Quantitative Evaluation of Environmental Loading Products and Thermal Expansion Effect for Correcting GNSS Vertical Coordinate Time Series in Taiwan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
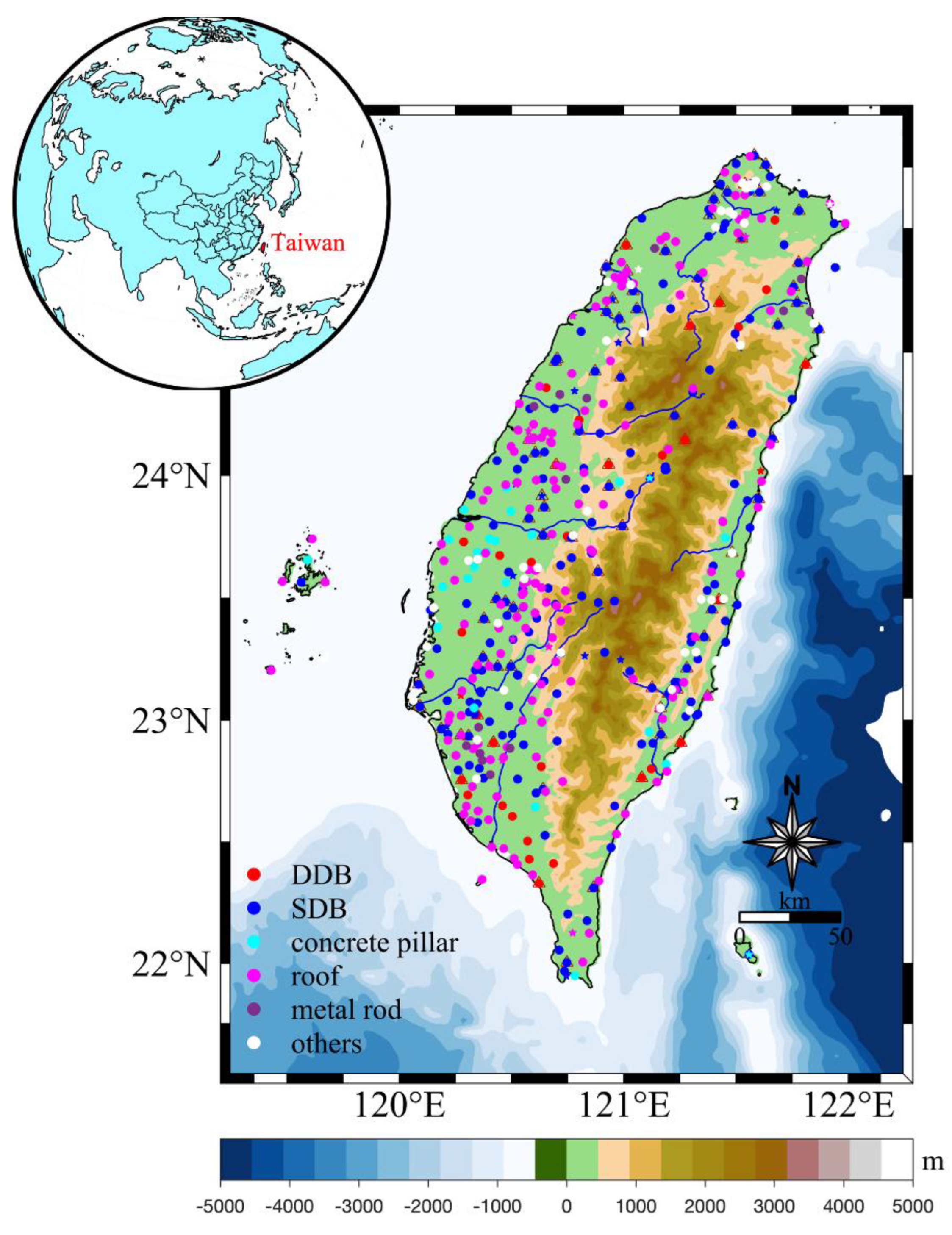
2.1. GNSS Data
2.2. Surface Mass Loading Effects
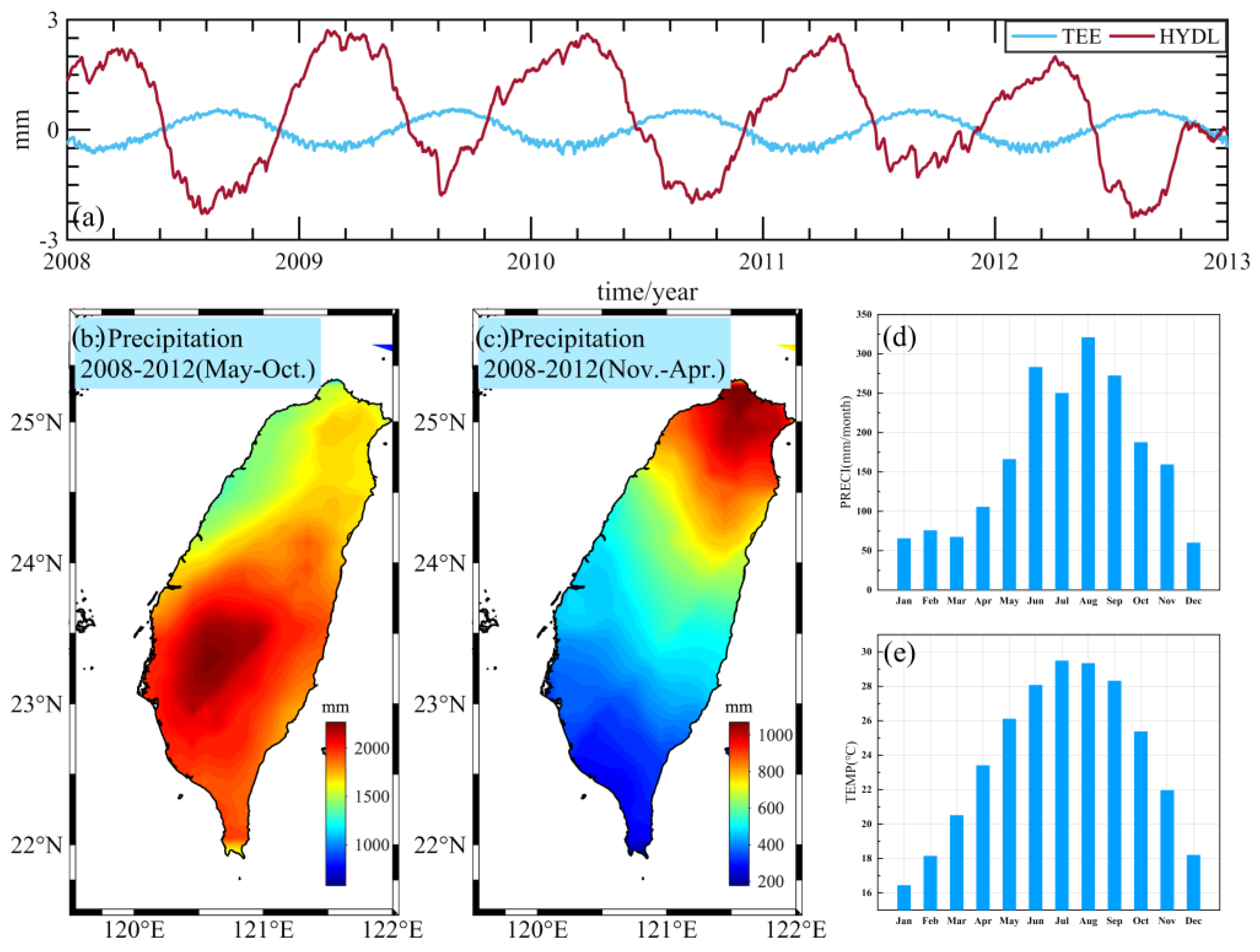
2.3. Temperature and Precipitation Data
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Calculation of Thermal Expansion Displacement
2.4.2. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
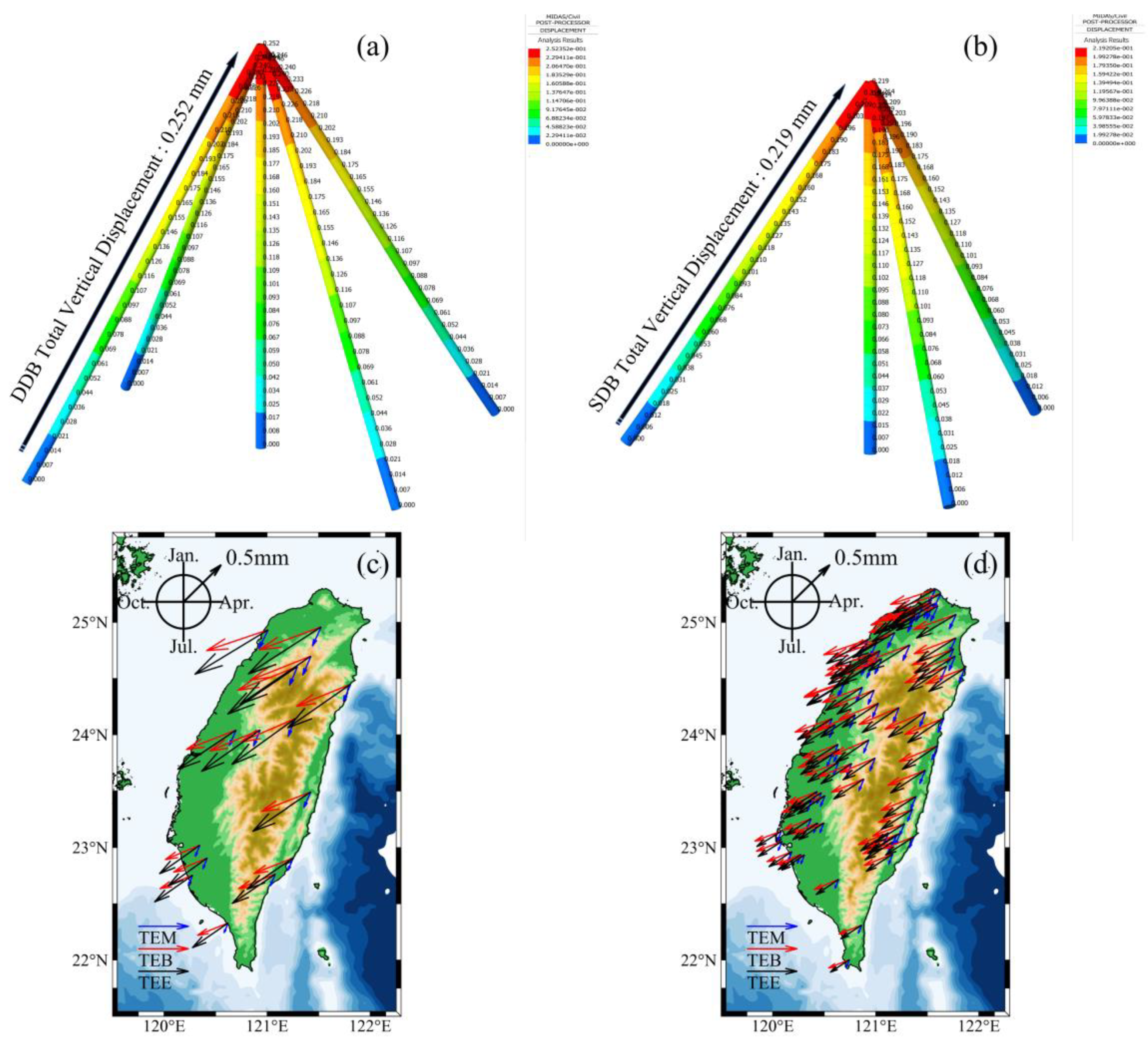
3.1. Quantitative Assessment of Environmental Loading Effects
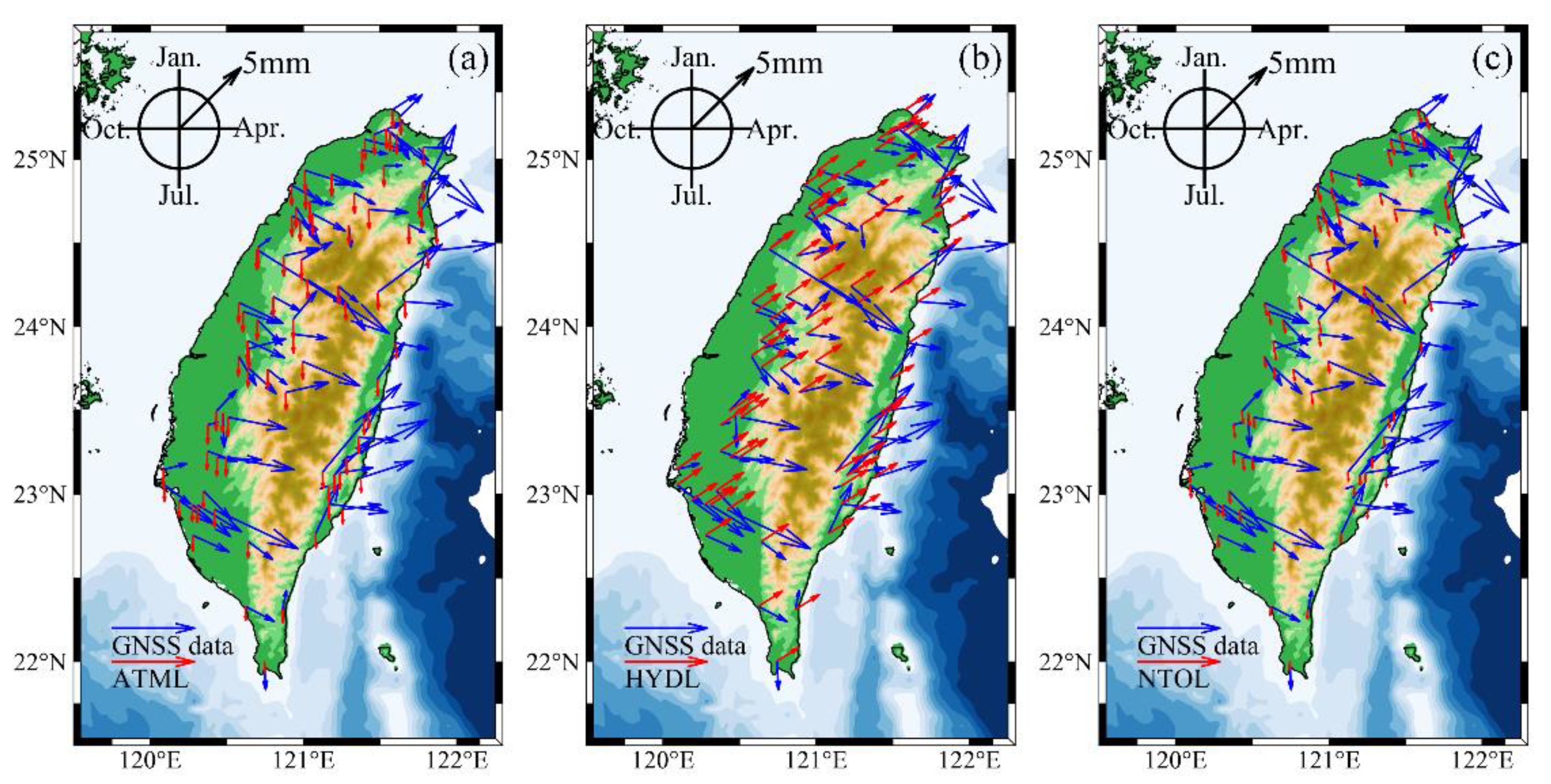
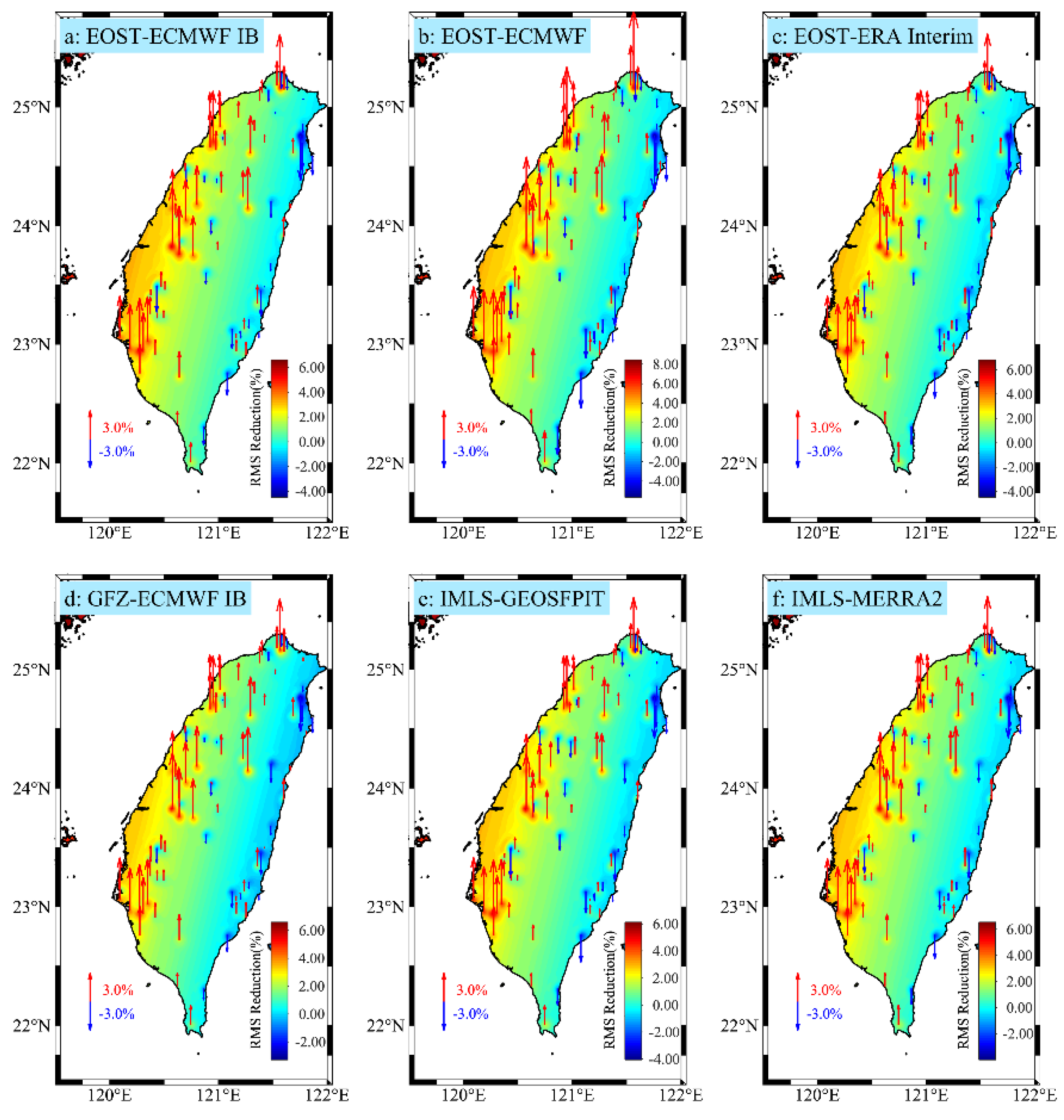
3.1.1. ATML Effects
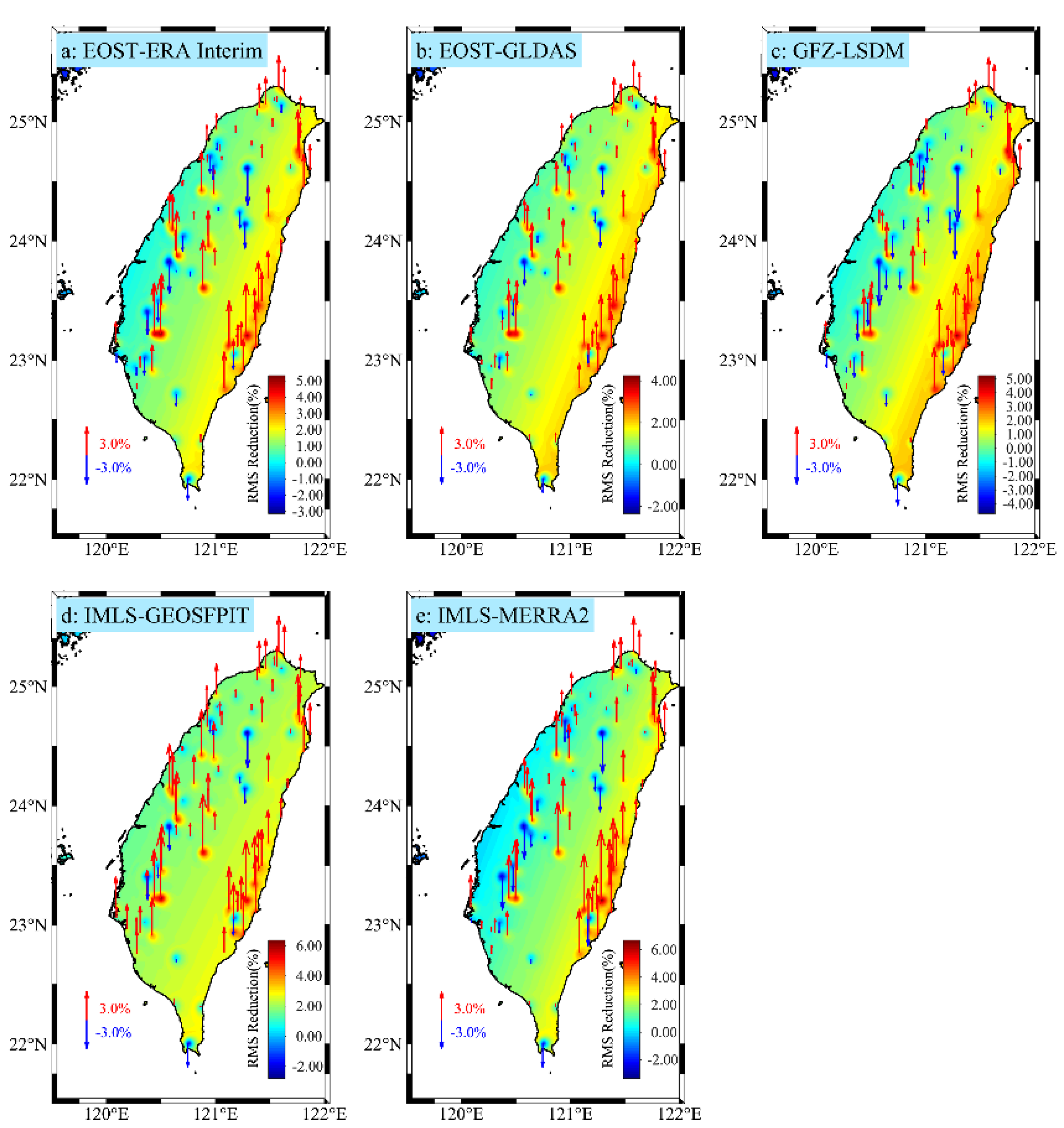
3.1.2. HYDL Effects
3.1.3. NTOL Effects
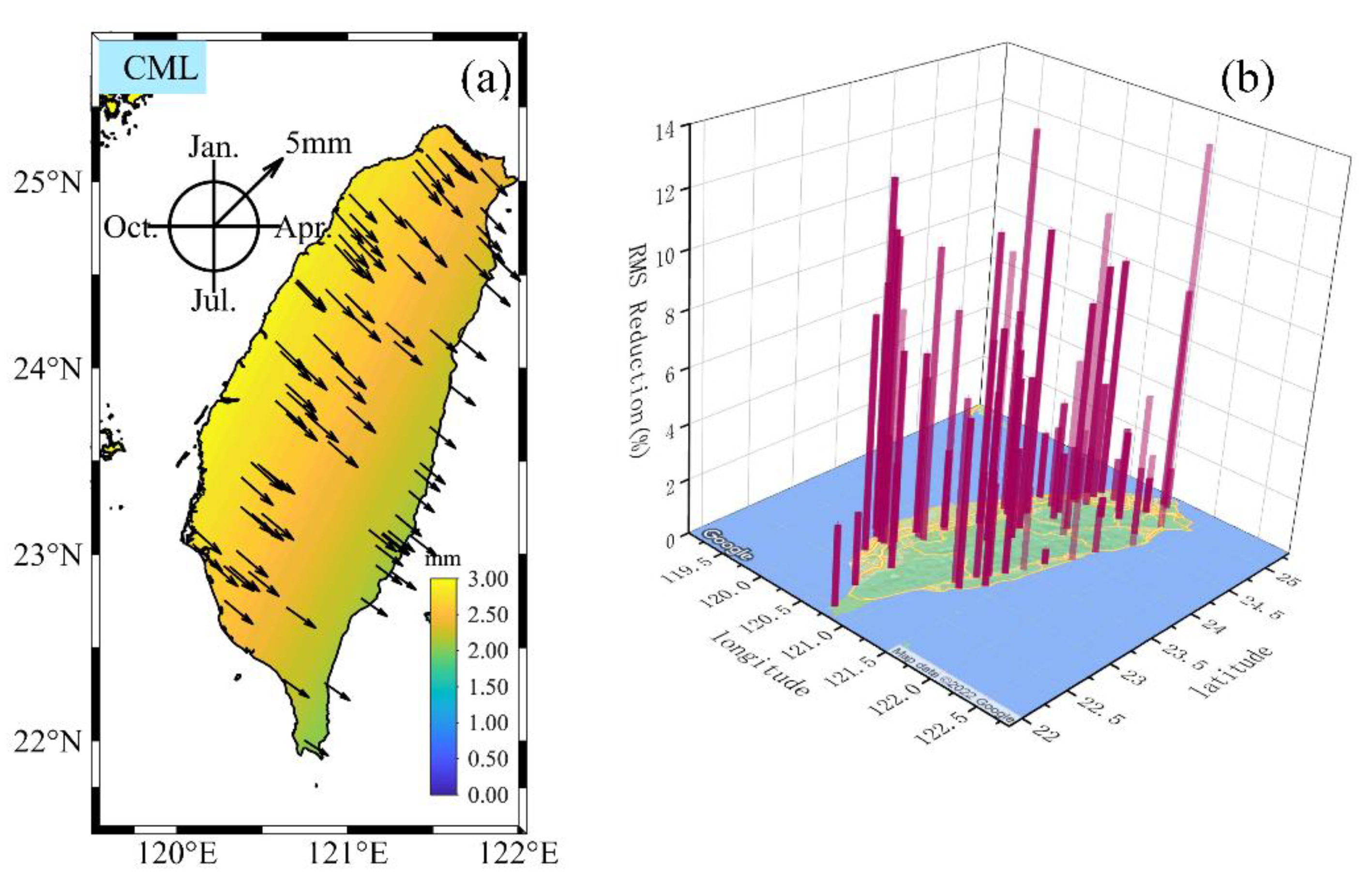
3.2. Quantitative Assessment of Thermal Expansion Effects
4. Discussions
4.1. Optimal Combination of Environmental Loading Models
4.2. The Effect of the Thermal Expansion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, R.S.; Blewitt, G.; Clarke, P.J.; Lavallée, D. Degree-2 harmonics of the Earth’s mass load estimated from GPS and Earth rotation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 1029–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.; Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; van Dam, T. Anomalous harmonics in the spectra of GPS position estimates. GPS Solut. 2008, 12, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Rothacher, M.; Schmid, R.; Rülke, A.; Fritsche, M.; Dietrich, R.; Tesmer, V. Effects of different antenna phase center models on GPS-derived reference frames. In Geodetic Reference Frames; Drewes, H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 134, pp. 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M.A.; Watson, C.S. Long GPS coordinate time series: Multipath and geometry effects. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B04403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrie, E.J.; King, M.A.; Moore, P.; Lavallée, D.A. Higher–order ionospheric effects on the GPS reference frame and velocities. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2010, 115, B03417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, T.; Wahr, J.; Milly, P.; Shmakin, A.; Blewitt, G.; Lavallée, D.; Larson, K. Crustal displacements due to continental water loading. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 651–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Fang, P.; Bock, Y.; Cheng, M.; Miyazaki, S.I. Anatomy of apparent seasonal variations from GPS-derived site position time series. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2002, 107, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, H.; Estermann, G.; Crétaux, J.-F.; Bergé-Nguyen, M.; van Dam, T. Investigation of hydrological and atmospheric loading by space geodetic techniques. In Satellite Altimetry for Geodesy, Geophysics and Oceanography; Hwang, C., Shum, C.K., Li, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 126, pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munekane, H.; Tobita, M.; Takashima, K. Groundwater-induced vertical movements observed in Tsukuba, Japan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L12608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, M. Contributions of thermal expansion of monuments and nearby bedrock to observed GPS height changes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Li, Z.; van Dam, T.; Ding, W. Comparative analysis of different environmental loading methods and their impacts on the GPS height time series. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, K.; Zhu, H.; Xue, C.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Q. A Comprehensive Analysis of Environmental Loading Effects on Vertical GPS Time Series in Yunnan, Southwest China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Huang, S.; Chen, Q.; van Dam, T.; Fok, H.S.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, X. Quantitative Evaluation of Environmental Loading Induced Displacement Products for Correcting GNSS Time Series in CMONOC. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Nie, G.; Meng, X.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Xue, C.; Li, H. Comparative Analysis of the Effect of the Loading Series from GFZ and EOST on Long-Term GPS Height Time Series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, C.; Zerbini, S.; Lago, L.; Richter, B.; Simon, D.; Domenichini, F.; Elmi, C.; Ghirotti, M. Influence of soil consolidation and thermal expansion effects on height and gravity variations. J. Geodyn. 2003, 35, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, M.; Liu, G. Thermal effects on vertical displacement of GPS stations in China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2010, 53, 825–832. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Xu, X.; Dong, D.; Chen, J.; Wu, B. Thermoelastic Seasonal Deformation in Chinese Mainland. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 1080–1097. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Wang, Y.; Lian, W.; Xiang, L. Comparison and Analysis of Crustal Vertical Deformation in Mainland China Observed by GPS from CMONOC and GRACE. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2018, 47, 899–906. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccara, G.; Hertzog, A.; Basdevant, C.; Vial, F. Accuracy of NCEP/NCAR reanalyses and ECMWF analyses in the lower stratosphere over Antarctica in 2005. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 113, D20115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R. Noise in GPS Coordinate Time Series II; Central Weather Bureau of the Ministry of Communications: Taipei City, Taiwan, 2014; Volume 64, pp. 281–327, (In Chinese). Available online: https://scweb.cwb.gov.tw/Uploads/Reports/MOTC-CWB-103-E-04.pdf (accessed on 7 August 2022).
- Kumar, U.; Chao, B.F.; Chang, E.T.Y. What Causes the Common-Mode Error in Array GPS Displacement Fields: Case Study for Taiwan in Relation to Atmospheric Mass Loading. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, B.; Dai, W.; Kuang, C.; Xing, X. Potential Contributors to Common Mode Error in Array GPS Displacement Fields in Taiwan Island. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.R.; Wang, L.; Bevis, M.; Fok, H.S.; Alanazi, A. Truncated singular value decomposition regularization for estimating terrestrial water storage changes using GPS: A case study over Taiwan. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.-J.; Fu, Y.; Bürgmann, R.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Lin, C.-C.; Tang, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-M. Assessing seasonal and interannual water storage variations in Taiwan using geodetic and hydrological data. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2020, 550, 116532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, T.; King, R.; McClusky, S. Documentation for the GAMIT Analysis Software, in Release 10.0 ed; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambrideg, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Altamimi, Z.; Collilieux, X.; Métivier, L. ITRF2008: An improved solution of the international terrestrial reference frame. J. Geod. 2011, 85, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, H.; Beutler, G.; Schaer, S.; Springer, T.; Rothacher, M. Processing aspects related to permanent GPS arrays. Earth Planets Space 2000, 52, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, J.; Heinkelmann, R.; Schuh, H. Short note: A global model of pressure and temperature for geodetic applications. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, R. Observation of Geodetic and Seismic Deformation with the Global Positioning System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, San Diego, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bitharis, S.; Fotiou, A.; Pikridas, C.; Rossikopoulos, D. A New Velocity Field of Greece Based on Seven Years (2008–2014) Continuously Operating GPS Station Data. In International Symposium on Earth and Environmental Sciences for Future Generations. International Association of Geodesy Symposia; Freymueller, J.T., Sánchez, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2016; Volume 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Montillet, J.P.; Fernandes, R.; Bos, M.; Yu, K.; Hua, X.; Jiang, W. Review of current GPS methodologies for producing accurate time series and their error sources. J. Geodyn. 2017, 106, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobslaw, H.; Bergmann-Wolf, I.; Dill, R.; Poropat, L.; Thomas, M.; Dahle, C.; Esselborn, S.; Koenig, R.; Flechtner, F. A new high-resolution model of non-tidal atmosphere and ocean mass variability for de-aliasing of satellite gravity observations: AOD1B RL06. Geophys. J. Int. 2017, 211, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, L. The international mass loading service. In REFAG 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Petrov, L.; Boy, J. Study of the atmospheric pressure loading signal in very long baseline interferometry observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rienecker, M.M.; Suarez, M.; Todling, R.; Bacmeister, J.; Takacs, L.; Liu, H.; Gu, W.; Sienkiewicz, M.; Koster, R.; Gelaro, R. The GEOS-5 Data Assimilation System: Documentation of Versions 5.0. 1, 5.1. 0, and 5.2. 0; Technical Report Series on Global Modeling and Data Assimilation Volume 27; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mémin, A.; Boy, J.-P.; Santamaría-Gómez, A. Correcting GPS measurements for non-tidal loading. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, R.; Dobslaw, H. Numerical simulations of global-scale high-resolution hydrological crustal deformations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2013, 118, 5008–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, K.; Deng, L.; Li, Z. Impact on Nonlinear Vertical Variation of GNSS Reference Stations Caused by Thermal Expansion. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2015, 44, 473–480. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Dong, D.; Bürgmann, R.; Materna, K.; Tan, W.; Peng, Y.; Chen, J. Separation of Sources of Seasonal Uplift in China Using Independent Component Analysis of GNSS Time Series. J. Geophys. Res.-Solid Earth 2019, 124, 11951–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q. Analyzing and Modeling Environmental Loading Induced Displacements with GPS and GRACE. Ph.D. Thesis, Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Wessel, P. Gridding with continuous curvature splines in tension. Geophysics 1990, 55, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Q. The non-tidal loading induced by tropical cyclones MATTHEW. Chin. J. Geophys. 2020, 63, 123–130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Institution | Type | Model | Spatiotemporal Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| EOST | ATML | ECMWF(IB) | |
| ATML | ECMWF | ||
| ATML | ERA interim | ||
| HYDL | ERA interim | ||
| HYDL | GLDAS/Noah | ||
| NTOL | ECCO2 | ||
| GFZ | ATML | ECMWF | |
| HYDL | LSDM | ||
| NTOL | EMPIOM | ||
| IMLS | ATML | GEOSFPIT | |
| ATML | MERRA2 | ||
| HYDL | GEOSFPIT | ||
| HYDL | MERRA2 | ||
| HYDL | MPIOM06 |
| ATML Model | D | RMS_Reduction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECMWF IB (EOST) | 0.2085 | 6.29 | 2.47 | |
| ECMWF | 0.2073 | 8.16 | 3.03 | |
| ERA interim | 0.2091 | 6.25 | 2.47 | |
| ECMWF IB (GFZ) | 0.2081 | 5.94 | 2.39 | |
| GEOSFPIT | 0.2080 | 5.84 | 2.23 | |
| MERRA2 | 0.2083 | 6.16 | 2.45 | |
| HYDL Model | D | RMS_Reduction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERA interim | 0.1924 | 6.04 | 2.40 | |
| GLDAS | 0.1973 | 4.56 | 1.97 | |
| LSDM | 0.1945 | 5.43 | 2.25 | |
| GEOSFPIT | 0.1682 | 7.10 | 2.72 | |
| MERRA2 | 0.1881 | 7.29 | 2.62 | |
| NTOL Model | D | RMS_Reduction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECCO2 | 0.2135 | 2.96 | 0.95 | |
| EMPIOM | 0.2049 | 6.41 | 2.00 | |
| MPIOM06 | 0.2055 | 5.14 | 1.87 | |
| Combinations | |
|---|---|
| GFZ-ECMWF IB and IMLS-MERRA2 and IMLS-MPIOM06 | 5.28 |
| IMLS-MERRA2 and IMLS-MERRA2 and IMLS-MPIOM06 | 5.21 |
| GFZ-ECMWF IB and IMLS-MERRA2 and GFZ-EMPIOM | 5.20 |
| EOST-ECMWF IB and IMLS-MERRA2 and IMLS-MPIOM06 | 5.17 |
| IMLS-MERRA2 and IMLS-MERRA2 and GFZ-EMPIOM | 5.12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Xing, X.; Tan, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, L. Quantitative Evaluation of Environmental Loading Products and Thermal Expansion Effect for Correcting GNSS Vertical Coordinate Time Series in Taiwan. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4480. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184480
Liu B, Ma X, Xing X, Tan J, Peng W, Zhang L. Quantitative Evaluation of Environmental Loading Products and Thermal Expansion Effect for Correcting GNSS Vertical Coordinate Time Series in Taiwan. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(18):4480. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184480
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Bin, Xiaojun Ma, Xuemin Xing, Jianbo Tan, Wei Peng, and Liqun Zhang. 2022. "Quantitative Evaluation of Environmental Loading Products and Thermal Expansion Effect for Correcting GNSS Vertical Coordinate Time Series in Taiwan" Remote Sensing 14, no. 18: 4480. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184480
APA StyleLiu, B., Ma, X., Xing, X., Tan, J., Peng, W., & Zhang, L. (2022). Quantitative Evaluation of Environmental Loading Products and Thermal Expansion Effect for Correcting GNSS Vertical Coordinate Time Series in Taiwan. Remote Sensing, 14(18), 4480. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14184480







