Quantifying Contributions of Local Emissions and Regional Transport to NOX in Beijing Using TROPOMI Constrained WRF-Chem Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Description and Configuration
2.2. TROPOMI Satellite Observation
2.3. TROPOMI-Derived Top-Down NOX Emissions
2.4. Horizontal Transportation Flux
2.5. Ancillary Data
3. Results and Discussion
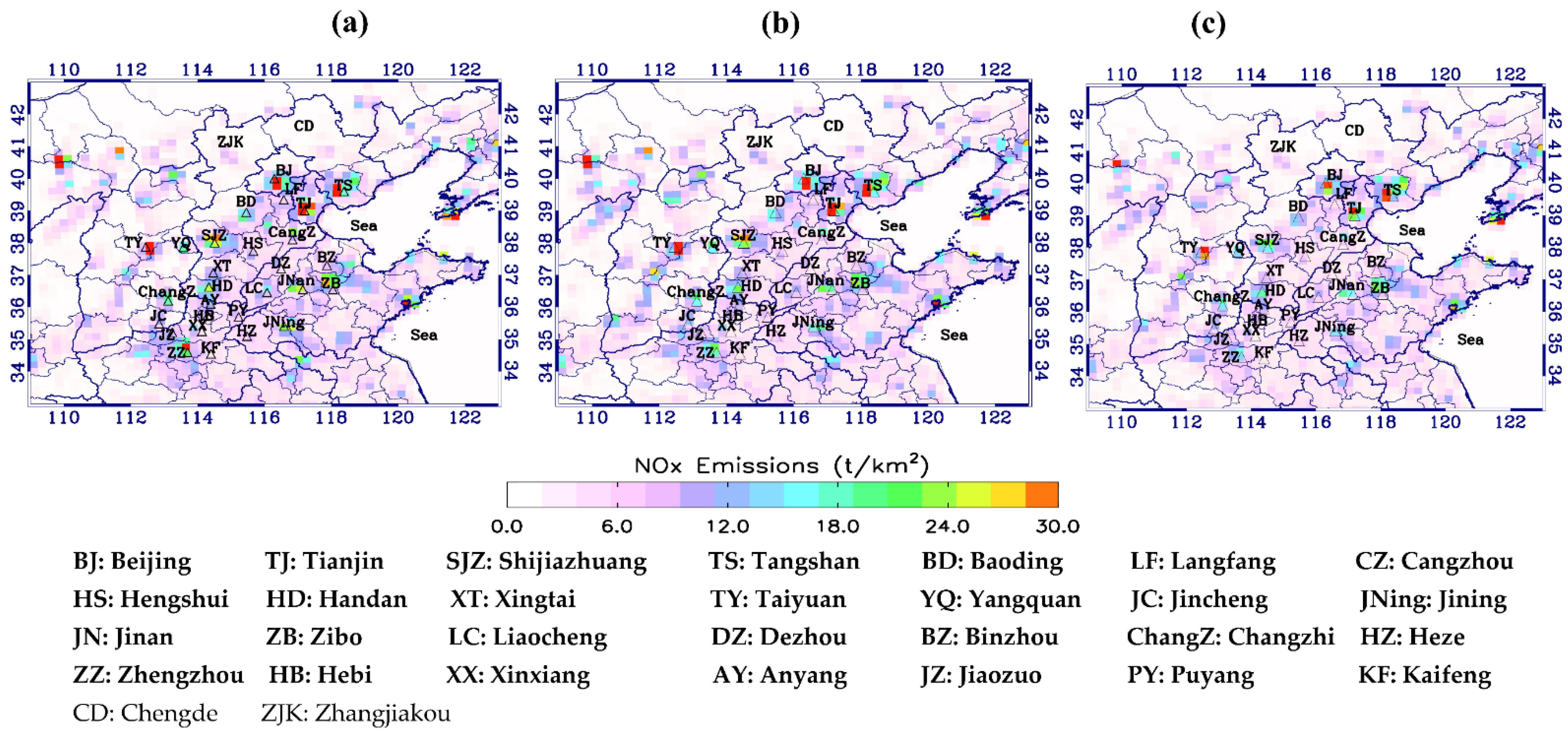
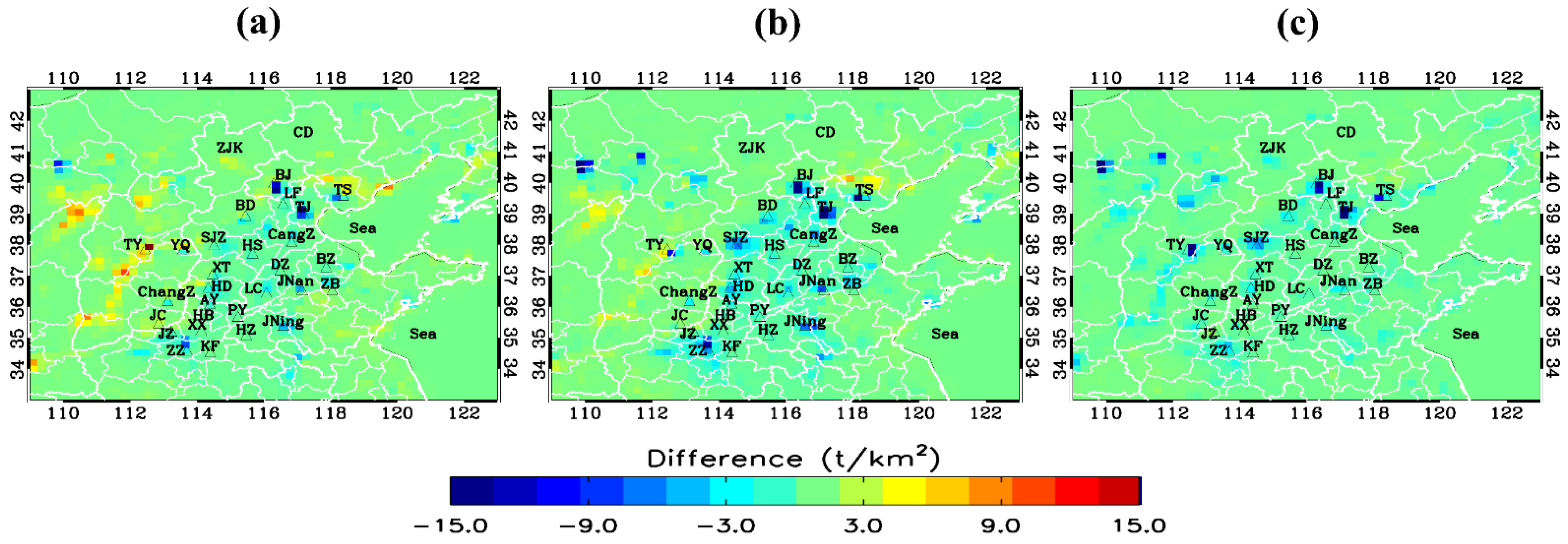
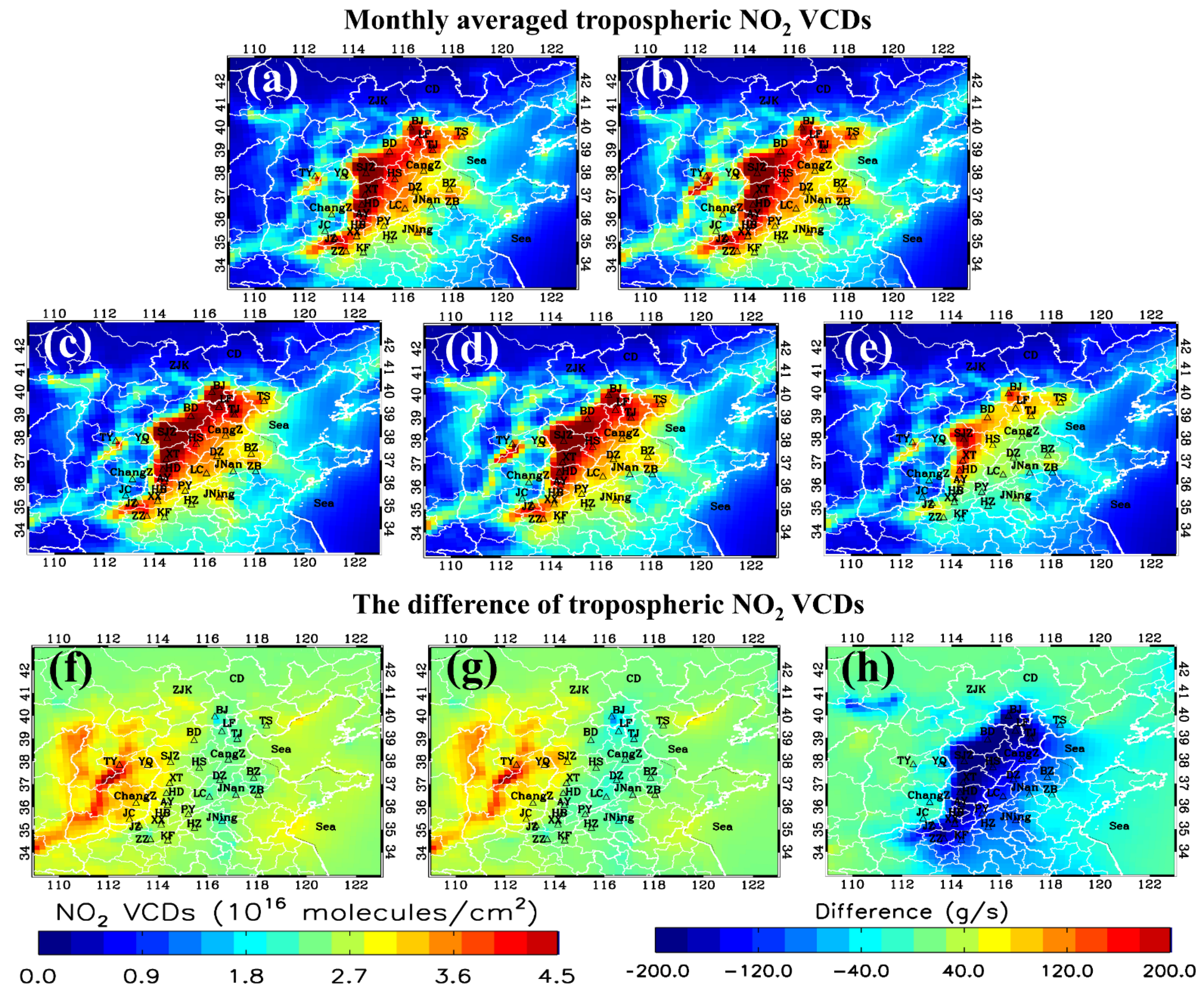
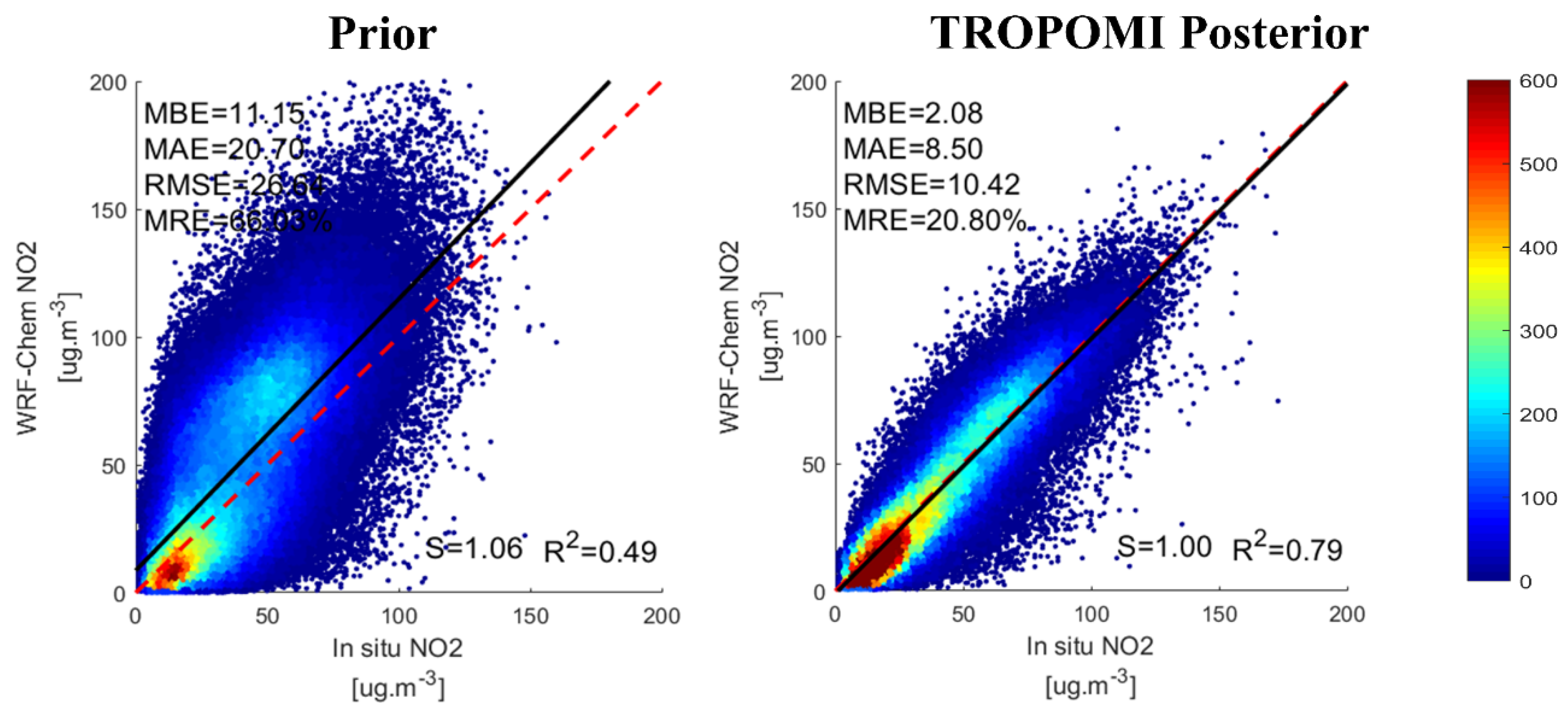
3.1. Top-down Emissions Evaluation
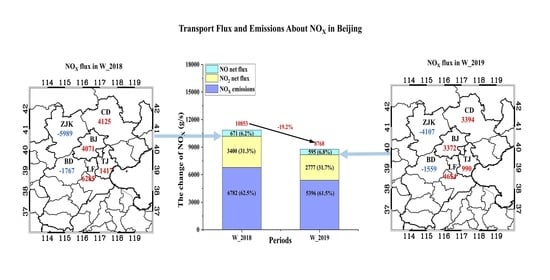
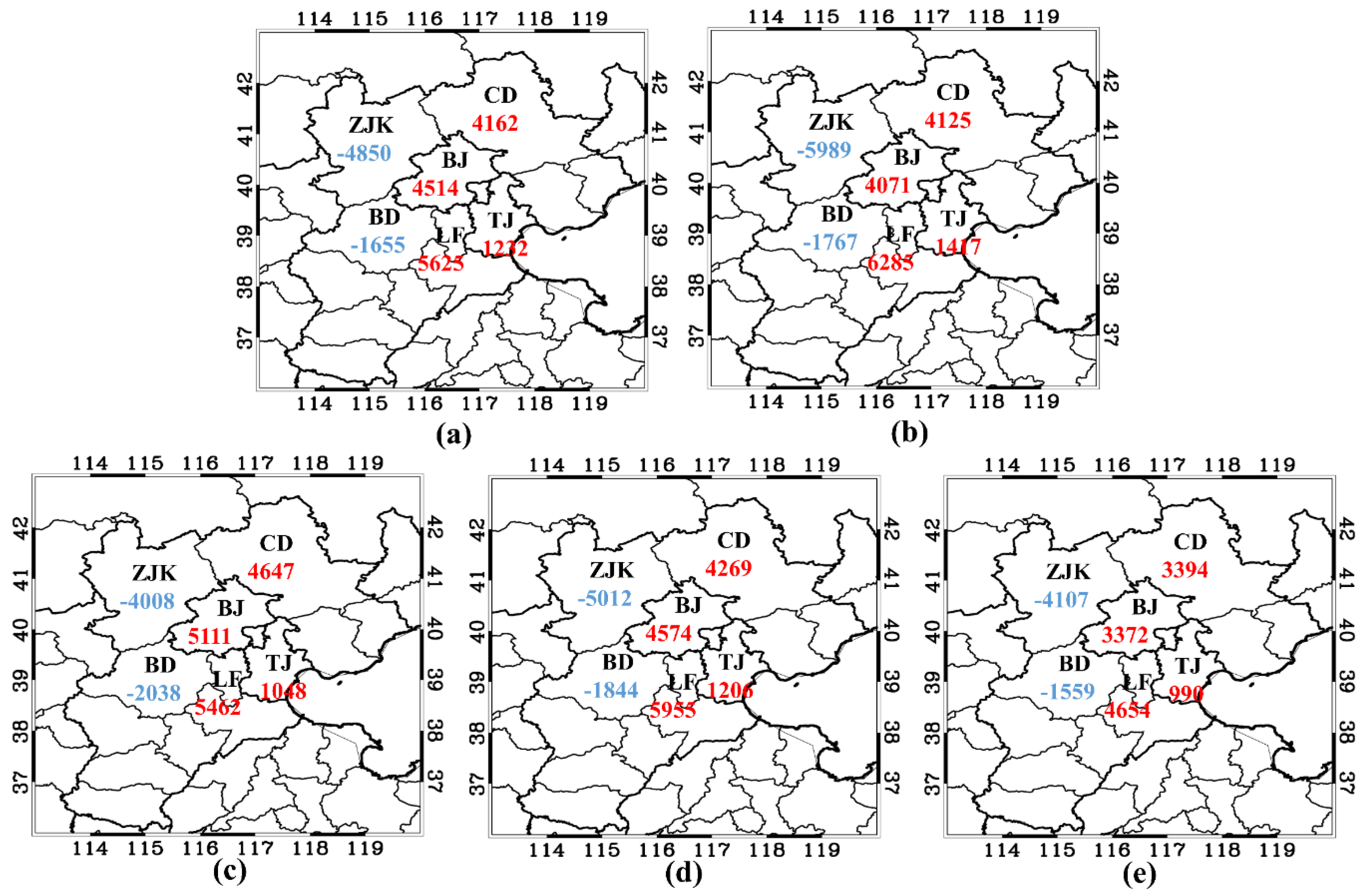
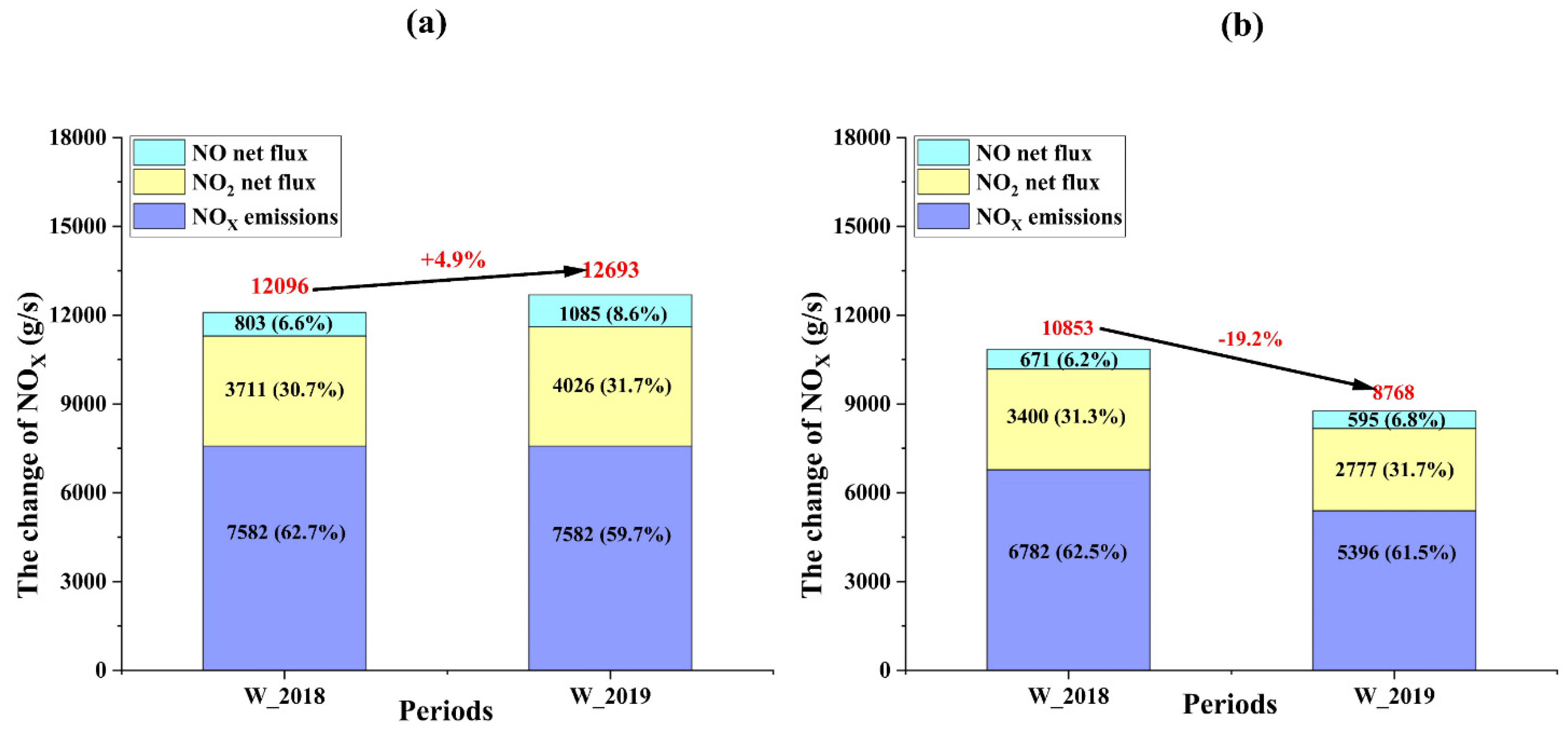
3.2. Regional Transport Flux
3.3. Assessment of City Boundary Transport Around BJ
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| “2 + 26” cities | |
| BJ | Beijing |
| TJ | Tianjin |
| SJZ | Shijiazhuang |
| TS | Tangshan |
| BD | Baoding |
| LF | Langfang |
| CZ | Cangzhou |
| HS | Hengshui |
| HD | Handan |
| XT | Xingtai |
| TY | Taiyuan |
| YQ | Yangquan |
| ChangZ | Changzhi |
| JC | Jincheng |
| JN | Jinan |
| ZB | Zibo |
| LC | Liaocheng |
| DZ | Dezhou |
| BZ | Binzhou |
| JNing | Jining |
| HZ | Heze |
| ZZ | Zhengzhou |
| XX | Xinxiang |
| HB | Hebi |
| AY | Anyang |
| JZ | Jiaozuo |
| PY | Puyang |
| KF | Kaifeng |
| ZJK | Zhangjiakou |
| CD | Chengde |
| Another two neighboring cities in the north of Beijing | |
| ZJK | Zhangjiakou |
| CD | Chengde |
References
- Vuuren, D.P.; Bouwman, L.F.; Smith, S.J.; Dentener, F. Global projections for anthropogenic reactive nitrogen emissions to the atmosphere: An assessment of scenarios in the scientific literature. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, A.; Javed, Z.; Jian, Z.; Zhang, S.; Bilal, M.; Xue, R.; Wang, S.; Bin, Z. Ground-Based MAX-DOAS observations of tropospheric NO2 and HCHO during COVID-19 lockdown and spring festival over Shanghai, China. Remote. Sens. 2021, 13, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Andersson, H.; Zhang, S. Air pollution control policies in China: A retrospective and prospects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Zhao, S.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.L.; Xie, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, H.; Xing, C.; et al. Estimation of winter time NOx emissions in Hefei, a typical inland city of China, using mobile MAX-DOAS observations. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.V.; Shi, Z.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Wang, S.; Harrison, R.M. Assessing the impact of clean air action on air quality trends in Beijing using a machine learning technique. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11303–11314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Guo, S.; Tan, Z.; Wang, H.; Shang, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y. Exploring atmospheric free-radical chemistry in China: The self-cleansing capacity and the formation of secondary air pollution. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Xing, C.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Xia, C.; Liu, H.; Cai, Z.; Liu, J. Tropospheric NO2, SO2, and HCHO over the East China Sea, using ship-based MAX-DOAS observations and comparison with OMI and OMPS satellite data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15387–15402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; de Foy, B.; Griffin, D.; McLinden, C.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Krotkov, N.A.; Eskes, H. Enhanced Capabilities of TROPOMI NO2: Estimating NOX from North American Cities and Power Plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12594–12601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucsela, E.J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Celarier, E.A.; Lamsal, L.N.; Swartz, W.H.; Bhartia, P.K.; Boersma, K.F.; Veefkind, J.P.; Gleason, J.F.; Pickering, K.E. A new stratospheric and tropospheric NO2 retrieval algorithm for nadir-viewing satellite instruments: Applications to OMI. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2607–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; van der, A.R.J.; Stammes, P.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J. Trends and trend reversal detection in 2 decades of tropospheric NO2 satellite observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 6269–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Jacob, D.J.; Li, K.; Silvern, R.F.; Zhai, S.; Liu, M.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Q. Effect of changing NOx lifetime on the seasonality and long-term trends of satellite-observed tropospheric NO2 columns over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, W.; Shan, C.; Hu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. FTIR time series of stratospheric NO2 over Hefei, China, and comparisons with OMI and GEOS-Chem model data. Opt. Express. 2019, 27, A1225–A1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrakou, T.; Müller, J.F.; Boersma, K.F.; De Smedt, I.; van der, A.R.J. Assessing the distribution and growth rates of NOx emission sources by inverting a 10-year record of NO2 satellite columns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorente, A.; Boersma, K.F.; Eskes, H.J.; Veefkind, J.P.; van Geffen, J.; de Zeeuw, M.B.; Denier van der Gon, H.A.C.; Beirle, S.; Krol, M.C. Quantification of nitrogen oxides emissions from build-up of pollution over Paris with TROPOMI. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.; Lin, J.; Zhang, R.; Liu, M.; Weng, H.; Ni, R.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, Q. High-resolution (0.05° × 0.05°) NOx emissions in the Yangtze River Delta inferred from OMI. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 12835–12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y. Assimilated inversion of NOx emissions over east Asia using OMI NO2 column measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.L.; Saide, P.E.; Lamsal, L.N.; de Foy, B.; Lu, Z.; Woo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Gao, M.; Carmichael, G.; et al. A top-down assessment using OMI NO2 suggests an underestimate in the NOx emissions inventory in Seoul, South Korea, during KORUS-AQ. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 1801–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinken, G.C.M.; Boersma, K.F.; van Donkelaar, A.; Zhang, L. Constraints on ship NOx emissions in Europe using GEOS-Chem and OMI satellite NO2 observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1353–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, Q.Z.; Zhang, R.; Lash, B.; Cohan, D.S.; Cooter, E.J.; Bash, J.O.; Lamsal, L.N. Enhanced representation of soil NO emissions in the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) model version 5.0.2. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 3177–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, A.H.; Choi, Y.; Jeon, W.; Li, X.; Pan, S.; Diao, L.; Westenbarger, D.A. Constraining NOx emissions using satellite NO2 measurements during 2013 DISCOVER-AQ Texas campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 131, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, B.A.; Laughner, J.L.; Wooldridge, P.J.; Crounse, J.D.; Dibb, J.; Diskin, G.; Peischl, J.; Podolske, J.R.; Pollack, I.B.; Ryerson, T.B.; et al. Lightning NOx emissions: Reconciling measured and modeled estimates with updated NOx chemistry. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9479–9488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Ding, K.; Huang, X.; Liu, L.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, F.; Fu, C.; Ding, A. Transport, mixing and feedback of dust, biomass burning and anthropogenic pollutants in eastern Asia: A case study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16345–16361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.J.; Duan, F.K.; Su, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Kimoto, T.; Chang, D.; et al. Exploring the severe winter haze in Beijing: The impact of synoptic weather, regional transport and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2969–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ding, A.; Cooper, O.; Huang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, D.; Wu, Z.; McClure-Begley, A.; Petropavlovskikh, I.; Andreae, M.O.; et al. ENSO and Southeast Asian biomass burning modulate subtropical trans-Pacific ozone transport. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xing, J.; Mathur, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Hao, J. Quantification of the enhancement of PM2.5 concentration by the downward transport of ozone from the stratosphere. Chemosphere 2020, 255, 126907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalmogith, S.S.; Harrison, R.M. The use of trajectory cluster analysis to examine the long-range transport of secondary inorganic aerosol in the UK. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6686–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Gui, H.; Du, P.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Lu, Y.; Liu, W.; Cheng, Y. Identification of long-range transport pathways and potential sources of PM2.5 and PM10 in Beijing from 2014 to 2015. J. Env. Sci. 2017, 56, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Q.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.L.; Hu, Q.; Xie, Z.; Liu, H.; Si, F.; Liu, J. Ship-based MAX-DOAS measurements of tropospheric NO2, SO2, and HCHO distribution along the Yangtze River. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 5931–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Ji, D.; Li, J.; Tang, X. Rapid formation and evolution of an extreme haze episode in Northern China during winter 2015. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Qingqing, Z.; Xuhui, C.; Mengting, G.; Yu, S.; Xiaoling, Z. Long-term mean footprint and its relationship to heavy air pollution episodes in Beijing. Acta Entiarum Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Yan, C.; Dong, C.; Meng, C.; Sui, X.; Yang, F.; Lu, Y.; Wang, W. Sources apportionment of PM2.5 in a background site in the North China Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Tao, M.; Xin, J.; Song, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, N.; Ying, K.; Wang, Y. PM2.5 Characteristics and regional transport contribution in five cities in southern north China plain, during 2013–2015. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Wang, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; Fu, S.; Qu, L.; Ji, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. PMF and PSCF based source apportionment of PM2.5 at a regional background site in North China. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Chan, K.L.; Gao, Y.; Huang, X.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.; Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; et al. Observations of the vertical distributions of summertime atmospheric pollutants and the corresponding ozone production in Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 14275–14289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhao, B.; Cai, S.; Hao, J. Assessment of inter-city transport of particulate matter in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4843–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Xing, J.; Chang, X.; Ding, D.; Zheng, H. Regional transport in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its changes during 2014–2017: The impacts of meteorology and emission reduction. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Xing, J.; Wang, S.; Chang, X.; Hao, J. Impacts of emissions and meteorological changes on China’s ozone pollution in the warm seasons of 2013 and 2017. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2019, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, X.; Brasseur, G.; Ying, Z. Impact of model resolution on chemical ozone formation in Mexico City: Application of the WRF-Chem model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8983–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Xie, Z.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Xie, P. A paradox for air pollution controlling in China revealed by “APEC Blue” and “Parade Blue”. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, H.; Geng, G.; Hong, C.; Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Cui, H.; Man, H.; et al. Anthropogenic emission inventories in China: A review. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 834–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s anthropogenic emissions since 2010 as the consequence of clean air actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu-Hua Chen, W.-Y.S. A one-dimensional time dependent cloud model. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacono, M.J.; Delamere, J.S.; Mlawer, E.J.; Shephard, M.W.; Clough, S.A.; Collins, W.D. Radiative forcing by long-lived greenhouse gases: Calculations with the AER radiative transfer models. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grell, G.A.; Freitas, S.R. A scale and aerosol aware stochastic convective parameterization for weather and air quality modeling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 13, 23845–23893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, M.; Chen, F.; Wang, W.; Dudhia, J.; LeMone, M.A.; Mitchell, K.M.; Ek, G.; Gayno, J.; Wegiel, R.; Cuenca, H. Implementation and verification of the unified NOAH land surface model in the WRF model. Geoscience 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.Y.; Yign, N.; Jimy, D. A new vertical diffusion package with an explicit treatment of entrainment processes. Mon. Weather Rev. 2006, 134, 2318–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Li, B.; Xing, C.; Tan, W.; Zhou, H.; Si, F.; et al. First observation of tropospheric nitrogen dioxide from the Environmental Trace Gases Monitoring Instrument onboard the GaoFen-5 satellite. Light Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cugny, B.; Karafolas, N.; Armandillo, E.; van der Valk, N.; Lobb, D.; de Vries, J.; Veefkind, P.; Aben, I.; Wood, T.; Bhatti, I.S.; et al. TROPOMI, the Sentinel 5 precursor instrument for air quality and climate observations: Status of the current design. In International Conference on Space Optics—ICSO 2012; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, Washington, DC, USA, 2017; Volume 10546, p. 105641Q. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Su, W.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Fan, G.; Xie, Z.; Huang, X.; Zhang, T.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Ji, X.; et al. Characterization of ozone in the lower troposphere during the 2016 G20 conference in Hangzhou. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayt, C.; De Smedt, I.; Letocart, V.; Merlaud, A.; Pinardi, G.; Van Roozendael, M.; Roozendael, M. QDOAS Software user manual. Belg. Inst. Space Aeron. Bruss. Belg. 2011, 1, 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Zara, M.; Boersma, K.F.; De Smedt, I.; Richter, A.; Peters, E.; van Geffen, J.H.G.M.; Beirle, S.; Wagner, T.; Van Roozendael, M.; Marchenko, S.; et al. Improved slant column density retrieval of nitrogen dioxide and formaldehyde for OMI and GOME-2A from QA4ECV: Intercomparison, uncertainty characterisation, and trends. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 4033–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurr, R.J.D. VLIDORT: A linearized pseudo-spherical vector discrete ordinate radiative transfer code for forward model and retrieval studies in multilayer multiple scattering media. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2006, 102, 316–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veefkind, J.P.; de Haan, J.F.; Sneep, M.; Levelt, P.F. Improvements to the OMI O2–O2 operational cloud algorithm and comparisons with ground-based radar-lidar observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 6035–6049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beirle, S.; Hormann, C.; Jockel, P.; Liu, S.; de Vries, M.P.; Pozzer, A.; Sihler, H.; Valks, P.; Wagner, T. The stratospheric estimation algorithm from Mainz (STREAM): Estimating stratospheric NO2 from nadir-viewing satellites by weighted convolution. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 9, 2753–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Cai, Z.; Su, W.; Xia, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, J. Satellite UV-Vis spectroscopy: Implications for air quality trends and their driving forces in China during 2005–2017. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlmann, G.; Hartl, A.; Cheung, H.M.; Lam, Y.F.; Wenig, M.O. A novel gridding algorithm to create regional trace gas maps from satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 451–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Liu, C.; Chan, K.L.; Hu, Q.; Liu, H.; Ji, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. An improved TROPOMI tropospheric HCHO retrieval over China. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 6271–6292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.W.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Leaitch, W.R.; MacDonald, A.M.; Anlauf, K.G.; Cohen, R.C.; Bertram, T.H.; Huey, L.G.; Avery, M.A.; et al. Trans-Pacific transport of reactive nitrogen and ozone to Canada during spring. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 8353–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamsal, L.N.; Martin, R.V.; Padmanabhan, A.; van Donkelaar, A.; Zhang, Q.; Sioris, C.E.; Chance, K.; Kurosu, T.P.; Newchurch, M.J. Application of satellite observations for timely updates to global anthropogenic NOx emission inventories. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.J.; Boersma, K.F.; Ganzeveld, L.N.; Krol, M.C. European NOx emissions in WRF-Chem derived from OMI: Impacts on summertime surface ozone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11821–11841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, T.; Xie, M.; Zhao, H. Numerical modeling of a continuous photochemical pollution episode in Hong Kong using WRF–chem. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8717–8727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhou, W.; Wu, S.; Niu, Z.; Cheng, P.; Xiong, X.; Li, G. High-resolution simulation of wintertime fossil fuel CO2 in Beijing, China: Characteristics, sources, and regional transport. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 198, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Yan, Y.; He, J. Relay transport of aerosols to Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region by multi-scale atmospheric circulations. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Lu, X.; Ji, D.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Carmichael, G.R. Distinguishing the roles of meteorology, emission control measures, regional transport, and co-benefits of reduced aerosol feedbacks in “APEC Blue”. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 167, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Voulgarakis, A.; Wang, T.; Kasoar, M.; Wells, C.; Yuan, C.; Varma, S.; Mansfield, L. A study of the effect of aerosols on surface ozone through meteorology feedbacks over China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 5705–5718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Uno, I.; Yumimoto, K.; Itahashi, S.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z. Impacts of COVID-19 lockdown, Spring Festival and meteorology on the NO2 variations in early 2020 over China based on in-situ observations, satellite retrievals and model simulations. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 244, 117972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, X.; Shen, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gui, K.; Zhao, T.; Liao, H. Fine particulate matter (PM2.5) trends in China, 2013–2018: Separating contributions from anthropogenic emissions and meteorology. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 11031–11041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, Q.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, A.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Shi, L.; Li, R.; Azari, M.; et al. Air quality changes during the COVID-19 lockdown over the Yangtze River Delta Region: An insight into the impact of human activity pattern changes on air pollution variation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, O.E.; Shepson, P.B.; Ren, X.; He, H.; Hall, D.L.; Dickerson, R.R.; Stirm, B.H.; Brown, S.S.; Fibiger, D.L.; McDuffie, E.E.; et al. Top-Down estimates of NOx and CO emissions from Washington, D.C.-Baltimore during the winter campaign. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Nielsen-Gammon, J.W.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of three planetary boundary layer schemes in the WRF model. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Schemes | Description |
|---|---|
| Microphysics | Purdue Lin Scheme [43] |
| Longwave radiation | Rapid radiative transfer model (RRTMG) scheme [44] |
| Shortwave radiation | RRTMG scheme |
| Cumulus parameterization | Grell–Freitas Ensemble Scheme [45] |
| Land surface | Unified Noah Land Surface Model [46] |
| Planetary boundary layer | Yonsei University scheme [47] |
| Chemical mechanism | Carbon-Bond Mechanism version Z |
| Photolysis scheme | Fast-J photolysis |
| Meteorological Parameter | Statistic | Unit | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed | MeanOBS | (m/s) | 4.32 | |
| MeanPRD | (m/s) | 3.97 | ||
| Bias | (m/s) | 0.37 | ≤±0.5 | |
| GrossError | (m/s) | 1.13 | <2 | |
| Root mean square error (RMSE) | (m/s) | 1.86 | <2 | |
| Wind Direction | MeanOBS | (°) | 337 | |
| MeanPRD | (°) | 288 | ||
| Bias | (°) | 5.25 | ≤10 | |
| GrossError | (°) | 48.32 | ≤±30 | |
| RMSE | (°) | 79.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Gao, M.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Tian, Y.; Yan, L.; Su, W.; Hong, X.; et al. Quantifying Contributions of Local Emissions and Regional Transport to NOX in Beijing Using TROPOMI Constrained WRF-Chem Simulation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091798
Zhu Y, Hu Q, Gao M, Zhao C, Zhang C, Liu T, Tian Y, Yan L, Su W, Hong X, et al. Quantifying Contributions of Local Emissions and Regional Transport to NOX in Beijing Using TROPOMI Constrained WRF-Chem Simulation. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091798
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yizhi, Qihou Hu, Meng Gao, Chun Zhao, Chengxin Zhang, Ting Liu, Yuan Tian, Liu Yan, Wenjing Su, Xinhua Hong, and et al. 2021. "Quantifying Contributions of Local Emissions and Regional Transport to NOX in Beijing Using TROPOMI Constrained WRF-Chem Simulation" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091798
APA StyleZhu, Y., Hu, Q., Gao, M., Zhao, C., Zhang, C., Liu, T., Tian, Y., Yan, L., Su, W., Hong, X., & Liu, C. (2021). Quantifying Contributions of Local Emissions and Regional Transport to NOX in Beijing Using TROPOMI Constrained WRF-Chem Simulation. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1798. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091798