Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity Based on GF-6 Image, Empirical Study in Southwest Mountainous County, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
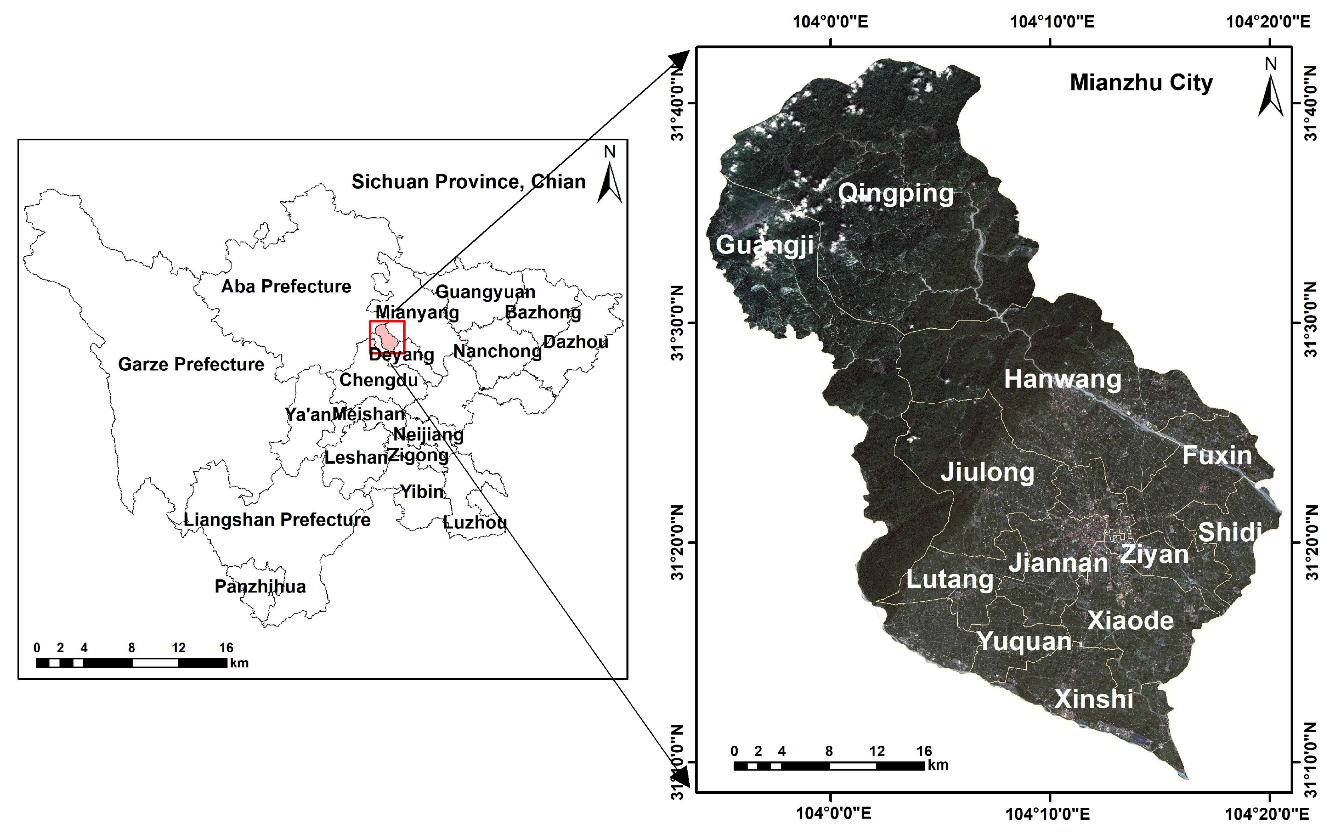
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity
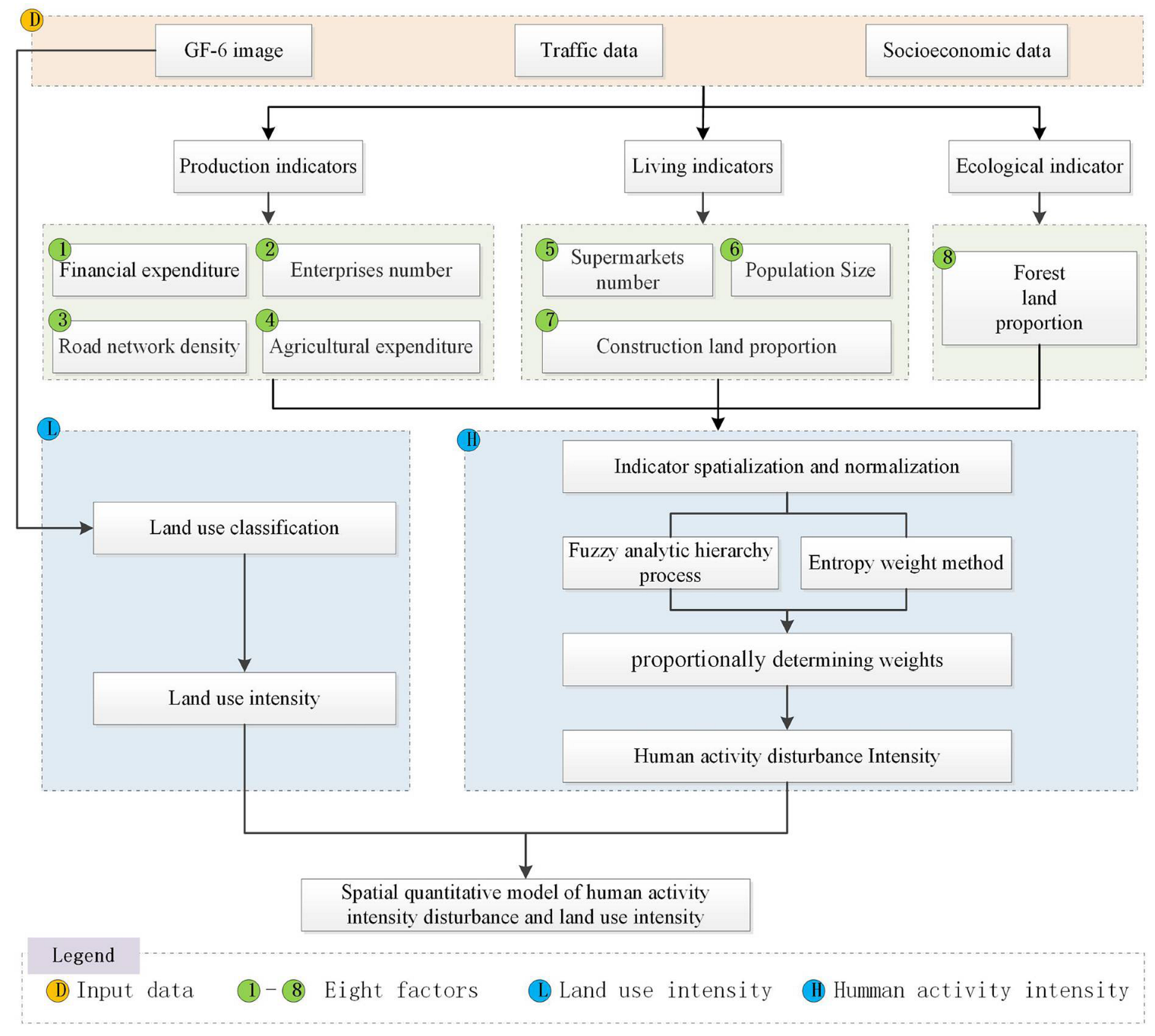
2.3.1. Framework of the Spatial Quantitative Model
2.3.2. Human Activity Disturbance Evaluation Factors
- Production indicators;
- (a)
- Enterprises number
- (b)
- Agricultural expenditure
- (c)
- Road network density
- (d)
- Financial income
- 2.
- Living indicators
- (a)
- Population size
- (b)
- Proportion of construction land
- (c)
- Supermarkets number
- 3.
- Ecological indicator
- 4.
- Factors normalization
2.4. Evaluation of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity
2.4.1. Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process
2.4.2. Entropy Weight Method
2.4.3. The Weights Determination
2.4.4. Human Activity Disturbance Intensity Calculation
2.5. Correlation Analysis between Human Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity
3. Results
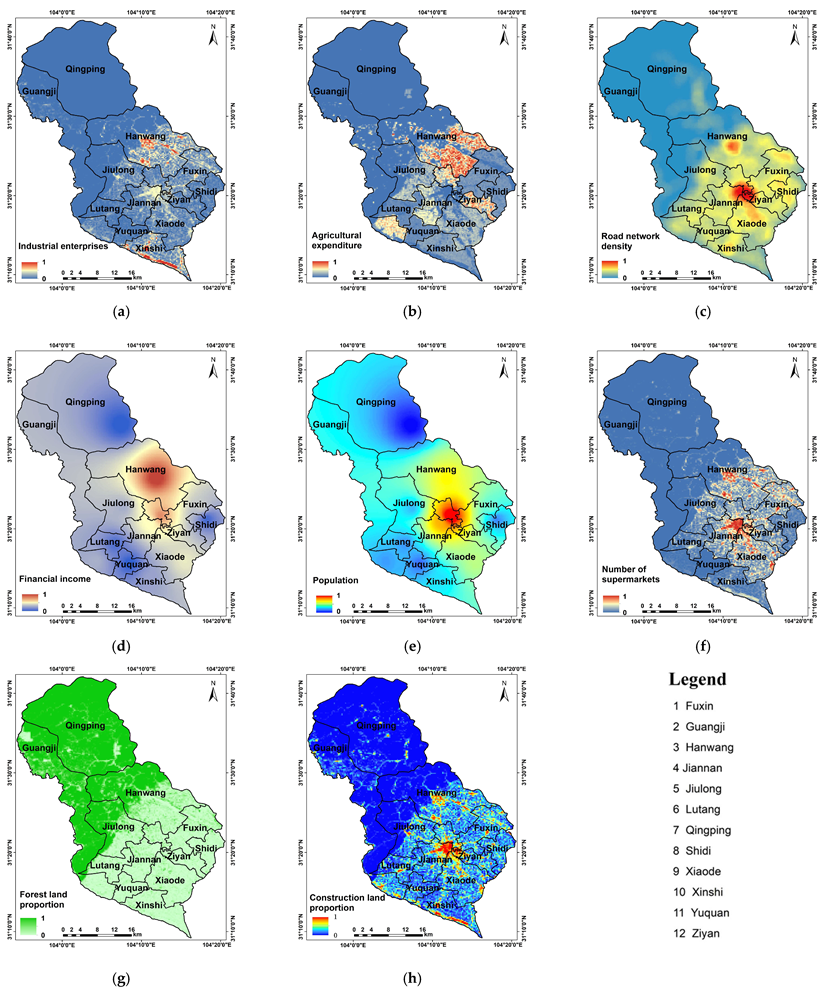
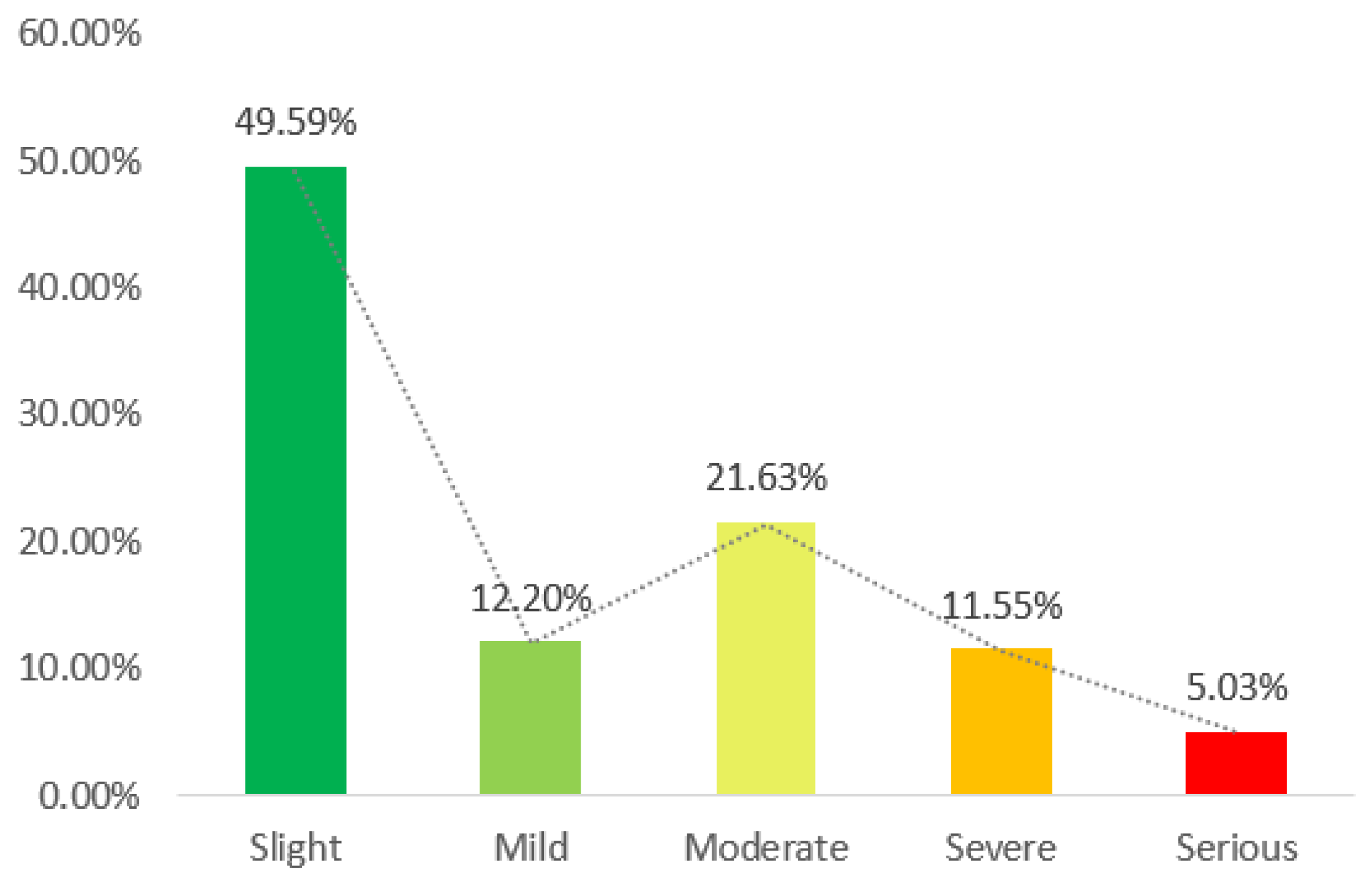
3.1. Human Activity Disturbance Factors Analysis
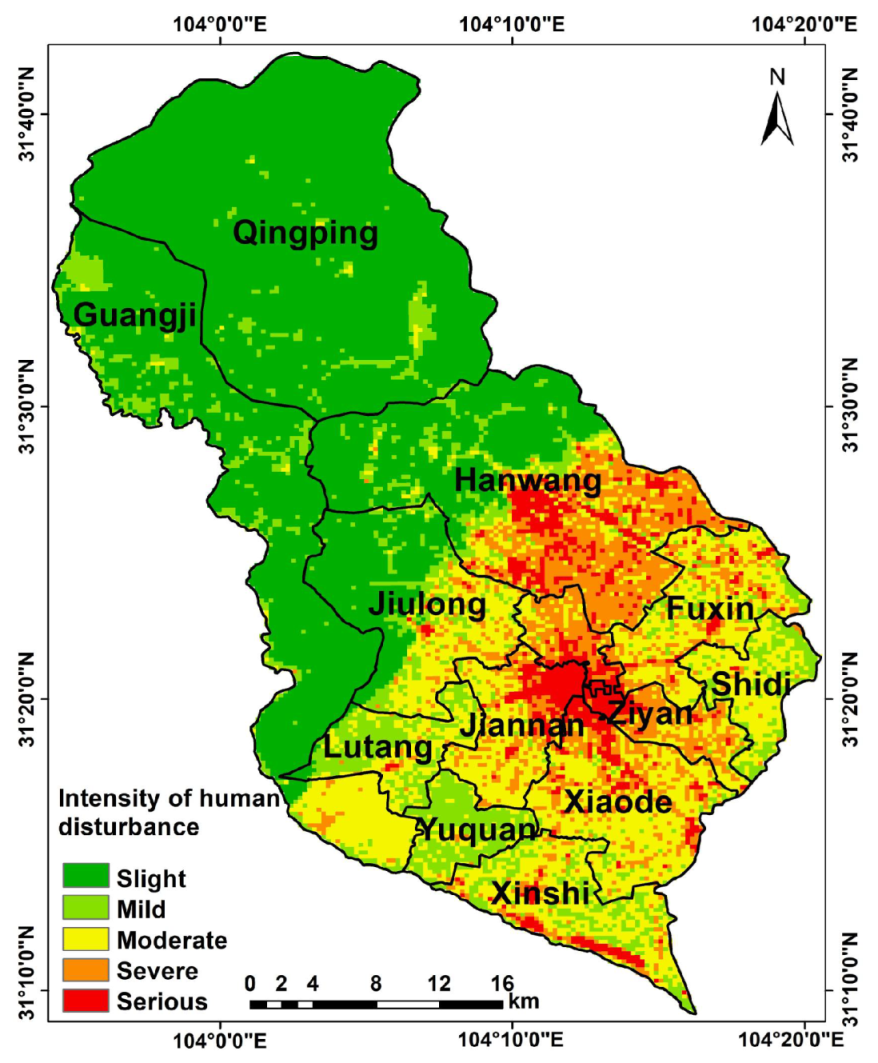
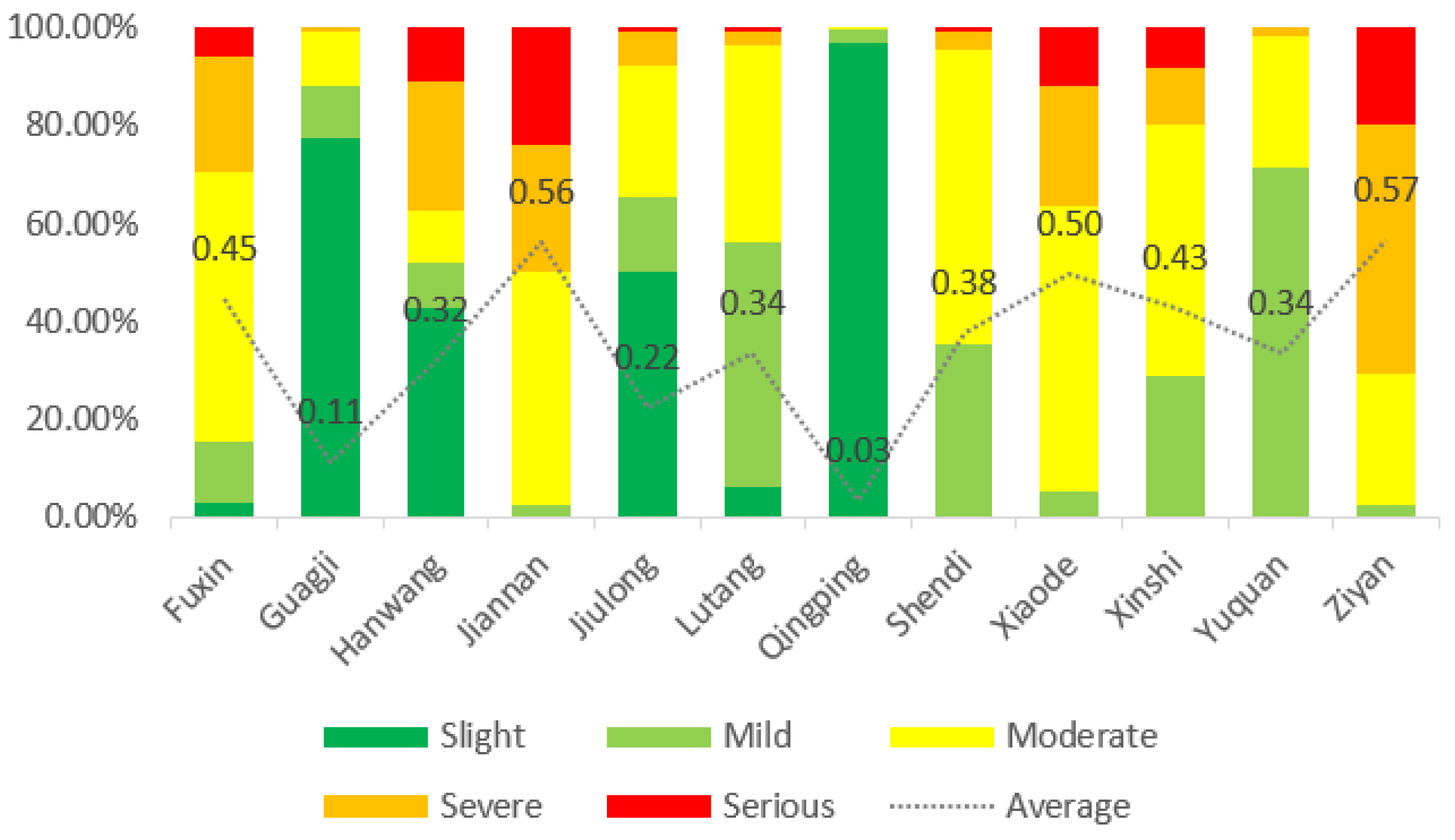
3.2. Spatial Analysis of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity
3.3. The Correlation Analysis between Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity
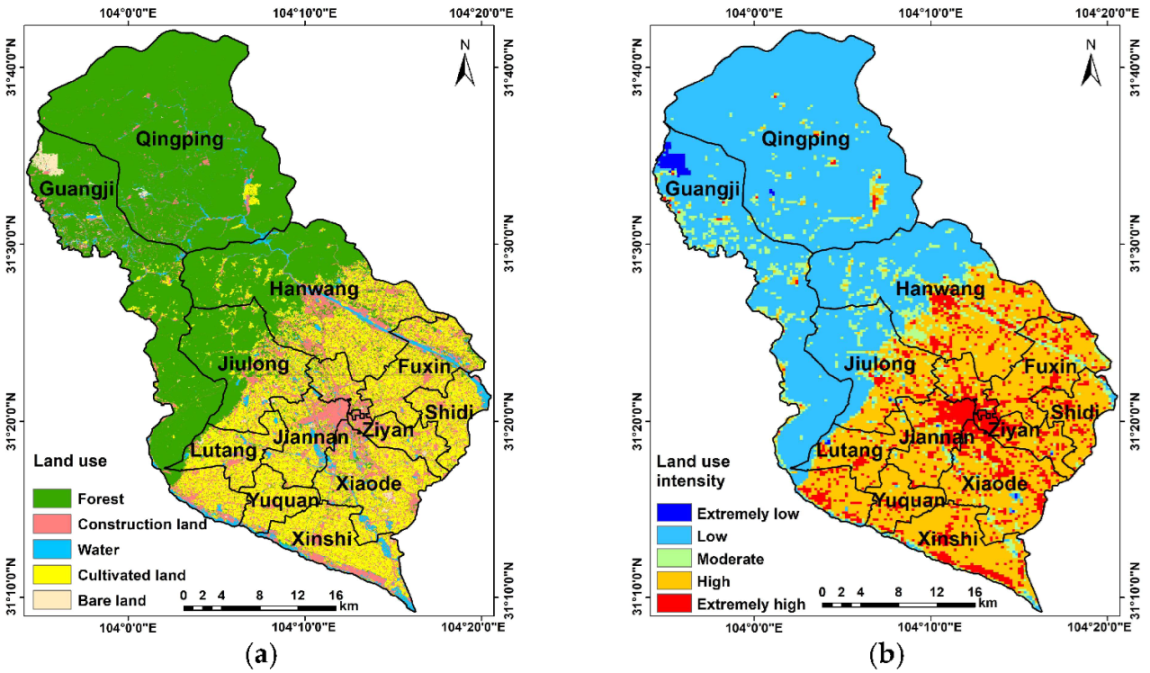
3.3.1. Land Use Intensity Analysis
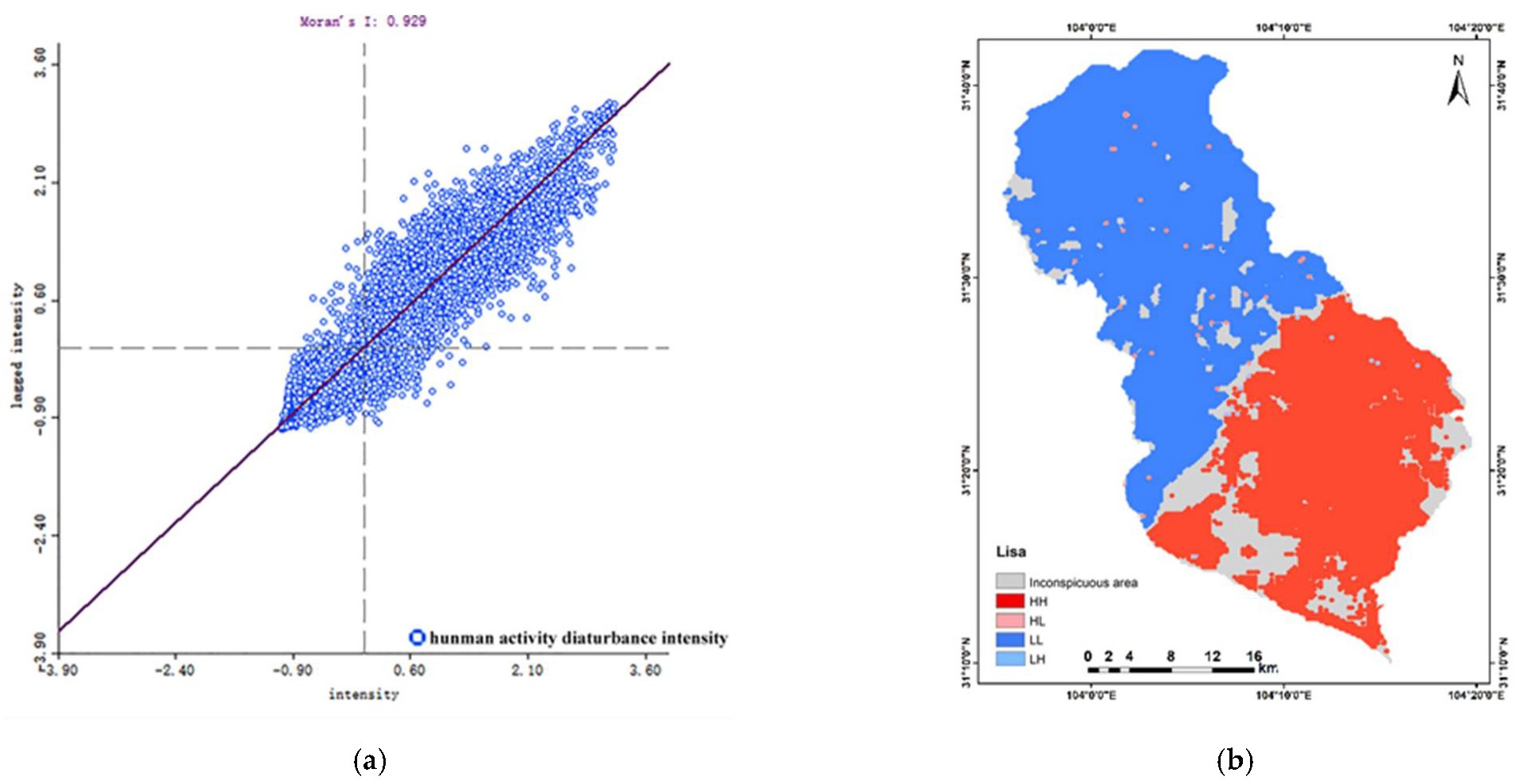
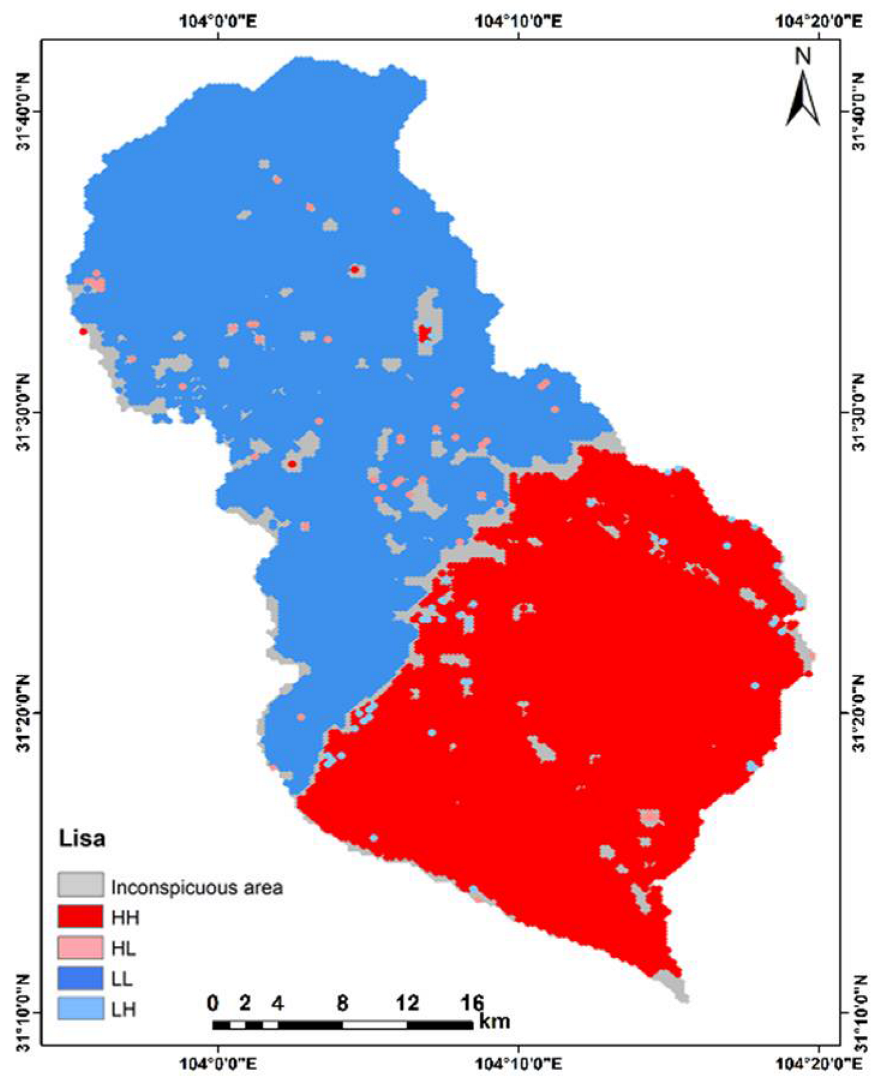
3.3.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delinom, R.M.; Assegaf, A.; Abidin, H.Z.; Taniguchi, M.; Suherman, D.; Lubis, R.F.; Yulianto, E. The contribution of human activities to subsurface environment degradation in Greater Jakarta Area, Indonesia. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3129–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Alberto, V.; Machado, C.; Criado, C. The impact of human activities on the natural environment of the Canary Islands (Spain) during the pre-Hispanic stage (3rd–2nd Century BC to 15th Century AD): An overview. Environ. Archaeol. 2009, 14, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-P.; Ying, B. Spatial distribution of mountainous regions and classifications of economic development in China. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 1120–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Li, N.; Ye, Q.; Dong, W.; Han, G.; Fang, W. Research on integrated disaster risk governance in the context of global environmental change. Int. J. Disaster Risk Sci. 2010, 1, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, D.; Fu, C.; Ji, J.; Dong, W.; Lü, J.; Wen, G.; Yan, X. Orderly human activities and subsistence environment. Adv. Earth Sci. 2001, 16, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Du, C.; Wei, R. Quantifying the effect of anthropogenic activities on water quality change in the Yangtze River from 1981 to 2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Lei, Y.; Zou, Y.; Cui, L. Characteristics of human activity in China’s coastal zone based on multi-source spatio-temporal data. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 3, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, Z.; Lu, M. Human Activities Introduced Degenerations of Wetlands (1975–2013) across the Sanjiang Plain North of the Wandashan Mountain, China. Land 2021, 10, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xing, H.; Hou, D. Analysis of carbon emissions from land cover change during 2000 to 2020 in Shandong Province, China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Chi, G. Spatiotemporal variations of land use intensity and its driving forces in China, 2000–2010. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2019, 19, 2583–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenchuk, P.; Plutzar, C.; Kastner, T.; Matej, S.; Bidoglio, G.; Erb, K.-H.; Essl, F.; Haberl, H.; Wessely, J.; Krausmann, F.; et al. Relative effects of land conversion and land-use intensity on terrestrial vertebrate diversity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Hou, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, G. Quantitative evaluation of human activity intensity on the regional ecological impact studies. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 39, 6797–6809. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, T.; Zhang, L.; Chen, B.; Yan, M. Human Disturbance on the Land Surface Environment in Tropical Islands: A Remote Sensing Perspective. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zha, P.; Yu, M.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, J.; You, Q.; Xie, X. Landscape Pattern Evolution and Its Response to Human Disturbance in a Newly Metropolitan Area: A Case Study in Jin-Yi Metropolitan Area. Land 2021, 10, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss, K.C.; Brown, M.T.; Lane, C.R. Characteristic community structure of Florida’s subtropical wetlands: The Florida wetland condition index for depressional marshes, depressional forested, and flowing water forested wetlands. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 18, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. Response of Landscape Evolution to Human Disturbances in the Coastal Wetlands in Northern Jiangsu Province, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Y. Analysis of spatial-temporal variation of human activity intensity in Loess Plateau region. Geogr. Res. 2017, 36, 661–672. [Google Scholar]
- Magalhães, J.L.L.; Lopes, M.A.; de Queiroz, H.L. Development of a Flooded Forest Anthropization Index (FFAI) applied to Amazonian areas under pressure from different human activities. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovarik, J.L.; van Beynen, P.E. Application of the Karst Disturbance Index as a raster-based model in a developing country. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Potapenko, J.; Casey, K.; Koenig, K.; Longo, C.; Lowndes, J.S.; Rockwood, R.C.; Selig, E.R.; Selkoe, K.A.; et al. Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world’s ocean. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ruan, Z. Spatial Correlation between Ecosystem Services and Human Disturbances: A Case Study of the Guangdong–Hong Kong–Macao Greater Bay Area, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Z. Functional Coupling Degree and Human Activity Intensity of Production–Living–Ecological Space in Underdeveloped Regions in China: Case Study of Guizhou Province. Land 2021, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dan, Y. Quantifying the impact of human activities on water quality based on spatialization of social data: A case study of the Pingzhai Reservoir Basin. Water Supply 2020, 20, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radionovs, A.; Užga-Rebrovs, O. Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchy Process for Ecological Risk Assessment. Inf. Technol. Manag. Sci. 2016, 19, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Xu, Z.; Hu, J.; Xue, Y.; Lin, P. A normal cloud model-based method for water quality assessment of springs and its application in Jinan. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Meng, X.X.; Liu, Y.B.; Pang, L.F. Risk Assessment of floor water inrush using entropy weight and variation coefficient model. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2019, 37, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, H.; Juneja, A.; Turabieh, H.; Malik, S.; Gupta, A.; Bitsue, Z.K.; Upadhyay, C. Exploration of crucial factors involved in plants development using the fuzzy AHP Method. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4279694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Bai, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, H.; Zha, X. Evaluation of watershed soil erosion hazard using combination weight and GIS: A case study from eroded soil in Southern China. Nat. Hazards 2021, 109, 1603–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Lv, L.; Meng, F.; Gao, F.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y. Landslide risk assessment based on combination weighting-improved TOPSIS. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 769, 032022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, F.; An, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Spatio-temporal variations and coupling of human activity intensity and ecosystem services based on the four-quadrant model on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140721. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Qiu, D.; Su, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, B.; Tao, Y. Water inrush risk assessment for an undersea tunnel crossing a fault: An analytical model. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2019, 37, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Dong, M.; Du, M.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, J. Fine-Grained Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Inbound Tourists Based on Geotagged Photos: A Case Study in Beijing, China. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28735–28745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Z. Correlation Study between Rural Human Settlement Health Factors: A Case Study of Xiangxi, China. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 2484850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chidi, C.L.; Sulzer, W.; Xiong, D.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Zhao, W.; Pradhan, P.K. Land use intensity dynamics in the Andhikhola watershed, middle hill of Nepal. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 1504–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avand, M.; Moradi, H.; Lasboyee, M.R. Using machine learning models, remote sensing, and GIS to investigate the effects of changing climates and land uses on flood probability. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Avand, M.; Yariyan, P.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Keesstra, S.; Tavangar, S.; Tabibian, S. A novel GIS-based ensemble technique for rangeland downward trend mapping as an ecological indicator change. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 117, 106591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, S.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Avand, M.; Janizadeh, S.; Tavangar, S.; Santosh, M. Assessment of land degradation using machine-learning techniques: A case of declining rangelands. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 32, 1452–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Data | Type | Source |
|---|---|---|
| GF-6 | raster data | National Space Administration Earth Observation and Data Center |
| Administrative division data | vector data | Resource and Environmental Science and Data Center of the Chinese Academy of Sciences |
| Township administrative divisions | The Ministry of Civil Affairs of China | |
| The number of enterprises | statistical data | “China County Statistical Yearbook Township Volume” |
| The number of large supermarkets | ||
| Agricultural expenditure data | Mianzhu Municipal People’s Government | |
| Township financial income data | ||
| Population data |
| Supermarkets Number | Construction Land Proportion | Forest Land Proportion | Population | Enterprises Number | Road Network Density | Financial Income | Agricultural Expenditure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1623 | 0.1755 | 0.1179 | 0.0569 | 0.1469 | 0.1363 | 0.0316 | 0.1726 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, M.; Jing, C. Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity Based on GF-6 Image, Empirical Study in Southwest Mountainous County, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184574
Zhang X, Wang X, Zhou Z, Li M, Jing C. Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity Based on GF-6 Image, Empirical Study in Southwest Mountainous County, China. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184574
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuedong, Xuedi Wang, Zexu Zhou, Mengwei Li, and Changfeng Jing. 2022. "Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity Based on GF-6 Image, Empirical Study in Southwest Mountainous County, China" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184574
APA StyleZhang, X., Wang, X., Zhou, Z., Li, M., & Jing, C. (2022). Spatial Quantitative Model of Human Activity Disturbance Intensity and Land Use Intensity Based on GF-6 Image, Empirical Study in Southwest Mountainous County, China. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4574. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184574









