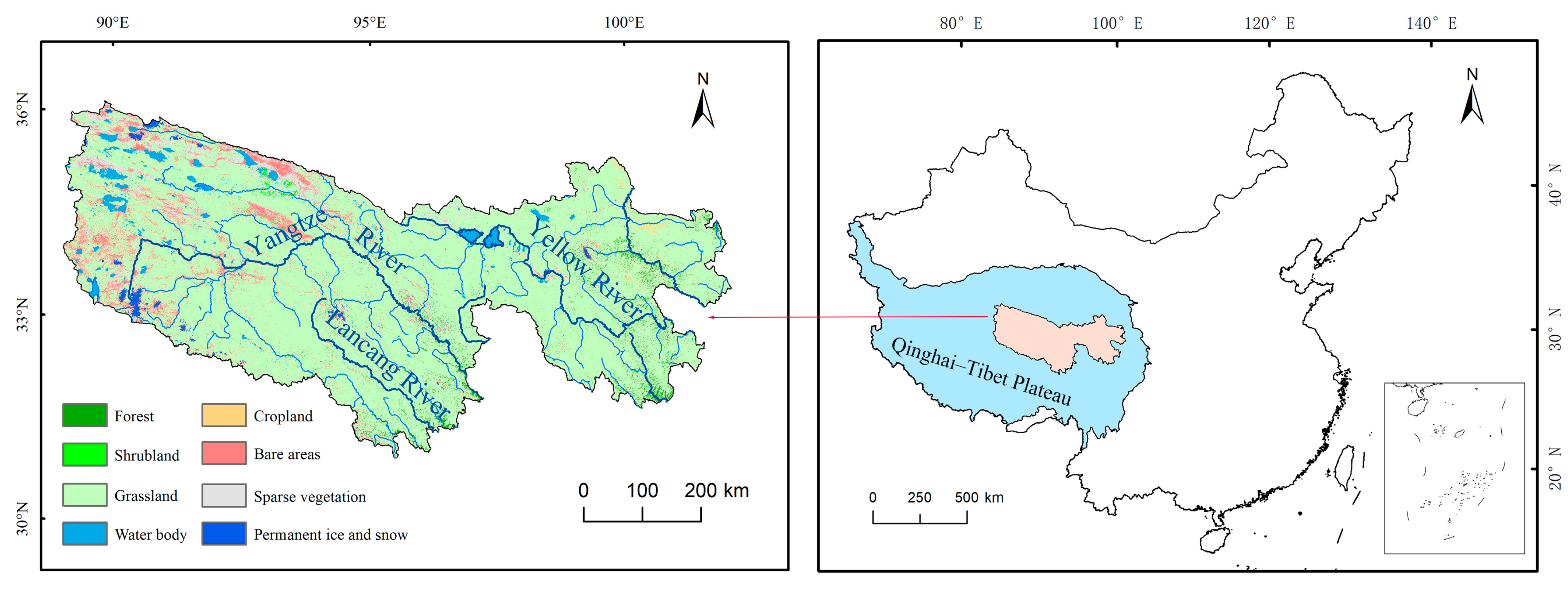
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
3. Methodology
3.1. Linear Regression Analysis
3.2. Coefficient of Variation
3.3. EEMD Method
3.4. Hurst Exponent Method
3.5. Correlation Analysis
3.6. Random Forest Model
4. Results and Analysis
4.1. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Vegetation Growth
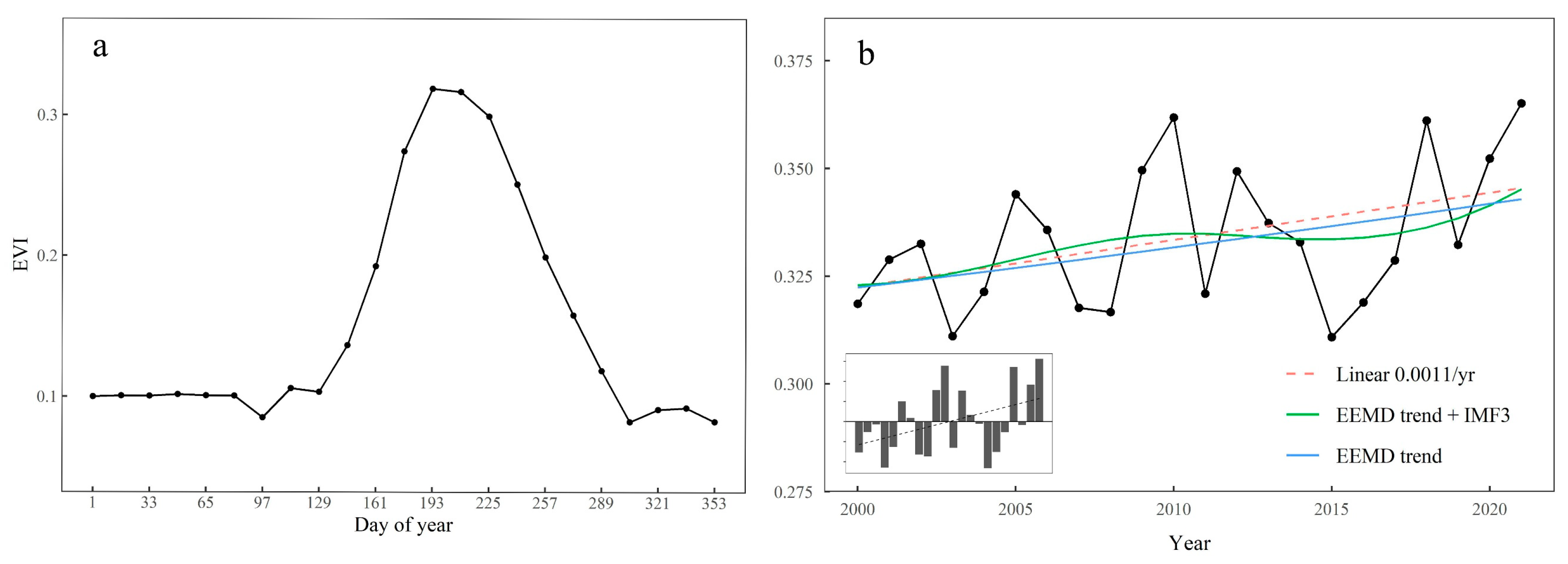
4.1.1. Temporal Characteristics of Vegetation Growth
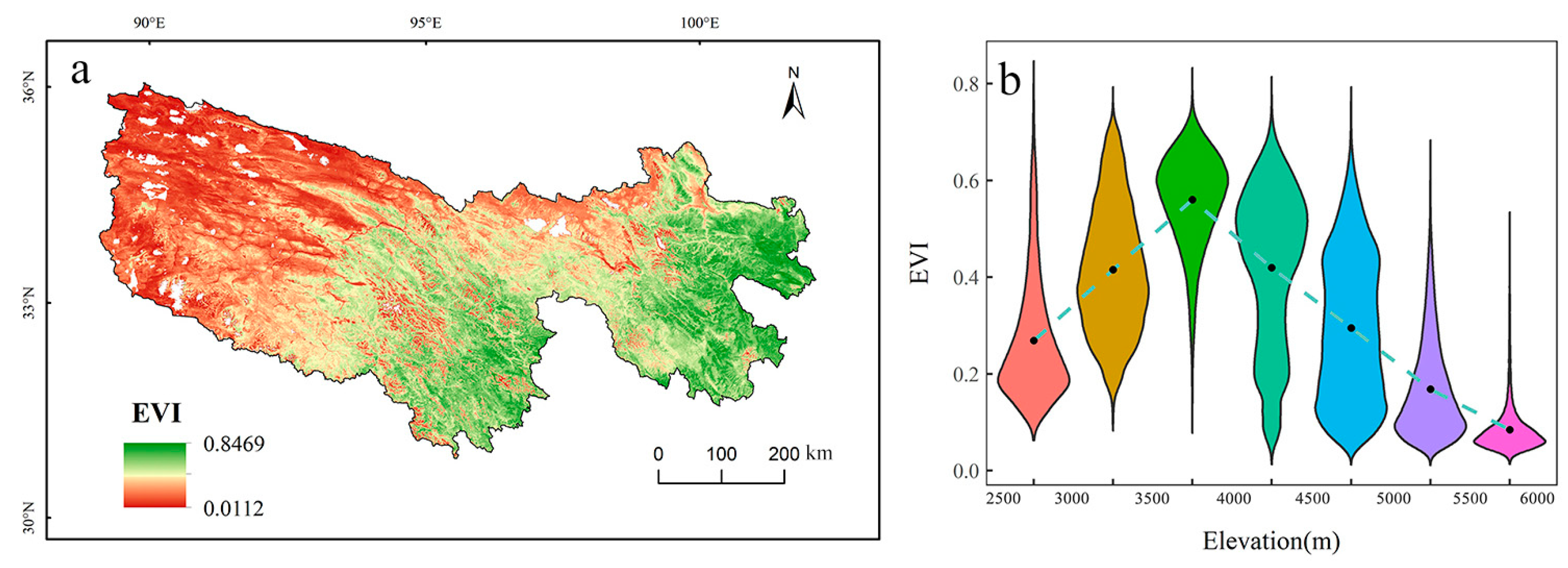
4.1.2. Spatial Characteristics of Vegetation Growth
4.2. Characteristics of Vegetation Growth Trend
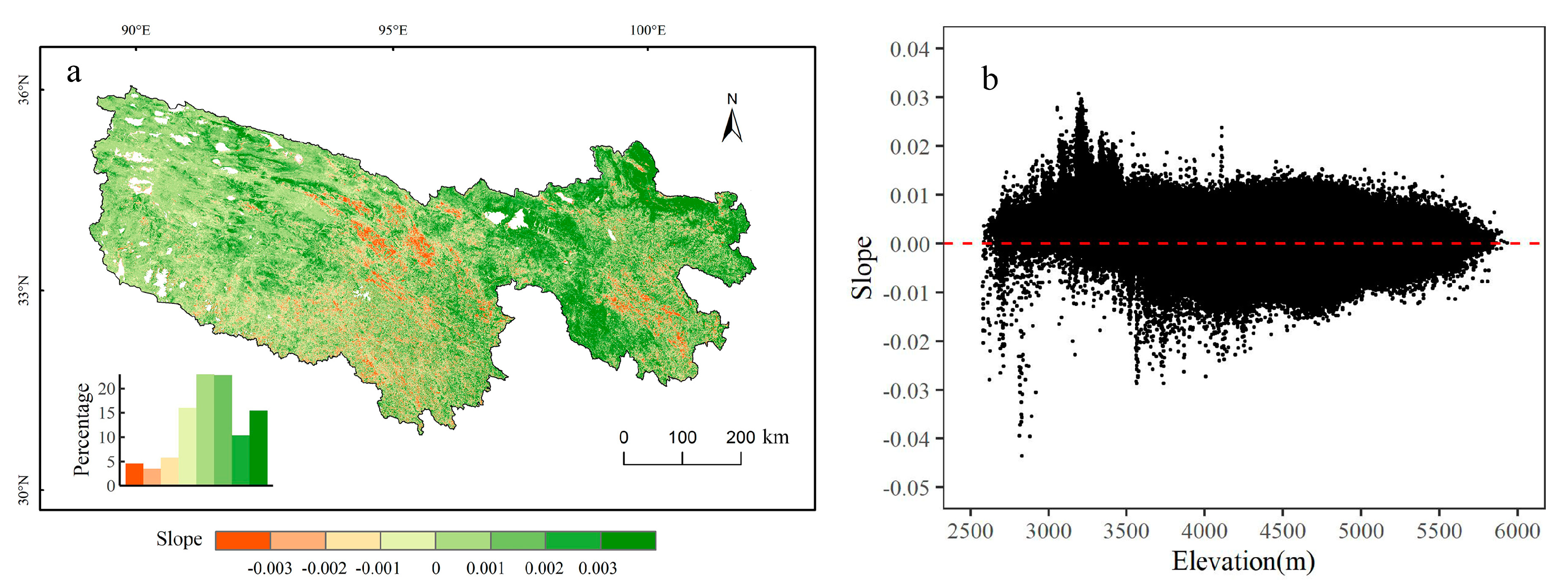
4.2.1. Vegetation Growth Trend
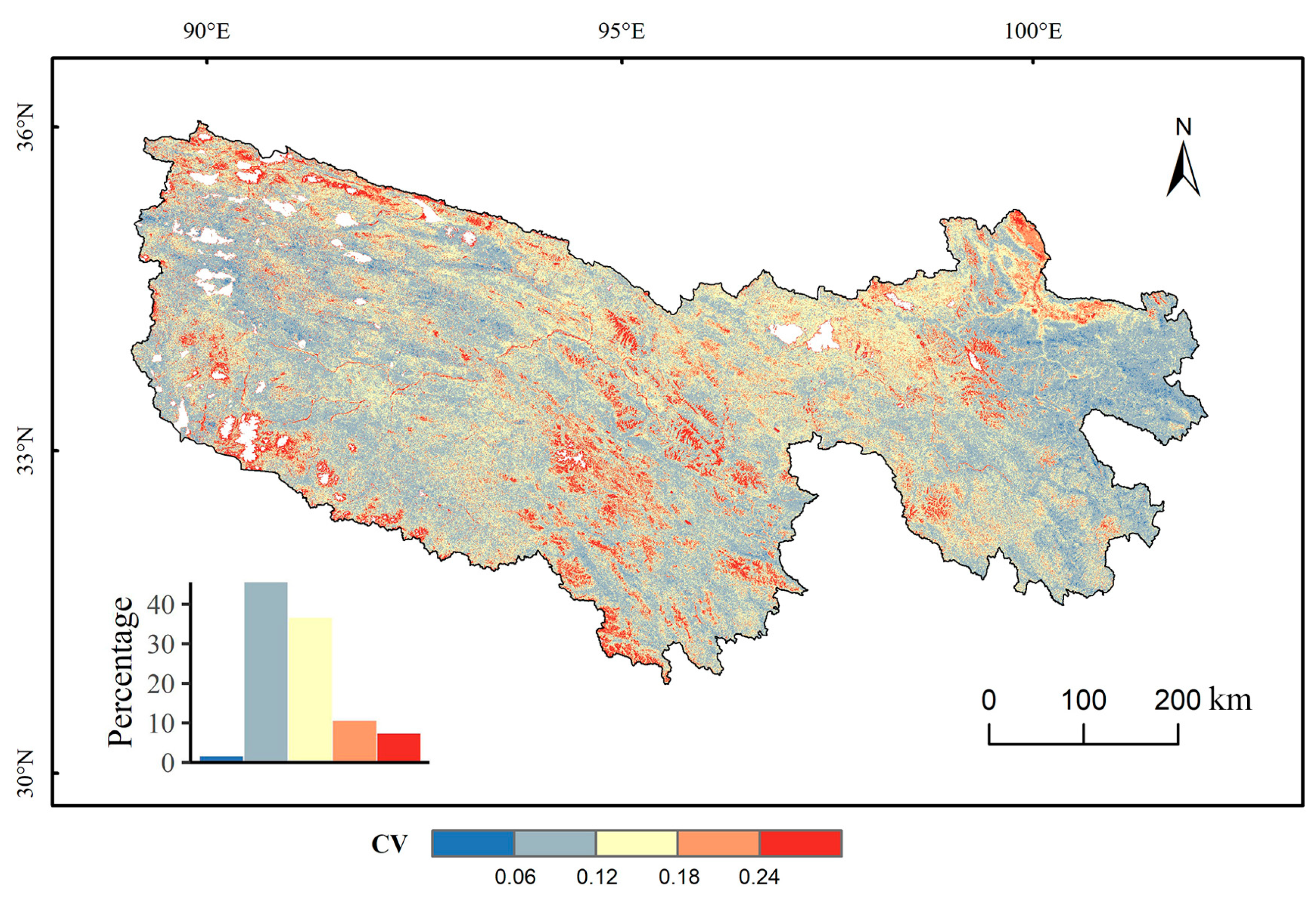
4.2.2. Vegetation Growth Volatility
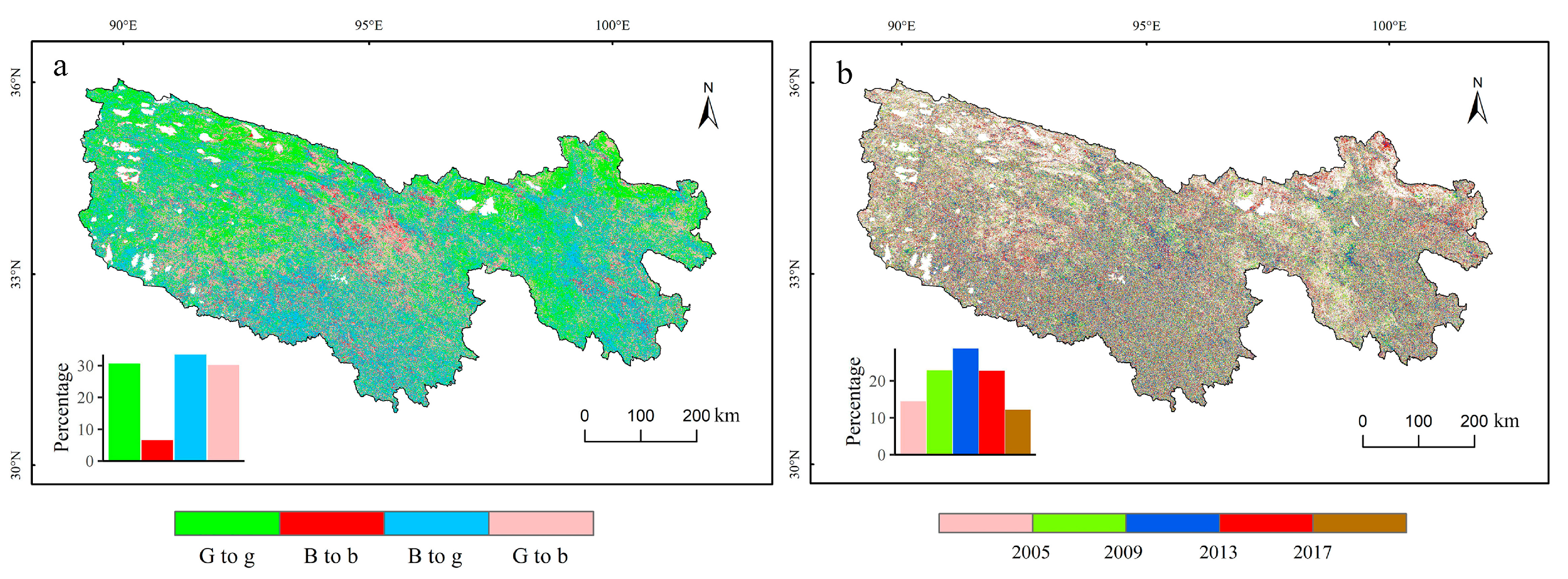
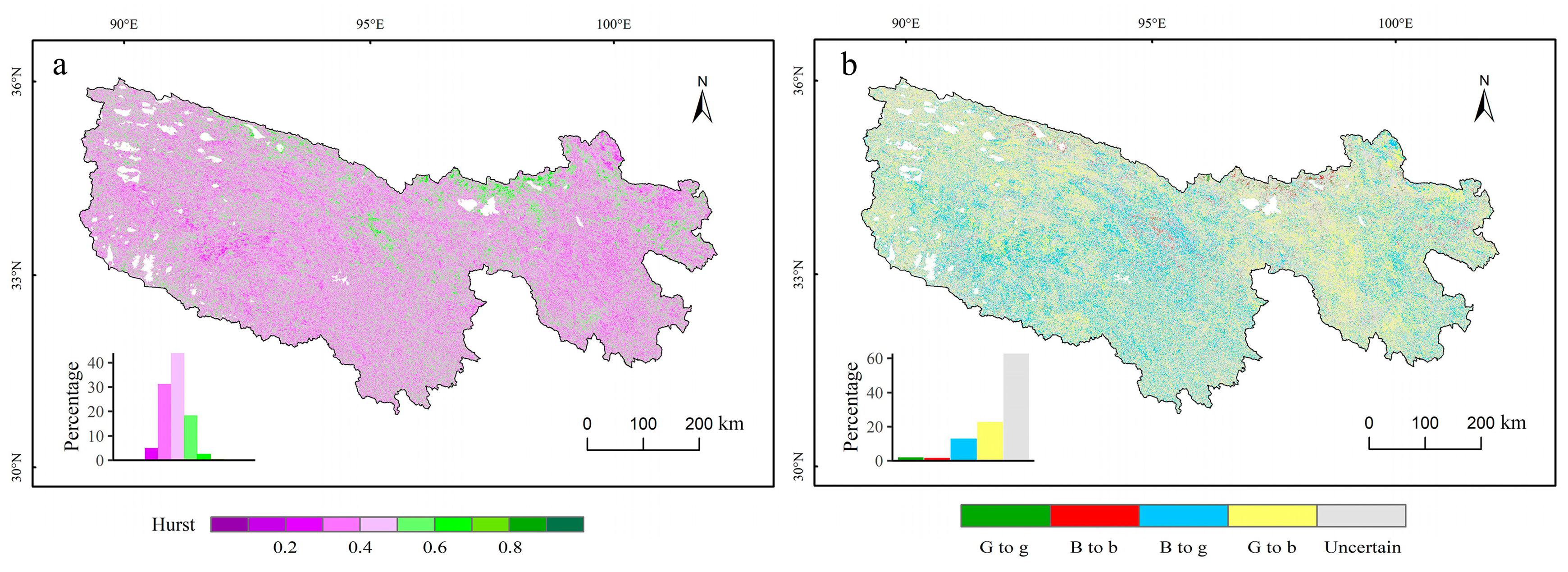
4.2.3. EEMD Trends of Vegetation Growth
4.2.4. Prediction of Future Vegetation Trends
4.3. Climatic Effects of Vegetation Growth
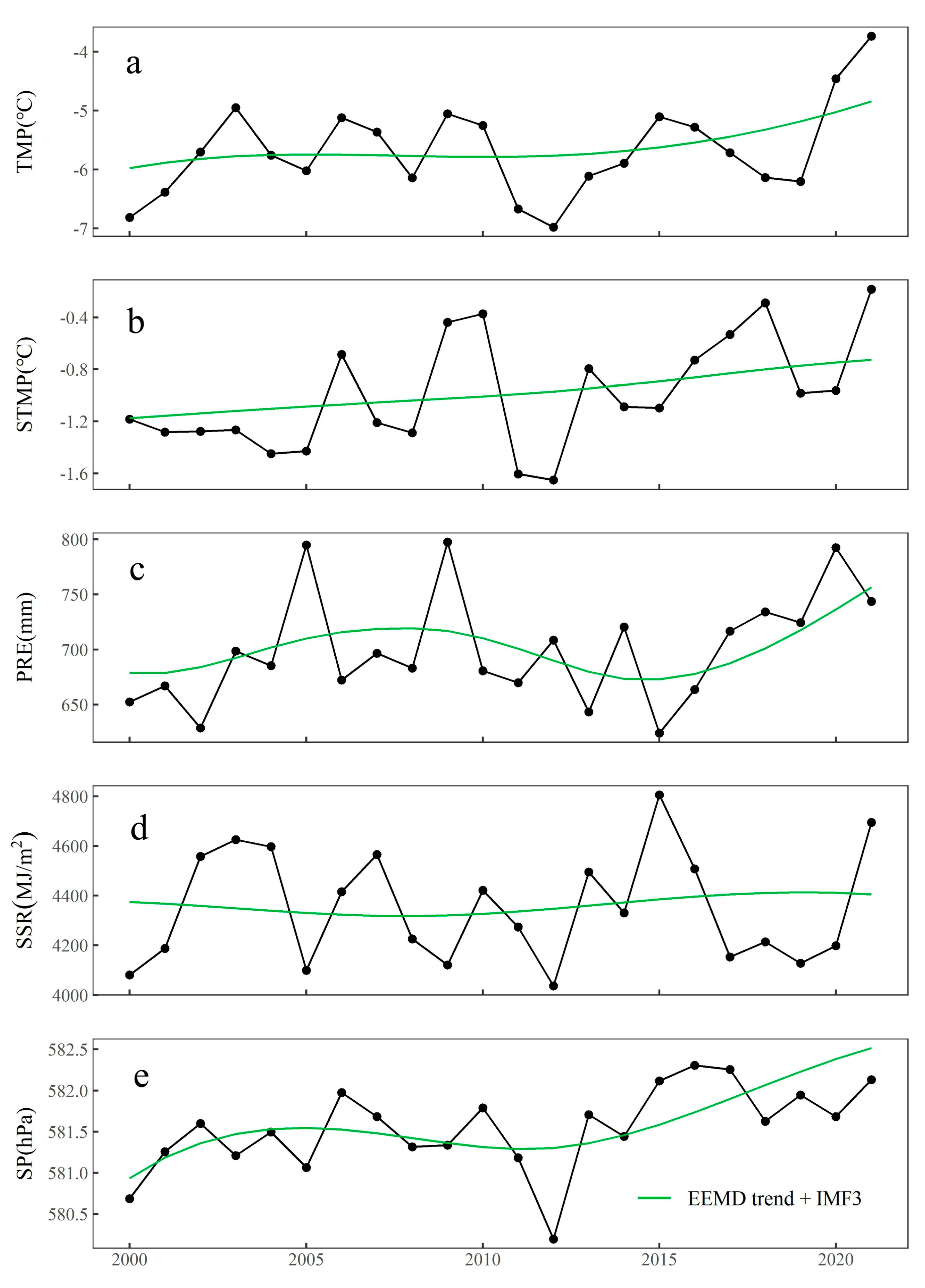
4.3.1. Changes in Climatic Factors
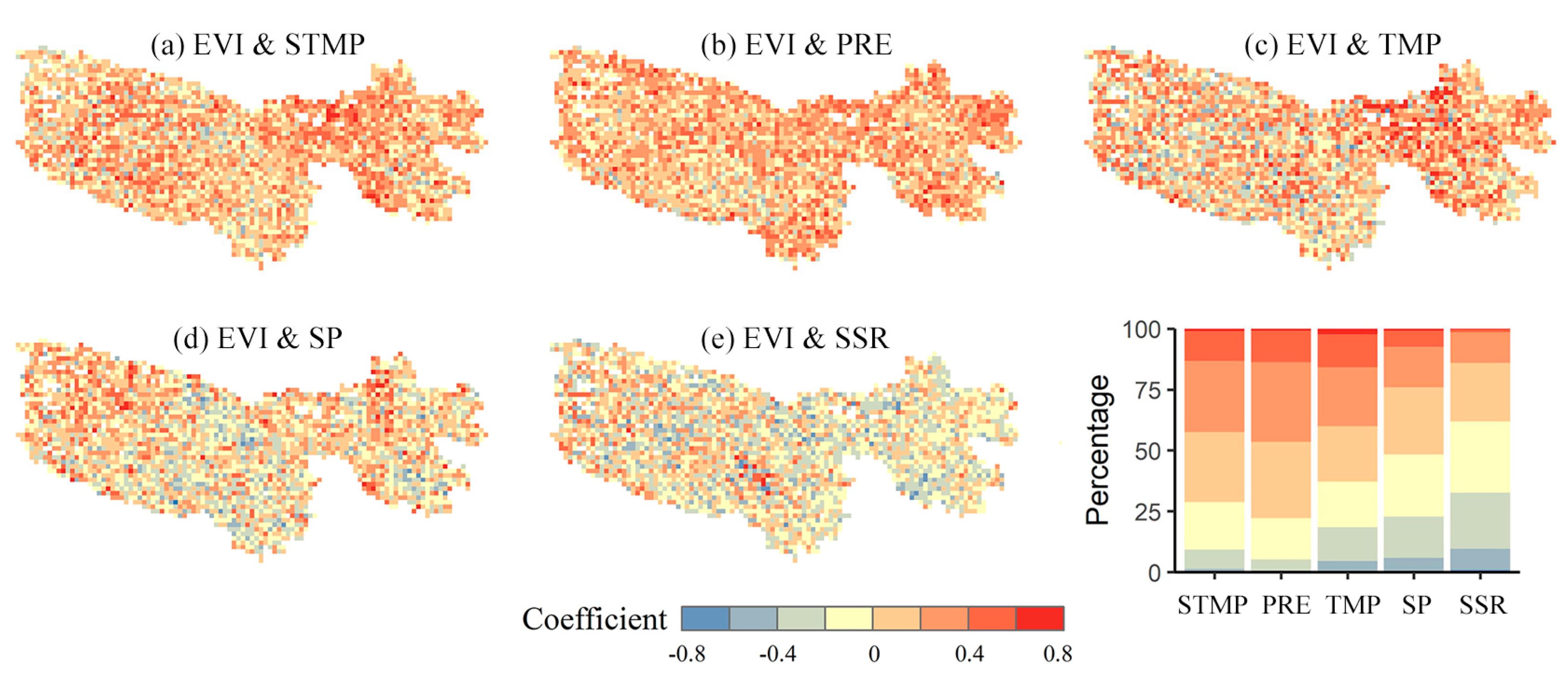
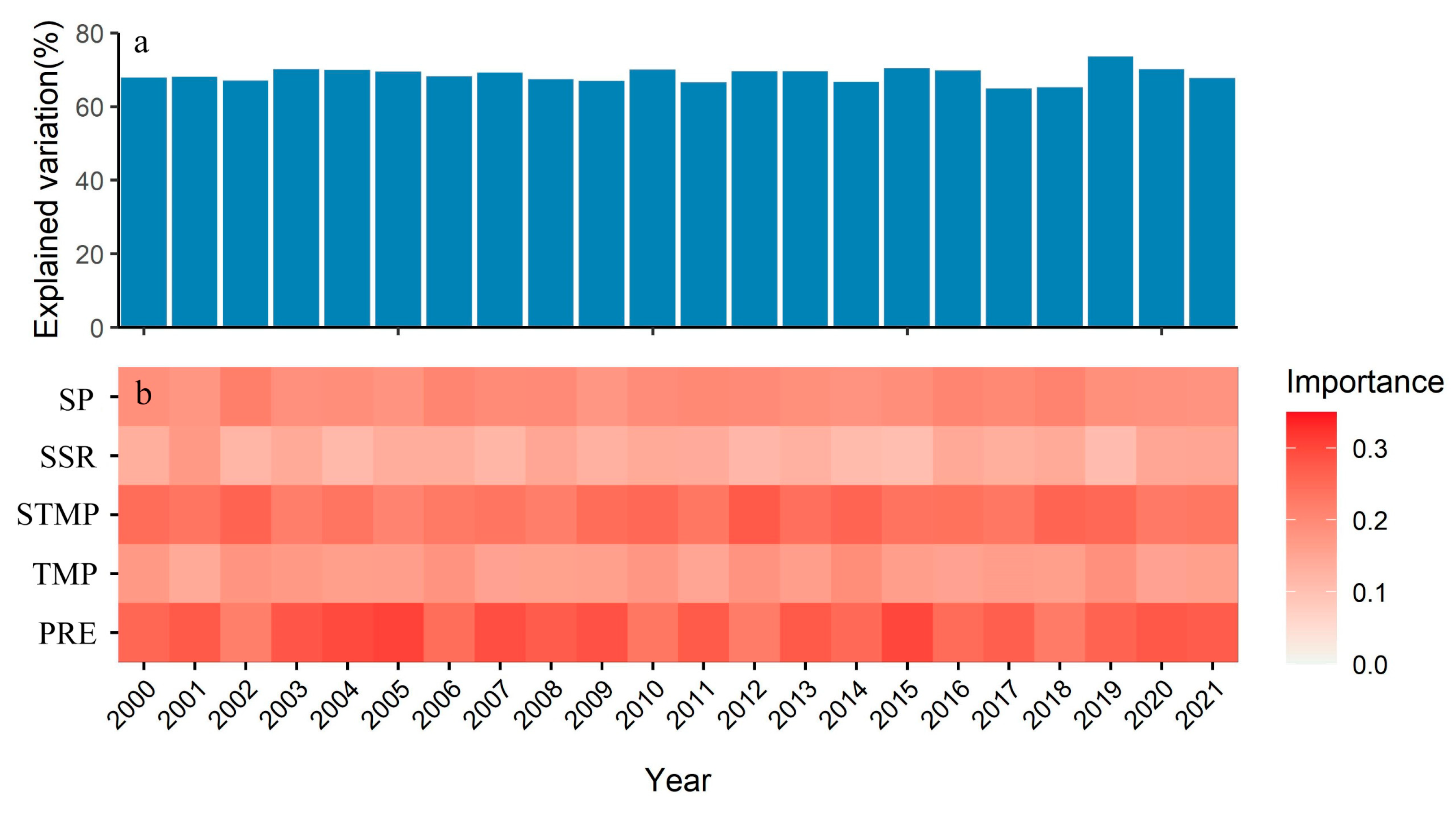
4.3.2. Vegetation Response to Climate Change
5. Discussion
5.1. Characteristics of Vegetation Change
5.2. Climate Response of Vegetation Growth
5.3. Effect of Elevation on Vegetation Growth
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Song, X.; Mu, X.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Spatiotemporal Vegetation Cover Variations Associated with Climate Change and Ecological Restoration in the Loess Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 209, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Wang, X.; Meng, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Piao, S. Three-dimensional Change in Temperature Sensitivity of Northern Vegetation Phenology. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 5189–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, X.; Jiao, L.; Liu, Z.; Jia, Q.; Zhong, J.; Fang, M.; Wang, W. Multi-Spatiotemporal Heterogeneous Legacy Effects of Climate on Terrestrial Vegetation Dynamics in China. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2022, 59, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, R.R.; Keeling, C.D.; Hashimoto, H.; Jolly, W.M.; Piper, S.C.; Tucker, C.J.; Myneni, R.B.; Running, S.W. Climate-Driven Increases in Global Terrestrial Net Primary Production from 1982 to 1999. Science 2003, 300, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and Climate Change: Forcings, Feedbacks, and the Climate Benefits of Forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Guan, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, L.; Yang, E.; Li, H.; Du, Q. Three-Dimensional Dynamic Characteristics of Vegetation and Its Response to Climatic Factors in the Qilian Mountains. Catena 2022, 208, 105694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate change 2021: The physical science basis [M/OL]. 2021 [2021-08-22]. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg1/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Myneni, R.B.; Ciais, P.; Saatchi, S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Piao, S.; Chen, H.; Vermote, E.F.; Song, C.; et al. Widespread Decline of Congo Rainforest Greenness in the Past Decade. Nature 2014, 509, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, X.; Wilson, A.M.; Silander, J.A. Predicting Autumn Phenology: How Deciduous Tree Species Respond to Weather Stressors. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 250, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Song, C.; Clark, J.S.; Seyednasrollah, B.; Rathnayaka, N.; Li, J. Understanding the Continuous Phenological Development at Daily Time Step with a Bayesian Hierarchical Space-Time Model: Impacts of Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the Radiometric and Biophysical Performance of the MODIS Vegetation Indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y. Estimating Spatiotemporal Patterns of Aboveground Biomass Using Landsat TM and MODIS Images in the Mu Us Sandy Land, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 200, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J.; Han, Y. Trend Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics in Qinghai–Tibet Plateau Using Hurst Exponent. Ecol. Indic. 2012, 14, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Lu, Q. Spatiotemporal Variation of Vegetation on the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau and the Influence of Climatic Factors and Human Activities on Vegetation Trend (2000–2019). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, C.; Degen, A.A.; Ahmad, A.A.; Wang, W.; Zhang, T.; Li, W.; Ma, L.; Huang, M.; Zeng, H.; et al. Climate Warming Benefits Alpine Vegetation Growth in Three-River Headwater Region, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, D.; Gao, X.; Li, B.; Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Xu, J. Diverse Chronic Responses of Vegetation Aboveground Net Primary Productivity to Climatic Changes on Three-River Headwaters Region. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 139, 108925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, R.B.; Breidt, F.J.; Dutin, A.; Ogle, S.M. Predicting Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI) Curves for Ecosystem Modeling Applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2186–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Ji, F.; Pan, S. Increasing Global Vegetation Browning Hidden in Overall Vegetation Greening: Insights from Time-Varying Trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, N.E. Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition: A Noise-Assisted Data Analysis Method. Adv. Adapt. Data Anal. 2009, 01, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Wu, Z.; Huang, J.; Chassignet, E.P. Evolution of Land Surface Air Temperature Trend. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Ma, D.; Wu, S.; Dai, E.; Zhu, Z.; Myneni, R.B. Nonlinear Variations of Forest Leaf Area Index over China during 1982–2010 Based on EEMD Method. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, H.; Jiao, F.; Gong, H.; Lin, Z. Time-Varying Trends of Vegetation Change and Their Driving Forces during 1981–2016 along the Silk Road Economic Belt. Catena 2020, 195, 104796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, B.; Yao, T.; Guo, Z.; Cui, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, R.; ZHANG, X.; ZHANG, Y.; FAN, J. Assessment of Past, Present and Future Environmental Changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, X.; Jiao, J.J. Review on Climate Change on the Tibetan Plateau during the Last Half Century. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3979–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Field, C.B. Changes in Ecologically Critical Terrestrial Climate Conditions. Science 2013, 341, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, J.; Ye, C.; Yong, Z.; Wang, Y.; He, D.; Xu, S. Relationships between Climate Change, Phenology, Edaphic Factors, and Net Primary Productivity across the Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. 2022, 107, 102708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lin, Z. Spatiotemporal Changes in Vegetation Coverage and Its Driving Factors in the Three-River Headwaters Region during 2000–2011. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Xie, H. Modeling Grassland Above-Ground Biomass Based on Artificial Neural Network and Remote Sensing in the Three-River Headwaters Region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, J.; Huang, Y.; Fassnacht, S.R.; Xie, S.; Lv, E.; Chen, M. Vegetation Response to Climate Conditions Based on NDVI Simulations Using Stepwise Cluster Analysis for the Three-River Headwaters Region of China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukko, P.J.J.; Helske, J.; Räsänen, E. Introducing Libeemd: A Program Package for Performing the Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition. Computation. Stat. 2016, 31, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, H.E. Long-Term Storage Capacity of Reservoirs. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1951, 116, 770–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Chen, J.; Lu, N.; Guo, K.; Liang, C.; Wei, Y.; Asko, N.; Ma, K.; Han, K. Predicting Plant Diversity Based on Remote Sensing Products in the Semi-Arid Region of Inner Mongolia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 2018–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Jiapaer, G.; Bao, A.; Guo, H.; Ndayisaba, F. Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Climate Change and Human Activities in Central Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599, 967–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach Learn 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, A.K.; Feilhauer, H.; Bräuning, A.; Rautio, P.; Braun, M. Remotely Sensed Estimation of Vegetation Shifts in the Polar and Alpine Tree-Line Ecotone in Finnish Lapland during the Last Three Decades. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 454, 117668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assal, T.J.; Steen, V.A.; Caltrider, T.; Cundy, T.; Stewart, C.; Manning, N.; Anderson, P.J. Monitoring Long-Term Riparian Vegetation Trends to Inform Local Habitat Management in a Mountainous Environment. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by RandomForest. R News 2002, 2, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, T.; Andrus, R.; Aravena, M.-C.; Ascoli, D.; Bergeron, Y.; Berretti, R.; Berveiller, D.; Bogdziewicz, M.; Boivin, T.; Bonal, R.; et al. Limits to Reproduction and Seed Size-Number Trade-Offs That Shape Forest Dominance and Future Recovery. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Gu, S.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, J.; Tang, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, S. High Positive Correlation between Soil Temperature and NDVI from 1982 to 2006 in Alpine Meadow of the Three-River Source Region on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs. 2011, 13, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-L.; Gao, J.; Brierley, G.; Qiao, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.-W. Rangeland Degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for Rehabilitation. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mipam, T.-D.; Zhong, L.-L.; Liu, J.-Q.; Miehe, G.; Tian, L.-M. Productive Overcompensation of Alpine Meadows in Response to Yak Grazing in the Eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miehe, G.; Schleuss, P.-M.; Seeber, E.; Babel, W.; Biermann, T.; Braendle, M.; Chen, F.; Coners, H.; Foken, T.; Gerken, T.; et al. The Kobresia Pygmaea Ecosystem of the Tibetan Highlands—Origin, Functioning and Degradation of the World’s Largest Pastoral Alpine Ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 754–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Ning, J.; Liang, F.; Bi, X. Evaluating the Effects of Government Policy and Drought from 1984 to 2009 on Rangeland in the Three Rivers Source Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Cao, W.; Fan, J.; Huang, L.; Xu, X. Effects of an Ecological Conservation and Restoration Project in the Three-River Source Region, China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fan, J.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, H. Ecological Protection and Restoration Program Reduced Grazing Pressure in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 70, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ju, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, L.; Kang, X.; He, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hao, Y.; et al. Attribution Analyses of Changes in Alpine Grasslands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 2406–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Huang, L.; Cao, W.; Liu, L. Target-Based Assessment on Effects of First-Stage Ecological Conservation and Restoration Project in Three-River Source Region, China and Policy Recommendations. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; An, R.; Li, F.; Nan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Li, M. Vegetation Changes in the Three-River Headwaters Region of the Tibetan Plateau of China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabricante, I.; Oesterheld, M.; Paruelo, J.M. Annual and Seasonal Variation of NDVI Explained by Current and Previous Precipitation across Northern Patagonia. J. Arid. Environ. 2009, 73, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C. Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Vegetation Cover in Hilly Southern China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 81, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Zu, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, M.; Paudel, B. Increasing Sensitivity of Alpine Grasslands to Climate Variability along an Elevational Gradient on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnert, L.W.; Wesche, K.; Trachte, K.; Reudenbach, C.; Bendix, J. Climate Variability Rather than Overstocking Causes Recent Large Scale Cover Changes of Tibetan Pastures. Sci. Rep-UK 2016, 6, 24367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, T.; Sivakumar, B.; Li, J.; Wang, G. Attribution of Growing Season Vegetation Activity to Climate Change and Human Activities in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. J. Hydroinform 2020, 22, 186–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.C.; Jeffers, E.S.; Petrokofsky, G.; Myers-Smith, I.; Macias-Fauria, M. Shrub Growth and Expansion in the Arctic Tundra: An Assessment of Controlling Factors Using an Evidence-Based Approach. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 085007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Tang, Y.; Cui, X.; Kato, T.; Du, M.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X. Energy Exchange between the Atmosphere and a Meadow Ecosystem on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2005, 129, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, Y.; Chen, R. Spatial and Temporal of Variations of Alpine Vegetation Cover in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers of the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2001. Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Fang, J.Y.; Pan, Y.D.; Ji, C.J. Aboveground Biomass in Tibetan Grasslands. J. Arid. Environ. 2009, 73, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Pan, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D. Thermal Growing Season and Response of Alpine Grassland to Climate Variability across the Three-Rivers Headwater Region, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2016, 220, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fang, J.; Tang, Y.; Ji, C.; Zheng, C.; He, J.; Zhu, B. Storage, Patterns and Controls of Soil Organic Carbon in the Tibetan Grasslands: SOIL ORGANIC CARBON IN TIBETAN GRASSLANDS. Glob. Change Biol. 2008, 14, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-L.; Ding, J.-Z.; Peng, Y.-F.; Li, F.; Yang, G.-B.; Liu, L.; Qin, S.-Q.; Fang, K.; Yang, Y.-H. Patterns and Drivers of Soil Microbial Communities in Tibetan Alpine and Global Terrestrial Ecosystems. J. Biogeogr. 2016, 43, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Kou, D.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Y. Substantial Non-growing Season Carbon Dioxide Loss across Tibetan Alpine Permafrost Region. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5200–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, S.; Cui, M.; Chen, A.; Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y. Altitude and Temperature Dependence of Change in the Spring Vegetation Green-up Date from 1982 to 2006 in the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H.; Liang, T.; Hou, F.; Xu, J.; Xue, P. Quantitative Spatial Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics and Potential Driving Factors in a Typical Alpine Region on the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau Using the Google Earth Engine. Catena 2021, 206, 105500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EEMD | H < 0.4 | 0.4 < H < 0.6 | H > 0.6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| G TO G B TO G | G TO B | Uncertain | G TO G |
| B TO B G TO B | B TO G | Uncertain | B TO B |
| Elevation/m | EVI | Slope | CV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2500–3000 | 0.2690 | 0.0029 | 0.1934 |
| 3000–3500 | 0.4155 | 0.0052 | 0.1591 |
| 3500–4000 | 0.5602 | 0.0019 | 0.0997 |
| 4000–4500 | 0.4196 | 0.0013 | 0.1241 |
| 4500–5000 | 0.2949 | 0.0008 | 0.1390 |
| 5000–5500 | 0.1686 | 0.0007 | 0.1787 |
| 5500–6000 | 0.0845 | 0.0005 | 0.3700 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, C.; Yan, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q. Spatiotemporal Variation in Vegetation Growth Status and Its Response to Climate in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195041
He C, Yan F, Wang Y, Lu Q. Spatiotemporal Variation in Vegetation Growth Status and Its Response to Climate in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195041
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Chenyang, Feng Yan, Yanjiao Wang, and Qi Lu. 2022. "Spatiotemporal Variation in Vegetation Growth Status and Its Response to Climate in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195041
APA StyleHe, C., Yan, F., Wang, Y., & Lu, Q. (2022). Spatiotemporal Variation in Vegetation Growth Status and Its Response to Climate in the Three-River Headwaters Region, China. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 5041. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195041





