Underwater Multispectral Laser Serial Imager for Spectral Differentiation of Macroalgal and Coral Substrates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
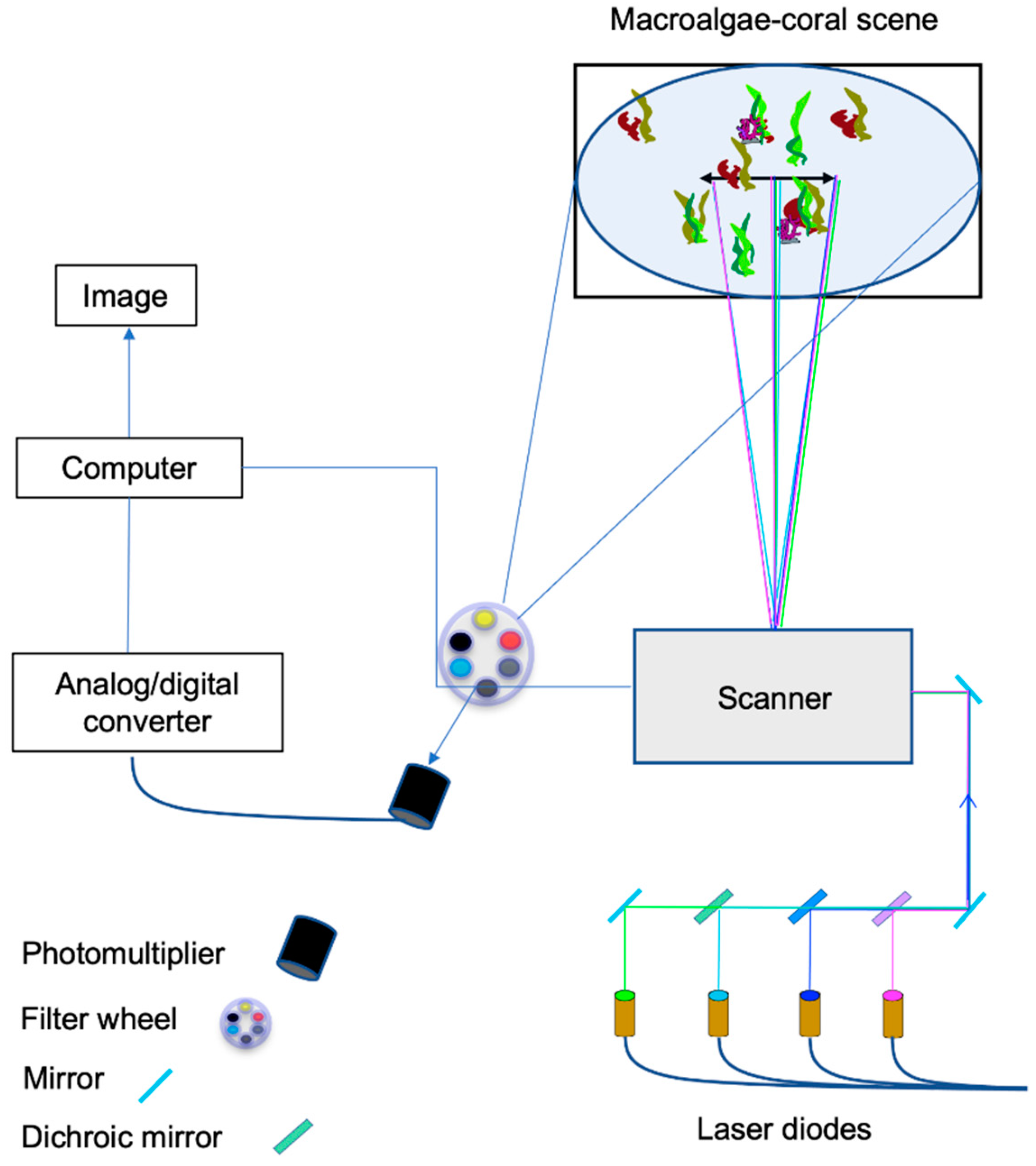
2.1. Laser Imaging Setup
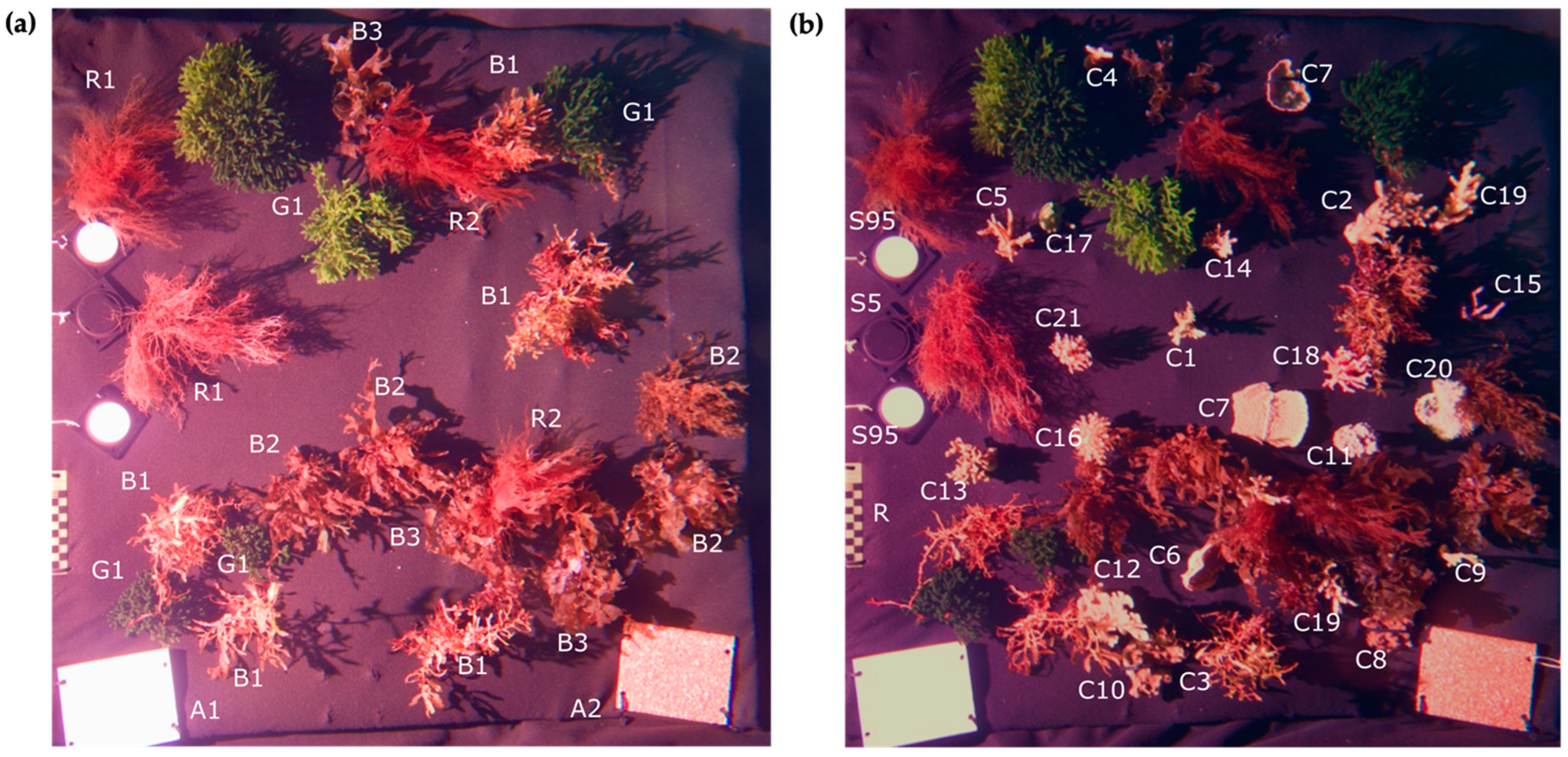
2.2. Imaging Environment
Experimental Saltwater Tank/Benthic Scene Recreation
2.3. Imager Spectral Characteristics
2.3.1. Contrast-Related Image Quality Metrics
2.3.2. Fluorescence-Related Imaging System Variance Measure
2.3.3. Reflectance and Practical Fluorescence Efficiency Estimation
2.4. Image Processing
3. Results
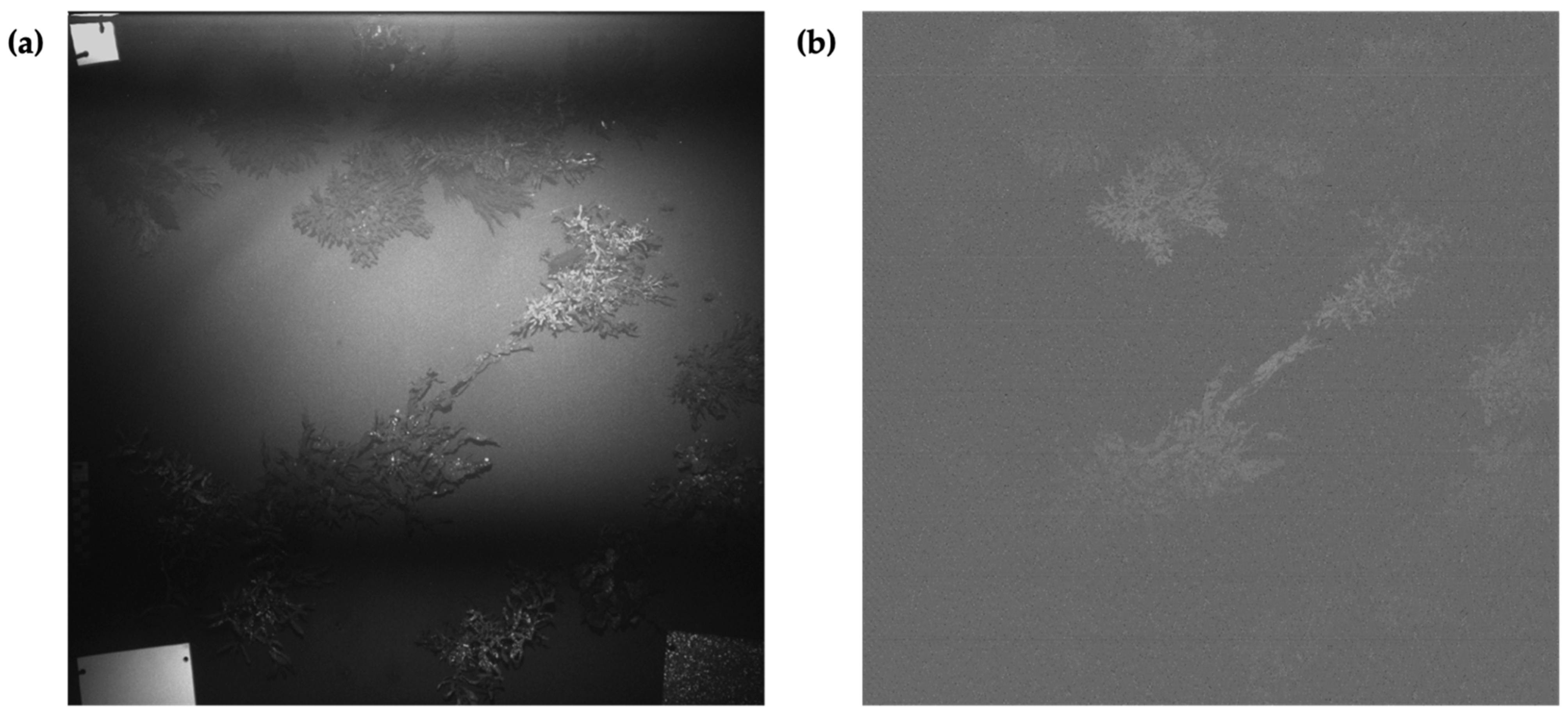
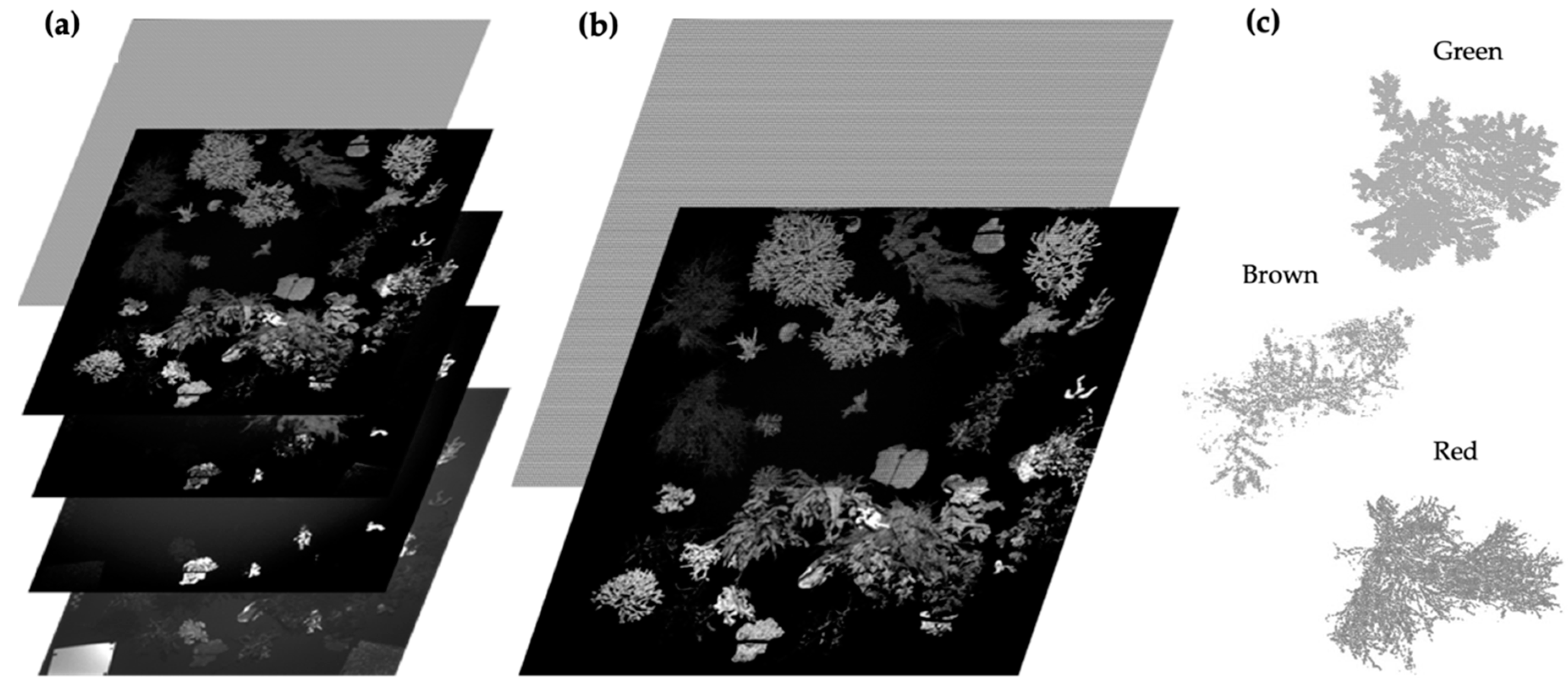
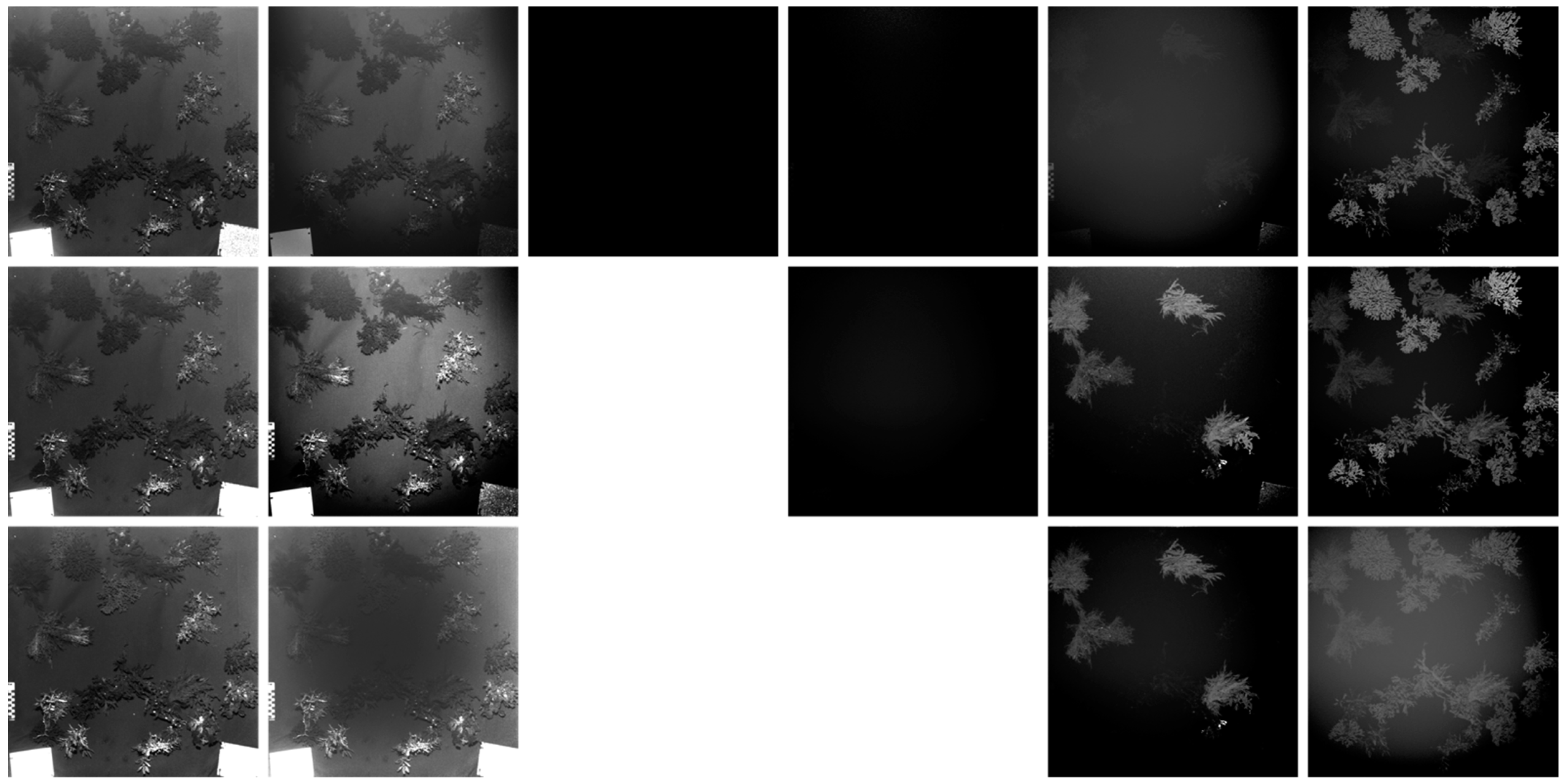
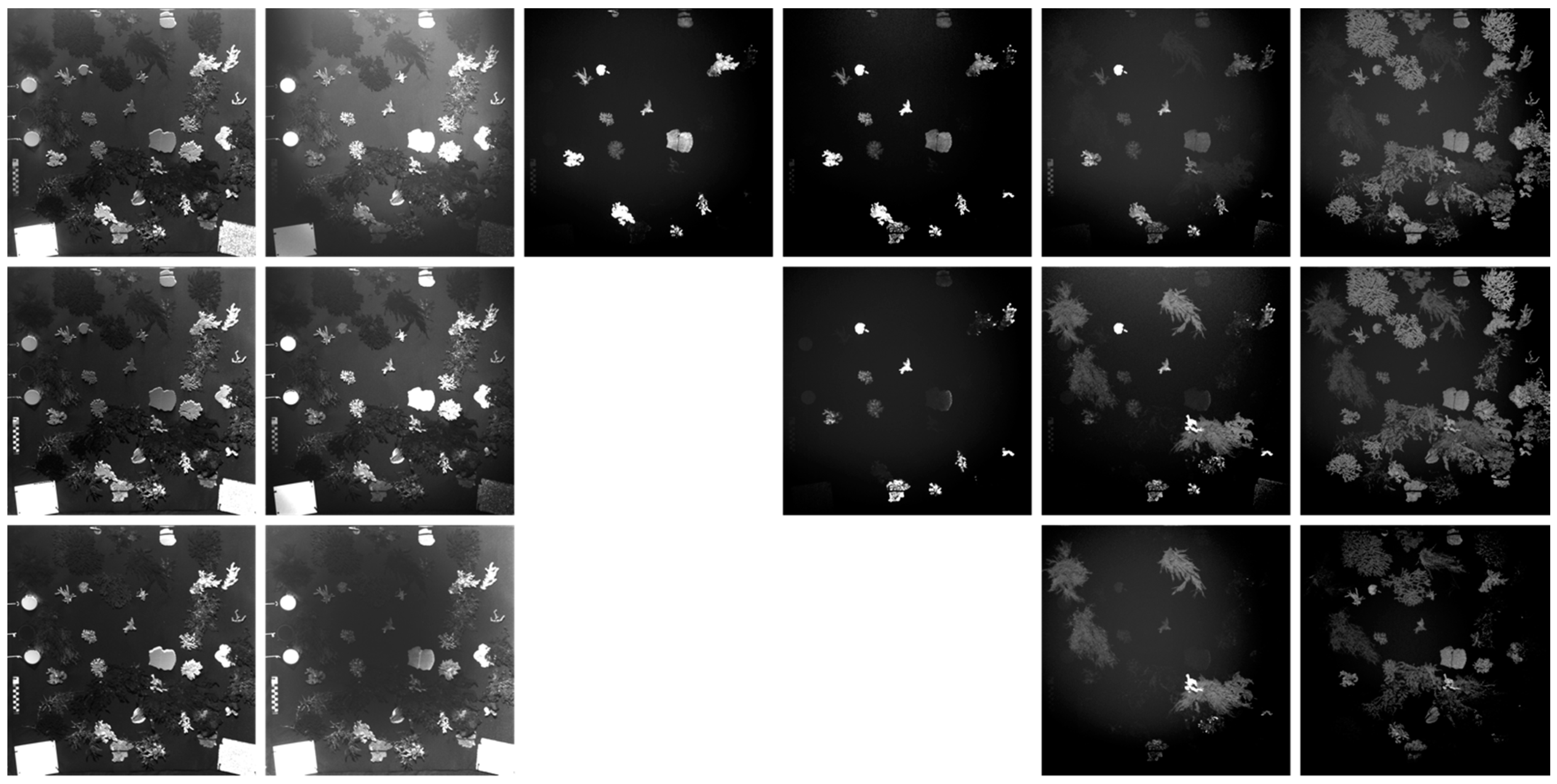
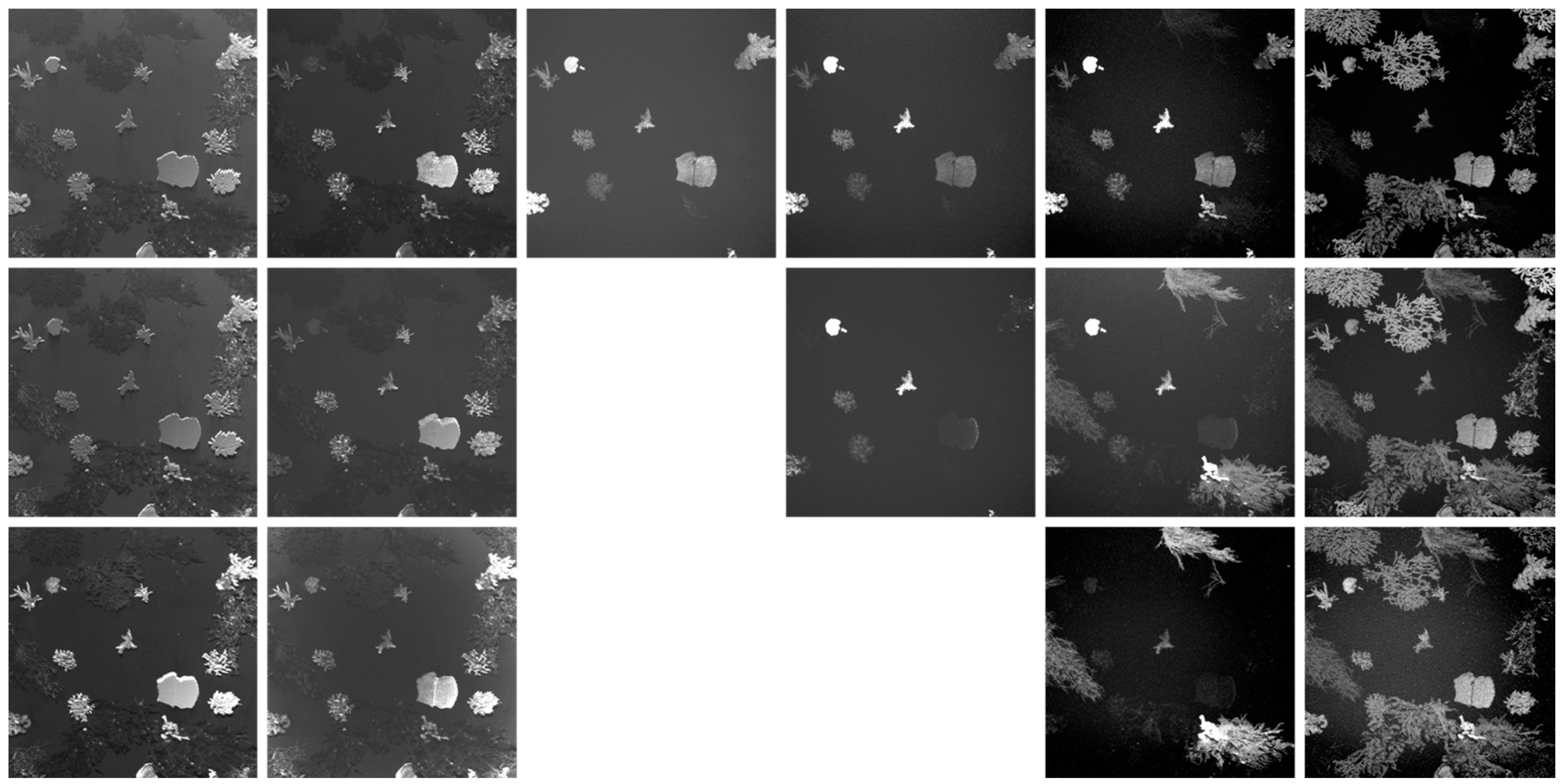
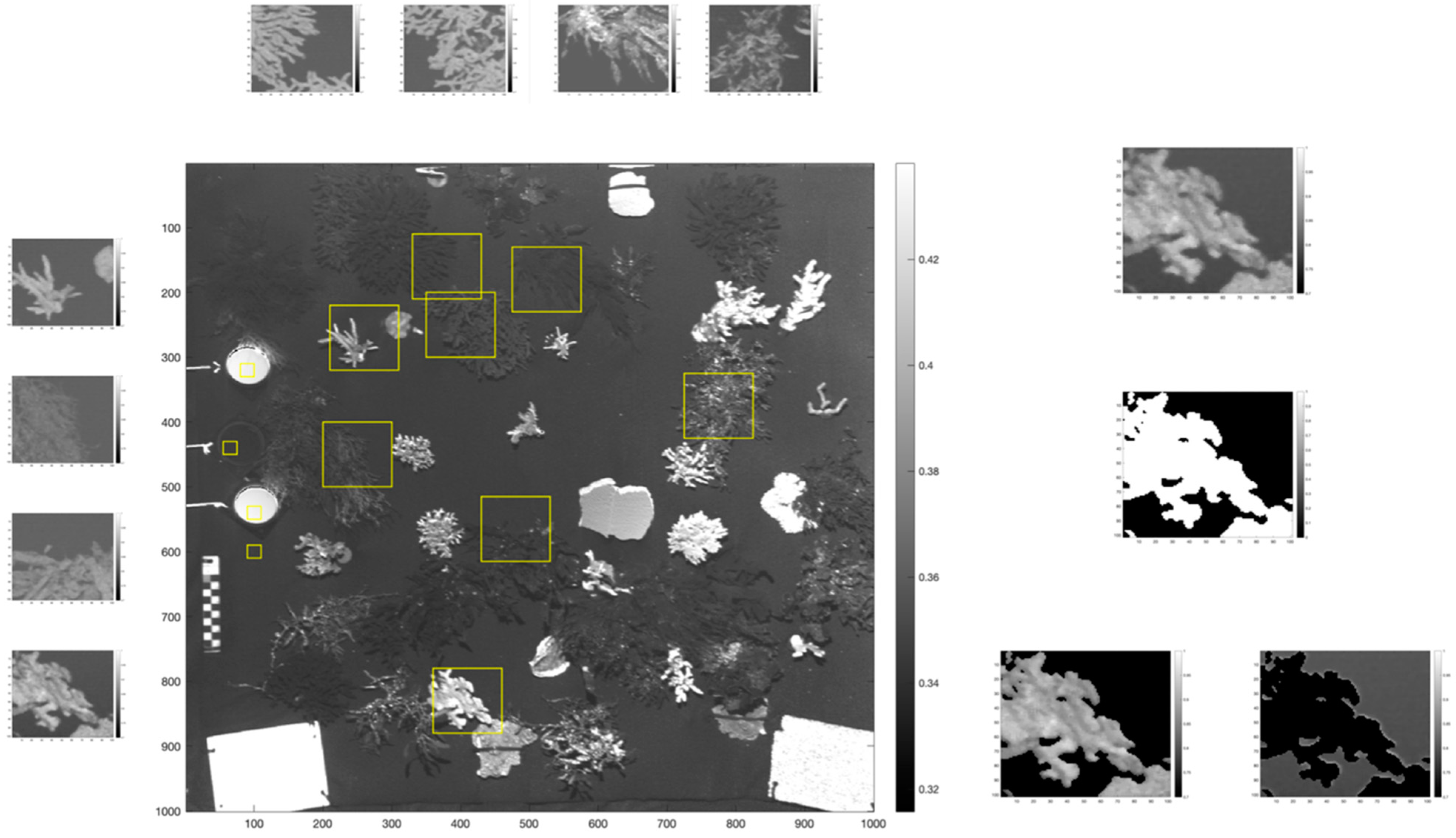
3.1. Image Normalization
3.1.1. Macroalgae Fluorescence Imaging Scenario
3.1.2. Macroalgae + Coral Fluorescence Imaging Scenario
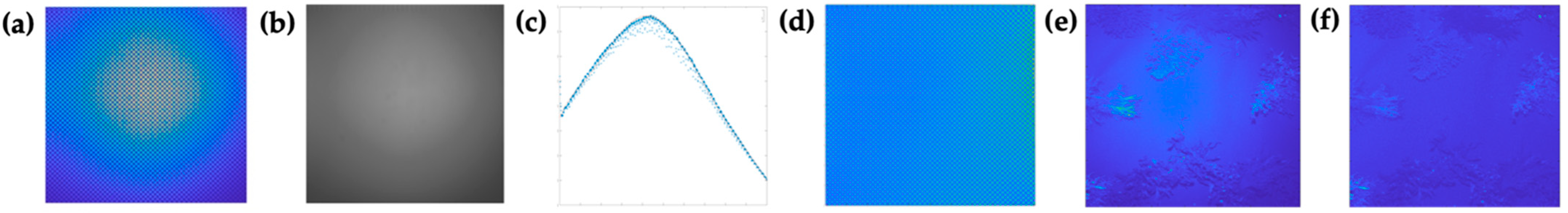
3.2. Illumination Falloff Correction
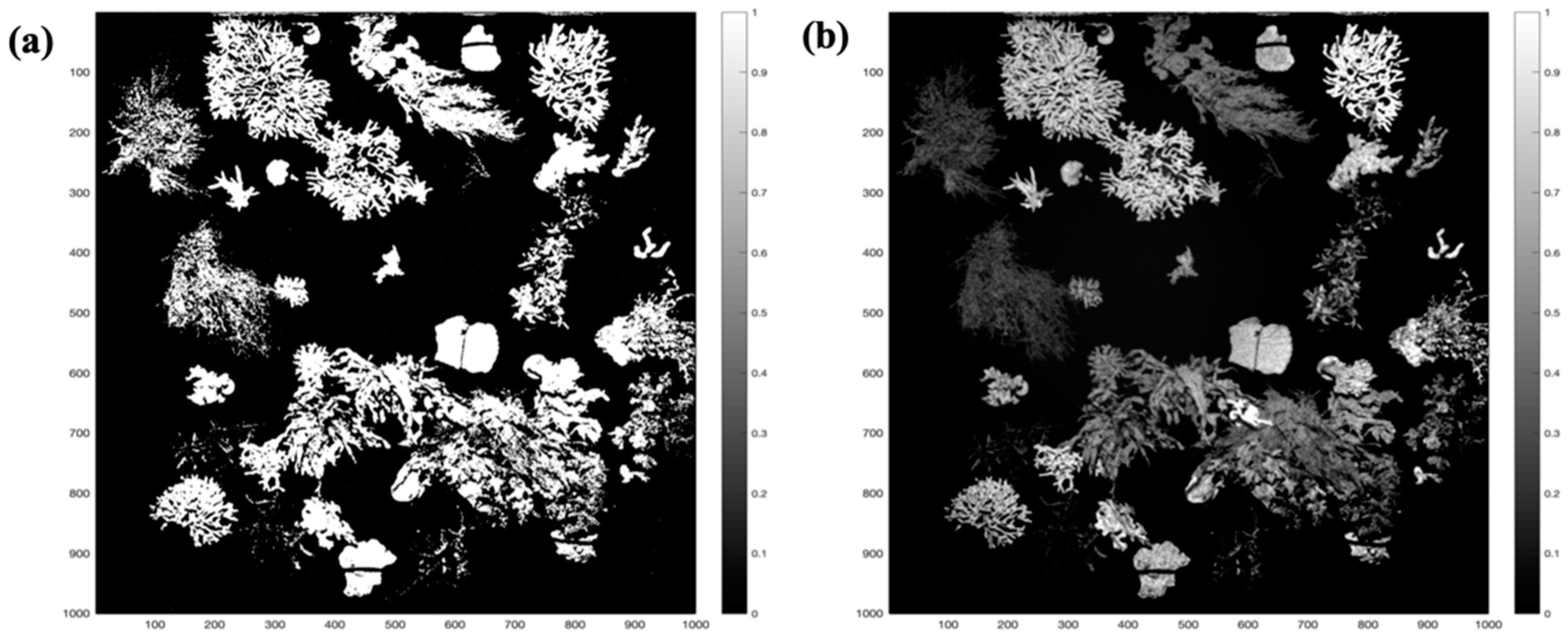
3.3. Fluorescence Intensity Thresholding for Pixel Segmentation
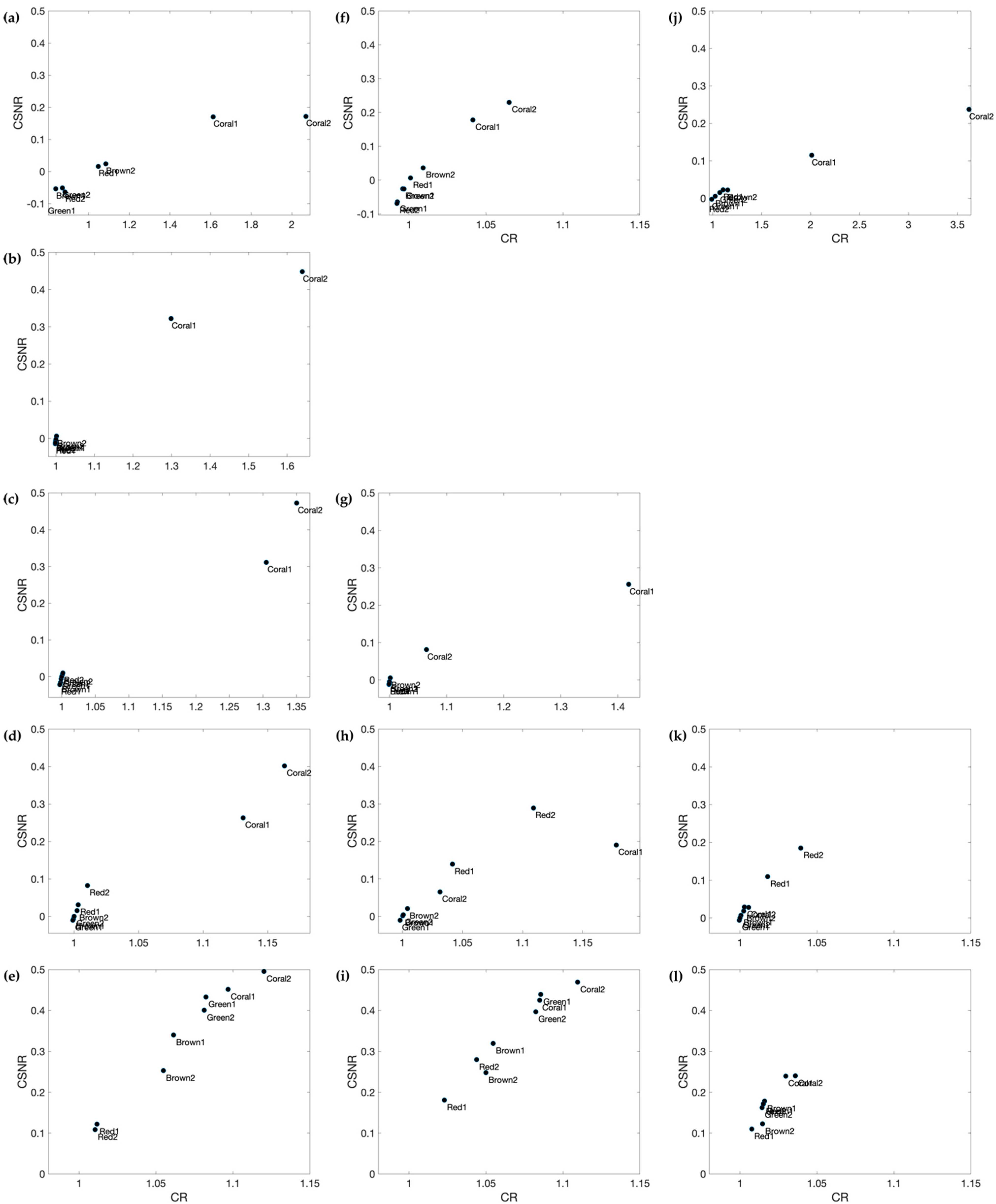
3.4. Contrast-Related Image Quality Metrics
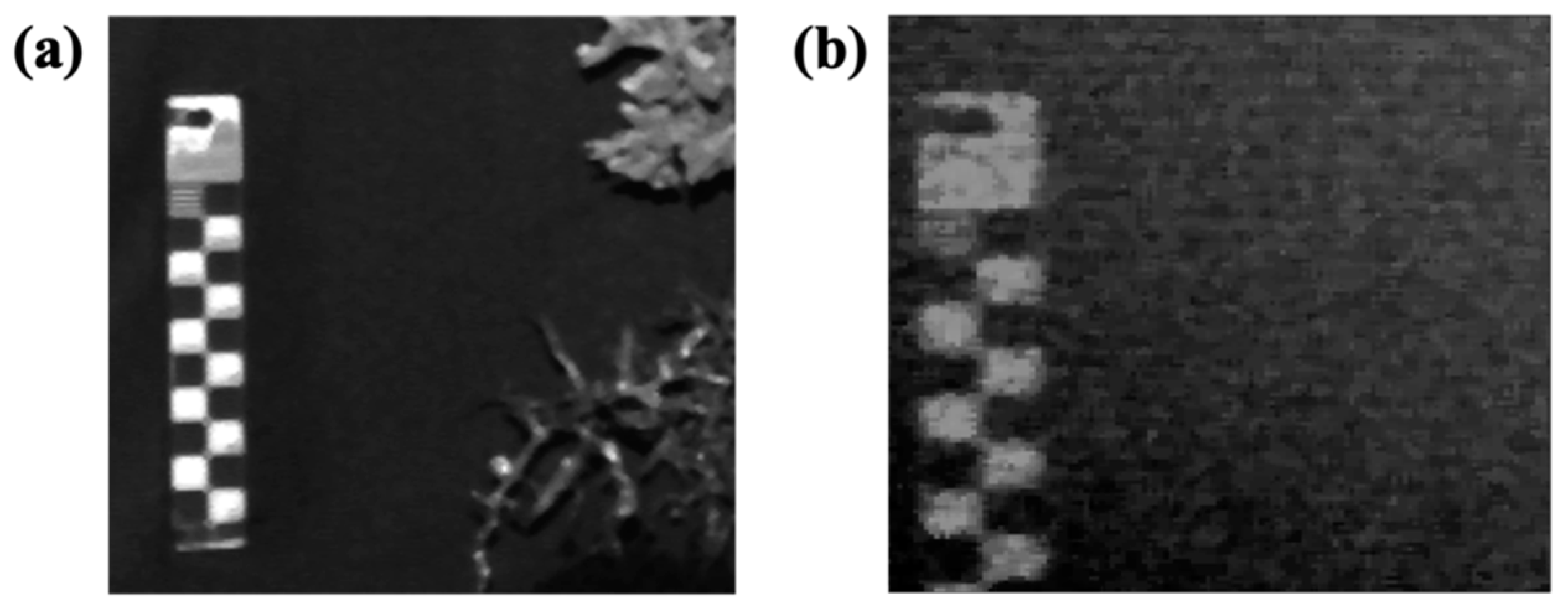
3.4.1. Resolution
3.4.2. Contrast Ratio (CR) and Contrast Signal-to-Noise-Ratio (CSNR)
3.5. Fluorescence-Related Imaging System Variance Measure
3.6. Irradiance on the Pixel-Photon Model for CW Line Scan
3.7. Reflectance and Practical Fluorescence Efficiency
4. Discussion
4.1. Generating Spectral Response with the Proposed Imager Design
4.2. Creating Radiometrically Correct Images for Spectral Analysis
4.3. Consideration for Wavelength-Dependent in-Water Differential Refraction Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Type | Genus | Species | Color Class | Known Distribution | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Macroalgae | Codium | sp. | Green | Eastern Florida Coast/Atlantic/Caribbean | |
| Sargassum | sp. | Brown | Eastern Florida Coast/Atlantic/Caribbean | ||
| Dictyota | sp. | Brown | Eastern Florida Coast/Atlantic/Caribbean | ||
| Padina | sp. | Brown | Eastern Florida Coast/Atlantic/Caribbean | ||
| Grateloupia | sp. | Red | Eastern Florida Coast/Atlantic/Caribbean | ||
| Halymenia | sp. | Red | Eastern Florida Coast/Atlantic/Caribbean | ||
| Type | Genus | Species | Structure | Shape | Known distribution |
| Coral | Acropora | austera | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea |
| cyatherea | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| nana | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| nasuta | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| nobilis | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| valida | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| Echinopora | lamellosa | Hard | Flat | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | |
| Montipora | capricornis | Hard | Flat | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | |
| confusa | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean | ||
| digitata | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| spongodes | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| Nephthea | sp | Soft | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean | |
| Pavona | decussatus | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean | |
| frondifera | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | ||
| Pinnigorgia | flava | Soft | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean | |
| Plexaura | flexuosa | Soft | Erect | Gulf of Mexico-Caribbean | |
| Pocilliopora | damicornis | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | |
| Psammocora | stellata | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | |
| Seriatopora | hystrix | Hard | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | |
| Stylophora | pistillata | Soft | Erect | Indian Ocean/Pacific Ocean/Red Sea | |
| Xenia | umbellata | Soft | Flat | Indian Ocean/Red Sea |
References
- Collin, A.; Planes, S. Enhancing Coral Health Detection Using Spectral Diversity Indices from Worldview-2 Imagery and Machine Learners. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 3244–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, E.J.; Atkinson, M.J.; Andréfouët, S. Spectral Reflectance of Coral Reef Bottom-Types Worldwide and Implications for Coral Reef Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.; Archambault, P.; Planes, S. Bridging Ridge-to-Reef Patches: Seamless Classification of the Coast Using Very High Resolution Satellite. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 3583–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagawa, T.; Mikami, A.; Aoki, M.N.; Komatsu, T. Mapping Seaweed Forests with IKONOS Image Based on Bottom Surface Reflectance. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of the Marine Environment II, Kyoto, Japan, 29 October–1 November 2012; Volume 8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, R.; Bell, S.; Meyer, C.; Baggett, L.; Zhao, Y. Mapping and Assessing Seagrass along the Western Coast of Florida Using Landsat TM and EO-1 ALI/Hyperion Imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 115, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Huang, Y. Seagrass Resource Assessment Using World View-2 Imagery in the Redfish Bay, Texas. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, H.M.; Chlus, A.; Russell, B. Remote Sensing of Environment Hyperspectral Discrimination of Fl Oating Mats of Seagrass Wrack and the Macroalgae Sargassum in Coastal Waters of Greater Florida Bay Using Airborne Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.; Long, B.; Archambault, P. Coastal Kelp Forest Habitat in the Baie Des Chaleurs, Gulf of St. Lawrence, Canada. In Seafloor Geomorphology as Benthic Habitat; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, J.D.; Costa, M.; Sharma, T. Remote Sensing of Shallow Coastal Benthic Substrates: In Situ Spectra and Mapping of Eelgrass (Zostera Marina) in the Gulf Islands National Park Reserve of Canada. Remote Sens. 2011, 3, 975–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, A.; Long, B.; Archambault, P. Merging Land-Marine Realms: Spatial Patterns of Seamless Coastal Habitats Using a Multispectral LiDAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 123, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossiter, T.; Furey, T.; McCarthy, T.; Stengel, D.B. UAV-Mounted Hyperspectral Mapping of Intertidal Macroalgae. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 242, 106789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossiter, T.; Furey, T.; McCarthy, T.; Stengel, D.B. Application of Multiplatform, Multispectral Remote Sensors for Mapping Intertidal Macroalgae: A Comparative Approach. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 30, 1595–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treibitz, T.; Neal, B.P.; Kline, D.I.; Beijbom, O.; Roberts, P.L.D.; Mitchell, B.G.; Kriegman, D. Wide Field-of-View Fluorescence Imaging of Coral Reefs. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, N.; Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.H.; Li, S. Satellite-Derived Bathymetry Using the ICESat-2 Lidar and Sentinel-2 Imagery Datasets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 250, 112047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennu, A.; Färber, P.; De’ath, G.; de Beer, D.; Fabricius, K.E. A Diver-Operated Hyperspectral Imaging and Topographic Surveying System for Automated Mapping of Benthic Habitats. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coles, B.W.; Radzelovage, W.; Jean-Laurant, P.; Reihani, K. Processing Techniques for Multi-Spectral Laser Line Scan Images. In Proceedings of the Oceans’98—Conference Proceedings, Nice, France, 28 September–1 October 1998; Volume 1–3, pp. 1766–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitter, D.N.; Gelbart, A. Laser-Induced Fluorescence Imaging of the Ocean Bottom. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, C.H.; Strand, M.P.; Lesser, M.P.; Crosby, M.P.; Coles, B.; Nevis, A.J. High Resolution Determination of Coral Reef Bottom Cover from Multispectral Fluorescence Laser Line Scan Imagery. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Strand, M. Fluorescence Imaging Laser Line Scan (FILLS) for Very Shallow Water Mine Countermeasures. In Proceedings of the An Ocean Odyssey. Conference Proceedings, Honolulu, HI, USA, 5–8 November 2001; Volume 1, pp. 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.; Zielinski, O.C.N.-G.C. Subsea Optics and Imaging; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2013; ISBN 9780857093417. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, C. Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gameiro, C.; Utkin, A.B.; Cartaxana, P. Characterisation of Estuarine Intertidal Macroalgae by Laser-Induced Fluorescence. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 167, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotta, J.; Remm, K.; Vahtmäe, E.; Kutser, T.; Orav-Kotta, H. In-Air Spectral Signatures of the Baltic Sea Macrophytes and Their Statistical Separability. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawada, D.G.; Mazel, C.H. Fluorescence-Based Classification of Caribbean Coral Reef Organisms and Substrates. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, C.H. Spectral Measurements of Fluorescence Emission in Caribbean Cnidarians. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 120, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, C.H.; Lesser, M.P.; Gorbunov, M.Y.; Barry, T.M.; Farrell, J.H.; Wyman, K.D.; Falkowski, P.G. Green-Fluorescent Proteins in Caribbean Corals. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.C.; Baker, K.S. Optical Properties of the Clearest Natural Waters (200–800 Nm). Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazel, C. Method for Determining the Contribution of Fluorescence to an Optical Signature, with Implications for Postulating a Visual Function. Front. Mar. Sci. 2017, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenfelt, P.; Cooper, J.M.; Hochstetter, A. Matrix-Masking to Balance Nonuniform Illumination in Microscopy. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 17279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, M.; Rehm, E.; Piché, M.; Archambault, P.; Département de biologie, Université Laval, Quebec, QC, G1V 0A6, Canada. Unpublished Data on Macroalgae Fluorescence. status (manuscript in preparation; to be submitted). 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, W.; Camps, A. Optical Imaging Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017; ISBN 9780128092545. [Google Scholar]
- Solonenko, M.G.; Mobley, C.D. Inherent Optical Properties of Jerlov Water Types. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppelt, N. Hyperspectral Classification Approaches for Intertidal Macroalgae Habitat Mapping: A Case Study in Heligoland. Opt. Eng. 2012, 51, 111703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao Rodríguez, Y.; Domínguez Gómez, J.A.; Sánchez-Carnero, N.; Rodríguez-Pérez, D. A Comparison of Spectral Macroalgae Taxa Separability Methods Using an Extensive Spectral Library. Algal Res. 2017, 26, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmedo-Masat, O.M.; Paula Raffo, M.; Rodríguez-Pérez, D.; Arijón, M.; Sánchez-Carnero, N. How Far Can We Classify Macroalgae Remotely? An Example Using a New Spectral Library of Species from the South West Atlantic (Argentine Patagonia). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, D.J.; Kiefer, D.A.; Soohoo, J.B.; Stuart McDermid, I. The Role of Reabsorption in the Spectral Distribution of Phytoplankton Fluorescence Emission. Deep. Sea Res. Part A Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1985, 32, 983–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, C.H. Coral Fluorescence Characteristics: Excitation/Emmission Spectra, Fluorescence Efficiences, and Contribution to Apparent Reflectance. Ocean. Opt. XIII 1997, 2963, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieleck, C.; Bousquet, B.; le Brun, G.; Cariou, J.; Lotrian, J. Laser Induced Fluorescence Imaging: Application to Groups of Macroalgae Identification. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 2561–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, M.; Rehm, E.; Dalgleish, F.R.; Piché, M.; Lambert-Girard, S.; Archambault, P. Characterizing Fluorescence and Reflectance Properties of Arctic Macroalgae as Future LiDAR Targets. In Proceedings of the Ocean Sensing and Monitoring X, Orlando, FL, USA, 25 May 2018; Hou, W., Arnone, R.A., Eds.; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Sasano, M.; Imasato, M.; Yamano, H.; Oguma, H. Development of a Regional Coral Observation Method by a Fluorescence Imaging LIDAR Installed in a Towable Buoy. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, E.; Dalgleish, F.; Huot, M.; Lagunas-Morales, J.; Lambert-Girard, S.; Matteoli, S.; Archambault, P.; Piché, M. Comparing Fluorescent and Differential Absorption LiDAR Techniques for Detecting Algal Biomass with Applications to Arctic Substrates. In Proceedings of the Ocean Sensing and Monitoring X, Orlando, FL, USA, 25 May 2018; SPIE: Washington, DC, USA, 2018; Volume 10631. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, F.; Gorbunov, M.Y.; Oliver, M.J.; Haskins, C.; Aragon, D.; Kohut, J.T.; Schofield, O. FIRe Glider: Mapping in Situ Chlorophyll Variable Fluorescence with Autonomous Underwater Gliders. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2020, 18, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameiro, C.; Cartaxana, P.; Utkin, A.B. Mapping of Algal Communities in Tagus Estuary Using Mobile LIF LIDAR Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference Laser Optics, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 30 June–4 July 2014; Volume 432, p. 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burggraaff, O.; Schmidt, N.; Zamorano, J.; Pauly, K.; Pascual, S.; Tapia, C.; Spyrakos, E.; Snik, F. Standardized Spectral and Radiometric Calibration of Consumer Cameras. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 19075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Quayle, B.; Lorenz, E.; Morelli, F. Active Fire Detection Using Landsat-8/OLI Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huot, M.; Dalgleish, F.; Archambault, P.; Piché, M.; Département de biologie, Université Laval, Quebec, QC, G1V 0A6, Canada. Unpublished Underwater Fluorescence LiDAR Data. status (manuscript in preparation; to be submitted). 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, T.; Authoritative Classification and Catalogue of Marine Organism Names. World Register of Marine Species (WoRMS). 2022. Available online: https://www.marinespecies.org (accessed on 6 April 2022).


| Substrate Type | Pixel Reflectance | Practical Fluorescence Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Green macroalgae | 0.0295 | 0.0219 |
| Brown macroalgae | 0.0287 | 0.0161 |
| Red macroalgae | 0.0302 | 0.0149 |
| Coral-hard | 0.0967 | 0.0260 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huot, M.; Dalgleish, F.; Rehm, E.; Piché, M.; Archambault, P. Underwater Multispectral Laser Serial Imager for Spectral Differentiation of Macroalgal and Coral Substrates. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133105
Huot M, Dalgleish F, Rehm E, Piché M, Archambault P. Underwater Multispectral Laser Serial Imager for Spectral Differentiation of Macroalgal and Coral Substrates. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(13):3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133105
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuot, Matthieu, Fraser Dalgleish, Eric Rehm, Michel Piché, and Philippe Archambault. 2022. "Underwater Multispectral Laser Serial Imager for Spectral Differentiation of Macroalgal and Coral Substrates" Remote Sensing 14, no. 13: 3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133105
APA StyleHuot, M., Dalgleish, F., Rehm, E., Piché, M., & Archambault, P. (2022). Underwater Multispectral Laser Serial Imager for Spectral Differentiation of Macroalgal and Coral Substrates. Remote Sensing, 14(13), 3105. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14133105






