Estimating Emissions from Crop Residue Open Burning in Central China from 2012 to 2020 Using Statistical Models Combined with Satellite Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
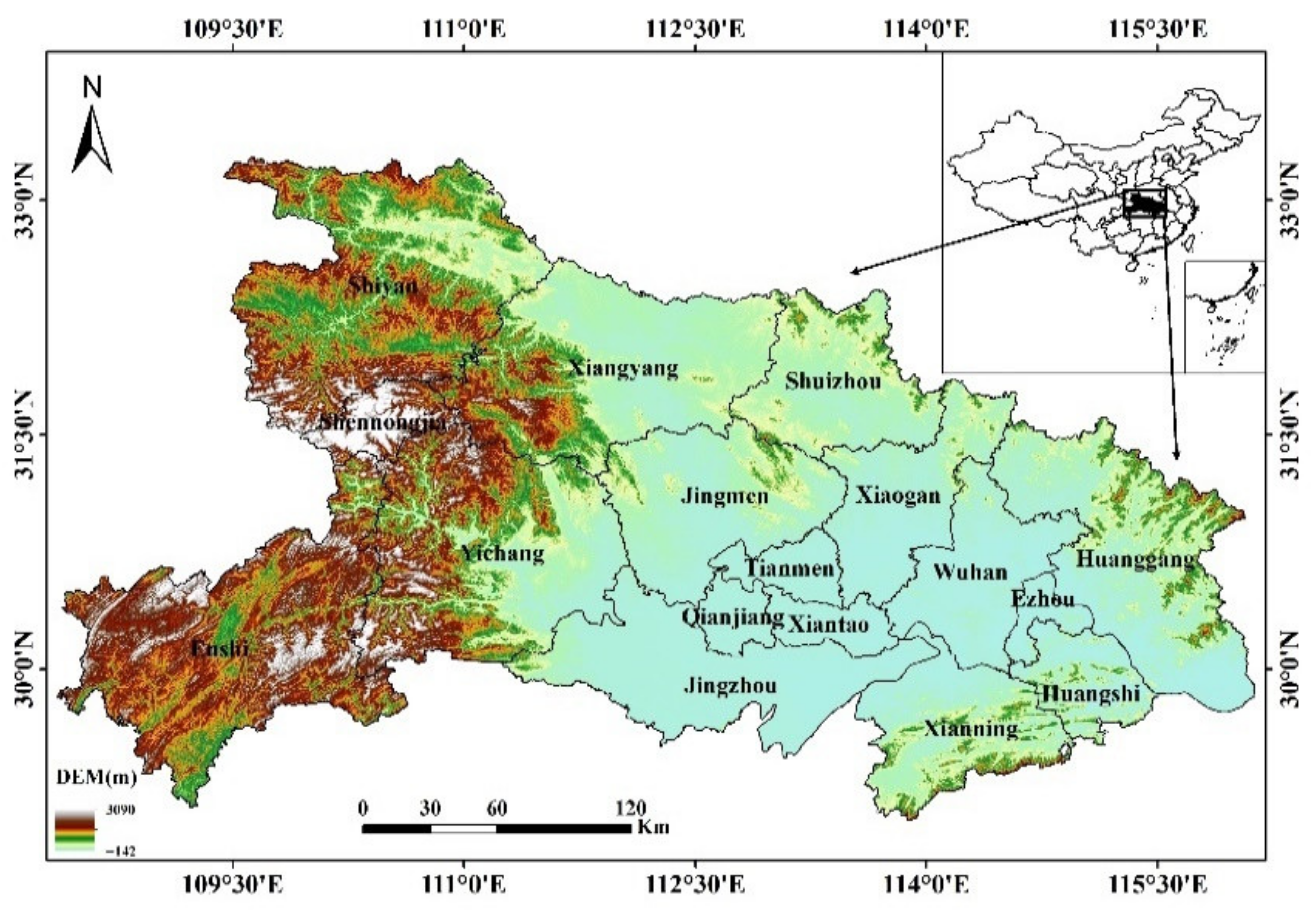
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods for Estimating Crop Residue Open Burning Emissions
2.2.1. Estimation of Residue Resources Burned in the Field
| Crop | Grain-to-Straw Ratio | Combustion Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Rice | 1.17 a | 0.93 d |
| Wheat | 1.39 b | 0.92 d |
| Corn | 0.98 b | 0.92 d |
| Rapeseed | 3.17 c | 0.8 e |
| Year | Fire Count | Rice | Wheat | Corn | Rapeseed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 4239 | 19.10% | 27.80% | 21.60% | 24.70% |
| 2013 | 8796 | 39.63% | 57.69% | 44.82% | 51.25% |
| 2014 | 6268 | 28.24% | 41.11% | 31.94% | 36.52% |
| 2015 | 3915 | 17.64% | 25.68% | 19.95% | 22.81% |
| 2016 | 3579 | 16.13% | 23.47% | 18.24% | 20.85% |
| 2017 | 3223 | 14.52% | 21.14% | 16.42% | 18.78% |
| 2018 | 3063 | 13.80% | 20.09% | 15.61% | 17.85% |
| 2019 | 4236 | 19.09% | 27.78% | 21.58% | 24.68% |
| 2020 | 1732 | 7.80% | 11.36% | 8.83% | 10.09% |
2.2.2. Emission Factors
2.3. Method for Spatial Allocation
2.4. Method for Temporal Allocation
2.5. Method for Uncertainties Analysis
3. Research Results
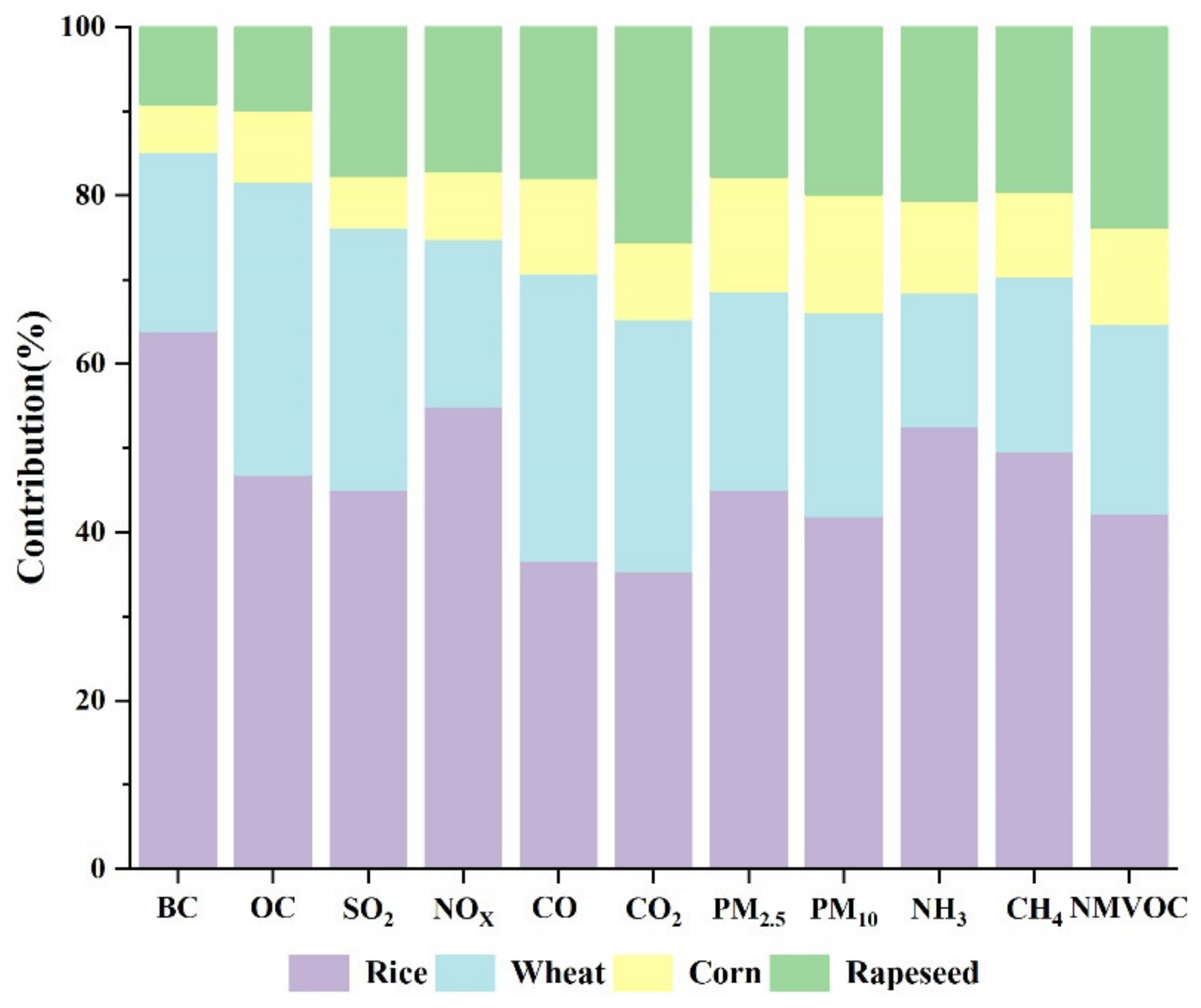
3.1. Emissions from Crop Residue Open Burning
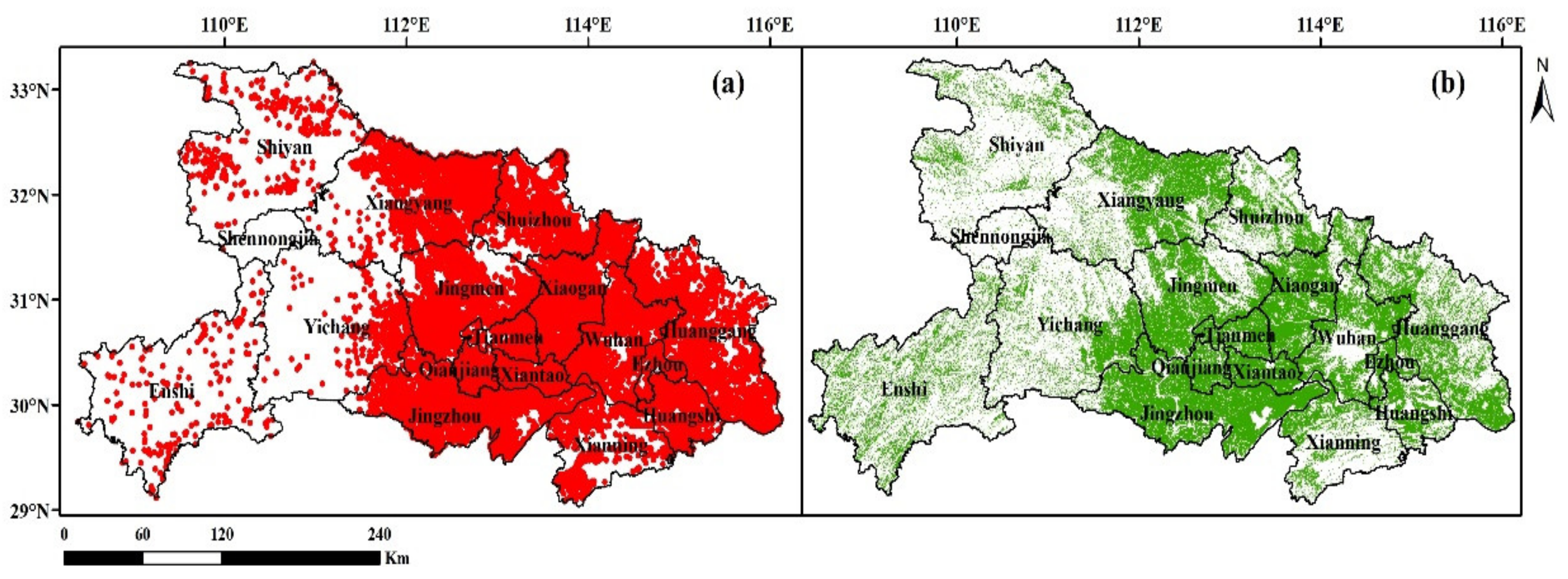
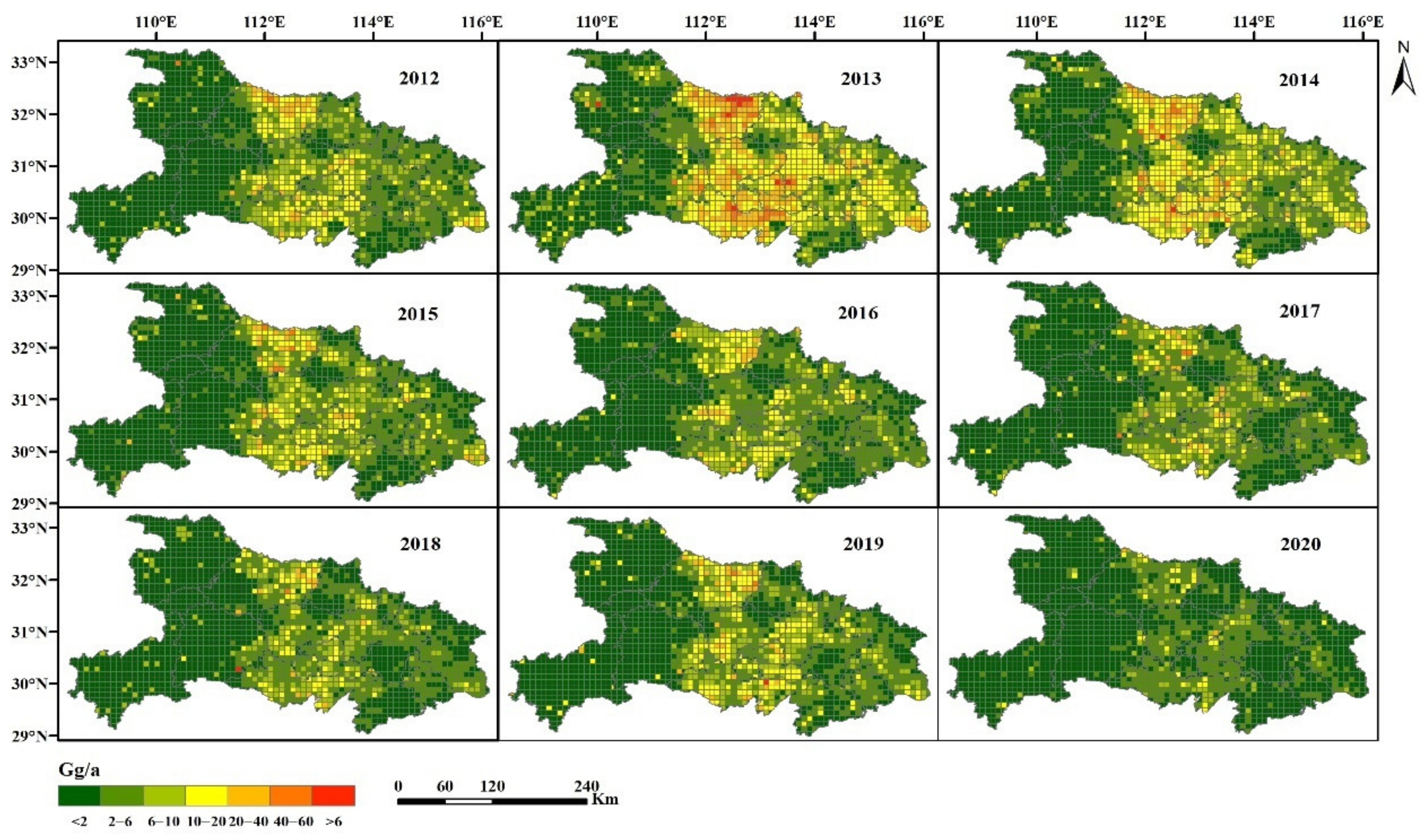
3.2. Spatial Distribution of Emissions
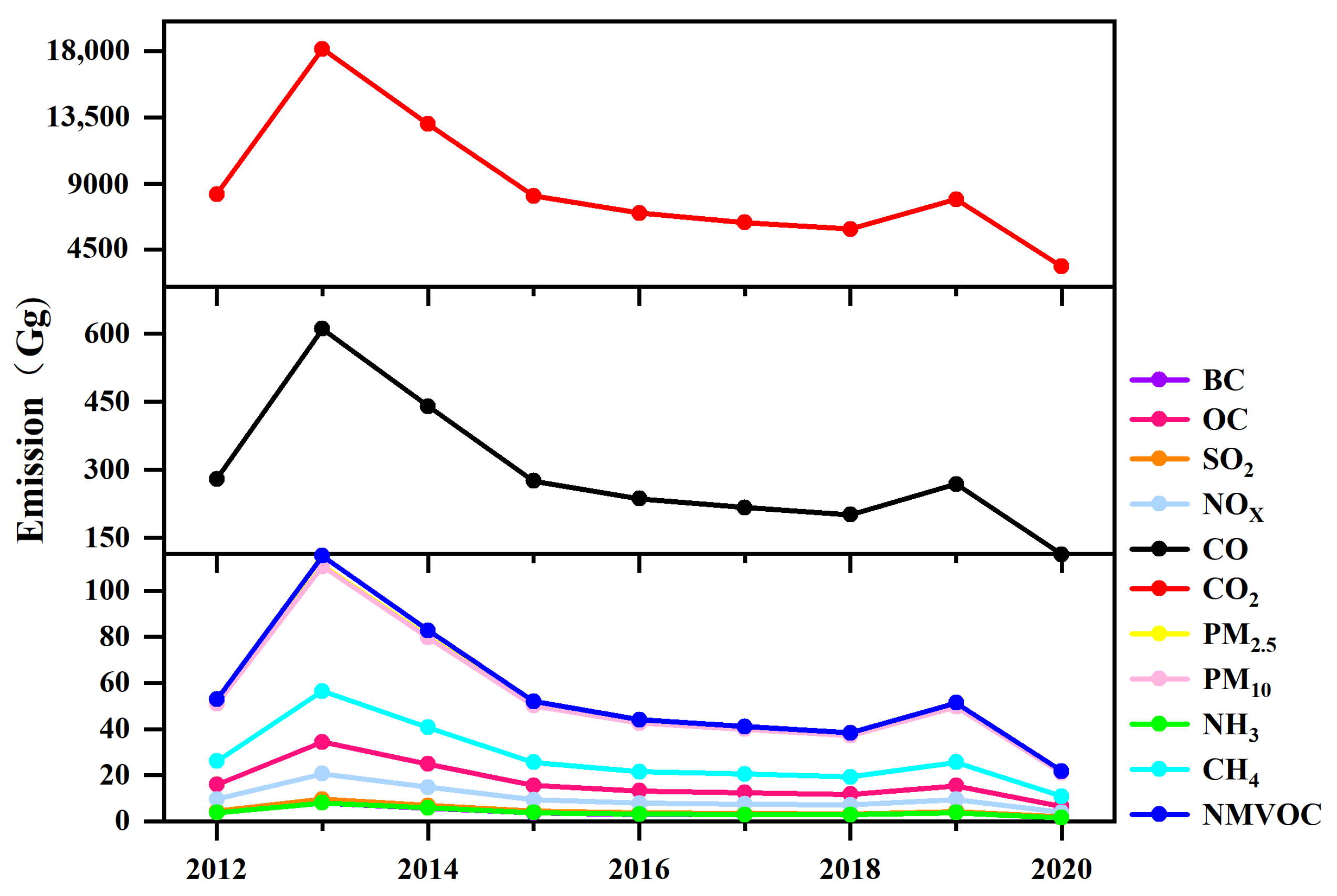
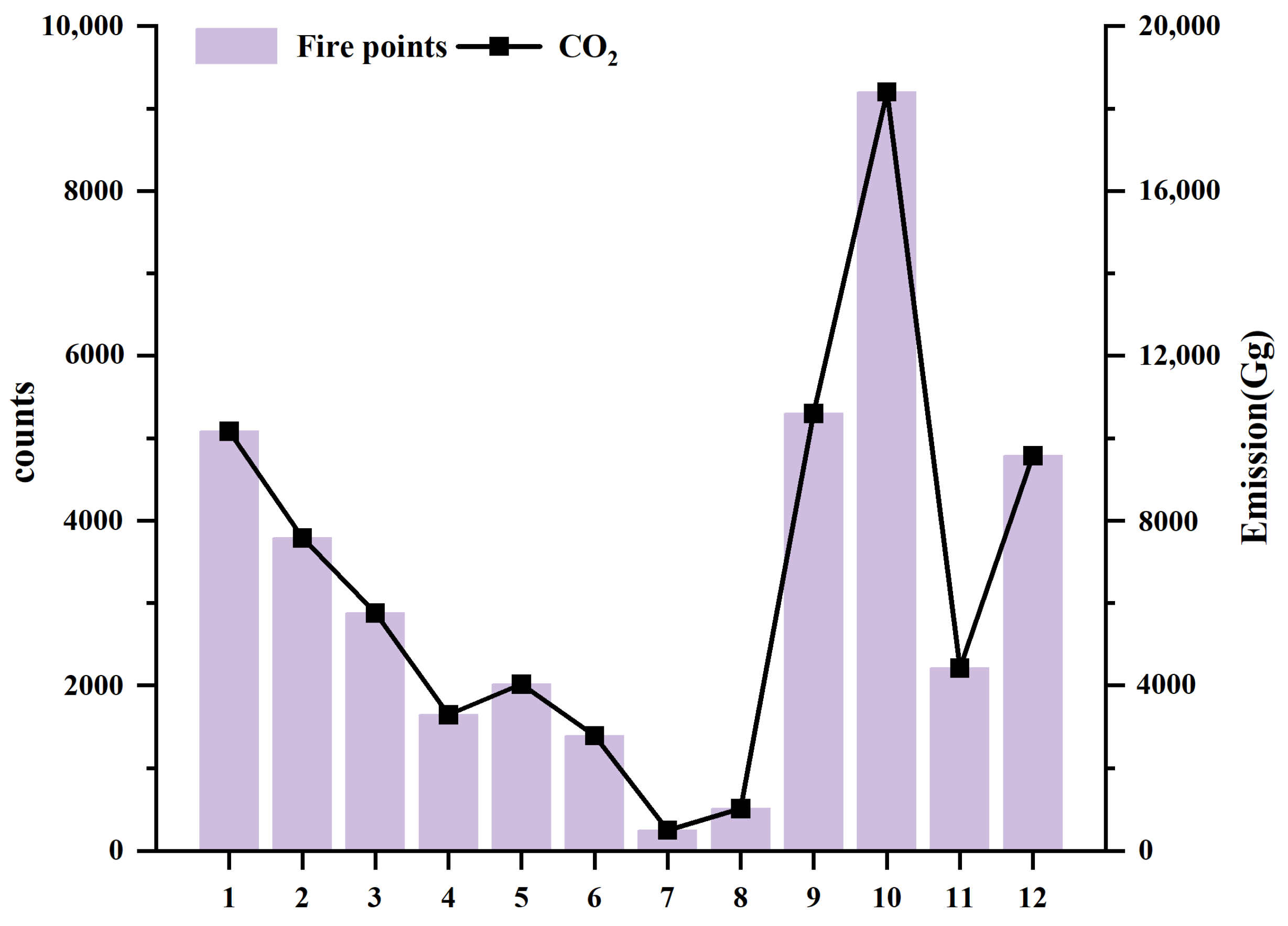
3.3. Temporal Variation of Emissions
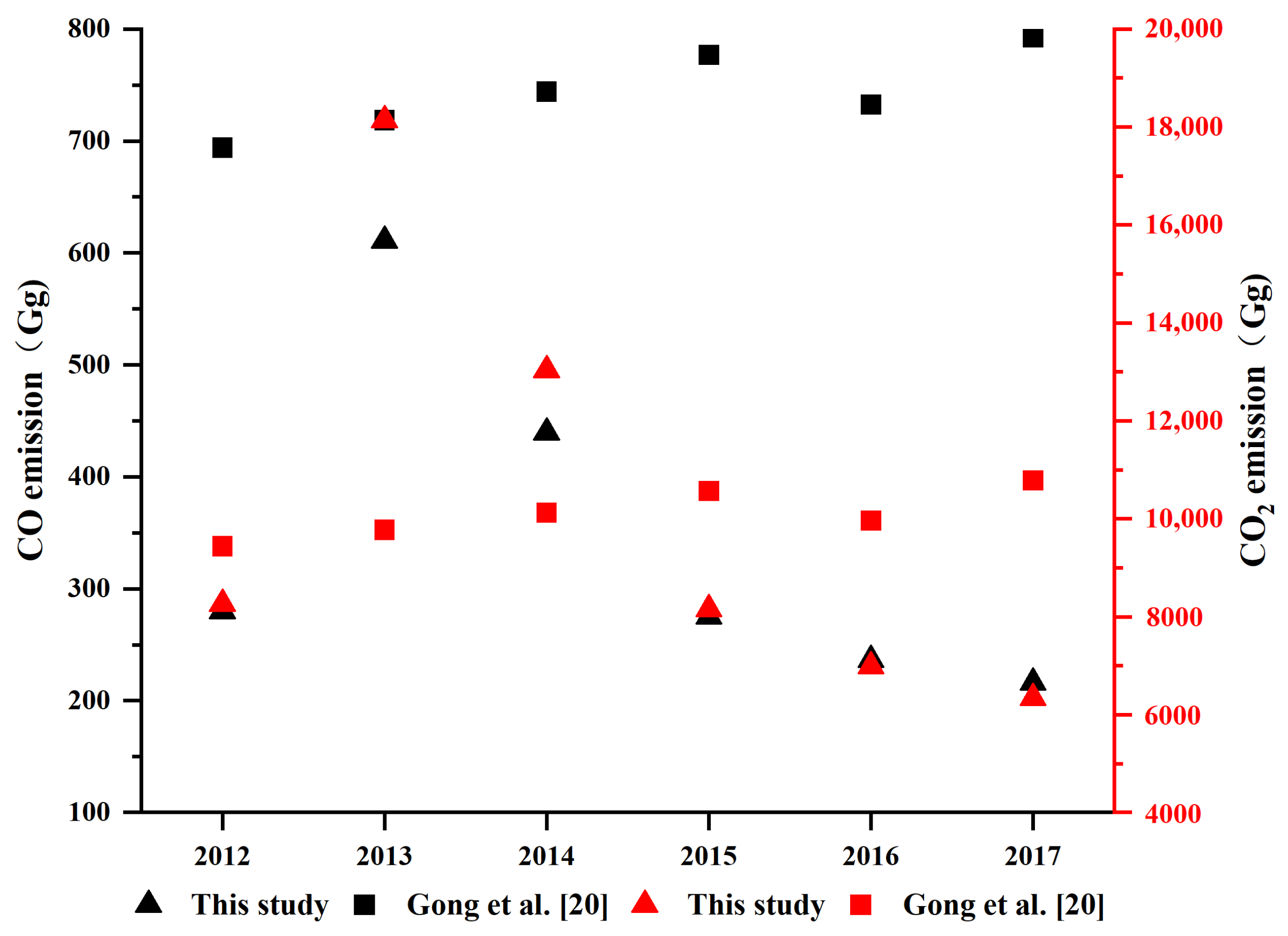
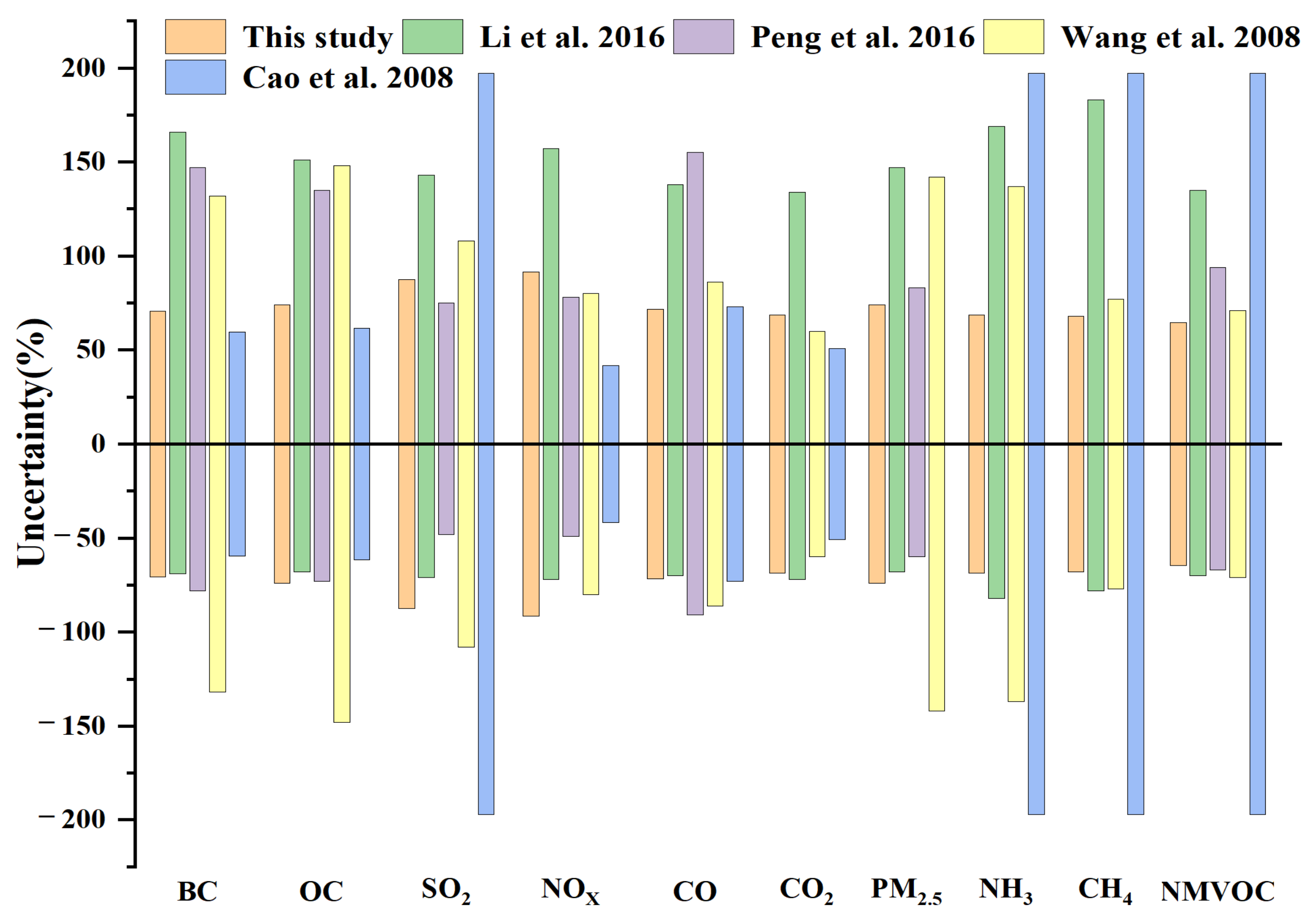
3.4. Comparison with Previous Studies
| Region | Reference | Year | BC | OC | SO2 | NOX | CO | CO2 | PM2.5 | PM10 | NH3 | CH4 | NMVOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hubei | This study | 2012 | 3.71 | 15.91 | 4.36 | 9.56 | 279.85 | 8268.48 | 51.33 | 50.87 | 3.73 | 26.1 | 52.84 |
| Li et al. [35] | 2012 | 2 | 14 | 3 | 19 | 307 | 6294 | 46 | - | 8 | 24 | 35 | |
| Li et al. [36] | 2010 | - | - | - | - | 469.7 | 6389.5 | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Peng et al. [21] | 2009 | 3 | 21 | 4 | 20 | 304 | 8090 | 75 | - | 4 | 21 | 44 | |
| Wang et al. [26] | 2006 | 1.2 | 11.9 | 1.5 | 8.9 | 181 | 3836 | 54 | - | 2.1 | 9.3 | 21.7 | |
| Wang et al. [34] | 2004 | - | 18.7 | 2.3 | 14.2 | 320.4 | 860.7 | - | 32.8 | 7.4 | 9.5 | - | |
| Cao et al. [37] | 2003 | 3.1 | 14.9 | 1.8 | 11.3 | 334.8 | 6836.5 | - | 26 | 5.9 | 9.9 | - | |
| Jingzhou Xiantao Tianmen Qianjiang | This study | 2012 | 0.86 | 3.38 | 0.99 | 2.24 | 59.86 | 1893.51 | 11.32 | - | 0.88 | 6.05 | - |
| Li et al. [19] | 2010 | 3.02 | 17.3 | 7.61 | 15.8 | 221 | 7181 | 68.2 | - | 5.31 | 9.9 | - |
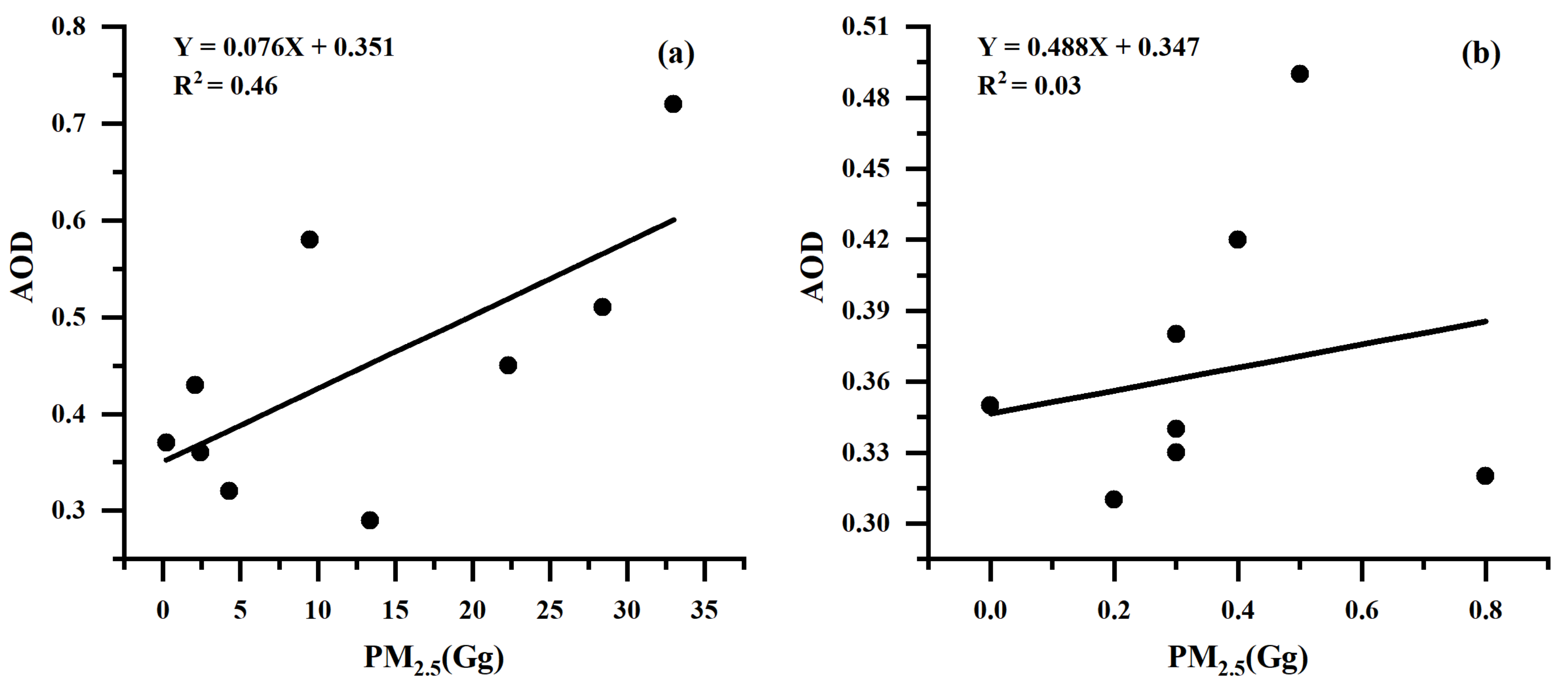
3.5. Comparison with AOD Retrieved by Satellite
3.6. Uncertainty Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Y.; Xing, X.; Lang, J.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S.; Wei, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, C. A comprehensive biomass burning emission inventory with high spatial and temporal resolution in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2839–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Jia, G.; Fan, M.; Cheng, L.; Chen, L.; Shao, M.; Zheng, J. Regional discrepancies in spatiotemporal variations and driving forces of open crop residue burning emissions in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Qian, X. A high-resolution inventory of air pollutant emissions from crop residue burning in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Ristovski, Z.; Milic, A.; Gu, Y.; Islam, M.S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhang, H.; He, C.; et al. A review of biomass burning: Emissions and impacts on air quality, health and climate in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1000–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Ma, Z.; Ye, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, R.; et al. Multi-pollutant emissions from the burning of major agricultural residues in China and the related health-economic effects. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 4957–4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Kong, S.; Wu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, S.; Yan, Q.; Zheng, H.; Yang, G.; Zheng, M.; Liu, D.; et al. Estimating the open biomass burning emissions in central and eastern China from 2003 to 2015 based on satellite observation. Atmos. Chem. Physics. 2018, 18, 11623–11646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, Y.; An, J.L.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xu, W.; et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of continuous hazes in China: A case study during the autumn of 2014 in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8165–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Hao, L. Contributions of open crop straw burning emissions to PM2.5 concentrations in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 014014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Tani, H.; Zhong, G.; Sun, Z. Study on spatial distribution of crop residue burning and PM2.5 change in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Duan, L.; Chai, F.; Wang, S.; Yu, Q.; Wang, S. Deriving high-resolution emission inventory of open biomass burning in China based on satellite observations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11779–11786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Song, Y.; Yao, H.; Kang, Y.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Hu, M. Estimating emissions from agricultural fires in the North China Plain based on MODIS fire radiative power. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 112, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Du, P.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M.; Xu, T.; Song, Y. Estimation of emissions from biomass burning in China (2003–2017) based on MODIS fire radiative energy data. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; de Jong, M.C.; Wooster, M.J.; Xu, W.; Wang, L. Trends in eastern China agricultural fire emissions derived from a combination of geostationary (Himawari) and polar (VIIRS) orbiter fire radiative power products. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10687–10705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, R.; Tao, M.; Wang, L.; Lin, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, L. Overview of the performance of satellite fire products in China: Uncertainties and challenges. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 268, 118838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Gao, H.; Liao, H.; Tian, X. Spatiotemporal Variations and Uncertainty in Crop Residue Burning Emissions over North China Plain: Implication for Atmospheric CO2 Simulation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Y.; Bo, Y.; Xie, S. High-resolution historical emission inventories of crop residue burning in fields in China for the period 1990–2013. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 138, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Jiang, W.; Gao, W.; Sun, S. Emission inventory of crop residue open burning and its high-resolution spatial distribution in 2014 for Shandong province, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Lang, J.; Xia, X.; Chen, D.; Cheng, S. Estimating air pollutant emissions from crop residue open burning through a calculation of open burning proportion based on satellite-derived fire radiative energy. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Song, Y.; Li, M.; Huang, X. Estimating Air Pollutants Emissions from Open Burning of Crop Residues in Jianghan Plain. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2015, 51, 647–656. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gong, S.; Guo, Y.; Ye, Q.; Lan, Y.; Wang, W.; Xiao, N. Estimation of carbon emission from burning of agricultural crop straw in hubei province. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2020, 59, 4. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. Emissions inventory of atmospheric pollutants from open burning of crop residues in china based on a national questionnaire. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 1109–1118. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, J.; Cui, K.; Huang, J.; He, F.; Peng, S. Responses of Physio-Biochemical Properties to N-Fertilizer Application and Its Relationship with Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Rice. Acta Agron. Sin. 2007, 33, 1168–1176. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Xue, S.; Xie, G. Value-taking for residue factor as a parameter to assess the field residue of field crops. J. China Agric. Univ. 2012, 17, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.; Lu, J.; Liao, Z.; Gong, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, H. Study on Response of Rapeseed to Boron Application and Critical Level of Soil Available B in Hubei Province. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2008, 41, 752–759. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ye, X.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, R. A laboratory study of agricultural crop residue combustion in China: Emission factors and emission inventory. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8432–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, C. Spatial and temporal distribution of air pollutant emissions from open burning of crop residues in China. China Sci. 2008, 5, 329–333. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Gong, S.; Zheng, F. Investigation on emission factors of particulate matter and gaseous pollutants from crop residue burning. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Huang, C.; Lou, S.; Qiao, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Chen, M.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q.; Li, G.; et al. Emission factors and PM chemical composition study of biomass burning in the Yangtze River Delta region. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 1623–1632. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- EPD: Guide for Compiling Atmospheric Pollutant Emission Inventory for Biomass Burning, Environmental Protection Department. 2014. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201501/t20150107_293955.htm (accessed on 26 June 2022). (In Chinese)
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L. Particulate and trace gas emissions from open burning of wheat straw and corn stover in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 6052–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akagi, S.K.; Yokelson, R.J.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Alvarado, M.J.; Reid, J.S.; Karl, T.; Crounse, J.D.; Wennberg, P.O. Emission factors for open and domestic biomass burning for use in atmospheric models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 4039–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Feng, X.; Mao, X. Emission Inventory of Crop Residues Field Burning and Its Temporal and Spatial Distribution in Sichuan Province. Environ. Sci. 2015, 36, 1208–1216. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y. Emission inventories of atmospheric pollutants discharged from biomass burning in China. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2011, 31, 349–357. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xu, Y. The Economic Losses Caused By Crop Residues Burnt in Open Field in China. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2008, 2, 170–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Bo, Y.; Xie, S. Estimating emissions from crop residue open burning in China based on statistics and MODIS fire products. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 44, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, J. Estimation of carbon emission from burning and carbon sequestration from biochar producing using crop straw in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhen, F. Inventory of emissions of pollutants from open burning crop residue. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2005, 24, 800–804. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Streets, D.G.; Yarber, K.F.; Woo, J.H.; Carmichael, G.R. Biomass burning in Asia: Annual and seasonal estimates and atmospheric emissions. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Nielsen, C.P.; Lei, Y.; McElroy, M.B.; Hao, J. Quantifying the uncertainties of a bottom-up emission inventory of anthropogenic atmospheric pollutants in China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2295–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, F. Estimation of emissions from field burning of crop straw in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Year | Region | Method | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qiu et al. [10] | 2013 | China | BA | The MODIS burned area product MCD64Al combined with the active fire product MCD14 ML were applied to develop a high-resolution emission inventory of open biomass burning; however, due to the coarse spatial resolution of MODIS, the small size agricultural fires were often missed. |
| Wu et al. [6] | 2003–2015 | Central and Eastern China | BA | |
| Liu et al. [11] | 2003–2014 | North China Plain | FRP | Emissions from crop burning in fields in the North China Plain were estimated using MODIS FRP derived from the Terra and Aqua satellites; however, many small agricultural fires may be undetected by MODIS sensors with the resolution of 1 km; moreover, the FRP retrieved by polar-orbiting satellites can only capture the agricultural fires in cloudless skies at the time of overpass. |
| Yin et al. [12] | 2003–2017 | China | FRP | Emissions inventories from biomass open burning were constructed using MODIS FRP data. Emissions from crop burning in fields may be underestimated. |
| Zhang et al. [13] | 2012–2015 | Eastern China | FRP | This study developed an agricultural burning emissions inventory by combining FRP observation from the VIIRS and Himawari-8 sensors. Although the FRP of agricultural small fires in this study was greatly increased, the total emissions were 2–5 times lower than the emissions estimated by statistical methods. |
| Fu et al. [15] | 2003–2019 | North China Plain | Three methods (Statistical-based method, BA-based method and FRP-based method) | This study investigated the crop residue burning emissions using three methods, and found that the statistical-based method is necessary for estimating local emissions. |
| Li et al. [16] | 1990–2013 | China | Statistical | More accurate time-varying statistical data and locally observed emission factors were utilized to estimate crop residue open burning emissions at the provincial level. |
| Gao et al. [17] | 2014 | Shandong | Statistical | An emission inventory of crop residue open burning was established in Shandong Province based on emission factors and activity data for a single year. |
| Li et al. [19] | 2010 | Jianghan Plain | Statistical | OBP is obtained through a household investigation with small survey samples, which may be not reliable enough. |
| Gong et al. [20] | 2009–2017 | Hubei | Statistical | The fixed OBP used in the model will introduce large uncertainty. |
| Pollutant | Rice | Wheat | Corn | Rapeseed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 0.64 h | 0.49 d | 0.35 d | 0.23 b |
| OC | 2.01 a | 3.46 a | 2.25 a | 1.08 b |
| SO2 | 0.53 c | 0.85 d | 0.44 d | 0.53 c |
| NOX | 1.42 b | 1.19 b | 1.28 g | 1.12 b |
| CO | 27.7 b | 60 d | 53 d | 34.3 b |
| CO2 | 791.3 g | 1557.9 g | 1261.5 g | 1445 i |
| PM2.5 | 6.26 e | 7.6 d | 11.7 d | 6.26 e |
| PM10 | 5.78 c | 7.73 c | 11.95 c | 6.93 c |
| NH3 | 0.53 c | 0.37 d | 0.68 d | 0.53 c |
| CH4 | 3.5 i | 3.4 d | 4.4 d | 3.5 i |
| NMVOC | 6.05 f | 7.5 f | 10 f | 8.64 f |
| City | BC | OC | SO2 | NOX | CO | CO2 | PM2.5 | PM10 | NH3 | CH4 | NMVOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wuhan | 1.43 | 5.22 | 1.49 | 3.64 | 89.58 | 2775.28 | 18.25 | 17.87 | 1.45 | 9.71 | 19.04 |
| Huangshi | 0.76 | 2.84 | 0.83 | 2.00 | 50.13 | 1590.10 | 10.05 | 9.91 | 0.80 | 5.37 | 10.71 |
| Shiyan | 0.97 | 5.26 | 1.36 | 2.79 | 103.11 | 2881.35 | 18.23 | 18.54 | 1.16 | 8.28 | 18.06 |
| Yichang | 1.65 | 7.51 | 2.08 | 4.83 | 150.68 | 4513.54 | 29.34 | 29.73 | 2.07 | 14.06 | 30.09 |
| Xiangyang | 6.24 | 34.44 | 8.57 | 15.67 | 602.39 | 16,046.38 | 94.97 | 94.90 | 5.73 | 44.11 | 92.32 |
| Ezhou | 0.42 | 1.50 | 0.45 | 1.09 | 26.41 | 862.30 | 5.31 | 5.24 | 0.43 | 2.91 | 5.78 |
| Jingmen | 3.66 | 15.39 | 4.30 | 9.44 | 269.78 | 8124.00 | 49.48 | 49.02 | 3.66 | 25.60 | 51.73 |
| Xiaogan | 2.97 | 11.58 | 3.20 | 7.26 | 189.85 | 5660.42 | 35.82 | 34.84 | 2.75 | 19.07 | 36.94 |
| Jingzhou | 5.71 | 22.06 | 6.45 | 14.80 | 386.21 | 12,188.37 | 74.00 | 73.13 | 5.80 | 39.70 | 79.45 |
| Huanggang | 3.94 | 14.24 | 4.21 | 10.09 | 244.86 | 7840.38 | 49.05 | 48.15 | 3.98 | 26.76 | 52.68 |
| Xianning | 1.31 | 4.63 | 1.33 | 3.32 | 78.50 | 2447.94 | 16.44 | 16.02 | 1.33 | 8.81 | 17.12 |
| Shuizhou | 1.94 | 8.49 | 2.20 | 4.59 | 137.18 | 3802.02 | 23.82 | 23.16 | 1.67 | 12.11 | 23.56 |
| Enshi | 0.99 | 4.71 | 1.17 | 3.08 | 100.03 | 2771.43 | 21.36 | 21.62 | 1.43 | 9.40 | 20.32 |
| Xiantao | 1.07 | 4.22 | 1.25 | 2.87 | 77.29 | 2461.47 | 14.85 | 14.82 | 1.15 | 7.85 | 16.04 |
| Qianjiang | 0.77 | 3.25 | 0.94 | 2.04 | 58.57 | 1825.21 | 10.62 | 10.61 | 0.80 | 5.58 | 11.44 |
| Tianmen | 1.00 | 4.31 | 1.21 | 2.57 | 75.24 | 2275.30 | 13.34 | 13.24 | 0.98 | 6.96 | 14.11 |
| Shennongjia | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 1.17 | 29.42 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 0.21 |
| Total | 34.84 | 149.72 | 41.06 | 90.11 | 2640.97 | 78,094.91 | 485.17 | 481.05 | 35.21 | 246.38 | 499.59 |
| Parameter | Distribution | Coefficients of Variation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | Wheat | Corn | Rapeseed | |||
| Activity data | Crop production | normal | 5% | |||
| Grain-to-straw ratio | 10% | |||||
| Combustion efficiency | 4.82% | 5.00% | 5.31% | 5.82% | ||
| Open burning proportion | 30% | |||||
| EFS | BC | 12.97% | 1.01% | 6.67% | 33.33% | |
| OC | 24.24% | 14.78% | 25.29% | 5.00% | ||
| SO2 | 69.53% | 3.03% | 4.76% | 35.90% | ||
| NOX | 34.51% | 48.76% | 36.53% | 5.00% | ||
| CO | 30.16% | 5.25% | 20.82% | 2.53% | ||
| CO2 | 32.39% | 4.84% | 3.49% | 1.23% | ||
| PM2.5 | 28.24% | 0.13% | 5.88% | 34.32% | ||
| PM10 | 30.32% | 16.84% | 10.85% | 18.77% | ||
| NH3 | 20.30% | 14.94% | 1.45% | 5.00% | ||
| CH4 | 9.86% | 21.00% | 1.12% | 6.85% | ||
| NMVOC | 0.41% | 1.96% | 1.96% | 4.74% | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, R.; He, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Mei, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L. Estimating Emissions from Crop Residue Open Burning in Central China from 2012 to 2020 Using Statistical Models Combined with Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153682
Li R, He X, Wang H, Wang Y, Zhang M, Mei X, Zhang F, Chen L. Estimating Emissions from Crop Residue Open Burning in Central China from 2012 to 2020 Using Statistical Models Combined with Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(15):3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153682
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Rong, Xinjie He, Hong Wang, Yi Wang, Meigen Zhang, Xin Mei, Fan Zhang, and Liangfu Chen. 2022. "Estimating Emissions from Crop Residue Open Burning in Central China from 2012 to 2020 Using Statistical Models Combined with Satellite Observations" Remote Sensing 14, no. 15: 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153682
APA StyleLi, R., He, X., Wang, H., Wang, Y., Zhang, M., Mei, X., Zhang, F., & Chen, L. (2022). Estimating Emissions from Crop Residue Open Burning in Central China from 2012 to 2020 Using Statistical Models Combined with Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing, 14(15), 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14153682







