Evaluating Anthropogenic CO2 Bottom-Up Emission Inventories Using Satellite Observations from GOSAT and OCO-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Satellite Observations
- Globally mapping XCO2 dataset based on GOSAT and OCO-2
- SIF
- Other Testing Data
2.1.2. Anthropogenic CO2 Emission Inventories
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Correlating Emission Inventories and Satellite Observed XCO2
2.2.2. Comparing Emission Inventories with Predicted Emissions by a Machine Learning-Based Model Based on Satellite Observations
- (1)
- Predicting area and year
- (2)
- GRNN structure
3. Results
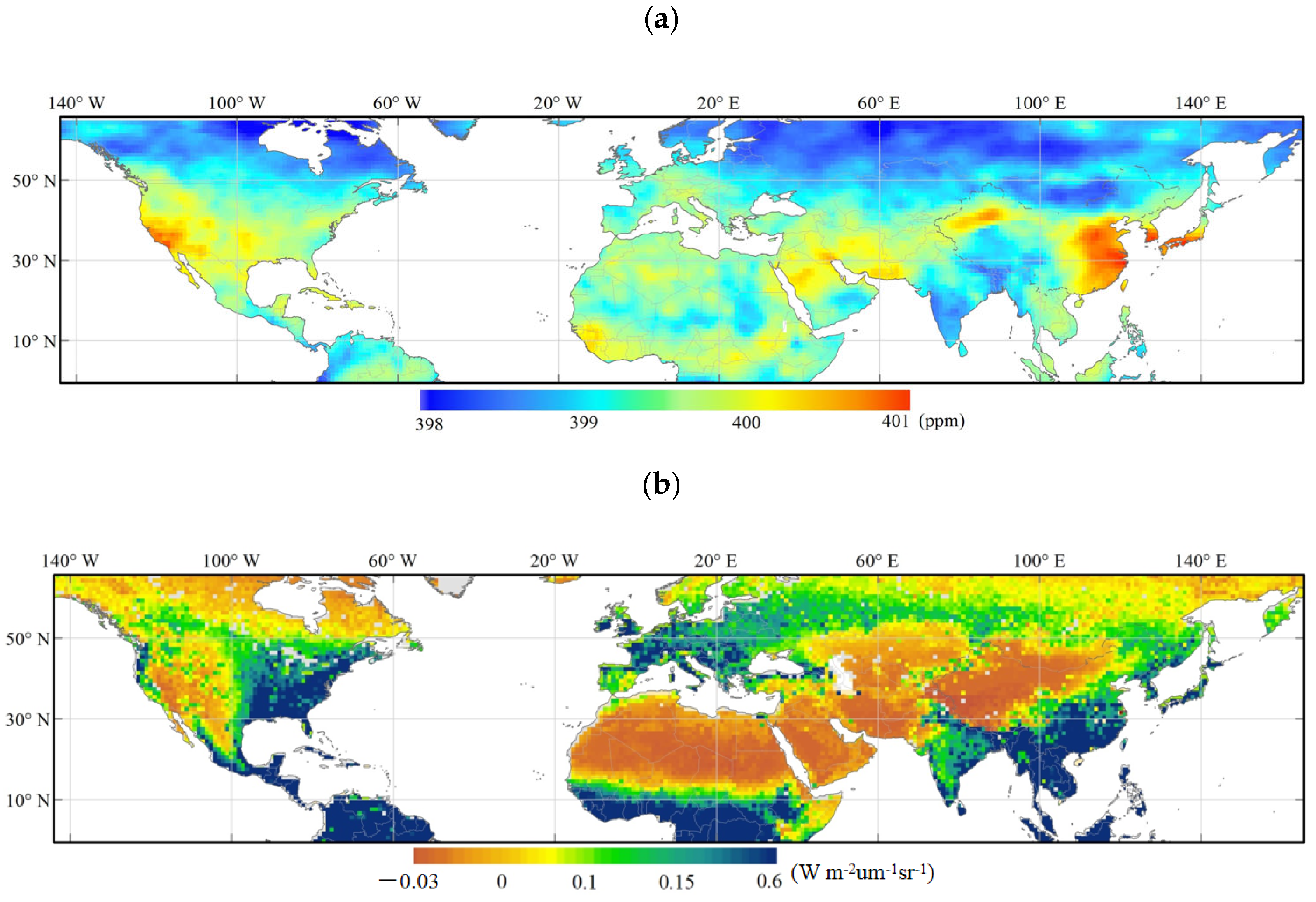
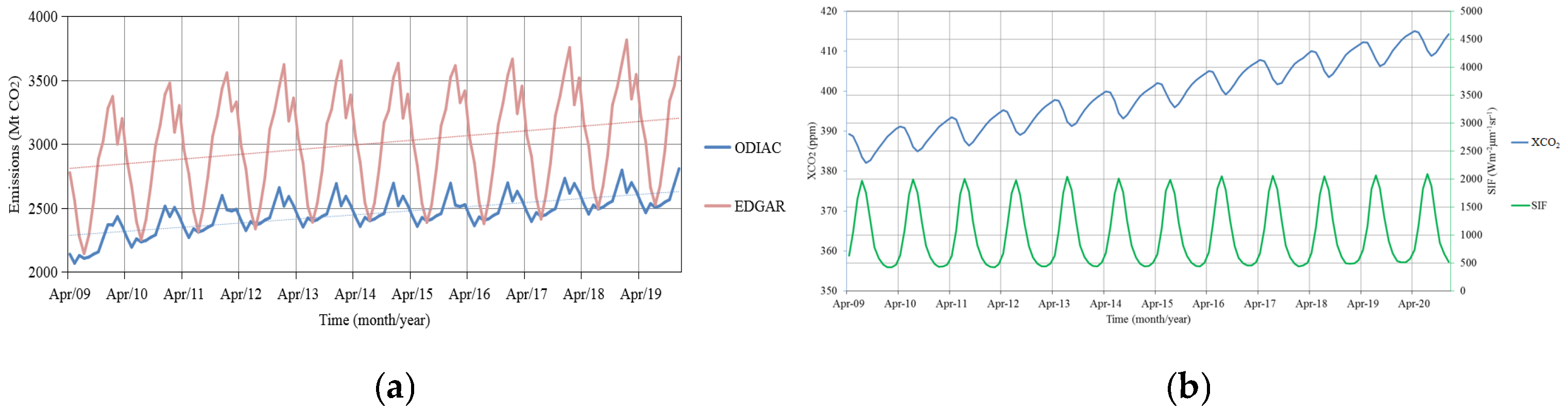
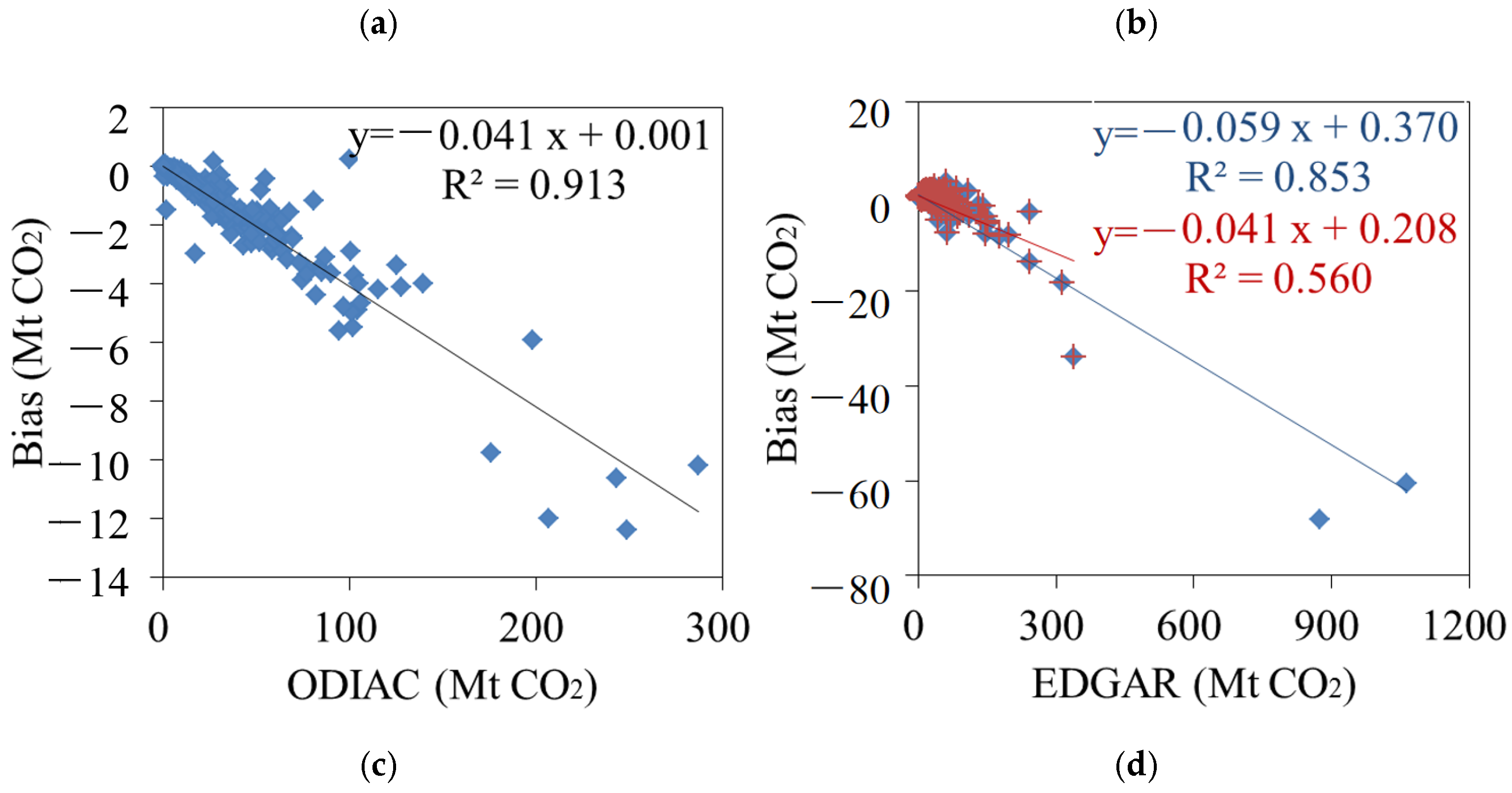
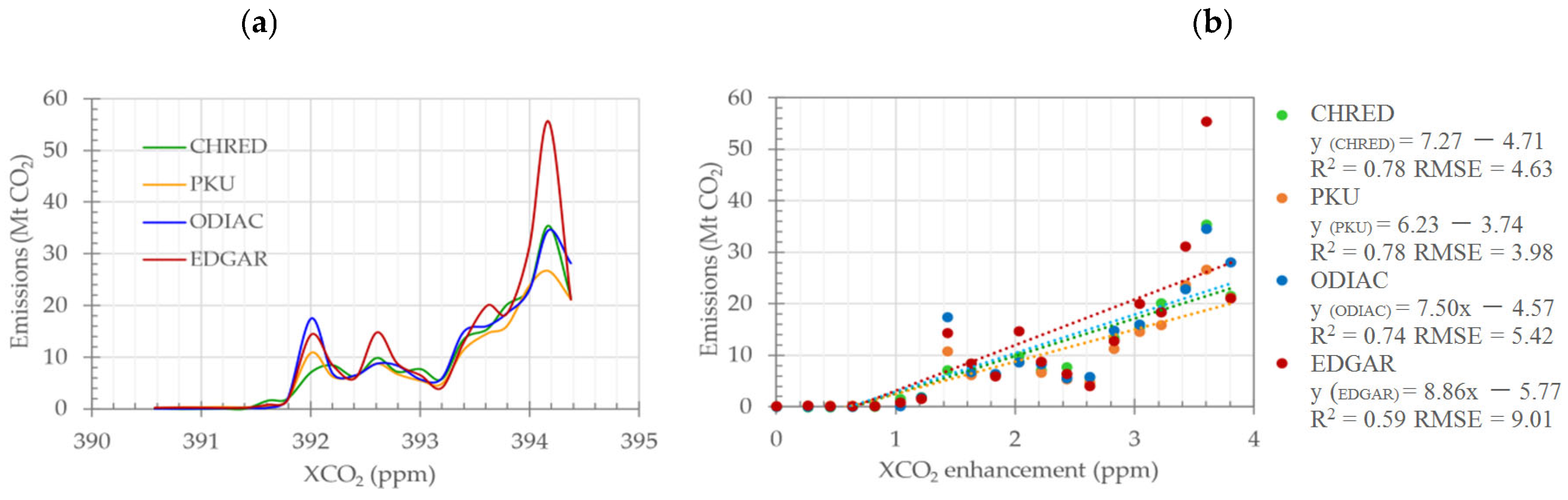
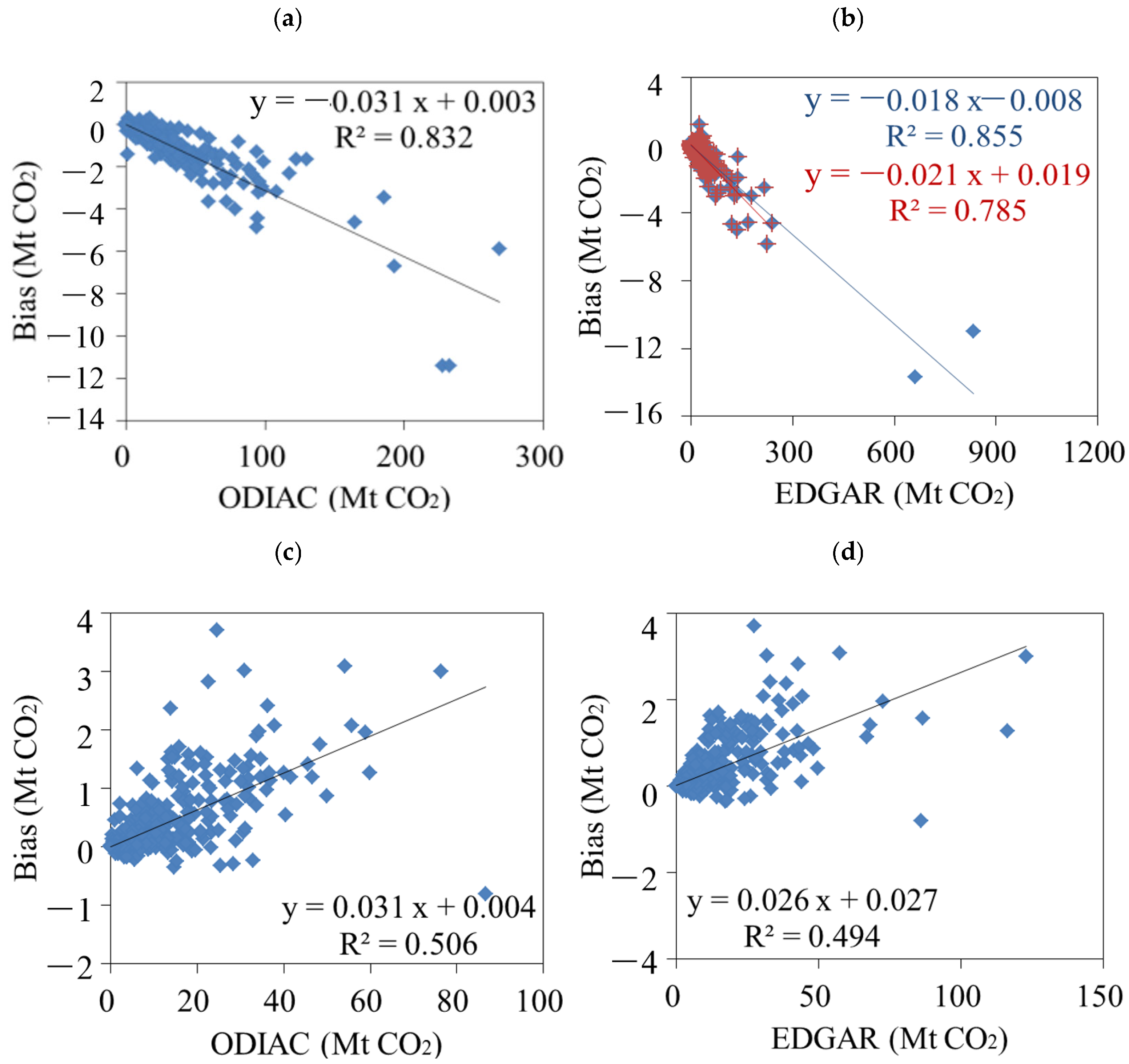
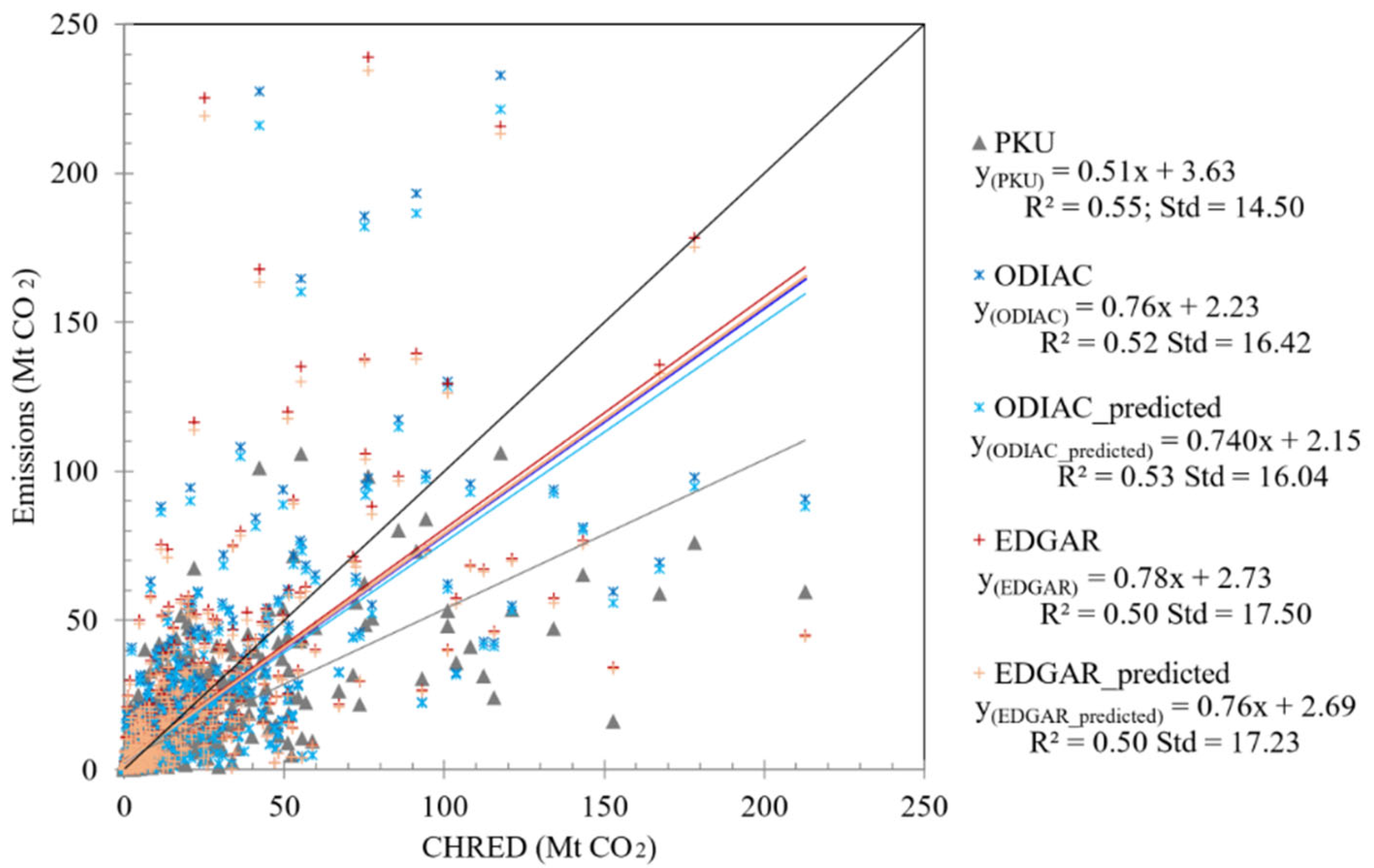
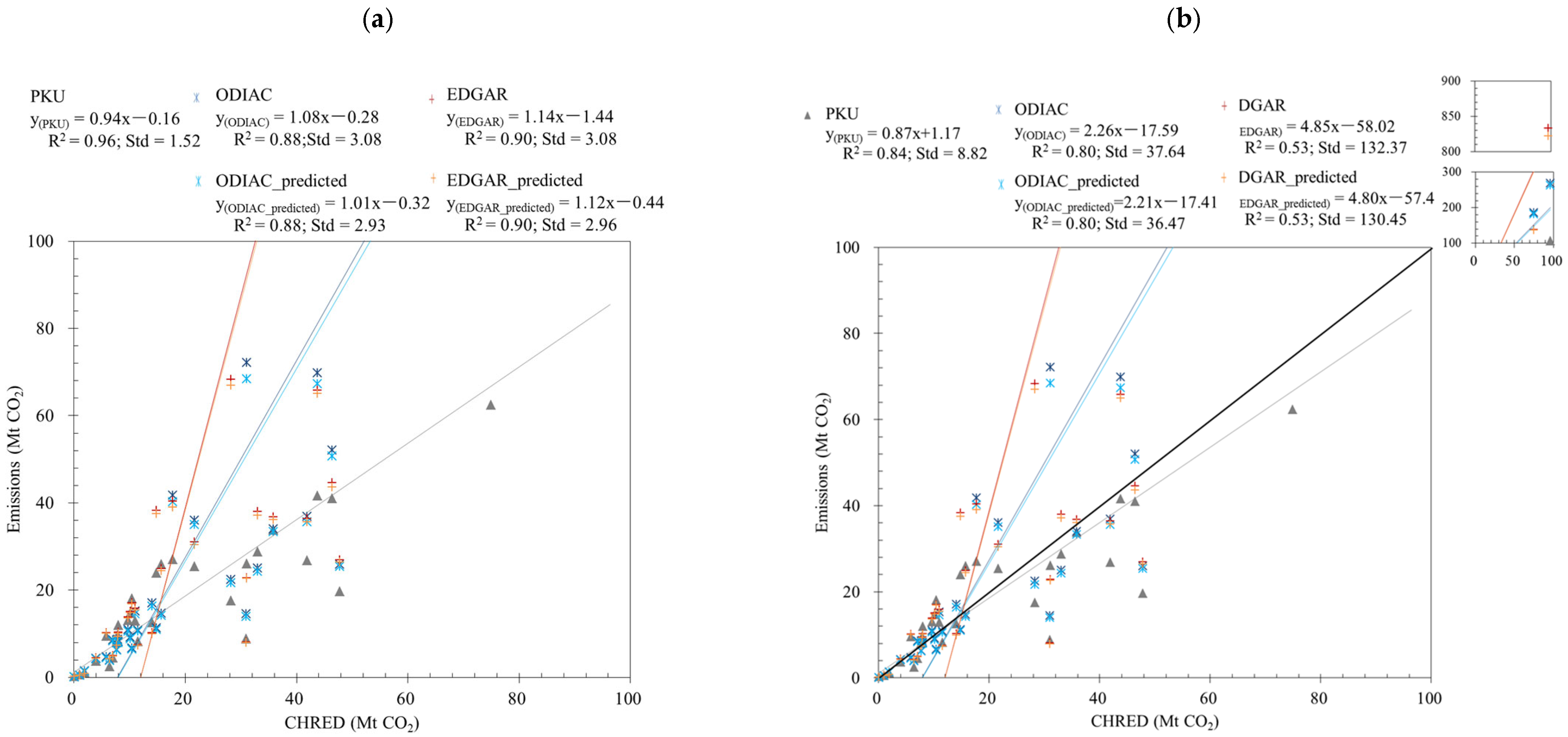
3.1. Correlations between Emission Inventories and Satellite-Observed XCO2
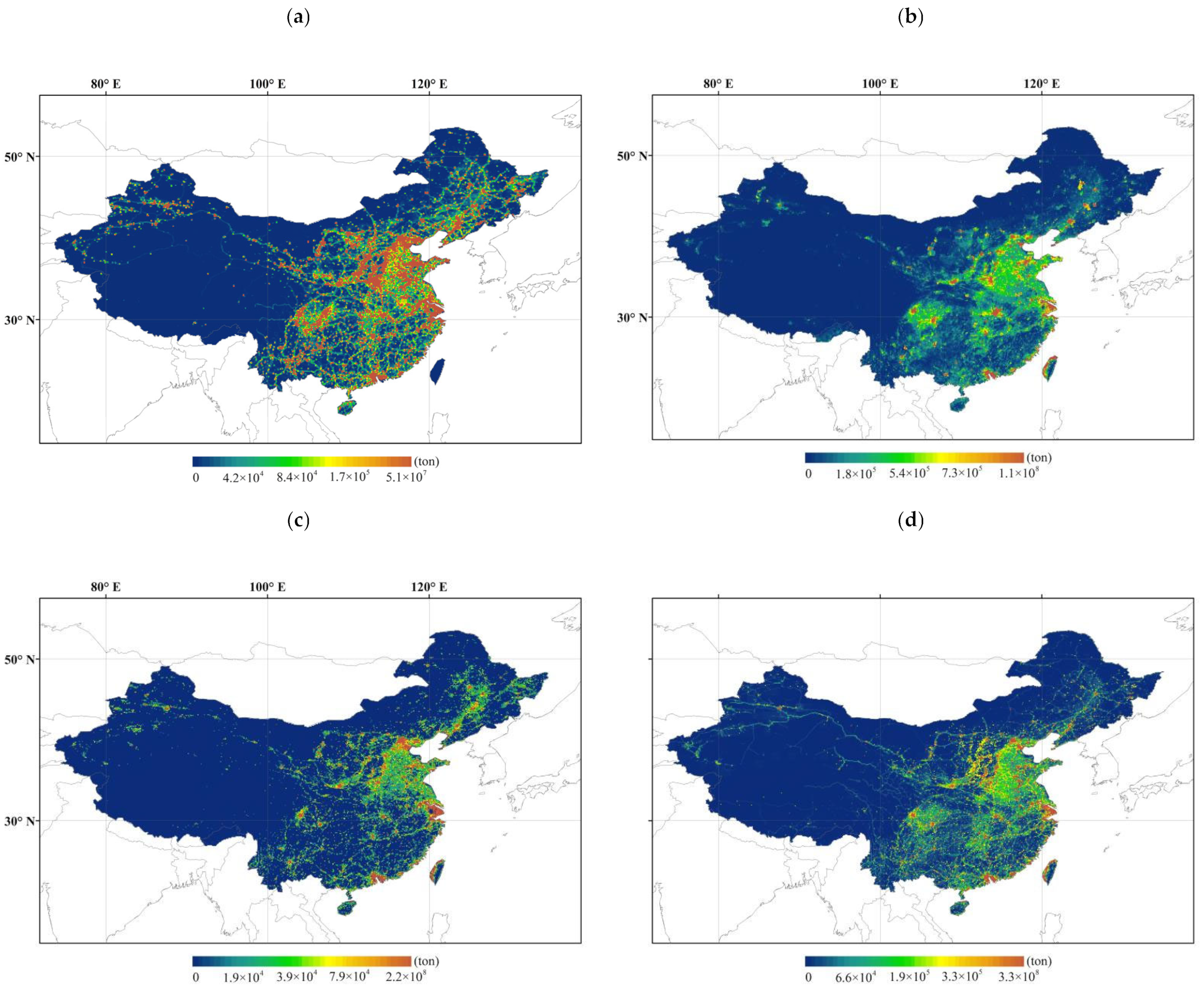
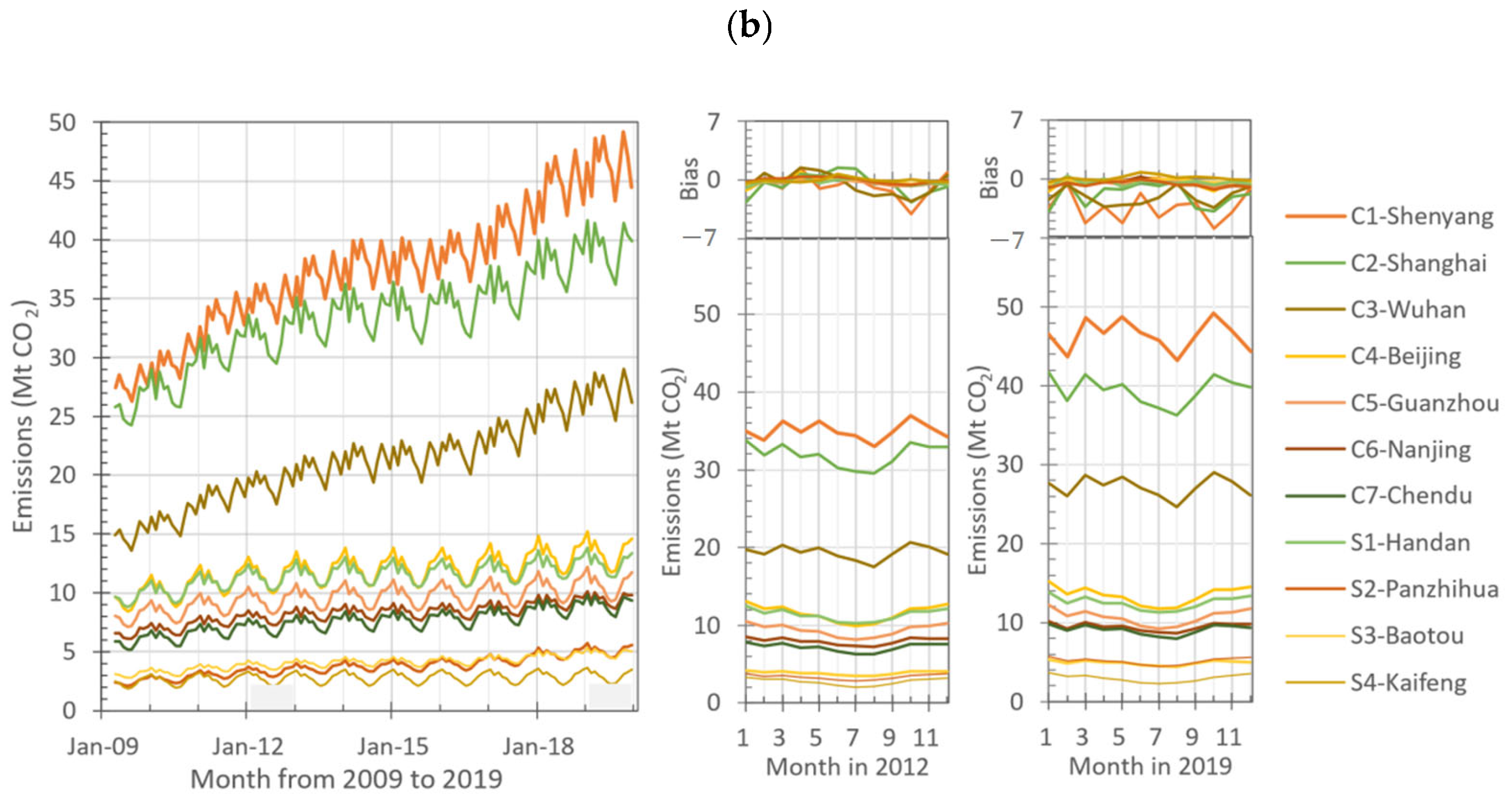
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Uncertainties of ODIAC and EDGAR
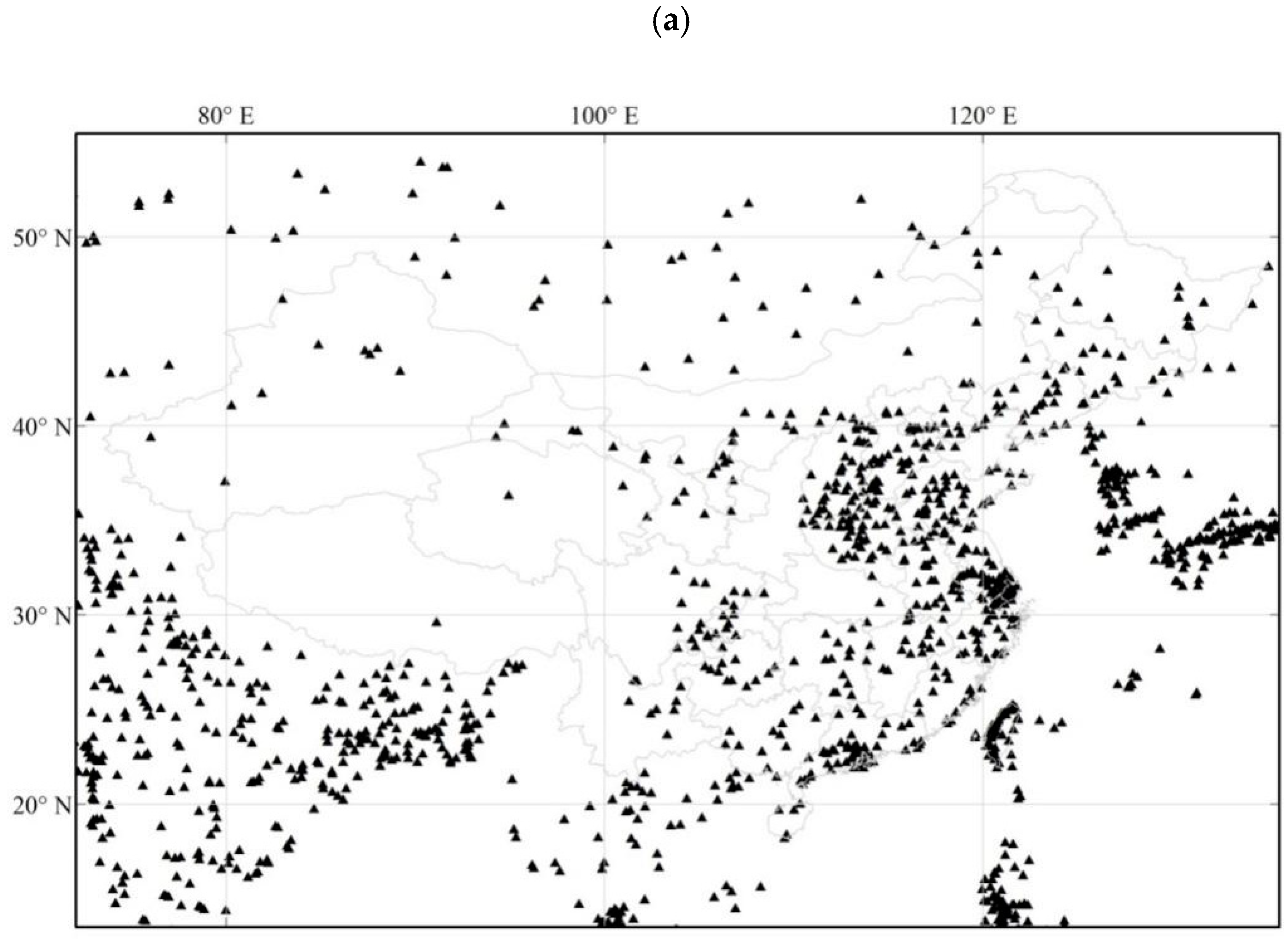
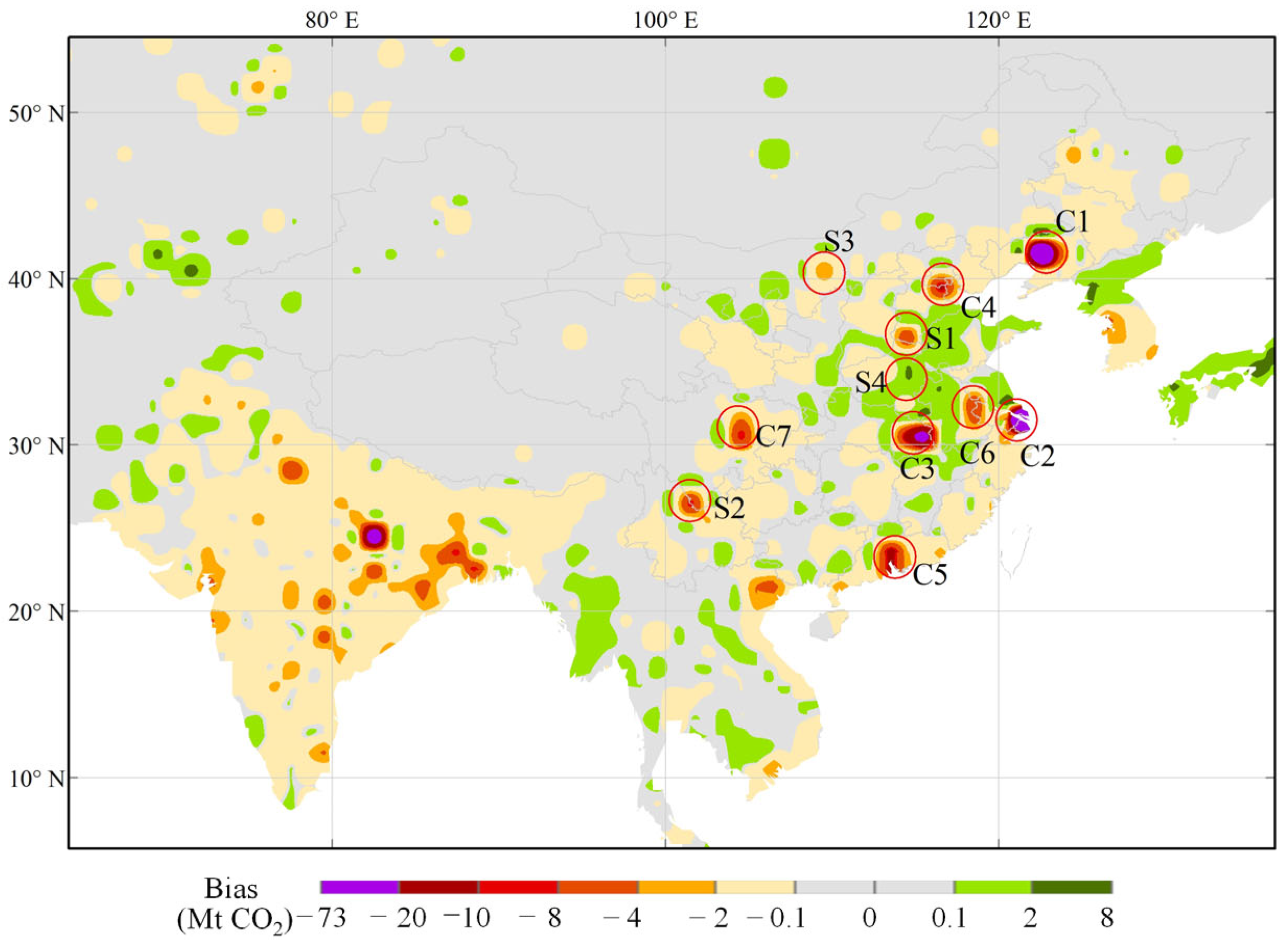
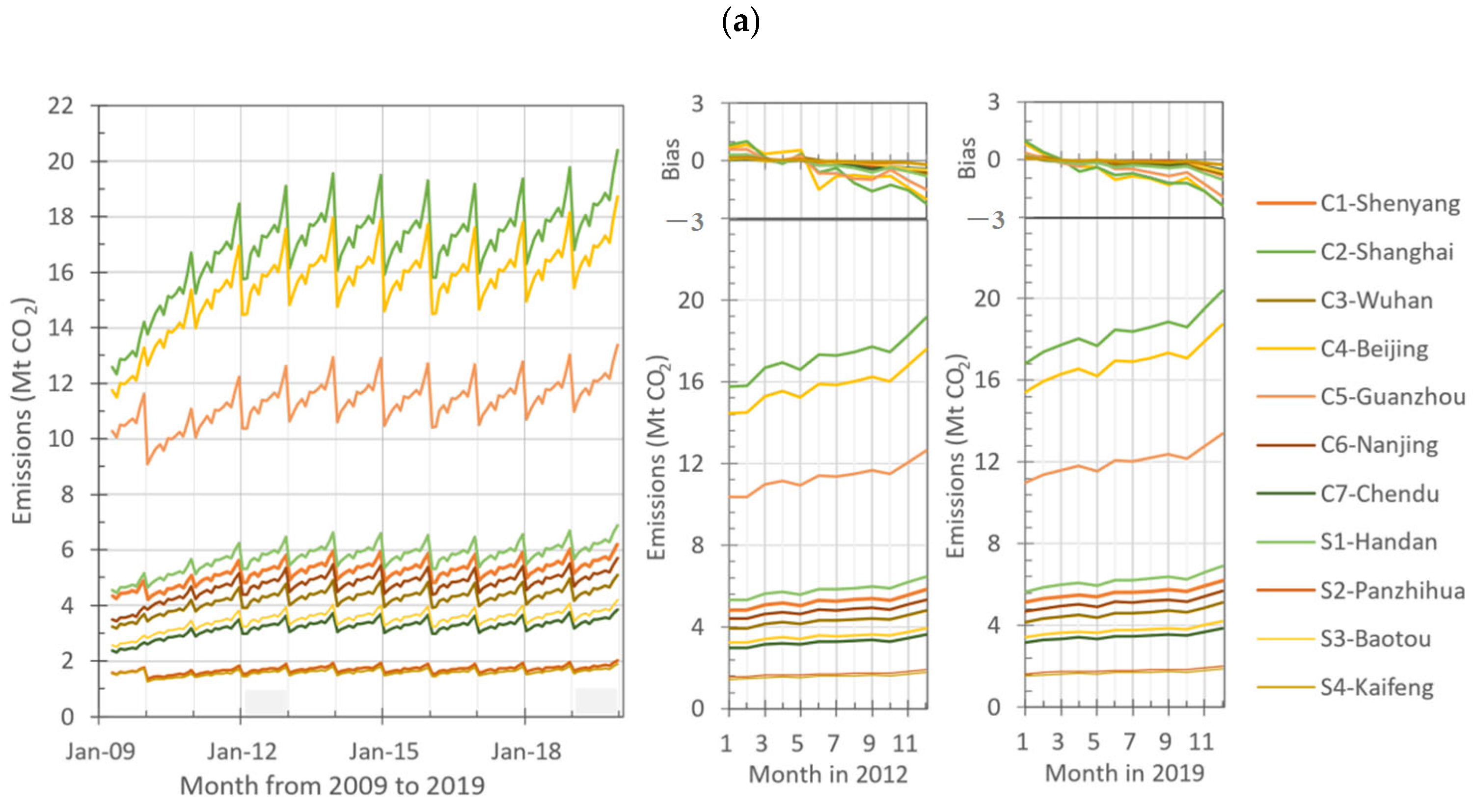
3.2.1. Spatial Distribution of Inventory Emissions
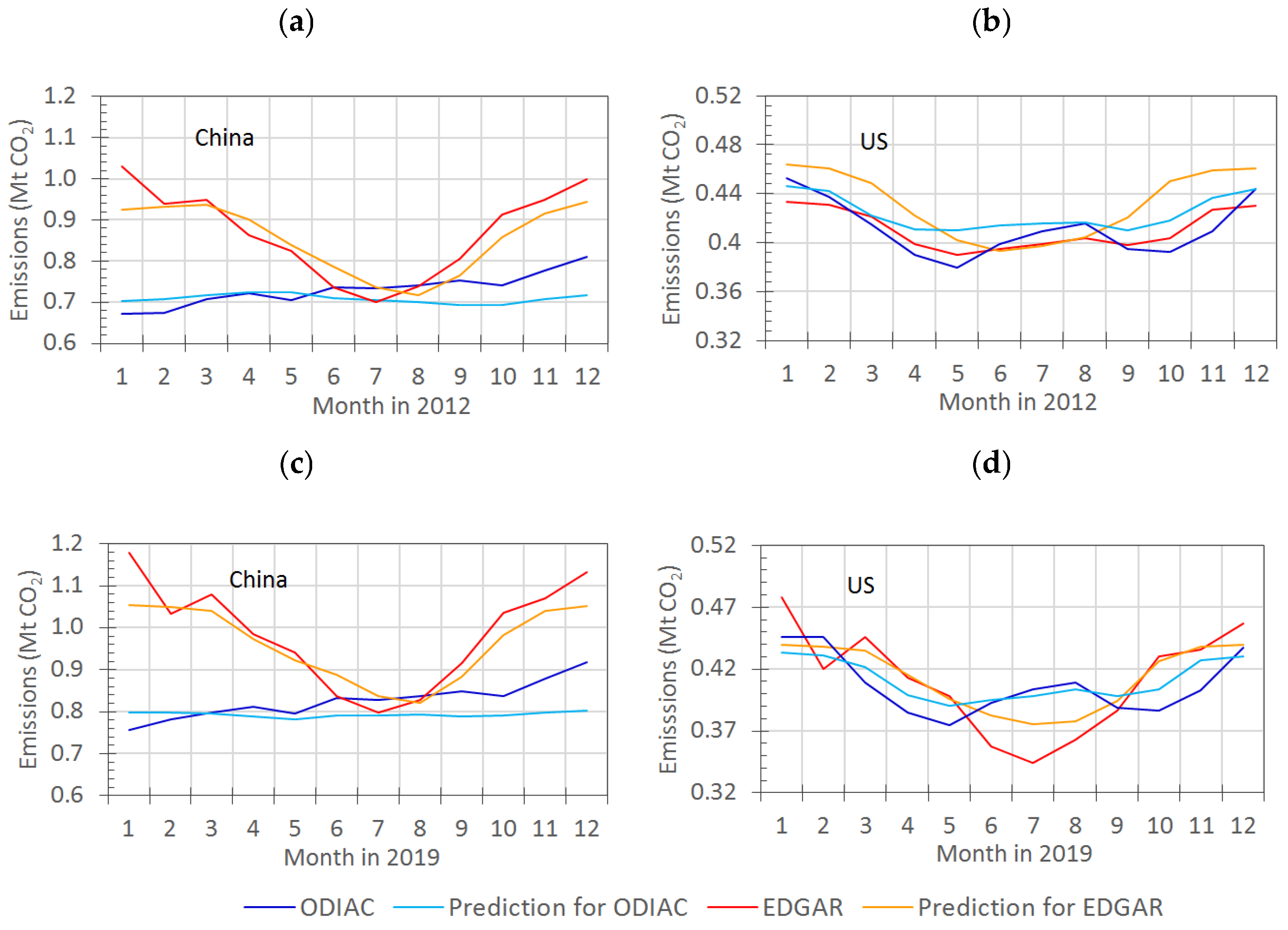
3.2.2. Seasonal Variation of Emissions in Inventories
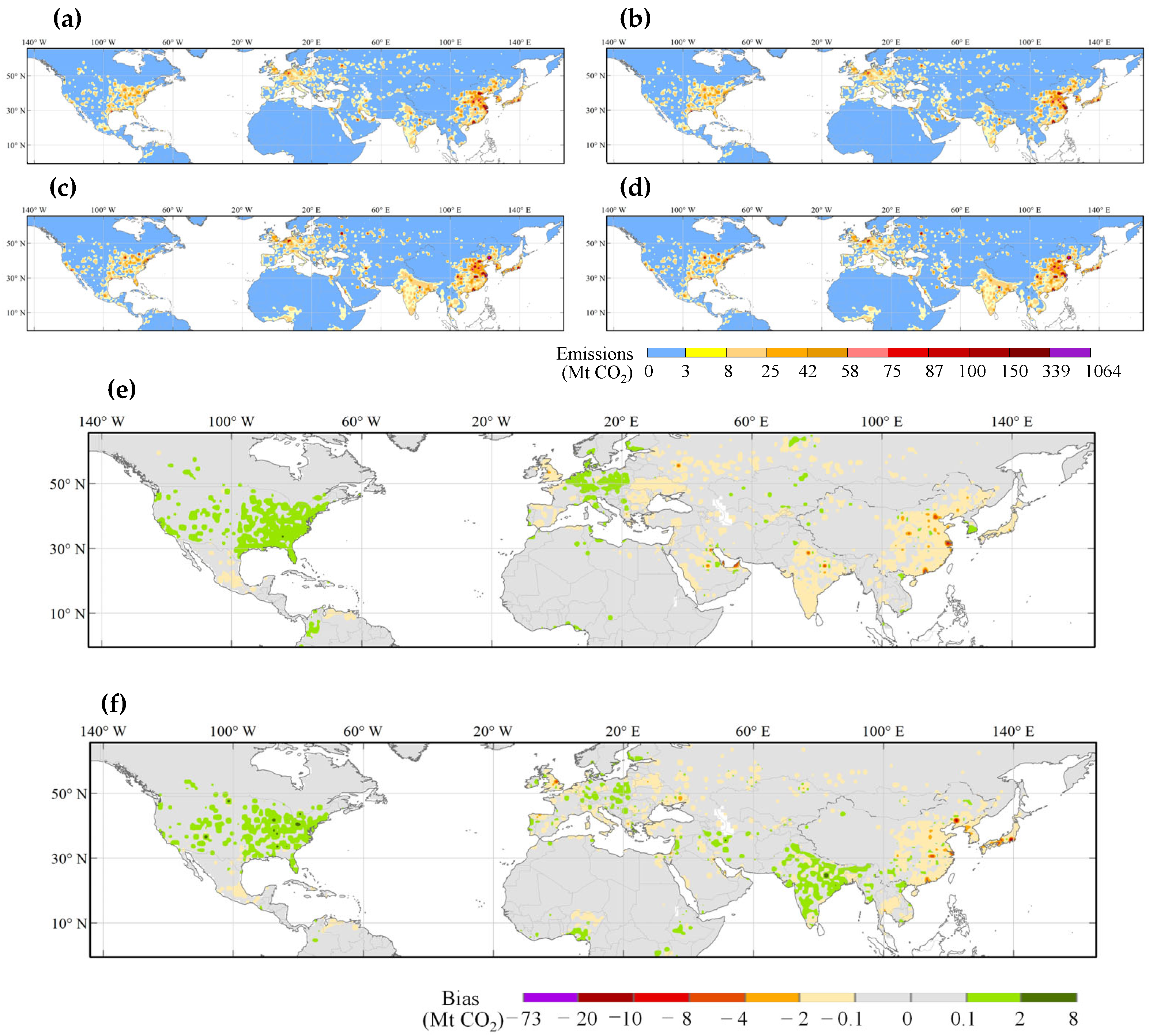
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Units (Mt CO2) | China | USA | India | Europe | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | ODIAC | Inventory | 9696 | 4763 | 1827 | 3453 |
| Prediction | 9396 | 4904 | 1751 | 3423 | ||
| Total bias | −300 | 141 | −76 | −30 | ||
| Mean bias | −0.27 | 0.15 | −0.28 | −0.05 | ||
| Maximum bias | 0.32 | 2.24 | 0.11 | 1.54 | ||
| Minimum bias | −11.42 | −0.19 | −6.30 | −3.16 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.78 | 0.27 | 0.59 | 0.32 | ||
| EDGAR | Inventory | 11,546 | 4844 | 2843 | 4119 | |
| Prediction | 11,334 | 4997 | 2883 | 4049 | ||
| Total bias | −212 | 153 | 41 | −70 | ||
| Mean bias | −0.19 | 0.16 | 0.15 | −0.11 | ||
| Maximum bias | 1.22 | 3.70 | 6.79 | 1.57 | ||
| Minimum bias | −13.68 | −0.81 | −1.51 | −7.75 | ||
| Standard deviation | 0.74 | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.54 | ||
| 2019 | ODIAC | Inventory | 10,372 | 4707 | 2455 | 3068 |
| Prediction | 9947 | 4754 | 2363 | 3252 | ||
| Total bias | −425 | 47 | −92 | 184 | ||
| Mean bias | −0.38 | 0.05 | −0.34 | 0.28 | ||
| Maximum bias | 0.22 | 2.71 | 0.01 | 8.64 | ||
| Minimum bias | −12.37 | −0.45 | −5.36 | −2.15 | ||
| Standard deviation | 1.04 | 0.16 | 0.62 | 0.73 | ||
| EDGAR | Inventory | 12,996 | 4752 | 3504 | 3777 | |
| Prediction | 12,641 | 4773 | 3224 | 3889 | ||
| Total bias | −355 | 21 | −280 | 113 | ||
| Mean bias | −0.32 | 0.02 | −1.03 | 0.17 | ||
| Maximum bias | 3.12 | 3.21 | 1.20 | 8.15 | ||
| Minimum bias | −73.43 | −4.87 | −31.06 | −1.35 | ||
| Standard deviation | 3.00 | 0.48 | 2.32 | 0.66 | ||
| Number of sampling grids | 1105 | 964 | 273 | 664 | ||



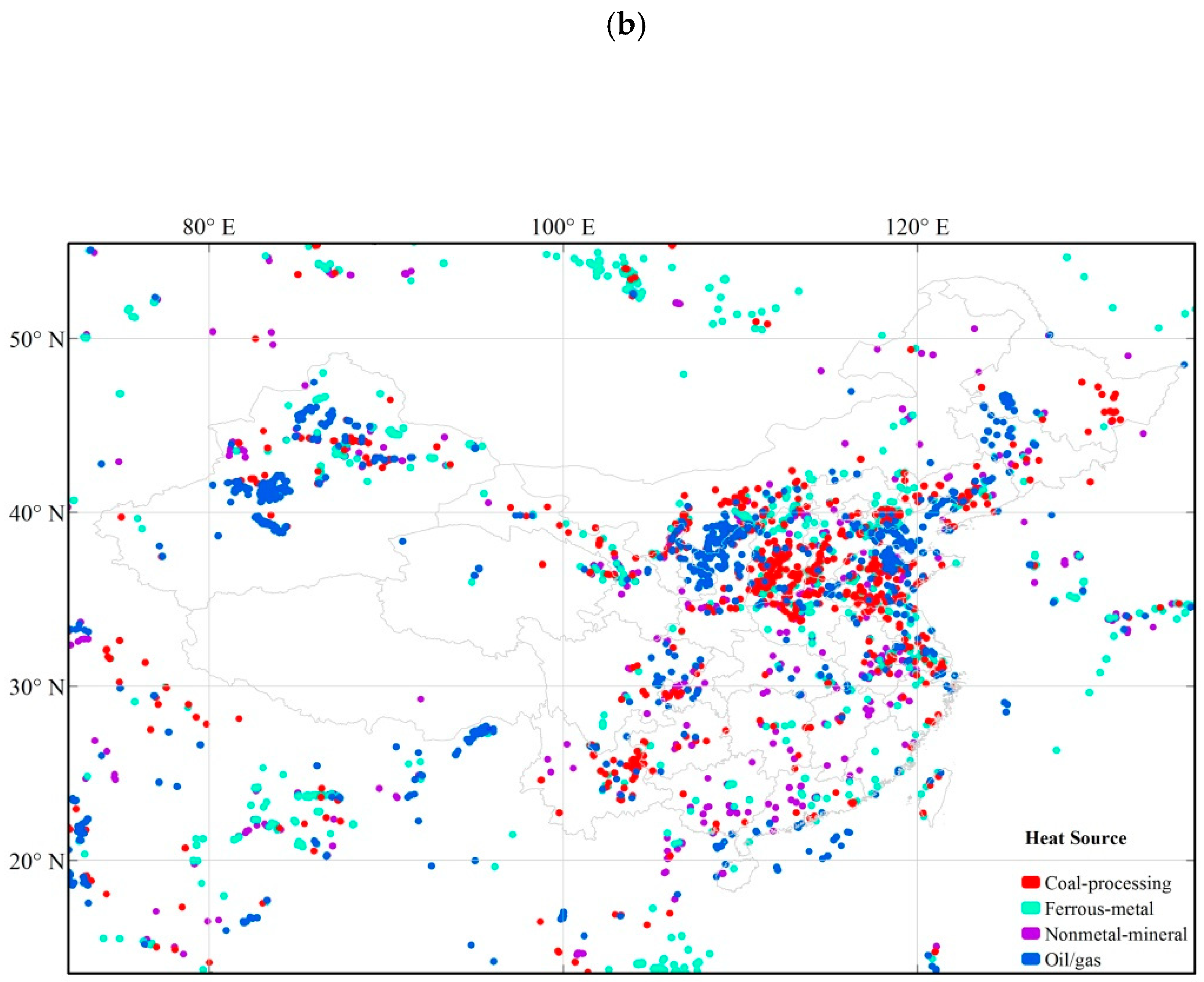
References
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S. A very high-resolution (1 km × 1 km) global fossil fuel CO2 emission inventory derived using a point source database and satellite observations of nighttime lights. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Maksyutov, S.; Andres, R.J. The Open-source Data Inventory for Anthropogenic Carbon dioxide (CO2), version 2016 (ODIAC2016): A global, monthly fossil-fuel CO2 gridded emission data product for tracer transport simulations and surface flux inversions. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Muntean, M.; Petrescu, A. Edgar v4.3.2 global atlas of the three major greenhouse gas emissions for the period 1970–2012. Earth Syst. Sci. Data Discuss. 2017, 11, 959–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Liang, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, J.; Cao, L.; Qu, S.; Xu, M.; Yang, Z. China high resolution emission database (CHRED) with point emission sources, gridded emission data, and supplementary socioeconomic data. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 129, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tao, S.; Ciais, P.; Shen, H.Z.; Huang, Y.; Chen, H.; Shen, G.F.; Wang, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; et al. High-resolution mapping of combustion processes and implications for CO2 emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5189–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.J.; Boden, T.A.; Higdon, D. A new evaluation of the uncertainty associated with CDIAC estimates of fossil fuel carbon dioxide emission. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2014, 66, 23616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Zeng, N.; Oda, T.; Lin, X.; Crippa, M.; Guan, D.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Shan, Y.; et al. Evaluating China’s fossil-fuel CO2 emissions from a comprehensive dataset of nine inventories. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 11371–11385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, R.J.; Boden, T.A.; Higdon, D.M. Gridded uncertainty in fossil fuel carbon dioxide emission maps, a CDIAC example. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 14979–14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, K.; Razlivanov, I.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Benes, B.; Abdul-Massih, M. Quantification of fossil fuel CO2 emission on the building/street scale for a large US city. Env. Sci Technol. 2012, 46, 12194–12202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, T.; Bun, R.; Kinakh, V.; Topylko, P.; Halushchak, M.; Marland, G.; Lauvaux, T.; Jonas, M.; Maksyutov, S.; Nahorski, Z.; et al. Errors and uncertainties in gridded carbon dioxide emissions inventory. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2019, 24, 1007–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauvaux, T.; Miles, N.L.; Deng, A.; Richardson, S.J.; Cambaliza, M.O.; Davis, K.J.; Gaudet, B.; Gurney, K.R.; Huang, J.; O’Keefe, D.; et al. High-resolution atmospheric inversion of urban CO2 emissions during the dormant season of the Indianapolis flux experiment (INFLUX). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 5213–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevallier, F.; Broquet, G.; Zheng, B.; Ciais, P.; Eldering, A. Large CO2 emitters as seen from satellite: Comparison to a gridded global emission inventory. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 49, e2021GL097540. [Google Scholar]
- Jonas, M.; Marland, G.; Krey, V.; Wagner, F.; Nahorski, Z. Uncertainty in an emissions-constrained world. Clim. Change 2014, 124, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneising, O.; Heymann, J.; Buchwitz, M.; Reuter, M.; Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J. Anthropogenic carbon dioxide source areas observed from space: Evaluatement of regional enhancements and trends. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 2445–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppel-Aleks, G.; Wennberg, P.O.; O’Dell, C.W.; Wunch, D. Towards constraints on fossil fuel emissions from total column carbon dioxide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4349–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.P.; Zhong, H.; He, Z.H.; Cai, B.F.; Yang, S.Y.; Wu, C.J.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhang, B. Assessment of atmospheric CO2 concentration enhancement from anthropogenic emissions based on satellite observations. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2017, 62, 2941–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Lei, L.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Rao, W.; Zhang, S. Detecting the Responses of CO2 Column Abundances to Anthropogenic Emissions from Satellite Observations of GOSAT and OCO-2. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovensmann, H.; Buchwitz, M.; Burrows, J.P.; Reuter, M.; Krings, T.; Gerilowski, K.; Schneising, O.; Heymann, J.; Tretner, A.; Erzinger, J. A remote sensing technique for global monitoring of power plant CO2 emissions from space and related applications. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 781–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Lei, L.P.; Guo, L.J.; Zeng, Z.C. A Cluster of CO2 Change Characteristics with GOSAT Observations for Viewing the Spatial Pattern of CO2 Emission and Absorption. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1695–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, N.; Lei, L.; He, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Cai, B. Specific patterns of XCO2 observed by gosat during 2009–2016 and assessed with model simulations over China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2020, 63, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkarainen, J.; Ialongo, I.; Tamminen, J. Direct space-based observations of anthropogenic CO2 emission areas from OCO-2. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lei, L.; Zeng, Z.; He, Z.; Zhong, H. An Evaluatement of Anthropogenic CO2 Emissions by Satellite-Based Observations in China. Sensors 2019, 19, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, F.; Bu, L.; Wang, Q.; Yao, N.; Shahzaman, M.; Bilal, M.; Aslam, R.W.; Iqbal, R.; Mustafa, F.; Bu, L.; et al. Neural Network Based Estimation of Regional Scale Anthropogenic CO2 Emissions Using OCO-2 Dataset Over East and West Asia. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 7277–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Dowell, M.; Zunker, H.; Brunhes, T.; Ciais, P.; Dee, D.; Denier van der Gon, H.; Dolman, H.; Drinkwater, M.; et al. Toward an operational anthropogenic CO2 emissions monitoring & verification support capacity—Baseline requirements, model components and functional architecture. Eur. Comm. Jt. Res. Cent. 2020, 101, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In Global Warming of 1.5 °C; Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Pörtner, H.-O., Roberts, D., Skea, J., Shukla, P.R., Pirani, A., Moufouma-Okia, W., Péan, C., Pidcock, R., et al., Eds.; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Goddard Earth Science Data Information and Services Center (GES DISC) at National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Available online: https://oco2.gesdisc.eosdis.nasa.gov/data/ (accessed on 19 January 2021).
- Crisp, D.; Frankenberg, C.; Messerschmidt, J.; Wennberg, P.O.; Wunch, D.; Yung, Y.L. The ACOS CO2 retrieval algorithm—Part II: Global XCO2 data characterization. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 687–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, C.W.; Eldering, A.; Wennberg, P.O.; Crisp, D.; Gunson, M.R.; Fisher, B.; Frankenberg, C.; Velazco, A. Improved retrievals of carbon dioxide from Orbiting Carbon observatory-2 with the version 8 ACOS algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6539–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiel, M.; O’Dell, C.W.; Fisher, B.; Eldering, A.; Nassar, R.; MacDonald, C.G.; Wennberg, P.O. How bias correction goes wrong: Measurement of XCO2 affected by erroneous surface pressure estimates. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 2241–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.-C.; Lei, L.; Hou, S.; Ru, F.; Guan, X.; Zhang, B. A regional gap-filling method based on spatiotemporal variogram model of columns. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 3594–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.-C.; Lei, L.; Strong, K.; Jones, D.B.A.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Deng, F.; Deutscher, N.M.; Dubey, M.K.; Griffith, D.W.T.; et al. Global land mapping of satellite-observed CO2 total columns using spatio-temporal geostatistics. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2017, 10, 426–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.J.; Lei, L.P.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Zou, P.F.; Liu, D.; Zhang, B. Evaluation of spatio-temporal variogram models for Mapping XCO2 using satellite observations: A Case Study in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Lei, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, M.; Wu, C.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.-C.; Welp, L.R. Spatio-temporal mapping of multi-satellite observed column atmospheric CO2 using precision-weighted kriging method. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, X.; He, B.; Arain, M.A.; Beringer, J.; Desai, A.R.; Emmel, C.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Krasnova, A.; Mammarella, I.; et al. Solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence exhibits a universal relationship with gross primary productivity across a wide variety of biomes. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, e4–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, J.; Nichol, C.; Disney, M.; Lewis, P.; Quaife, T.; Bowyer, P. Can we measure terrestrial photosynthesis from space directly, using spectral reflectance and fluorescence? Glob. Change Biol. 2007, 13, 1484–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meroni, M.; Rossini, M.; Guanter, L.; Alonso, L.; Rascher, U.; Colombo, R.; Moreno, J. Remote sensing of solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence: Review of methods and applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2037–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmström, C.M.; Thompson, M.V.; Juday, G.P.; Los, S.O.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B. Interannual variation in global-scale net primary production: Testing model estimates. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1997, 11, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC). Available online: https://ladsweb.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Copernicus Climate Data Store (CDS). Available online: https://cds.climate.copernicus.eu/ (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Stephen, M.; Stephanie, W.; Calvin, L. VIIRS day/night band (DNB) stray light characterization and correction. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–29 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Integrated Carbon Observation System(ICOS). Available online: https://meta.icos-cp.eu/collections/unv31HYRKgullLjJ99O5YCsG/ (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- Kuenen, J.J.P.; Visschedijk, A.J.H.; Jozwicka, M.; van der Gon, H.A.C.D. Tno-macc_ii emission inventory; a multi-year (2003–2009) consistent high-resolution european emission inventory for air quality modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 10963–10976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, J.; Gerbig, C.; Denbeck, C.R.; Karstens, U.; Minejima, C.; Mukai, H. The CO2 release and oxygen uptake from fossil fuel emission estimate (coffee) dataset: Effects from varying oxidative ratios. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 6855–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Liu, Z.; Geng, Y.; Lindner, S.; Hubacek, K. The gigatonne gap in China’s carbon dioxide inventories. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppel-Aleks, G.; Wennberg, P.O.; Schneider, T. Sources of variations in total column carbon dioxide. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 3581–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchins, M.G.; Colby, J.D.; Marland, G.; Marland, E. A comparison of five high-resolution spatially-explicit, fossil-fuel, carbon 395 dioxide emission inventories for the United States. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Change 2017, 22, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldt, C. Updating and Upgrading the PHOXA Emission Data Base to 1990; TNO report; Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research: Apeldoorn, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 92–118. [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich, R.; Reis, S. Emissions of Air Pollutants—Measurements, Calculations and Uncertainties; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Specht, D.F. A general regression neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1991, 2, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigizoglu, H.K.; Alp, M. Generalized regression neural network in modelling river sediment yield. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2006, 37, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Global Development (CGD). Available online: https://www.cgdev.org/ (accessed on 24 January 2021).
- Wang, C.; Corbett, J.J.; Firestone, J. Improving Spatial Representation of Global Ship Emissions Inventories. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Builtjes, P.J.H. The LOTOS Long Term Ozone Simulation Project; Summary Report TNO Technical Report R92/245 TNO-MW; TNO: Delft, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Andres, R.J.; Gregg, J.S.; Losey, L.; Marland, G.; Boden, T.A. Monthly, global emissions of carbon dioxide from 355 fossil fuel consumption. Tellus B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 309–327. [Google Scholar]
- The People’s Republic of China on the 13th Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development Program [EB/OL]. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2016-03/17/content_5054992.html/ (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Ma, C.; Yang, J.; Xia, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. A Model for Expressing Industrial Information Based on Object-Oriented Industrial Heat Sources Detected Using Multi-Source Thermal Anomaly Data in China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Chen, L.F.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.X.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, N.M.; Ju, W.M.; Jiang, F.; Yin, Z.S.; Liu, G.H. Satellite remote sensing for global stocktaking: Methods, progress and perspectives. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 243–267. [Google Scholar]

| Specification | CHRED | PKU | ODIAC | EDGAR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Covering area | China | Global | Global | Global |
| Period used | 2012 | 2012 | 2009–2019 | 2009–2019 |
| Resolution (Time/space) | Monthly/10 km | Monthly/0.1 deg | Monthly/1 km | Monthly/0.1 deg |
| Emission factor for raw coal (tC per ton coal) | 0.518 | 0.518 | 0.746 | 0.713 |
| Uncertainty | 8% | 19% | 17.5% | 15% |
| Energy statistic source | CESY | CESY | IEA | IEA |
| Point source | FCPSC | CARMA 2.0 | CARMA 2.0 | CARMA 3.0 |
| Line source | national road, railway, navigation network, and traffic flows | Not available | Not available | OpenStreetMap and OpenRailway Map, Int.aviation and bunker |
| Area source | Population density, land use, human activity | Night-time light, Population density, Vegetation | Night-time light | Night-time light, Population density |
| Version | CHRED | PKU-CO2-v2 | ODIAC2020 | EDGARv4.3.2_bp |
| Released source | Data developer | http://inventory.pku.edu.cn/download/download.html (accessed on 10 January 2021) | http://db.cger.nies.go.jp/dataset/ODIAC/ (accessed on 10 January 2021) | https://meta.icos-cp.eu/collections/unv31HYRKgullLjJ99O5YCsG (accessed on 10 January 2021) |
| References | Cai et al. (2018) [4] | Wang et al. (2013) [5] | Oda et al. (2018) [2] | Janssens-Maenhout (2017) [3] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Lei, L.; Sheng, M.; Song, H.; Li, L.; Guo, K.; Ma, C.; Liu, L.; Zeng, Z. Evaluating Anthropogenic CO2 Bottom-Up Emission Inventories Using Satellite Observations from GOSAT and OCO-2. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5024. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195024
Zhang S, Lei L, Sheng M, Song H, Li L, Guo K, Ma C, Liu L, Zeng Z. Evaluating Anthropogenic CO2 Bottom-Up Emission Inventories Using Satellite Observations from GOSAT and OCO-2. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):5024. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195024
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shaoqing, Liping Lei, Mengya Sheng, Hao Song, Luman Li, Kaiyuan Guo, Caihong Ma, Liangyun Liu, and Zhaocheng Zeng. 2022. "Evaluating Anthropogenic CO2 Bottom-Up Emission Inventories Using Satellite Observations from GOSAT and OCO-2" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 5024. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195024
APA StyleZhang, S., Lei, L., Sheng, M., Song, H., Li, L., Guo, K., Ma, C., Liu, L., & Zeng, Z. (2022). Evaluating Anthropogenic CO2 Bottom-Up Emission Inventories Using Satellite Observations from GOSAT and OCO-2. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 5024. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14195024





