Occlusion and Deformation Handling Visual Tracking for UAV via Attention-Based Mask Generative Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an attention-based mask generative network-based (AMGN-based) tracker. First, we adopt a base deep CNN to extract the deep features of the candidate regions. Next, we use AMGN to generate a series of attention-based masks, which are applied to the deep feature to augment hard positive samples. Then, we design a feature fusion method to compensate for the possible over-subtraction of the features of hard positive samples by the masks and to compensate for target location information. Finally, these hard positive samples are used for subsequent generative adversarial learning, thereby improving the ability of the tracker to handle occlusion and deformation.
- We develop an attention-based mask generative network (AMGN). After CNN extracts the deep features of the candidate region of which the salient positions are obtained through the attention module, masks for occluding the corresponding positions are generated. Multiply these masks with the deep features to simulate target occlusion and deformation in the feature space.
- We design a feature fusion method. When multiplying the masks with the deep features, some features are discarded, and there is a chance that too many features are discarded in the process. To alleviate this problem, we incorporate shallower-layer features into deeper-layer features processed by masks, thus avoiding extreme cases of tracking drift due to excessive feature loss.
2. Related Work
2.1. Occlusion and Deformation Handling in Visual Tracking
2.2. Attentional Mechanisms in Neural Networks
2.3. Generative Adversarial Learning
3. Method
3.1. Overview
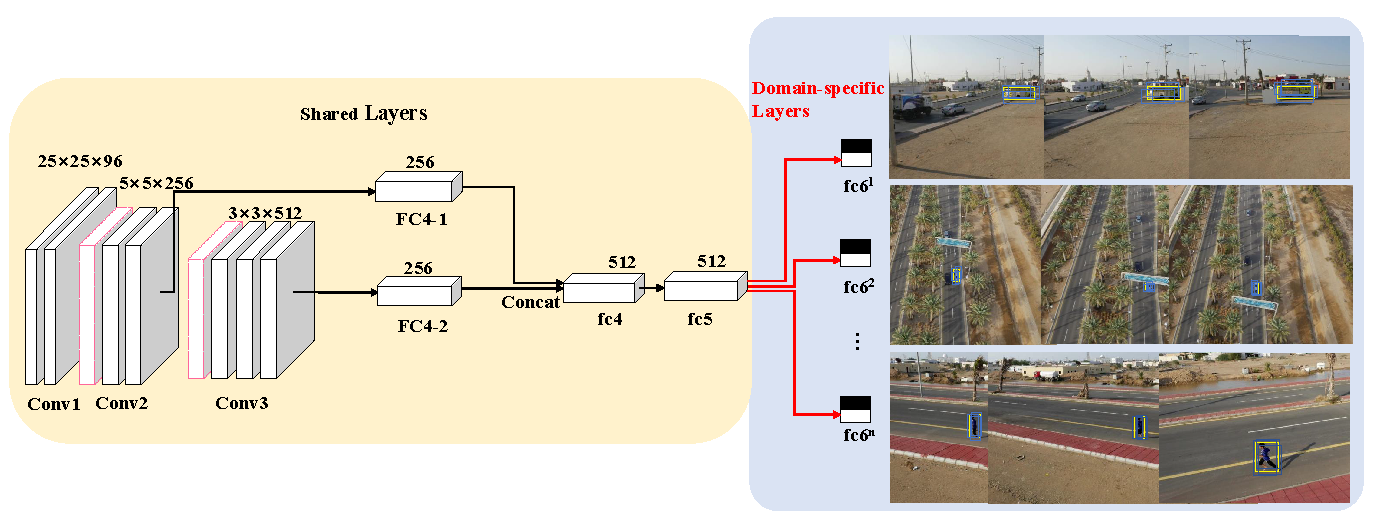
3.2. Base Deep CNN and Tracking Network
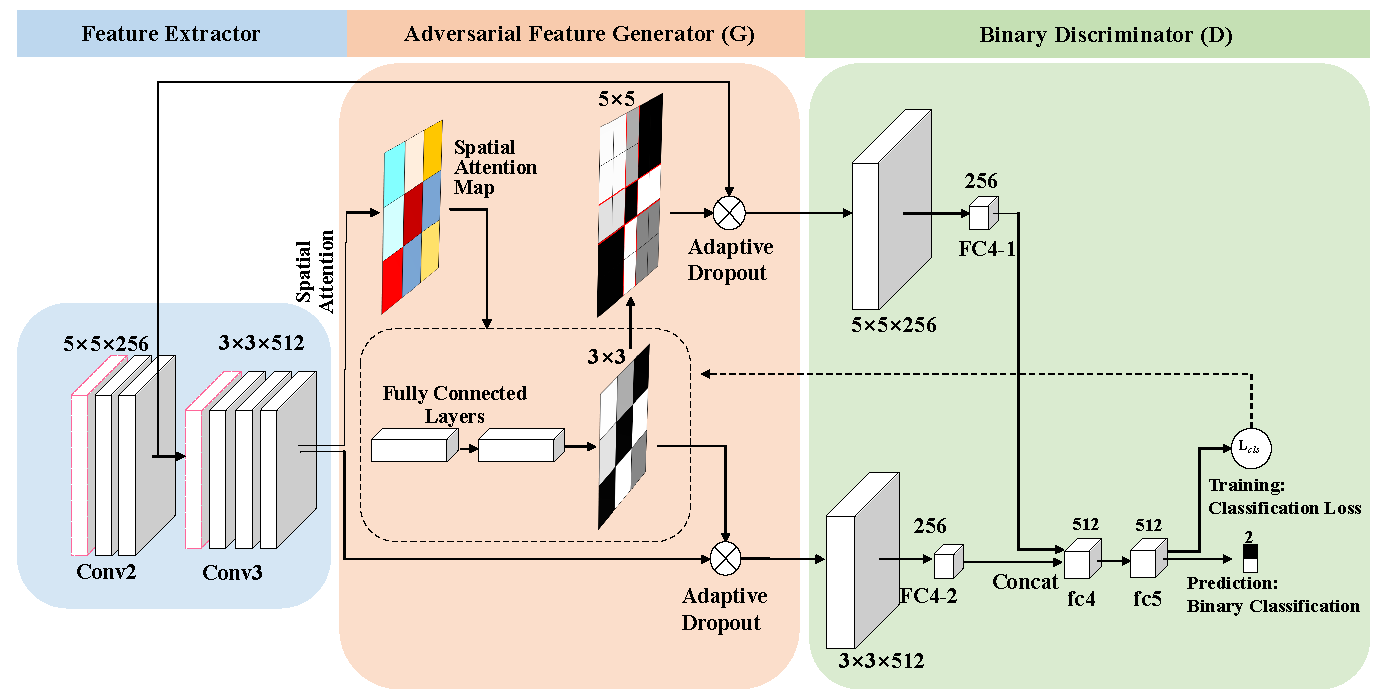
3.3. Attention-Based Mask Generative Network
3.4. Feature Fusion
3.5. Tracking Process
- (1)
- Model Initialization: The base CNN is initialized by VGG-M [53] trained in the classification task from ImageNet. The parameters in Conv1-Conv3 of the base CNN are fixed and the others are initiated according to offline pre-training by multidomain learning, which is fine-tuned online.
- (2)
- Online Detection: Generated multiple candidate boxes on the first frame of the tracking sequence or previous frame and its predicted target position are sampled by base CNN in each and fed into the tracking network to obtain probability scores.
- (3)
- Online Model Update: According to the target position given in the first frame and the predicted target position in other frames, we generate multiple candidate boxes around them and assign two-category labels divided by intersection-over-union (IoU) scores. The labeled samples are used to jointly train AMGN (as the generator G of GAN) and tracker (as the discriminator D of GAN) to complete the adversarial processes. AMGN produces the attention-based mask firstly as the C input, the mask adjustment process then meets the size of the mask to C and obtains the fused occluded feature maps. With the label unchanged, D is studied through supervised learning. After training, D will suffice for identifying the target features occluded. In return, D guides G to generate more difficult masks for D.
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation
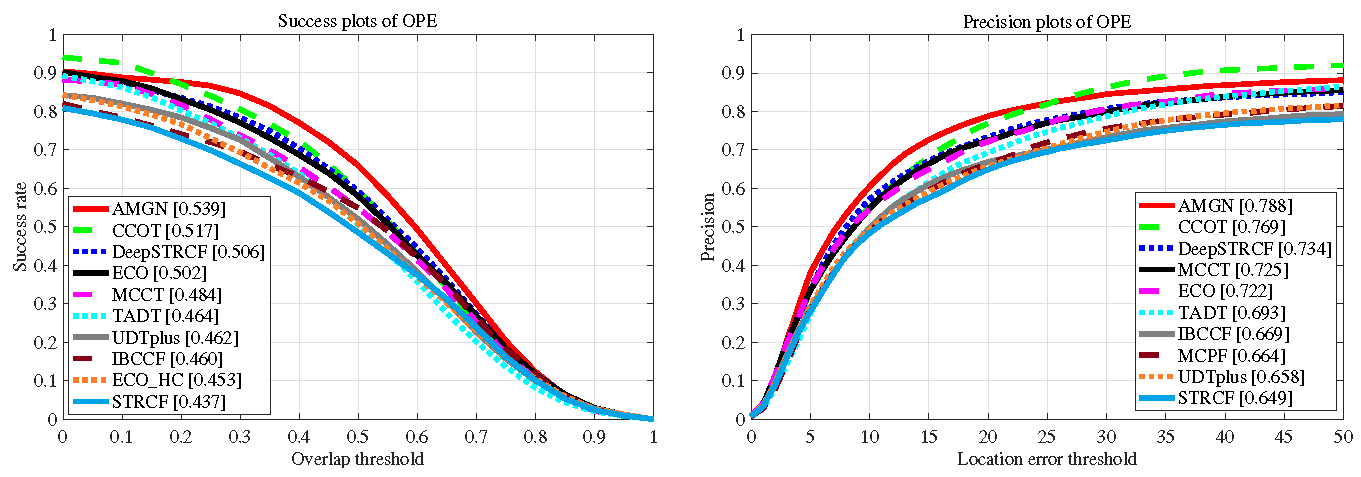
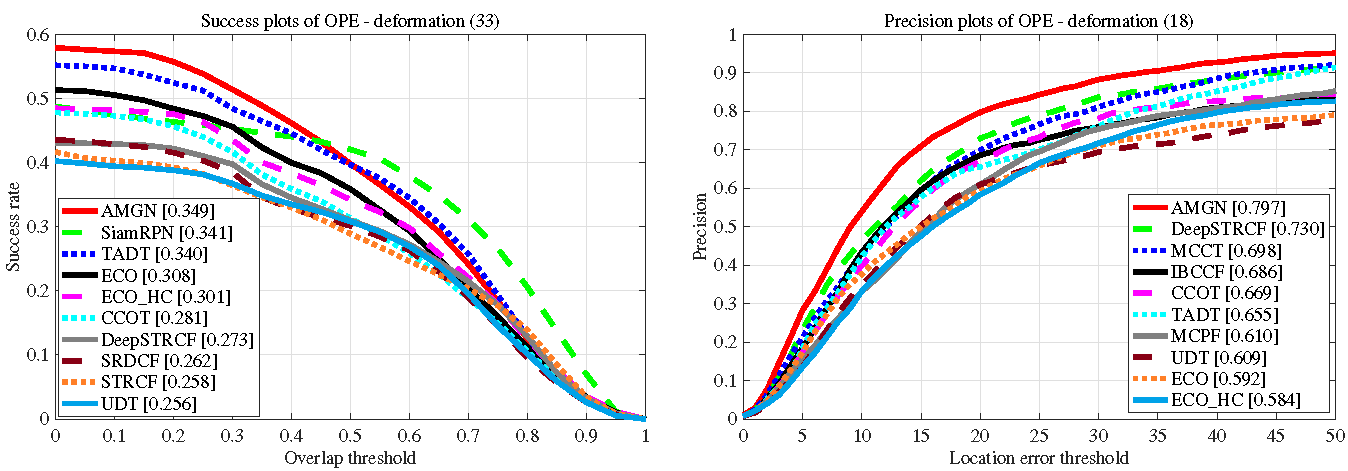
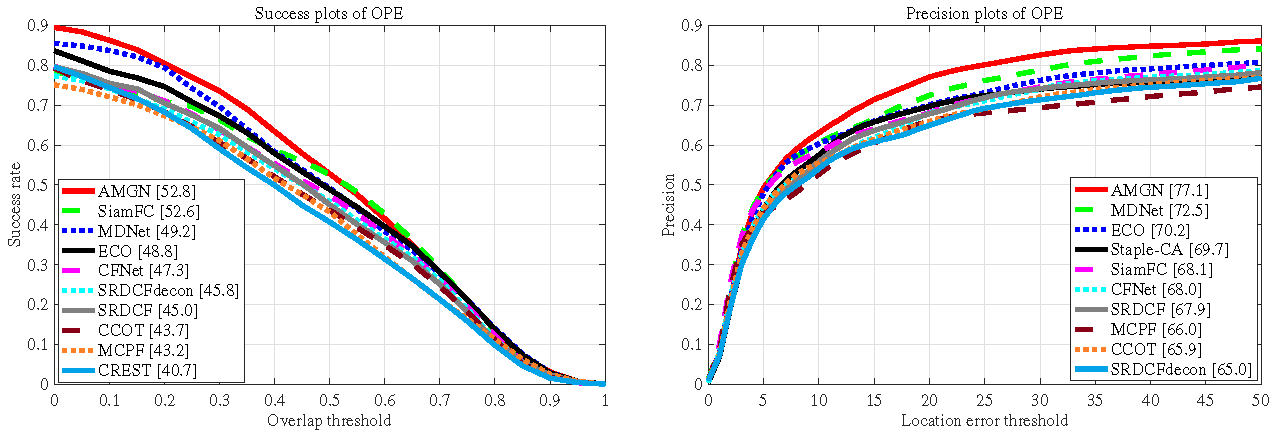
4.2. Evaluation on UAV123
4.3. Evaluation on DTB70
4.4. Evaluation on UAVDT
4.5. Evaluation on VOT2016
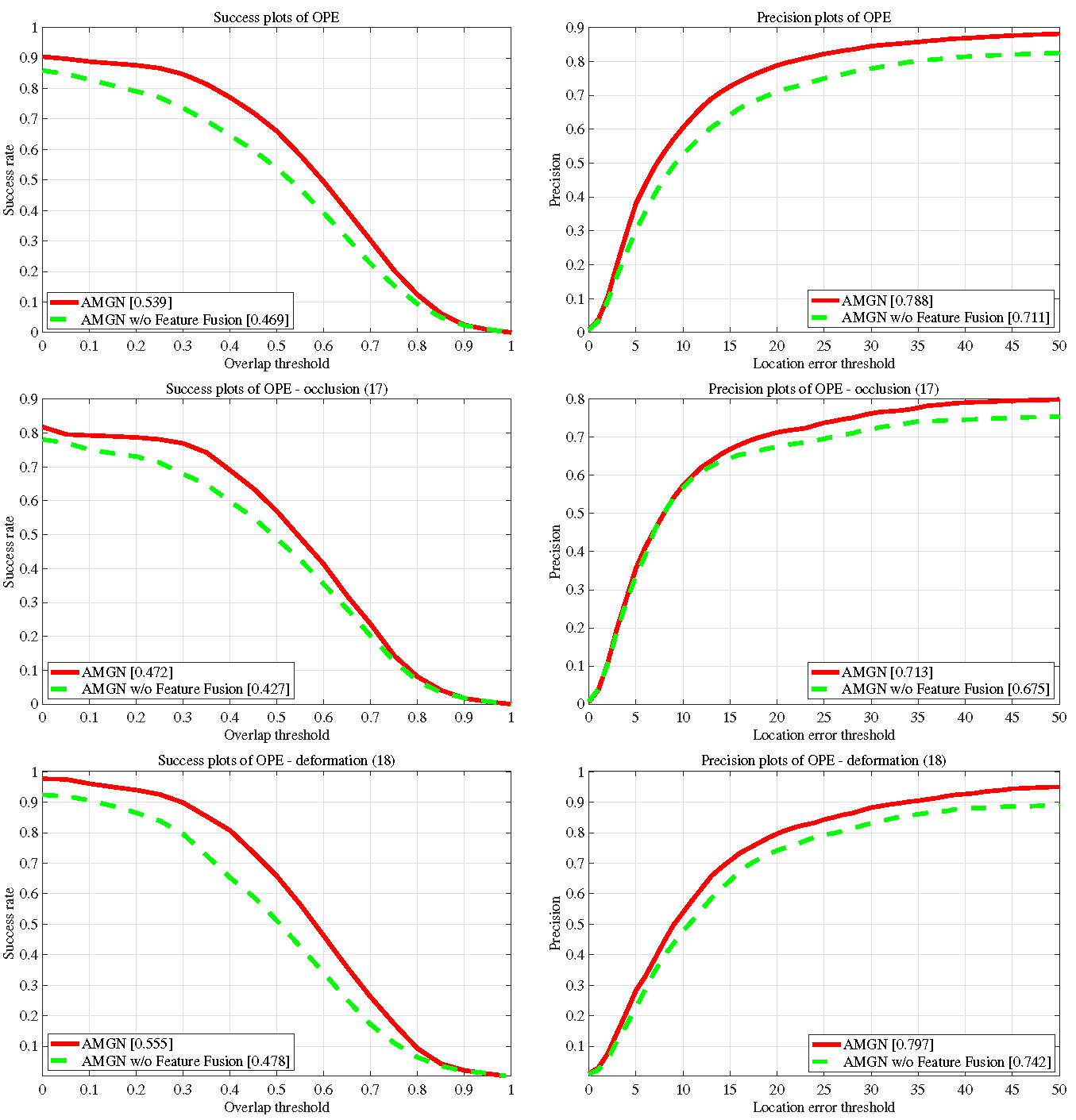
4.6. Ablation Studies
4.6.1. Effectiveness of Attention Module and Adversarial Learning
4.6.2. Effectiveness of Feature Fusion
4.7. Qualitative Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.-H.; Hwang, J.-N. On-Road Pedestrian Tracking Across Multiple Driving Recorders. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2015, 17, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X. SAT: Single-shot adversarial tracker. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 67, 9882–9892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, D.; Cao, Z.; Yu, J. Vision-based target-following guider for mobile robot. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 9360–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, M.; Wen, C.; Shan, M.; Ng, C.L.; Zou, Y. Real-time event-triggered object tracking in the presence of model drift and occlusion. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 2054–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolme, D.S.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A.; Lui, Y.M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer SOCIETY Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2544–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Fu, C.; Ding, F.; Ye, J.; Lin, F. ADTrack: Target-aware dual filter learning for real-time anti-dark UAV tracking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, Shaanxi, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 496–502. [Google Scholar]
- Çintaş, E.; Özyer, B.; Şimşek, E. Vision-based moving UAV tracking by another UAV on low-cost hardware and a new ground control station. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 194601–194611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Fu, C.; He, Y.; Xiong, W.; Li, F. ReCF: Exploiting Response Reasoning for Correlation Filters in Real-Time UAV Tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 10469–10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Chen, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J. SiamSTA: Spatio-Temporal Attention based Siamese Tracker for Tracking UAVs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 1204–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Ma, C.; Wu, X.; Gong, L.; Bao, L.; Zuo, W.; Shen, C.; Lau, R.W.; Yang, M.H. Vital: Visual tracking via adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8990–8999. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, L.; Yan, J.; Wei, W.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, X. High Performance Visual Tracking with Siamese Region Proposal Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Fu, C.; Ding, F.; Huang, Z.; Lu, G. AutoTrack: Towards high-performance visual tracking for UAV with automatic spatio-temporal regularization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11923–11932. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Fu, Y. Deep Alignment Network Based Multi-Person Tracking With Occlusion and Motion Reasoning. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2019, 21, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. Stably Adaptive Anti-Occlusion Siamese Region Proposal Network for Real-Time Object Tracking. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161349–161360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chu, J.; Leng, L.; Miao, J.; Kim, B.G. A scale-adaptive object-tracking algorithm with occlusion detection. Eurasip J. Image Video Process. 2020, 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, A. A-Fast-RCNN: Hard Positive Generation via Adversary for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Su, L.; Huang, Q.; Yang, M.H. Learning attribute-specific representations for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 8835–8842. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Y.; Qin, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Yao, H. Robust visual tracking via scale-and-state-awareness. Neurocomputing 2019, 329, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; He, R. Adversarial occlusion-aware face detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th International Conference on Biometrics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS), Redondo Beach, CA, USA, 22–25 October 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Javanmardi, M.; Qi, X. Appearance variation adaptation tracker using adversarial network—ScienceDirect. Neural Netw. 2020, 129, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souly, N.; Spampinato, C.; Shah, M. Semi Supervised Semantic Segmentation Using Generative Adversarial Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Li, C.; Luo, B.; Jin, T. SINT++: Robust Visual Tracking via Adversarial Positive Instance Generation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Jia, K.; Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Ahuja, N. Partial occlusion handling for visual tracking via robust part matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1258–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Aa, A.; Js, B.; Knp, A. Sample-based adaptive Kalman filtering for accurate camera pose tracking. Neurocomputing 2019, 333, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Z.; Hu, J. Multiple pedestrian tracking by combining particle filter and network flow model. Neurocomputing 2019, 351, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Pan, D. Research on scale adaptive particle filter tracker with feature integration. Appl. Intell. 2019, 49, 3864–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojir, T.; Noskova, J.; Matas, J. Robust scale-adaptive mean-shift for tracking. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 49, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Distractor-aware visual tracking using hierarchical correlation filters adaptive selection. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 6129–6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Zheng, Y. Satellite Video Tracking by Multi-Feature Correlation Filters with Motion Estimation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Yao, H.; Sun, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q. Structure-aware multi-object discovery for weakly supervised tracking. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Paris, France, 27–30 October 2014; pp. 466–470. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Q. Release the power of online-training for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Voume 34; pp. 12645–12652. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Gool, L.V.; Timofte, R. Probabilistic regression for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7183–7192. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Han, B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4293–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Chan, A.B. Learning dynamic memory networks for object tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 152–167. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Chan, A.B. Recurrent filter learning for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2010–2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Ji, R. Siamese box adaptive network for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6668–6677. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. Atom: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 4660–4669. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Yang, X. High-performance long-term tracking with meta-updater. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 6298–6307. [Google Scholar]
- Gilroy, S.; Jones, E.; Glavin, M. Overcoming occlusion in the automotive environment—A review. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 22, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Jalil, A.; Ali, A.; Khan, B.; Murad, M.; Cheema, K.M.; Milyani, A.H. Spatio-Temporal Context, Correlation Filter and Measurement Estimation Collaboration Based Visual Object Tracking. Sensors 2021, 21, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, K.; Ali, A.; Jalil, A.; Khan, B.; Cheema, K.M.; Murad, M.; Milyani, A.H. Efficient Online Object Tracking Scheme for Challenging Scenarios. Sensors 2021, 21, 8481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortylewski, A.; He, J.; Liu, Q.; Yuille, A.L. Compositional convolutional neural networks: A deep architecture with innate robustness to partial occlusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8940–8949. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Zhu, C.; Xiao, S. Deformable Faster R-CNN with Aggregating Multi-Layer Features for Partially Occluded Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, G.; Gou, R.; Tang, Z. Detector–tracker integration framework and attention mechanism for multi–object tracking. Neurocomputing 2021, 464, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, H.; Lu, T. Learning spatial-channel attention for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China (ICCC), Changchun, China, 11–13 August 2019; pp. 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, J.; Sun, Z.; Wen, Y.; Tao, D.; Ye, J. A review on generative adversarial networks: Algorithms, theory, and applications. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olshausen, B.A.; Anderson, C.H.; Van Essen, D.C. A neurobiological model of visual attention and invariant pattern recognition based on dynamic routing of information. J. Neurosci. 1993, 13, 4700–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatfield, K.; Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.3531. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M.; Smith, N.; Ghanem, B. A benchmark and simulator for uav tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 445–461. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Yeung, D.Y. Visual object tracking for unmanned aerial vehicles: A benchmark and new motion models. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Du, D.; Qi, Y.; Yu, H.; Yang, Y.; Duan, K.; Li, G.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Q.; Tian, Q. The unmanned aerial vehicle benchmark: Object detection and tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 370–386. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, L.; Zhu, P.; Du, D.; Bian, X.; Ling, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, C.; Cheng, H.; Liu, X.; Ma, W.; et al. Visdrone-sot2018: The vision meets drone single-object tracking challenge results. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, J.; Yang, M.H. Object Tracking Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristan, M.; Matas, J.; Leonardis, A.; Felsberg, M.; Cehovin, L.; Fernández, G.; Vojir, T.; Häger, G.; Lukežič, A.; Fernández, G.; et al. The visual object tracking vot2016 challenge results. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Volume 2, p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, K. Got-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 43, 1562–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, F.; Zhou, H.; Tao, D.; Li, X. Siamese local and global networks for robust face tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 9152–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6638–6646. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Robinson, A.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Beyond correlation filters: Learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 472–488. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Tian, C.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.H. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4904–4913. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, B.; He, Z.; Yang, M.H. Target-aware deep tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1369–1378. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Hager, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4310–4318. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Hager, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Adaptive decontamination of the training set: A unified formulation for discriminative visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1430–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature integration. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 254–265. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Golodetz, S.; Miksik, O.; Torr, P.H. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 1401–1409. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, M.; Smith, N.; Ghanem, B. Context-aware correlation filter tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1396–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Henriques, J.F.; Caseiro, R.; Martins, P.; Batista, J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Xie, L.; Yuan, J. Kernel Cross-Correlator. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Second AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-18), New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Häger, G.; Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Accurate scale estimation for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Nottingham, UK, 1–5 September 2014; BMVA Press: Nottingham, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Song, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhou, W.; Liu, W.; Li, H. Unsupervised deep tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 1308–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Kiani Galoogahi, H.; Fagg, A.; Lucey, S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Lukezic, A.; Vojir, T.; Čehovin Zajc, L.; Matas, J.; Kristan, M. Discriminative correlation filter with channel and spatial reliability. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6309–6318. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, S.; Sclaroff, S. MEEM: Robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 188–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Suganthan, P.N. Robust Visual Tracking via Co-trained Kernelized Correlation Filters. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 69, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, W.; Tian, Q.; Hong, R.; Wang, M.; Li, H. Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4844–4853. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Yang, M.H. Multi-task correlation particle filter for robust object tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4335–4343. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Häger, G.; Khan, F.S.; Felsberg, M. Discriminative scale space tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, D.; Zuo, W.; Yang, M.H. Integrating boundary and center correlation filters for visual tracking with aspect ratio variation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2001–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P. Fully-Convolutional Siamese Networks for Object Tracking; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Ma, C.; Gong, L.; Zhang, J.; Lau, R.W.; Yang, M.H. Crest: Convolutional residual learning for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2555–2564. [Google Scholar]
- Valmadre, J.; Bertinetto, L.; Henriques, J.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H. End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2805–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Kristan, M.; Matas, J.; Leonardis, A.; Vojíř, T.; Pflugfelder, R.; Fernandez, G.; Nebehay, G.; Porikli, F.; Čehovin, L. A novel performance evaluation methodology for single-target trackers. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 2137–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
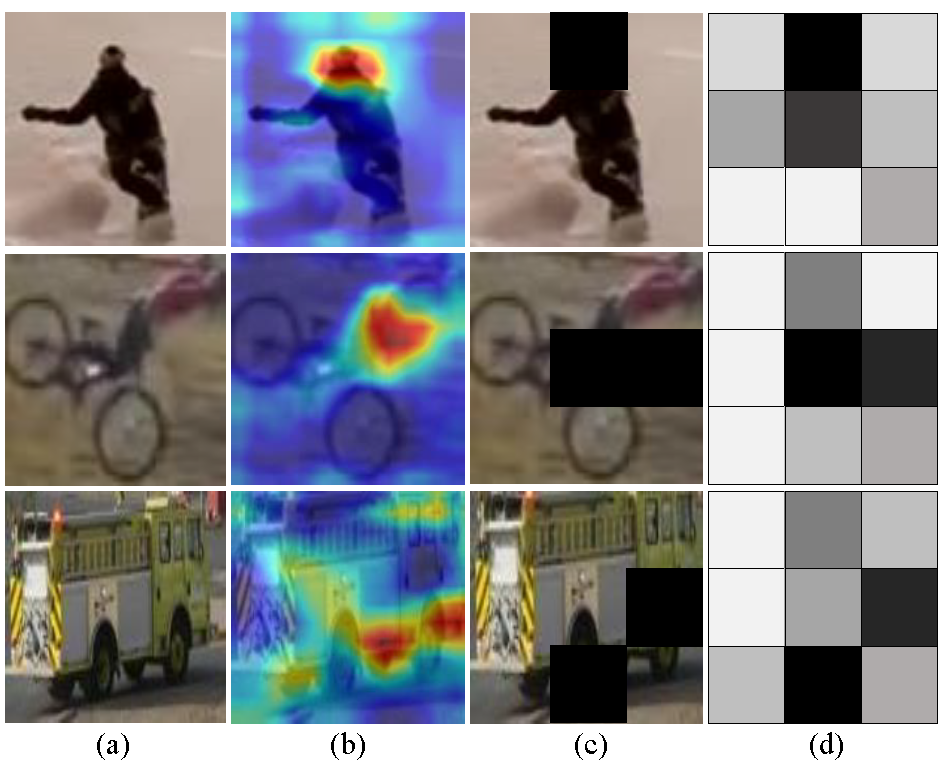






| ECO | CCOT | VITAL | MDNet | CREST | Staple | AMGN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EAO ↑ | 0.374 | 0.331 | 0.323 | 0.257 | 0.283 | 0.295 | 0.340 |
| Accuracy ↑ | 0.54 | 0.52 | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.51 | 0.54 | 0.576 |
| Robustness ↓ | 0.72 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 1.20 | 1.08 | 0.35 | 0.191 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, Q. Occlusion and Deformation Handling Visual Tracking for UAV via Attention-Based Mask Generative Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194756
Bai Y, Song Y, Zhao Y, Zhou Y, Wu X, He Y, Zhang Z, Yang X, Hao Q. Occlusion and Deformation Handling Visual Tracking for UAV via Attention-Based Mask Generative Network. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194756
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yashuo, Yong Song, Yufei Zhao, Ya Zhou, Xiyan Wu, Yuxin He, Zishuo Zhang, Xin Yang, and Qun Hao. 2022. "Occlusion and Deformation Handling Visual Tracking for UAV via Attention-Based Mask Generative Network" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194756
APA StyleBai, Y., Song, Y., Zhao, Y., Zhou, Y., Wu, X., He, Y., Zhang, Z., Yang, X., & Hao, Q. (2022). Occlusion and Deformation Handling Visual Tracking for UAV via Attention-Based Mask Generative Network. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4756. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194756







