Hyperspectral Band Selection via Optimal Combination Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Clustering Method
2.2. Ranking Method
2.3. Subspace Partitioning Method
3. Optimal Combination Strategy
3.1. Subspace Grouping
3.1.1. Coarse Grouping
3.1.2. Fine Grouping
3.2. Candidate Representative Bands
3.3. Optimal Combination Strategy
| Algorithm 1: Optimal combination strategy |
 |
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. Indian Pines
4.1.2. Pavia University
4.1.3. Salinas
4.1.4. Botswana
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.2.1. Classifier Setting
4.2.2. Comparison Methods
4.2.3. Number of Selected Bands
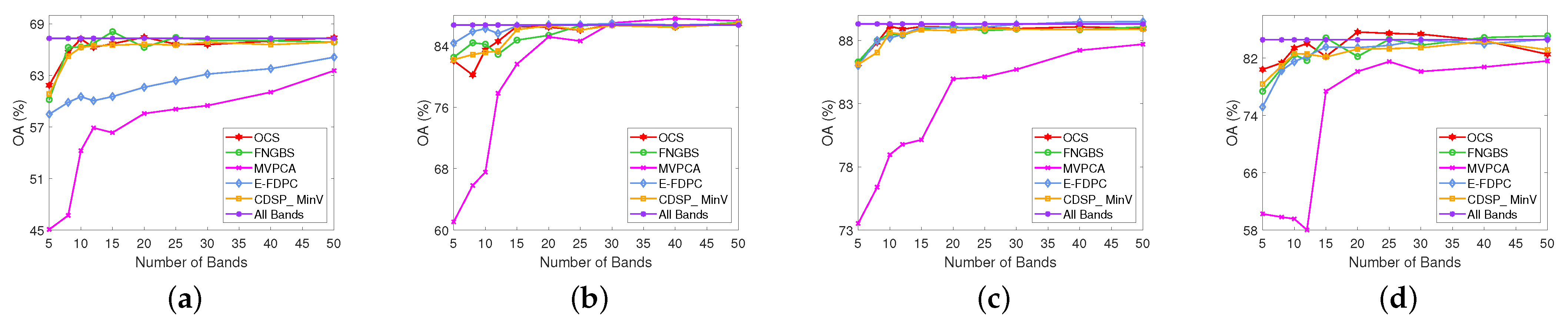
4.3. Results
4.3.1. Parameter Analysis
4.3.2. Study of Candidate Representative Bands
4.3.3. Effectiveness of Search Strategy
4.3.4. Comparison of Classification Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meng, Z.; Li, L.; Jiao, L.; Liang, M. Fully dense multiscale fusion network for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Mariotto, I.M.; Gumma, K.; Middleton, E.M.; Landis, D.R.; Huemmrich, K.F. Selection of hyperspectral narrowbands (HNBs) and composition of hyperspectral twoband vegetation indices (HVIs) for Biophysical Characterization and Discrimination of Crop Types Using Field Reflectance and Hyperion/EO-1 Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saralıoğlu, E.; Görmüş, E.T.; Güngör, O. Mineral exploration with hyperspectral image fusion. In Proceedings of the 2016 24th Signal Processing and Communication Application Conference, Zonguldak, Turkey, 16–19 May 2016; pp. 1281–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, C.; Choi, J.; Chan, S.; Zhou, J.; Budavari, B. A super-resolution and fusion approach to enhancing hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, J.; Chen, C.L.P. Dimension reduction using spatial and spectral regularized local discriminant embedding for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, T.-J.; Suter, D. Incremental kernel principal component analysis. IEEE Trans. Image. Process. 2007, 16, 1662–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chang, C. Independent component analysis-based dimensionality reduction with applications in hyperspectral image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1586–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, Y.; Tong, Y.; Feng, W.; Dauphin, G.; Xing, M. Relative total variation structure analysis-based fusion method for hyperspectral and LiDAR data classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MartÍnez-UsÓMartinez-Uso, A.; Pla, F.; Sotoca, J.M.; GarcÍa-Sevilla, P. Clustering-based hyperspectral band selection using information measures. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 4158–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Du, Q.; Chen, G.; Du, P. Optimized hyperspectral band selection using particle swarm optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 2659–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Jiao, L.C.; Zhang, X.; Sun, T. Hyperspectral band selection based on trivariate mutual information and clonal selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 4092–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Du, Q.; Chen, G. Unsupervised hyperspectral band selection using graphics processing units. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.; Du, Q. Sparse and low-rank graph for discriminant analysis of hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 4094–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Li, H.-C.; Li, W.; Chen, X.-D.; Wu, G.-N.; Du, Q. Discriminant analysis of hyperspectral imagery using fast kernel sparse and low-rank graph. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6085–6098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-J.; Li, H.-C.; Pan, L.; Shao, L.-Y.; Du, Q.; Emery, W.J. Modified tensor locality preserving projection for dimensionality reduction of hyperspectral images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 15, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, K.; Du, Q.; Emery, W.J. Tensor low-rank discriminant embedding for hyperspectral image dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 7183–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-I.; Wang, S. Constrained band selection for hyperspectral imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.C.; Chang, C.-I.; Li, Y.; Wang, L. Constrained multiple band selection for hyperspectral imagery. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Beijing, China, 11–15 July 2016; pp. 6149–6152. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Zhao, E.; Song, M.; Wen, C.H.; Chang, C.I. Constrained-target band selection for multiple-target detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6079–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, A.; Farah, M.; Farah, I.R.; Solaiman, B. Hyperspectral imagery semantic interpretation based on adaptive constrained band selection and knowledge extraction techniques. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Qian, Y.; Tang, Y.Y. Constrained manifold learning for hyperspectral imagery visualization. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, A.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, A. Combination of clustering and ranking techniques for unsupervised band selection of hyperspectral images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2814–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, M.; Berthoumieu, Y. Multiple-feature kernel-based probabilistic clustering for unsupervised band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 6675–6689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.-I.; Kuo, Y.-M.; Chen, S.; Liang, C.-C.; Ma, K.Y.; Hu, P.F. Self-mutual information-based band selection for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5979–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, H.; Pižurica, A. A structural subspace clustering approach for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Dikshit, O. Segmentation-based projected clustering of hyperspectral images using mutual nearest neighbour. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 5237–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, X. Hyperspectral band selection via adaptive subspace partition strategy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, X. Constrained-target band selection with subspace partition for hyperspectral target detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2021, 14, 9147–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, X. A fast neighborhood grouping method for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 5028–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, X. Optimal clustering framework for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 5910–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.; Du, Q.; Sun, T.; Althouse, M.L.G. A joint band prioritization and band-decorrelation approach to band selection for hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Tang, G.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q. A novel ranking-based clustering approach for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 3–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, L.; Feng, J.; Liu, F.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X. Semisupervised affinity propagation based on normalized trivariable mutual information for hyperspectral band selection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2760–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Bruzzone, L.; Guan, R.; Du, P. A feature-metric-based affinity propagation technique for feature selection in hyperspectral image classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 10, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Jia, S.; Li, J. An enhanced density peak-based clustering approach for hyperspectral band selection. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS, Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 1116–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Erven, T.V.; Harremos, P. Rényi divergence and kullback-leibler divergence. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 3797–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polyanskiy, Y.; Wu, Y. Peak-to-average power ratio of good codes for gaussian channel. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 7655–7660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Gao, J.; Li, B.; Wu, O.; Du, J.; Maybank, S. Anomaly detection using local kernel density estimation and context-based regression. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 32, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Datta, N. Min- and max-relative entropies and a new entanglement monotone. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2009, 55, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gour, G.; Tomamichel, M. Entropy and relative entropy from information-theoretic principles. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2021, 67, 6313–6327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoyiannis, I.; Madiman, M. Sumset and inverse sumset inequalities for differential entropy and mutual information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2014, 60, 4503–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, P.; Susilo, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, T.; Wu, Q.; Liang, K. ROSE: Robust searchable encryption with forward and backward security. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2022, 17, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouhamer Immink, K.A.; Weber, J.H. Hybrid minimum pearson and Euclidean distance detection. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2015, 63, 3290–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Number of Iterations | Subspace Partitioning Points |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1, 4, 8, 14, 17, 20, 28, 31, 36, 37, 44, 45, 50, 55, 60, 62, 64, 73, 77, 81, 82, 85, 88, 97, 99, 105, 107, 113, 116, 118, 125, 128, |
| 132, 137, 142, 145, 147, 153, 158, 161, 163, 170, 174, 175, 181, 183, 186, 189, 195, 198, 204 | |
| 2 | 1, 3, 6, 14, 17, 19, 28, 31, 37, 38, 44, 45, 50, 58, 62, 63, 64, 76, 80, 82, 84, 85, 88, 99, 103, 107, 111, 113, 116, 118, 125, 128, |
| 135, 140, 144, 145, 147, 153, 160, 161, 163, 173, 175, 179, 181, 183, 186, 188, 192, 198, 204 | |
| 3 | 1, 3, 5, 10, 14, 17, 28, 31, 37, 38, 44, 45, 50, 60, 62, 63, 64, 79, 82, 84, 85, 86, 88, 99, 106, 107, 113, 114, 116, 118, 125, 132, |
| 138, 143, 145, 146, 147, 153, 161, 162, 163, 175, 176, 181, 182, 183, 186, 188, 191, 195, 204 | |
| 4 | 1, 3, 5, 8, 14, 17, 28, 31, 37, 38, 44, 45, 50, 62, 63, 64, 65, 81, 82, 84, 85, 86, 88, 103, 107, 111, 113, 116, 117, 118, 128, 136, |
| 141, 145, 146, 147, 151, 153, 161, 162, 163, 175, 179, 181, 182, 183, 186, 188, 191, 195, 204 | |
| 5 | 1, 3, 5, 8, 14, 17, 28, 31, 37, 38, 44, 45, 50, 62, 63, 64, 65, 82, 84, 85, 86, 88, 96, 106, 107, 113, 114, 116, 117, 118, 132, 139, |
| 144, 145, 146, 147, 153, 154, 161, 162, 163, 175, 181, 182, 183, 184, 186, 188, 191, 195, 204 | |
| 6 | 1, 3, 5, 8, 14, 17, 28, 31, 37, 38, 44, 45, 50, 62, 63, 64, 65, 82, 84, 85, 86, 88, 96, 106, 107, 113, 114, 116, 117, 118, 132, 139, |
| 144, 145, 146, 147, 153, 154, 161, 162, 163, 175, 181, 182, 183, 184, 186, 188, 191, 195, 204 |
| Select Strategy | 5 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| High Information Entropy and Similarity | 86.16 | 87.85 | 89.12 | 88.90 | 89.10 | 89.05 | 89.24 | 88.94 | 89.08 | 88.96 |
| High Information Entropy | 85.60 | 86.93 | 88.33 | 88.23 | 88.57 | 88.96 | 89.22 | 89.21 | 89.06 | 89.12 |
| High Similarity | 87.12 | 87.25 | 88.69 | 88.81 | 89.01 | 89.05 | 88.32 | 88.30 | 89.20 | 89.22 |
| Select Strategy | 5 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| High Information Entropy and Similarity | 87.89 | 90.33 | 91.39 | 91.51 | 91.73 | 92.12 | 92.19 | 92.34 | 92.33 | 92.52 |
| High Information Entropy | 87.86 | 89.89 | 91.00 | 91.45 | 91.60 | 91.89 | 92.14 | 92.31 | 92.41 | 92.63 |
| High Similarity | 89.29 | 89.79 | 91.02 | 91.36 | 91.63 | 92.00 | 91.71 | 92.08 | 92.61 | 92.74 |
| Select strategy | KNN | SVM |
| High Information Entropy and Similarity | 88.61 | 91.52 |
| High Information Entropy | 88.32 | 91.32 |
| High Similarity | 88.50 | 91.34 |
| Classifier | Method | Pavia University | Salines |
|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | FNGBS-OCS | 85.40 | 88.81 |
| FNGBS [29] | 85.12 | 88.49 | |
| SVM | FNGBS-OCS | 85.65 | 88.96 |
| FNGBS [29] | 85.38 | 88.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Peng, B.; Fang, L.; Li, Q. Hyperspectral Band Selection via Optimal Combination Strategy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122858
Li S, Peng B, Fang L, Li Q. Hyperspectral Band Selection via Optimal Combination Strategy. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(12):2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122858
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuying, Baidong Peng, Long Fang, and Qiang Li. 2022. "Hyperspectral Band Selection via Optimal Combination Strategy" Remote Sensing 14, no. 12: 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122858
APA StyleLi, S., Peng, B., Fang, L., & Li, Q. (2022). Hyperspectral Band Selection via Optimal Combination Strategy. Remote Sensing, 14(12), 2858. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14122858






