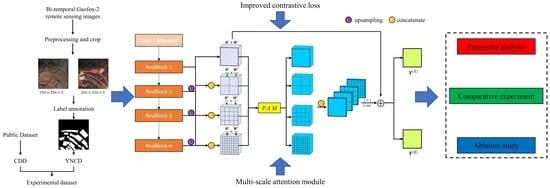
Change Detection for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on a Multi-Scale Attention Siamese Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
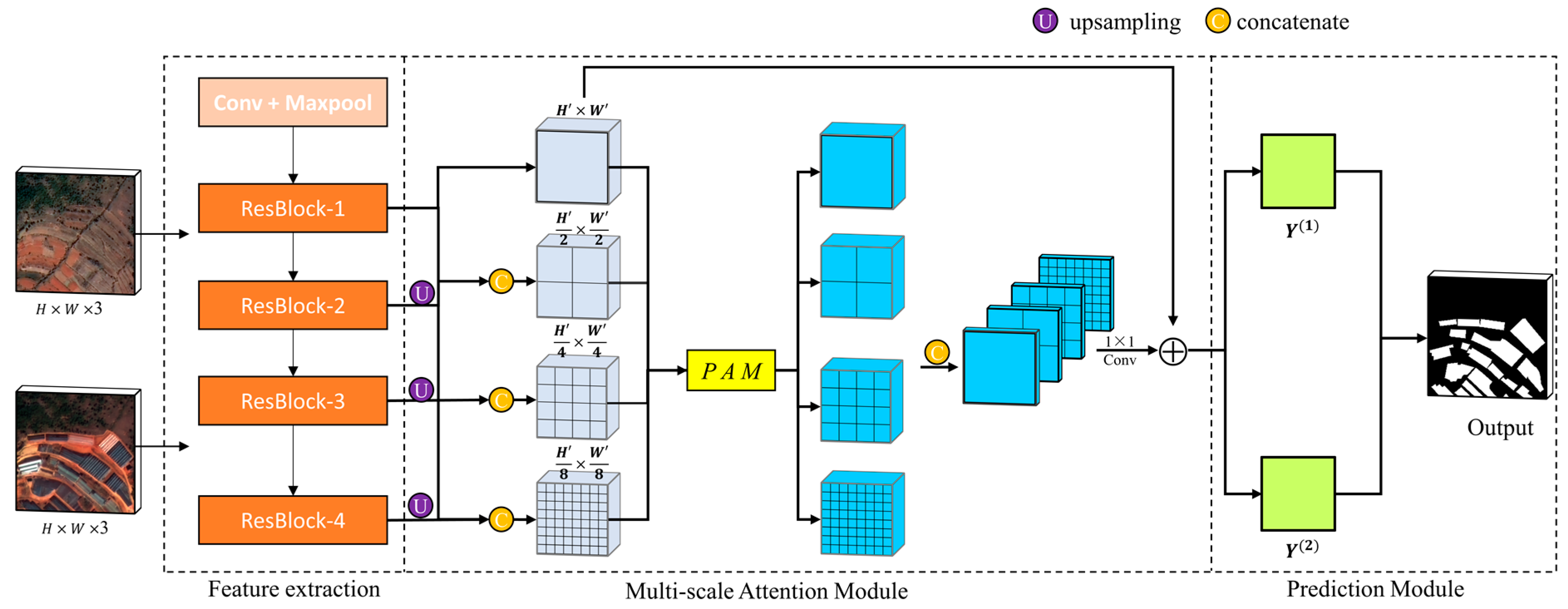
2.1. Change Detection Model
2.1.1. Siamese Network
2.1.2. Attention Mechanism
2.1.3. Multi-Scale Attention Siamese Network
2.2. Loss Function
3. Dataset
3.1. CDD
3.2. YNCD
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Parameters Setting
4.2. Comparative Experiment
4.2.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.2.2. Comparative Analysis of Results of MASNet with and without YNCD
4.2.3. Comparison Methods and Result Comparisons
- (1)
- STANet (Spatial-Temporal Attention Network) [24]: STANet utilizes a weight-sharing Siamese deep semantic segmentation network to generate two independent features and designs a spatial-temporal attention mechanism that captures the rich global spatial-temporal relationships between pixels in the whole spatial-temporal space and generates more discriminative features by calculating the attention weights of any two pixels at different times and locations. Finally, the metric learning method is used to calculate the distance between the two features and generate prediction maps.
- (2)
- MANet (Multi-scale Attention Net) [26]: The MANet network designs two modules: the Position-wise Attention Block (PAB) and the Multi-Scale Fusion Attention Block (MFAB). PAB analyzes the interdependencies of modeled features in the spatial dimension, thereby capturing the spatial dependencies between pixels in a global view. MFAB captures the channel dependencies between any feature maps through multi-scale semantic feature fusion.
- (3)
- PAN (Pyramid Attention Networks) [27]: PAN method combines an attention mechanism with a spatial pyramid, performs a spatial pyramid attention structure on high-level feature output, and combines global pooling to learn better feature representation. A Global Attention Upsample module is introduced on each decoder layer to serve as the global contextual information for the localization details of the low-level feature selection category.
- (4)
- FC-EF (Fully Convolutional Early Fusion) [15]: FC-EF is based on U-Net model and EF strategy. It concatenates the bi-temporal images before passing them through the network and uses the skip connection structure to fuse the low- and high-level features.
- (5)
- FC-Siam-Conc (Fully Convolutional Siamese-Concatenation) [15]: With a similar structure to the feature extraction module in MASNet, a Siamese network model combines three features from the two encoder branches and corresponding layers of the decoder. The graph performs skip connections to supplement the deeper, more abstract, and less localized information with low-level spatial detail information, resulting in more accurate boundary predictions in the output image.
- (6)
- FC-Siam-Diff (Fully Convolutional Siamese-Difference) [15]: The difference between FC-Siam-Diff and FC-Siam-Conc is that different temporal features are not processed in channel stacking, but the absolute difference of bi-temporal image features in the encoder is combined with the features of the decoder through skip connections in FC-Siam-Diff method.
4.3. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, G.F.; Li, Y.; Ding, W.L.; Yue, X.Y. Review of remote sensing image change detection. J. Image Graph. 2015, 20, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, D.; Cheng, A.; Wei, H.; Stanley, D. Change detection from remotely sensed images: From pixel-based to object-based approaches. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 80, 91–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, T. Unsupervised change detection in satellite images using principal component analysis and k -means clustering. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2009, 6, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.A.; Conradsen, K.; Simpson, J.J. Multivariate alteration detection (MAD) and MAF postprocessing in multispectral, bitemporal image data: New approaches to change detection studies. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 64, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Du, B.; Zhang, L.P. Slow feature analysis for change detection in multispectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 2858–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Niu, Z.; Chen, F.; Li, B.; Ban, Y. Object-based land cover change detection for cross-sensor images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 6723–6737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, M.; Blaschke, T.; Ma, X.; Tiede, D.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, D. Object-based change detection in urban areas: The effects of segmentation strategy, scale, and feature space on unsupervised methods. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Peng, D.F.; Huang, X. Object-based change detection for VHR images based on multiscale uncertainty analysis. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.S.; Li, G.J.; Cui, W.H. High-resolution remote sensing image change detection by statistical-object-based method. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2440–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.J.; He, X.F.; Wang, J. Coastal wetlands change detection combining pixel-based and object-based methods. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2020, 22, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.L.; Chen, X.W.; Li, F.; Yang, T. Change detection method for high resolution remote sensing images using deep learning. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2017, 46, 999–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Fu, K.; Yan, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Qiu, X. Change detection based on deep siamese convolutional network for optical aerial images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1845–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Vosselman, G.; Gerke, M.; Tuia, D.; Yang, M.Y. Change detection between multimodal remote sensing data using siamese CNN. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.09562. [Google Scholar]
- Hughes, L.H.; Schmitt, M.; Mou, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, X.X. Identifying corresponding patches in SAR and optical images with a pseudo-siamese CNN. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daudt, R.C.; Le Saux, B.; Boulch, A. Fully convolutional siamese networks for change detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Athens, Greece, 7–10 October 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 4063–4067. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yue, P.; Tapete, D.; Jiang, L.; Shangguan, B.; Huang, L.; Liu, G. A deeply supervised image fusion network for change detection in high resolution bi-temporal remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yuan, Z.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.; Huang, H.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H. DASNet: Dual attentive fully convolutional siamese networks for change detection in high-resolution satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 1194–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhao, W.F.; Wang, S. Multiscale context aggregation network for building change detection using high resolution remote sensing images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Li, K.; Shao, J.; Li, Z. SNUNet-CD: A densely connected siamese network for change detection of VHR images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaraju, K.S.; Sravya, N.; Lal, S.; Nalini, J.; Reddy, C.S.; Dell’Acqua, F. UCDnet: A deep learning model for urban change detection from bi-temporal multispectral sentinel-2 satellite images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Lu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Du, B.; Plaza, A. A Siamese Network Based U-Net for Change Detection in High Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2022, 15, 2357–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent models of visual attention. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1406.6247. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.J.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Shi, Z.W. A spatial-temporal attention-based method and a new dataset for remote sensing image change detection. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedev, M.A.; Vizilter, Y.V.; Vygolov, O.V.; Knyaz, V.A.; Rubis, A.Y. Change Detection in Remote Sensing Images Using Conditional Adversarial Networks. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 42, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.L.; Wang, G.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H. Ma-net: A multi-scale attention network for liver and tumor segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 179656–179665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.C.; Xiong, P.F.; An, J.; Wang, L. Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10180. [Google Scholar]









| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Image Pairs | 1540 |
| Total Changed Pixels | 8,000,699 |
| Total Unchanged Pixels | 92,924,741 |
| Image Size | 256 × 256 |
| Image Resolution | 1 m |
| Time Interval | 6 years |
| Type | RGB image |
| Datasets | OA | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDD | 90.32 | 34.61 | 19.49 | 24.94 |
| CDD + YNCD | 95.34 | 79.78 | 81.52 | 80.64 |
| Method | P | R | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FC-Siam-Conc | 64.94 | 53.78 | 58.84 |
| FC-Siam-Diff | 63.82 | 60.08 | 61.89 |
| FC-EF | 70.31 | 60.65 | 65.12 |
| PAN | 73.14 | 66.13 | 69.46 |
| MANet | 74.62 | 73.62 | 74.12 |
| STANet | 78.46 | 77.00 | 77.72 |
| MASNet | 79.78 | 81.52 | 80.64 |
| ICL | MSA | OA | P | R | F1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ① | ✓ | 94.25 | 70.46 | 74.03 | 72.20 | |
| ② | ✓ | 94.61 | 71.78 | 78.26 | 74.88 | |
| ③ | ✓ | ✓ | 95.34 | 79.78 | 81.52 | 80.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y. Change Detection for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on a Multi-Scale Attention Siamese Network. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143464
Li J, Zhu S, Gao Y, Zhang G, Xu Y. Change Detection for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on a Multi-Scale Attention Siamese Network. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(14):3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143464
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiankang, Shanyou Zhu, Yiyao Gao, Guixin Zhang, and Yongming Xu. 2022. "Change Detection for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on a Multi-Scale Attention Siamese Network" Remote Sensing 14, no. 14: 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143464
APA StyleLi, J., Zhu, S., Gao, Y., Zhang, G., & Xu, Y. (2022). Change Detection for High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on a Multi-Scale Attention Siamese Network. Remote Sensing, 14(14), 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14143464