A Large-Scale Deep-Learning Approach for Multi-Temporal Aqua and Salt-Culture Mapping
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
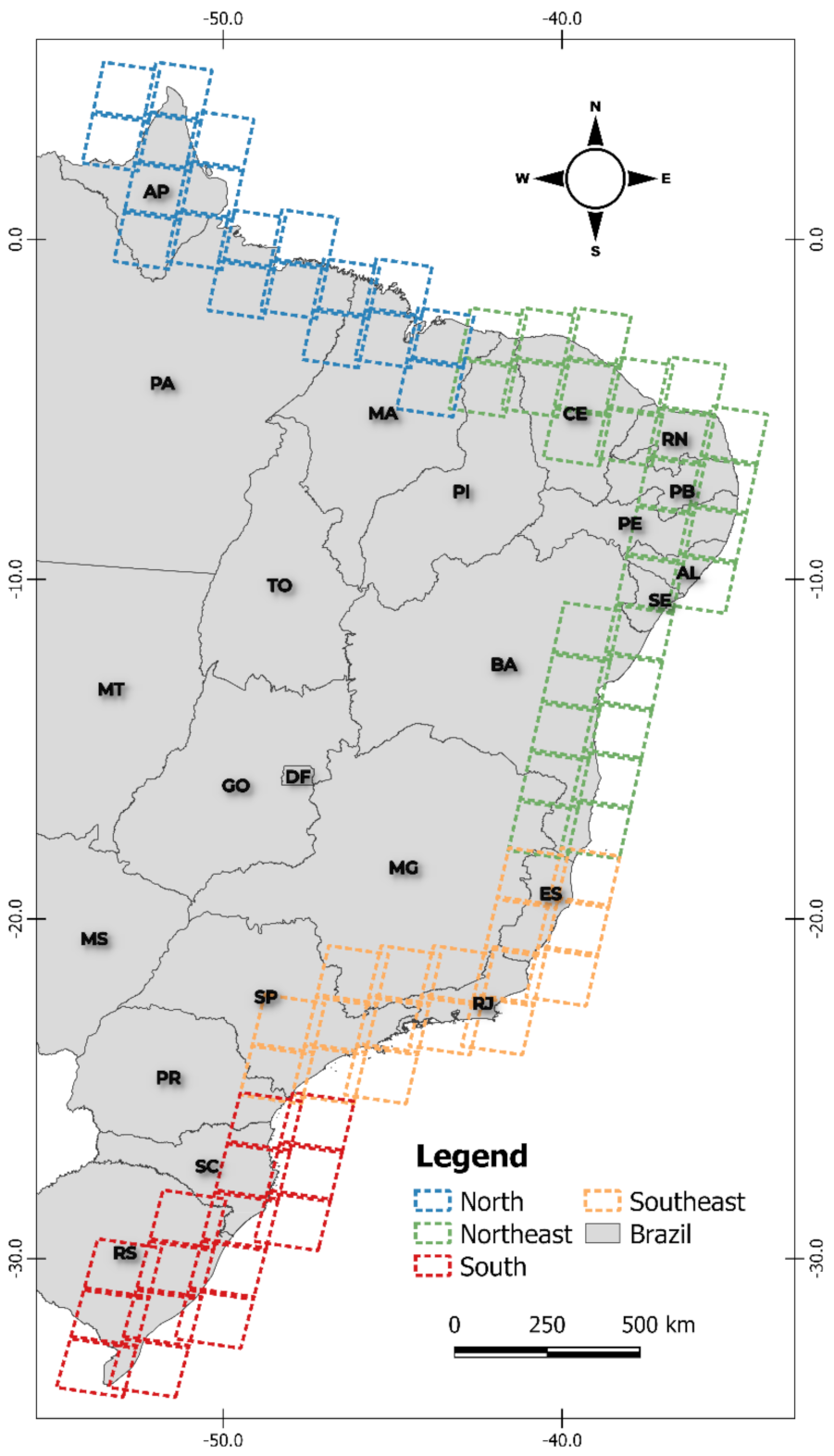
2.1. Study Site
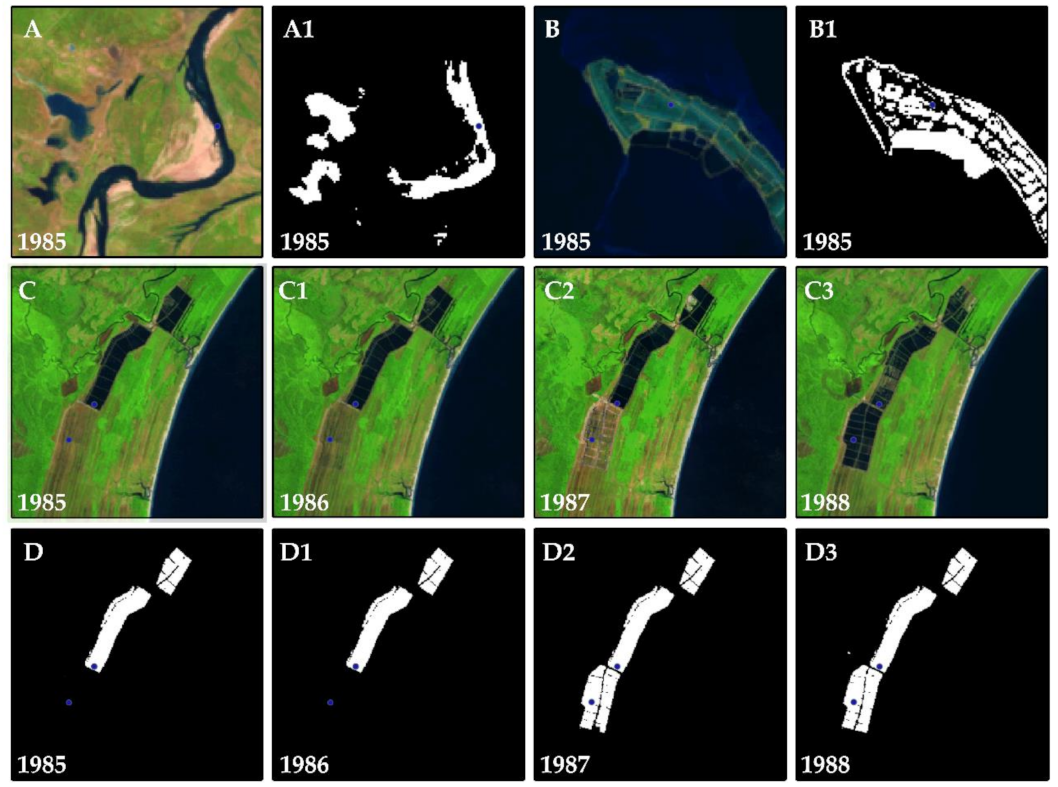
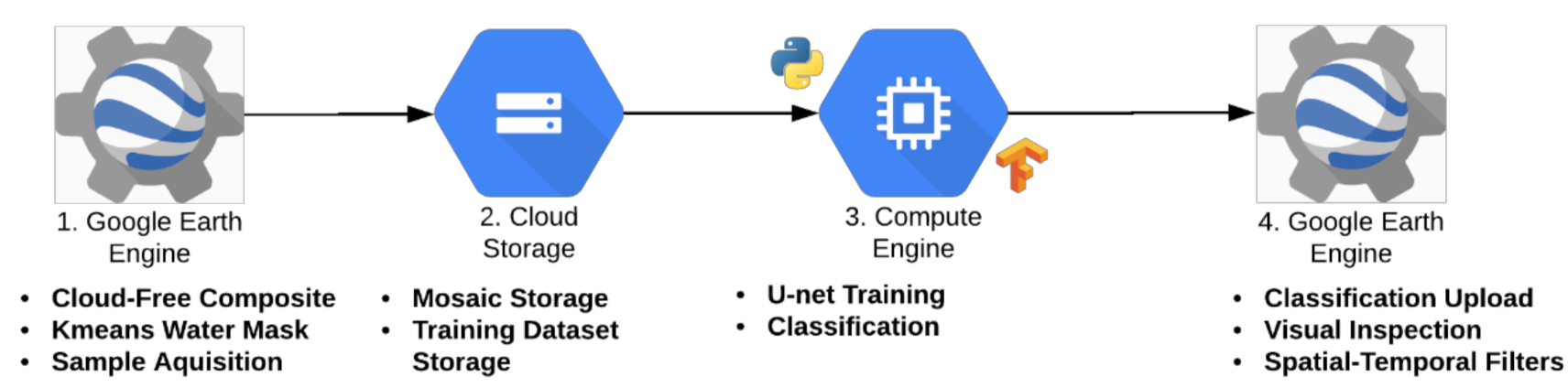
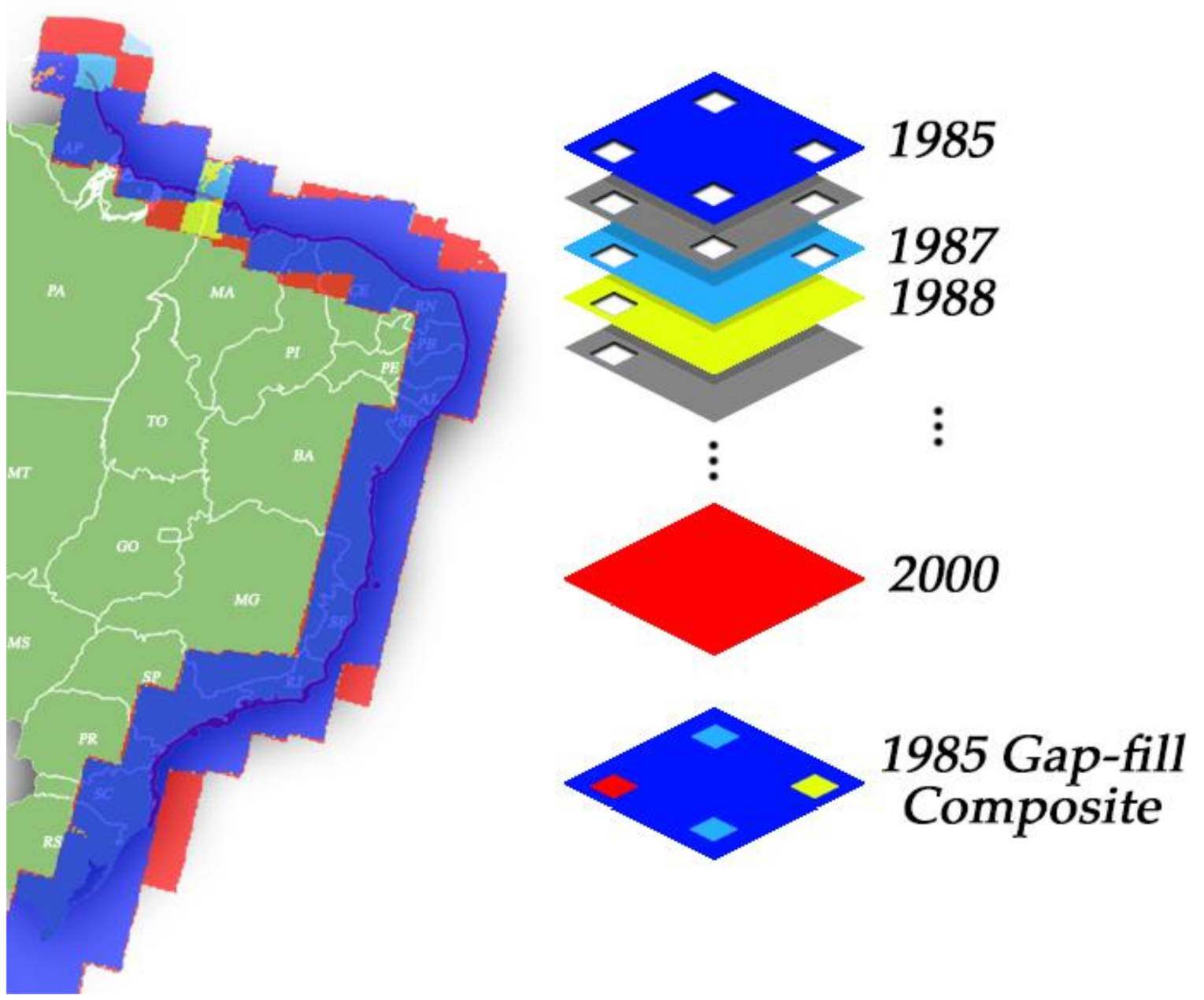
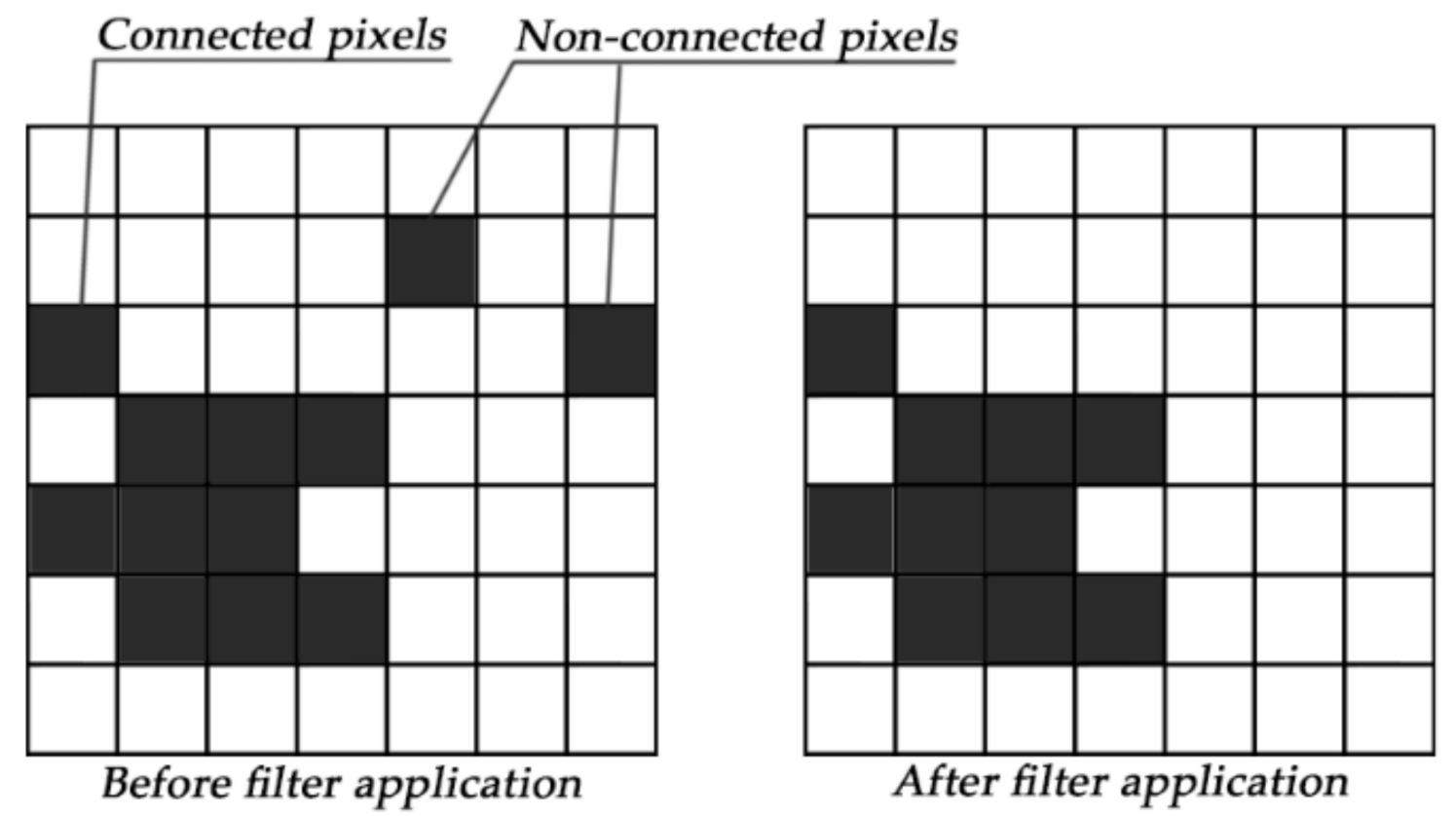
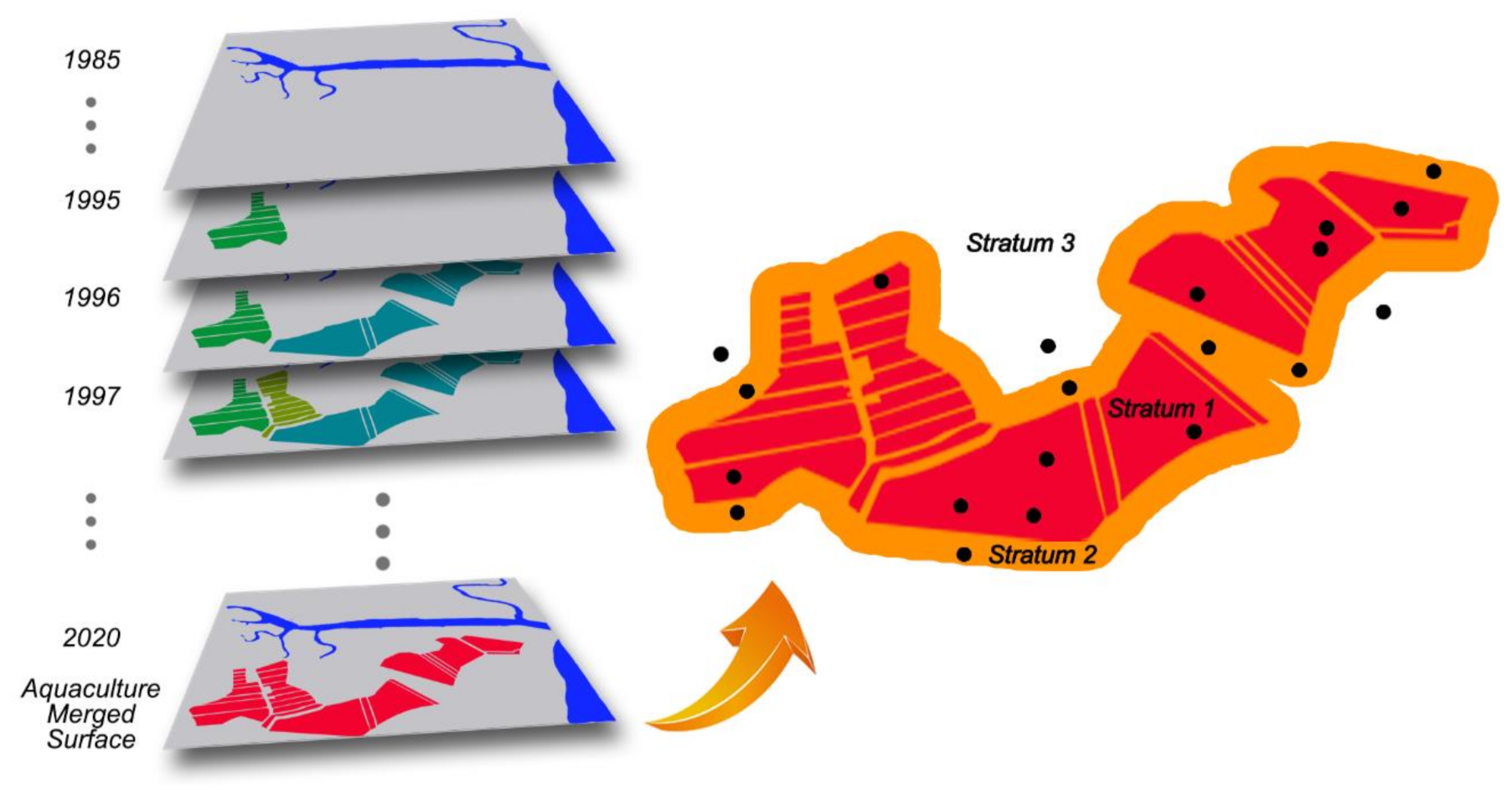
2.2. Data Processing
- where;
- , is the sample size.
- , is the population size.
- , is the score of the normal distribution at a given confidence degree.
- , is the confidence degree.
- , is the population proportion to be estimated.
- , the maximum error margin.
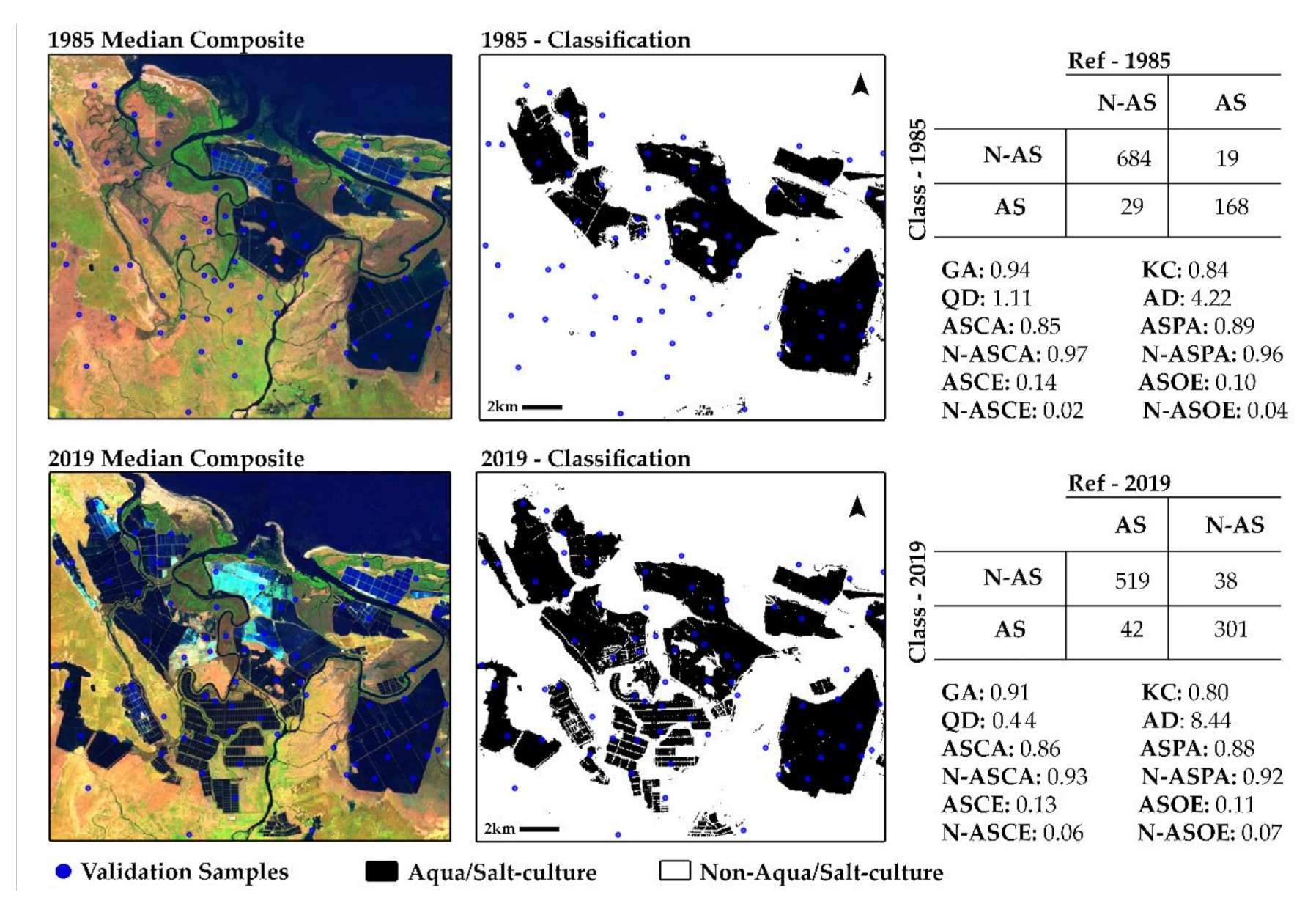
3. Results
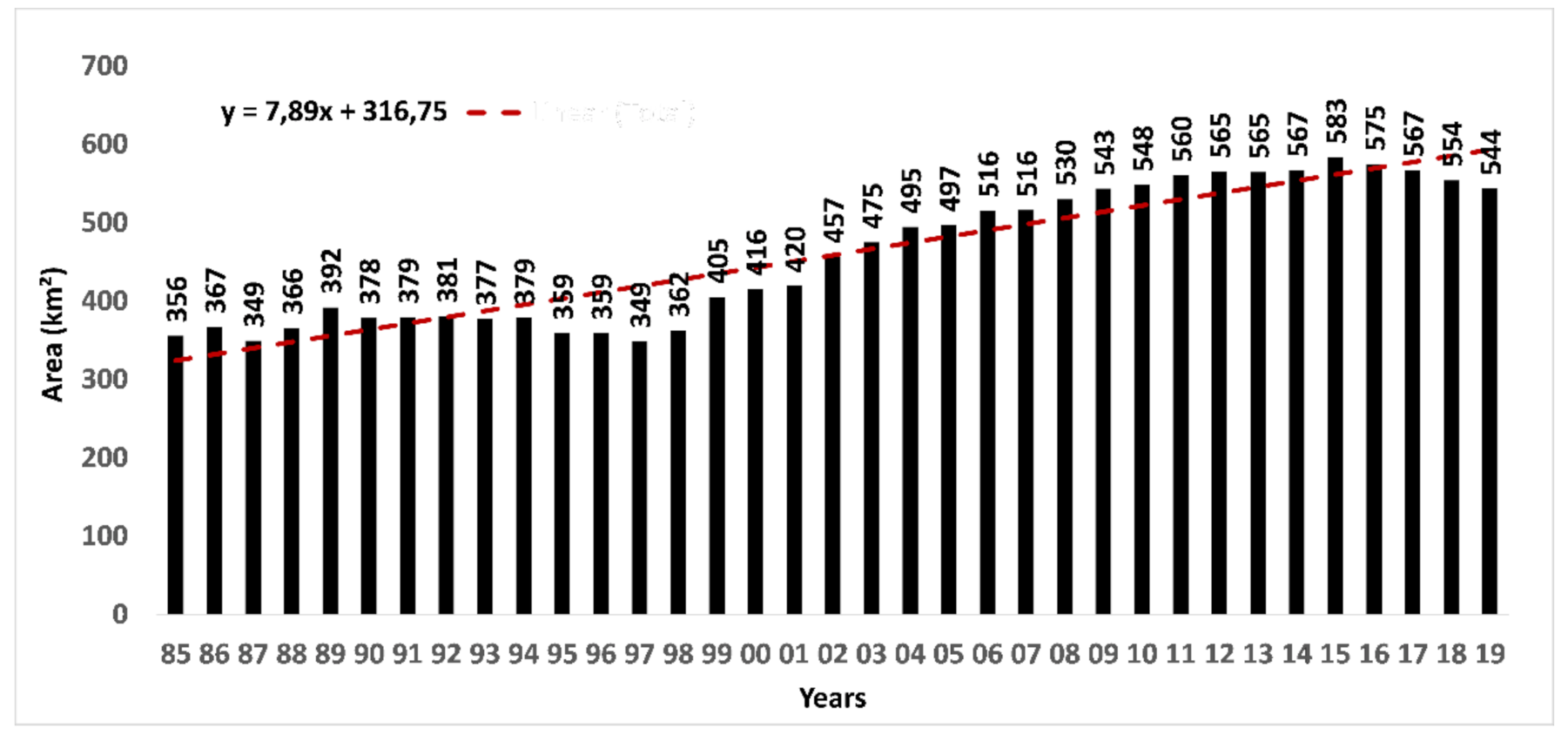
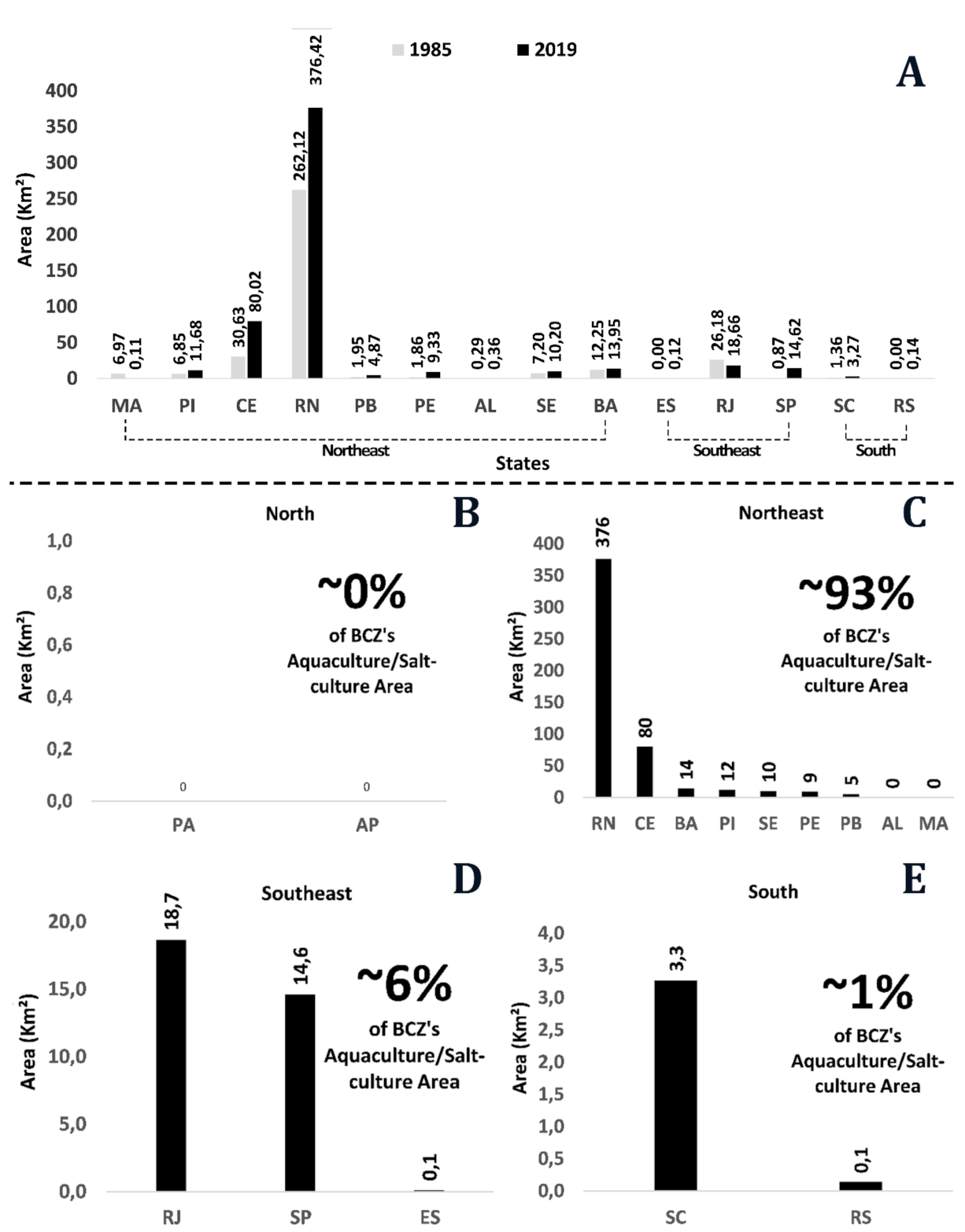
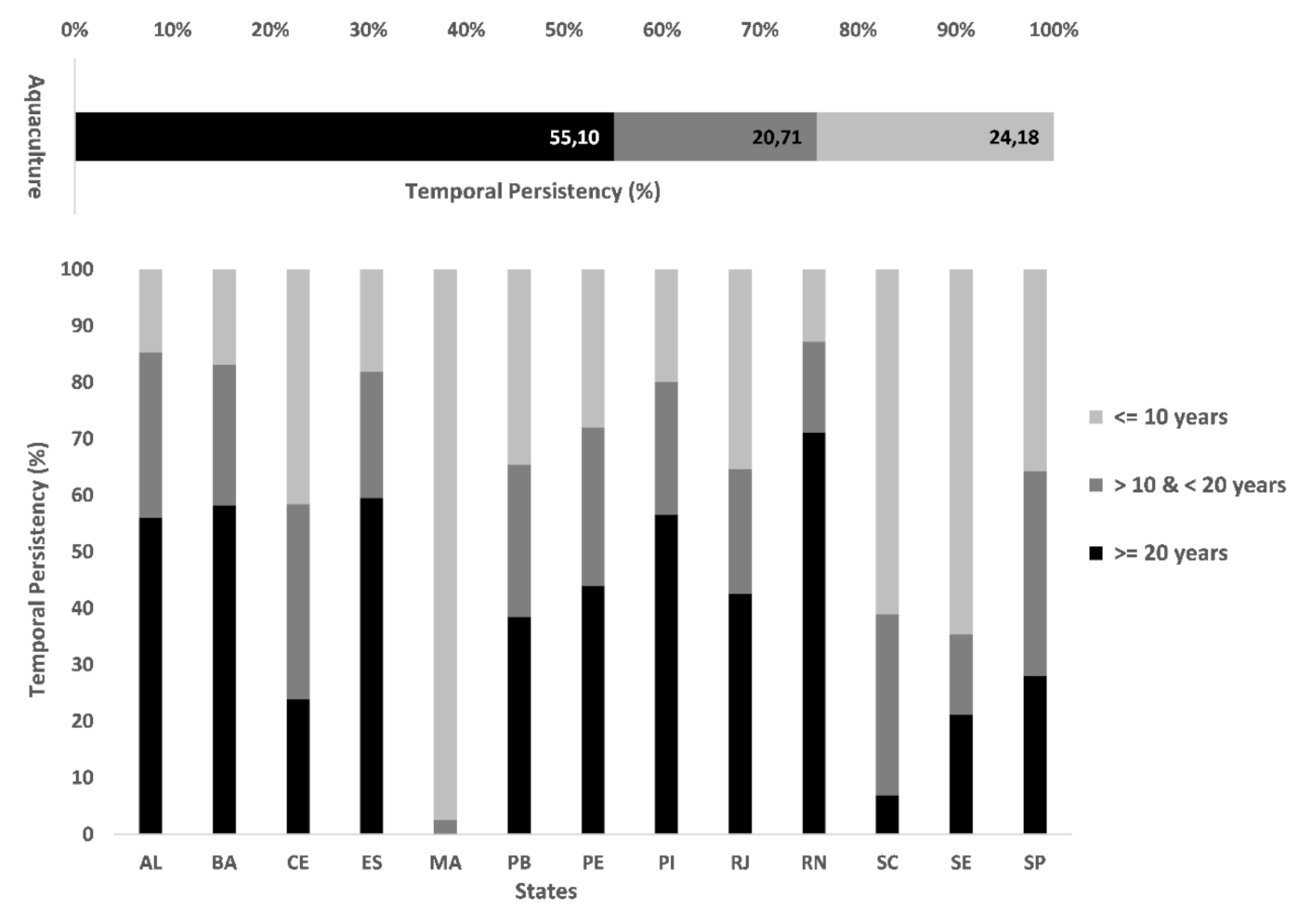
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Changes of Aqua-Salt Culture Ponds In BCZ
3.2. Aqua-Salt Culture Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food And Agriculture Organization (FAO). Fishery and Aquaculture Statistics—2017; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019; ISBN 9789251316696. [Google Scholar]
- Food And Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2018—Meeting the Sustainable Development Goals; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 9789251305621. [Google Scholar]
- Food And Agriculture Organization (FAO). The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ottinger, M.; Clauss, K.; Kuenzer, C. Aquaculture: Relevance, distribution, impacts and spatial assessments—A review. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2016, 119, 244–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, C.; Ochieng, E.; Tieszen, L.L.; Zhu, Z.; Singh, A.; Loveland, T.; Masek, J.; Duke, N. Status and distribution of mangrove forests of the world using earth observation satellite data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2011, 20, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Bunting, P.; Lucas, R.; Hardy, A.; Rosenqvist, A.; Fatoyinbo, T. Mapping Mangrove Extent and Change: A Globally Applicable Approach. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunting, P.; Rosenqvist, A.; Lucas, R.M.; Rebelo, L.M.; Hilarides, L.; Thomas, N.; Hardy, A.; Itoh, T.; Shimada, M.; Finlayson, C.M. The global mangrove watch—A new 2010 global baseline of mangrove extent. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, C.; Cortinhas, L.; Nerino, G.; Rodrigues, J.; Sadeck, L.; Adami, M.; Souza-Filho, W.P. Brazilian Mangrove Status: Three Decades of Satellite Data Analysis. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.-F.; Cottam, A.; Gorelick, N.; Belward, A.S. High-resolution mapping of global surface water and its long-term changes. Nature 2016, 540, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijendijk, A.; Hagenaars, G.; Ranasinghe, R.; Baart, F.; Donchyts, G.; Aarninkhof, S. The State of the World’s Beaches. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, T.A.; zu Ermgassen, P.S.E.; Friess, D.A.; Krauss, K.W.; Lovelock, C.E.; Thorley, J.; Tingey, R.; Woodroffe, C.D.; Bunting, P.; Cormier, N.; et al. A global biophysical typology of mangroves and its relevance for ecosystem structure and deforestation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomasino, D.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Lee, S.; Feliciano, E.; Trettin, C.; Simard, M. A Comparison of Mangrove Canopy Height Using Multiple Independent Measurements from Land, Air, and Space. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagomasino, D.; Fatoyinbo, T.; Lee, S.; Feliciano, E.; Trettin, C.; Shapiro, A.; Mangora, M.M. Measuring mangrove carbon loss and gain in deltas. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 25002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Liu, S.; Ji, H. Mapping national-scale aquaculture ponds based on the Google Earth Engine in the Chinese coastal zone. Aquaculture 2020, 520, 734666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Guo, X.; Chen, R. Automatic extraction of aquaculture ponds based on Google Earth Engine. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 198, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.R.; Filizola Junior, N.P.; Cremon, É.H. Analysis of Suspended Sediment in the Anavilhanas Archipelago, Rio Negro, Amazon Basin. Water 2020, 12, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, R.R.; Harmel, T.; Martinez, J.-M.; Filizola Junior, N.P. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Suspended Sediments in the Negro River, Amazon Basin, from In Situ and Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2021, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertes, L.A.K.; Smith, M.O.; Adams, J.B. Estimating suspended sediment concentrations in surface waters of the Amazon River wetlands from Landsat images. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 43, 281–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.; Souza-Filho, P.; Novo, E.; Carlos, F.; Barbosa, C. Mapping Mining Areas in the Brazilian Amazon Using MSI/Sentinel-2 Imagery (2017). Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. CoRR 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer-Novelli, Y.; Cintrón-Molero, G.; Adaime, R.R.; de Camargo, T.M.; Cintron-Molero, G.; de Camargo, T.M. Variability of Mangrove Ecosystems along the Brazilian Coast. Estuaries 1990, 13, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, S.W.P.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M. Use of Multi-Sensor Data to Identify and Map Tropical Coastal Wetlands in the Amazon of Northern Brazil. Wetlands 2011, 31, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Filho, P.W.M. Costa de manguezais de macromaré da Amazônia: Cenários morfológicos, mapeamento e quantificação de áreas usando dados de sensores remotos. Rev. Bras. Geofísica 2005, 23, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, W.R., Jr.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Proisy, C.; Lucas, R.M.; Rosenqvist, A. Mapping changes in the largest continuous Amazonian mangrove belt using object-based classification of multisensor satellite imagery. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 117, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, J.M.L. The Coastal Zone of Brazil. In Geology and Geomorphology of Holocene Coastal Barriers of Brazil; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 17–51. ISBN 978-3-540-44771-9. [Google Scholar]
- IBGE. Sistema IBGE de Recuperação Automática (SIDRA)—Produção da Aquicultura Brasileira; Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística: Brasília, Brazil, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, J.M.P.; de Souza, E.N.V.; Candido, J.R.B.; Dantas, M.D.A.; Nunes, A.R.D.; Ribeiro, K.; Teixeira, D.I.A.; Lanza, D.C.F. Alternative PCR primers for genotyping of Brazilian WSSV isolates. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 162, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bandeira, J.T.; de Morais, R.S.M.M.; e Silva, R.P.P.; Mendes, E.S.; da Silva, S.M.B.C.; dos Santos, F.L. First report of white spot syndrome virus in wild crustaceans and mollusks in the Paraíba River, Brazil. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.N.; Varela, A.P.M.; Cibulski, S.P.; Esmaile, S.; Lima, F.; Rosado Spilki, F.; Schemes Heinzelmann, L.; Bordin da Luz, R.; Abreu, P.C.; Roehe, P.M.; et al. A Brief History of White spot syndrome virus and Its Epidemiology in Brazil. Virus Rev. Res. 2013, 18, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubach, R.; Correia, E.S.; Zaiden, S.; Martino, R.C.; Cavalli, R.O. Aquaculture in Brazil. World Aquac. Rouge 2003, 34, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Tenório, G.S.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M.; Ramos, E.M.L.S.; Alves, P.J.O. Mangrove shrimp farm mapping and productivity on the Brazilian Amazon coast: Environmental and economic reasons for coastal conservation. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2015, 104, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rocha, I.P. Shrimp farming in Brazil: Burgeoning industry recovering, future holds potential. In Global Aquaculture Alliance; Abccam: Recife, Brazil, 2010; pp. 43–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bueno, G.W.; Ostrensky, A.; Canzi, C.; de Matos, F.T.; Roubach, R. Implementation of aquaculture parks in Federal Government waters in Brazil. Rev. Aquac. 2015, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.B.; Oliveira, F.J.M.; Giacomini, H.C.; Lima-Junior, D.P. Expansion of aquaculture parks and the increasing risk of non-native species invasions in Brazil. Rev. Aquac. 2018, 10, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Landsat 8 (L8) Data Users Handbook; EROS: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Storey, J.; Choate, M.; Lee, K. Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager On-Orbit Geometric Calibration and Performance. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11127–11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, P.M.; Barker, J.L.; Markham, B.L.; Irish, R.R.; Fedosejevs, G.; Storey, J.C. Radiometric cross-calibration of the Landsat-7 ETM+ and Landsat-5 TM sensors based on tandem data sets. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 78, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. Landsat Collection 1 Level 1 Product Definition; EROS: Sioux Falls, SD, USA, 2017; p. 26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and photographic infrared linear combinations for monitoring vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.S.; Kearney, M.S. Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh Thematic Mapper scenes using spectral indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2317–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, P.; Foody, G.M.; Herold, M.; Stehman, S.V.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wulder, M.A. Good practices for estimating area and assessing accuracy of land change. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 42–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Santacruz, A. Quantity, exchange, and shift components of difference in a square contingency table. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 7543–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehman, S.V. Estimating area and map accuracy for stratified random sampling when the strata are different from the map classes. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 4923–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.T.M.; Vasconcelos, F.P.; Diniz, M.T.M.; Vasconcelos, F.P. Natural conditions for the sea salt production in Brazil. Mercator 2017, 16, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.F.d.S.; da Silva, A.A.; Medeiros, D.H.M.; Lucena Filho, M.A.; Rocha, R.D.M.; Lillebo, A.I.; Soares, A.M.V.M. Breve revisão sobre a evolução histórica da atividade salineira no estado do Rio Grande do Norte (Brasil). Soc. Nat. 2013, 25, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, M.T.M.; Vasconcelos, F.P.; Martins, M.B. Inovação tecnológica na produção brasileira de sal marinho e as alterações sócioterritoriais dela decorrentes: Uma análise sob a ótica da Teoria do Empreendedorismo de Schumpeter. Soc. Nat. 2015, 27, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, A.H.; Sharma, K.C.; Banday, U.J. Impact of Climatic Variability on Salt Production in Sambhar Lake, a Ramsar Wetland of Rajasthan, India. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2015, 23, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, K.C. Impactos Econômicos das Mudanças Climáticas sobre a Indústria de Sal Marinho na Principal Região Produtora do Brasil. Rev. Bras. Geogr. Física 2017, 10, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICMBio. Atlas dos Manguezais do Brasil, 1st ed.; ICMBio: Brasília, Brazil, 2017; ISBN 978-85-61842-75-8. [Google Scholar]

| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Classifier | U-Net |
| Tile-Size | 256 × 256 pixels |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Learning Rate | 0.1 |
| Momentum | 0.9 |
| Decay | 1e−4 |
| Samples | 8400 (geometries) |
| Attributes | MNDWI, NDVI, and NDSI |
| Classes | 2 (Aqua-Salt-culture and Non-Aqua-Salt-culture) |
| Rule | Input (Year) | Output | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T3 | T1 | T2 | T3 | |
| GR | AS | N-AS | AS | AS | AS | AS |
| GR | N-AS | AS | N-AS | N-AS | N-AS | N-AS |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, C.; Cortinhas, L.; Pinheiro, M.L.; Sadeck, L.; Fernandes Filho, A.; Baumann, L.R.F.; Adami, M.; Souza-Filho, P.W.M. A Large-Scale Deep-Learning Approach for Multi-Temporal Aqua and Salt-Culture Mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081415
Diniz C, Cortinhas L, Pinheiro ML, Sadeck L, Fernandes Filho A, Baumann LRF, Adami M, Souza-Filho PWM. A Large-Scale Deep-Learning Approach for Multi-Temporal Aqua and Salt-Culture Mapping. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(8):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081415
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Cesar, Luiz Cortinhas, Maria Luize Pinheiro, Luís Sadeck, Alexandre Fernandes Filho, Luis R. F. Baumann, Marcos Adami, and Pedro Walfir M. Souza-Filho. 2021. "A Large-Scale Deep-Learning Approach for Multi-Temporal Aqua and Salt-Culture Mapping" Remote Sensing 13, no. 8: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081415
APA StyleDiniz, C., Cortinhas, L., Pinheiro, M. L., Sadeck, L., Fernandes Filho, A., Baumann, L. R. F., Adami, M., & Souza-Filho, P. W. M. (2021). A Large-Scale Deep-Learning Approach for Multi-Temporal Aqua and Salt-Culture Mapping. Remote Sensing, 13(8), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13081415







