Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area
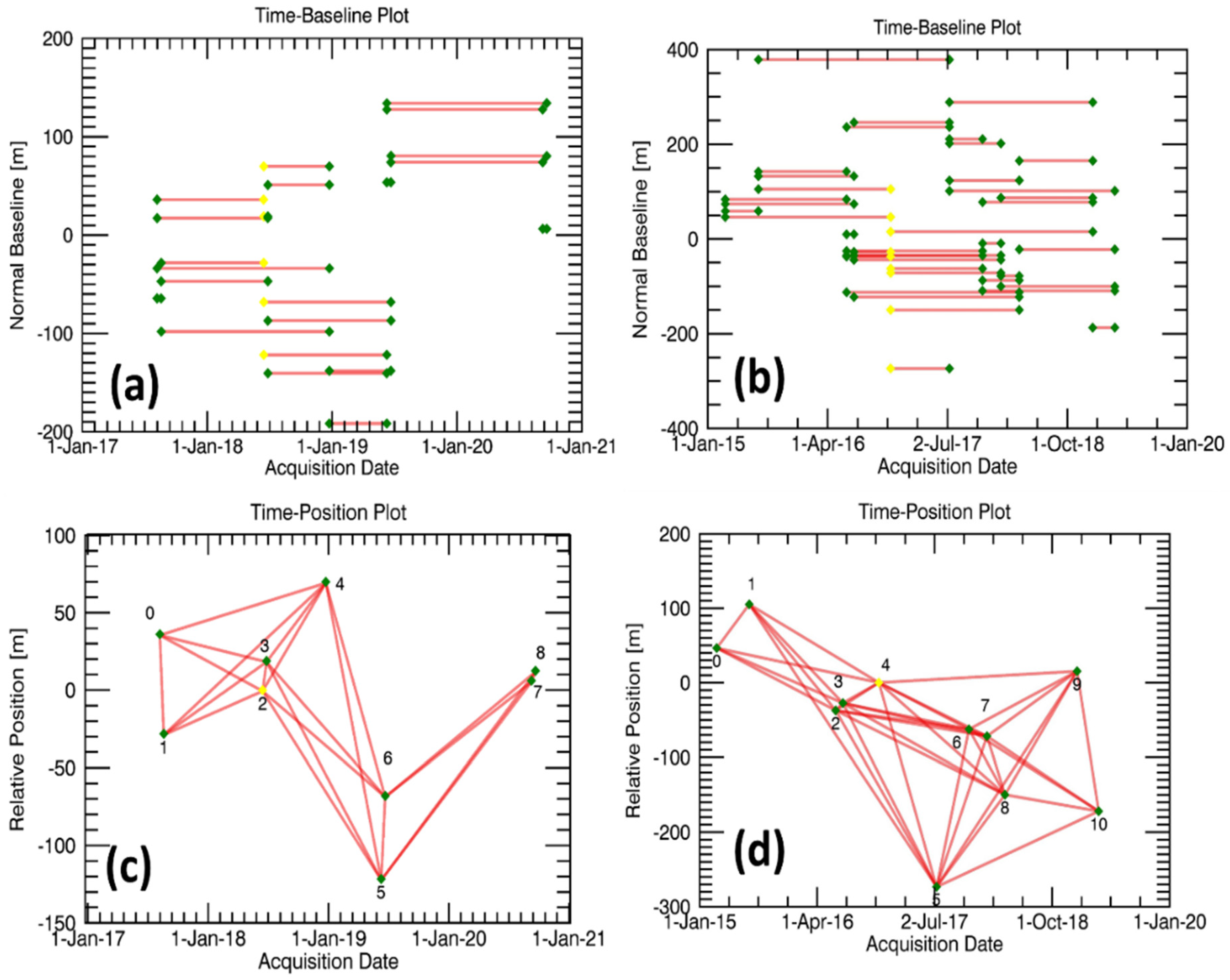
3. Datasets
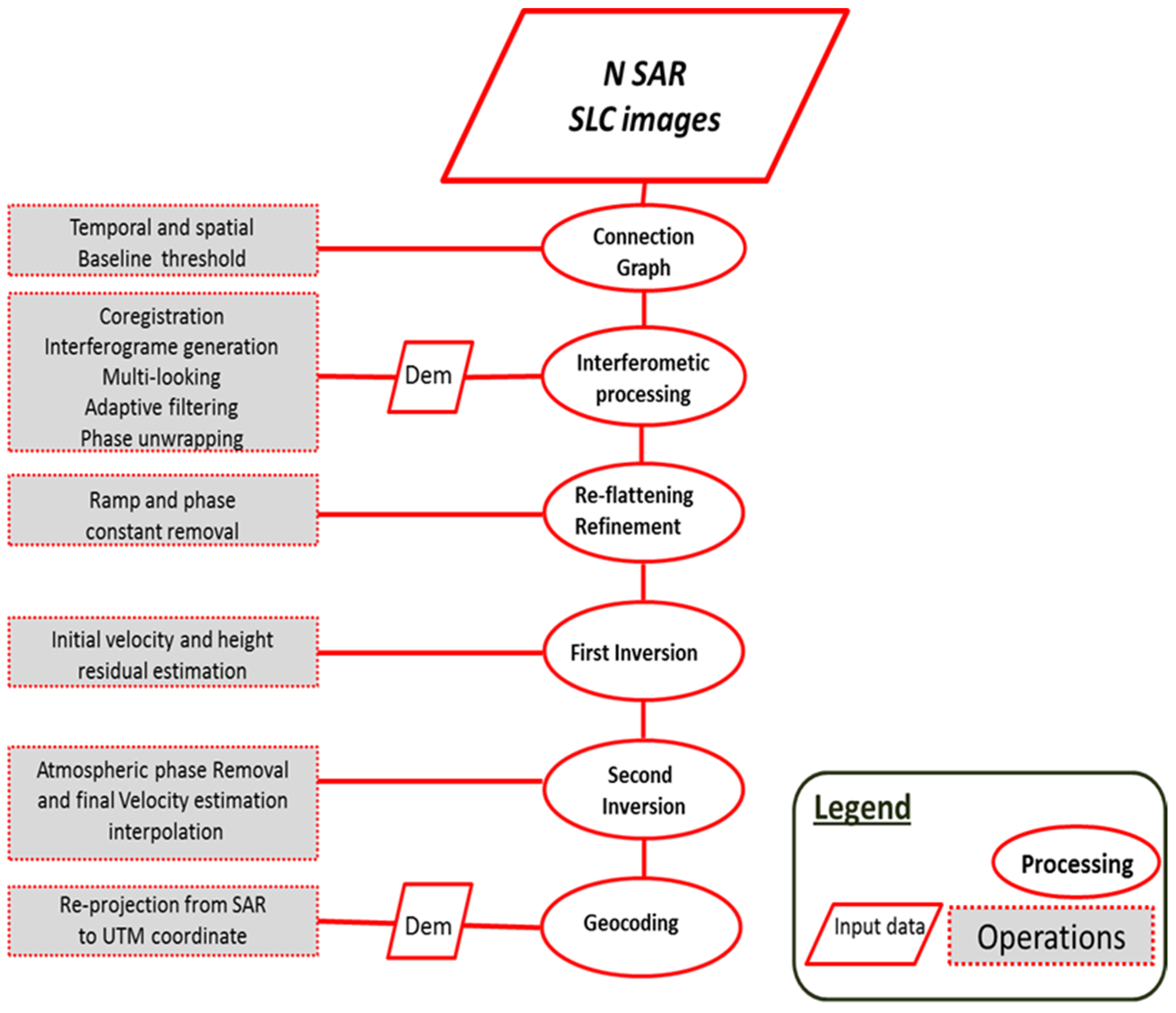
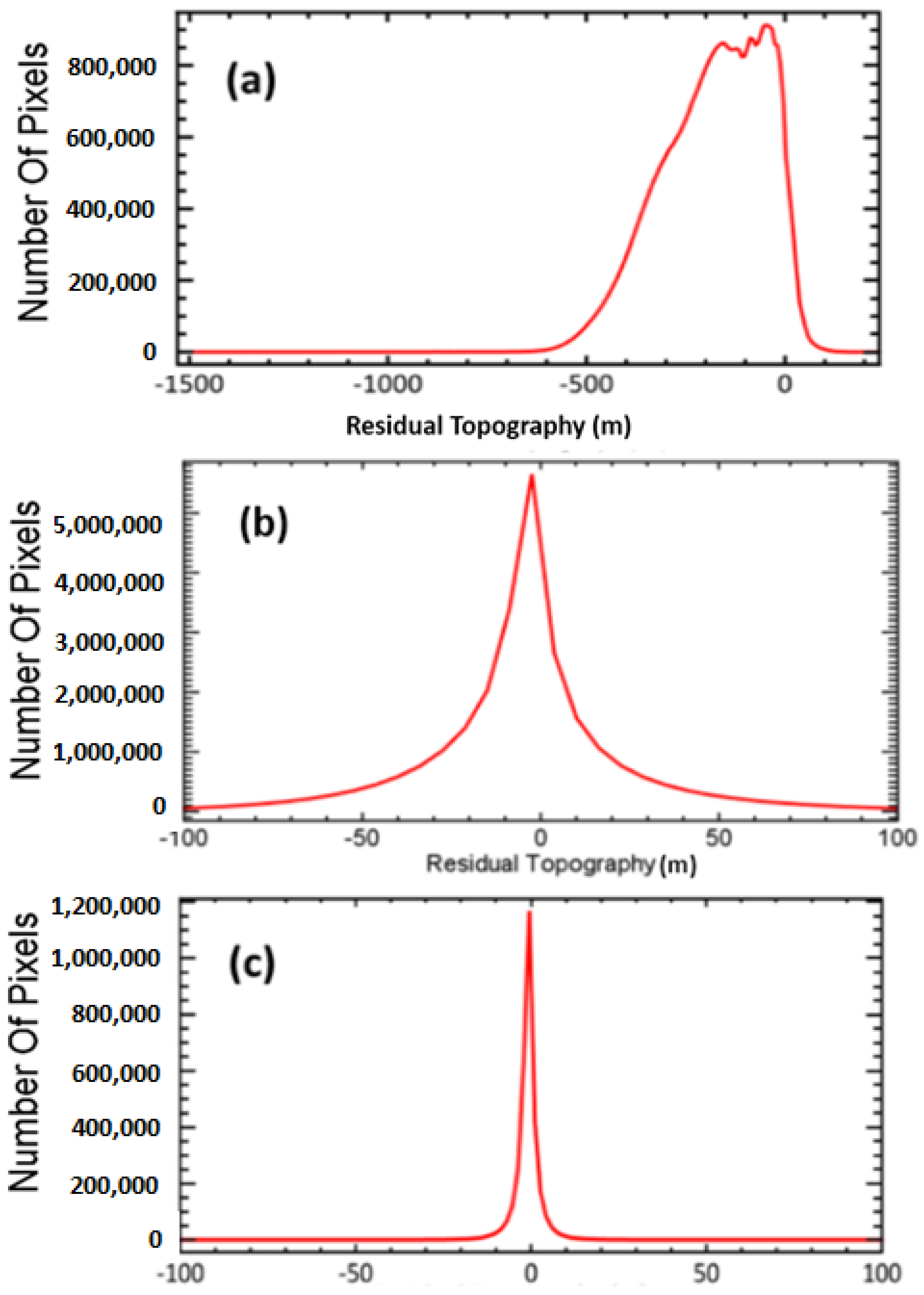
4. SBAS Processing
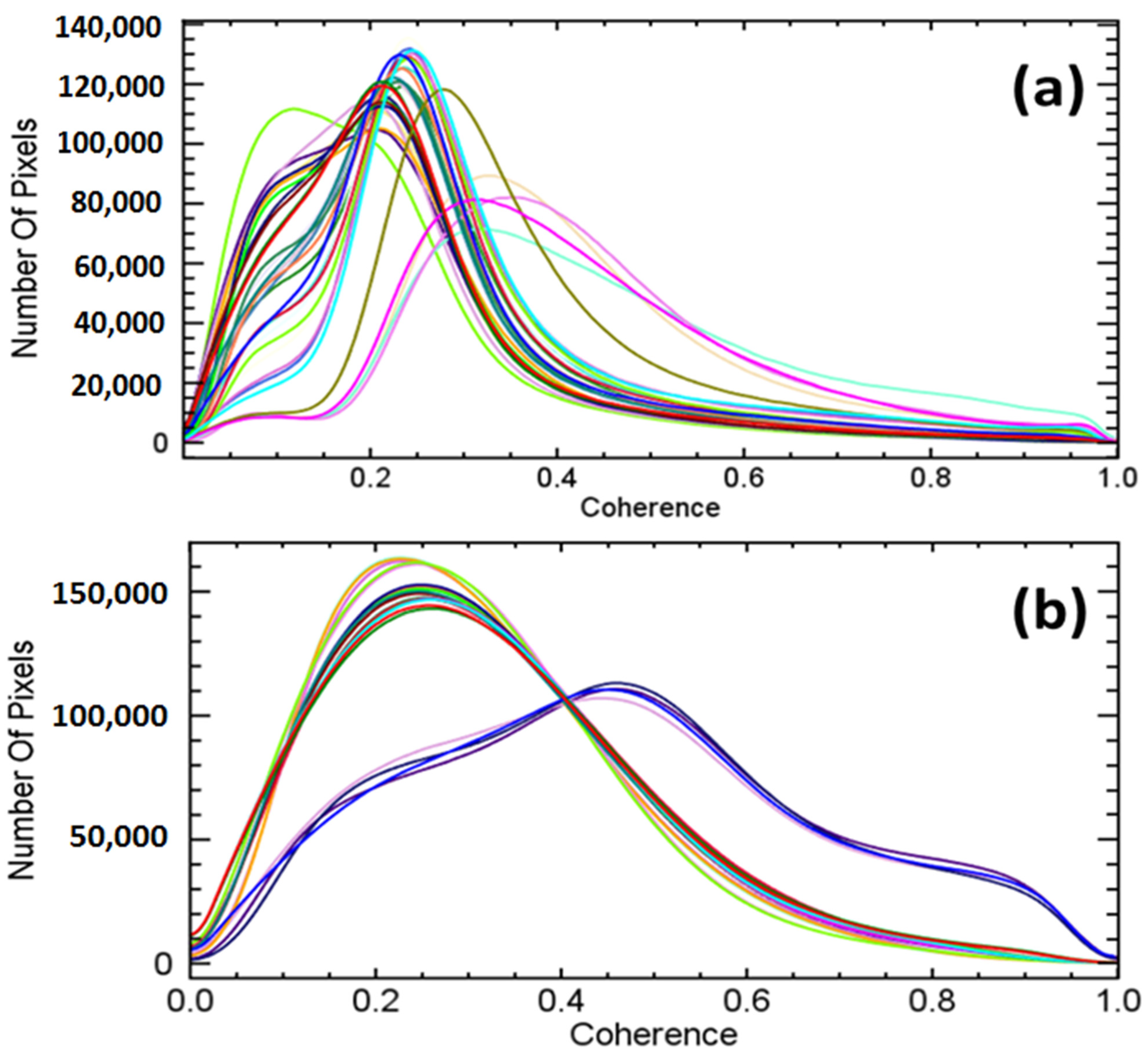
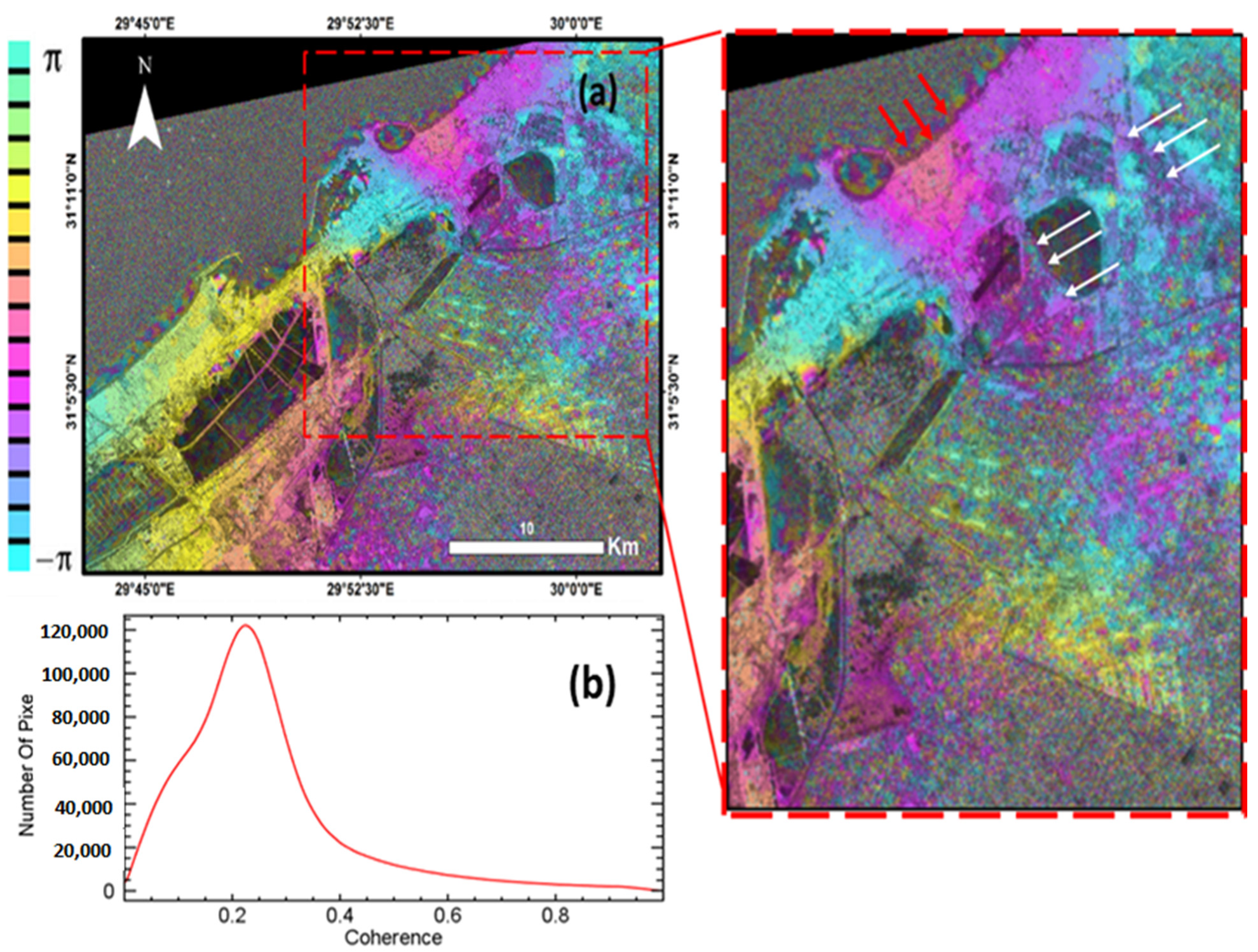
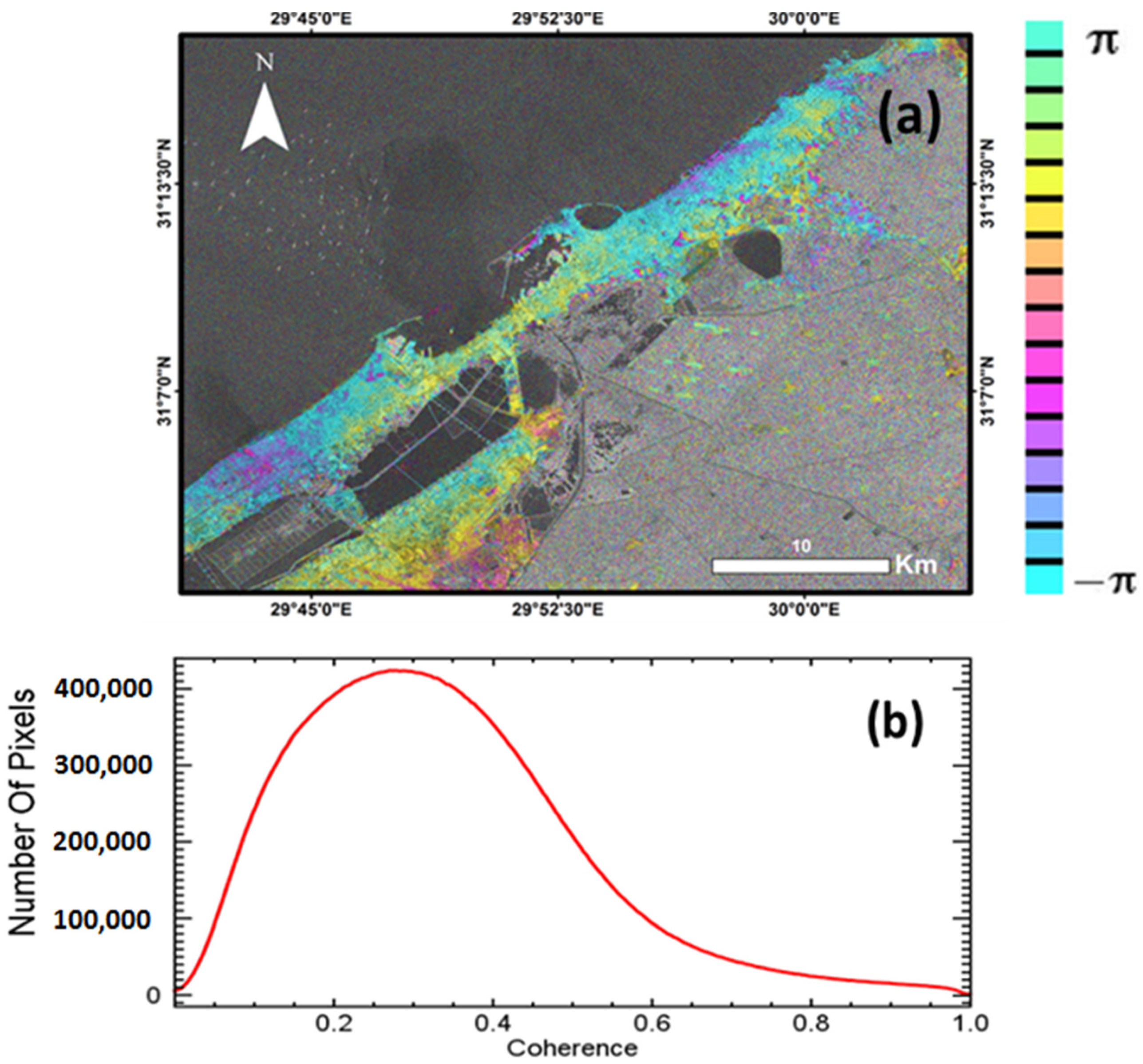
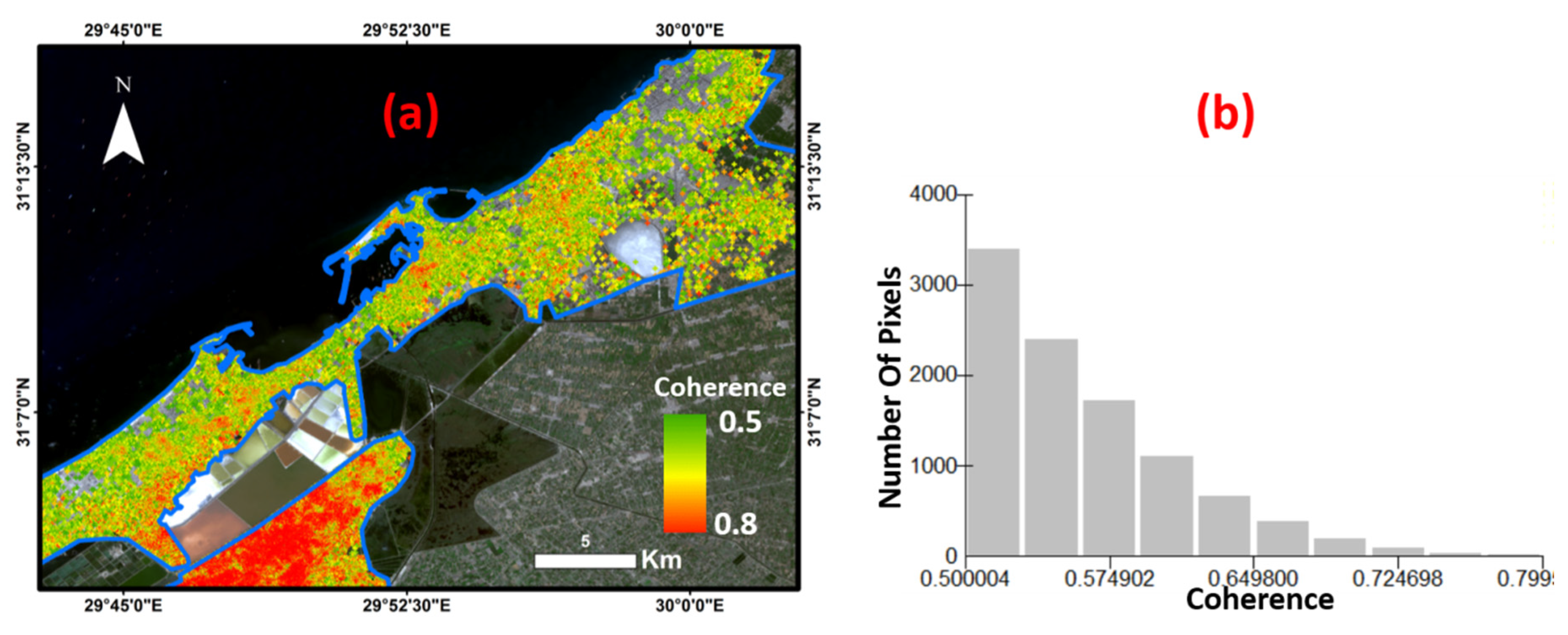
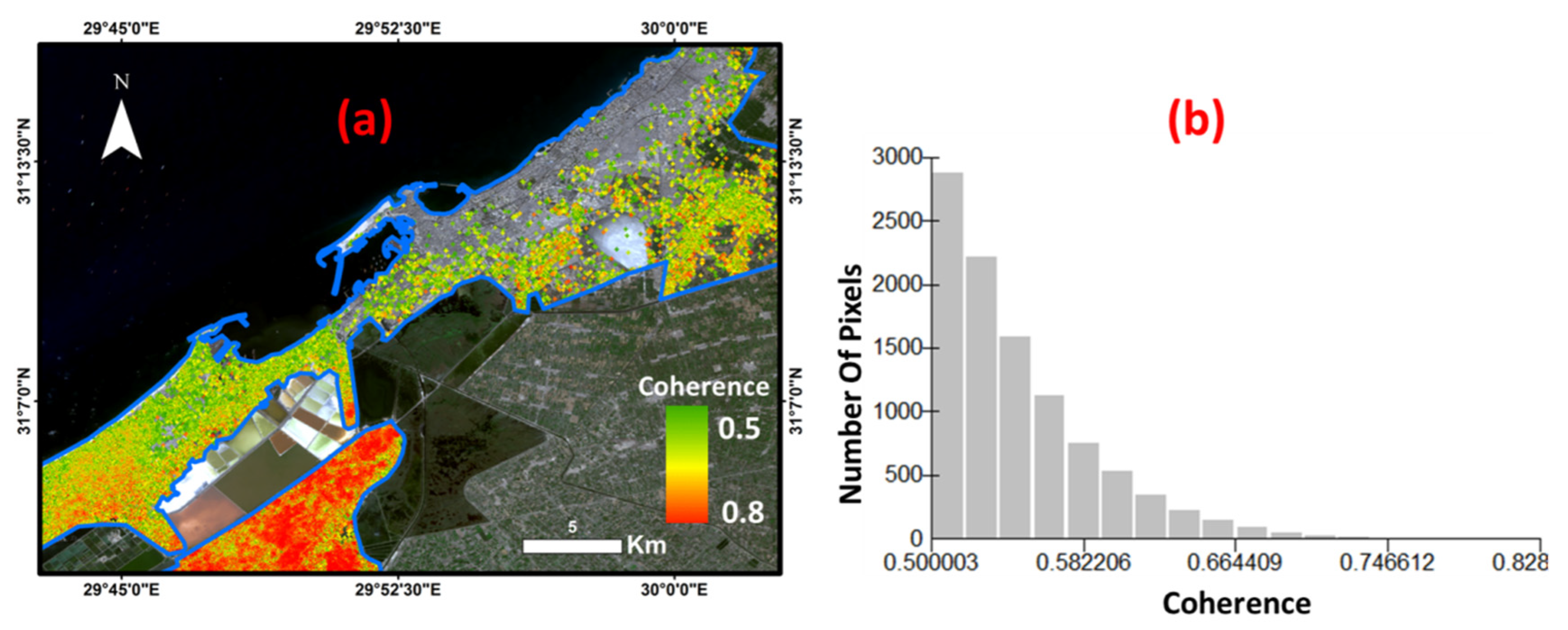
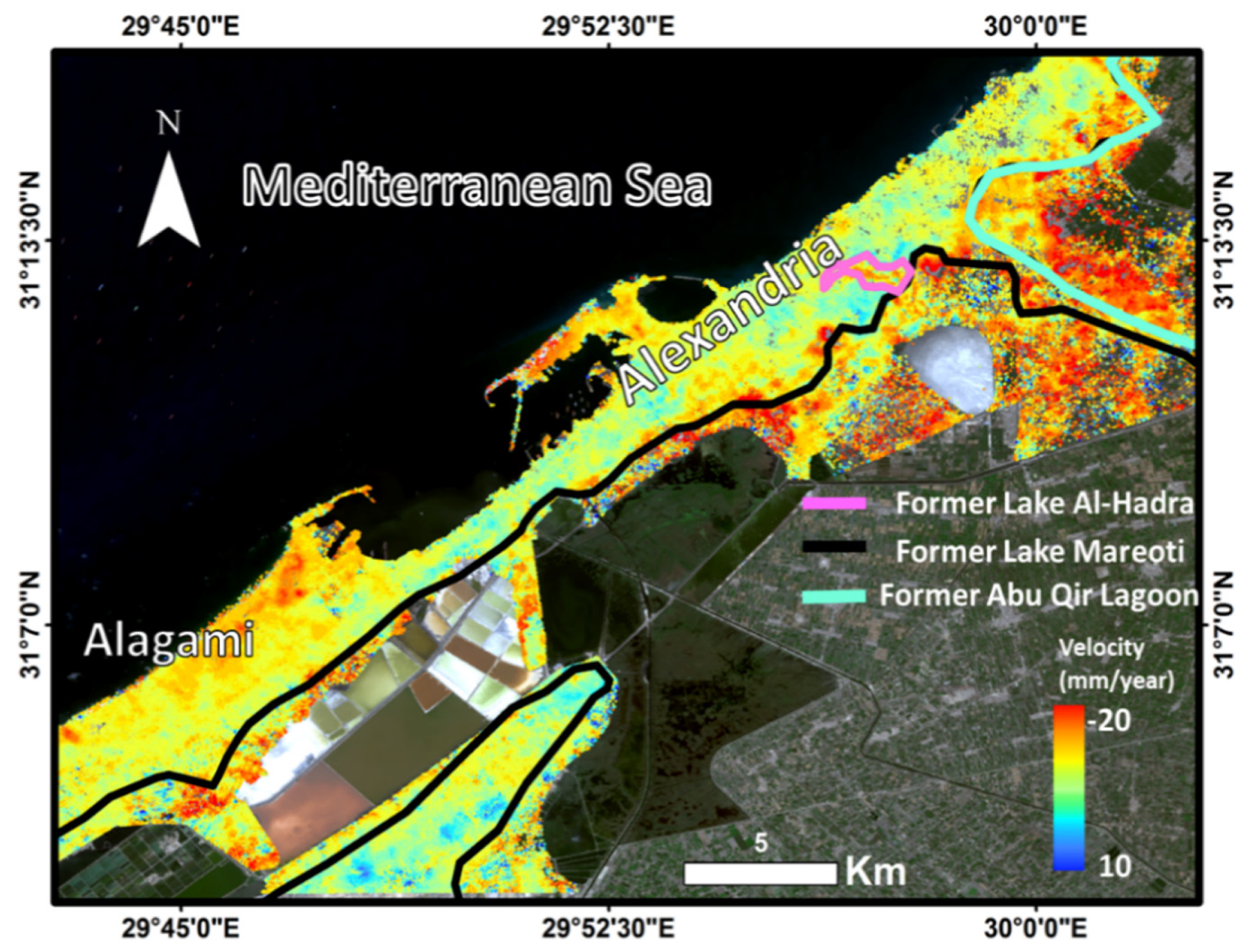
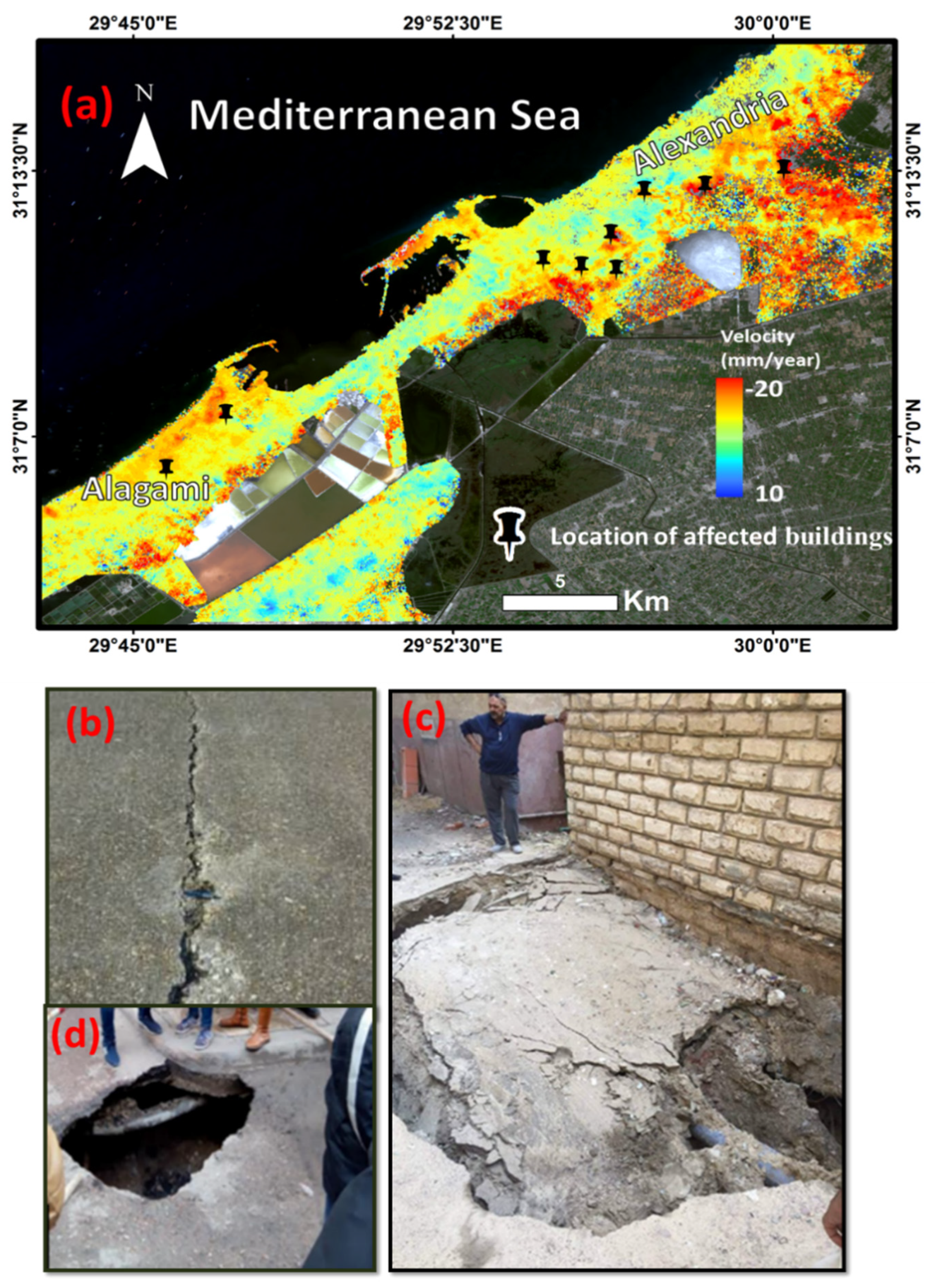
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frihy, O.E. Some proposals for coastal management of the Nile delta coast. Ocean Coast. Manag. 1996, 30, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warne, A.G.; Stanley, J.D. Late Quaternary evolution of the northwest Nile delta and adjacent coast in the Al-exandria region, Egypt. J. Coast. Res. 1993, 9, 26–64. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, D.J.; Warne, A.G. Nile Delta in its destruction phase. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 795–825. [Google Scholar]
- Bridge, J.S. Rivers and Floodplains: Forms, Processes, and Sedimentary Record; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Kwoun, O.-I. Radarsat-1 and ERS InSAR Analysis Over Southeastern Coastal Louisiana: Implications for Mapping Water-Level Changes Beneath Swamp Forests. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 2167–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Lin, H.; Cheng, S. Monitoring and assessing reclamation settlement in coastal areas with advanced InSAR techniques: Macao city (China) case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3565–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P. InSAR Observations and Modeling of Earth Surface Displacements in the Yellow River Delta (China); University of Glasgow: Glasgow, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Jiang, L.; Li, C.; Qiu, G. InSAR reveals coastal subsidence in the Pearl River Delta, China. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver-Cabrera, T.; Wdowinski, S. InSAR-based mapping of tidal inundation extent and amplitude in Louisiana coastal wetlands. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wdowinski, S.; Oliver-Cabrera, T.; Koirala, R.; Jo, M.J.; Osmanoglu, B. Mapping the Extent and Magnitude of Sever Flooding Induced by Hurricane Irma with Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Sar and Insar Observations. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 3, 2237–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ma, G.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T.; Liu, M.; Gao, W.; Falabella, F.; Mastro, P.; Pepe, A. Generation of long-term InSAR ground displacement time-series through a novel multi-sensor data merging technique: The case study of the Shanghai coastal area. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.H. Radar Interferometry for Monitoring Land Subsidence and Coastal Change in the Nile Delta, Egypt. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, R.H.; Sultan, M. Land subsidence in the Nile Delta: Inferences from radar interferometry. Holocene 2009, 19, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereher, M.E. Vulnerability of the Nile Delta to sea level rise: An assessment using remote sensing. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2010, 1, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Asmar, H.M.; Hereher, M.E. Change detection of the coastal zone east of the Nile Delta using remote sensing. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 62, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, M.H.; Klein, A.G.; Zebker, H.A.; Giardino, J.R. Land subsidence in the Nile Delta of Egypt observed by persistent scatterer interferometry. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 3, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouali, E.; Sultan, M.; Becker, R.; Cherif, O. Using Persistent Scatterers Interferometry to Create a Subsidence Map of the Nile Delta in Egypt; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hassaan, M.A.; Abdrabo, M.A. Vulnerability of the Nile Delta coastal areas to inundation by sea level rise. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 185, 6607–6616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugate, J.M. Measurements of Land Subsidence Rates on the North-Western Portion of the Nile Delta Using Radar Interferometry Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Toledo, Toledo, OH, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gaber, A.; Darwish, N.; Sultan, Y.; Arafat, S.; Koch, M. Monitoring Building Stability in Port-Said City, Egypt Using Differential SAR Interferometry. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, A.; Darwish, N.; Koch, M. Minimizing the Residual Topography Effect on Interferograms to Improve DInSAR Results: Estimating Land Subsidence in Port-Said City, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.-D.; Clemente, P.L. Increased Land Subsidence and Sea-Level Rise Are Submerging Egypt’s Nile Delta Coastal Margin. GSA Today 2017, 27, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, E.; Sultan, M.; Becker, R.; El Bastawesy, M.; Cherif, O.; Emil, M. Assessing Land Deformation and Sea Encroachment in the Nile Delta: A Radar Interferometric and Inundation Modeling Approach. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 3208–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sataer, G.; Sultan, M.; Emil, M.K.; Palaseanu, M.; Becker, R.; Kehew, A.; Yellich, J.A.; Kincare, K. Visualizing and Monitoring Bluff Retreat Using Sentinel 1 Radar Interferometry and UAV Imagery; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rateb, A.; Abotalib, A.Z. Inferencing the land subsidence in the Nile Delta using Sentinel-1 satellites and GPS between 2015 and 2019. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 729, 138868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.G.; Rosser, N.J.; Kincey, M.E.; Benjamin, J.; Oven, K.J.; Densmore, A.L.; Milledge, D.G.; Robinson, T.R.; Jordan, C.A.; Dijkstra, T.A. Satellite-based emergency mapping using optical imagery: Experience and reflections from the 2015 Nepal earthquakes. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 18, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargel, J.S.; Leonard, G.J.; Shugar, D.H.; Haritashya, U.K.; Bevington, A.; Fielding, E.J.; Fujita, K.; Geertsema, M.; Miles, E.S.; Steiner, J.; et al. Geomorphic and geologic controls of geohazards induced by Nepals 2015 Gorkha earthquake. Science 2015, 351, aac8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessette-Kirton, E.K.; Cerovski-Darriau, C.; Schulz, W.H.; Coe, J.A.; Kean, J.W.; Godt, J.W.; Thomas, M.A.; Hughes, K.S. Landslides triggered by Hurricane Maria: Assessment of an extreme event in Puerto Rico. GSA Today 2019, 29, 4–10. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, T.R.; Rosser, N.; Walters, R.J. The Spatial and Temporal Influence of Cloud Cover on Satellite-Based Emergency Mapping of Earthquake Disasters. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12455–12459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, K.; Li, Z.; Tomás, R.; Liu, G.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Chen, J.; Stockamp, J. Monitoring activity at the Daguangbao mega-landslide (China) using Sentinel-1 TOPS time series interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonì, R.; Bordoni, M.; Colombo, A.; Lanteri, L.; Meisina, C. Landslide state of activity maps by combining multi-temporal A-DInSAR (LAMBDA). Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 172–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handwerger, A.L.; Fielding, E.J.; Huang, M.; Bennett, G.L.; Liang, C.; Schulz, W.H. Widespread Initiation, Reactivation, and Acceleration of Landslides in the Northern California Coast Ranges due to Extreme Rainfall. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2019, 124, 1782–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Bürgmann, R.; Lu, Z.; Handwerger, A.L.; Wang, T.; Miao, R. Mobility, Thickness, and Hydraulic Diffusivity of the Slow-Moving Monroe Landslide in California Revealed by L-Band Satellite Radar Interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2019, 124, 7504–7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, G.; Foumelis, M.; Raucoules, D.; De Michele, M.; Bernardie, S.; Cakir, Z. Landslide Mapping and Monitoring Using Persistent Scatterer Interferometry (PSI) Technique in the French Alps. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.; Handwerger, A.L.; Agram, P.; Kirschbaum, D.B. InSAR-based detection method for mapping and monitoring slow-moving landslides in remote regions with steep and mountainous terrain: An application to Nepal. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 249, 111983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Carmona, C.; Barra, A.; Galve, J.P.; Monserrat, O.; Pérez-Peña, J.V.; Mateos, R.M.; Notti, D.; Ruano, P.; Millares, A.; López-Vinielles, J. Sentinel-1 DInSAR for Monitoring Active Landslides in Critical Infrastructures: The Case of the Rules Reservoir (Southern Spain). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solari, L.; Del Soldato, M.; Raspini, F.; Barra, A.; Bianchini, S.; Confuorto, P.; Casagli, N.; Crosetto, M. Review of Satellite Interferometry for Landslide Detection in Italy. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitelli, G.; Bonsignore, F.; Carbognin, L.; Ferretti, A.; Strozzi, T.; Teatini, P.; Tosi, L.; Vittuari, L. Radar interferome-try-based mapping of the present land subsidence along the low-lying northern Adriatic coast of Italy. Land Subsidence, Associated Hazards and the Role of Natural Resources Development. In Proceedings of the EISOLS 2010, Queretaro, Mexico, 17–22 October 2010; pp. 279–286. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, A.M.; Caro, M.; Sousa, J.J.; Gil, A.J.; Hanssen, R.F.; Perski, Z.; Galindo-Zaldívar, J.; de Galdeano, C.S. Land subsidence monitoring in the southern Spanish coast using satellite radar interferometry. Sci. Total Environ. J. 2018, 636, 670–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Macedo, K.A.C.; Ramos, F.L.G.; Gaboardi, C.; Moreira, J.R.; Vissirini, F.; Da Costa, M.S. A Compact Ground-Based Interferometric Radar for Landslide Monitoring: The Xerém Experiment. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Armenteros, A.M.; Lazecky, M.; Ruiz-Constán, A.; Bakoň, M.; Delgado, J.M.; Sousa, J.J.; Galindo-Zaldívar, J.; de Galdeano, C.S.; Caro-Cuenca, M.; Martos-Rosillo, S. Monitoring continuous subsidence in the Costa del Sol (Málaga province, southern Spanish coast) using ERS-1/2, Envisat, and Sentinel-1A/B SAR interferometry. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 138, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achache, J.; Fruneau, B.; Delacourt, C. Applicability of SAR interferometry for monitoring of landslides. In Proceedings of the ERS Applications Workshop, London, UK, 6–8 December 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Fruneau, B.; Achache, J.; Delacourt, C. Observation and modelling of the Saint-Étienne-de-Tinée landslide using SAR interferometry. Tectonophysics 1996, 265, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vietmeier, J.W.; Wagner, W.; Dikau, R. Monitoring moderate slope movements (landslides) in the southern French Alps using differential SAR interferometry. In Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on ERS SAR Interferometry, FRINGE’99, Liège, Belgium, 10−12 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rizo, V.; Tesauro, M. SAR interferometry and field data of Randazzo landslide (Eastern Sicily, Italy). Phys. Chem. Earth Part B Hydrol. Oceans Atmos. 2000, 25, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squarzoni, C.; Delacourt, C.; Allemand, P. Nine years of spatial and temporal evolution of the La Valette landslide observed by SAR interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2003, 68, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A. A Decision from the Governor of Alexandria Regarding Land Subsidence and the Neighborhood: The Geb Factory. Egypt News. Available online: https://www.eg24.news (accessed on 28 March 2021).
- Agrawala, S.; Moehner, A.; El Raey, M.; Conway, D.; Van Aalst, M.; Hagenstad, M.; Smith, J. Development and climate change in Egypt: Focus on coastal resources and the Nile. Organ. Econ. Coop. Dev. 2004, 1, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- El-Raey, M. Impacts and implications of climate change for the coastal zones of Egypt. In Coastal Zones and Climate Change; The Henry L. Stimson Center: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; pp. 31–49. ISBN 978-0-9821935-5-6. [Google Scholar]
- Sampsell, B.M.; van Hasselt, B. Geology of Egypt; The American University in Cairo Press: Cairo, Egypt, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Said, R. The Geological Evolution of the River Nile; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, J.-D.; Clemente, P.L. Clay distributions, grain sizes, sediment thicknesses, and compaction rates to in-terpret subsidence in Egypt’s northern Nile Delta. J. Coast. Res. 2014, 30, 88–101. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, J.-D. Growth faults, a distinct carbonate-siliciclastic interface and recent coastal evolution, NW Nile Delta, Egypt. J. Coast. Res. 2005, 42, 309–318. [Google Scholar]
- Foumelis, M.; Blasco, J.M.D.; Desnos, Y.-L.; Engdahl, M.; Fernández, D.; Veci, L.; Lu, J.; Wong, C. ESA SNAP-StaMPS integrated processing for Sentinel-1 persistent scatterer interferometry. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium—IGARSS 2018, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 1364–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Wöppelmann, G.; Le Cozannet, G.; De Michele, M.; Raucoules, D.; Cazenave, A.; Garcin, M.; Hanson, S.; Marcos, M.; Santamaría-Gómez, A. Is land subsidence increasing the exposure to sea level rise in Alexandria, Egypt? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2953–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liosis, N.; Marpu, P.R.; Pavlopoulos, K.; Ouarda, T.B. Ground subsidence monitoring with SAR interferometry techniques in the rural area of Al Wagan, UAE. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Casu, F.; Manzo, M.; Zeni, G.; Berardino, P.; Manunta, M.; Pepe, A. An Overview of the Small Baseline Subset Algorithm: A DInSAR Technique for Surface Deformation Analysis. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2007, 164, 637–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, X.; Bai, Z.; Wu, K.; Zhou, D.; Li, Z. Assessment of mining-induced damage to structures using InSAR time series analysis: A case study of Jiulong Mine, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B. Monitoring of Ground Deformation due to Excessive Withdrawal of Natural Gas Using SBAS. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaabani, A.; Deffontaines, B. Application of the SBAS-DInSAR technique for deformation monitoring in Tunis City and Mornag plain. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 1346–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A. A multi-temporal InSAR method incorporating both persistent scatterer and small baseline approaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierull, C. Statistical analysis of multilook SAR interferograms for CFAR detection of ground moving targets. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 691–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhouse, I.H. Introduction to Microwave Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmap. PS Tutorial: Version 0.9. 2014. Available online: http://sarmap.ch/page.php?page=tutorials (accessed on 16 February 2016).
- Gama, F.F.; Cantone, A.; Mura, J.C.; Pasquali, P.; Paradella, W.R.; dos Santos, A.R.; Silva, G.G. Monitoring subsidence of open pit iron mines at Carajás Province based on SBAS interferometric technique using TerraSAR-X data. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2017, 8, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Jordan, C.; Novellino, A.; Dijkstra, T.; Chen, G. Investigating slow-moving landslides in the Zhouqu region of China using InSAR time series. Landslides 2018, 15, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loesch, E.; Sagan, V. SBAS Analysis of Induced Ground Surface Deformation from Wastewater Injection in East Central Oklahoma, USA. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Nonlinear subsidence rate estimation using permanent scatterers in differential SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 2202–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendry, L.F.; Salvatore, J. Individual and social benefits of online discussion forums. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 50, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Goldstein, R.M. Topographic mapping from interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1986, 91, 4993–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, O.; Lanari, R.; Mallorqui, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for monitoring localized deformation phenomena based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, X.; Tang, Y. Small baseline subsets approach of DInSAR for investigating land surface deformation along the high-speed railway. In SPIE Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing; SPIE International Society for Optics and Photonics: Beijing, China, 2014; p. 92601C. [Google Scholar]
- Bekaert, D.; Walters, R.; Wright, T.; Hooper, A.; Parker, D. Statistical comparison of InSAR tropospheric correction techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 170, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.-D.; Toscano, M.A. Ancient archaeological sites buried and submerged along Egypt’s Nile delta coast: Gauges of Holocene delta margin subsidence. J. Coast. Res. 2009, 25, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



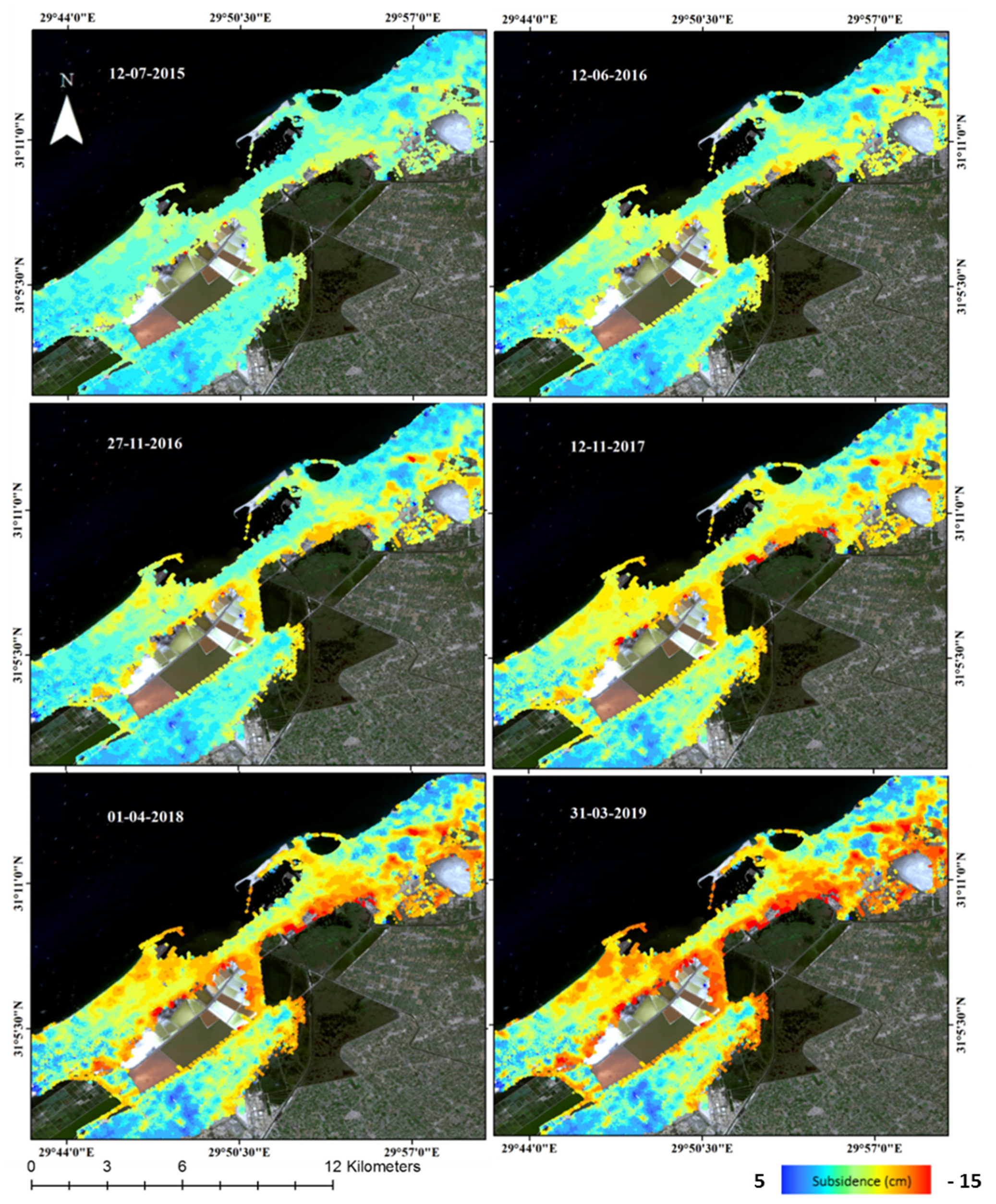
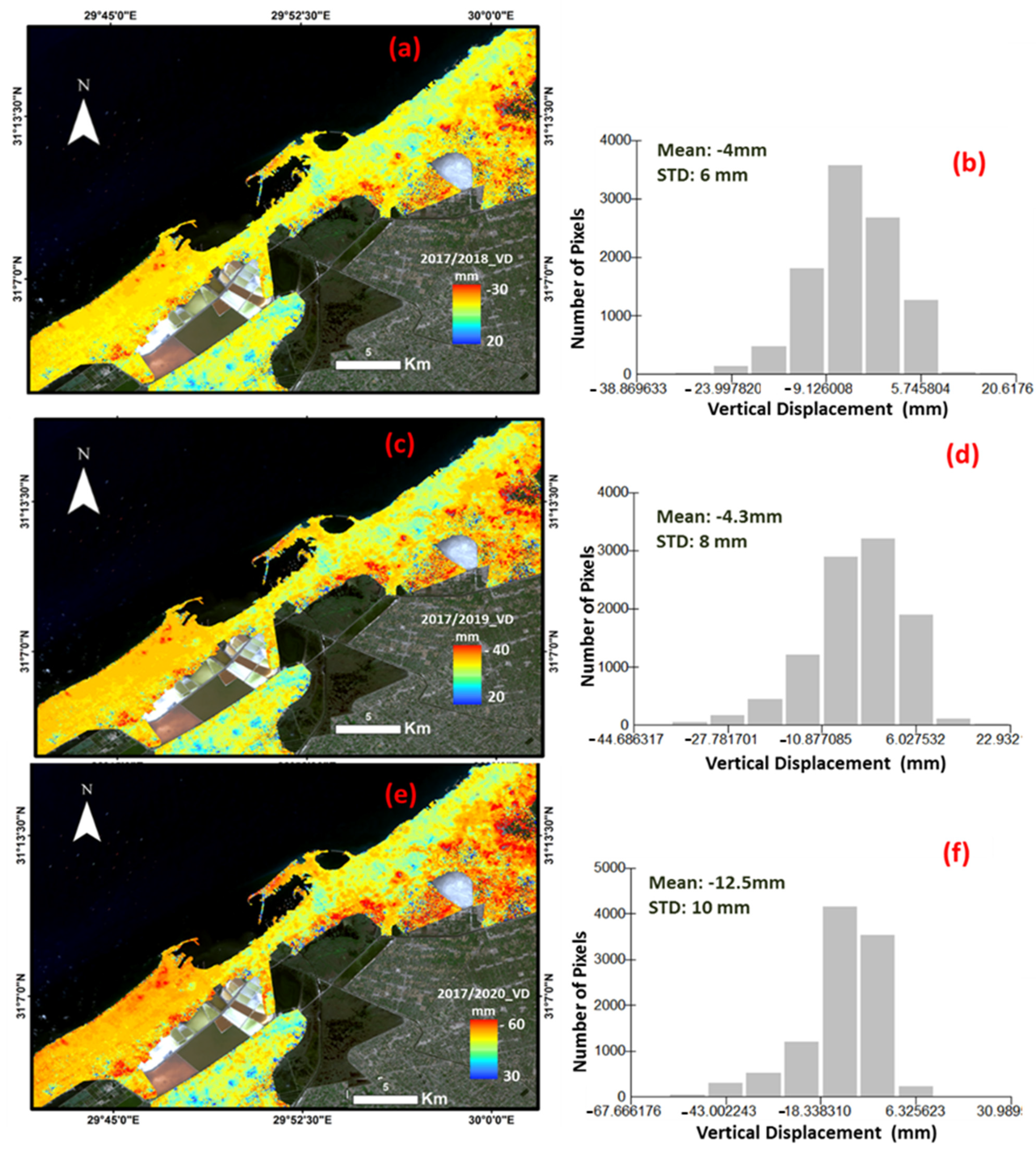
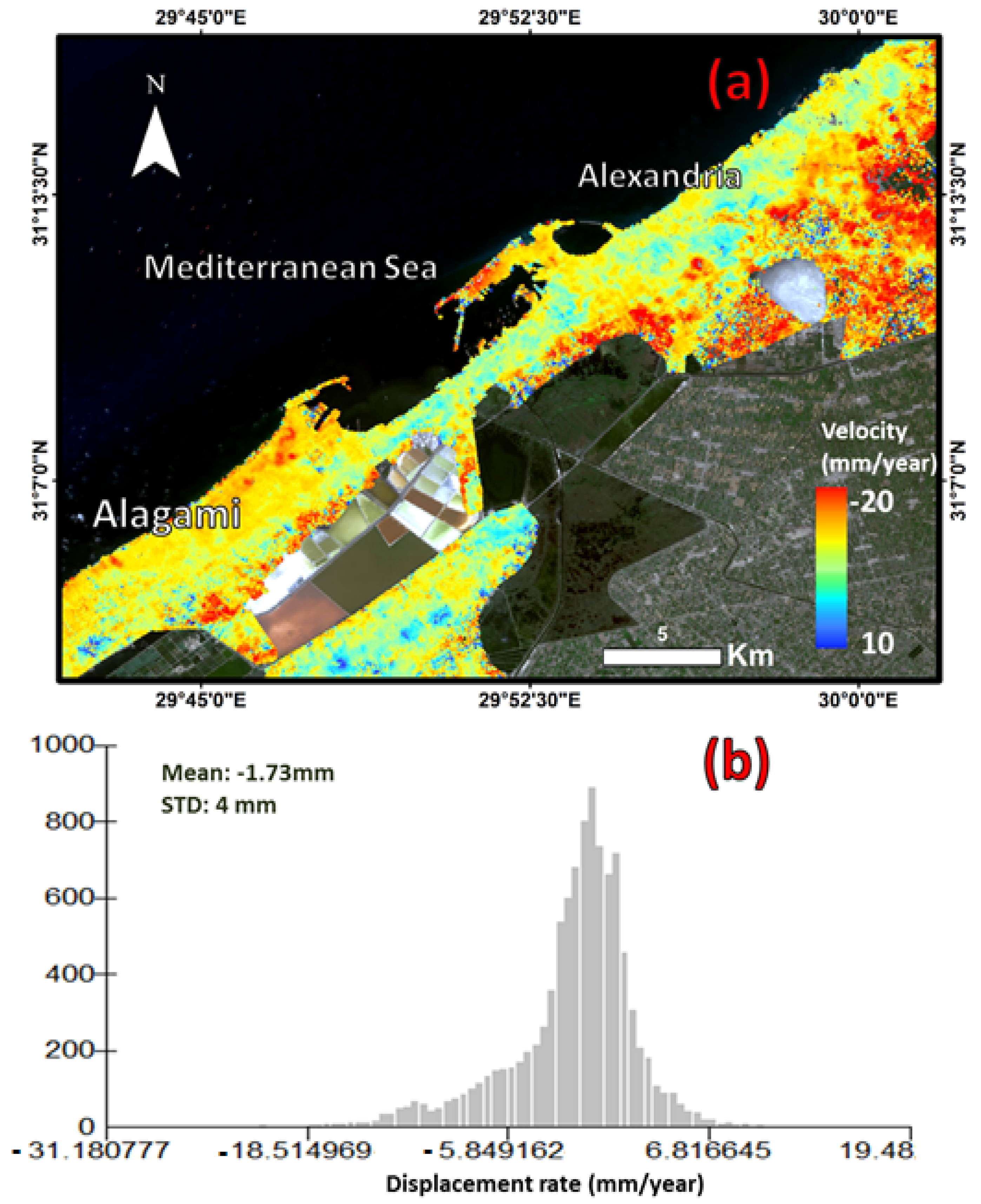
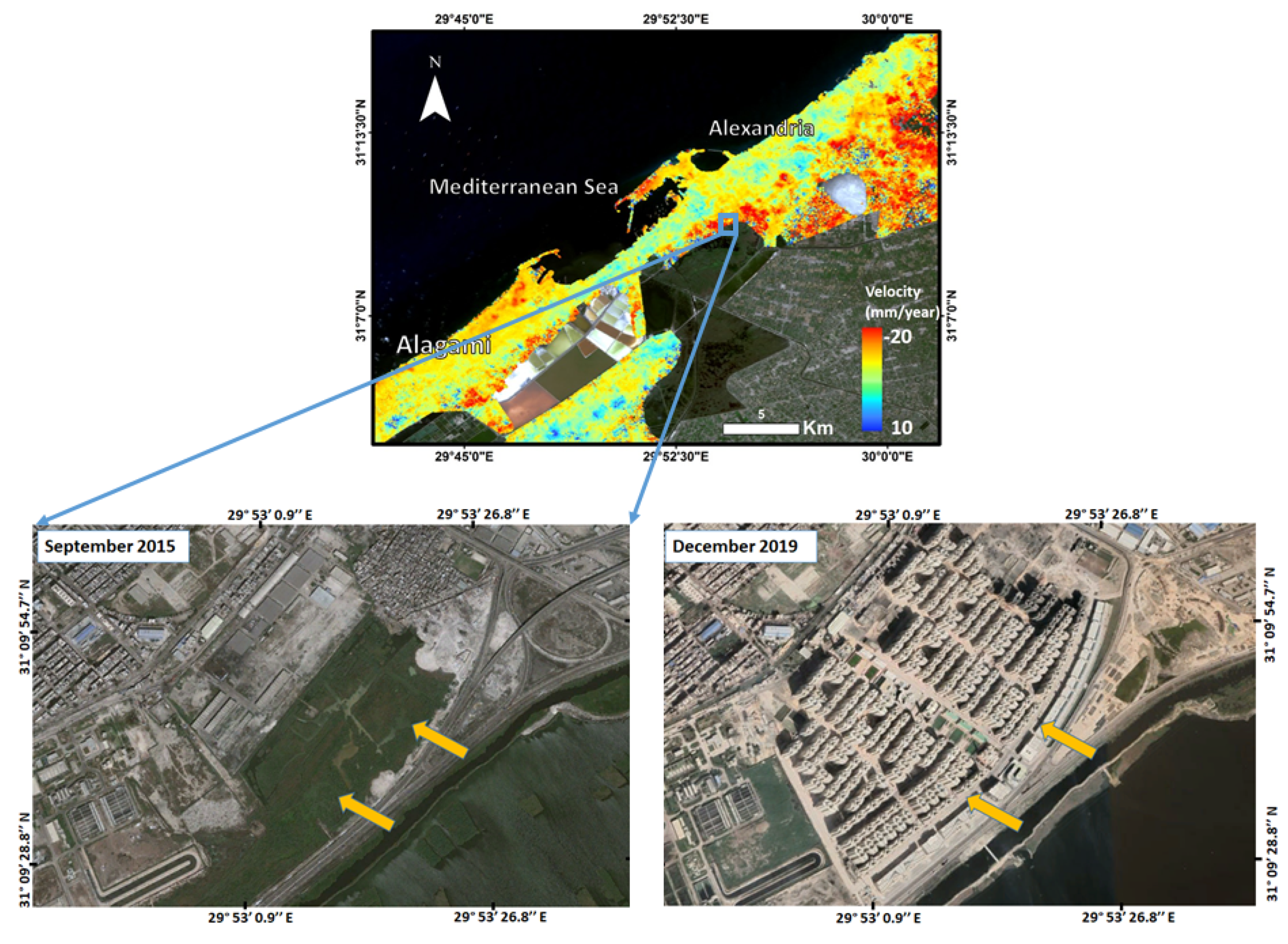
| Satellite | ALOS/PALSAR-2 | Sentinel-1A |
|---|---|---|
| Band | L | C |
| Orbit | Ascending | Descending |
| Master image | 27 November 2016 | 27 June 2018 |
| Number of scenes | 11 | 9 |
| Acquisition period | 2015–2019 | 2017–2020 |
| λ (cm) | 23.6 | 5.6 |
| Polarization | HH | VV |
| Revisit cycle | 14 days | 12 days |
| Mode | ScanSAR | IW |
| Master | Slave | Normal Baseline (m) | Temporal Baseline (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7/8/2017 | 19/8/2017 | −62 | 12 |
| 15/6/2018 | −36 | 312 | |
| 27/6/2018 | −20 | 324 | |
| 24/12/2018 | 34 | 504 | |
| 19/8/2017 | 15/6/2018 | 28 | 300 |
| 26/6/2018 | 44 | 312 | |
| 24/12/2018 | 95 | 492 | |
| 15/6/2018 | 27/6/2018 | 18 | 12 |
| 24/12/2018 | 69 | 192 | |
| 10/6/2019 | −121 | 360 | |
| 22/6/2019 | −68 | 372 | |
| 27/6/2018 | 28/12/2018 | 53 | 180 |
| 10/6/2019 | −138 | 348 | |
| 22/6/2019 | −84 | 360 | |
| 24/12/2018 | 22/6/2019 | −191 | 168 |
| 10/6/2019 | −138 | 180 | |
| 10/6/2019 | 22/6/2019 | 54 | 12 |
| 8/9/2020 | 126 | 456 | |
| 20/9/2020 | 134 | 468 | |
| 22/6/2019 | 8/9/2020 | 72 | 444 |
| 20/9/2020 | 80 | 456 | |
| 8/9/2020 | 20/9/2020 | 13 | 12 |
| Master | Slave | Normal Baseline (m) | Temporal Baseline (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8/3/2015 | 12/7/2015 | 84 | 126 |
| 12/6/2016 | −56 | 462 | |
| 10/7/2016 | −34 | 490 | |
| 12/7/2015 | 12/6/2016 | −134 | 336 |
| 10/7/2016 | −111 | 364 | |
| 27/11/2016 | −105 | 504 | |
| 12/6/2016 | 10/7/2016 | 22 | 28 |
| 27/11/2016 | 37 | 168 | |
| 9/7/2017 | −242 | 392 | |
| 12/11/2017 | −35 | 518 | |
| 21/1/2018 | −36 | 588 | |
| 10/7/2016 | 21/1/2018 | −58 | 560 |
| 12/11/2017 | −57 | 490 | |
| 9/7/2017 | −264 | 384 | |
| 27/11/2016 | 27 | 140 | |
| 27/11/2016 | 1/4/2018 | −149 | 490 |
| 21/1/2018 | −71 | 420 | |
| 12/11/2017 | −62 | 350 | |
| 9/7/2017 | −273 | 224 | |
| 9/7/2017 | 6/1/2019 | 287 | 546 |
| 1/4/2018 | 128 | 266 | |
| 21/1/2018 | 206 | 196 | |
| 12/11/2017 | 211 | 126 | |
| 12/11/2017 | 31/3/2019 | −109 | 504 |
| 6/1/2019 | 76 | 420 | |
| 1/4/2018 | −87 | 140 | |
| 21/1/2018 | −18 | 70 | |
| 21/10/2018 | 31/3/2019 | −102 | 434 |
| 6/1/2019 | 83 | 390 | |
| 1/4/2018 | 134 | 468 | |
| 1/4/2018 | 6/1/2019 | −79 | 70 |
| 31/3/2019 | −23 | 364 | |
| 6/1/2019 | 31/3/2019 | −185 | 84 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Darwish, N.; Kaiser, M.; Koch, M.; Gaber, A. Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091838
Darwish N, Kaiser M, Koch M, Gaber A. Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091838
Chicago/Turabian StyleDarwish, Noura, Mona Kaiser, Magaly Koch, and Ahmed Gaber. 2021. "Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091838
APA StyleDarwish, N., Kaiser, M., Koch, M., & Gaber, A. (2021). Assessing the Accuracy of ALOS/PALSAR-2 and Sentinel-1 Radar Images in Estimating the Land Subsidence of Coastal Areas: A Case Study in Alexandria City, Egypt. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091838







