A Comparison of Wintertime Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights Determined by Tethered Balloon Soundings and Lidar at the Site of SACOL
Abstract
1. Introduction
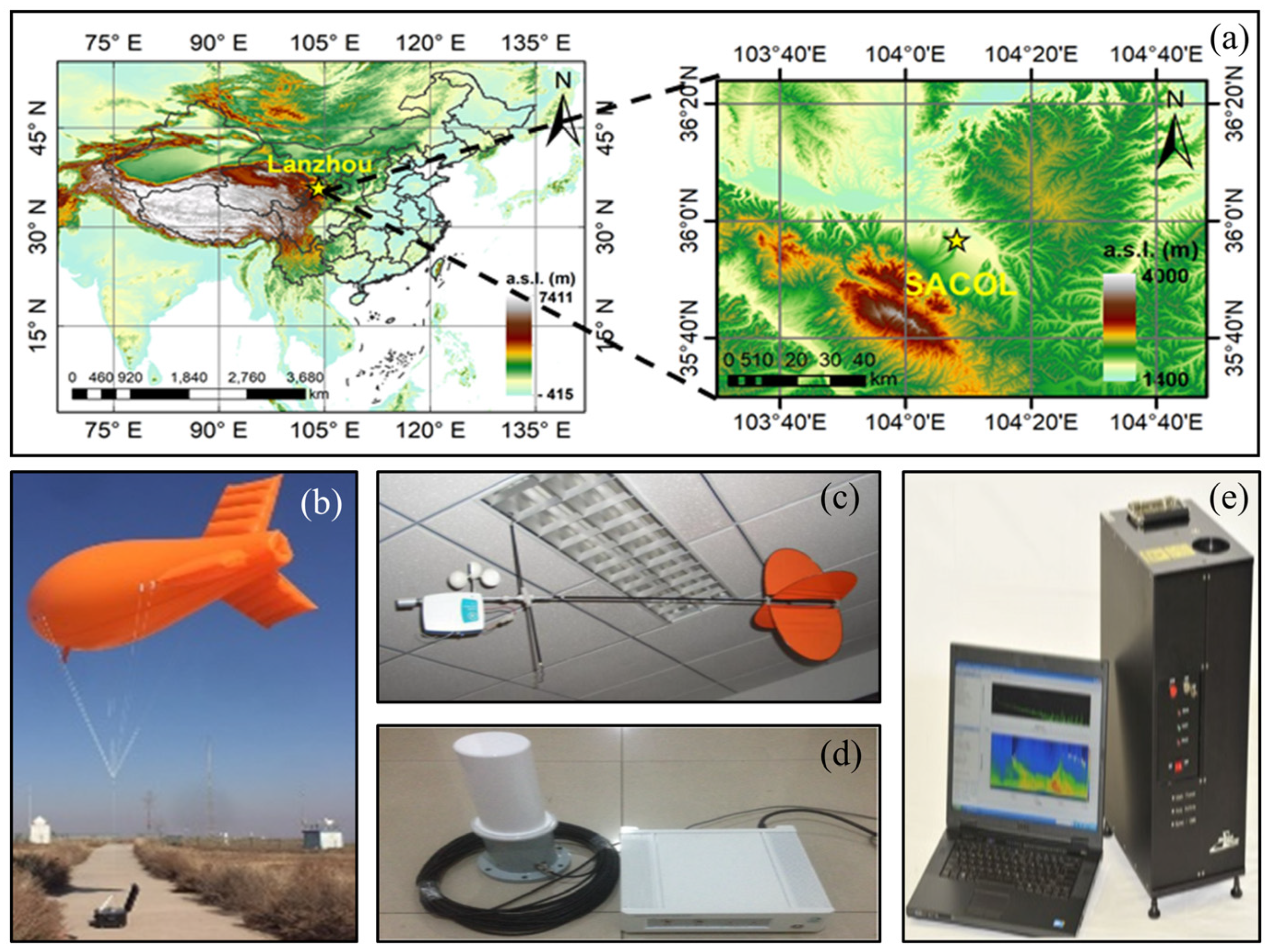
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
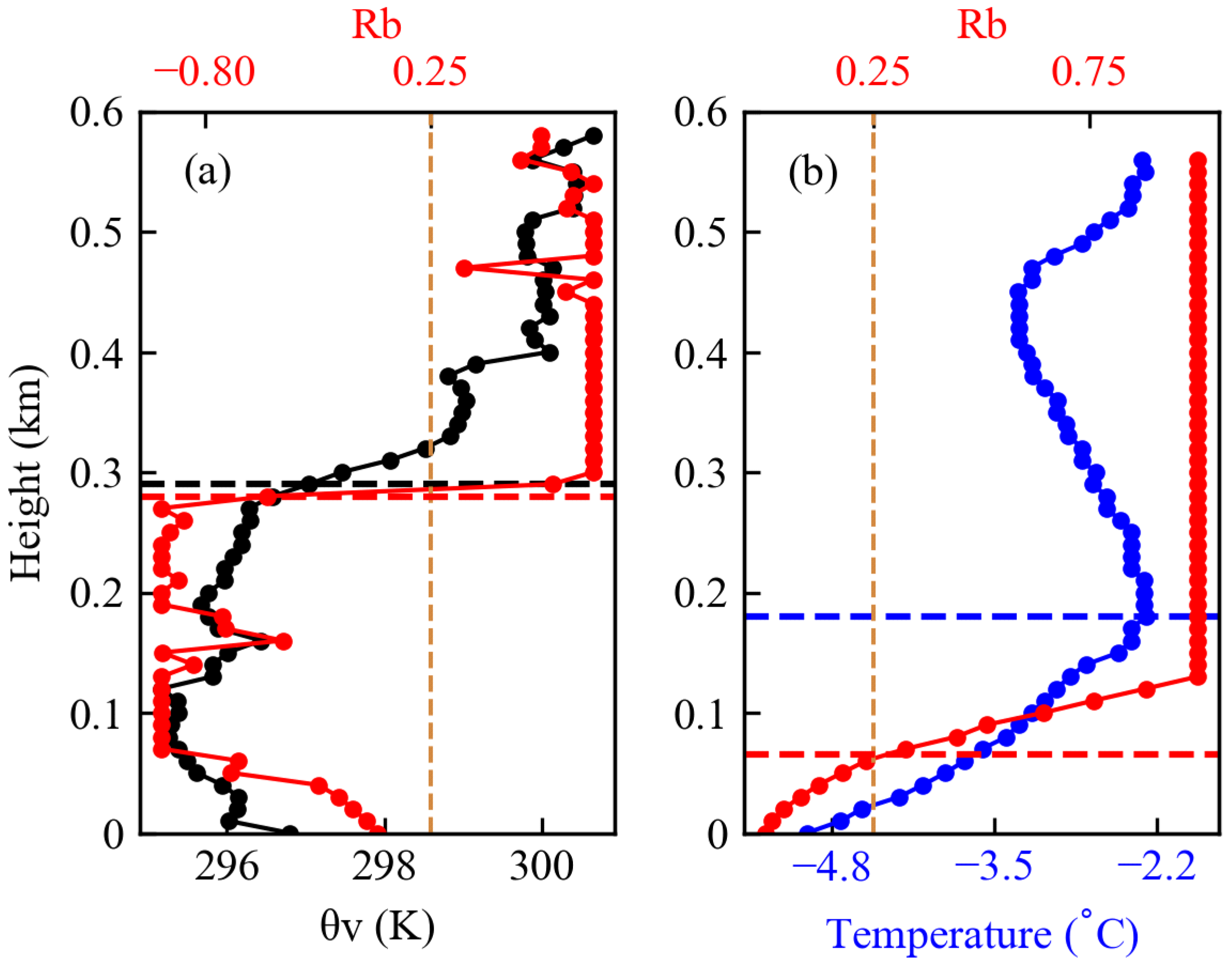
2.2. Determining BLH from TBS Data
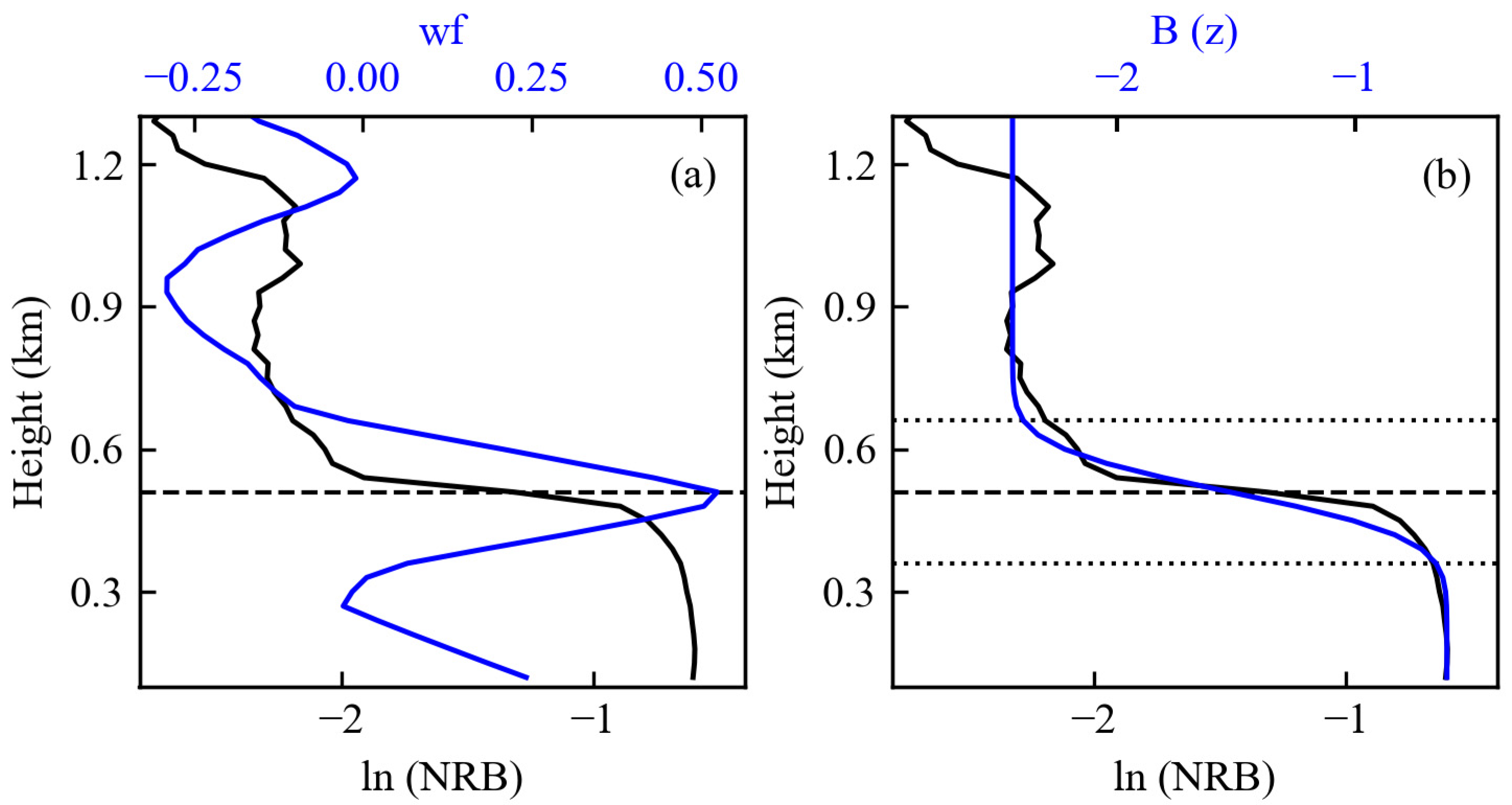
2.3. Determining BLH from Lidar Observations
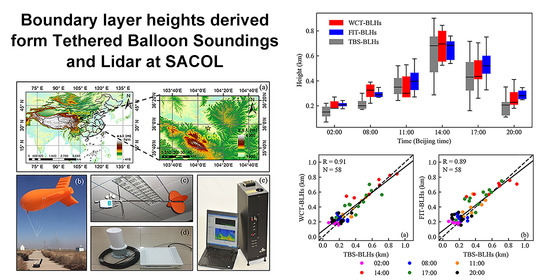
3. Results
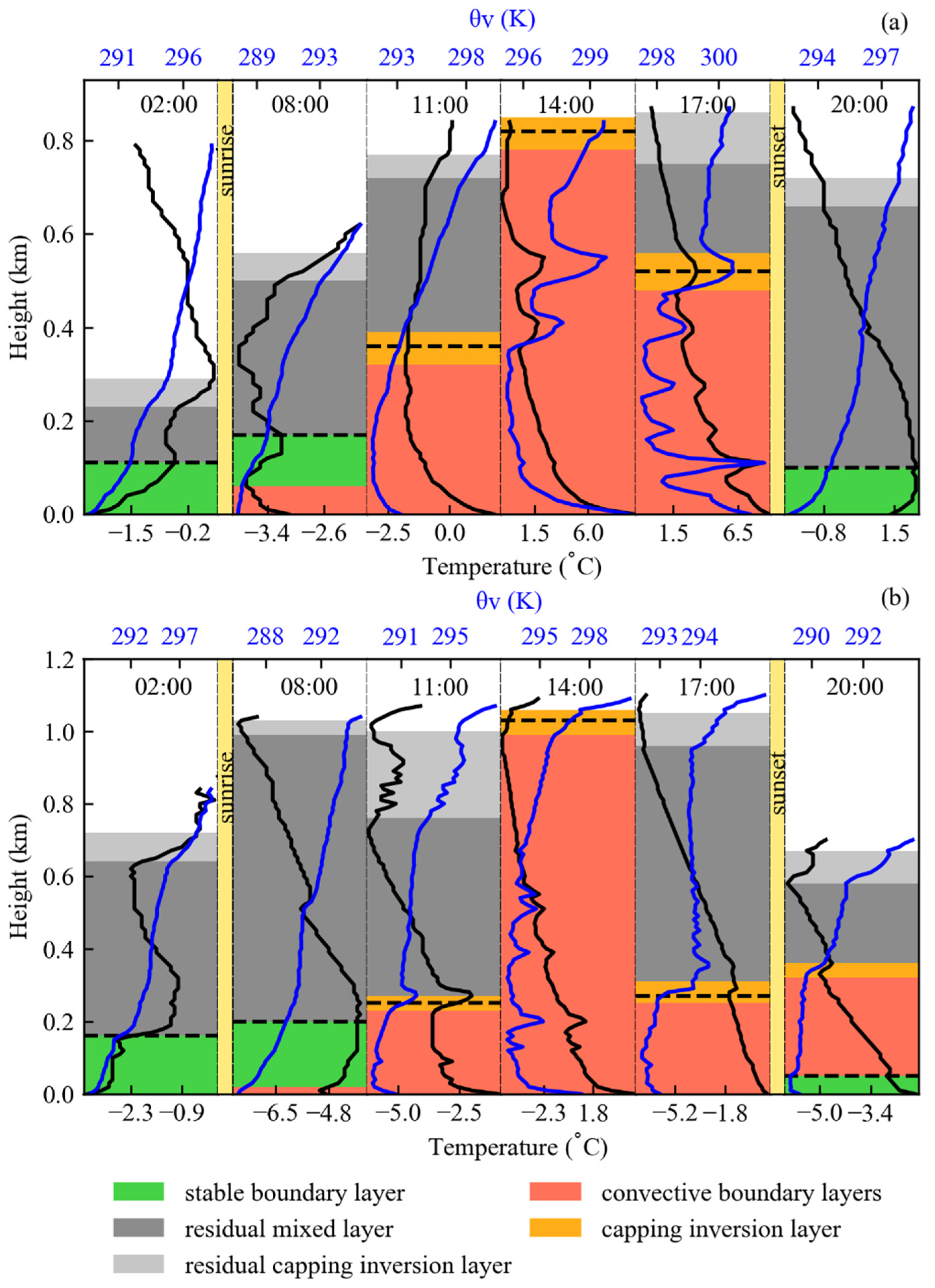
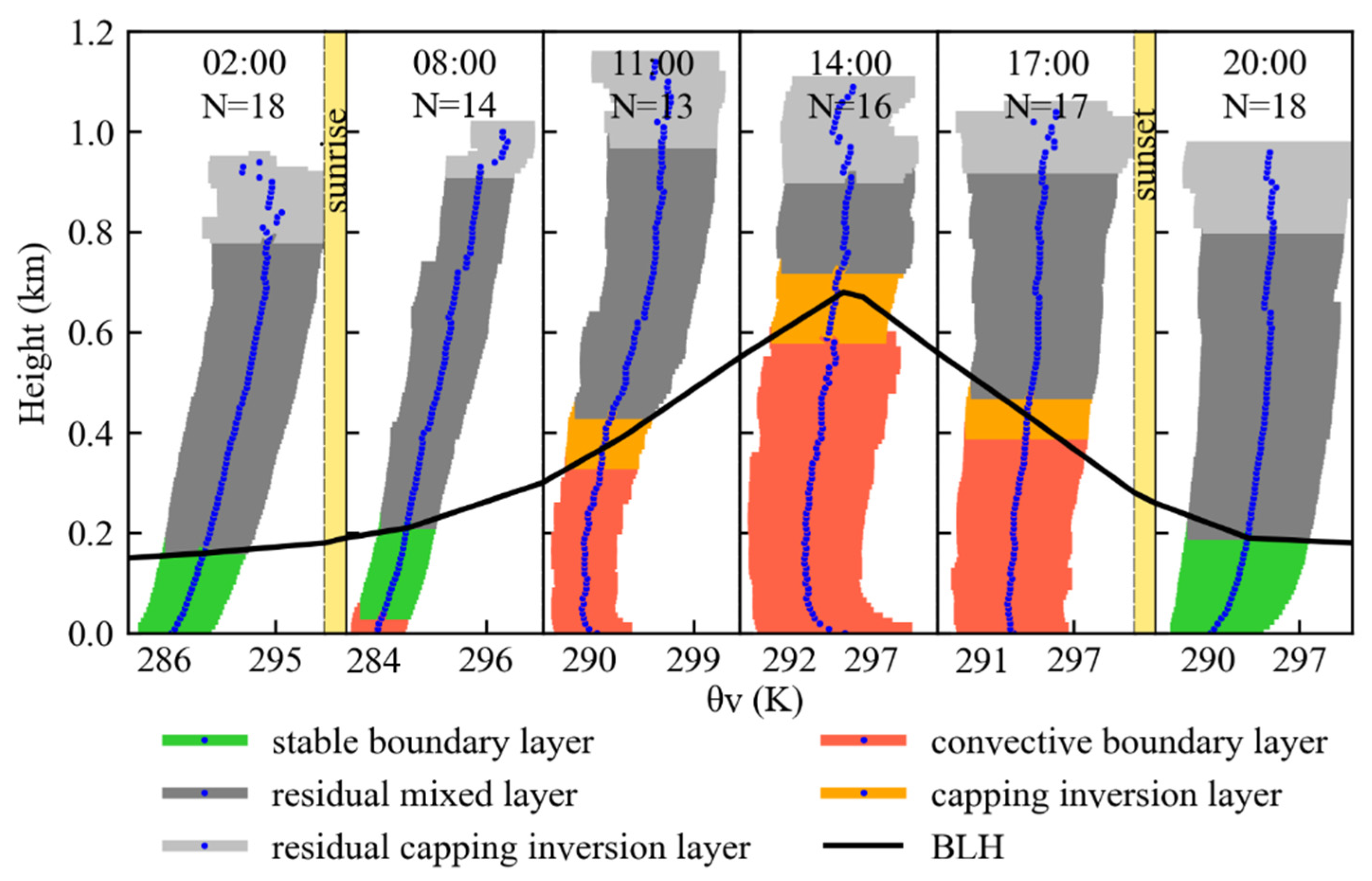
3.1. Diurnal Variations in Atmospheric Boundary Layer from TBS Data
3.2. Diurnal Variations in Atmospheric Boundary Layer from Lidar Data
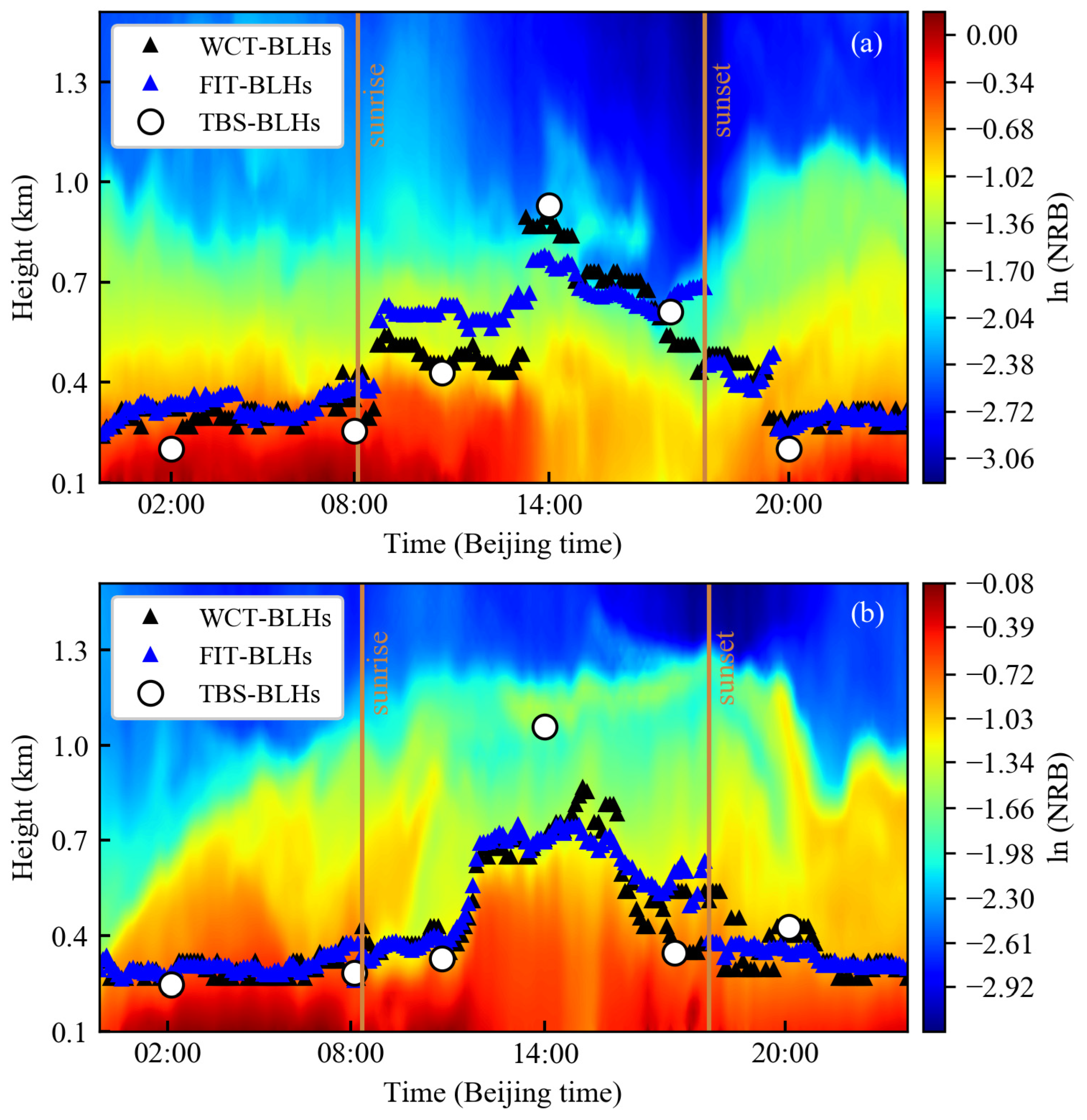
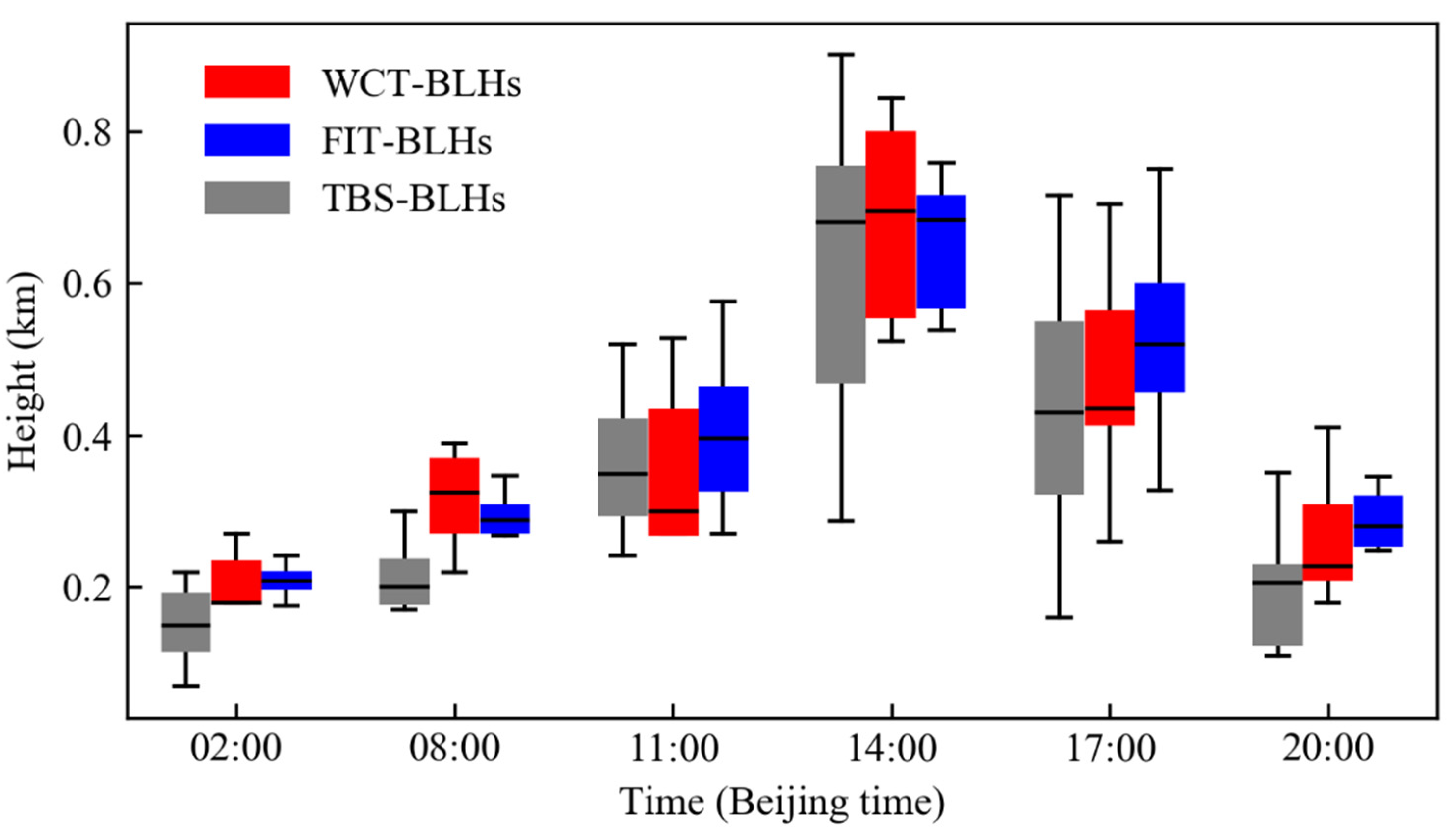
3.3. Comparison between BLHs Derived from Lidar Observations and TBS Data
4. Summary and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stull, R.B. An Introduction to Boundary Layer Meteorology. Atmos. Sci. Libr. 1988, 8, 89. [Google Scholar]
- Barbaro, E.; de Arellano, J.V.-G.; Ouwersloot, H.G.; Schröter, J.S.; Donovan, D.P.; Krol, M.C. Aerosols in the convective boundary layer: Shortwave radiation effects on the coupled land-atmosphere system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 5845–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, G.; Guo, J.; Hu, B.; Song, T.; Wang, L.; Xin, J.; Gao, W.; Münkel, C.; Schäfer, K.; et al. Mixing layer height on the North China Plain and meteorological evidence of serious air pollution in southern Hebei. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4897–4910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Su, T.; Chen, T.; Wei, J.; Cribb, M. The Urban–Rural Heterogeneity of Air Pollution in 35 Metropolitan Regions across China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Gao, W.; Cheng, M.; Xin, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Mortality and air pollution in Beijing: The long-term relationship. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 150, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandou, A.; Tombrou, M.; Schäfer, K.; Emeis, S.; Protonotariou, A.P.; Bossioli, E.; Soulakellis, N.; Suppan, P. A Comparison Between Modelled and Measured Mixing-Layer Height Over Munich. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2009, 131, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Kahn, R. Relationships between the planetary boundary layer height and surface pollutants derived from lidar observations over China: Regional pattern and influencing factors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 15921–15935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, S.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, R.; Liu, S. Interaction Between Planetary Boundary Layer and PM2.5 Pollution in Megacities in China: A Review. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2019, 5, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Lv, L.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Z. Atmosphere boundary layer height and its effect on air pollutants in Beijing during winter heavy pollution. Atmos. Res. 2019, 215, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H.; Miao, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Yim, S.H.L.; et al. Diurnal Evolution of the Wintertime Boundary Layer in Urban Beijing, China: Insights from Doppler Lidar and a 325-m Meteorological Tower. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, D.; Zhao, C.; Kwan, M.P.; Cai, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Influence of meteorological conditions on PM2.5 concentrations across China: A review of methodology and mechanism. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Ding, A.; Liao, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Xue, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, B. Aerosol and boundary-layer interactions and impact on air quality. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 810–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Gao, C.Y.; Hong, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, S.; Zhu, B. Surface Meteorological Conditions and Boundary Layer Height Variations During an Air Pollution Episode in Nanjing, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 3350–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Cai, X.; Fan, S.; Song, Y.; Hu, F.; Che, H.; Quan, J.; Kang, L.; et al. Research Progress on Estimation of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height. J. Meteorol. Res. 2020, 34, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrero, L.; Riccio, A.; Perrone, M.G.; Sangiorgi, G.; Ferrini, B.S.; Bolzacchini, E. Mixing height determination by tethered balloon-based particle soundings and modeling simulations. Atmos. Res. 2011, 102, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Zhang, Y.; Beljaars, A.; Golaz, J.-C.; Jacobson, A.R.; Medeiros, B. Climatology of the planetary boundary layer over the continental United States and Europe. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Bian, L.; et al. The climatology of planetary boundary layer height in China derived from radiosonde and reanalysis data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 13309–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Liu, H.; Song, Y.; Fang, Z.; He, J.; Lou, M.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. On the Summertime Planetary Boundary Layer with Different Thermodynamic Stability in China: A Radiosonde Perspective. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, P.; Ma, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Climatology of mixing layer height in China based on multi-year meteorological data from 2000 to 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allabakash, S.; Lim, S. Climatology of Planetary Boundary Layer Height-Controlling Meteorological Parameters Over the Korean Peninsula. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Xiang, P.; Lau, A.K.-H.; Guo, J.; Yang, D.; Miao, Y. An intercomparison of long-term planetary boundary layer heights retrieved from CALIPSO, ground-based lidar, and radiosonde measurements over Hong Kong. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 3929–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Arruda Moreira, G.; Guerrero-Rascado, J.L.; Bravo-Aranda, J.A.; Benavent-Oltra, J.A.; Ortiz-Amezcua, P.; Róman, R.; Bedoya-Velásquez, A.E.; Landulfo, E.; Alados-Arboledas, L. Study of the planetary boundary layer by microwave radiometer, elastic lidar and Doppler lidar estimations in Southern Iberian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 213, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Tang, G.; Lv, F.; Hu, B.; Cheng, M.; Münkel, C.; Schäfer, K.; Xin, J.; An, X.; Wang, G.; et al. The spatial representativeness of mixing layer height observations in the North China Plain. Atmos. Res. 2018, 209, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Pan, Y.N.; Wang, W. Random Sample Fitting Method to Determine the Planetary Boundary Layer Height Using Satellite-Based Lidar Backscatter Profiles. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Gao, Z.; Kalogiros, J.; Li, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, X. Estimate of boundary-layer depth in Nanjing city using aerosol lidar data during 2016–2017 winter. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 205, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotthaus, S.; Haeffelin, M.; Drouin, M.-A.; Dupont, J.-C.; Grimmond, S.; Haefele, A.; Hervo, M.; Poltera, Y.; Wiegner, M. Tailored Algorithms for the Detection of the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height from Common Automatic Lidars and Ceilometers (ALC). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Guo, J.; Gong, W.; Shi, Y.; Jin, S. Boundary Layer Height as Estimated from Radar Wind Profilers in Four Cities in China: Relative Contributions from Aerosols and Surface Features. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiridis, V.; Melas, D.; Balis, D.S.; Papayannis, A.; Founda, D.; Katragkou, E.; Giannakaki, E.; Mamouri, R.E.; Gerasopoulos, E.; Zerefos, C. Aerosol Lidar observations and model calculations of the Planetary Boundary Layer evolution over Greece, during the March 2006 Total Solar Eclipse. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 6181–6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.R.; Welton, E.J.; Molod, A.M.; Joseph, E. Improved boundary layer depth retrievals from MPLNET. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9870–9879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, K.; Giannakaki, E.; Mielonen, T.; Pfüller, A.; Laakso, L.; Vakkari, V.; Baars, H.; Engelmann, R.; Beukes, J.P.; Van Zyl, P.G.; et al. Atmospheric Boundary Layer Top Height in South Africa: Measurements with Lidar and Radiosonde Compared to Three Atmospheric Models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4263–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ye, J.; Xin, J.; Zhang, W.; Vilà-Guerau de Arellano, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, D.; Dai, L.; Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; et al. The Stove, Dome, and Umbrella Effects of Atmospheric Aerosol on the Development of the Planetary Boundary Layer in Hazy Regions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.J.; Gamage, N.; Hagelberg, C.R.; Kiemle, C.; Lenschow, D.H.; Sullivan, P.P. An Objective Method for Deriving Atmospheric Structure from Airborne Lidar Observations: American Meteorological Society. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2000, 17, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisperuza, D.J.; Bedoya, A.E.; Alegría, D.L.; Múnera, M.; Jiménez, J.F.; Zapata, C.E.; Bastidas, Á. Lidar measurements and wavelet covariance transform method to estimate the atmospheric boundary layer heights in Medellín, Colombia. Óptica Pura Aplicada 2014, 47, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelini, F.; Gobbi, G.P. Some remarks about lidar data preprocessing and different implementations of the gradient method for determining the aerosol layers. Ann. Geophys. 2014, 57, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Steven, D.G.; Baldi, M.; Hoff, R.M. The Detection of Mixed Layer Depth and Entrainment Zone Thickness from Lidar Backscatter Profiles: American Meteorological Society. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 1999, 16, 953–959. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gbaguidi, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Wang, X.; Matsui, I.; Sun, Y. Technical note: Boundary layer height determination from lidar for improving air pollution episode modeling: Development of new algorithm and evaluation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 6215–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkalis, P.; Alexiou, D.; Papayannis, A.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Soupiona, O.; Raptis, P.-I.; Mylonaki, M.; Tzanis, C.G.; Christodoulakis, J. Application and Testing of the Extended-Kalman-Filtering Technique for Determining the Planetary Boundary-Layer Height over Athens, Greece. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2020, 176, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Li, Z.; Kahn, R. A new method to retrieve the diurnal variability of planetary boundary layer height from lidar under different thermodynamic stability conditions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Gong, W.; Logan, T. Linear segmentation algorithm for detecting layer boundary with lidar. Opt Express 2013, 21, 26876–26887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, V.; Li, Z. Detection, variations and intercomparison of the planetary boundary layer depth from radiosonde, lidar and infrared spectrometer. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltera, Y.; Martucci, G.; Collaud Coen, M.; Hervo, M.; Emmenegger, L.; Henne, S.; Brunner, D.; Haefele, A. PathfinderTURB: An automatic boundary layer algorithm. Development, validation and application to study the impact on in situ measurements at the Jungfraujoch. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 10051–10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. Atmosphere Boundary Layer Height (ABLH) Determination under Multiple-Layer Conditions Using Micro-Pulse Lidar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Wang, N.; Shen, X.; Xiao, D.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, D. Determination of Planetary Boundary Layer height with Lidar Signals Using Maximum Limited Height Initialization and Range Restriction (MLHI-RR). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, P.; Beyrich, F.; Gryning, S.-E.; Joffre, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Tercier, P. Review and intercomparison of operational methods for the determination of the mixing height. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 1, 569–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, D.J.; Ao, C.O.; Li, K. Estimating climatological planetary boundary layer heights from radiosonde observations: Comparison of methods and uncertainty analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, J.; Goloub, P. Determination and climatology of the diurnal cycle of the atmospheric mixing layer height over Beijing 2013–2018: Lidar measurements and implications for air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 8839–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Notholt, J.; Zhou, B.; Liu, R.; Zhang, B. Lidar measurement of planetary boundary layer height and comparison with microwave profiling radiometer observation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 1965–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrigtsen, B.H. Calibration of the AIRS microwave instruments. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, V.; Rappenglück, B.; Lefer, B.; Morris, G.; Toledo, D.; Delgado, R. Comparison of aerosol lidar retrieval methods for boundary layer height detection using ceilometer aerosol backscatter data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 1609–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, J.C.; Delgado, R.; Berkoff, T.A.; Hoff, R.M. Determination of Planetary Boundary Layer Height on Short Spatial and Temporal Scales: A Demonstration of the Covariance Wavelet Transform in Ground-Based Wind Profiler and Lidar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeffelin, M.; Angelini, F.; Morille, Y.; Martucci, G.; Frey, S.; Gobbi, G.P.; Lolli, S.; O’Dowd, C.D.; Sauvage, L.; Xueref-Rémy, I.; et al. Evaluation of Mixing-Height Retrievals from Automatic Profiling Lidars and Ceilometers in View of Future Integrated Networks in Europe. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2011, 143, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S. A Review of Techniques for Diagnosing the Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height (ABLH) Using Aerosol Lidar Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Jin, L.; Chen, H.; Wen, H. Measuring boundary-layer height under clear and cloudy conditions using three instruments. Particuology 2016, 28, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Hong, J.-W.; Lee, K.; Hong, J.; Velasco, E.; Lim, Y.J.; Lee, J.B.; Nam, K.; Park, J. Ceilometer Monitoring of Boundary-Layer Height and Its Application in Evaluating the Dilution Effect on Air Pollution. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2019, 172, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Hu, X.-M.; Huang, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T. Evaluation of retrieval methods of daytime convective boundary layer height based on lidar data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 4578–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J. Determination of boundary layer top on the basis of the characteristics of atmospheric particles. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 178, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, F.; Fan, G.; Zhang, Z. Multiple technical observations of the atmospheric boundary layer structure of a red-alert haze episode in Beijing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 4887–4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, M.; Pérez, C.; Rocadenbosch, F.; Baldasano, J.M.; García-Vizcaino, D. Mixed-Layer Depth Determination in the Barcelona Coastal Area from Regular Lidar Measurements: Methods, Results and Limitations. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2005, 119, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzworth, G.C. Estimates of mean maximum mixing depths in the contiguous United States. Mon. Weather Rev. 1964, 92, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelezang, D.H.P.; Holtslag, A.A.M. Evaluation and Model Impacts of Alternative Boundary-Layer Height Formulations. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1996, 81, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.S.; Keimig, F.T.; Diaz, H.F. Recent changes in the North American Arctic boundary layer in winter. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 8851–8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, M.C.; Praz, C.; Haefele, A.; Ruffieux, D.; Kaufmann, P.; Calpini, B. Determination and climatology of the planetary boundary layer height above the Swiss plateau by in situ and remote sensing measurements as well as by the COSMO-2 model. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13205–13221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichugina, Y.L.; Banta, R.M. Stable Boundary Layer Depth from High-Resolution Measurements of the Mean Wind Profile. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbu, T. Robust Anisotropic Diffusion Scheme for Image Noise Removal. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2014, 35, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilitinkevich, S.; Baklanov, A. Calculation of The Height of the Stable Boundary Layer in Practical Applications. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2002, 105, 389–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, I.M. Finding Boundary Layer Top: Application of a Wavelet Covariance Transform to Lidar Backscatter Profiles. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2003, 20, 1092–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eresmaa, N.; Karppinen, A.; Joffre, S.M.; Rasanen, J.; Talvitie, H. Mixing height determination by ceilometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, N.; Hagelberg, C. Detection and Analysis of Microfronts and Associated Coherent Evebts Using Localized Transforms. J. Atmos. Sci. 1993, 50, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vettering, W.T.; Flannery, B.R. Numerical Recipes in Fortran: The Art of Scientific Computing. Mathematics of Computation; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Perona, P.; Malik, J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Computer Vision, Osaka, Japan, 4–7 December 1990; pp. 629–639. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. A study on atmospheric boundary layer structure during a clear day in the arid region in northwest China. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2008, 66, 599–608. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Bu, S. The effects of the “two-way feedbackmechanism” on themaintenance of persistent heavy aerosol pollution over areas with relatively light aerosol pollution in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 688C, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Wiedensohler, A.; Eichler, H.; Heintzenberg, J.; Tesche, M.; Ansmann, A.; Wendisch, M.; Su, H.; Althausen, D.; Herrmann, H.; et al. Relative humidity dependence of aerosol optical properties and direct radiative forcing in the surface boundary layer at Xinken in Pearl River Delta of China: An observation based numerical study. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6373–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, J.Y.; Shen, X.J.; Zhang, Y.M.; Che, H.; Ma, Q.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ogren, J.A. Observations of relative humidity effects on aerosol light scattering in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8439–8454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen-Gammon, J.W.; Powell, C.L.; Mahoney, M.J.; Angevine, W.M.; Senff, C.; White, A.; Berkowitz, C.; Doran, C.; Knupp, K. Multisensor Estimation of Mixing Heights over a Coastal City. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2008, 47, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haman, C.L.; Lefer, B.; Morris, G.A. Seasonal Variability in the Diurnal Evolution of the Boundary Layer in a Near-Coastal Urban Environment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2012, 29, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Franco, J.L.; Stremme, W.; Bezanilla, A.; Ruiz-Angulo, A.; Grutter, M. Variability of the Mixed-Layer Height Over Mexico City. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2018, 167, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.-S.; Park, M.-S.; Chae, J.-H.; Kang, M. Integrated System for Atmospheric Boundary Layer Height Estimation (ISABLE) using a Ceilometer and Microwave Radiometer. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liang, X.Z. Observed Diurnal Cycle Climatology of Planetary Boundary Layer Height. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5790–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Dai, T.; Chen, S. An improved method for automatic determination of the planetary boundary layer height based on lidar data. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2020, 257, 107382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Tian, P.; Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Liang, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, L. A Comparison of Wintertime Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights Determined by Tethered Balloon Soundings and Lidar at the Site of SACOL. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091781
Zhang M, Tian P, Zeng H, Wang L, Liang J, Cao X, Zhang L. A Comparison of Wintertime Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights Determined by Tethered Balloon Soundings and Lidar at the Site of SACOL. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091781
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Min, Pengfei Tian, Huiyu Zeng, Ligong Wang, Jiening Liang, Xianjie Cao, and Lei Zhang. 2021. "A Comparison of Wintertime Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights Determined by Tethered Balloon Soundings and Lidar at the Site of SACOL" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091781
APA StyleZhang, M., Tian, P., Zeng, H., Wang, L., Liang, J., Cao, X., & Zhang, L. (2021). A Comparison of Wintertime Atmospheric Boundary Layer Heights Determined by Tethered Balloon Soundings and Lidar at the Site of SACOL. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091781