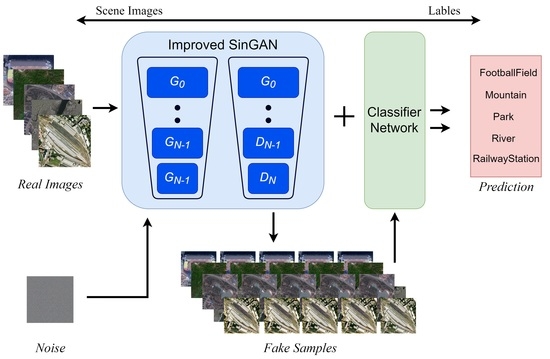
Improved SinGAN Integrated with an Attentional Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- In this work, a GAN to generate samples by using competitive and collaborative learning is proposed. SinGAN is a bottom-up GAN, while the attention mechanism is mostly used for forward-propagating network structures. Whether the combination of the two networks can effectively deliver the learned features to the end remains to be proven.
- (2)
- The structure of the SinGAN pyramid multiscale generation adversarial network and the attention mechanism are adapted to solve the problem of generated samples with a certain diversity and fidelity under the rare training sets. The SinGAN is optimized in an unsupervised model to generate fake samples from a single natural image. The attention mechanism is aimed at observing the key features in a natural image. The combined framework of SinGAN and the attention mechanism is proposed to determine whether significant features can be availably extracted from a single remote sensing image to generate high-simulated samples.
- (3)
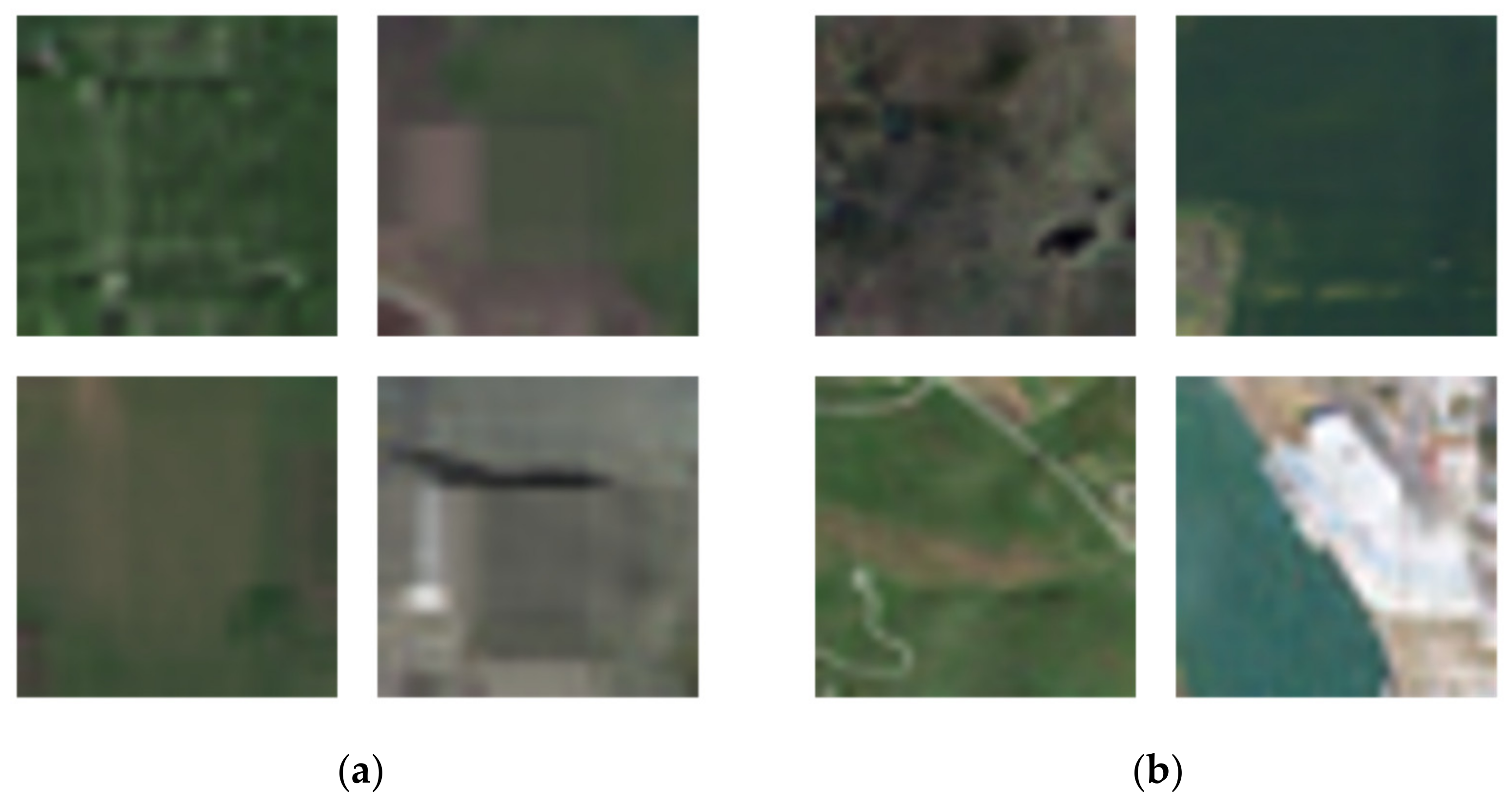
- Rich training samples and sufficient feature information are required for the performance of the classifier network. In the improved SinGAN, features are extracted and compressed into generated samples. These fake generated samples are incorporated into the classifier network as training datasets to test if the classification accuracy improves.
2. Methods
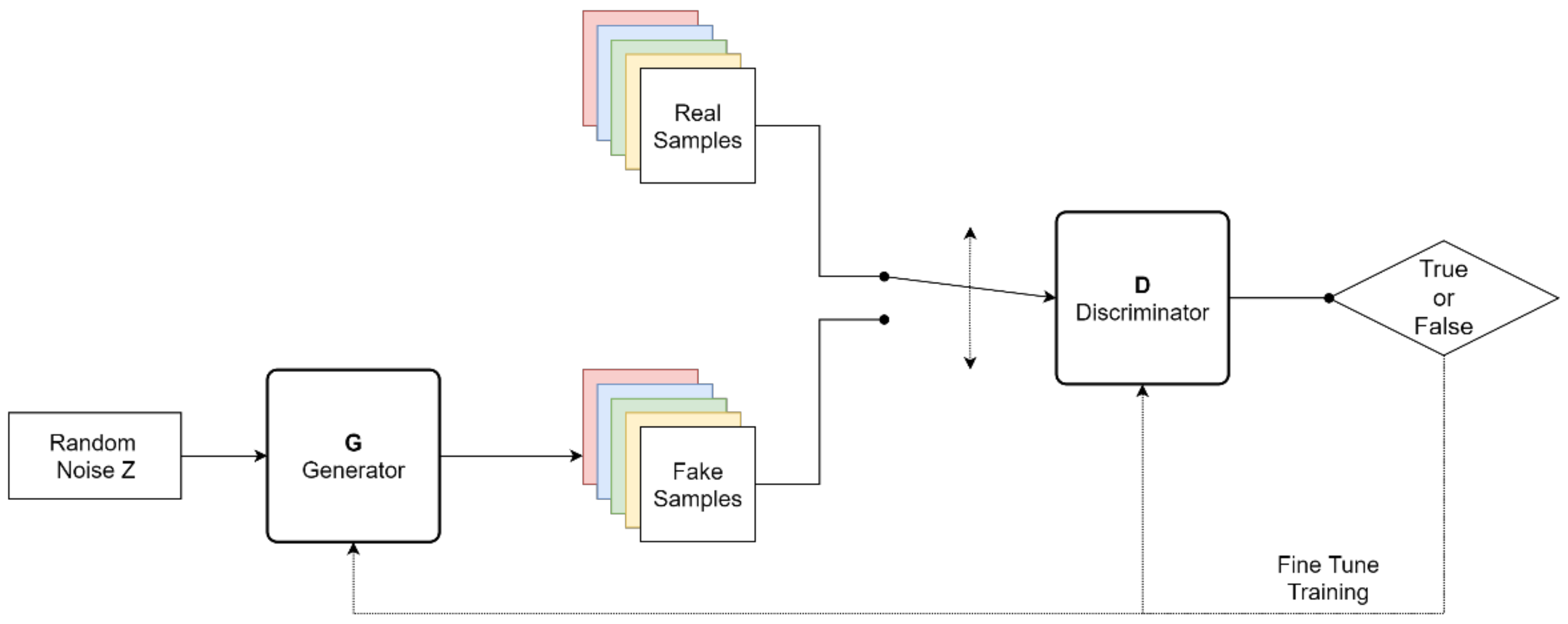
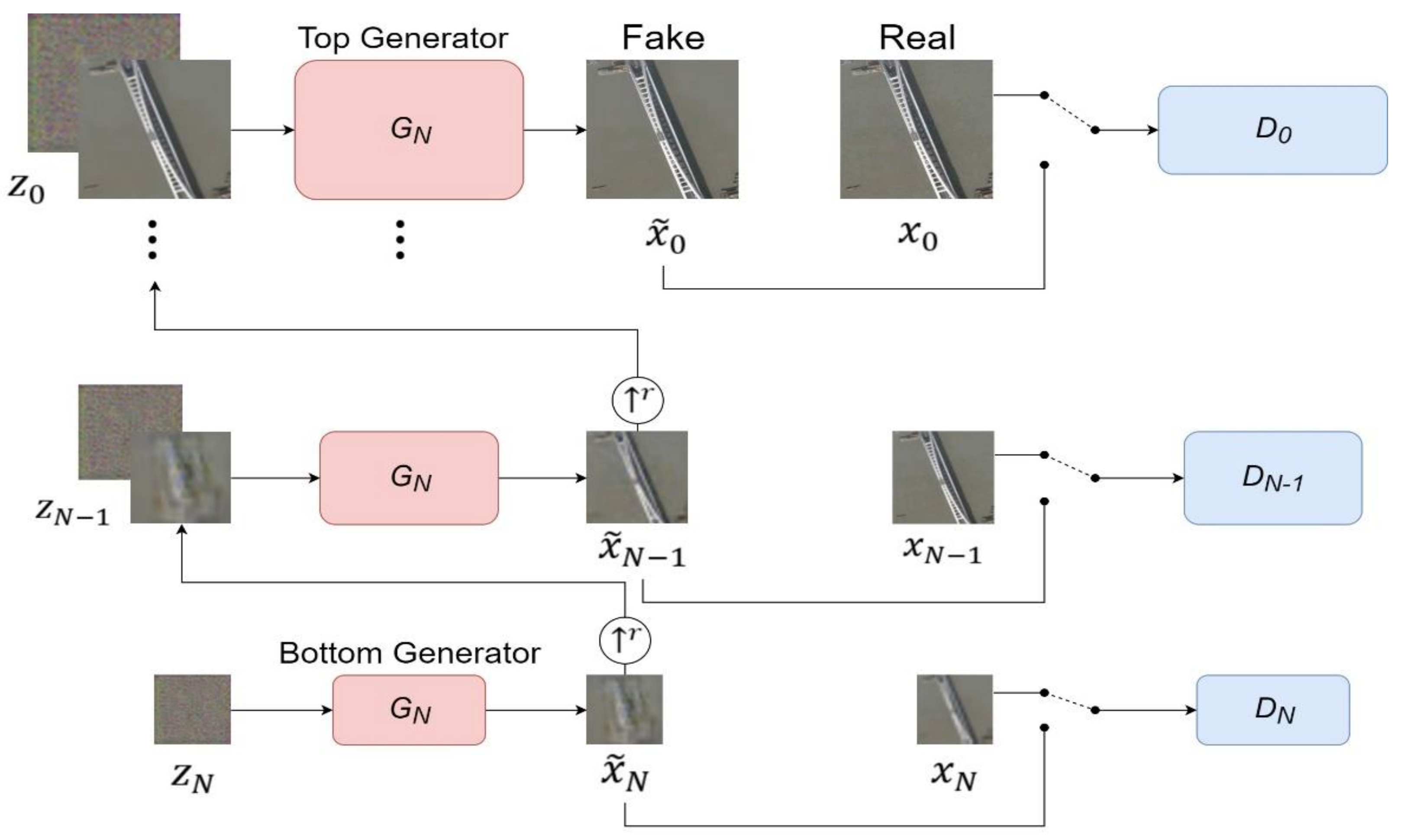
2.1. SinGAN
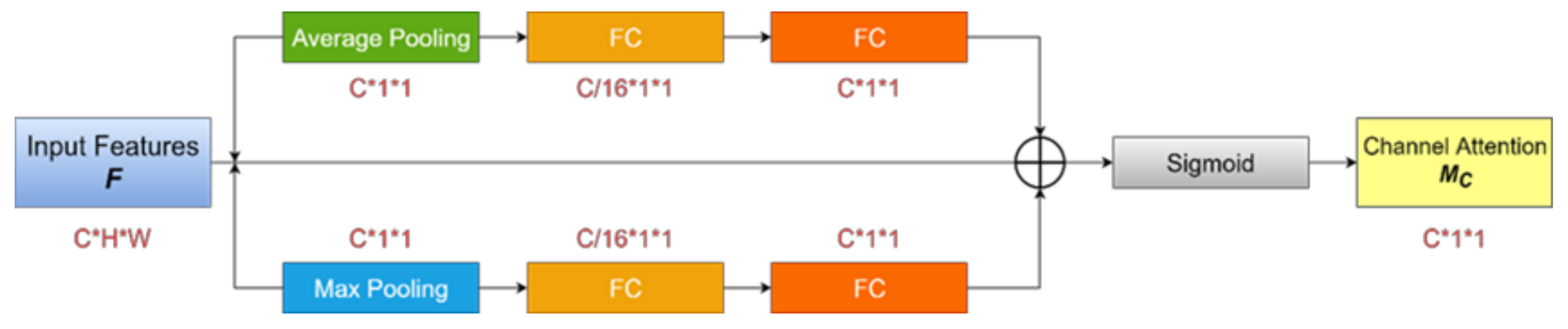
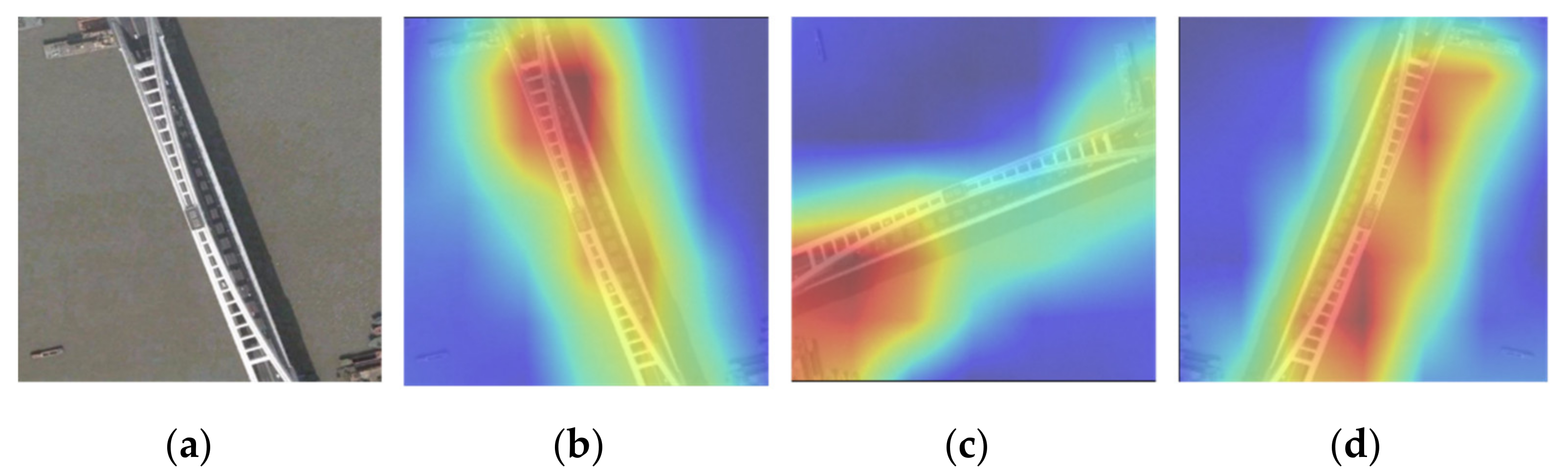
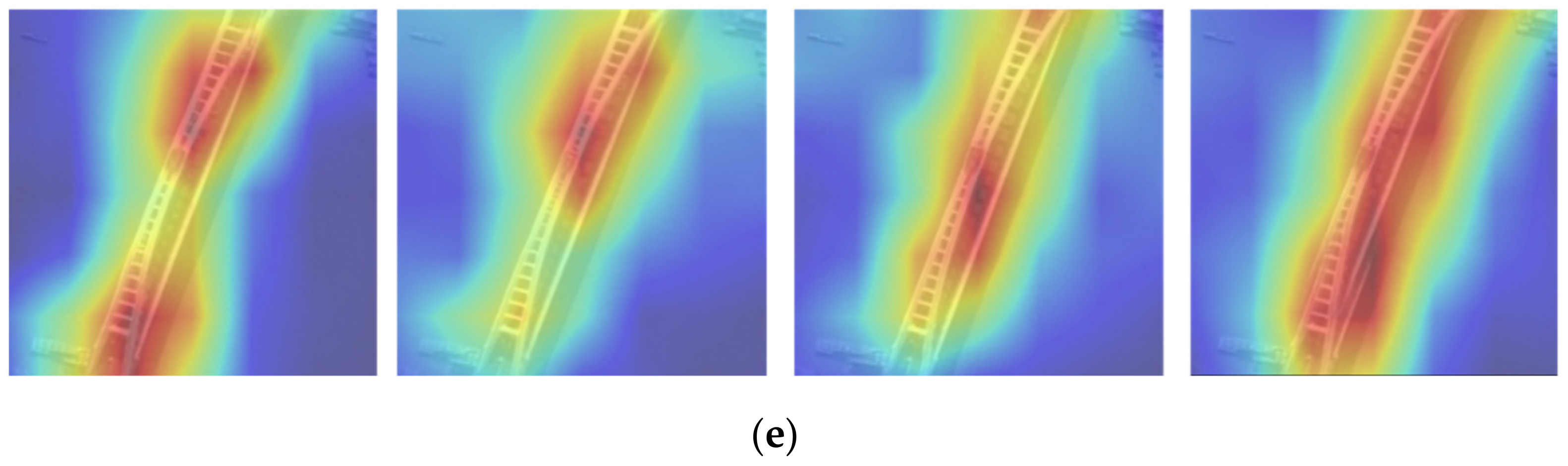
2.2. Attentional Mechanism
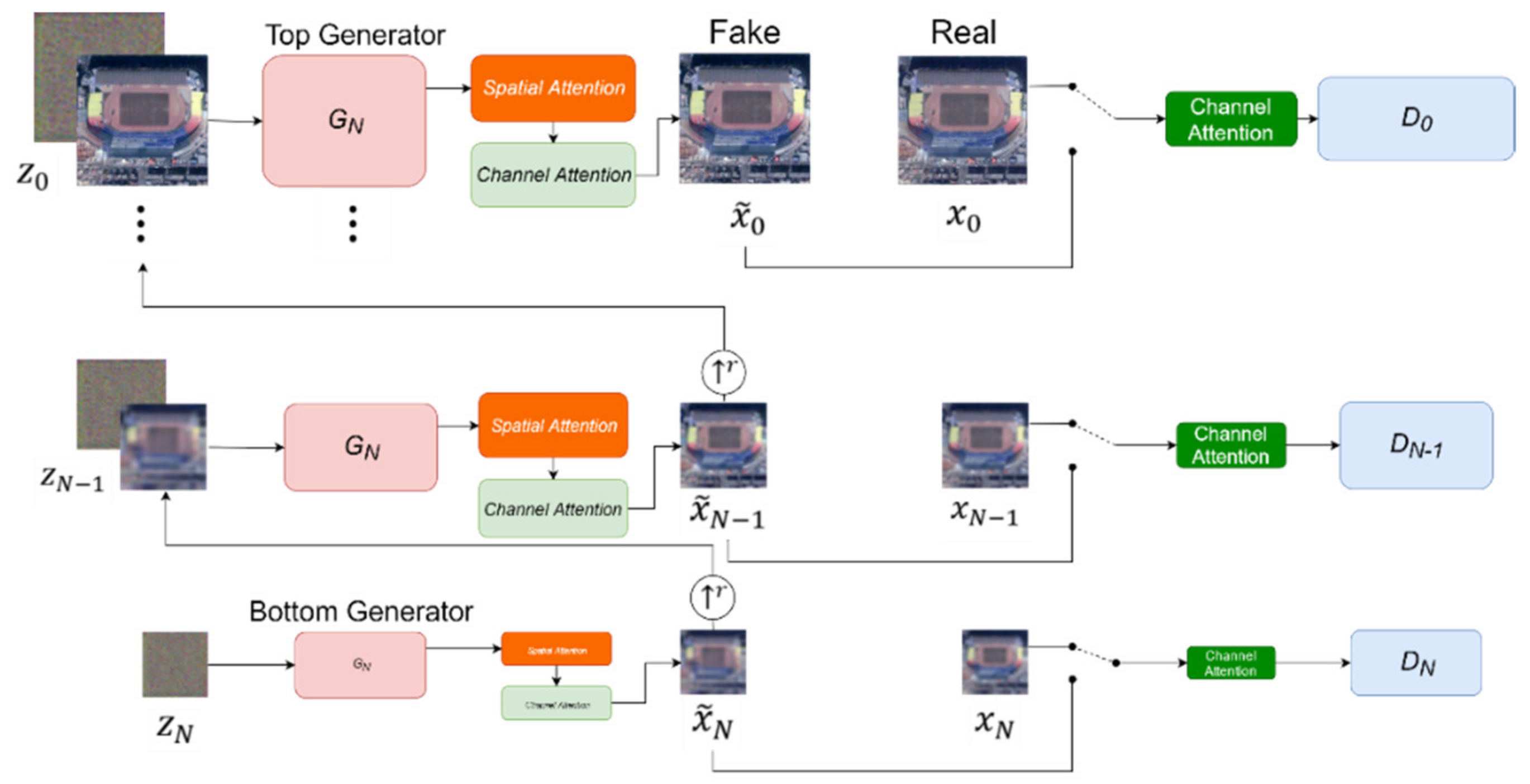
2.3. Improved SinGAN
3. Experiment and Results
3.1. Experimental Configuration
3.2. Evaluation Index and Dataset Description
- Datasets
- 2.
- Accuracy validation methods
- 3.
- Parameter setting
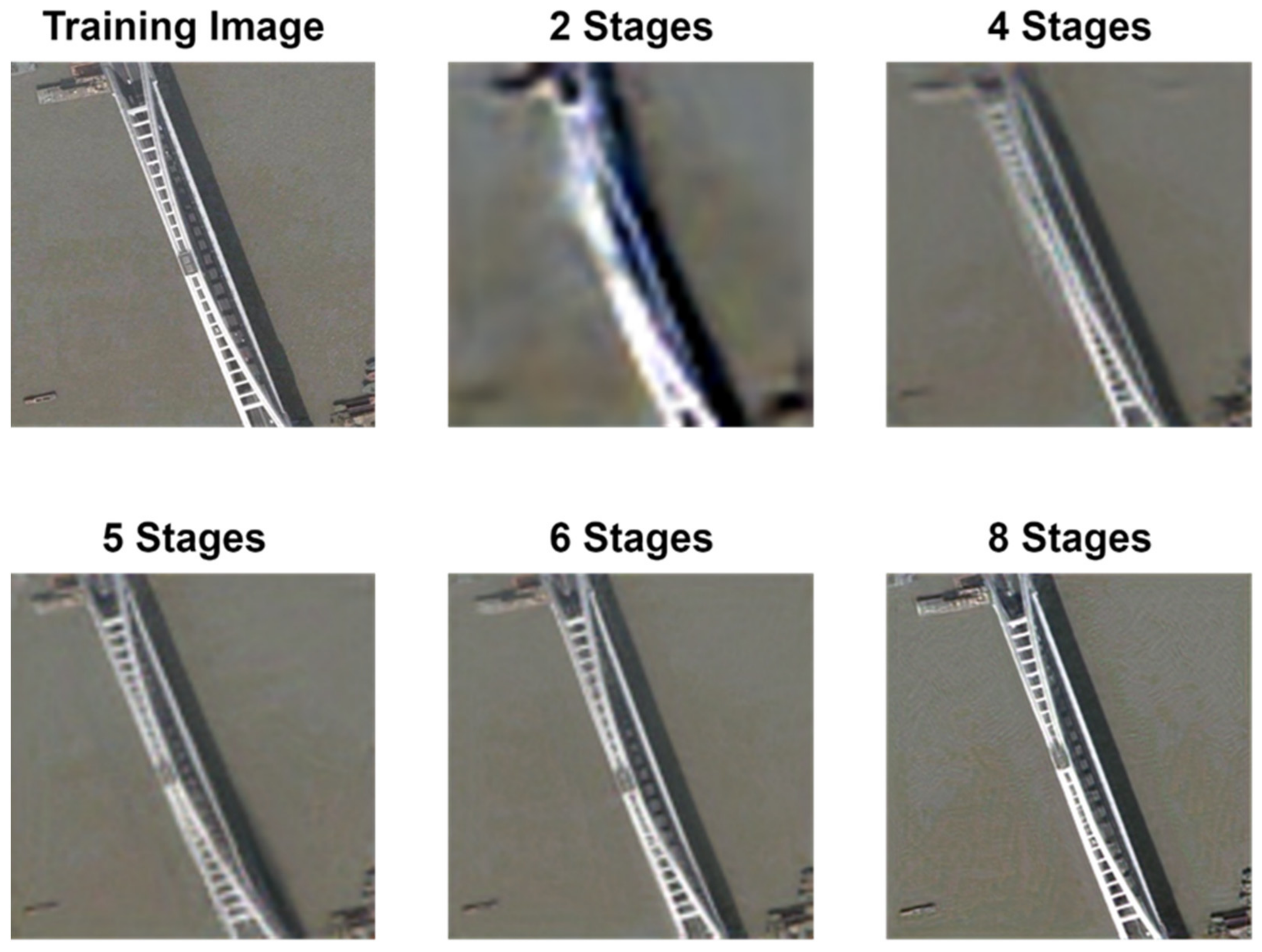
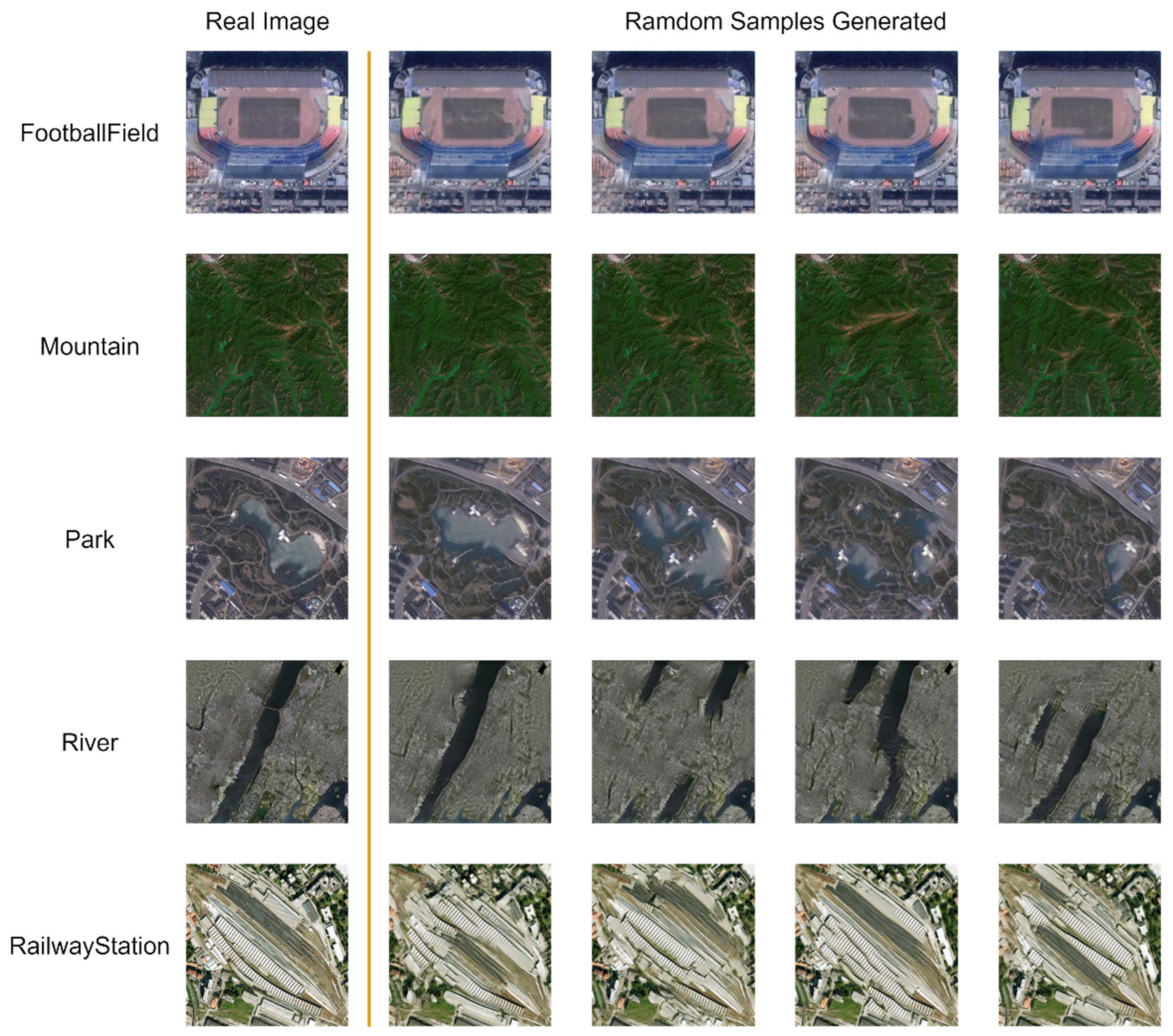
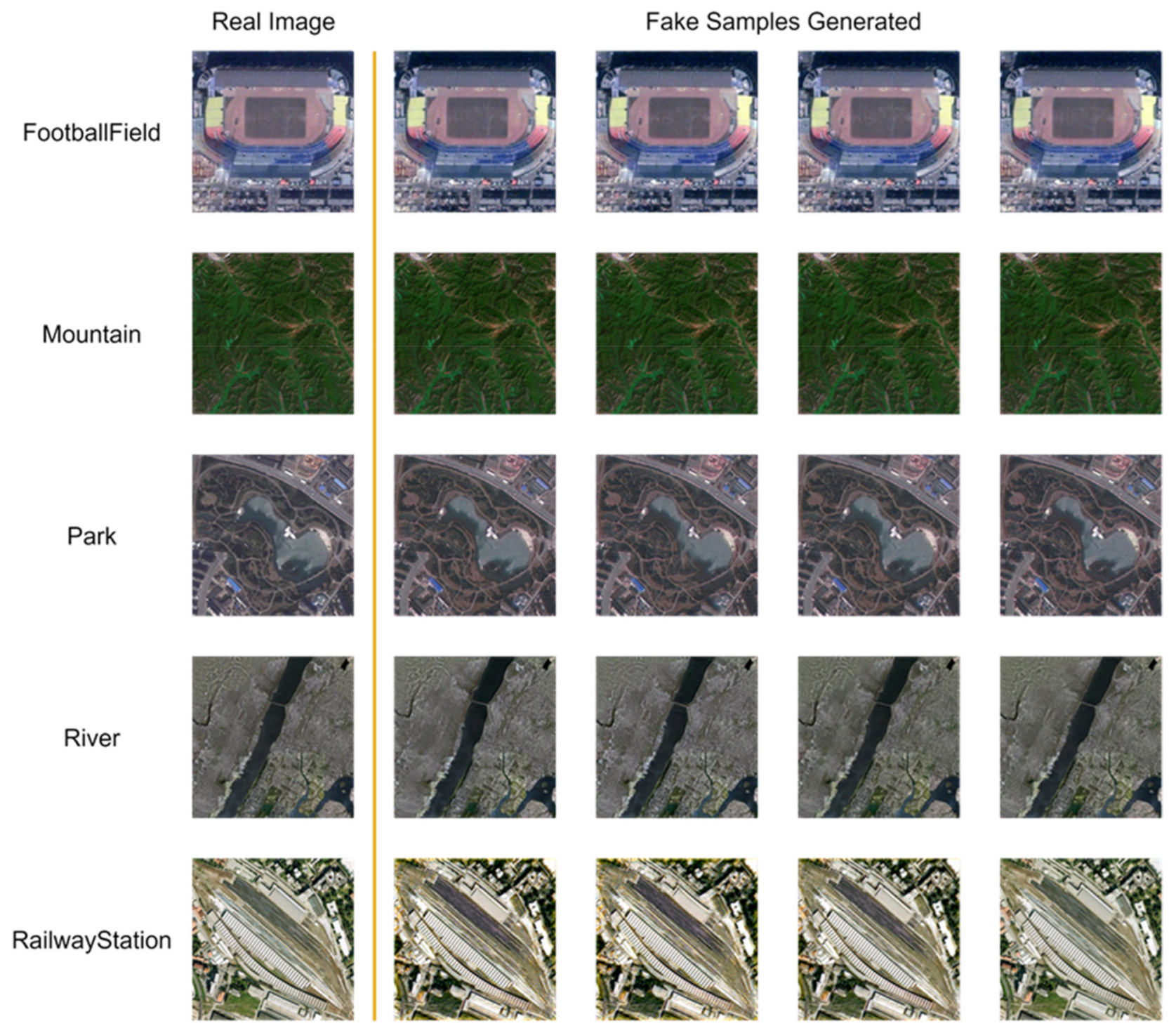
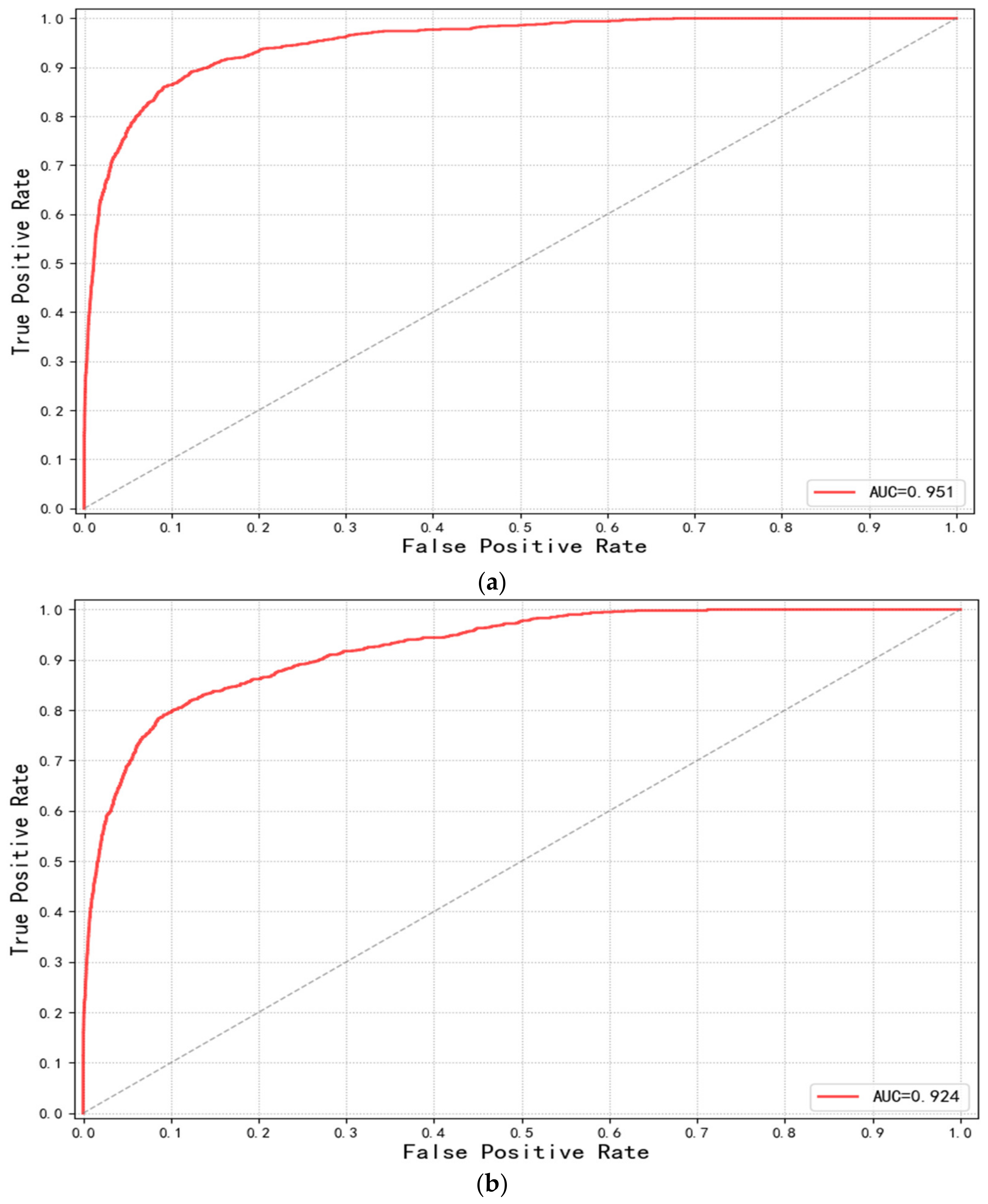
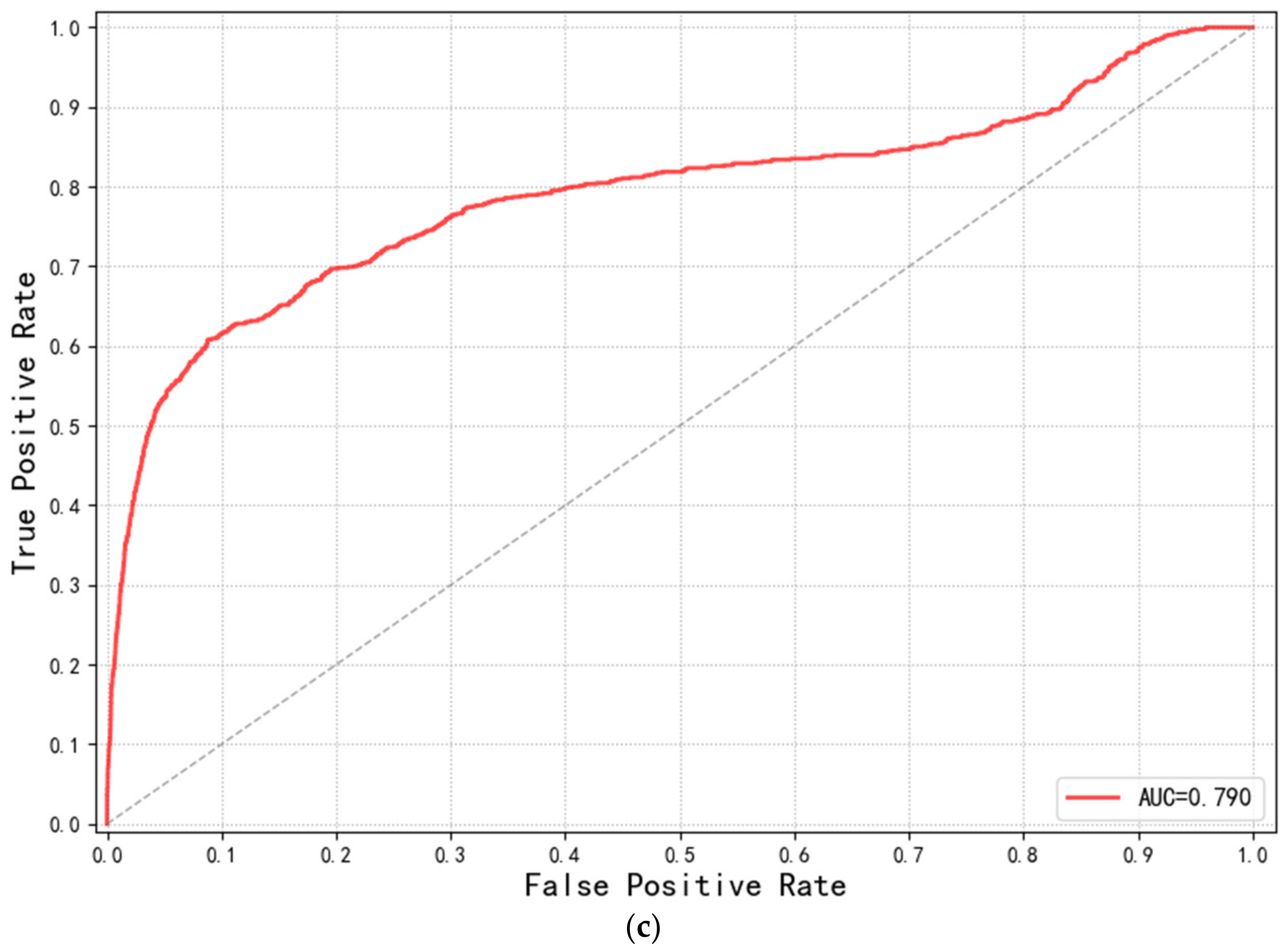
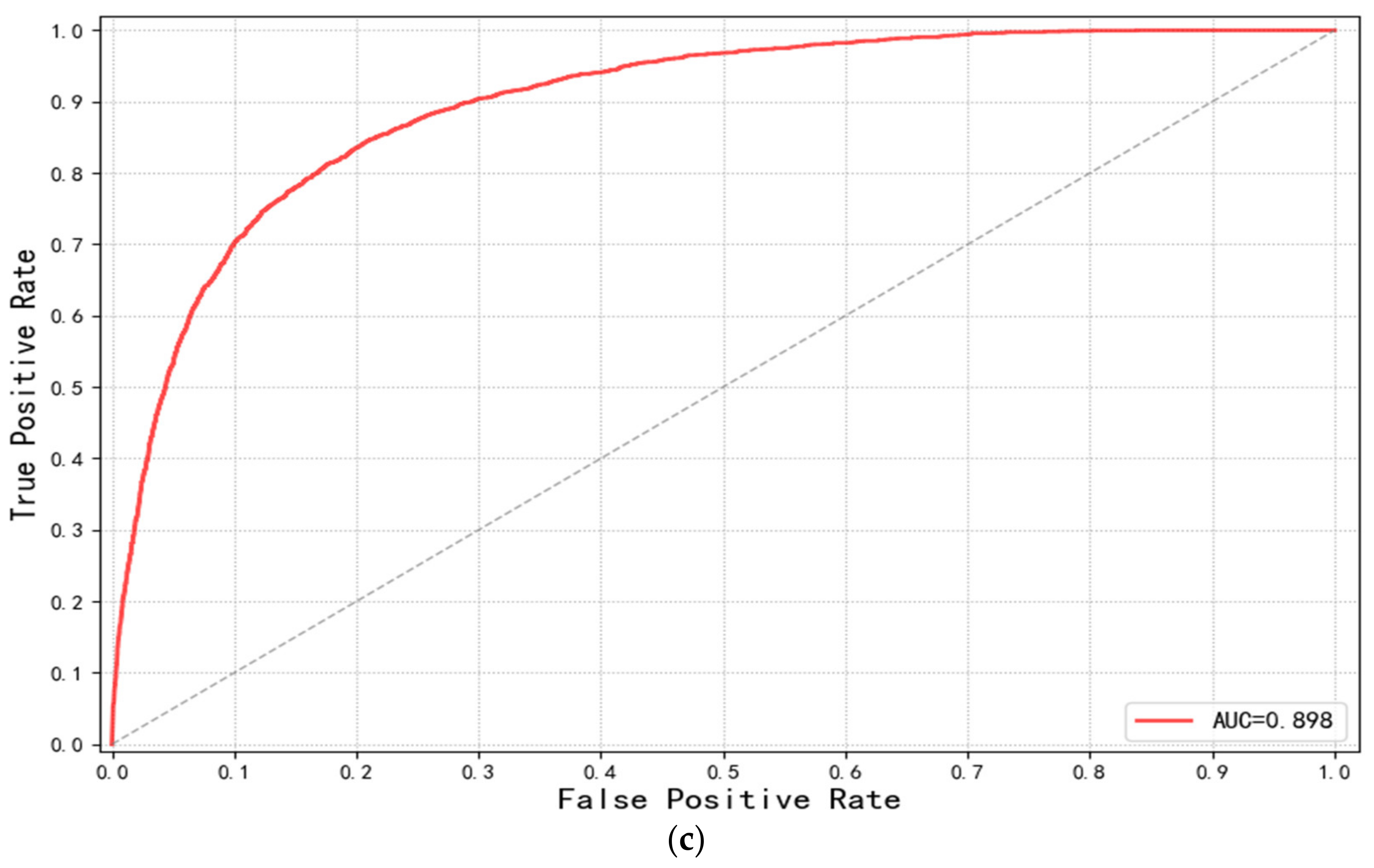
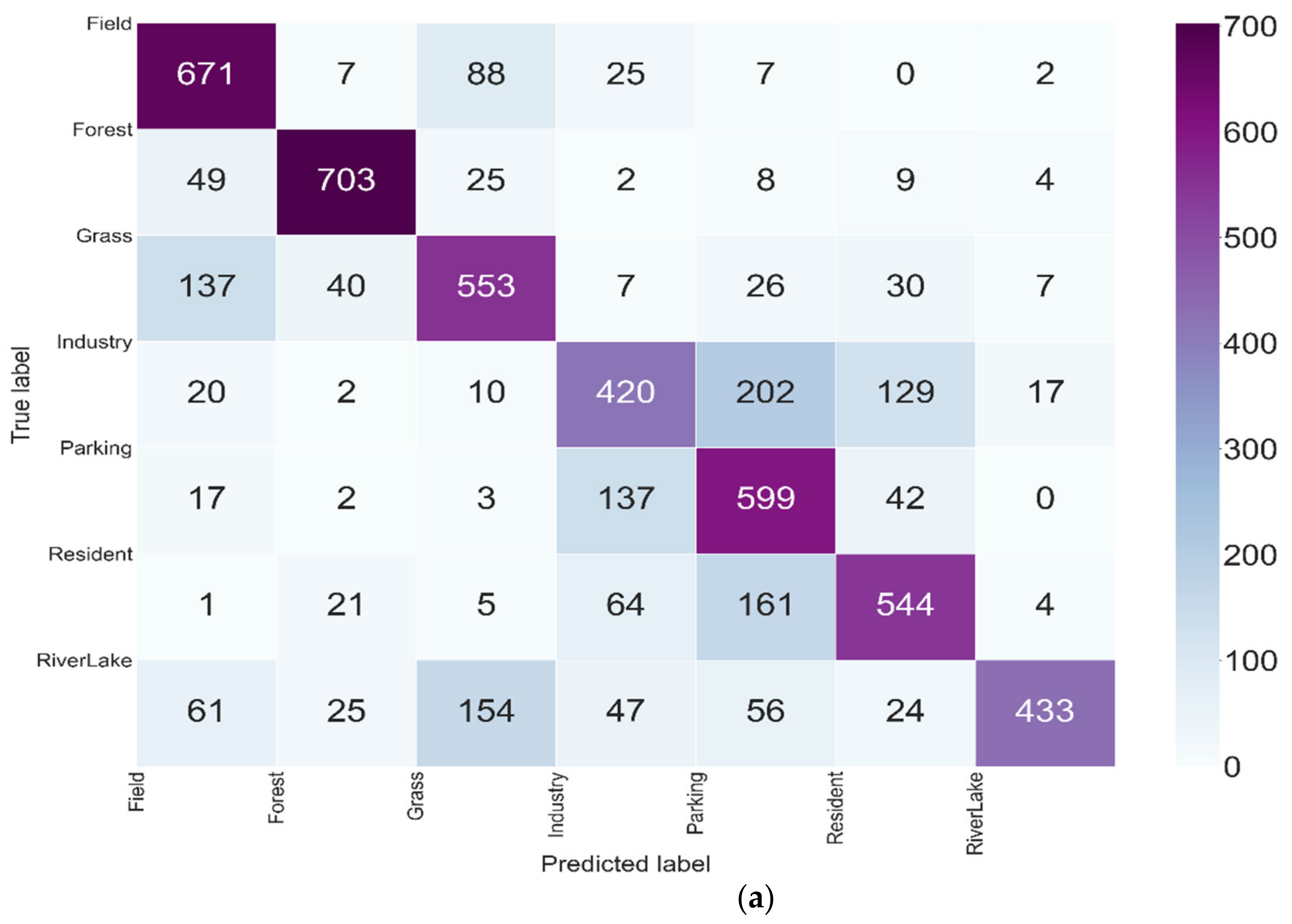
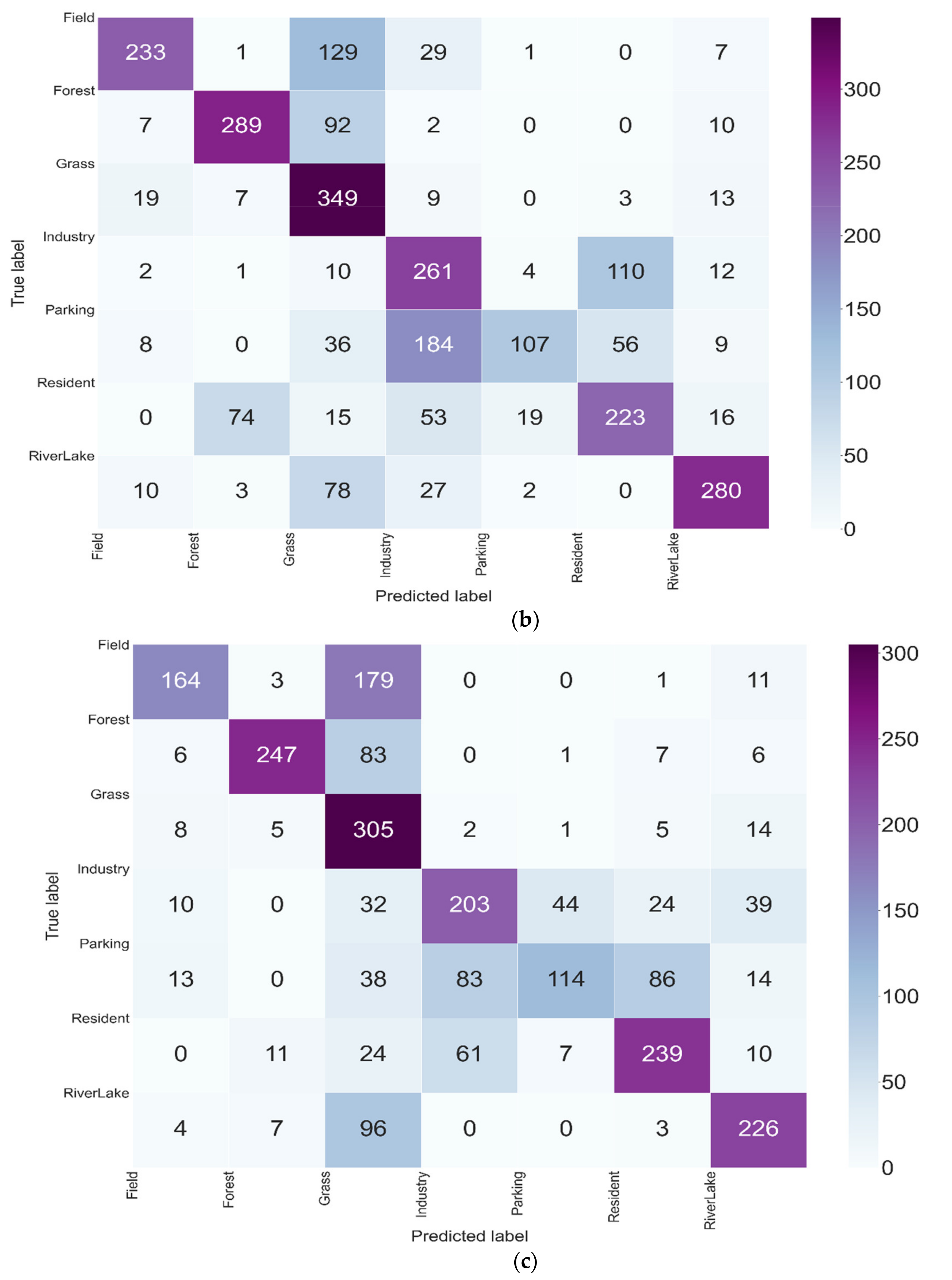
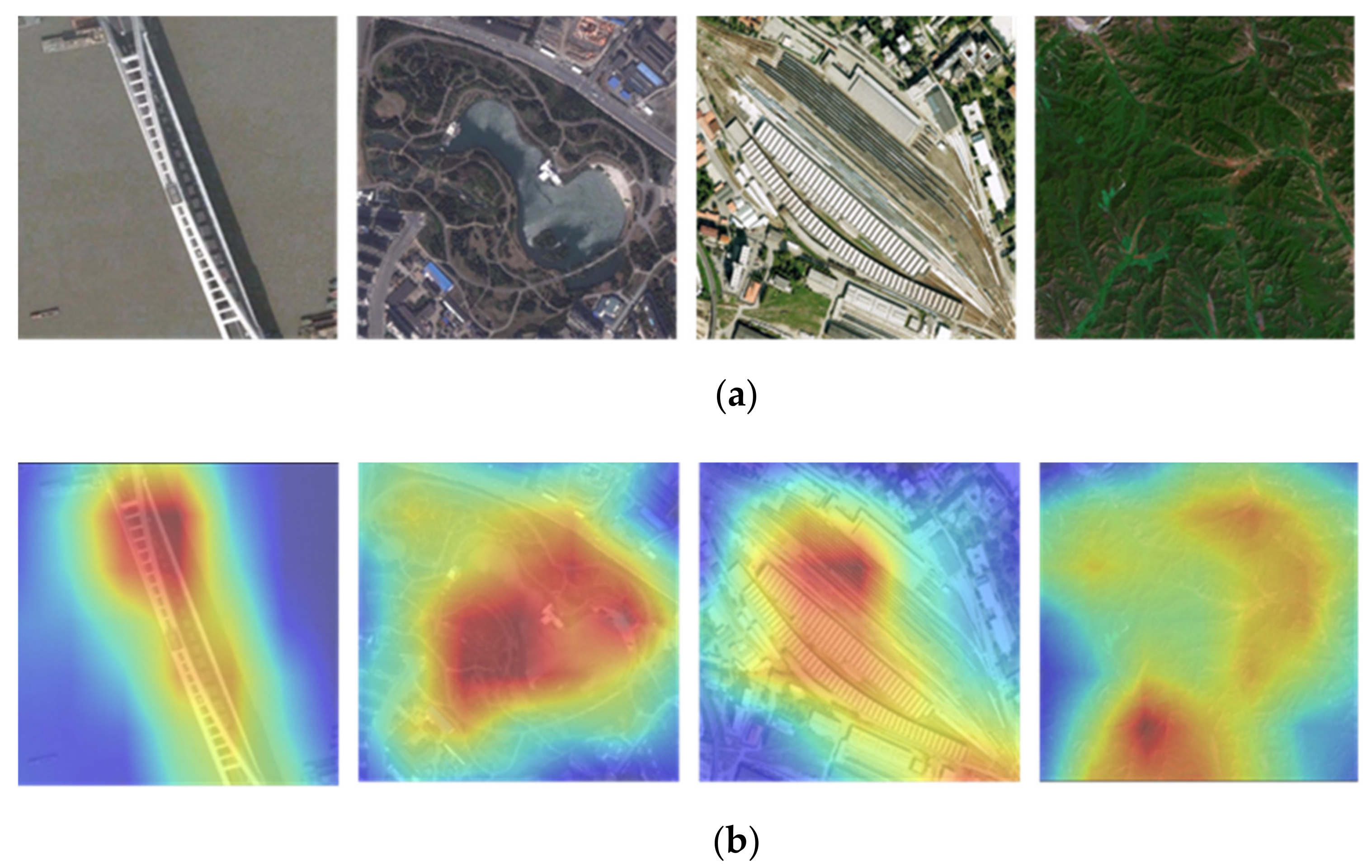
3.3. Evolution of the Model Performance
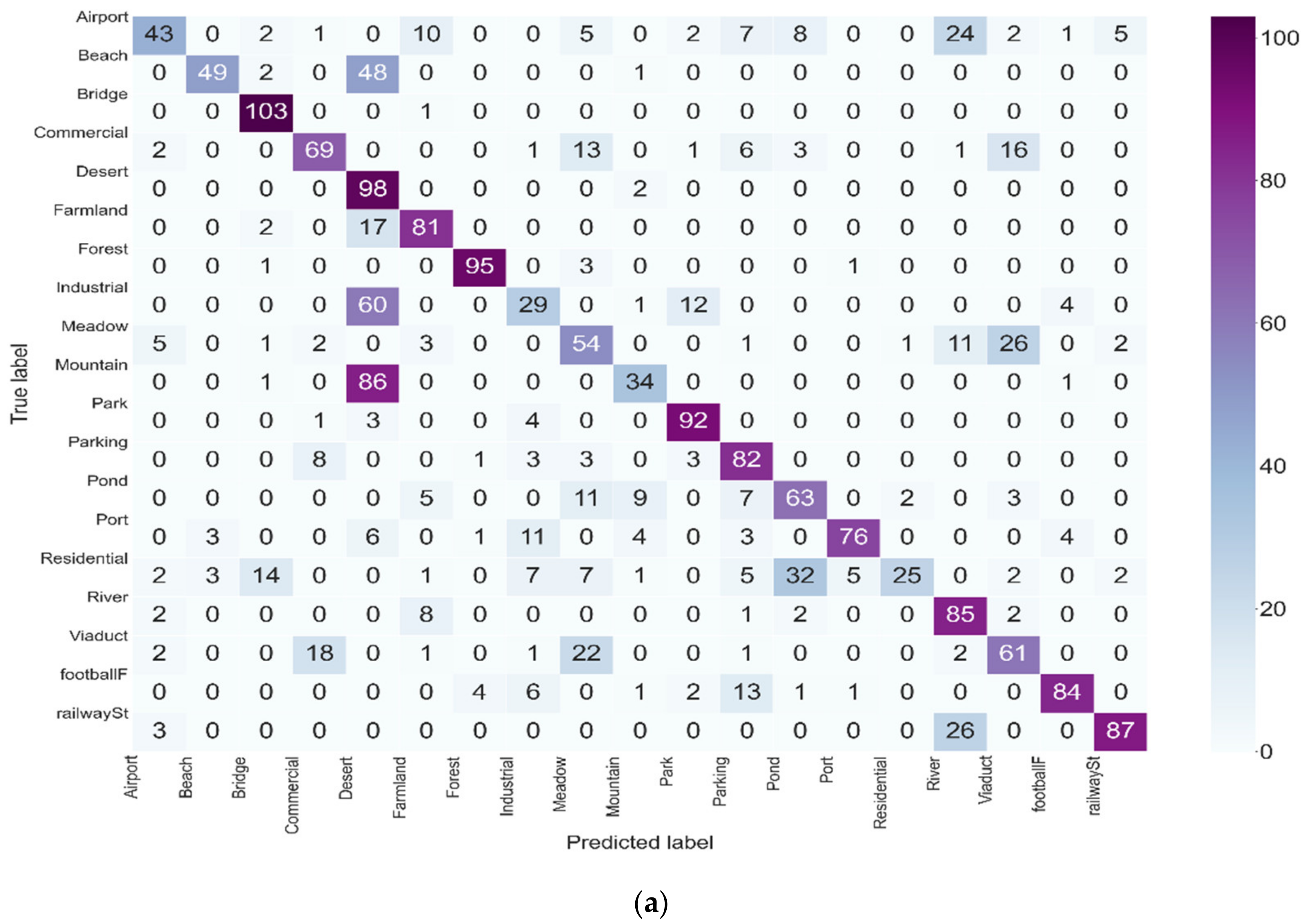
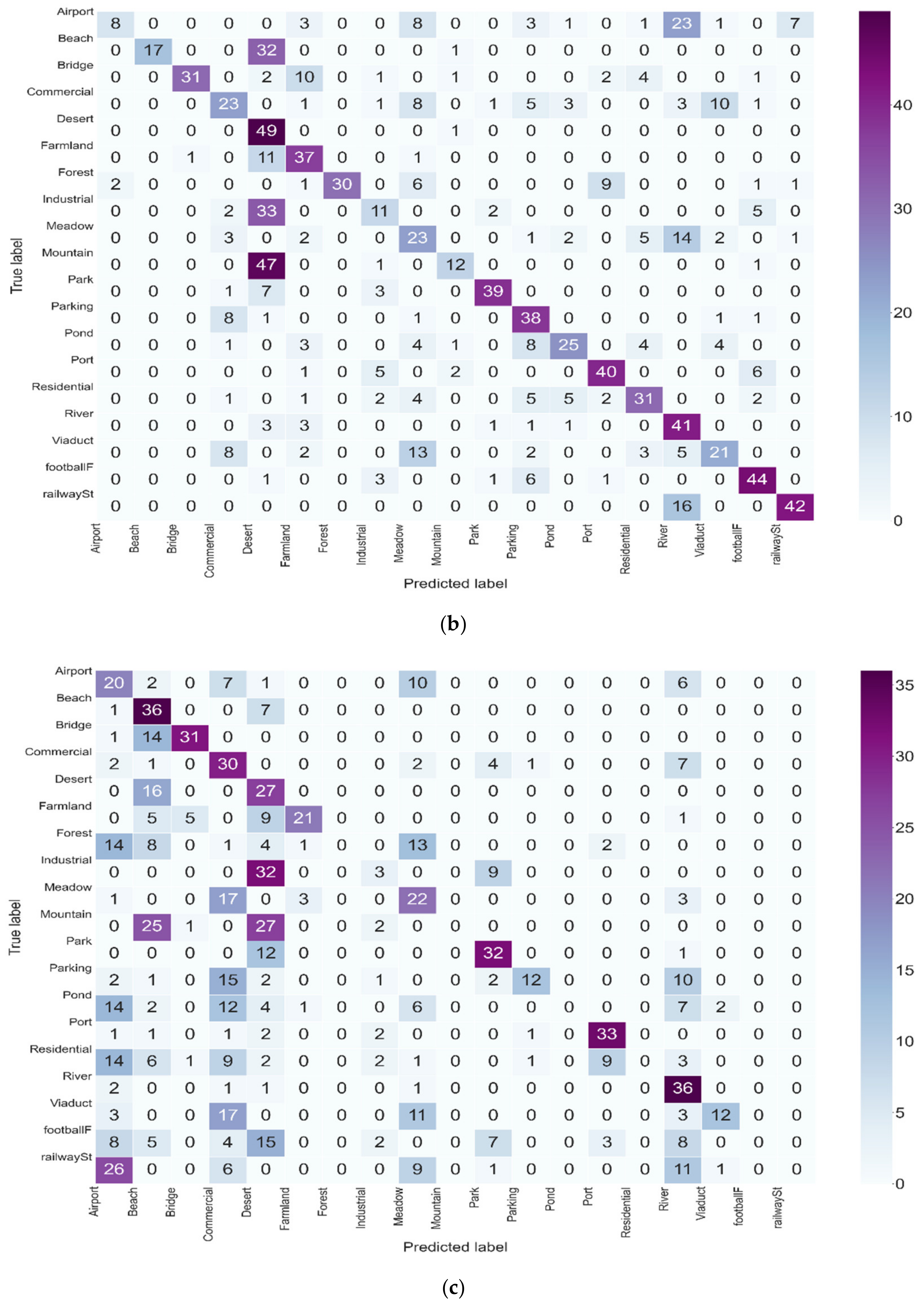
3.4. Evolution of the Classification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, F.; Xia, G.-S.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L. Transferring Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for the Scene Classification of High-Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 14680–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Li, Z.; Han, J.; Yao, X.; Guo, L. Exploring Hierarchical Convolutional Features for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6712–6722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Q. Fast Spectral Clustering for Unsupervised Hyperspectral Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Shen, H.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Tan, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Deep learning in environmental remote sensing: Achievements and challenges. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 241, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep learning in remote sensing applications: A meta-analysis and review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J. Implementation of training convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.01195. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Cui, Z.; Gan, Z.; Liu, F. Residual group channel and space attention network for hyperspectral image classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, Q.S.U.; Tao, L.; Sun, F.; Yang, S. A Fast and Robust Sparse Approach for Hyperspectral Data Classification Using a Few Labeled Samples. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 50, 2287–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yokoya, N.; Yao, J.; Chanussot, J.; Du, Q.; Zhang, B. More Diverse Means Better: Multimodal Deep Learning Meets Remote-Sensing Imagery Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, T.; Torr, P.H.; Hospedales, T.M. Learning to compare: Relation network for few-shot learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1199–1208. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sun, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, S.; Chua, T.-S.; Schiele, B. Learning to self-train for semi-supervised few-shot classification. Adv. Neural Inf. Proc. Syst. 2019, 32, 10276–10286. [Google Scholar]
- De Lima, R.P.; Marfurt, K. Convolutional Neural Network for Remote-Sensing Scene Classification: Transfer Learning Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B. Improved convolutional neural network in remote sensing image classification. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Tao, X.; Xu, M.; Han, C.; Lu, J. GAN-NL: Unsupervised representation learning for remote sensing image classification. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Anaheim, CA, USA, 26–29 November 2018; pp. 375–379. [Google Scholar]
- Li, E.; Xia, J.; Du, P.; Lin, C.; Samat, A. Integrating Multilayer Features of Convolutional Neural Networks for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 5653–5665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Yang, C.; Yao, X.; Guo, L.; Han, J. When Deep Learning Meets Metric Learning: Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification via Learning Discriminative CNNs. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inform. Proc. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Mu, X.; Chai, D.; Zhang, X. Remote sensing image scene classification based on generative adversarial networks. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, G.; Gu, J.; Han, J. Pruning Convolutional Neural Networks with an Attention Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Electronics 2020, 9, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Li, B.; Zhu, J.-Y.; He, W.; Liu, M.; Song, D. Generating Adversarial Examples with Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.02610. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Metz, L.; Chintala, S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06434. [Google Scholar]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L. Banach wasserstein gan. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.06621. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J. A Scene Images Diversity Improvement Generative Adversarial Network for Remote Sensing Image Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Hu, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, X. Semisupervised Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 15, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Fu, K.; Wang, Y.; Xu, G.; Sun, X. MARTA GANs: Unsupervised Representation Learning for Remote Sensing Image Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 2092–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, J.; Lei, L.; Zou, H. Multi-scale object detection in remote sensing imagery with convolutional neural networks. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaham, T.R.; Dekel, T.; Michaeli, T. SinGAN: Learning a generative model from a single natural image. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 4569–4579. [Google Scholar]
- Hinz, T.; Fisher, M.; Wang, O.; Wermter, S. Improved techniques for training single-image gans. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.11512. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, W.; Xiong, Z.; Cui, Y.; Lv, Y. Deep multi-feature fusion network for remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 11, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Mu, X.; Sha, D. Multi-Layers Feature Fusion of Convolutional Neural Network for Scene Classification of Remote Sensing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 121685–121694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Dai, X.; Liu, L. Remote Sensing Scene Classification Based on Multi-Structure Deep Features Fusion. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28746–28755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, B.-D. ESinGAN: Enhanced single-image GAN using pixel attention mechanism for image super-resolution. In Proceedings of the 2020 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Beijing, China, 6–9 December 2020; Volume 1, pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, H.; Shen, J.; Jiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Hou, B. A Spatial-Channel Collaborative Attention Network for Enhancement of Multiresolution Classification. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; So Kweon, I. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Dan, J. CBAM-GAN: Generative adversarial networks based on convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Q.; Ni, L.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Q. Deep Learning Based Feature Selection for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 2321–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Newsam, S. Bag-of-visual-words and spatial extensions for land-use classification. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems (ACM GIS), San Jose, CA, USA, 2–5 November 2010; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, F. Attention GANs: Unsupervised Deep Feature Learning for Aerial Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4700–4708. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]







| Method | Time (ms) |
|---|---|
| DCGAN | 1,925,730 |
| WGAN | 2,463,846 |
| MARTA GAN | 16,245,770 |
| Attention GAN | 15,123,386 |
| SinGAN | 14,966,700 |
| Improved SinGAN | 13,686,128 |
| Dataset | VGG16 | VGG19 | DenseNet121 | MobileNet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fake Samples | OA (%) | 60.70 | 57.08 | 62.31 | 66.21 |
| Kappa (%) | 58.55 | 54.71 | 60.21 | 64.33 | |
| True Samples | OA (%) | 55.72 | 52.58 | 53.03 | 53.31 |
| Kappa (%) | 53.30 | 49.93 | 50.39 | 50.73 | |
| Random Samples | OA (%) | 41.75 | 37.36 | 38.22 | 40.44 |
| Kappa (%) | 38.61 | 33.97 | 34.77 | 37.12 | |
| Dataset | VGG16 | VGG19 | DenseNet121 | MobileNet | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fake Samples | OA (%) | 64.17 | 59.31 | 66.21 | 72.12 |
| Kappa (%) | 58.19 | 52.53 | 60.57 | 67.47 | |
| True Samples | OA (%) | 58.93 | 54.37 | 62.44 | 64.64 |
| Kappa (%) | 52.08 | 51.80 | 56.19 | 58.74 | |
| Random Samples | OA (%) | 57.40 | 50.37 | 59.70 | 60.19 |
| Kappa (%) | 55.02 | 46.81 | 53.00 | 53.57 | |
| Input Size | 32 × 32 | 64 × 64 | 128 × 128 | 224 × 224 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 44.68 | 55.60 | 60.70 | 62.19 |
| Kappa (%) | 41.56 | 53.14 | 58.55 | 60.12 |
| Dataset | Categories | 5 Classes | 10 Classes | 19 Classes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fake Samples | OA (%) | 81.83 | 63.32 | 60.70 |
| Kappa (%) | 77.28 | 59.34 | 58.55 | |
| True Samples | OA (%) | 77.64 | 57.39 | 55.72 |
| Kappa (%) | 72.08 | 52.78 | 53.30 | |
| Random Samples | OA (%) | 63.12 | 51.04 | 41.75 |
| Kappa (%) | 54.07 | 45.59 | 38.61 |
| Sample Multiple | Origin | ×1 | ×3 | ×5 | ×10 | ×30 | ×50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 55.72 | 57.25 | 61.27 | 61.41 | 61.53 | 61.75 | 60.70 |
| Kappa (%) | 53.30 | 54.92 | 59.20 | 59.31 | 59.01 | 59.66 | 58.55 |
| Method | Fake Samples | TAM | Fake Samples + TAM |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA (%) | 60.70 | 63.57 | 65.77 |
| Kappa (%) | 58.55 | 62.74 | 63.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, S.; Zhang, R.; Luo, H.; Li, M.; Feng, H.; Tang, X. Improved SinGAN Integrated with an Attentional Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091713
Gu S, Zhang R, Luo H, Li M, Feng H, Tang X. Improved SinGAN Integrated with an Attentional Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(9):1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091713
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Songwei, Rui Zhang, Hongxia Luo, Mengyao Li, Huamei Feng, and Xuguang Tang. 2021. "Improved SinGAN Integrated with an Attentional Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification" Remote Sensing 13, no. 9: 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091713
APA StyleGu, S., Zhang, R., Luo, H., Li, M., Feng, H., & Tang, X. (2021). Improved SinGAN Integrated with an Attentional Mechanism for Remote Sensing Image Classification. Remote Sensing, 13(9), 1713. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13091713