Review of Automatic Processing of Topography and Surface Feature Identification LiDAR Data Using Machine Learning Techniques
Abstract
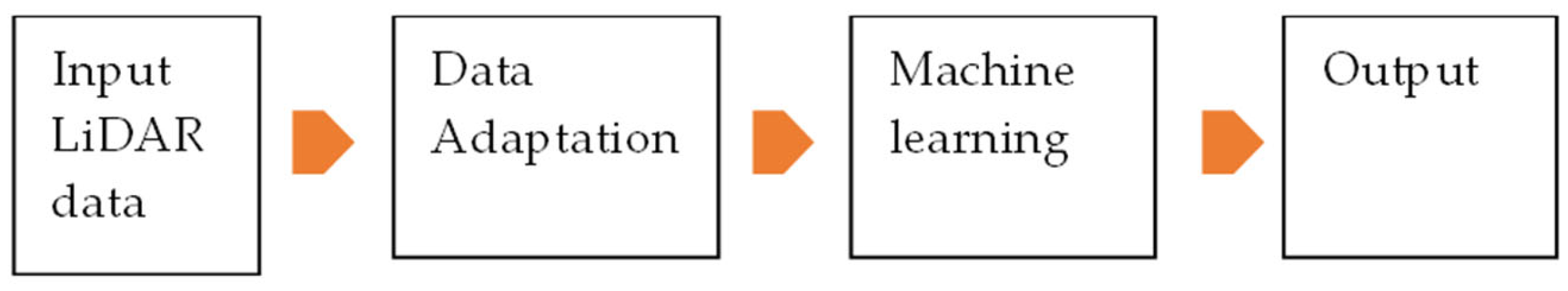
1. Introduction
2. Input Data
2.1. LiDAR Point Clouds
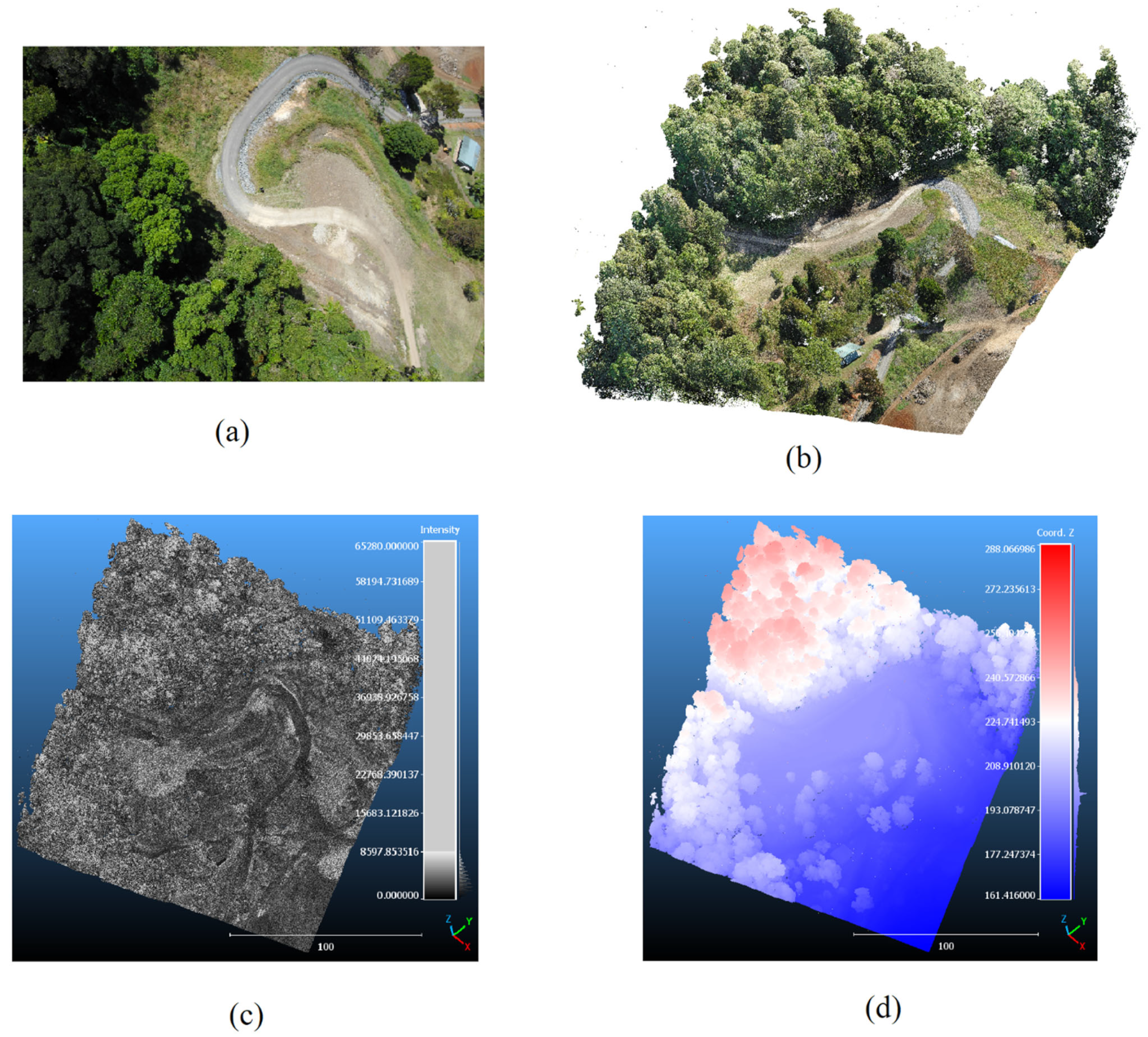
2.1.1. Airborne LiDAR Point Cloud
2.1.2. Terrestrial LiDAR Point Cloud
2.1.3. Point Cloud and Laser Intensity
2.2. Point Cloud and Imagery
2.3. Multispectral LiDAR Data
2.4. Full-Waveform Representation and Point Cloud
2.5. Different Other Data
3. Concepts of Point Cloud Structure for Applying ML Algorithms
3.1. Voxelization
3.2. Graphic Structure
3.3. Kernel-Based Convolution
3.4. Reducing of Point Cloud Density (Downsampling)
4. Employed ML Techniques
4.1. Random Forest (RF) and Support Vector Machine (SVM)
4.2. Neural Network and Deep Learning
4.3. Encoder–Decoder Structure
5. Applications of ML on LiDAR Data
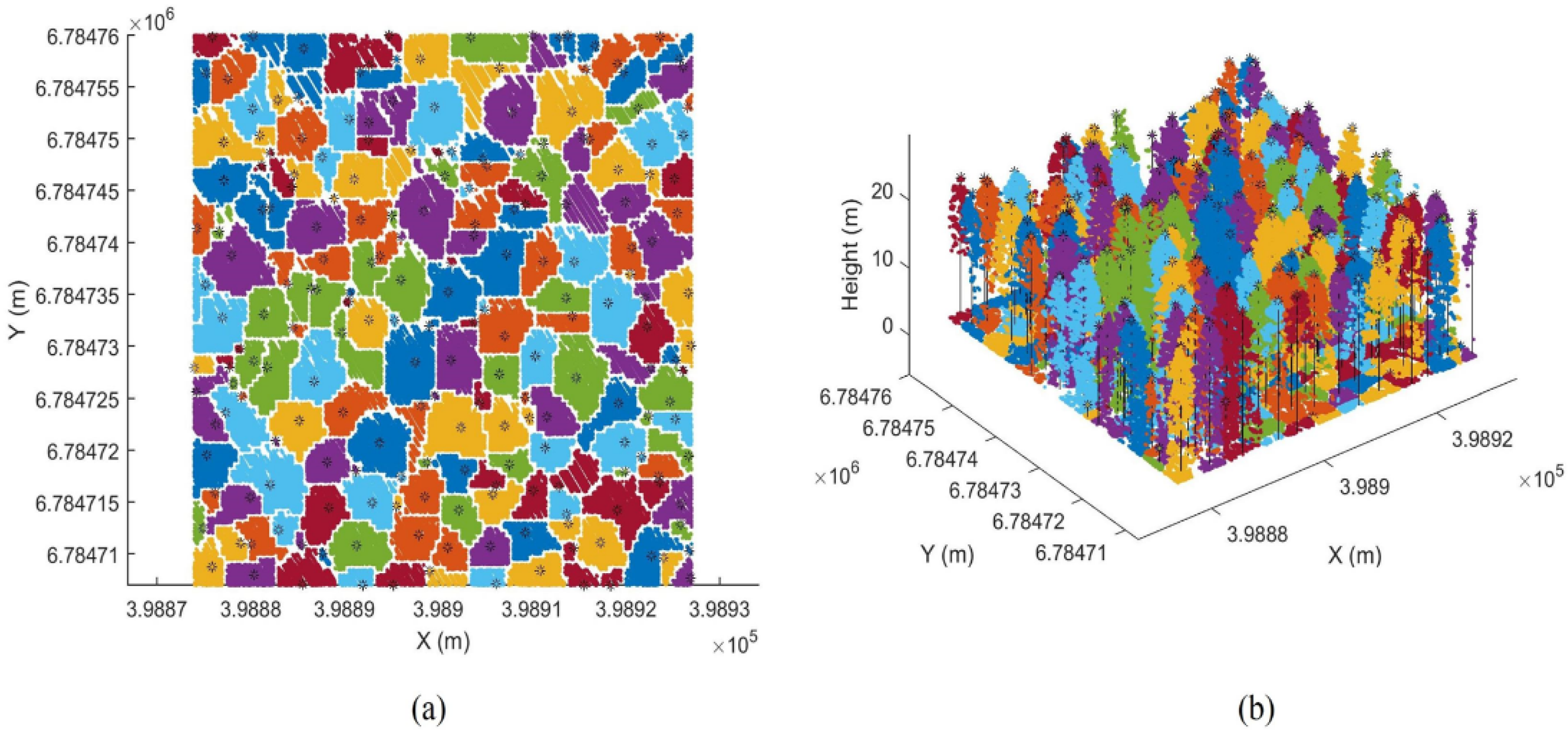
5.1. Building Detection
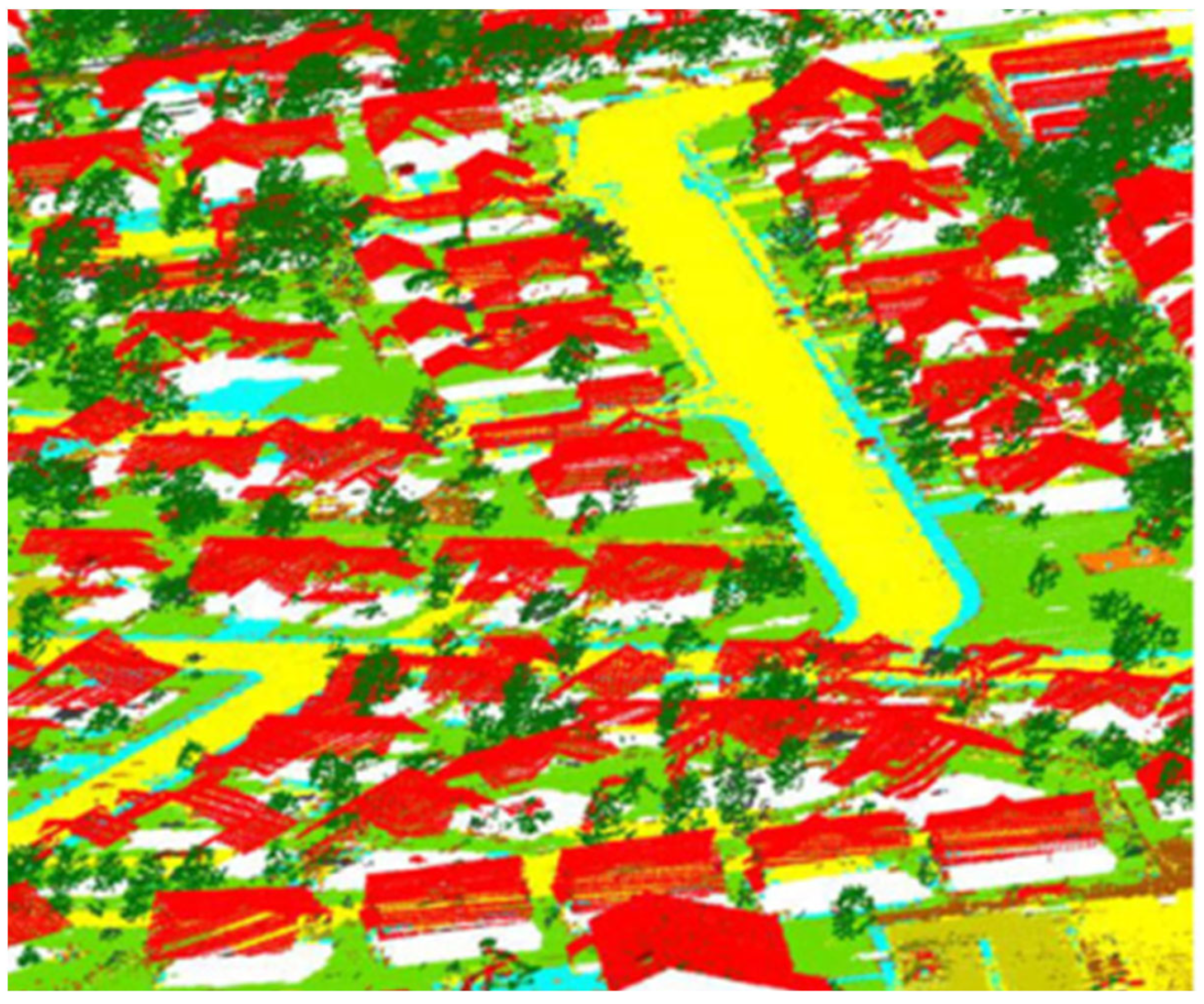
5.2. Scene Segmentation
5.3. Vegetation Detection
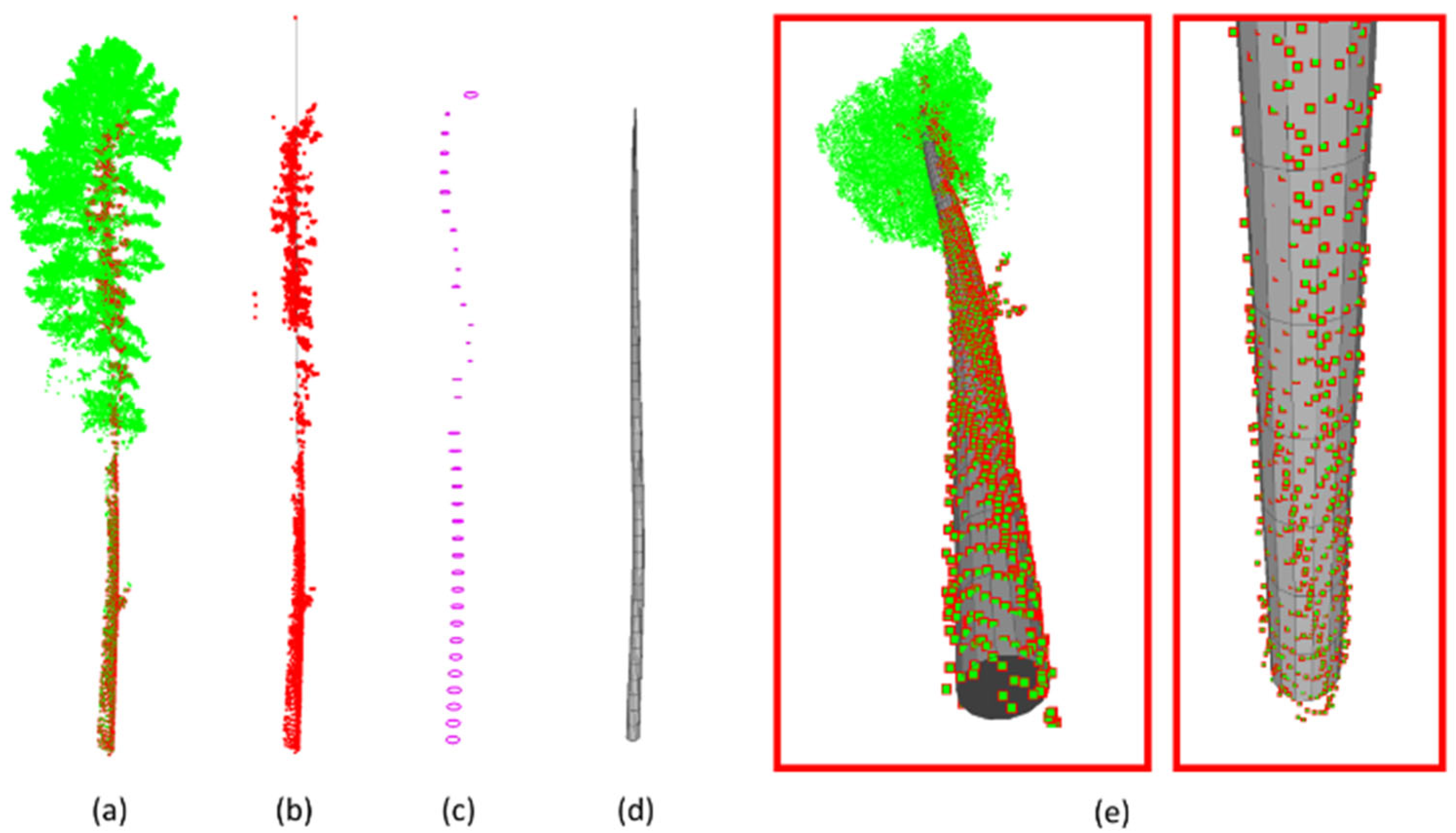
5.4. Classification of Tree Species
5.5. Road Marking Classification
5.6. Other Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Gharineiat, Z.; Campbell, G.; Dey, E.K.; Awrangjeb, M. Full series algorithm of automatic building extraction and modelling from LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the 2021 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Gold Coast, Australia, 29 November–1 December 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Toth, C.K. Topographic Laser Ranging and Scanning Principles and Processing, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; 630p, ISBN 13: 978-1-4987-7227-3. [Google Scholar]
- Vayghan, S.S.; Salmani, M.; Ghasemkhani, N.; Pradhan, B.; Alamri, A. Artificial intelligence techniques in extracting building and tree footprints using aerial imagery and LiDAR data. Geocarto Int. 2022, 37, 2967–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayazi, S.M.; SaadatSeresht, M. Comparison of traditional and machine learning base methods for ground point cloud labeling. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Gharineiat, Z.; Campbell, G.; Awrangjeb, M.; Dey, E.K. Automatic filtering of LiDAR building point cloud in case of trees associated to building roof. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Geyter, S.; Bassier, M.; Vergauwen, M. Automated training data creation for semantic segmentation of 3D point clouds. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2022, 46, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowska, M.; Rapiński, J. A Review of tree species classification based on airborne LiDAR data and applied classifiers. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Toth, C.K. Topographic Laser Ranging and Scanning Principles and Processing; Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; 593p, ISBN 13: 978-1-4200-5142-1. [Google Scholar]
- Dey, E.K.; Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Awrangjeb, M.; Stantic, B. Effective selection of variable point neighbourhood for feature point extraction from aerial building point cloud data. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shabat, Y.; Lindenbaum, M.; Fischer, A. Nesti-net: Normal estimation for unstructured 3D point clouds using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10112–10120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinmann, M.; Jutzi, B.; Hinz, S.; Mallet, C. Semantic point cloud interpretation based on optimal neighborhoods, relevant features and efficient classifiers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 105, 286–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; Denis, F.; Coeurjolly, D.; Dupont, F.; Trassoudaine, L.; Checchin, P. Robust normal vector estimation in 3D point clouds through iterative principal component analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 163, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Goulette, F.; Deschaud, J.; Marcotegui, B.; LeGall, Y. Semantic classification of 3D point clouds with multiscale spherical neighborhoods. In Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Verona, Italy, 5–8 September 2018; pp. 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, A.; Teferle, F.N.; Laefer, D.F.; Lindenbergh, R.C.; Hunegnaw, A. A two-step feature extraction algorithm: Application to deep learning for point cloud classification. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 46, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. Joint combination of point cloud and DSM for 3D building reconstruction using airborne laser scanner data. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE GRSS/WG III/2+5, VIII/1, VII/4 Joint Workshop on Remote Sensing & Data Fusion over Urban Areas and 6th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Urban Areas, Télécom Paris, Paris, France, 11–13 April 2007; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P.; Koehl, M. Model-driven and data-driven approaches using Lidar data: Analysis and comparison. In ISPRS Workshop, Photogrammetric Image Analysis (PIA07); Institut für Photogrammetrie und Fernerkundung (IPF): Munich, Germany, 2007; Part 3 W49A; Volume XXXVI, pp. 87–92. ISSN 1682-1750. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Xu, E.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Y.; Wei, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, Z. BushNet: Effective semantic segmentation of bush in large-scale point clouds. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 193, 106653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiwarter, L.; Esmorís Pena, A.M.; Weiser, H.; Anders, K.; Martínez Sánchez, J.; Searle, M.; Höfle, B. Virtual laser scanning with HELIOS++: A novel take on ray tracing-based simulation of topographic full-waveform 3D laser scanning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 269, 112772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Vosselman, G.; Yang, M.Y. Weakly supervised semantic segmentation of airborne laser scanning point clouds. SPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 187, 79–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Chen, K.; Diao, W.; Sun, X.; Lu, X.; Fu, K.; Weinmann, M. Beyond single receptive field: A receptive field fusion-and-stratification network for airborne laser scanning point cloud classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 188, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Su, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J. One-Class Classification of Airborne LiDAR Data in Urban Areas Using a Presence and Background Learning Algorithm. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Cai, G.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Su, J.; Marcato Junior, J.; Smit, J.; Li, J. ResDLPS-Net: Joint residual-dense optimization for large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 182, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Kim, K.S.; Shinohara, T.; Chang, Q.; Matsuoka, M. Enhancing local feature learning for 3D point cloud processing using unary-pairwise attention. In Proceedings of the 32nd British Machine Vision Conference, Online, 22–25 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Khoshelham, K.; Chen, C.; He, H. Individual tree extraction from urban mobile laser scanning point clouds using deep pointwise direction embedding. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 175, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Abid, F.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-H. SectorGSnet: Sector learning for efficient ground segmentation of outdoor LiDAR point clouds. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 11938–11946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Cheng, M.; Wang, C.; Xia, Y.; Li, J. Tree classification in complex forest point clouds based on deep learning. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.C.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sarma, S.E.; Bronstein, M.M.; Solomon, J.M. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. 2019, 38, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Y.C.; Hou, Y.L.; Zhang, S.M.; Shan, J. Graph attention convolution for point cloud semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 10288–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Yang, B.; Xie, L.; Rosa, S.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Randla-Net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11108–11117. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Su, S.; Wang, B.; Hong, Q.; Sun, L. Local K-NNs pattern in omni-direction graph convolution neural network for 3D point clouds. Neurocomputing 2020, 413, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, M.; Asghar, M.A.; Bibi, R.; Malik, M.N.; Shorfuzzaman, M.; Mehmood, R.M.; Kim, S.-H. DFT-Net: Deep feature transformation based network for object categorization and part segmentation in 3-dimensional point clouds. Sensors 2022, 22, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Kong, X.; Zhao, X.; Huang, T.; Li, W.; Wen, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y. RINet: Efficient 3D Lidar-based place recognition using rotation invariant neural network. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 4321–4328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.; Pereira, P.; Machado, R.; Névoa, R.; Melo-Pinto, P.; Fernandes, D. Customizable FPGA-based hardware accelerator for standard convolution processes empowered with quantization applied to LiDAR data. Sensors 2022, 22, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, J.; Shi, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Robust self-supervised LiDAR odometry via representative structure discovery and 3D inherent error modeling. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.; Marcuzzi, R.; Chen, X.; Behley, J.; Stachniss, C. SegContrast: 3D point cloud feature representation learning through self-supervised segment discrimination. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Xie, S.; Girshick, R. Momentum contrast for unsupervised visual representation learning. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9726–9735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, G.; Zhu, M. Fast momentum contrast learning for unsupervised person re-identification. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2021, 28, 2073–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yuan, J.; Qiao, C. Generation for unsupervised domain adaptation: A Gan-based approach for object classification with 3D point cloud data. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022–2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 3753–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, C.K. The strip adjustment and registration. In Topographic Laser Ranging and Scanning Principles and Processing; Shan, J., Toth, C.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 254–2287. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.; Yang, L.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Chi, T. Directionally constrained fully convolutional neural network for airborne LiDAR point cloud classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Sun, T.; Wang, S.; Fan, H.; Li, J. A graph attention network for road marking classification from mobile LiDAR point clouds. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, X.; Apan, A.; Deo, R.; Maraseni, T. Rapid assessment of mine rehabilitation areas with airborne LiDAR and deep learning: Bauxite strip mining in Queensland, Australia. Geocarto Int. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Xing, H.; Wong, M.S.; Kwan, M.-P.; Xing, H.; Meng, Y.A. Stacking ensemble deep learning model for building extraction from remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirmard, H.; Farahbakhsh, E.; Müller, R.D.; Chandra, R. A review of machine learning in processing remote sensing data for mineral exploration. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 268, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahhas, F.H.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Sameen, M.I.; Pradhan, B.; Mansor, S. Deep learning approach for building detection using LiDAR–orthophoto fusion. Hindawi J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 7212307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Guo, L.; Yang, W. 3D urban buildings extraction based on airborne lidar and photogrammetric point cloud fusion according to U-Net deep learning model segmentation. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 20889–20897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, J.; Gong, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, G. An improved lightweight deep neural network with knowledge distillation for local feature extraction and visual localization using images and LiDAR point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 184, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing: Fundamentals and Practices; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. 466. ISBN 9781498731591. [Google Scholar]
- Marrs, J.; Ni-Meister, W. Machine learning techniques for tree species classification using co-registered LiDAR and hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Litkey, P.; Kaartinen, H.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M. Single-sensor solution to tree species classification using multispectral airborne laser scanning. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Guan, H.; Li, D.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, K.; Junior, J.M.; Li, J. Airborne multispectral LiDAR point cloud classification with a feature Reasoning-based graph convolution network. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 105, 102634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, L.; Luo, Y. Fusion of UAV Hyperspectral Imaging and LiDAR for the Early Detection of EAB Stress in Ash and a New EAB Detection Index—NDVI (776,678). Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tu, B.; Zhou, C.; Li, Q. Multiview Hierarchical Network for Hyperspectral and LiDAR Data Classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 1454–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stilla, U.; Jutzi, B. Waveform analysis for small-footprint pulsed Laser systems. In Topographic Laser Ranging and Scanning Principles and Processing; Shan, J., Toth, C.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; pp. 234–253. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Ji, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q. Deep learning-based tree classification using mobile Lidar data. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomley, R.; Hovi, A.; Weinmann, M.; Hinz, S.; Korpela, I.; Jutzi, B. Tree species classification using within crown localization of waveform LiDAR attributes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 133, 142–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Ma, Y.; Li, R.; Jing, J.; Dian, Y. Tree species classification by employing multiple features acquired from integrated sensors. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, T.; Xiu, H.; Matsuoka, M. FWNet: Semantic segmentation for full-waveform LiDAR data using deep learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.H.; Son, K.W.; Lee, D.C. Semantic segmentation and building extraction from airborne LiDAR data with multiple return using PointNet++. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Proc. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 5099–5108. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ge, L.; Hensley, S.; Metternicht, G.I.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R. PolGAN: A deep-learning-based unsupervised forest height estimation based on the synergy of PolInSAR and LiDAR data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 186, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Guldmann, J.M. Creating 3D city models with building footprints and LiDAR point cloud classification: A machine learning approach. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 75, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.C.; Guo, Z. Automating parameter learning for classifying terrestrial LiDAR point cloud using 2D land cover maps. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmohl, S.; Narváez Vallejo, A.; Soergel, U. Individual tree detection in urban ALS point clouds with 3D convolutional networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, T.; Tomczak, A.; Słowik, A.; Oberski, T. Seabed modelling by means of airborne laser bathymetry data and imbalanced learning for offshore mapping. Sensors 2022, 22, 3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarella, M.; Di Benedetto, A.; Fiani, M. Application of Supervised Machine Learning Technique on LiDAR Data for Monitoring Coastal Land Evolution. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, Z.; Ozcan, K.; Atik, M.E. Classification of photogrammetric and airborne LiDAR point clouds using machine learning algorithms. Drones 2021, 5, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Badruddin Khan, M.; Bashier, E.B.M. Machine Learning Algorithms and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; p. 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P. MATLAB Deep Learning with Machine Learning, Neural Networks and Artificial Intelligence; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2017; p. 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, K.; Arashpour, M.; Asadi, E.; Masoumi, H.; Bai, Y.; Behnood, A. 3D point cloud data processing with machine learning for construction and infrastructure applications: A comprehensive review. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 51, 101501, ISSN 1474-0346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maturana, D.; Scherer, S. Voxnet: A 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–3 October 2015; pp. 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargoum, S.A.; Koch, J.C.; El-Basyouny, K. A voxel-based method for automated detection and mapping of light poles on rural highways using lidar data. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, F.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Qu, R.; Li, P. AFE-RCNN: Adaptive feature enhancement RCNN for 3D object detection. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, K.T.; Paek, D.; Kong, S.H. Multiview attention for 3D object detection in Lidar point cloud. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Jeju Island, Korea, 21–24 February 2022; pp. 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovsky, M.; Komodakis, N. Dynamic edge-conditioned filters in convolutional neural networks on graphs. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Samari, B.; Siddiqi, K. Local spectral graph convolution for point set feature learning. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Ferrari, V., Hebert, M., Sminchisescu, C., Weiss, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; p. 11208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Shen, X.; Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Li, D. AGFP-Net: Attentive geometric feature pyramid network for land cover classification using airborne multispectral LiDAR data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 108, 102723, ISSN 0303-2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Li, X.; Yao, X.; Peng, L.; Chi, T. Airborne LiDAR point cloud classification with global-local graph attention convolution neural network. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Di, D.; Chen, G.; Wang, J. AGNet: An attention-based graph network for point cloud classification and segmentation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, W.; Lin, H.; Nurunnabi, A.; Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.-P.; Li, J. WGNet: Wider graph convolution networks for 3D point cloud classification with local dilated connecting and context-aware. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defferrard, M.; Bresson, X.; Vandergheynst, P. Convolutional neural networks on graphs with fast localized spectral filtering. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 5–10 December 2016; pp. 3844–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Xie, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Yuan, D.; Qiu, Q. DGANet: A dilated graph attention-based network for local feature extraction on 3D point clouds. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, B.; Tran, M.; Yeung, S. Pointwise convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klokov, R.; Lempitsky, V. Escape from cells: Deep KD-networks for the recognition of 3D point cloud models. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; He, F.; Duan, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yan, X. A kernel correlation-based approach to adaptively acquire local features for learning 3D point clouds. Comput.-Aided Des. 2022, 146, 103196, ISSN 0010-4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Amakhchan, W.; Gharineiat, Z. Random Forest machine learning technique for automatic vegetation detection and modelling in LiDAR data. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Nat. Resour. 2021, 28, 556234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, S. Forested landslide detection using LiDAR data and the random forest algorithm: A case study of the three Gorges, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhu, J. Using Random Forest to integrate LiDAR data and hyperspectral imagery for land cover classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 3978–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Q.; Dong, P.; Yang, X.; Wu, Q.; Han, R. Automatic extraction of grasses and individual trees in urban areas based on airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M.; Viitala, R. Predicting individual tree attributes from airborne laser point clouds based on the random forests technique. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, S.R.; Hessenmöller, D.; Schulze, E.D. Scaling wood volume estimates from inventory plots to landscapes with airborne LiDAR in temperate deciduous forest. Carbon Balance Manag. 2016, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Luo, L. Random forests-based feature selection for land-use classification using LiDAR data and orthoimagery. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2012, XXXIX-B7, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, A.; Laslier, M.; Dufour, S.; Hubert-Moy, L. Riparian trees genera identification based on leaf-on/leaf-off airborne laser scanner data and machine learning classifiers in northern France. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 1645–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumäe, T.; Lang, M.; Sims, A.; Laarmann, D. Planning of commercial thinnings using machine learning and airborne lidar data. Forests 2022, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, Y.; Hou, M. The point cloud semantic segmentation method for the Ming and Qing dynasties’ official-style architecture roof considering the construction regulations. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Tang, S.; Liao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Guo, R. A Supervoxel-based random forest method for robust and effective airborne LiDAR point cloud classification. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, L.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, K.R. A 3D shape recognition method using hybrid deep learning network CNN–SVM. Electronics 2020, 9, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Ning, X. SVM-based classification of segmented airborne LiDAR point clouds in urban areas. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3749–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, D.; Rastiveis, H.; Sheikholeslami, S.M.; Shah-hosseini, R.; Li, J. Fast extraction of power lines from mobile LiDAR point clouds based on SVM classification in non-urban area. Earth Obs. Geomat. Eng. 2022, 5, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Advances in neural information processing systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2014), Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 27, pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Lin, G.; Yap, K.H.; Hung, T.Y.; Xie, L. Multi-path region mining for weakly supervised 3D semantic segmentation on point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 4383–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Kähler, O.; Pfeifer, N. A comparison of deep learning methods for airborne Lidar point clouds classification. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 6467–6486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, B.; Engelcke, M.; Maaten, L.V.D. 3D semantic segmentation with submanifold sparse convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 9224–9232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. KPConv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6411–6420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théodose, R.; Denis, D.; Chateau, T.; Frémont, V.; Checchin, P. A deep learning approach for LiDAR resolution-agnostic object detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 14582–14593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, L.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Kwon, K.R. GSV-NET: A Multi-modal deep learning network for 3D point cloud classification. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kakillioglu, B.; Velipasalar, S. Background-aware 3-D point cloud segmentation with dynamic point feature aggregation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, D.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Xin, Y.; Sung, Y.; Choi, R. 2D&3DHNet for 3D object classification in LiDAR point cloud. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3146. [Google Scholar]
- Badrinarayanan, V.; Kendall, A.; Cipolla, R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 2481–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, F.P.; Paffenroth, R. Machine learning in LiDAR 3D point clouds. In Advances in Data Science; Association for Women in Mathematics Series, 26; Demir, I., Lou, Y., Wang, X., Welker, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Qi, Z.; Fuxin, L. Pointconv: Deep convolutional networks on 3D point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9613–9622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Akhtar, N.; Ullah, K.; Mian, A. Exploiting Structured CNNs for Semantic Segmentation of Unstructured Point Clouds from LiDAR Sensor. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedianfar, A.; Mohamedou, C.; Kangas, A.; Vauhkonen, J. Deep learning for forest inventory and planning: Acritical review on the remote sensing approaches so far and prospects for further applications. Forestry 2022, 95, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241, LNCS. 9351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojogbane, S.S.; Mansor, S.; Kalantar, B.; Khuzaimah, Z.B.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Ueda, N. Automated building detection from airborne LiDAR and very high-resolution aerial imagery with deep neural network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydi, S.T.; Hasanlou, M.; Amani, M. A new end-to-end multi-dimensional CNN framework for land cover/land use change detection in multi-source remote sensing datasets. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Gu, Y. A Discriminative tensor representation model for feature extraction and classification of multispectral LiDAR data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1568–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekhtari, N.; Glennie, C.; Fernandez-Diaz, J.C. Classification of airborne multispectral lidar point clouds for land cover mapping. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2068–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Peng, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Cheng, L. PEMCNet: An efficient multi-scale point feature fusion network for 3D LiDAR point cloud classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Wang, T.; Tao, S. Hybrid CNN-LSTM architecture for LiDAR point clouds semantic segmentation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 5811–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, F.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. MSIDA-Net: Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation via Multi-Spatial Information and Dual Adaptive Blocks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Qiu, X.; Zeng, W.; Peng, D. Combining sample plot stratification and machine learning algorithms to improve forest aboveground carbon density estimation in northeast China using airborne LiDAR data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Nurunnabi, A.; Li, J. Detection of individual trees in UAV LiDAR point clouds using a deep learning framework based on multichannel representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, A.P.D.; Souza, D.V.; Rex, F.E.; Sanquetta, C.R.; Mohan, M.; Silva, C.A.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; Prata, G.; Alves de Almeida, D.R.; Trautenmüller, J.W.; et al. Forest inventory with high-density UAV-Lidar: Machine learning approaches for predicting individual tree attributes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 179, 105815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windrim, L.; Bryson, M. Detection, segmentation, and model fitting of individual tree stems from airborne laser scanning of forests using deep learning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yun, T. Individual tree crown segmentation directly from UAV-borne LiDAR data using the PointNet of deep learning. Forests 2021, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, T.; Ishii, A.; Nakamura, H.; Inoue, T.; Takamatsu, H. Lidar-Based Individual Tree Species Classification Using Convolutional Neural Network; Proc. SPIE 10332, Videometrics, Range Imaging, and Applications XIV; SPIE Optical Metrology: Munich, Germany, 2017; p. 103320O. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budei, B.; St-Onge, B.; Hopkinson, C.; Audet, F.A. Identifying the genus or species of individual trees using a three-wavelength airborne Lidar system. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 204, 632–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.; Demir, B.; Dalponte, M. Weighted support vector machines for tree species classification using Lidar data. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019–2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 6740–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hell, M.; Brandmeier, M.; Briechle, S.; Krzystek, P. Classification of tree species and standing dead trees with Lidar point clouds using two deep neural networks: PointCNN and 3DmFV-Net. PFG 2022, 90, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. PointCNN: Convolution on x-transformed points. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information processing systems 31 (NIPS 2018), Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 December 2018; pp. 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shabat, Y.; Lindenbaum, M.; Fischer, A. 3DmFV: Three-dimensional point cloud classification in real-time using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Robot Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 3145–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Habib, A. A deep learning framework for road marking extraction, classification and completion from mobile laser scanning point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 147, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Junior, J.M.; Goncalves, W.N.; Chapman, M.A. Capsule-based networks for road marking extraction and classification from mobile LiDAR point clouds. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 1981–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Ma, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, K.; Luo, W. Extracting urban road footprints from airborne LiDAR point clouds with PointNet++ and two-step post-processing. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajahan, D.A.; Nayel, V.; Muthuganapathy, R. Roof classification from 3-D LiDAR point clouds using multiview CNN with self-attention. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1465–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.; Fernandes, D.; Névoa, R.; Monteiro, J.; Novais, P.; Girão, P.; Afonso, T.; Melo-Pinto, P. Resource-constrained onboard inference of 3D object detection and localisation in point clouds targeting self-driving applications. Sensors 2021, 21, 7933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, S. A Deep Learning-Based Perception Algorithm Using 3D LiDAR for Autonomous Driving: Simultaneous Segmentation and Detection Network (SSADNet). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Wong, A.; Lee, B.; Kim, J. Real-time semantic segmentation of 3D point cloud for autonomous driving. Electronics 2021, 10, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, W.; Huang, H.; Cai, P.; Liu, M. PointMoSeg: Sparse Tensor-Based End-to-End Moving-Obstacle Segmentation in 3-D Lidar Point Clouds for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 6, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Fei, J.; Yang, K.; Roitberg, A.; Zhang, J.; Bieder, F.; Heidenreich, P.; Stiller, C.; Stiefelhagen, R. MASS: Multi-Attentional Semantic Segmentation of LiDAR Data for Dense Top-View Understanding. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15824–15840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Li, M.; Yang, S.J.; Cho, K. Reflective noise filtering of large-scale point cloud using transformer. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurunnabi, A.; Teferle, F.N.; Li, J.; Lindenbergh, R.C.; Hunegnaw, A. An efficient deep learning approach for ground point filtering in aerial laser scanning point clouds. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spatial Inf. Sci. 2021, XLIII-B1-2021, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Scaioni, M. 3DLEB-Net: Label-efficient deep learning-based semantic segmentation of building point clouds at LoD3 level. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiao, W.; Mills, J.P. Optimizing moving object trajectories from roadside Lidar data by joint detection and tracking. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Guo, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Li, H. PV-RCNN: Point-voxel feature set abstraction for 3D object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10526–10535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Wang, B.; Gan, V.J.L. Automated classification of piping components from 3D LiDAR point clouds using SE-PseudoGrid. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakhchan, W.; Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Gharineiat, Z.; Boulaassal, H.; El Kharki, O. Automatic filtering of LiDAR building point cloud using multilayer perceptron Neuron Network. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Big Data and Machine Learning (BML’22), Istanbul, Turkey, 22–23 December 2022; Available online: https://bml.maasi.org/ (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Mammoliti, E.; Di Stefano, F.; Fronzi, D.; Mancini, A.; Malinverni, E.S.; Tazioli, A.A. Machine learning approach to extract rock mass discontinuity orientation and spacing, from laser scanner point clouds. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gharineiat, Z.; Tarsha Kurdi, F.; Campbell, G. Review of Automatic Processing of Topography and Surface Feature Identification LiDAR Data Using Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194685
Gharineiat Z, Tarsha Kurdi F, Campbell G. Review of Automatic Processing of Topography and Surface Feature Identification LiDAR Data Using Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(19):4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194685
Chicago/Turabian StyleGharineiat, Zahra, Fayez Tarsha Kurdi, and Glenn Campbell. 2022. "Review of Automatic Processing of Topography and Surface Feature Identification LiDAR Data Using Machine Learning Techniques" Remote Sensing 14, no. 19: 4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194685
APA StyleGharineiat, Z., Tarsha Kurdi, F., & Campbell, G. (2022). Review of Automatic Processing of Topography and Surface Feature Identification LiDAR Data Using Machine Learning Techniques. Remote Sensing, 14(19), 4685. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14194685






