1. Introduction
VHF radar has the unique advantages of anti-stealth, anti-radiation, and long-distance detection. It has been widely used in air defense early-warning tasks to detect targets and provides target range and coordinate information [
1,
2,
3,
4]. In general, the VHF radar can provide high-precision range and azimuth information, but when tracking a low-angle target, the multipath phenomenon seriously limits the pitch measurement performance. For low-angle target tracking, the target and multipath signals are within the same range and Doppler cell. Meanwhile, due to the limitation of aperture, the VHF radar has a wide beam, and the target and multipath signals are within the same beamwidth, making it difficult to separate them in the spatial, temporal, and Doppler domains [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9].
In addition, the traditional multipath signal model based on the smooth reflection flat has only one multipath. In practice, when the radar is in a complex geomorphic environment, such as mountains, hills, and islands, there are several multipaths, the specular reflection hypothesis between the multipaths and the direct wave is no longer satisfied, and the energy distribution is uneven. In this case, the echo signal is seriously mismatched with the single reflection center signal model, which leads to performance degradation and even failure of the traditional DOA algorithm. Therefore, it is crucial to find a high-precision DOA estimation method in a complex terrain environment for low-elevation targets.
Low-angle target measurement is essential to distinguish and estimate the angle of two closely correlated signals in space. Extensive studies have been devoted to array signal processing to seek higher measurement accuracy in a multipath environment. Generally, the existing methods can be mainly classified into three categories, i.e., subspace-based, maximum-likelihood (ML), and compressive sensing (CS) methods.
The first category of methods is mainly based on the multiple signal classification (MUSCI) framework [
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. The MUSIC algorithm has good performance for spatially uncorrelated sources. Due to the strong coherence between the direct wave and multipath, the covariance matrix of the received signal will not have a full-rank matrix, and the vectors of signal subspace are less than the signal sources by eigendecomposition. In this case, accurate estimation of coherent sources cannot be achieved. To restore the signal covariance matrix to a full-rank matrix, signal correlation is eliminated by the spatial smoothing technique via moving between subarrays. However, many antennas are required to compensate for the loss of array aperture, which is not always available in VHF radar [
15,
16]. To solve this problem, the general MUSIC algorithm is presented in [
17]. This algorithm can realize coherent signal estimation by using the geometric relationship of mirror symmetry between direct wave and multipath signal. However, the algorithm does consider the influence of the perturbation factor, so it is only applicable to the ideal smooth reflecting surface. Furthermore, ref. [
18] fully considers the influence of the perturbation factor on the multipath signal in the rough reflector, and combines alternating projection (AP) techniques and the general MUSIC method to update the specular reflection coefficient, which improves the applicability of the algorithm, whereas in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and limited snapshots scenarios, these algorithms suffer from significant performance degradation (or fail to work).
The second category of methods includes a variety of ML estimation techniques [
19,
20,
21,
22]. On the whole, these methods use the statistical information of signals to solve the likelihood function. There are not affected by the coherence of signals, and have good estimation performance under the low SNR condition. However, the solution of the likelihood function is a highly nonlinear optimization problem, and the computation costs increase exponentially with the number of targets, making it difficult for the algorithms to meet real-time requirements. To solve this problem, the AP technique is introduced to perform ML in [
23], and the multi-dimensional optimization problem is transformed into multiple one-dimensional optimization problems, which greatly reduces the computational cost. To further reduce the computation cost of the algorithm, some priori information are used to reduce the number of unknown parameters in [
22], such as direct wave, multipath mirror geometry, and radar height. Though the a priori information contributes to a good performance of ML methods, these methods are usually only applicable to the ideal smooth reflecting surface. Meanwhile, it is difficult to obtain the relevant parameters in practice.
Furthermore, as one of the super-resolution algorithms, the compressive sensing (CS) theory uses the spatial sparsity of the targets to obtain an accurate DOA estimation. The last category methods include a series of CS estimation techniques [
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. In general, these methods can directly estimate the DOA of the coherent sources, and most of them provide better estimation performance under the condition of few snapshots and low SNR. A terrain matching method for low-angle targets with a priori information on the environment and terrain is developed in [
29]. Based on the orthogonal matching pursuit (OMP), the method can achieve accurate estimation of low-angle targets by updating the perturbation parameter. Moreover, the sparse Bayesian learning (SBL)-based methods provide the target angle, perturbation parameter, and reflecting coefficient through the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm. This method has higher estimation accuracy than the work in [
29] and achieves smaller reconstruction errors for the sparsest solution.
In the above-mentioned low-angle target tracking methods, the CS estimation techniques have higher performance under the condition of fewer snapshots and low SNR, but the reflecting surface is assumed to be perfectly smooth and flat with only one multipath propagation path. Furthermore, the multipath attenuation coefficient of the ground surface is considered a constant, which is usually inaccurate in practice. When the topography of the reflecting surface area is complex, there are multiple multipath reflecting waves from different reflecting points, and the number of the multipaths is unknown. Moreover, under different reflecting media, the different multipath echoes have different reflection angles and uneven energy distribution. In this case, the received signal will be seriously mismatched with the single multipath signal model for both smooth and rough reflecting surface. Based on the above analysis, to achieve accurate estimation of multipaths and the direct wave in a complex terrain, the estimation algorithm needs high multiples of super-resolution. In practical applications, due to a limited SNR, the existing algorithms struggle to meet the requirements.
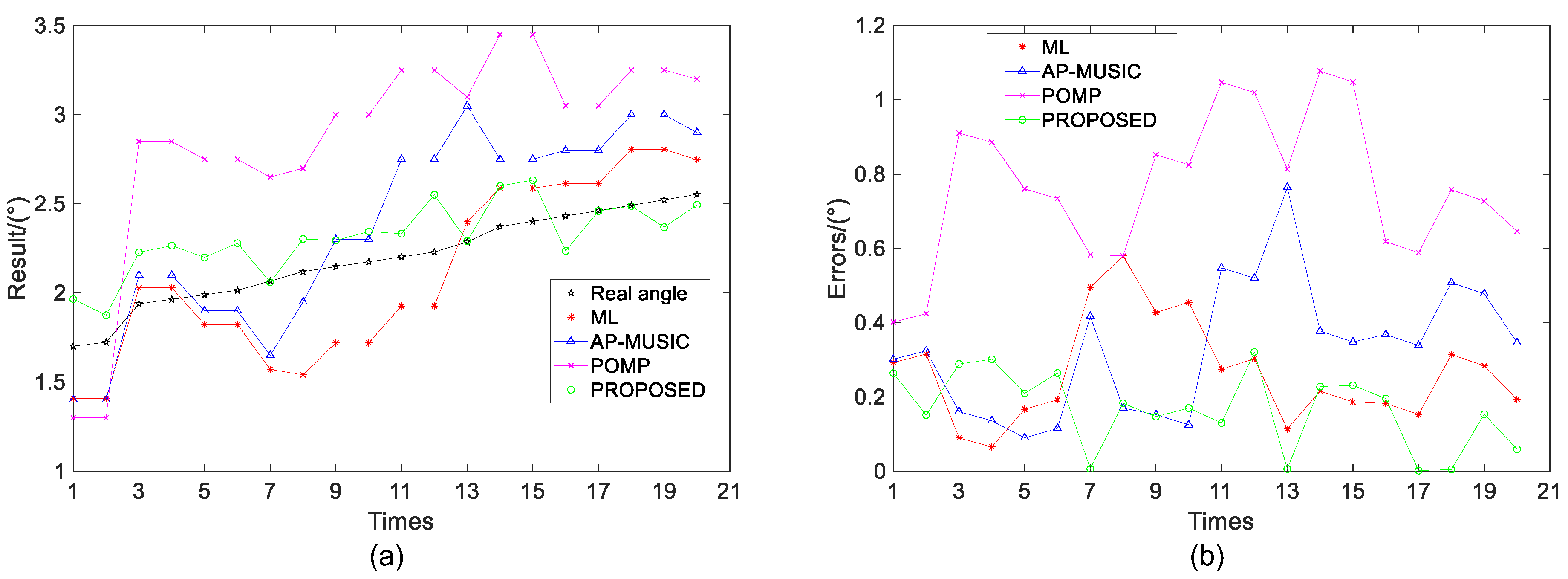
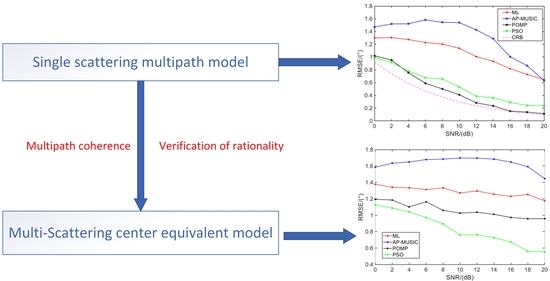
To solve the above problems, a novel model and an algorithm for low-angle target DOA estimation are proposed. Firstly, a multiple reflection center signal model for VHF radar in complex terrain is presented. In this model, multipath echo is modeled as multiple incident signals that are coherent with the direct wave, and the number of multipaths and incidence angles are unknown. In this case, an equivalent model of multipath is proposed for the first time under the narrow bandwidth conditions. That is, after the addition of the multiple multipath signal, it is equivalent to a multipath signal whose reflection angle is within the range of negative half-power beamwidth to zero. Then, the rationality of the proposed hypothesis is verified by analysis and simulation experiments.
Based on the multipath equivalent model, the array-received signal can be considered to be composed of a target direct wave with a positive angle and a multipath equivalent wave with a negative angle. Thus, the angle estimation results can be obtained by the sparse reconstruction method. However, most of the -norm-based and sparse Bayesian learning (SBL)-based methods do not use angle constraints due to the nature of the method. The OMP-based methods can use the number of sources to achieve the estimation, but they have no advantages in the condition of low SNR. Therefore, this paper transforms the super-resolution problem into a parameter estimation problem with a sparsity of two and a limit of positive and negative angles. Meanwhile, to avoid the estimation performance degradation caused by initial value selection when the optimization function is non-convex, this paper introduces the PSO strategy into low-angle target DOA estimation. The fitness function is constructed using the new model, and the target DOA estimation is achieved through collaboration and information sharing among particles. In addition, a Monte Carlo simulation and a real data analysis are performed to evaluate the performance of the proposed method. Compared with the traditional model and methods, the equivalent model proposed in this paper fully considers the influence of complex terrain on multipath signals, which is more consistent with the actual situation. Additionally, the proposed method does not require any prior information and does not need to mesh the estimation angle set, so it can be applied to different terrain environments.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. A brief introduction to the equivalent multipath model for low-angle target localization is given in
Section 2. In
Section 3, the proposed method is described in detail. The experimental results based on simulation data and measured data, as well as the comparison to some other methods, are discussed in
Section 4. Finally,
Section 5 concludes this paper.
2. Multiple Reflection Center Model
Consider a digital array radar system composed of
M isotropic sensors with uniform line array configuration. The interelement spacing is
d, and the wavelength is
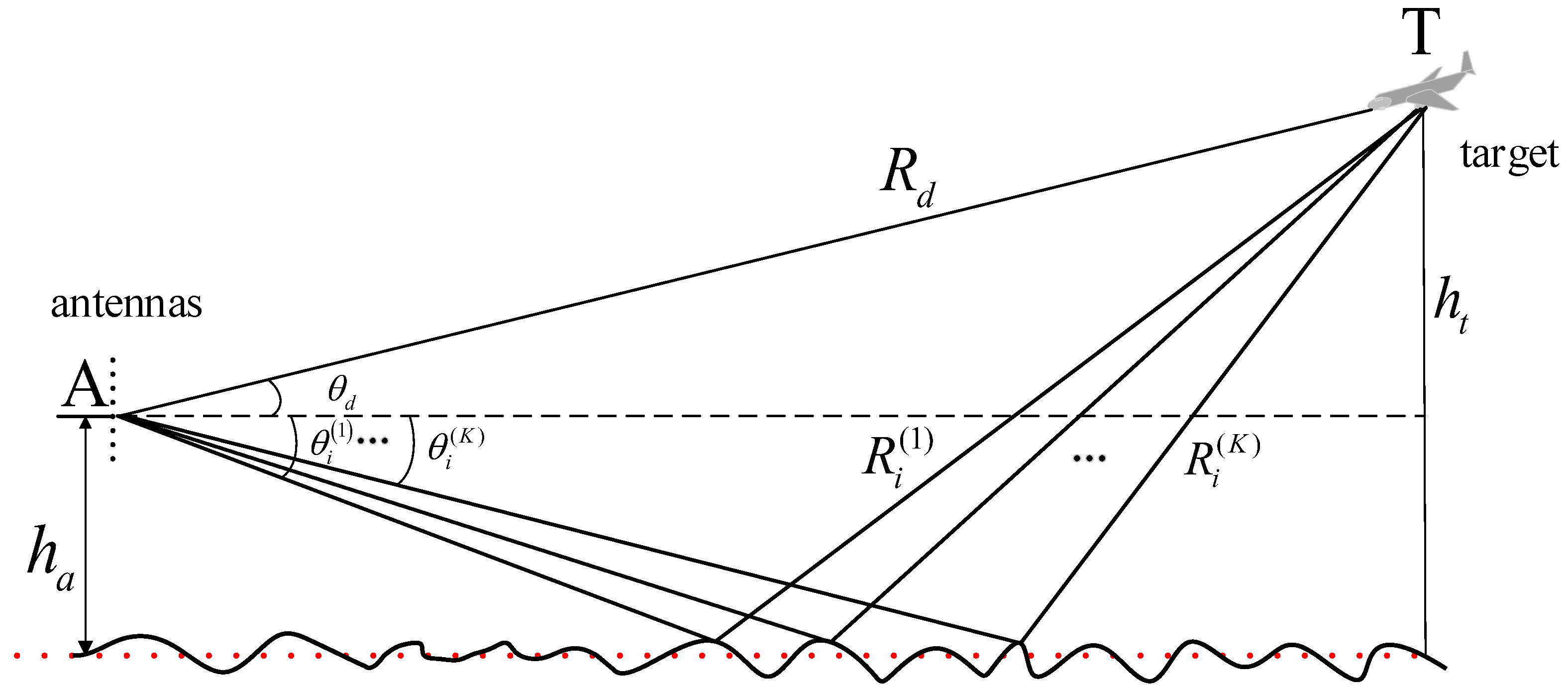
. A sample illustration of the multipath propagation geometry based on the reflecting center is illustrated in
Figure 1. The following assumptions are applied to the multipath propagation model: for an airborne target, it is located at such a distance from the receiving array that the impinging wave can be considered as far-field stationary narrowband plane wave. In the classical multipath model, the direct wave and the multipath wave are modeled as a pair of airspace approximate symmetrical coherent signals. However, in practice, especially when the terrain environment around the radar erection location is complex, the reflecting point is not in the center of reflecting region, but is distributed in the Fresnel region. In this case, the radar-received signal contains multiple multipaths with different paths. In addition, due to different reflection media, the reflecting surface has an unknown modulation effect on the amplitude and phase of the multipath signal. As shown in
Figure 1, the multipath signal is modeled by a set of coherent models with an unknown number and reflection angle, and the dotted line represents the horizontal plane. Assume that the angle above the horizon is positive and the angle below the horizon is negative. The array-received echo consists of a direct signal and
K multipath signals. There is a direct path between the target T and the radar A with elevation
, and the
kth incident angle is
, where
,
, and
donate the propagation paths of the direct and the
kth multipath signal, respectively. The path difference of the direct and the multipath signal can be calculated by
;
and
are the height of the array antenna center and the target, respectively.
2.1. Received Signal Model
Suppose the emitted signal
is a narrow-band signal, which is expressed as
where
is the baseband signal;
and
are the carrier frequency and the initial phase, respectively. The target is located at such a distance that the arriving waves can be considered as being planar. In complex terrain, due to different reflection media at each reflecting point on the ground, the reflection coefficients of multipath signals are not the same, so the output of the sensor can be expressed as
where
is the target reflection coefficient;
is the multipath reflection coefficient;
is the additive Gaussian white noise;
and
are the time delays of the direct path and the
kth multipath for the
mth sensor, respectively. When the reference element is determined,
and
can be further expressed as
where
is the time delay from the target to the referenced sensor;
is the time delay difference between the direct path and the
kth multipath;
and
are the relative delays between the
mth sensor and the referenced sensor, respectively. Since the received waveform is narrowband, the time delay within the terms of the baseband signal in Equation (
2) can be ignored. Thus, the following representation is obtained:
Using Equations (
3) and (
4), Equation (
2) can be rewritten as
where
, and
represents the multipath attenuation coefficient, which includes the specular reflection coefficient and the time delay difference between the direct path and the
kth multipath;
is defined as the ratio of the electric field phasor of the image signal to that of the target signal, and the detailed explanation of
can be found in [
30,
31]. Ignoring the influence of propagation delay from the target to the reference sensor on signal envelope, and after modulation, target detection, and target date extraction, the received signal can be expressed as
where
is the output signal of the array at time
t;
is a multipath vector-matrix composed of various multipath steering vectors;
and
are the steering vectors of the target direction, and they can be written as
where
represents the multipath attenuation coefficient matrix; and
represents the noise vector matrix.
2.2. Signal Equivalent Model Analysis
The sparse reconstruction methods [
26,
27] have good estimation performance under the ideal smooth reflecting surface of the single reflection model. This is because the array-received signals contain only the target direct wave and a multipath reflection wave signal, and the geometric relations between the direct wave from target and multipath reflection wave signal can be used. In this case, the sparse construction method only needs twofold super-resolution within the beam range. However, in a complex terrain environment, the reflection points of the multipaths are randomly distributed in the reflection plane, and there is more than one multipath. Assuming that the number of multipaths is
K, the algorithm needs
times super-resolution performance to achieve accurate estimation, which makes the existing method difficult to implement. This is because the sparse reconstruction technology aims to achieve the minimum overall fitting error between the incident signal and the reconstructed signal output, but this does not mean that each signal component of the incident signal can be reconstructed accurately. Especially, the multipaths are adjacent coherent signals with strong coherence in spatial domain, and after sparse reconstruction, there will be a greater difference between the overall fitting error and the accurate recovery of each component of the signal.
To solve the above problem, this paper starts with the signal model. In both the ideal reflecting model and the multiple reflecting center model of complex terrain, the direct wave from the target is generally considered to be within the range of the positive beam angle, while the multipath signal is within the range of the negative beam angle. According to Equation (
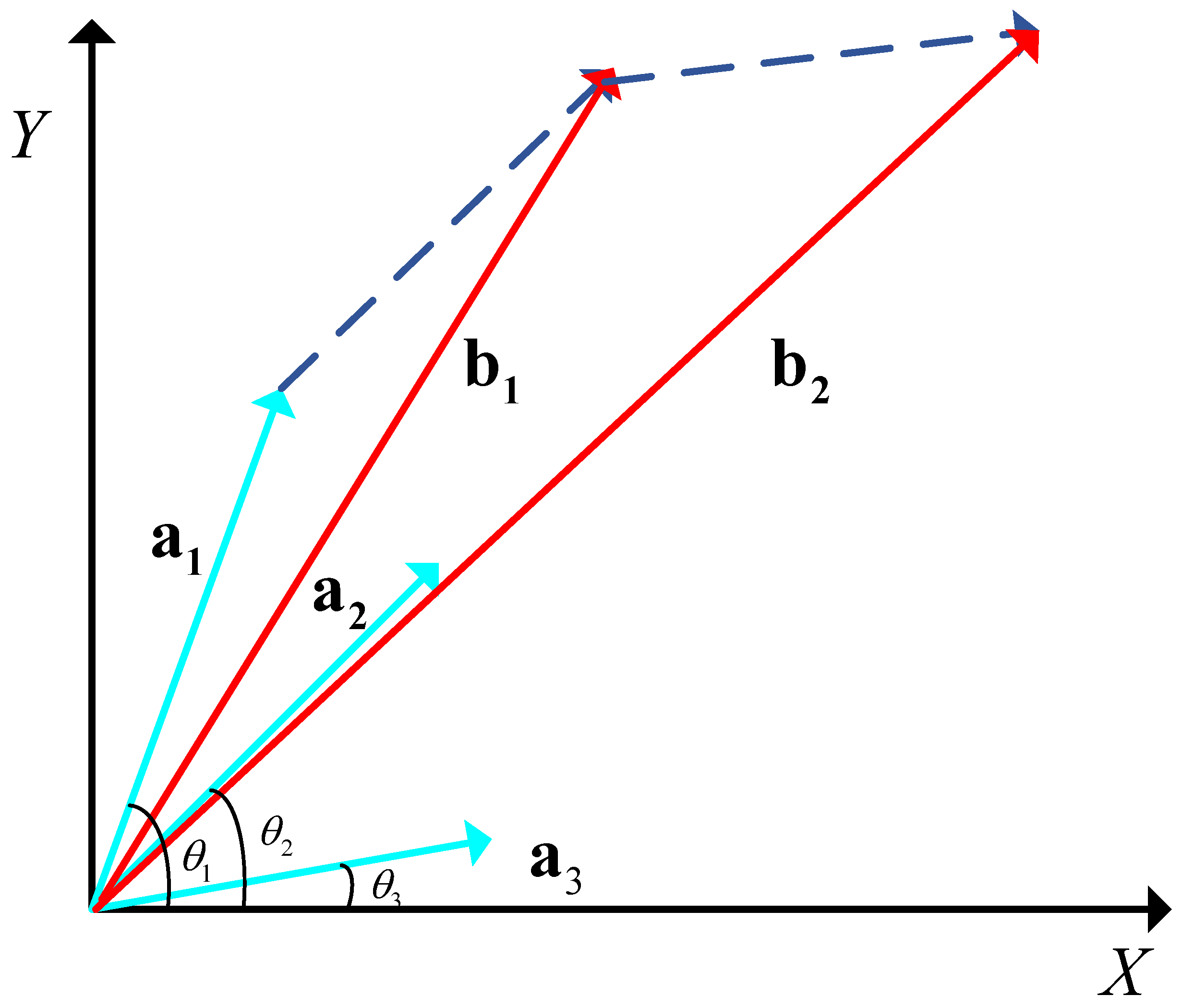
2), the received multipath signal can be represented as the sum of multiple multipath signals. Then, by taking a certain array element as a reference point, each multipath signal can be regarded as a signal vector with different sizes and angles under a narrowband condition. Suppose that the array element received three multipath vectors from different directions, as shown in
Figure 2,
represent multipath vectors with incident angles of
, and
, respectively
According to the triangle rule, then the resultant vectors
satisfy
Meanwhile, the incident angle
corresponding to the resultant vector
satisfies
where
, and
, where
represents half-power beamwidth.
To sum up, the incident angle of the resultant signal incident angle must lie between the negative half-power beamwidth and zero. Thus, this paper proposes an equivalent multipath model hypothesis based on narrowband signals, i.e., the sum of different multipath signal vectors can be equivalent to a multipath signal with an incident angle between the negative half-power beamwidth and zero. The detailed reasoning and experimental verification will be given in the following part.
First, let
represent possible multipath incident angles, and they are divided into
N equal parts to obtain
. Then, the steering vector matrix composed of the steering vectors corresponding to each angle can be represented as
. According to Equation (
2), the vector sum of
K multipath signals received by the array can be expressed as
where
represents the attenuation coefficient corresponding to each angle in a complete set of angles. When
, the value of the element corresponding to
is the attenuation coefficient, and the value of other elements in
is zero.
To find an equivalent multipath closest to the actual received signal, the constraint condition on the number of multipaths is added, and the solution to the equivalent multipath problem can be transformed into the optimization problem of Equation (
12):
Since the limit of the number of multipaths is set to one, the least square method can be adopted to solve the attenuation coefficient corresponding to each angle value. The attenuation coefficient corresponding to the angle can be expressed as
To verify the equivalent performance, the relative error of the equivalent multipath signal and the actual received multipath signal can be used to measure the equivalent effect. The relative error can be defined as
The smaller the relative error, the more consistent the equivalent multipath with the actual multipath synthesis result, and the better the equivalent performance. Let us define the minimum relative errors as
, and the ordinal number corresponding to the
u as
l. Generally, when
, it can be considered that the equivalent signal is approximate to the original one. The value of incident angle and the corresponding attenuation coefficient of the equivalent multipath can be determined by Equations (
13) and (
14). Then, this paper defines the equivalent multipath incident angle as
, and the attenuation coefficient as
. Thus, the array-received multipath signal can be approximated to
To verify the rationality of the equivalent model, experiments are conducted in different terrain environments. Due to the influence of terrain factors, the amplitude and phase of multipath signals are unknown modulated, and the different multipaths have different attenuation coefficients. Therefore, the attenuation coefficient is expressed in a complex form:
where
and
represent the attenuation coefficient amplitude and phase perturbation parameter, respectively. The perturbation coefficient
is defined, and the value of the perturbation coefficient reflects the complexity of the position. It is assumed that
and
are subjected to uniform distribution:
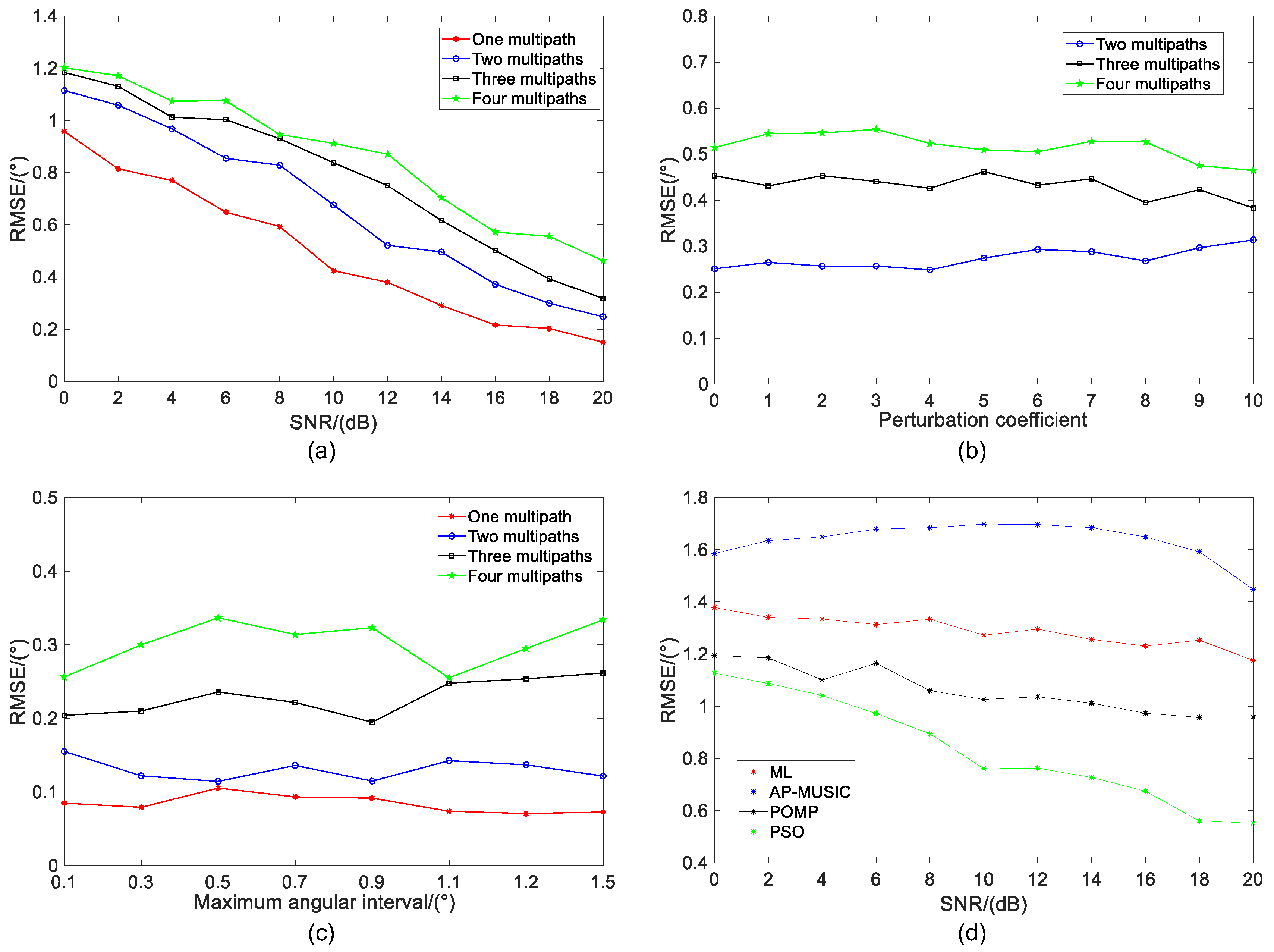
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the equivalent model, several groups of simulation experiments were set up according to the number of multipaths, the angular interval between the multipaths, and the perturbation parameter. In the simulation experiments of this section, the array parameters are kept consistent. The array is composed of 16 half-wavelength arrays of the same properties, the center frequency is 300 MHz, the wavelength is 1 m, and the number of multipaths is set to 2–4. This is because when four multipaths are used, five times the super-resolution performance is required to achieve accurate estimation, and existing methods are already difficult to complete. Therefore, experiments with four multipaths are enough to demonstrate the superiority of the model proposed in this paper.
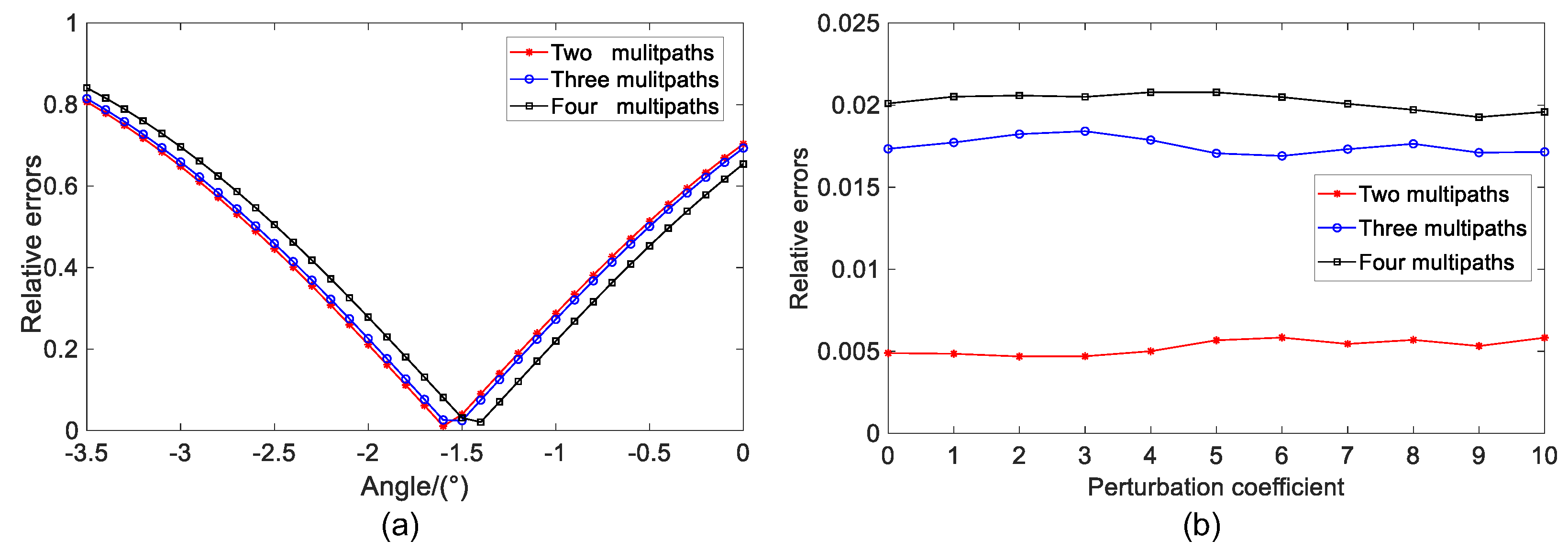
Firstly, the terrain environment with relatively flat plane is considered. In this case, multipath reflection angle is near the mirror reflection angle of the direct wave. Assume that the incident angle of the direct wave is
, and the multipath reflection angle is randomly distributed within
∼
. According to different numbers of multipaths,
Figure 3a illustrates the equivalent multipath relative error results of different angles. In this case, the corresponding incident angles of the four multipaths are
,
,
, and
. According to the corresponding sequence, the optimal angles of two, three, and four multipaths are
,
, and
. Although the relative error of the equivalent multipath corresponding to the optimal angle increases with the increase of multipath number, the relative error values are small values and close to 0, indicating that the equivalent result is basically the same as that of the actual multipath signal.
When the scattering plane is rough, the influence of the perturbation coefficient should be considered.
Figure 3b shows the relative error results of the equivalent multipath under different values of the perturbation coefficient
. Meanwhile, Monte Carlo experiments are performed 500 times for each perturbation coefficient. The experimental results show that the relative error of the two multipaths is basically 0. As the number of multipaths increase, the relative error value becomes larger, but it is still a small value close to 0. For a fixed number of multipaths, the relative error values show a relatively gentle trend with the increase of the perturbation coefficient. It can be considered that when the multiple multipath reflection angles are in a relatively small range, the perturbation coefficient has little influence on the equivalent performance of the multipaths.
The above experimental analysis results indicate the effectiveness of the equivalent model of multipath reflection angle in a relatively small range. However, in a complex terrain environment, the unknown separation effect of the reflection area on signals is more obvious, and the multipath reflection angle does not meet the above experimental conditions at all. Therefore, to investigate the influence of different multipath angle ranges on the equivalent results, this paper firstly defines the multipath incident angle range as , and the maximum multipath angle difference is . Assume that the incident angle and the mirror angle of the direct wave are, respectively, and . As for the center point of the multipath angle range, we have and , and the maximum value of can be set according to the beamwidth.
Figure 4a shows the relative error results of the equivalent model after 500 times Monte Carlo experiments with different angle differences when the perturbation coefficient is not added. It can be seen that the relative error increases with the increase of the maximum angle difference of the multipath, but the relative error is basically the same after the multipath synthesis with different numbers. Specifically, when the maximum angle difference is
, the relative error value is about 0.02. Although the relative error value increases significantly compared with that at a small angle difference, it is far less than 0.1. This indicates that under the ideal condition, even if the angle difference between multipaths is large, a good equivalent performance can still be achieved. Meanwhile, in order to illustrate the influence of the perturbation coefficient on the equivalent model, experiments are conducted under the condition of the maximum multipath angular difference
. It can be seen from
Figure 4b that as the number of multipaths increases, the relative error of the equivalent multipath increases. Additionally, the relative error of the multipath equivalent results shows a gentle variation with the increase of the perturbation coefficient, i.e., the perturbation coefficient has little effect on the equivalent model. This result is consistent with the result obtained under the ideal condition. Although the relative error value of the equivalent multipath increases with the increase of the number of multipaths, it is still small.
3. Proposed Method
In the above section, the deficiency of the sparse reconstruction method under the condition of multiple reflection centers is analyzed from the signal model, and an equivalent model of multiple reflection centers is proposed. This section analyzes from the point of view of algorithm, and seeks an estimation method suitable for multiple reflection centers in complex terrain.
It can be seen from the equivalent model that the direct wave and the equivalent multipath are the signals with positive and negative angles, respectively, and this can be considered as a set of constraints on the direct wave and the multipath wave. Although the sparse reconstruction methods have a good estimation accuracy under the single reflection model, there are several problems under the equivalent model:
Although the SBL-based methods can achieve high-precision estimation, the angle prior information cannot be used. The OMP-based methods use the prior information; due to the insufficient resolution performance of the algorithm, the accuracy is poor under a small direct wave and multipath wave interval angle and a low SNR.
The sparse reconstruction methods require angle division for the whole beam range. The estimation accuracy cannot be guaranteed when the angle division interval is large, and the intensive mesh division increases the computational overhead.
To solve the above problems, based on the equivalent model, this paper transforms the super-resolution problem into a parameter estimation problem with a sparsity of two and a limitation of positive and negative angles. Meanwhile, in order to avoid the estimation performance degradation caused by initial value selection when the optimization function is non-convex. This paper proposes a DOA estimation method for low-elevation targets based on the PSO algorithm.
The PSO algorithm regards the solution of the optimization problem as an individual (called particle) without weight and volume in the search space [
32,
33,
34,
35]. It uses fitness of the particle to measure the quality of the optimization solution, and finds the optimal solution through continuous iterations. The PSO algorithm does not need to mesh the angle set, and the estimation result is a value in the continuous angle space. The algorithm does not require scene prior information and has a fast convergence speed. Therefore, the application of the PSO algorithm has good estimation performance, especially in the complex environment without prior information.
The algorithm proposed in this paper is mainly composed of three parts: Firstly, the particle fitness function is determined by the signal model, and the optimal particle position is obtained by loop iteration. Secondly, to prevent the solution process from falling into local extreme values, a particle mutation strategy is used. Finally, the target angle information is acquired according to the global optimal position.
By using the equivalent model introduced in the previous section, multiple multipaths are equivalent to one multipath. Based on this, the array-received signal can be expressed as
According to the PSO algorithm, a group of random particles is initialized to represent the initial solution. Both the direct wave and the equivalent multipath have three unknown parameters, i.e., amplitude, phase of the attenuation coefficient, and incident angle, so each particle has six parameters, corresponding to a six-dimensional search space.
Suppose that the particle swarm consists of
N particles, and each particle has speed and position attributes, which represent the speed and direction of the particle in the search space, respectively. Defining
as the position vector of the
ith particle and
as the speed vector of the
ith particle, the expressions of
and
are as follows:
where
, respectively, represent position information of the attenuation coefficient amplitude, phase, and incident angle of the direct wave,
;
represent the attenuation coefficient amplitude, phase, and incident angle of equivalent multipath, respectively. Similarly, the first three and the last three terms of velocity vector represent the velocity information of the direct wave parameters and the equivalent multipath, respectively.
According to the signal model, the particle fitness function is defined as follows:
where
,
are steering vectors formed by the direct wave and the equivalent multipath incident angle, respectively. The smaller the particle fitness is, the closer the particle is to the array-received signal. The target parameter information can be obtained by finding the particle corresponding to the minimum fitness. Therefore, the process of finding the optimal particle can be transformed into the optimization problem as follows:
The constraint condition of each parameter is to prevent particles from flying out of the search space, so the particle position is set within a certain range.
According to the idea of PSO algorithm, the optimization solution is realized through loop iteration. Meanwhile, each particle continuously updates its position and velocity information in the iteration. Two parameters are introduced in the updating process: one is the optimal value found by the ith particle, and the other is the global optimal value found by the entire particle swarm. Define as the optimal position of the ith particle during the k iterations. If the fitness value of the current particle in the k iterations is less than the corresponding value at the optimal position of the particle, then the optimal position of the particle is updated. Define as the global optimal solution position of the ith iteration. The particle with the smallest fitness in k iterations of the population is found. If the fitness value of the particle is less than the corresponding value at the global optimal position in the iterations, then the global optimal position is updated.
Once the individual and global extremes are found, each particle updates its velocity and position as follows:
where
are a random numbers within
;
is the individual learning factor of particles, and
is the particle social learning factor. Usually, we set
;
w is the inertia weight. To accelerate the convergence of the algorithm,
w can be set to a dynamically adjusted form according to the number of iterations:
where
is the maximum weighting coefficient, and
is the minimum weighting coefficient. In the early stage of the search, a large value of
w is helpful for the particle search in a large space. As the number of iterations increases, the population will concentrate in a certain area. At this time, a smaller value of
w is used to enhance the local optimization ability of the particles [
17].
In addition, the selection of velocity parameters also plays an important role in particle optimization. If the velocity is too large, the particle will easily fly over the optimal position; if the velocity is too small, the particle will easily fail into the local optimum. Generally, the amplitude speed is limited to the range of , the phase speed is limited to the range of , and the angular speed is limited to the range of .
When the size of the particle swarm is small, the PSO algorithm is prone to premature convergence in the iterative process, but increasing the size of the particle swarm will affect the speed of the algorithm. To achieve a balance between convergence and speed, a mutation strategy is introduced in [
36]. When the global optimal position information does not change significantly for a long time (such as ten iterations), the
n particles with the best fitness in the population are subjected to a mutation with a probability of
P. The specific implementation process is as follows. Firstly, define
as a random number in the range of
, where
, and then set the mutation probability
P. If
, the particle position is updated with (23), where
is a random variable subjected to Gauss (0,1) distribution.
After the above processing, the estimation value of the target incident angle
can be obtained by the optimal particle position information, and the estimation value of the target height
can be calculated by using the target incident angle. The height calculation method is discussed in [
18]. For the targets in a short distance, generally within a range of tens of kilometers, the height calculation of the target can be estimated by the following formula:
For long-distance targets greater than 100 kilometers, the influence of the curvature of the Earth needs to be considered. In this case, the target height can be estimated as follows:
where
is the equivalent radius of the Earth.
The computational complexity of the algorithm proposed in this paper is analyzed below. Suppose the size of the particle swarm is N, the number of iterations is K, the number of mutation particles is M, and the total number of mutations is T. The main computational complexity of this algorithm lies in the following aspects: the time complexity of speed and position update is , the time complexity of fitness update is , and the time complexity of mutation operation is . Therefore, according to the above analysis, the total time complexity of the algorithm is .