A New Coupling Method for PM2.5 Concentration Estimation by the Satellite-Based Semiempirical Model and Numerical Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MODIS AOD Data
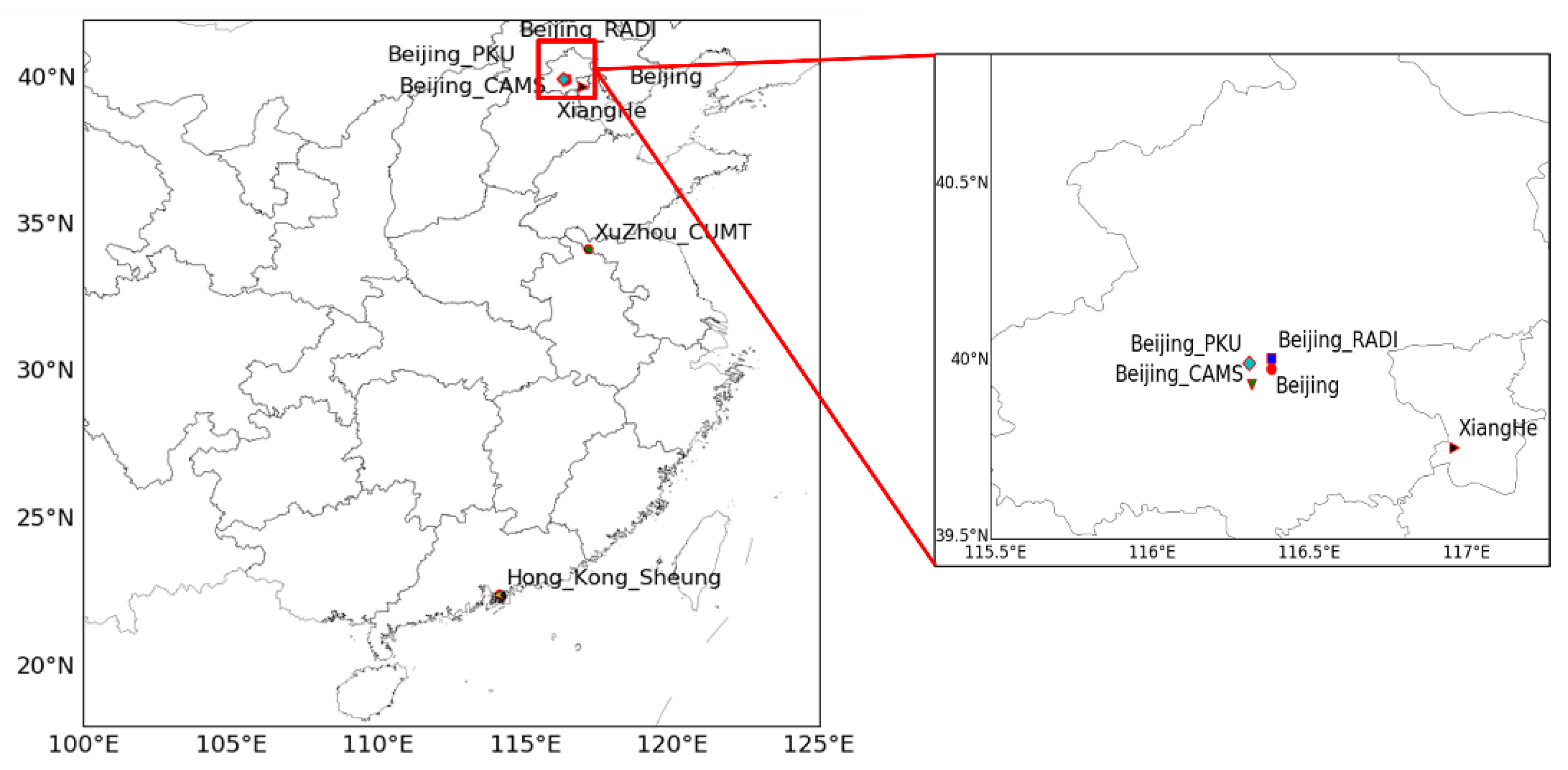
2.2. Ground Monitoring Data
2.3. The SEM
2.4. The WRF-Chem Model
2.5. The CSEN Model
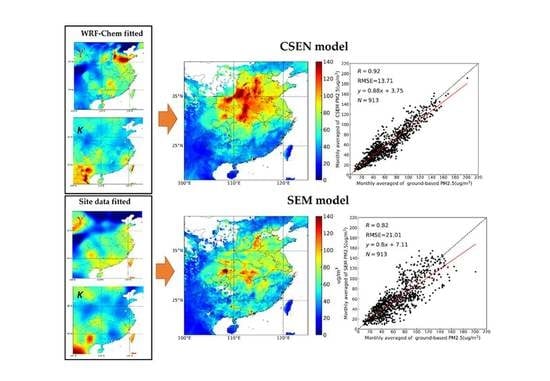
3. Results
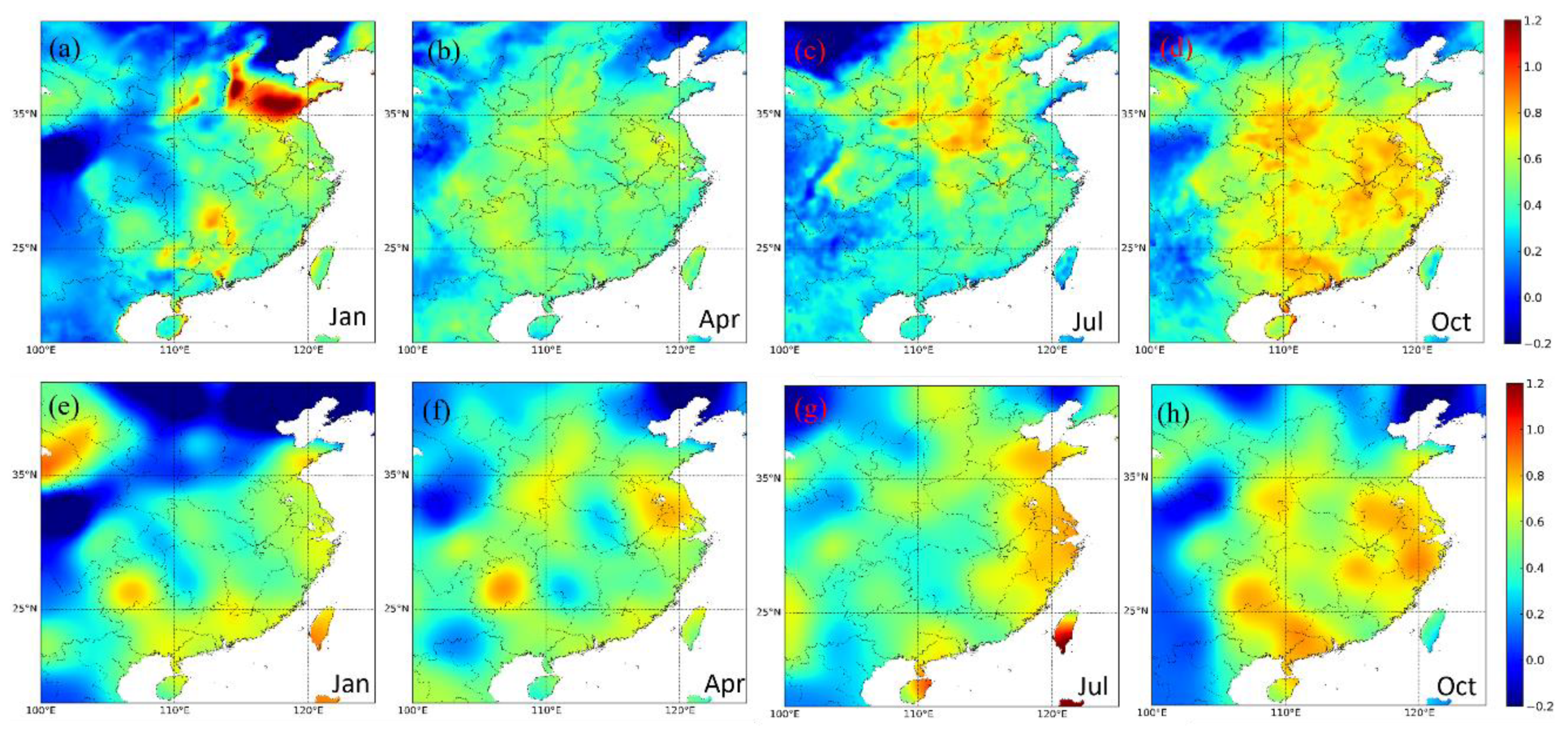
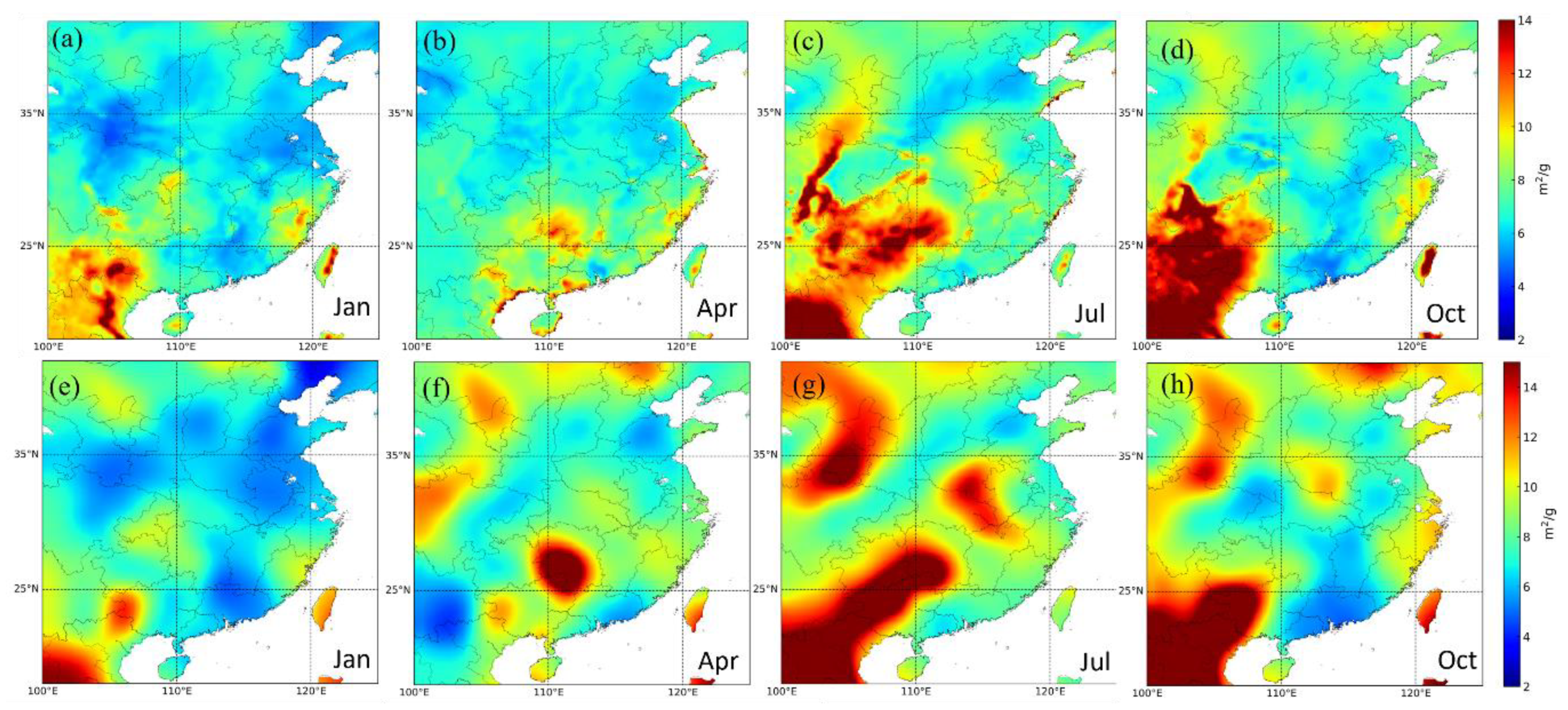
3.1. Evaluation of Aerosol Characteristics from WRF-Chem: γ′ and K
3.2. Validation of the Estimated PM2.5
3.2.1. Statistical Results
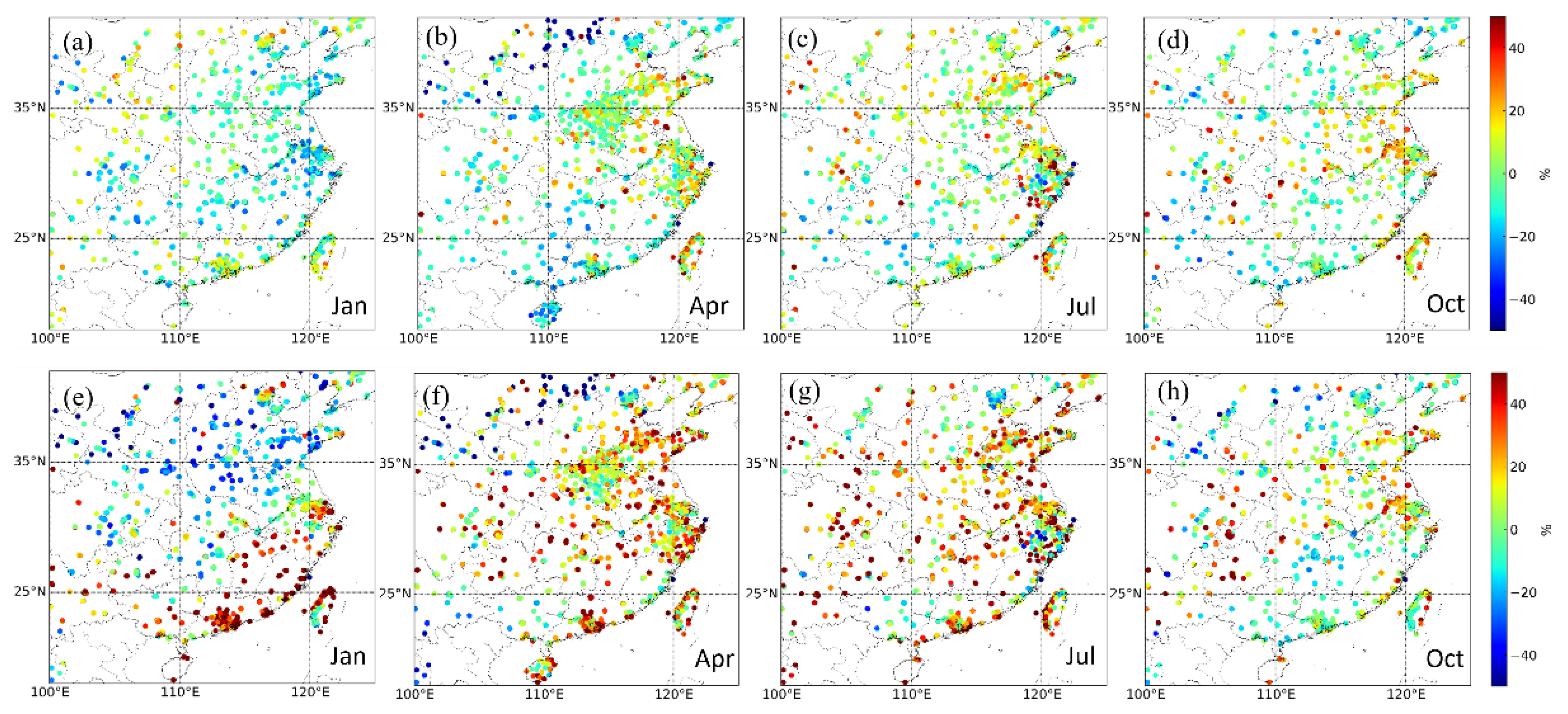
3.2.2. The Seasonal Variation in Spatial Distribution
3.2.3. The Seasonal Variation in Major Clusters
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Site | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| Beijing | 39.977°N | 116.381°E |
| Beijing CAMS | 39.933°N | 116.317°E |
| Beijing_PKU | 39.992°N | 116.31°E |
| Beijing RADI | 40.005°N | 116.379°E |
| Xianghe | 39.754°N | 116.962°E |
| XuZhou_CUMT | 34.217°N | 117.142°E |
| Hong Kong Sheung | 22.483°N | 114.117°E |

References
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Park, R.J. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 using aerosol optical depth determined from satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, F.W.; Li, Y.; Cheng, T.H.; Gao, J.H.; Yuan, S.Y. Estimating the Column Concentrations of Black Carbon Aerosols in China Using MODIS Products. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 11025–11036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexeeff, S.E.; Schwartz, J.; Kloog, I.; Chudnovsky, A.; Koutrakis, P.; Coull, B.A. Consequences of kriging and land use regression for PM2.5 predictions in epidemiologic analyses: Insights into spatial variability using high-resolution satellite data. J. Exp. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brauer, M.; Freedman, G.; Frostad, J.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Dentener, F.; van Dingenen, R.; Estep, K.; Amini, H.; Apte, J.S.; et al. Ambient Air Pollution Exposure Estimation for the Global Burden of Disease 2013. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A., 3rd; Burnett, R.T.; Turner, M.C.; Cohen, A.; Krewski, D.; Jerrett, M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Thun, M.J. Lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality associated with ambient air pollution and cigarette smoke: Shape of the exposure-response relationships. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tie, X.X.; Wu, D.; Brasseur, G. Lung cancer mortality and exposure to atmospheric aerosol particles in Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2375–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, N.S.; Leung, C.C.; Li, Y.; Poon, C.M.; Yao, S.; Wong, E.L.Y.; Lin, C.; Lau, A.K.H.; Lee, S.S. PM2·5 concentration and elderly tuberculosis: Analysis of spatial and temporal associations. Lancet 2017, 390, S68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Lau, A.K.H.; Deng, X.; Tse, T.K.T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Li, C.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X.; et al. Estimation of long-term population exposure to PM2.5 for dense urban areas using 1-km MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 179, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.S.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Lu, H.S.; Lu, Y.A.; Mao, Z.F.; Chen, X.; Li, N.; Ren, M.; et al. A Review on Predicting Ground PM2.5 Concentration Using Satellite Aerosol Optical Depth. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, B.H.Q.; Heal, M.R.; Reis, S. Land-Use Regression Modelling of Intra-Urban Air Pollution Variation in China: Current Status and Future Needs. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, S.; Fan, S.; Song, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Q.; Liu, Y. Satellite Remote Sensing for Estimating PM2.5 and Its Component. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2021, 7, 72–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Kang, Y.; Park, S.; Im, J.; Yoo, C.; Quackenbush, L.J. Estimating ground-level particulate matter concentrations using satellite-based data: A review. GISci. Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh Yazdi, M.; Kuang, Z.; Dimakopoulou, K.; Barratt, B.; Suel, E.; Amini, H.; Lyapustin, A.; Katsouyanni, K.; Schwartz, J. Predicting fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the greater london area: An ensemble approach using machine learning methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.X.; Tang, Q.H.; Gong, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in Beijing using a satellite-based geographically and temporally weighted regression model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 198, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.Q.; Sun, W.W.; Yang, G.; Du, Q. A Full-Coverage Daily Average PM2.5 Retrieval Method with Two-Stage IVW Fused MODIS C6 AOD and Two-Stage GAM Model. Remote Sen. 2019, 11, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Im, J.; Song, C.K.; Choi, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, R.; Kim, S.M.; Yoon, J.; et al. Estimation of spatially continuous daytime particulate matter concentrations under all sky conditions through the synergistic use of satellite-based AOD and numerical models. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Zheng, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, X.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal continuous estimates of PM2.5 concentrations in China, 2000-2016: A machine learning method with inputs from satellites, chemical transport model, and ground observations. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.B.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, C.C.; Fung, J.C.H. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Guang, J.; Tugui, A.; She, L.; Qin, K.; Fan, C.; Che, Y.H.; Xie, Y.Q.; Wen, Y.N.; et al. Hourly PM2.5 Estimation over Central and Eastern China Based on Himawari-8 Data. Remote Sen. 2020, 12, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.N.; de Leeuw, G.; Yang, Z.Q.; Chen, X.F.; Su, X.L.; Jiao, J.S. Estimating Spatio-Temporal Variations of PM2.5 Concentrations Using VIIRS-Derived AOD in the Guanzhong Basin, China. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, D.A.; Tsai, T.C.; Chen, J.P.; Chang, S.C.; Jeng, Y.J.; Chiang, W.L.; Lin, N.H. Interpreting aerosol lidar profiles to better estimate surface PM2.5 for columnar AOD measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emili, E.; Popp, C.; Petitta, M.; Riffler, M.; Wunderle, S.; Zebisch, M. PM10 remote sensing from geostationary SEVIRI and polar-orbiting MODIS sensors over the complex terrain of the European Alpine region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2485–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; Homan, C.D.; Matthijsen, J. Comparison of spatial and temporal variations of aerosol optical thickness and particulate matter over Europe. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 5304–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, C.Q.; Lau, A.K.H.; Liao, C.H.; Zhang, Y.B.; Zeng, W.T.; Li, C.C.; Fung, J.C.H.; Tse, T.K.T. Assessing Long-Term Trend of Particulate Matter Pollution in the Pearl River Delta Region Using Satellite Remote Sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 11670–11678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaap, M.; Apituley, A.; Timmermans, R.M.A.; Koelemeijer, R.B.A.; de Leeuw, G. Exploring the relation between aerosol optical depth and PM2.5 at Cabauw, the Netherlands. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 909–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, J.H.; Zhang, M.G.; Chen, L.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Su, L.; Ge, C.; Han, X.; Zou, M.M. A method to estimate concentrations of surface-level particulate matter using satellite-based aerosol optical thickness. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2013, 56, 1422–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Park, R.J.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, Q.B.; Kilaru, V.; Sarnat, J.A. Mapping annual mean ground-level PM2.5 concentrations using Multiangle Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol optical thickness over the contiguous United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D22206. [Google Scholar]
- van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.; Levy, R.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global estimates of ambient fine particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: Development and application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Zhu, B.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Bao, F. What have we missed when studying the impact of aerosols on surface ozone via changing photolysis rates? Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 10831–10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Geng, F.; Guenther, A.; Cao, J.; Greenberg, J.; Zhang, R.; Apel, E.; Li, G.; Weinheimer, A.; Chen, J.; et al. Megacity impacts on regional ozone formation: Observations and WRF-Chem modeling for the MIRAGE-Shanghai field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5655–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; DeNero, S.P.; Joe, D.K.; Lee, H.H.; Chen, S.H.; Michalakes, J.; Kleeman, M.J. Development of a source oriented version of the WRF/Chem model and its application to the California regional PM10/PM2.5 air quality study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 485–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.M.; Xue, M.; Kong, F.Y.; Zhang, H.L. Meteorological Conditions During an Ozone Episode in Dallas-Fort Worth, Texas, and Impact of Their Modeling Uncertainties on Air Quality Prediction. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 1941–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Han, Z.W.; Liu, Z.R.; Li, M.; Xin, J.Y.; Tao, Z.N.; Li, J.W.; Kang, J.E.; Huang, K.; Dong, X.Y.; et al. Air quality and climate change, Topic 3 of the Model Inter-Comparison Study for Asia Phase III (MICS-Asia III)—Part 1: Overview and model evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4859–4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.H.; Zhu, B.; Xiao, H.; Kang, H.Q.; Pan, C.; Wang, D.D.; Wang, H.L. Effects of black carbon and boundary layer interaction on surface ozone in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 7081–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Sarnat, J.A.; Kilaru, V.; Jacob, D.J.; Koutrakis, P. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 in the eastern United States using satellite remote sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 3269–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Woo, J.H.; He, K.B.; Lu, Z.F.; Ohara, T.; Song, Y.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; et al. MIX: A mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, A.; Karl, T.; Harley, P.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Palmer, P.I.; Geron, C. Estimates of global terrestrial isoprene emissions using MEGAN (Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 3181–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, G.J.; Duan, F.K.; Su, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Kimoto, T.; Chang, D.; et al. Exploring the severe winter haze in Beijing: The impact of synoptic weather, regional transport and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2969–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elser, M.; Huang, R.-J.; Wolf, R.; Slowik, J.G.; Wang, Q.; Canonaco, F.; Li, G.; Bozzetti, C.; Daellenbach, K.R.; Huang, Y.; et al. New insights into PM2.5 chemical composition and sources in two major cities in China during extreme haze events using aerosol mass spectrometry. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 3207–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Q.S.; Zhou, G.Q.; Geng, F.H.; Gao, W.; Yu, W. Spatial distribution of aerosol hygroscopicity and its effect on PM2.5 retrieval in East China. Atmos. Res. 2016, 170, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.Q.; Ma, Y.J.; Xin, J.Y.; Liu, Z.R.; Ma, Y.N.; Gao, D.D.; Wu, J.S.; Zhang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Shen, P.K. The aerosol optical properties and PM2.5 components over the world’s largest industrial zone in Tangshan, North China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 201, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.G.; Li, J.; Qu, Y.; Han, T.; Hou, L.; Gu, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; et al. Formation and evolution mechanism of regional haze: A case study in the megacity Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4501–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, Y.; Wang, J.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Formation mechanism of continuous extreme haze episodes in the megacity Beijing, China, in January 2013. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, M.L.; Peng, J.; Hu, M.; Guo, S.; Marrero-Ortiz, W.; Shang, D.; Zheng, J.; Du, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, R. Wintertime aerosol properties in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14329–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Jin, S.; Ma, Y.; Fan, R.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Liu, B. Haze events at different levels in winters: A comprehensive study of meteorological factors, Aerosol characteristics and direct radiative forcing in megacities of north and central China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 245, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhao, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Yan, P.; Zhou, X. A novel method for distinguishing fog and haze based on PM2.5, visibility, and relative humidity. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 2156–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Lv, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, X.; Sun, Y.; Cribb, M. Aerosol hygroscopic growth, contributing factors, and impact on haze events in a severely polluted region in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1327–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jung, C.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, Y.P. Multicomponent aerosol mass efficiency with various mixture types for polydispersed aerosol. Part. Sci. Technol. 2018, 36, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Huang, Y.; Peng, S. Monitoring the trends of water-erosion desertification on the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau, China from 1989 to 2016 using time-series Landsat images. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y. Study of aerosol optical properties at Kunming in southwest China and long-range transport of biomass burning aerosols from North Burma. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 169, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
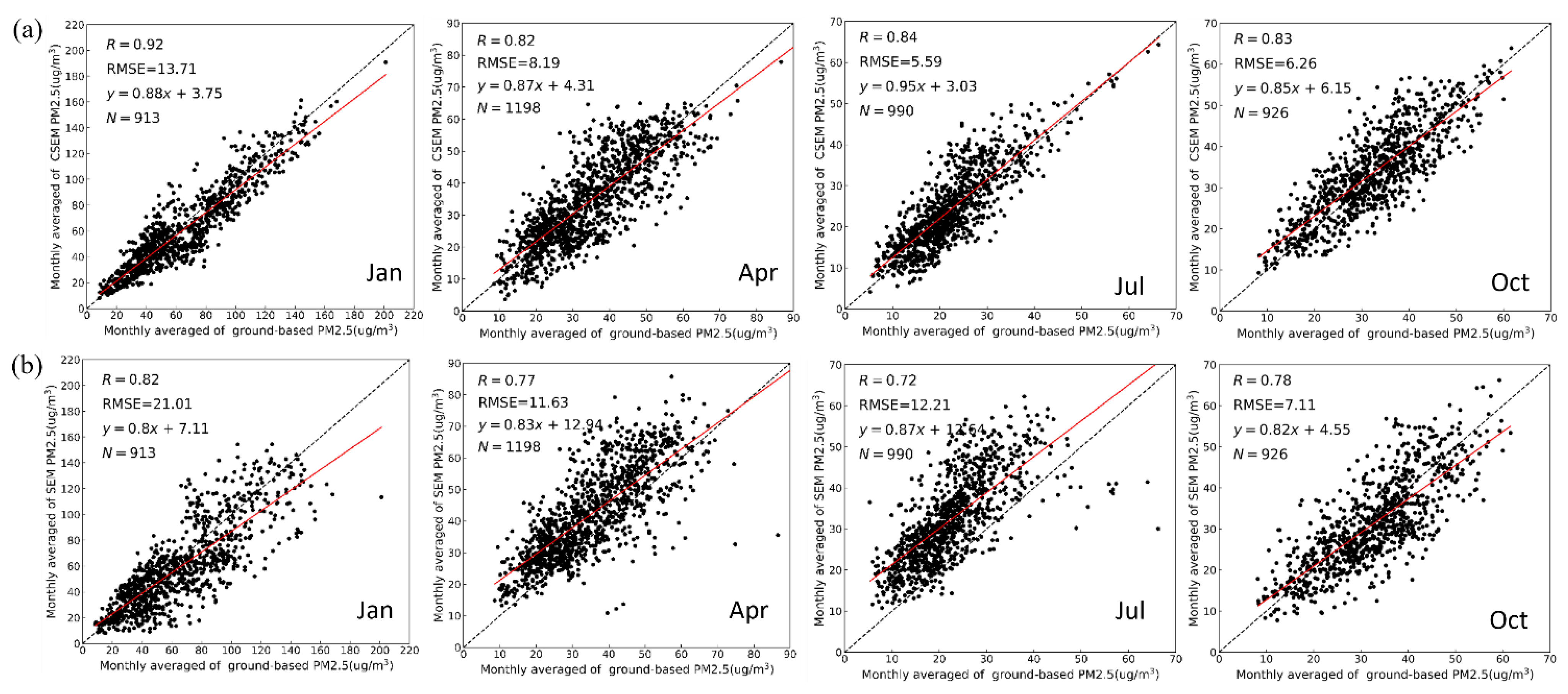

| Method | Month | R 1 | RMSE 2 (µg/m3) | MAE 3 (µg/m3) | MRE 4 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSEN | Jan | 0.92 | 13.71 | 8.56 | 10.22 |
| Apr | 0.82 | 8.19 | 7.22 | 11.36 | |
| Jul | 0.84 | 5.59 | 4.65 | 12.29 | |
| Oct. | 0.83 | 6.26 | 5.71 | 15.88 | |
| SEM | Jan | 0.8 | 21.01 | 21.11 | 21.32 |
| Apr | 0.77 | 11.63 | 9.40 | 23.17 | |
| Jul | 0.72 | 12.21 | 10.03 | 37.32 | |
| Oct. | 0.72 | 7.11 | 6.83 | 20.15 | |
| WRF-chem | Jan | 0.59 | 21.56 | 22.41 | 22.55 |
| Apr | 0.67 | 13.25 | 11.21 | 23.94 | |
| Jul | 0.73 | 11.89 | 10.13 | 22.21 | |
| Oct. | 0.71 | 8.61 | 7.88 | 21.45 |
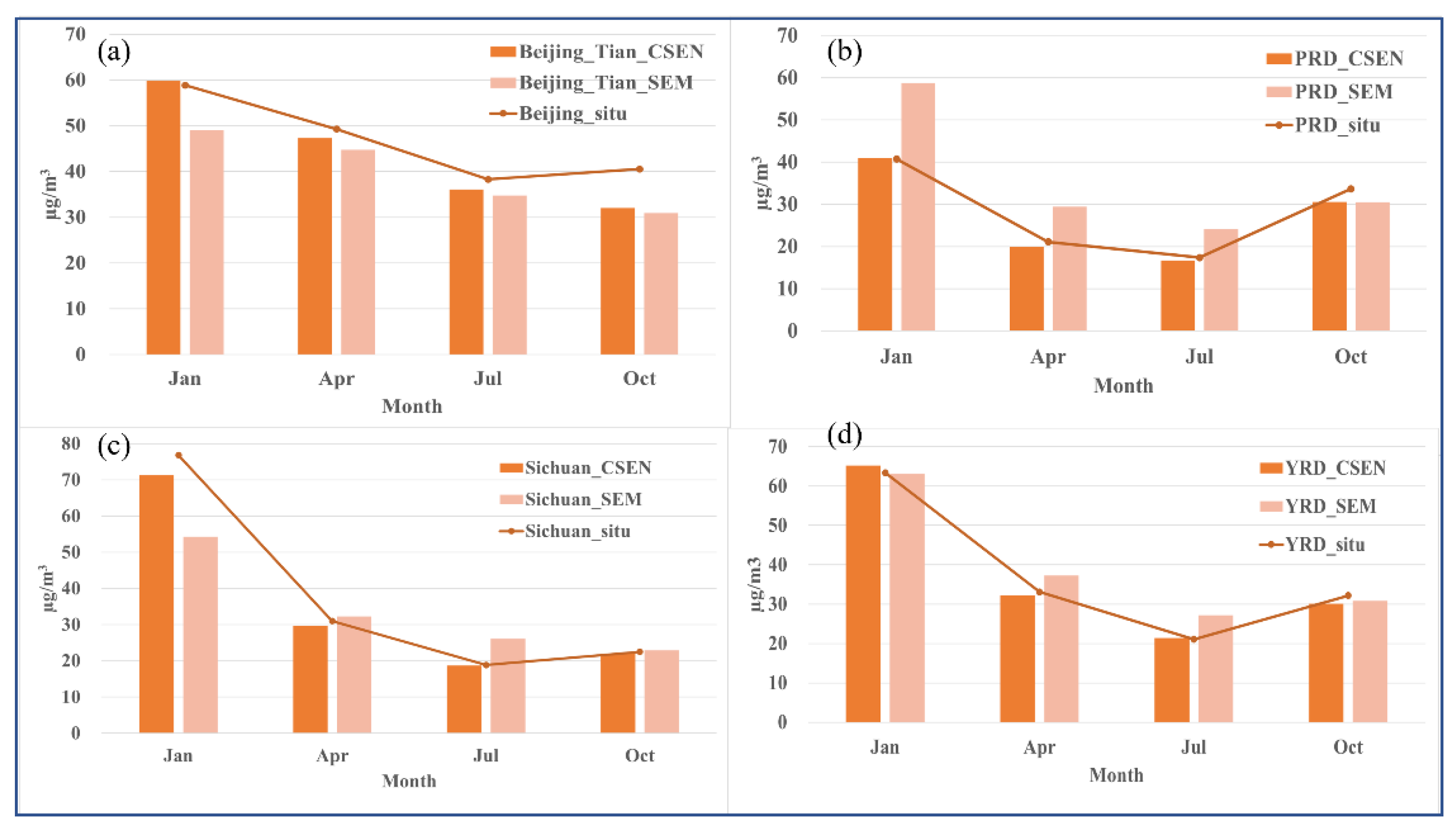
| Region | Month | In Situ (µg/m3) | CSEN-MRE (%) | SEM-MRE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing–Tianjin | Jan | 58.85 | 1.69 | −16.70 |
| Apr | 49.27 | −3.97 | −9.17 | |
| Jul | 38.27 | −5.58 | −9.11 | |
| Oct. | 40.53 | −20.94 | −23.71 | |
| PRD | Jan | 40.71 | 0.59 | 44.32 |
| Apr | 21.09 | −5.44 | 39.57 | |
| Jul | 17.38 | −3.86 | 38.76 | |
| Oct. | 33.64 | −9.15 | −9.33 | |
| Sichuan | Jan | 76.80 | −7.18 | −29.33 |
| Apr | 30.99 | −3.93 | 4.05 | |
| Jul | 18.85 | −0.82 | 38.25 | |
| Oct. | 22.49 | −2.23 | 1.79 | |
| YRD | Jan | 63.37 | 2.84 | −0.49 |
| Apr | 33.10 | −2.61 | 12.57 | |
| Jul | 21.09 | 1.66 | 29.08 | |
| Oct. | 32.16 | −6.36 | −4.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Bao, F. A New Coupling Method for PM2.5 Concentration Estimation by the Satellite-Based Semiempirical Model and Numerical Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102360
Yuan S, Li Y, Gao J, Bao F. A New Coupling Method for PM2.5 Concentration Estimation by the Satellite-Based Semiempirical Model and Numerical Model. Remote Sensing. 2022; 14(10):2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102360
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Shuyun, Ying Li, Jinhui Gao, and Fangwen Bao. 2022. "A New Coupling Method for PM2.5 Concentration Estimation by the Satellite-Based Semiempirical Model and Numerical Model" Remote Sensing 14, no. 10: 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102360
APA StyleYuan, S., Li, Y., Gao, J., & Bao, F. (2022). A New Coupling Method for PM2.5 Concentration Estimation by the Satellite-Based Semiempirical Model and Numerical Model. Remote Sensing, 14(10), 2360. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs14102360