Sparse Constrained Low Tensor Rank Representation Framework for Hyperspectral Unmixing
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A new sparsity-constrained low-rank tensor factorization model (SCLT) is proposed for unmixing, which aims at maintaining the low-rank spatial structure of the raw data and the sparsity of the abundance tensor in the iterative process.
- A regularization is designed to explore the low-rank structure of data, which can learn the low-rank representation of 4-D tensor containing similarity patches in spectral mode, spatial mode and non-local similarity mode.
- The sparsity constraint is embedded in the proposed model to explore the sparsity structure of the abundance tensor through the norm, which can improve the performance of unmixing.
2. Related Work
3. Problem Formulation
3.1. Concepts
3.2. NTF Model
4. Proposed Method
4.1. SCLT Model
4.2. Optimization
| Algorithm 1 The proposed method SCLT |
| Input: |
| —the observed hyperspectral image; P—the number of endmembers; |
| r—the size of window; K—the number of similarity group; Parameter , and . |
| Initialize by VCA-based method, by FCLS, , , , , , , , , , , , |
| While not convergence |
| 1. Update the endmember matrix by (14); |
| 2. Update the abundance tensor via (17); |
| 3. Update the variables by (18), by (21), by (23), , and via (25) and (27); |
| 4. Update the Lagrangian multipliers , , , , , by (28). |
| end |
| Output: |
| —the abundance tensor; —the endmember matrix. |
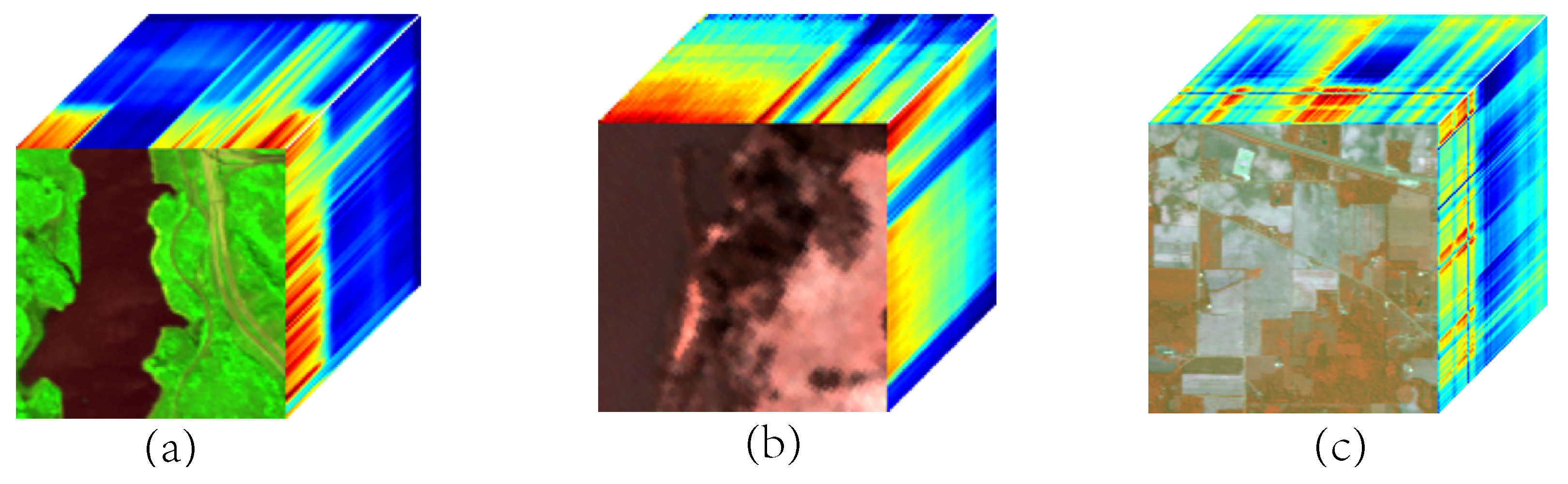
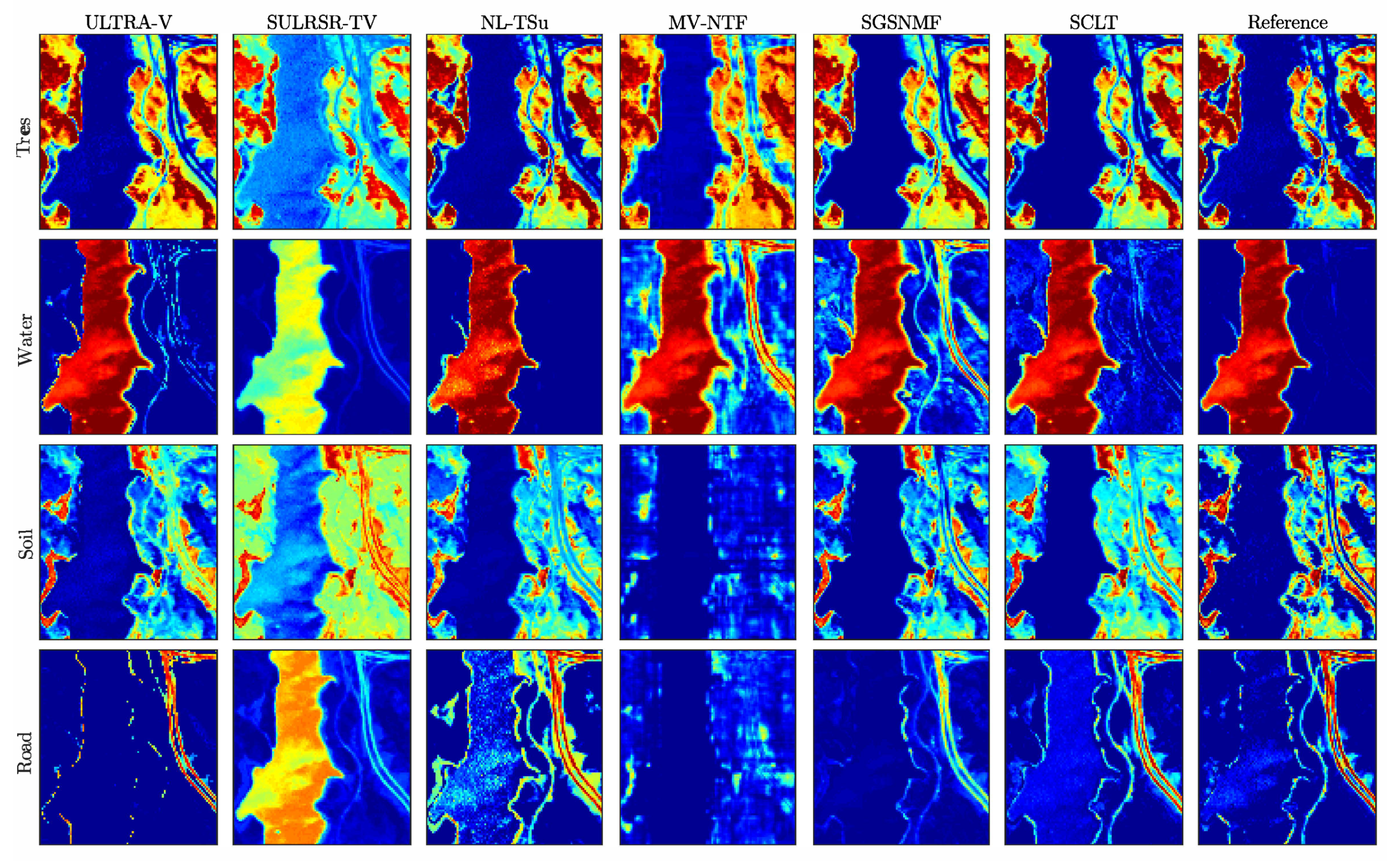
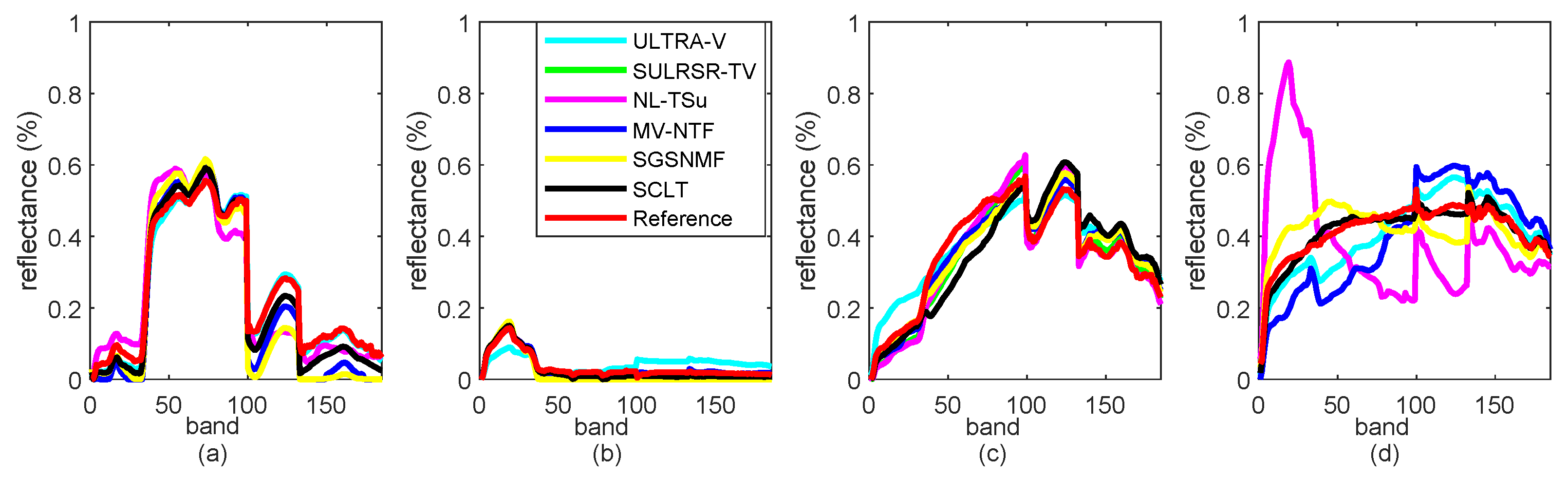
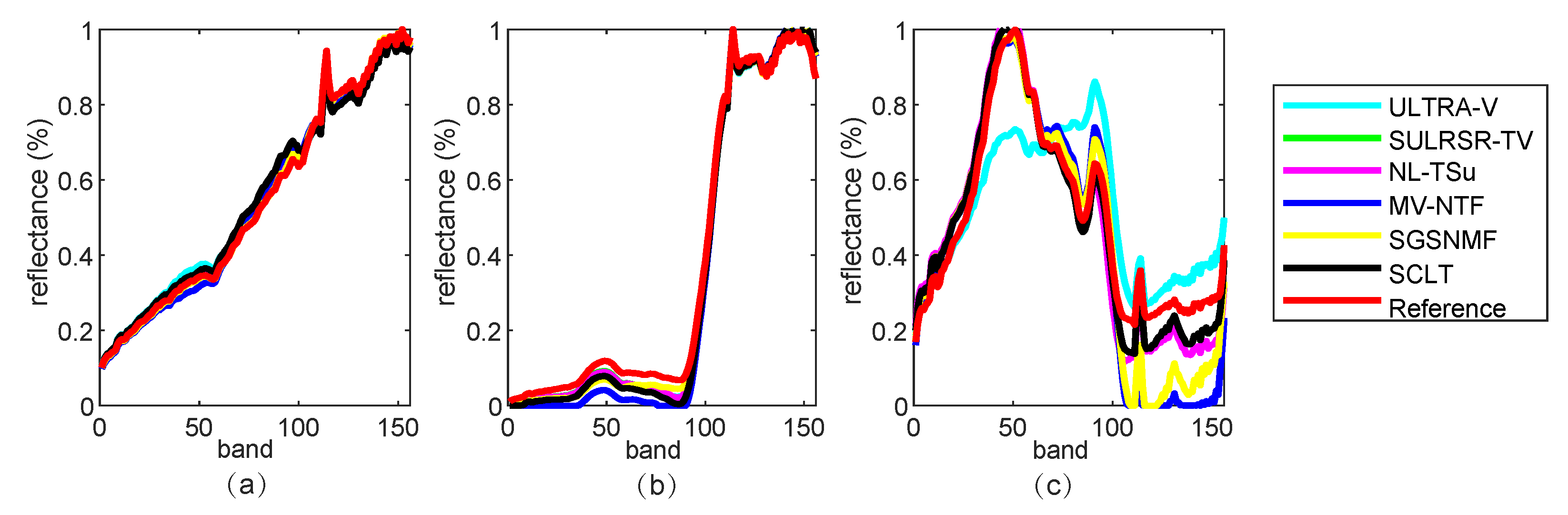
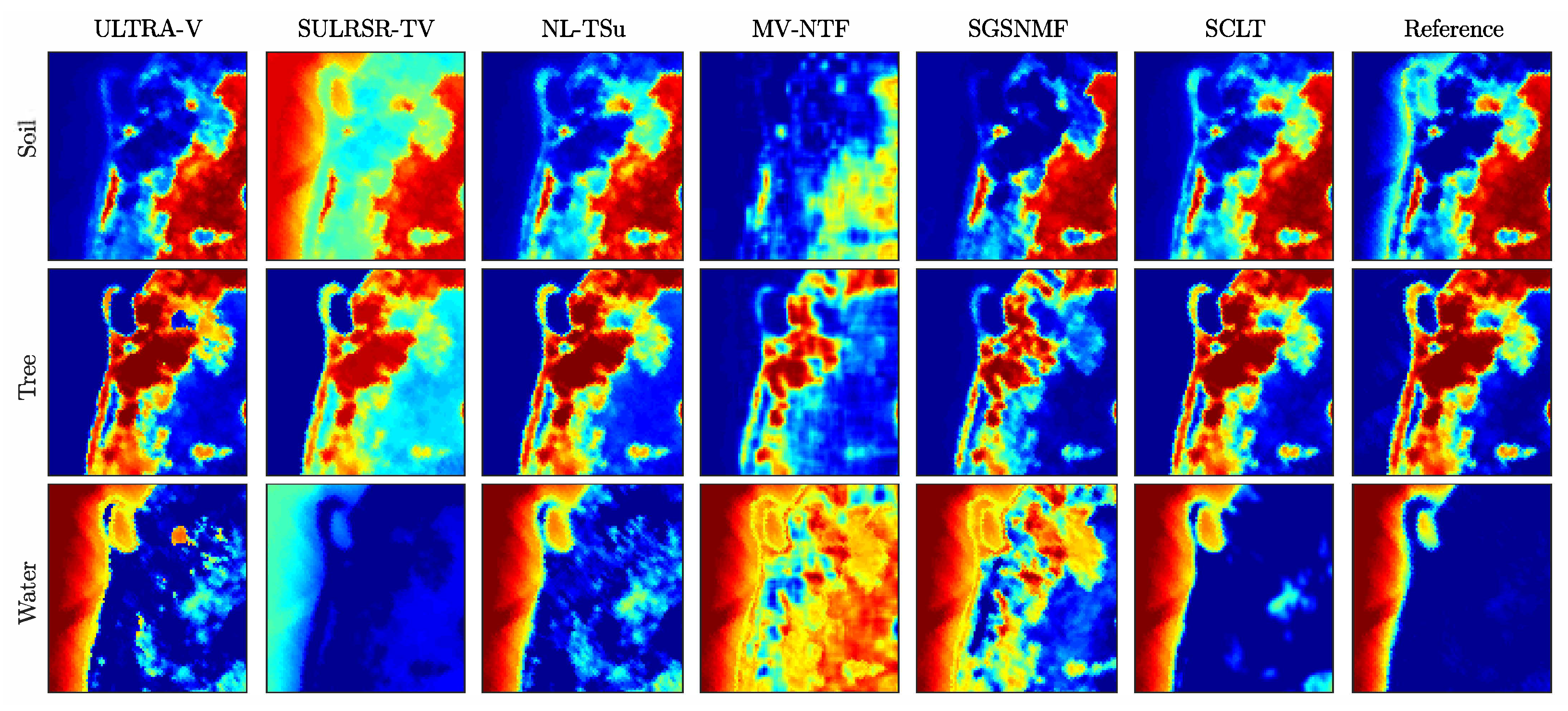
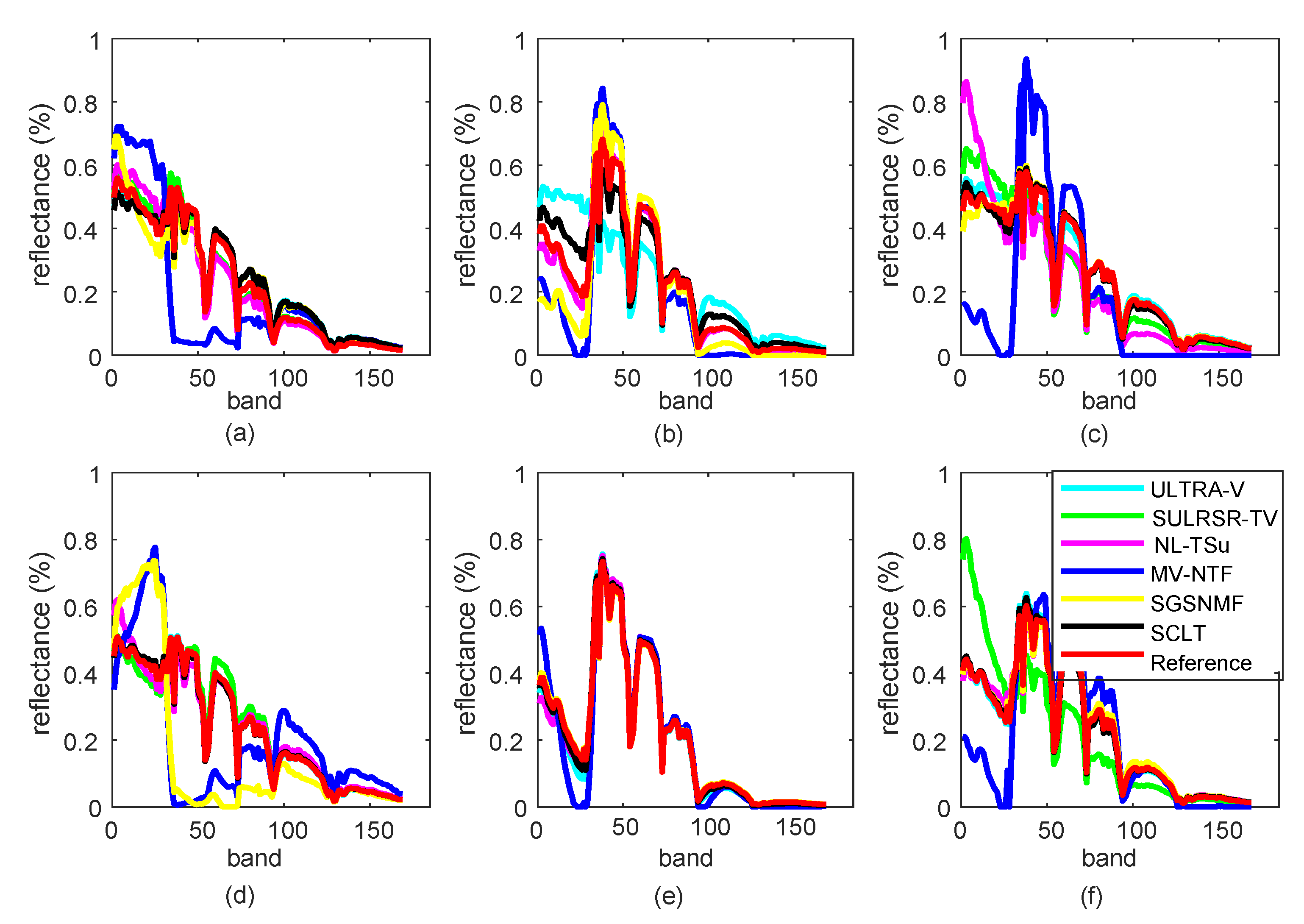
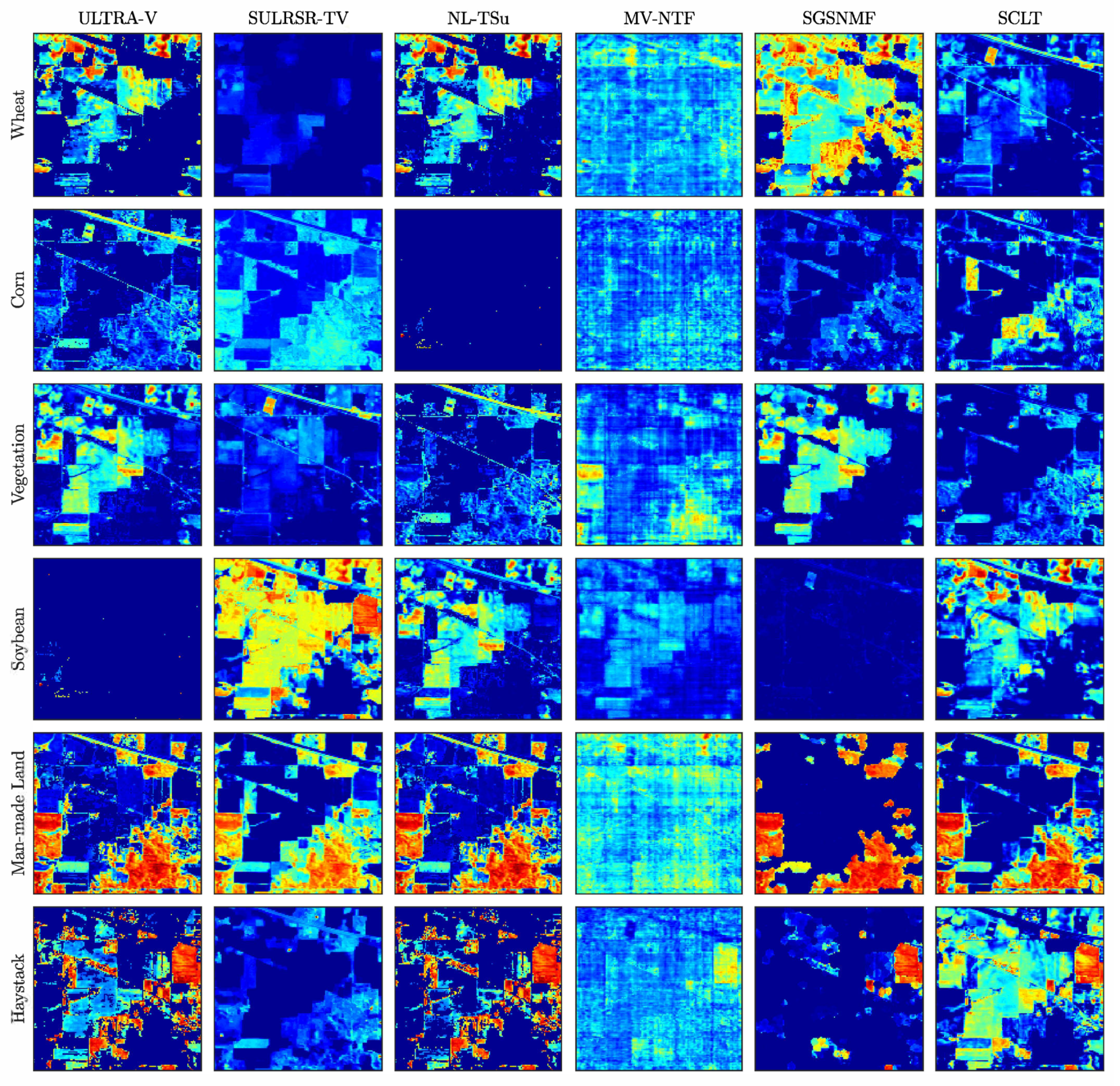
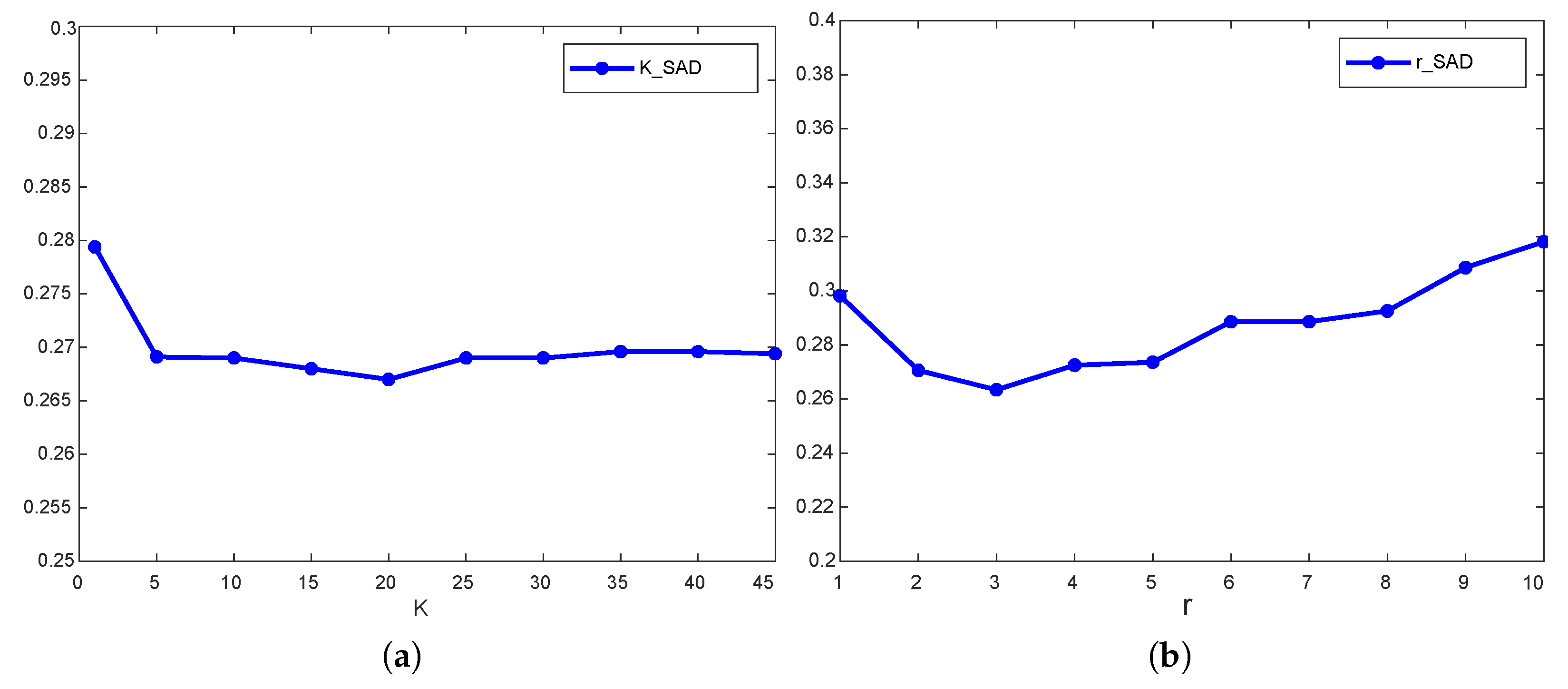
5. Experiments
5.1. Evaluation Indexes
5.2. Experiments on the Real Data
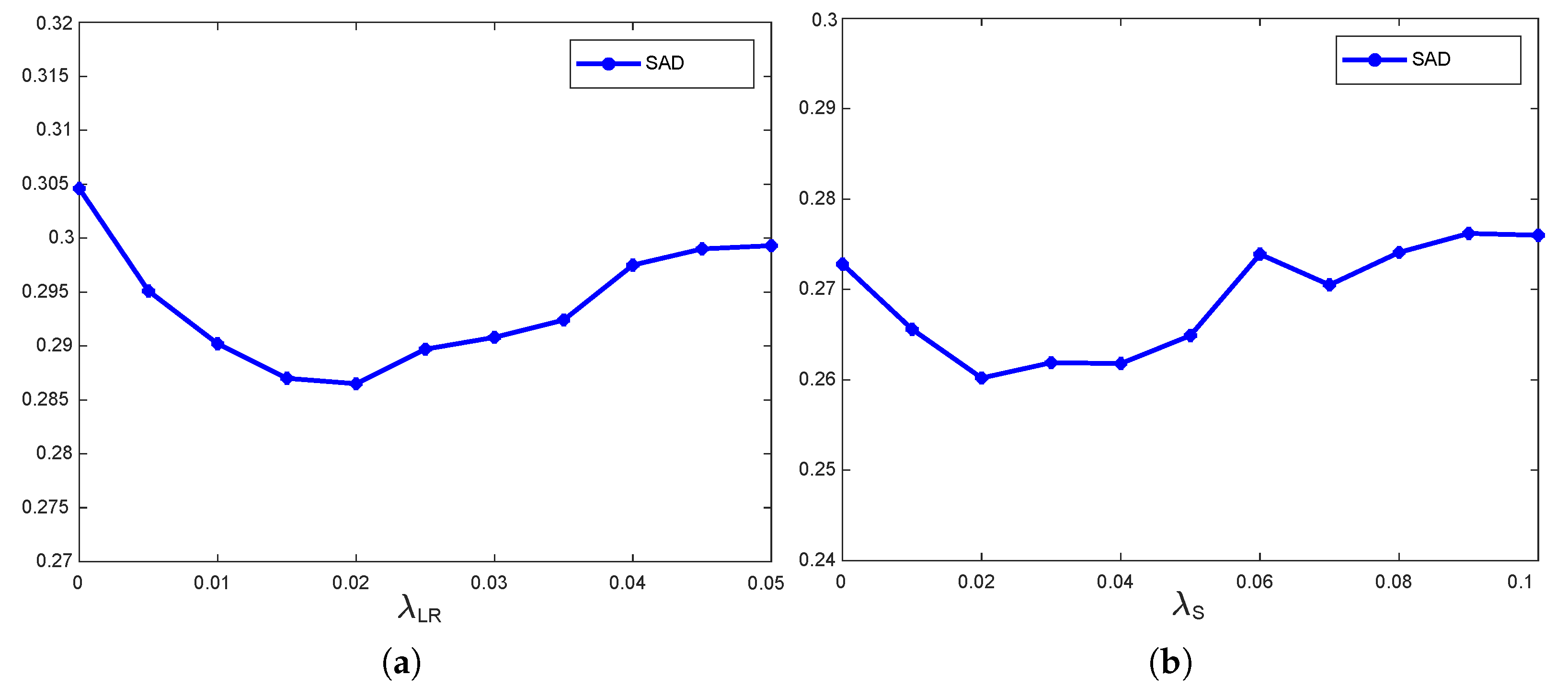
5.3. Parameter Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, X.; Sun, H.; Zheng, X. A Feature Aggregation Convolutional Neural Network for Remote Sensing Scene Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7894–7906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Gao, L.; Yao, J.; Zhang, B.; Plaza, A.; Chanussot, J. Graph Convolutional Networks for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Shao, T.; Zhou, S. A robust spectral target recognition method for hyperspectral data based on combined spectral signatures. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 4328–4331. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Similarity Constrained Convex Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Hyperspectral Anomaly Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4810–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Lu, X. Remote Sensing Scene Classification by Gated Bidirectional Network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.W. Mapping target signatures via partial unmixing of aviris data. In Proceedings of the JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 23–26 January 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, X.; Gao, L.; Yang, L. Endmember Extraction of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Images Based on the Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2635–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Dong, L.; Yuan, Y. Subspace Clustering Constrained Sparse NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 3007–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizel, F.; Benediktsson, J.A. Spatially Enhanced Spectral Unmixing Through Data Fusion of Spectral and Visible Images from Different Sensors. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Qi, H. Endmember Extraction From Highly Mixed Data Using Minimum Volume Constrained Nonnegative Matrix Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liao, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y. Bilateral Filter Regularized L2 Sparse Nonnegative Matrix Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wittman, T.; Osher, S. L1 unmixing and its application to hyperspectral image enhancement. International Society for Optics and Photonics. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 13 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhou, J.; Robles-Kelly, A. Hyperspectral unmixing via L_{1/2} sparsity-constrained nonnegative matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4282–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chang, X.; Xu, F.; Zhang, H. L1/2 regularization: A thresholding representation theory and a fast solver. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2012, 23, 1013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Meng, D.; Zhao, Q.; Cao, W.; Xu, Z. Nonconvex-Sparsity and Nonlocal-Smoothness-Based Blind Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehani, Y.E.; Gazor, S. Smooth and Sparse Regularization for NMF Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3677–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Peng, J.; Su, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yu, B. Combined Nonlocal Spatial Information and Spatial Group Sparsity in NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 17, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Guan, N. Cauchy sparse NMF with manifold regularization: A robust method for hyperspectral unmixing. Knowl. Based Syst. 2019, 184, 104898.1–104898.16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Yang, S. Group Low-Rank Nonnegative Matrix Factorization with Semantic Regularizer for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, F.; Shim, H.J.; Sun, L. Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Image with Nonlocal Low-Rank Prior. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Yokoya, N.; Chanussot, J.; Zhu, X.X. An Augmented Linear Mixing Model to Address Spectral Variability for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Xiong, F.; Zeng, S.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Y.Y. Matrix-Vector Nonnegative Tensor Factorization for Blind Unmixing of Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1776–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilius, L.B.; Pentiuc, S.G. Improving the Analysis of Hyperspectral Images Using Tensor Decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Development and Application Systems (DAS), Suceava, Romania, 21–23 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chatzichristos, C.; Kofidis, E.; Morante, M.; Theodoridis, S. Blind fMRI Source Unmixing via Higher-Order Tensor Decompositions. J. Neurosci. Methods 2019, 315, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Qian, Y. Superpixel-Based Nonnegative Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2018—2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Valencia, Spain, 22–27 July 2018; pp. 6392–6395. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, F.; Qian, Y.; Zhou, J.; Tang, Y.Y. Hyperspectral Unmixing via Total Variation Regularized Nonnegative Tensor Factorization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 2341–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B. NMF hyperspectral unmixing algorithm combined with spatial and spectral correlation analysis. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 22, 265–276. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Lu, X. Projection-Based NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 2632–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chang, X.; Liang, Y. L 1/2 regularization. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2010, 53, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauca, V.P.; Piper, J.; Plemmons, R.J. Nonnegative matrix factorization for spectral data analysis. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 2006, 416, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhu, F.; Guo, A.J.X. A Robust Multilinear Mixing Model with l 2,1 norm for Unmixing Hyperspectral Images. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), Macau, China, 1–4 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Li, C.; Mei, X.; Liu, C.; Ma, J. Robust Sparse Hyperspectral Unmixing with ℓ2,1 Norm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 1227–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, T.Z.; Zhao, X.L.; Deng, L.J. Nonlocal Tensor-Based Sparse Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Wang, J. Constrained Nonnegative Tensor Factorization for Spectral Unmixing of Hyperspectral Images: A Case Study of Urban Impervious Surface Extraction. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbiriba, T.; Borsoi, R.A.; Bermudez, J.C.M. Low-Rank Tensor Modeling for Hyperspectral Unmixing Accounting for Spectral Variability. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 1833–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, F.; Zhan, T.; Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Jeon, B. Weighted Nonlocal Low-Rank Tensor Decomposition Method for Sparse Unmixing of Hyperspectral Images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, G.; Deng, C.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Plaza, A. Spectral-Spatial Weighted Sparse Nonnegative Tensor Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Online. 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 2177–2180. [Google Scholar]
- Arthur, D.; Vassilvitskii, S. K-Means++: The Advantages of Careful Seeding. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth Acm-siam Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–9 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Dian, R.; Li, S.; Fang, L. Learning a Low Tensor-Train Rank Representation for Hyperspectral Image Super-Resolution. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 2672–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Mian, A. RCMF: Robust Constrained Matrix Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3354–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Fu, M.; Lu, X. Substance Dependence Constrained Sparse NMF for Hyperspectral Unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, R.; Wang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L. Superpixel-Based Reweighted Low-Rank and Total Variation Sparse Unmixing for Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 59, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Y. Spatial group sparsity regularized nonnegative matrix factorization for hyperspectral unmixing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 6287–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.M.P.; Dias, J.M.B. Vertex component analysis: A fast algorithm to unmix hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 898–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, H. Deep Nonnegative Dictionary Factorization for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Fan, B.; Xiang, S.; Meng, G.; Pan, C. Spectral Unmixing via Data-Guided Sparsity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2014, 23, 5412–5427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| SULRSR-TV | SGSNMF | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | SCLT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 0.2012 ± 0.0187 | 0.1955 ± 0.0013 | 0.2416 ± 0.0136 | 0.2081 ± 0.0306 | 0.0502 ± 0.0003 | 0.2761 ± 0.0081 |
| Soil | 0.2336 ± 0.0011 | 0.5131 ± 0.0011 | 0.2601 ± 0.0089 | 0.2334 ± 0.0001 | 0.1422 ± 0.0342 | 0.1107 ± 0.0001 |
| Water | 0.6194 ± 0.1761 | 0.1943 ± 0.0069 | 0.1586 ± 0.0956 | 0.4929 ± 0.2715 | 0.5641 ± 0.0013 | 0.3820 ± 0.0140 |
| Road | 0.2943 ± 0.0722 | 0.2994 ± 0.0063 | 0.4544 ± 0.0706 | 0.3665 ± 0.1179 | 0.0362 ± 0.0033 | 0.1368 ± 0.0013 |
| Mean | 0.3863 ± 0.0357 | 0.3005 ± 0.0039 | 0.3024 ± 0.0396 | 0.3723 ± 0.0482 | 0.3002 ± 0.0010 | 0.2516 ± 0.0024 |
| SULRSR-TV | SGSNMF | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | SCLT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tree | 0.0247 ± 0.0121 | 0.0099 ± 0.0001 | 0.0433 ± 0.0129 | 0.0288 ± 0.0161 | 0.0340 ± 0.0272 | 0.0465 ± 0.0019 |
| Water | 0.0495 ± 0.0011 | 0.0511 ± 0.0017 | 0.0953 ± 0.0011 | 0.0496 ± 0.0001 | 0.0566 ± 0.0090 | 0.0648 ± 0.0006 |
| Soil | 0.1299 ± 0.0004 | 0.2189 ± 0.0024 | 0.2810 ± 0.0050 | 0.1289 ± 0.0003 | 0.2401 ± 0.0221 | 0.0937 ± 0.0031 |
| Mean | 0.0818 ± 0.0019 | 0.1299 ± 0.0011 | 0.1733 ± 0.0036 | 0.0825 ± 0.0026 | 0.1438 ± 0.0154 | 0.0711 ± 0.0002 |
| SULRSR-TV | SGSNMF | MV-NTF | NL-TSUn | ULTRA-V | SCLT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Man-made land | 0.0942 ± 0.0226 | 0.1266 ± 0.0618 | 0.5500 ± 0.1006 | 0.1090 ± 0.0128 | 0.0973 ± 0.0107 | 0.0938 ± 0.0007 |
| Wheat | 0.2861 ± 0.2175 | 0.3439 ± 0.2205 | 0.3730 ± 0.0374 | 0.3320 ± 0.1958 | 0.4456 ± 0.0028 | 0.4203 ± 0.0793 |
| Corn | 0.2669 ± 0.0746 | 0.0608 ± 0.0235 | 0.7127 ± 0.0294 | 0.2022 ± 0.1006 | 0.0807 ± 0.0310 | 0.0774 ± 0.0100 |
| Soybean | 0.0867 ± 0.0084 | 0.0608 ± 0.0235 | 0.4952 ± 0.1611 | 0.1138 ± 0.0713 | 0.0090 ± 0.0011 | 0.0089 ± 0.0036 |
| Vegetation | 0.0624 ± 0.0092 | 0.0270 ± 0.0151 | 0.2666 ± 0.0539 | 0.0651 ± 0.0085 | 0.0730 ± 0.0063 | 0.0689 ± 0.0128 |
| Haystack | 0.1375 ± 0.1453 | 0.0611 ± 0.0363 | 0.4638 ± 0.0661 | 0.0725 ± 0.0812 | 0.0381 ± 0.0321 | 0.0375 ± 0.0018 |
| Mean | 0.2079 ± 0.0352 | 0.3225 ± 0.0340 | 0.5041 ± 0.0184 | 0.1993 ± 0.0353 | 0.1921 ± 0.0011 | 0.1618 ± 0.0312 |
| Data | K | r | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jasper | 20 | 3 | 0.020 | 0.02 |
| Samon | 20 | 3 | 0.015 | 0.01 |
| Indiana | 50 | 5 | 0.010 | 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, L.; Yuan, Y. Sparse Constrained Low Tensor Rank Representation Framework for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081473
Dong L, Yuan Y. Sparse Constrained Low Tensor Rank Representation Framework for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081473
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Le, and Yuan Yuan. 2021. "Sparse Constrained Low Tensor Rank Representation Framework for Hyperspectral Unmixing" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081473
APA StyleDong, L., & Yuan, Y. (2021). Sparse Constrained Low Tensor Rank Representation Framework for Hyperspectral Unmixing. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1473. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081473





