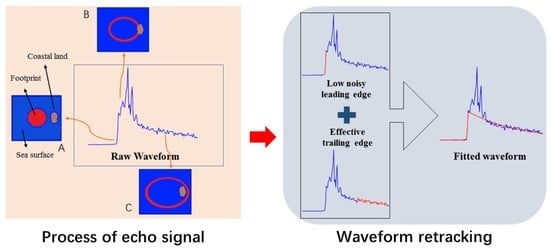
Coastal Waveform Retracking for HY-2B Altimeter Data by Determining the Effective Trailing Edge and the Low Noise Leading Edge
Abstract
1. Introduction
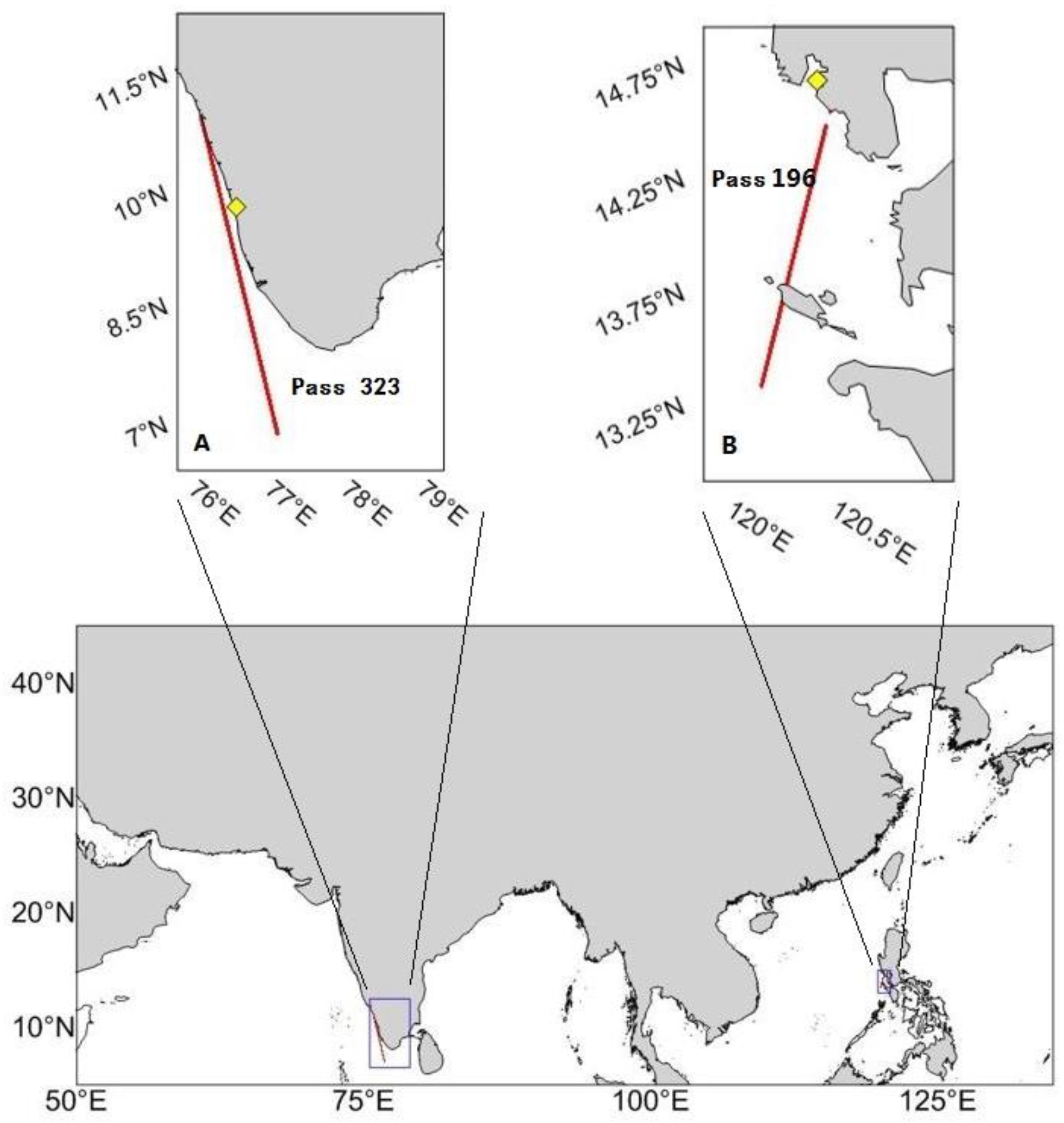
2. Study Areas and Data
3. Method
3.1. The Retracking Functional Form
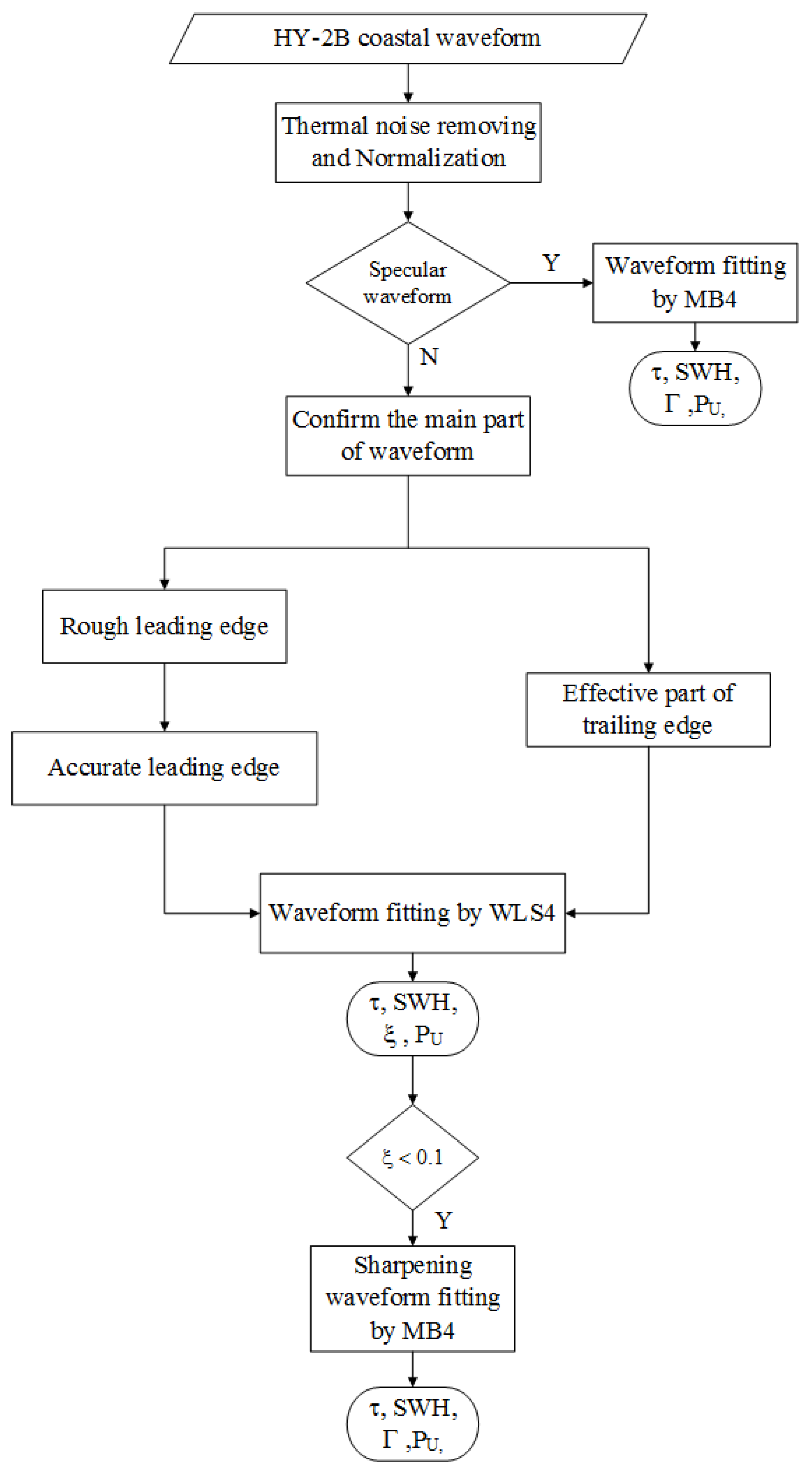
3.2. Waveform Retracking Method
3.2.1. Thermal Noise Removal and Normalization
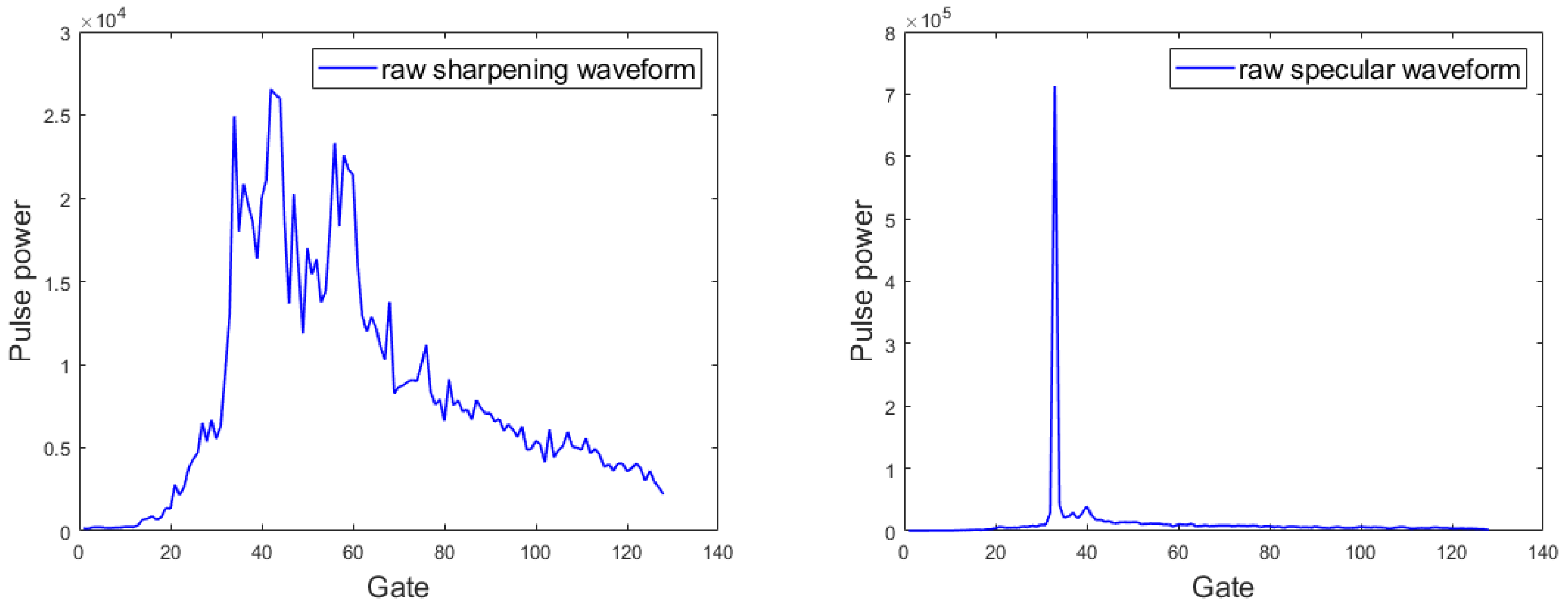
3.2.2. Specular Echo Processing
3.2.3. Non-Specular Echo Processing
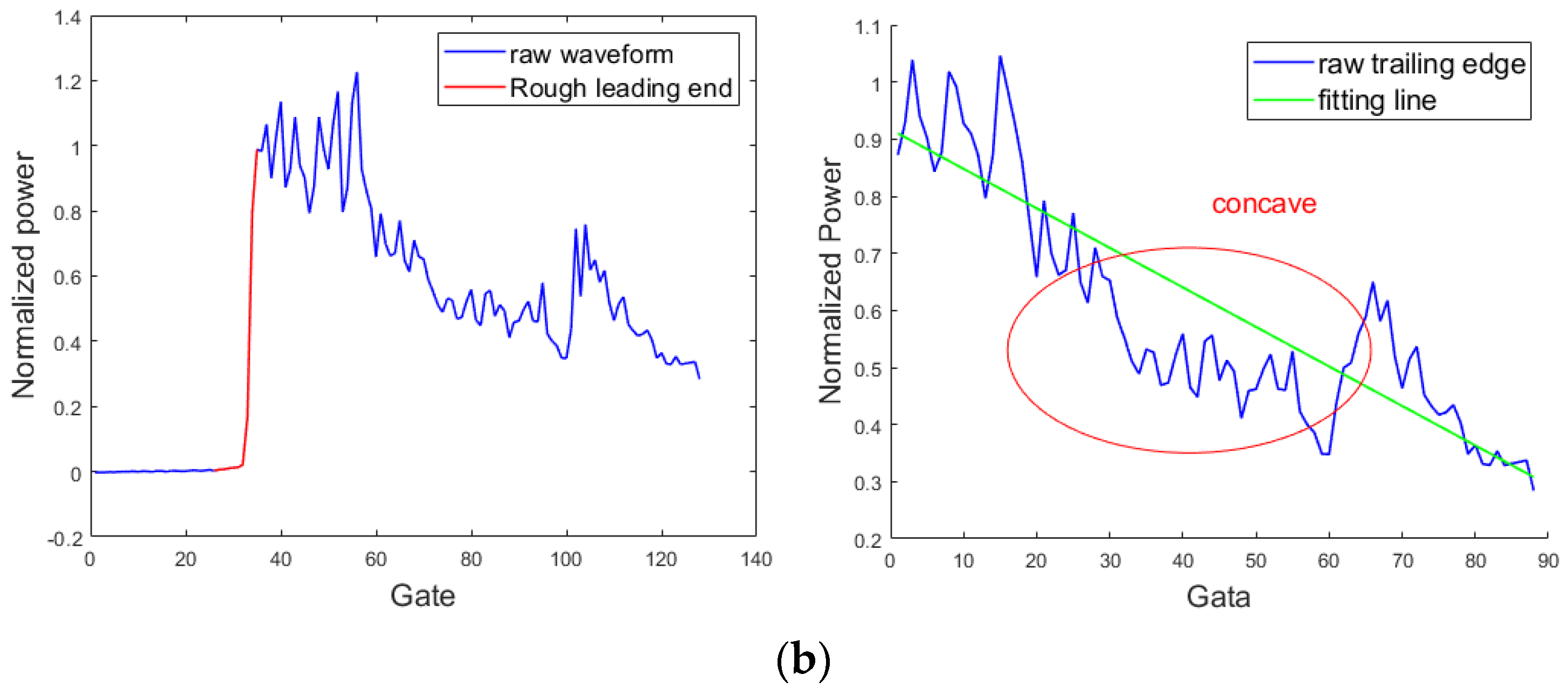
- Confirming the main part of waveform
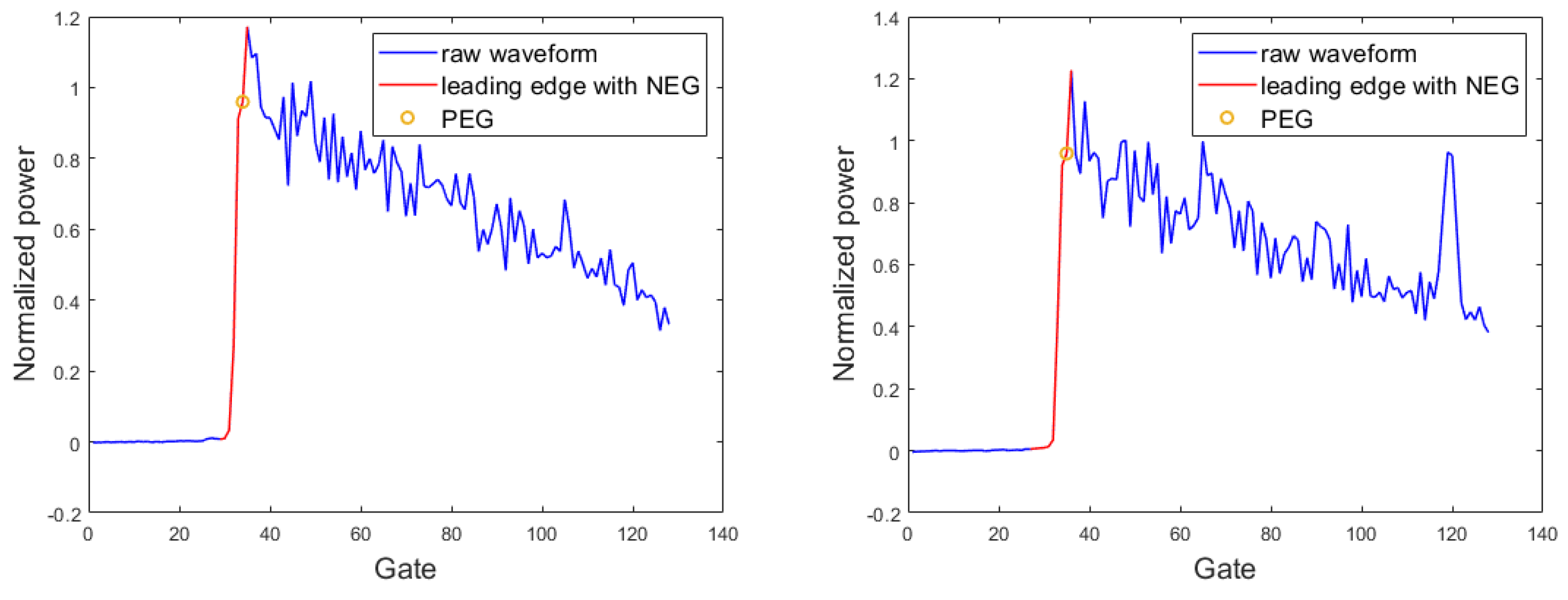
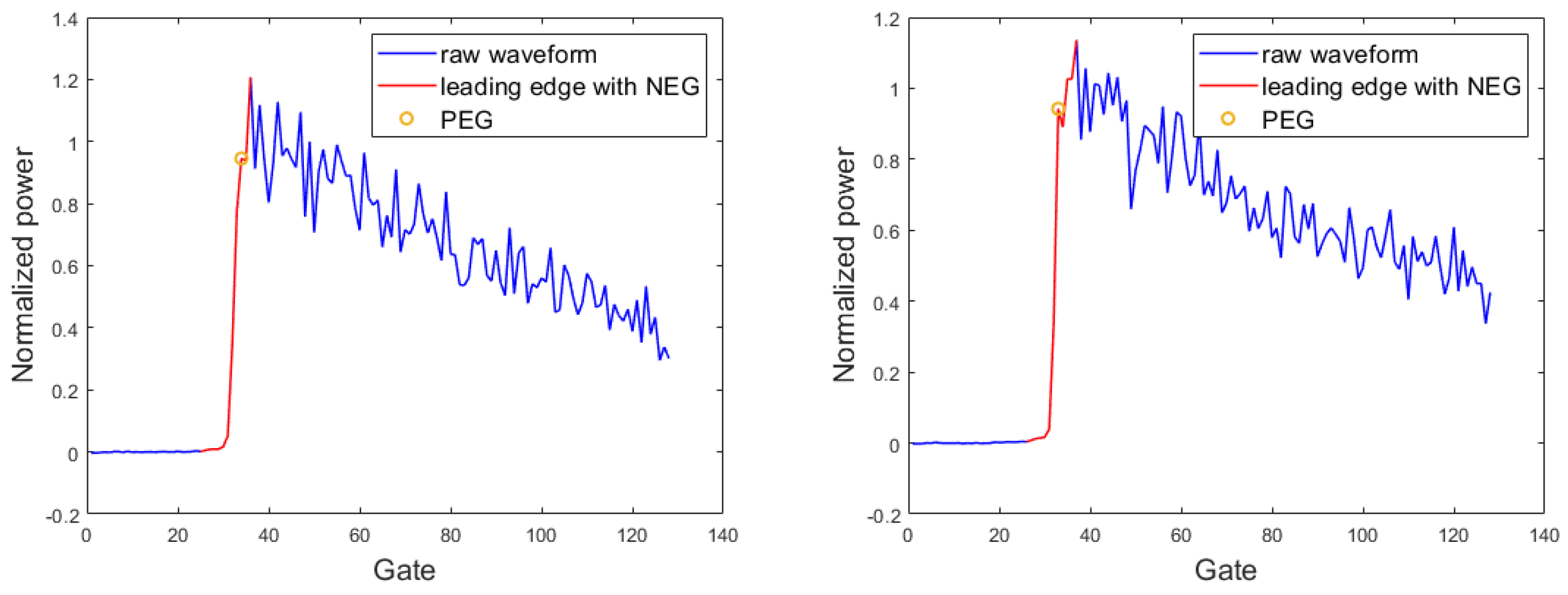
- Leading edge processing
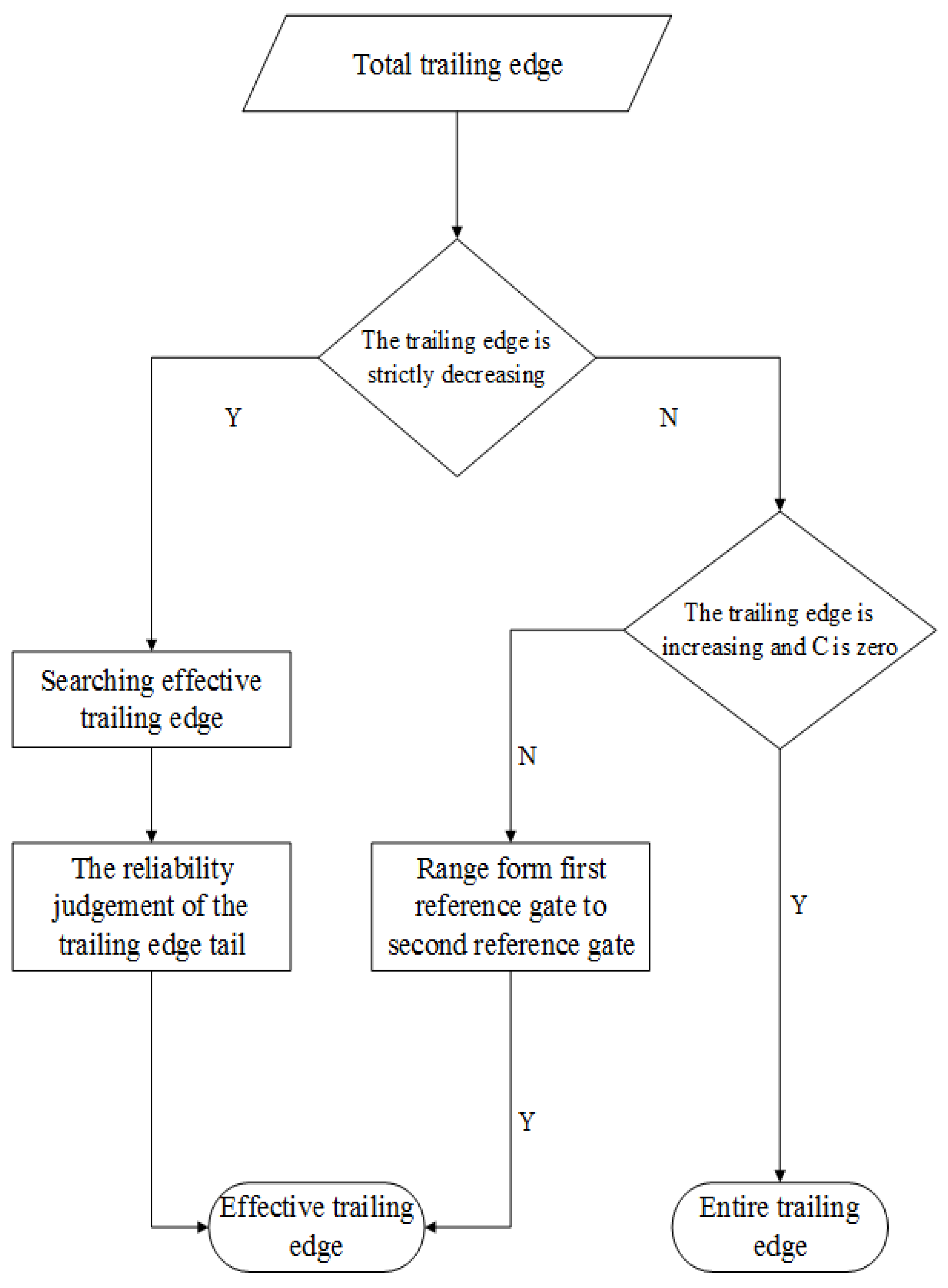
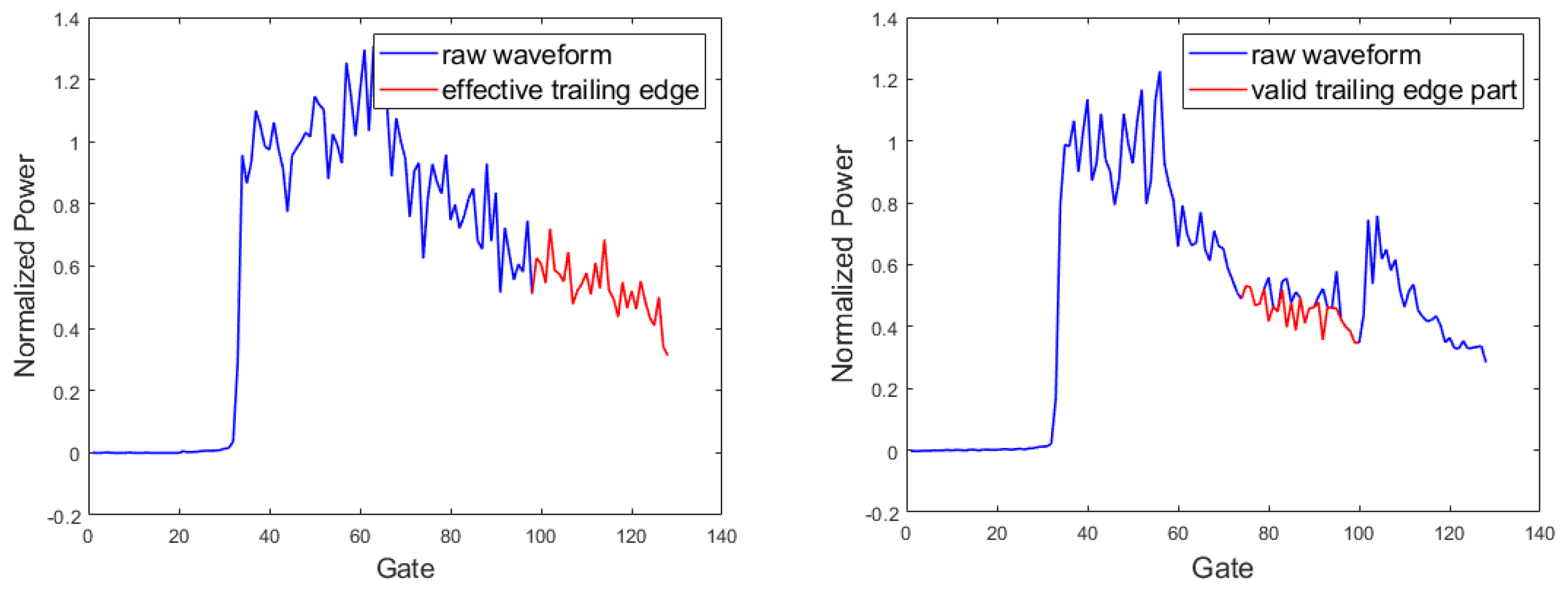
- The processing of trailing edge
- Weighting and fitting
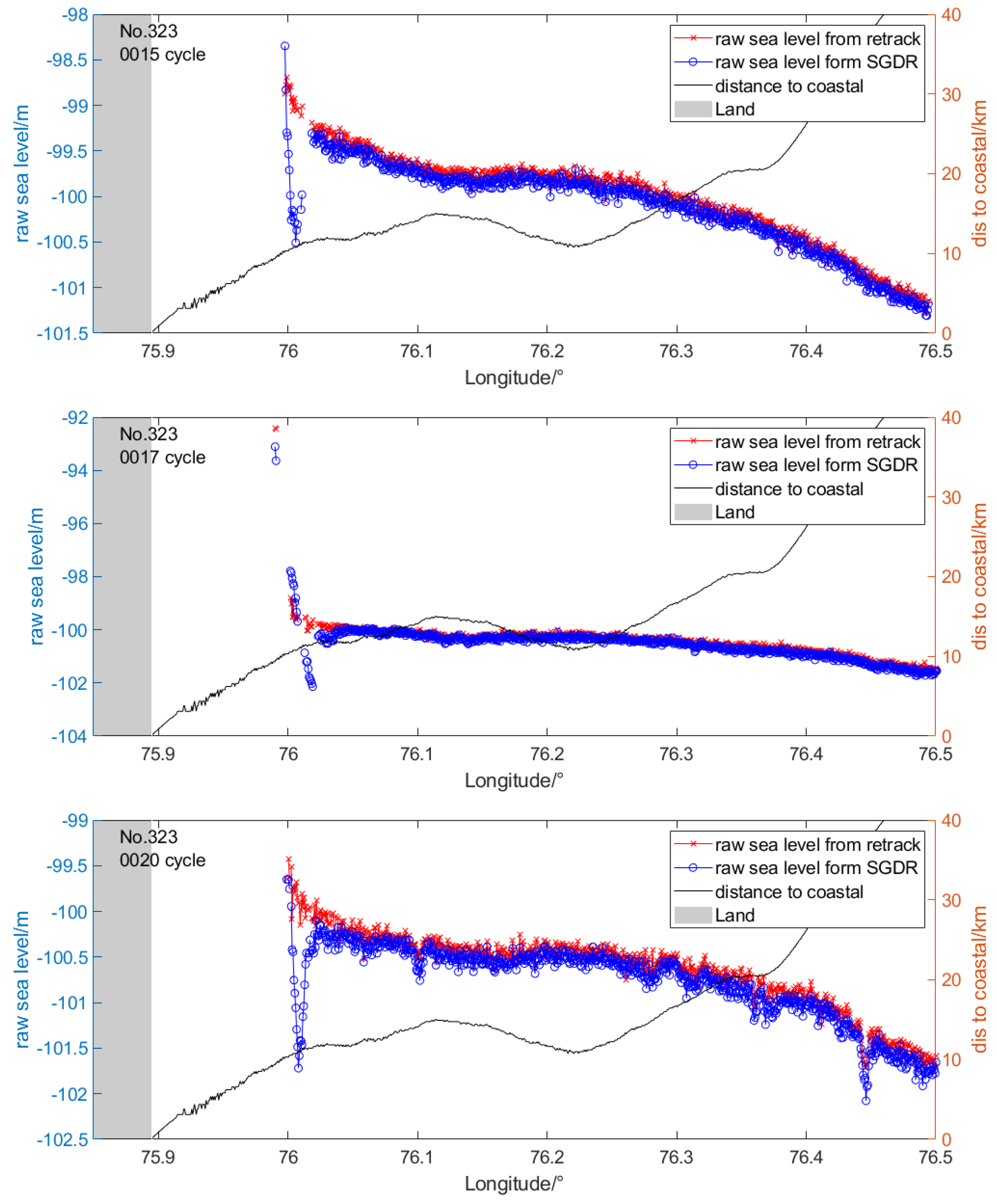
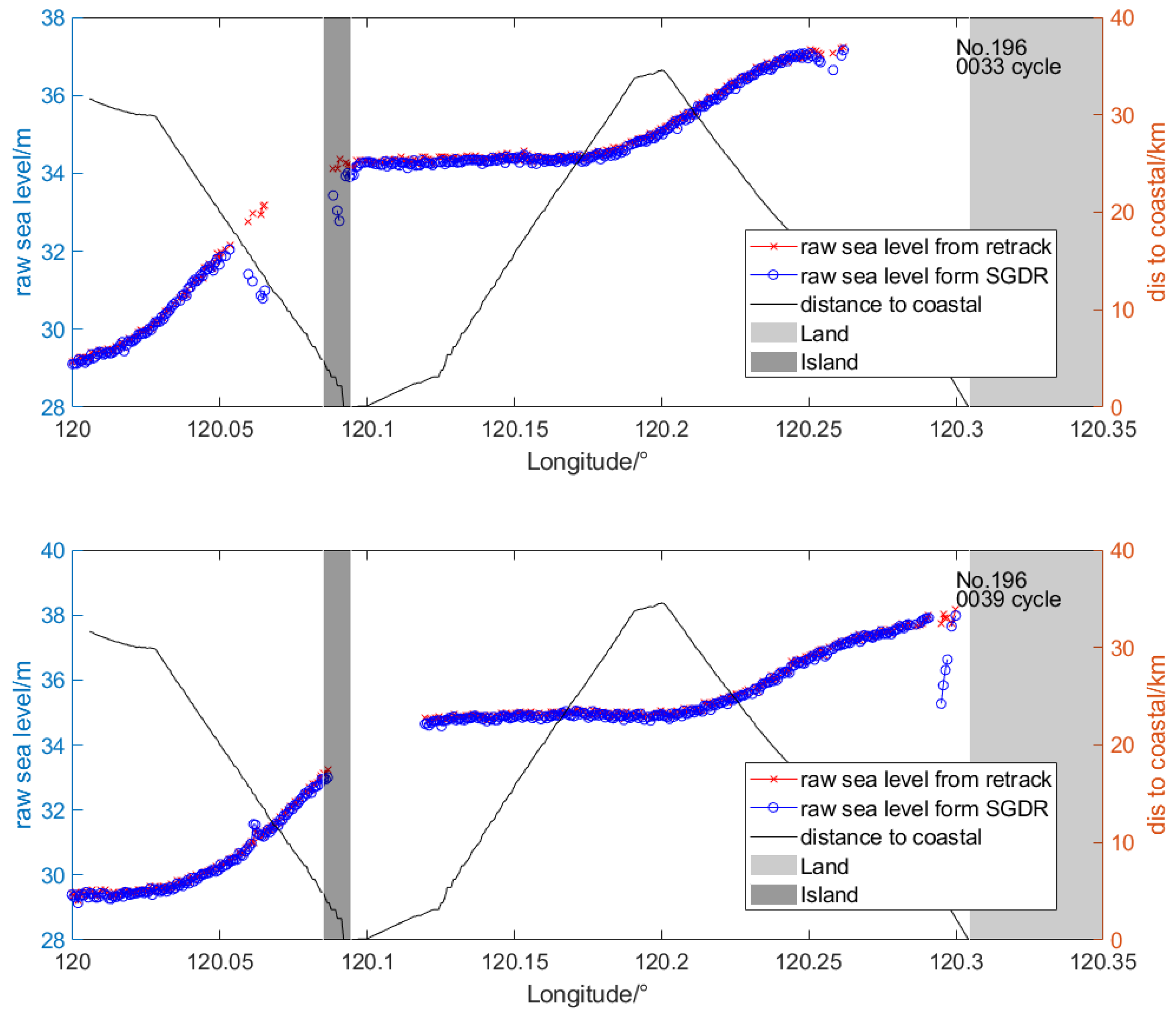
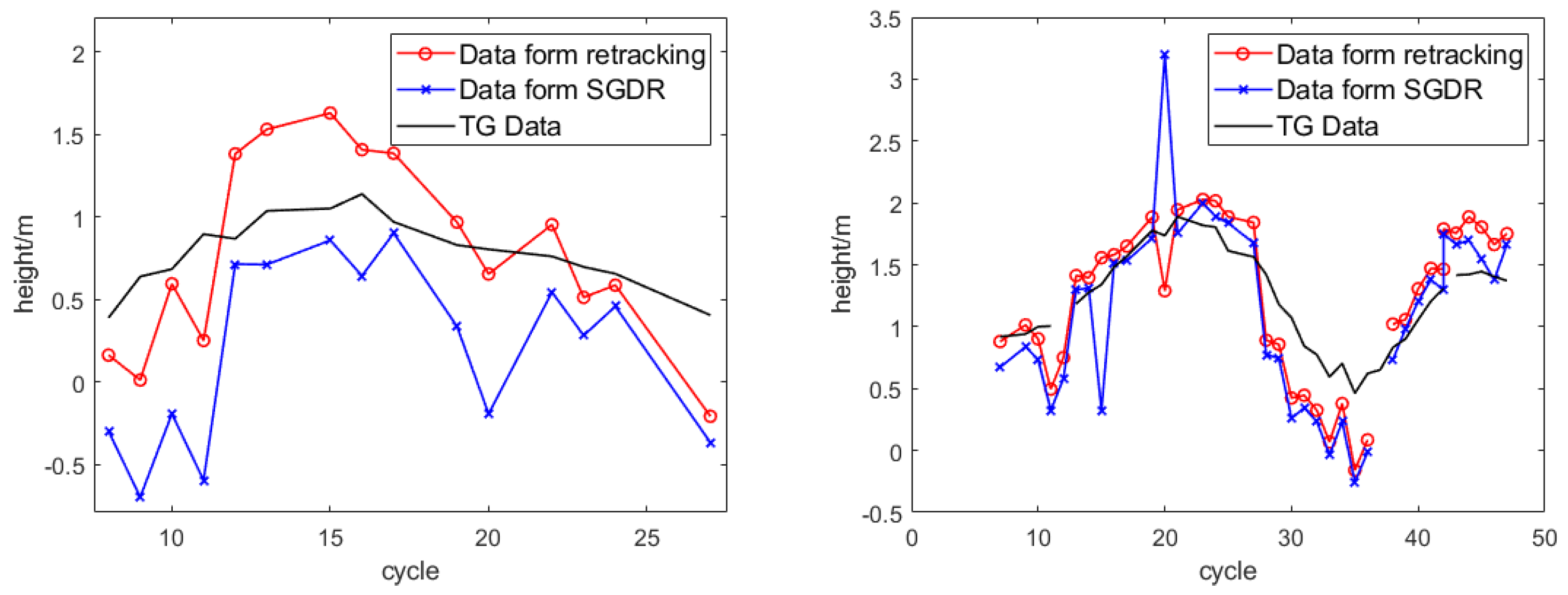
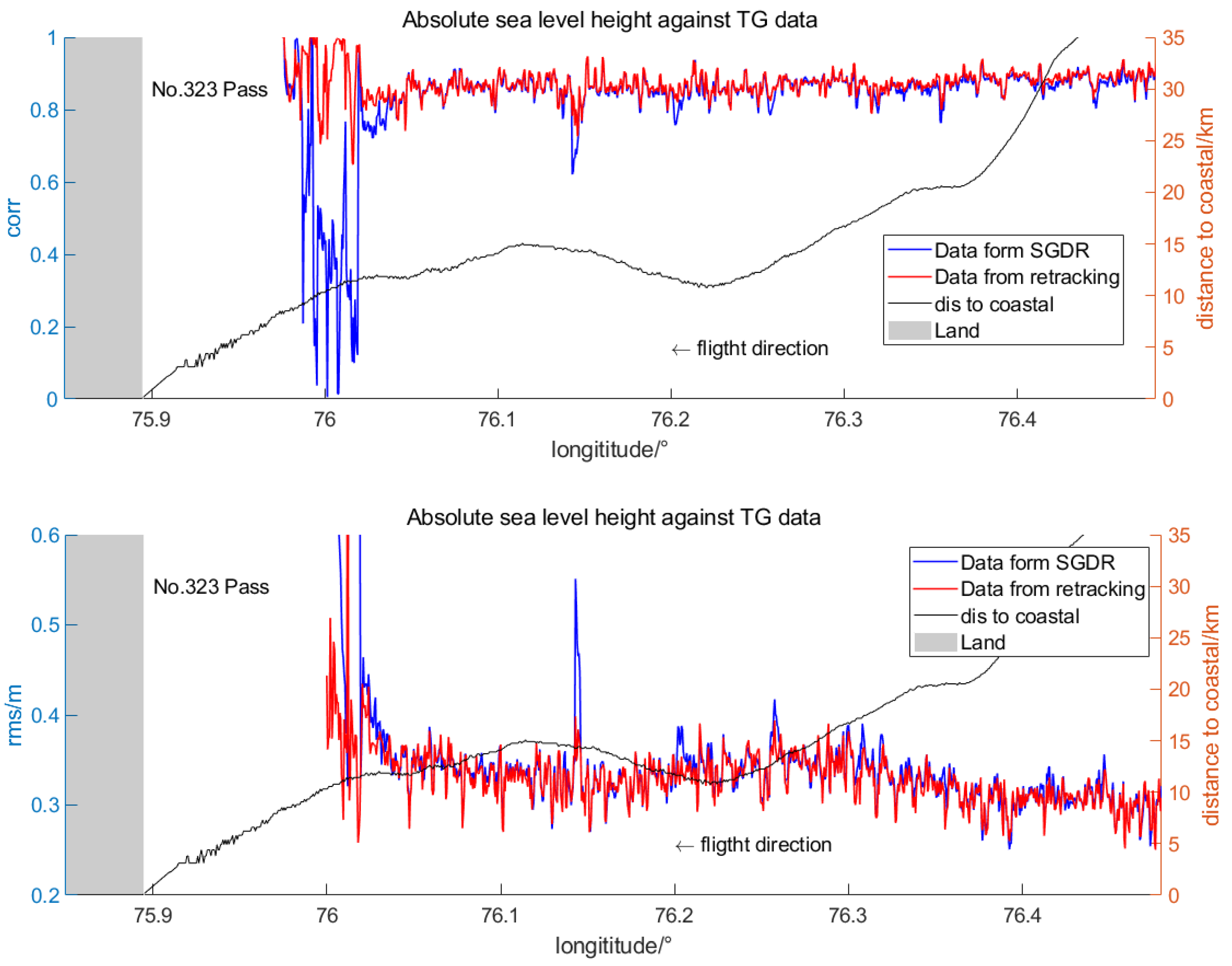
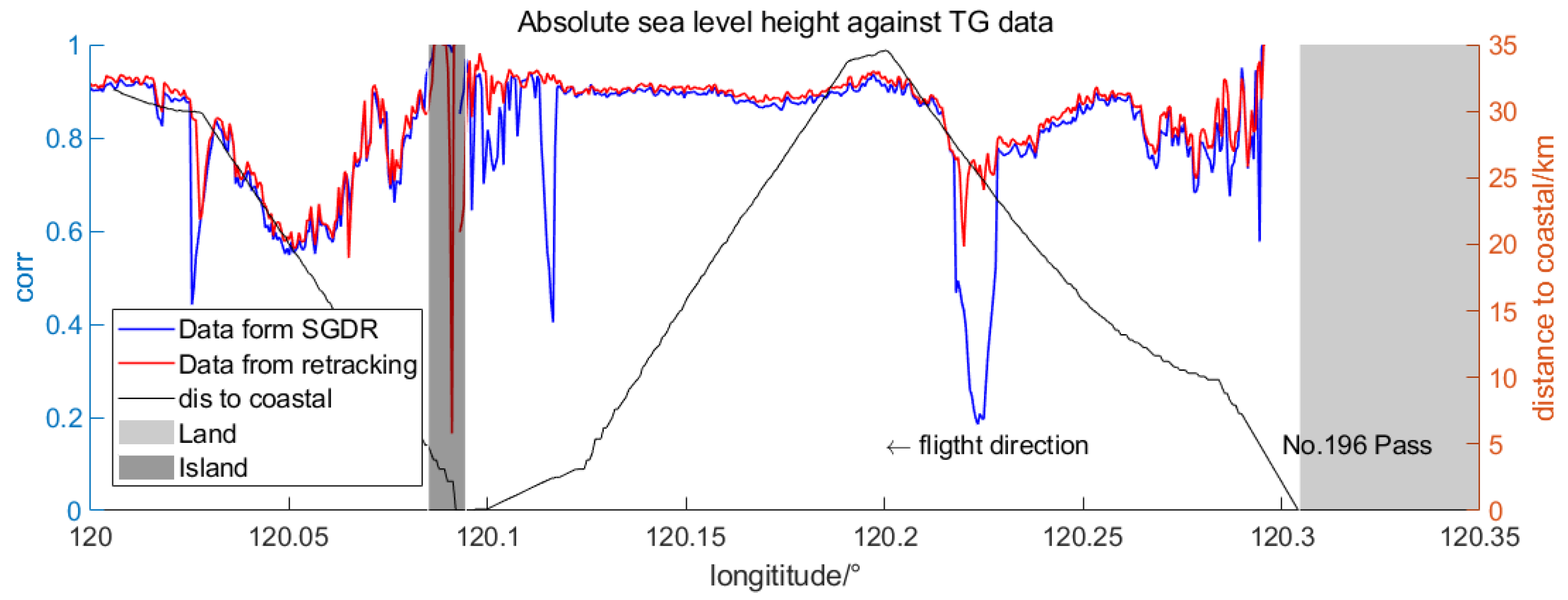
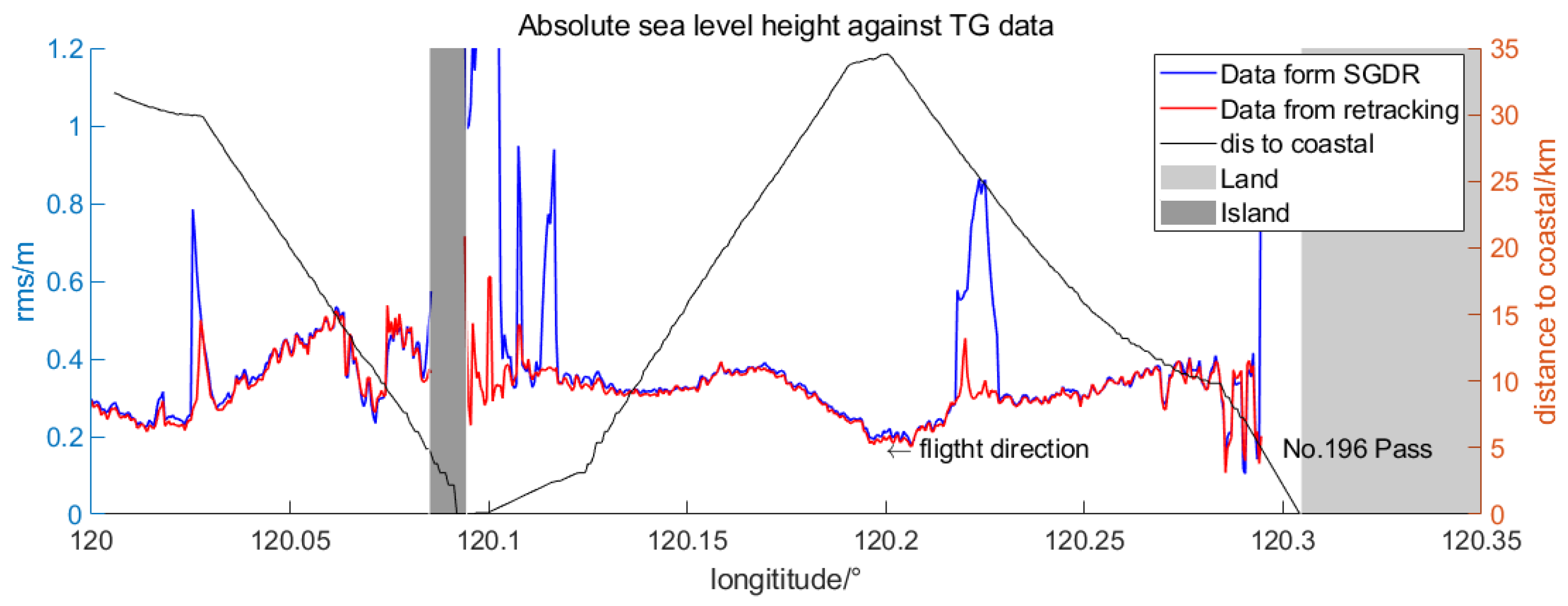
4. Waveform Retracking Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, G. The average impulse response of a rough surface and its applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1997, 25, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayne, G.S. Radar altimeter mean return waveforms from near-normal-incidence ocean surface scattering. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1980, 28, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.V.; Zwally, H.J.; Brenner, A.C. Analysis and retracking of continental ice sheet radar altimeter waveforms. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 1983, 88, 1608–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingham, D.J.; Raplet, C.G.; Griffiths, H. New techniques in satellite tracking system. In Proceedings of the IGARSS’86 Symposium, Zurich, Switzerland, 8 September 1986; pp. 1339–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.H. A robust threshold retracking algorithm for measuring ice-sheet surface elevation change from satellite radar altimeters. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 974–979. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.; Guo, J.; Deng, X.; Hsu, H.Y.; Liu, Y. Coastal gravity anomalies from retracked GEOSAT/GM altimetry: Improvement, limitation and the role of airborne gravity data. J. Geod. 2006, 80, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.T.; Smith, W. Retracking RES-1 altimeter waveforms for optimal gravity field recovery. Geophys. J. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 163, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartly, G.D.; Smith, W.H.F.; Passaro, M. Removing Intra-1-Hz Covariant Error to Improve Altimetric Profiles of σ0 and Sea Surface Height. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3741–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, M.; Cipollini, P.; Vignudelli, S.; Quartly, G.D.; Snaith, H.M. ALES: A multi-mission adaptive subwaveform retracker for coastal and open ocean altimetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, M.; Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Cipollini, P. Validation of significant wave height from improved satellite altimetry in the german bight. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2046–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birol, F.; Léger, F.; Passaro, M.; Cazenave, A.; Benveniste, J. The X-TRACK/ALES multi-mission processing system: New advances in altimetry towards the coast. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 67, 2398–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmering, D.; Müller, F.L.; Oelsmann, J.; Passaro, M.; Seitz, F. North SEAL: A new dataset of sea level changes in the North Sea from satellite altimetry. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3733–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arabsahebi, R.; Voosoghi, B.; Tourian, M.J. The Inflection-Point Retracking Algorithm: Improved Jason-2 Sea Surface Heights in the Strait of Hormuz. Mar. Geod. 2018, 41, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscher, R.; Uebbing, B.; Kusche, J. STAR: Spatio-temporal altimeter waveform retracking using sparse representation and conditional random fields. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 201, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlembach, F.; Passaro, M.; Quartly, G.D.; Kurekin, A.; Donlon, C. Round Robin Assessment of Radar Altimeter Low Resolution Mode and Delay-Doppler Retracking Algorithms for Significant Wave Height. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ichikawa, K.; Wei, D. Coastal Waveform Retracking in the Slick-Rich Sulawesi Sea of Indonesia Based on Variable Footprint Size with Homogeneous Sea Surface Roughness. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartly, G.D. Determination of Oceanic Rain Rate and Rain Cell Structure from Altimeter Waveform Data. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1998, 15, 1361–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartly, G.D. Hyperbolic Retracker: Removing Bright Target Artefacts from Altimetric Waveform Data. In ESA SP-686, Living Planet Symposium; ESA Publication: Bergen, Norway, 2010; SP-686. [Google Scholar]
- Tournadre, J. Signature of lighthouses, ships, and small islands in altimeter waveforms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2007, 24, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ichikawa, K. Coastal Waveform Retracking for Jason-2 Altimeter Data Based on Along-Track Echograms around the Tsushima Islands in Japan. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Deng, X. A new retracking technique for Brown peaky altimetric waveforms. Mar. Geod. 2017, 41, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Deng, X. Validation of Sentinel-3A SAR mode sea level anomalies around the Australian coastal region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Featherstone, W.E. A coastal retracking system for satellite radar altimeter waveforms: Application to ERS-2 around Australia. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2006, 111, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.E.; Lin, M.; Liu, Q.; Pan, D. A coastal altimetry retracking strategy based on waveform classification and sub-waveform extraction. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 7806–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurul, I.; Xiaoli, D.; Ami, M.D.; Nurul, I. CAWRES: A Waveform Retracking Fuzzy Expert System for Optimizing Coastal Sea Levels from Jason-1 and Jason-2 Satellite Altimetry Data. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 603. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, F.; Deng, X.; Cheng, X. Quantifying the precision of retracked Jason-2 sea level data in the 0–5 km Australian coastal zone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 263, 112539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C. Global Assessments of the HY-2B Measurements and Cross-Calibrations with Jason-3. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarouche, L.; Thibaut, P.; Zanife, O.Z.; Dumont, J.P.; Vincent, P.; Steunou, N. Improving the Jason-1 ground retracking to better account for attitude effects. Mar. Geod. 2004, 27, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, J.C.; Ouartly, G.D.; Kurekin, A.A.; Thibaut, P.; Hoang, D.; Nencioli, F. Development of an ENVISAT altimetry processor providing sea level continuity between open ocean and Arctic leads. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5299–5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halimi, A.; Mailhes, C.; Tourneret, J.Y.; Thibaut, P.; Boy, F. Parameter estimation for peaky altimetric waveforms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 1568–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, N.R.; Laxon, S.W. Sea surface height determination in the Arctic ocean from ERS altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2004, 109, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelton, D.B.; Walsh, E.J.; Macarthur, J.L. Pulse compression and sea level tracking in satellite altimetry. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1989, 6, 407–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipollini, P.; Calafat, F.M.; Jevrejeva, S.; Melet, A.; Prandi, P. Monitoring Sea Level in the Coastal Zone with Satellite Altimetry and Tide Gauges. Surv. Geophys. 2017, 38, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passaro, M.; Nadzir, Z.A.; Quartly, G.D. Improving the precision of sea level data from satellite altimetry with high-frequency and regional sea state bias corrections. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 218, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Deng, X. Improving precision of high-rate altimeter sea level anomalies by removing the sea state bias and intra-1-Hz covariant error. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenoglio-Marc, L.; Fehlau, M.; Ferri, L.; Becker, M.; Bao, Y.; Vignudelli, S. Coastal sea surface heights from improved altimeter data in the Mediterranean Sea. Gravity Geoid Earth Obs. 2010, 135, 253–261. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, Z.; Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Jia, Y.; Fan, C.; Cui, W. Coastal Waveform Retracking for HY-2B Altimeter Data by Determining the Effective Trailing Edge and the Low Noise Leading Edge. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195026
Hong Z, Yang J, Liu S, Jia Y, Fan C, Cui W. Coastal Waveform Retracking for HY-2B Altimeter Data by Determining the Effective Trailing Edge and the Low Noise Leading Edge. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195026
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Zhiheng, Jungang Yang, Shanwei Liu, Yongjun Jia, Chenqing Fan, and Wei Cui. 2022. "Coastal Waveform Retracking for HY-2B Altimeter Data by Determining the Effective Trailing Edge and the Low Noise Leading Edge" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195026
APA StyleHong, Z., Yang, J., Liu, S., Jia, Y., Fan, C., & Cui, W. (2022). Coastal Waveform Retracking for HY-2B Altimeter Data by Determining the Effective Trailing Edge and the Low Noise Leading Edge. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 5026. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195026