Shadow Detection and Compensation from Remote Sensing Images under Complex Urban Conditions
Abstract
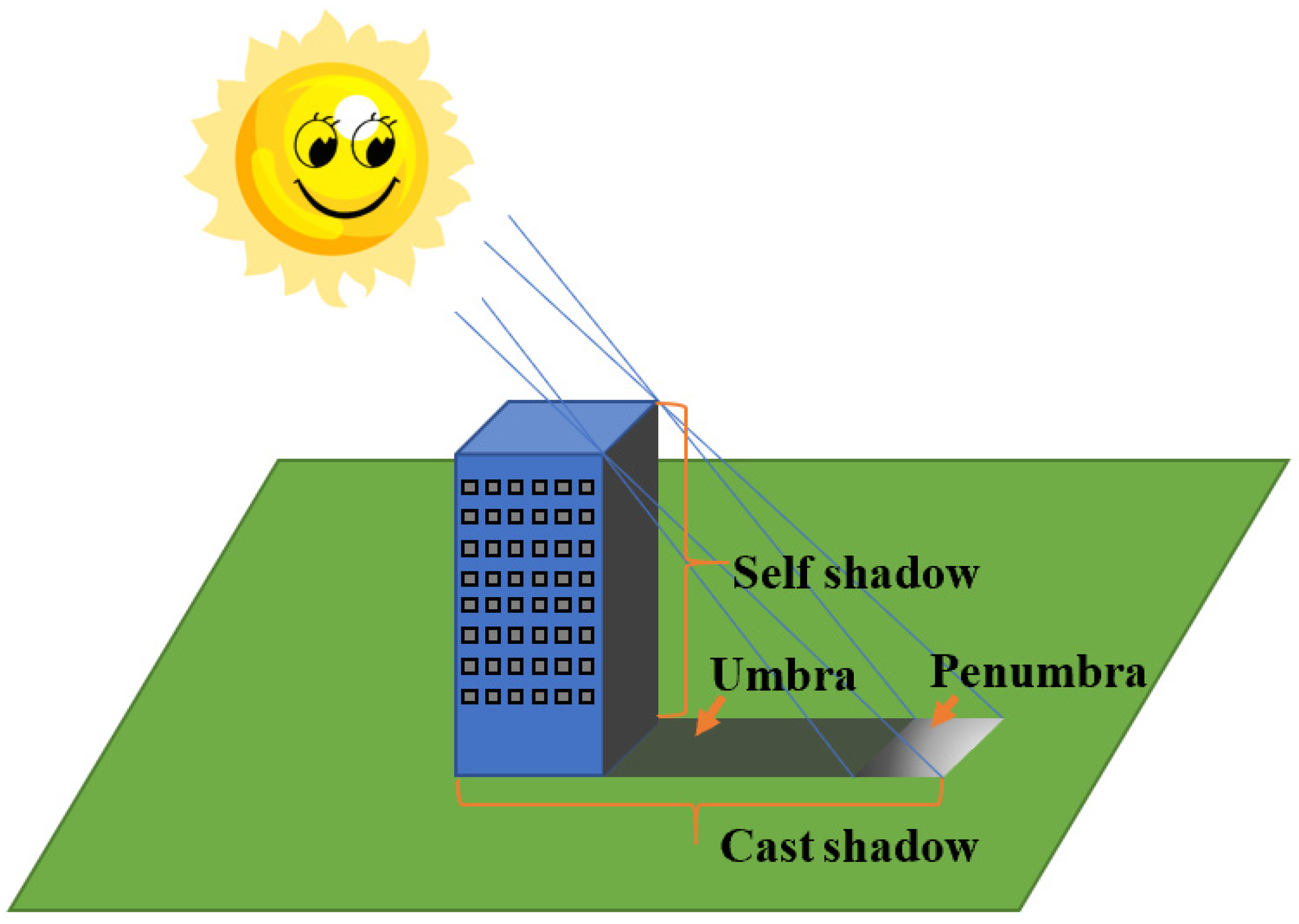
1. Introduction
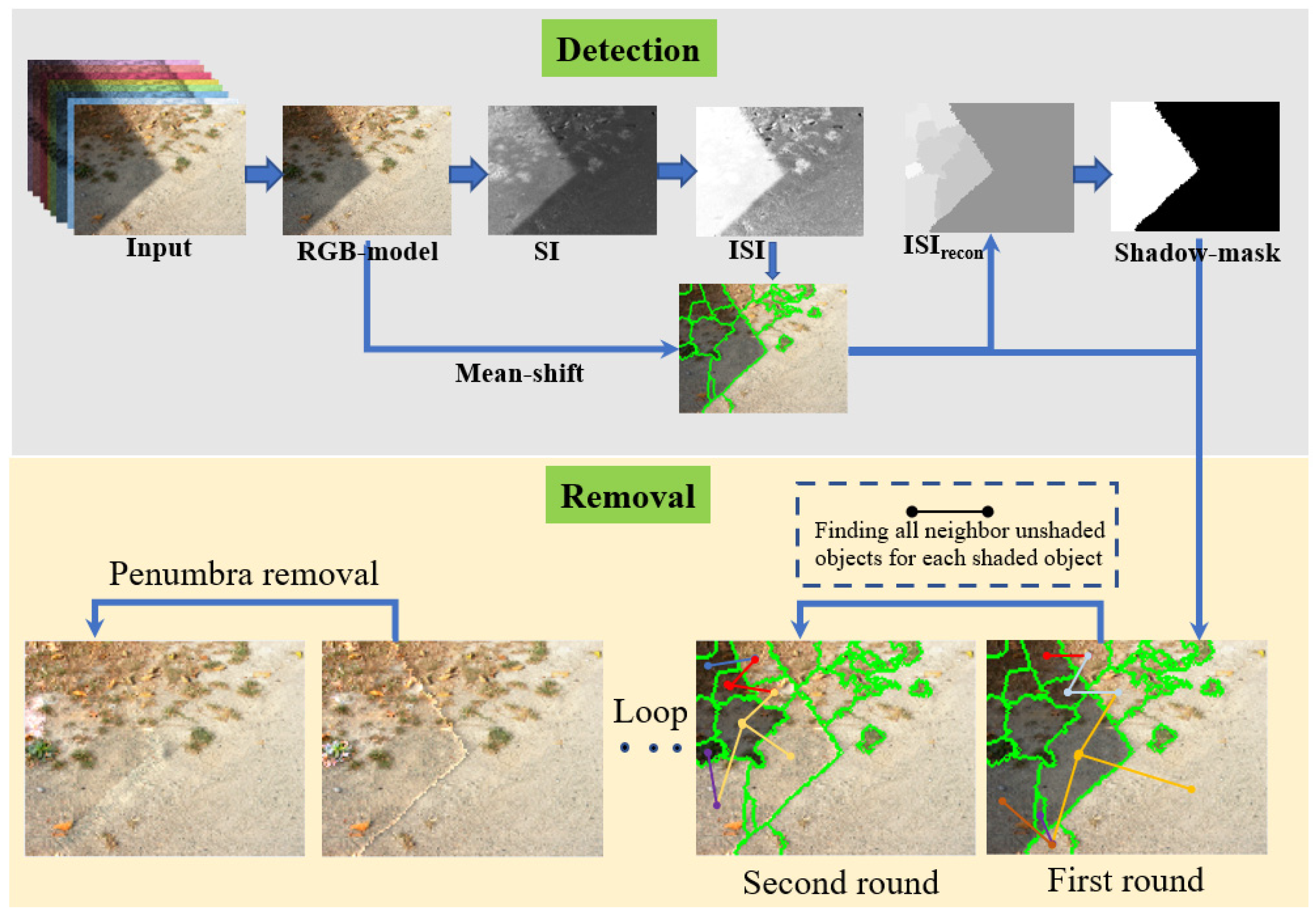
2. Shadow Detection
2.1. Image Segmentation with Mean-Shift Method
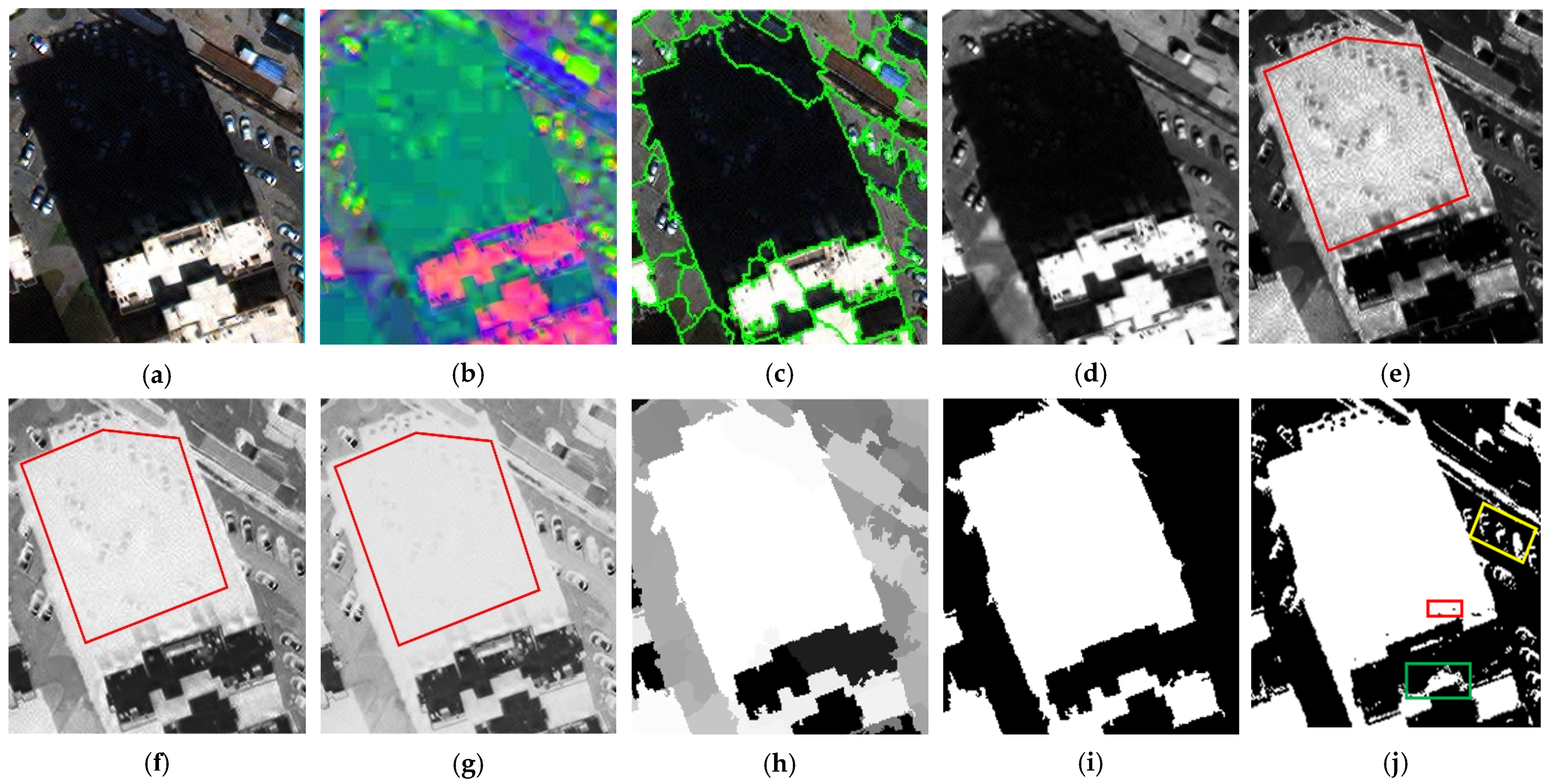
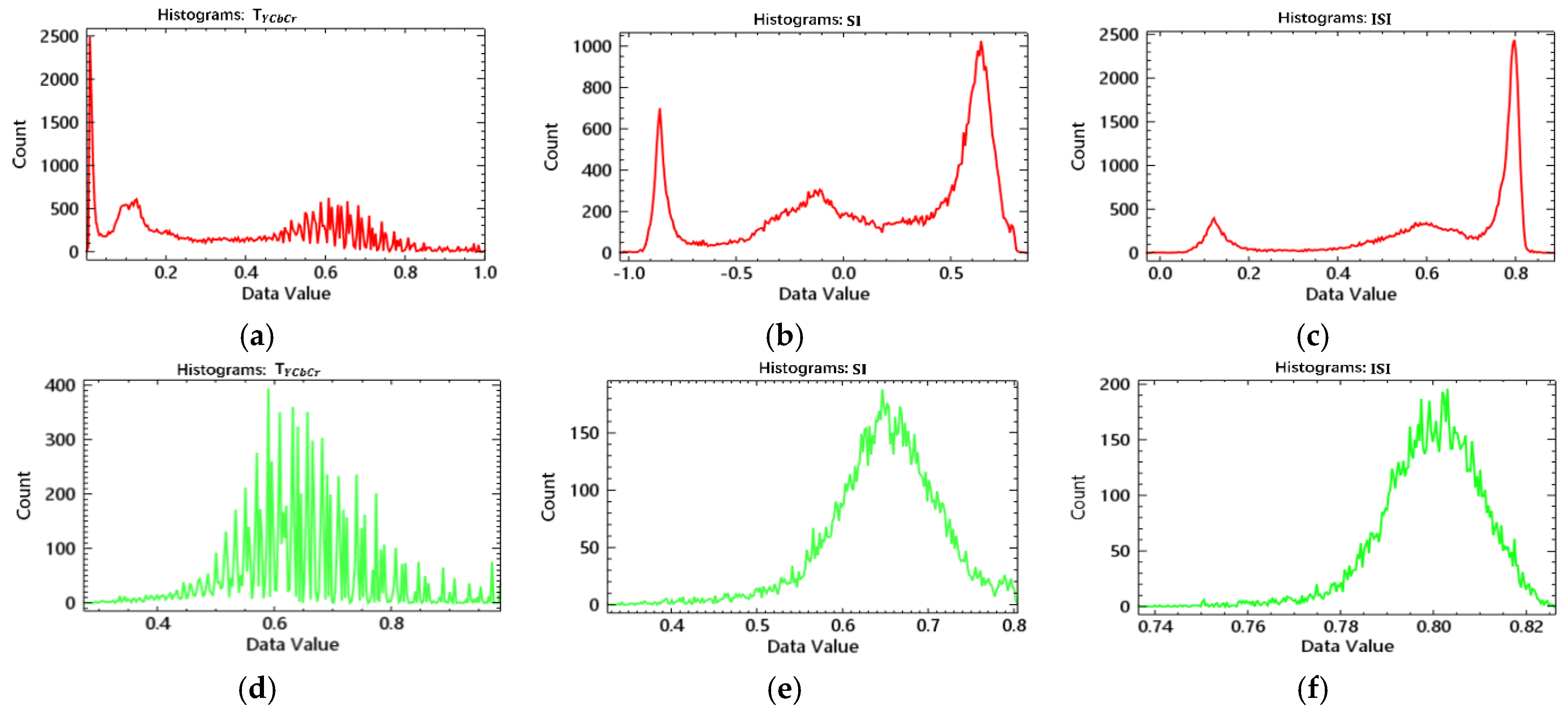
2.2. Improved Shadow Index (ISI)
2.3. Reconstruction of ISI and Shadow Classification
3. Shadow Compensation and Post-Processing
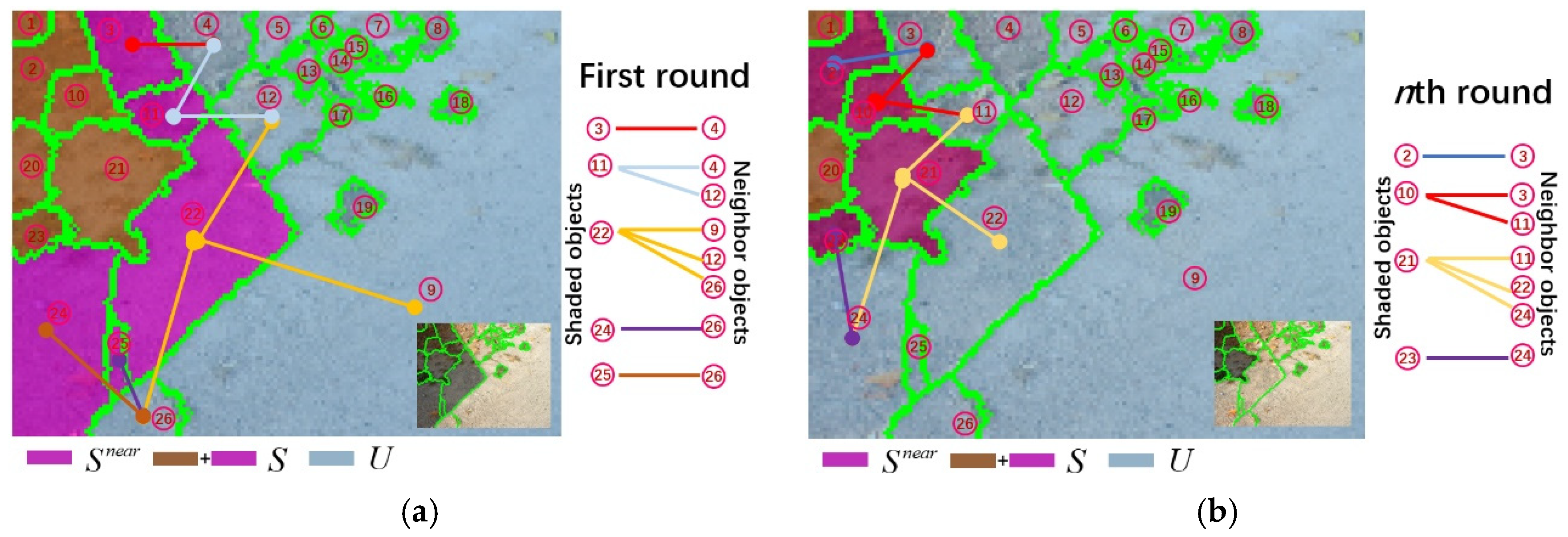
3.1. Shadow Compensation Based on the Information from Adjacent Objects
- Mark the shadow region as containing objects, and label all the non-shadow regions as with objects;
- Find all the shadow objects directly adjacent to the non-shadow region labeled as with objects;
- Describe a shadow object in as , , find all non-shadow objects adjacent to , and mark them as containing objects;
- For the ith shadow object , its average value in band is , , and the average value of adjacent non-shadow objects in band is , . and are used to calculate the ratio of the direct light intensity to the ambient light intensity, then to get the mean value of the ratios:
- Then ( pixels) treated with shadow compensation in band is :The after shadow compensation is :
- Repeat Step 3 to 5 until , and the after shadow compensation is:
- Update , , and : , , , and ;
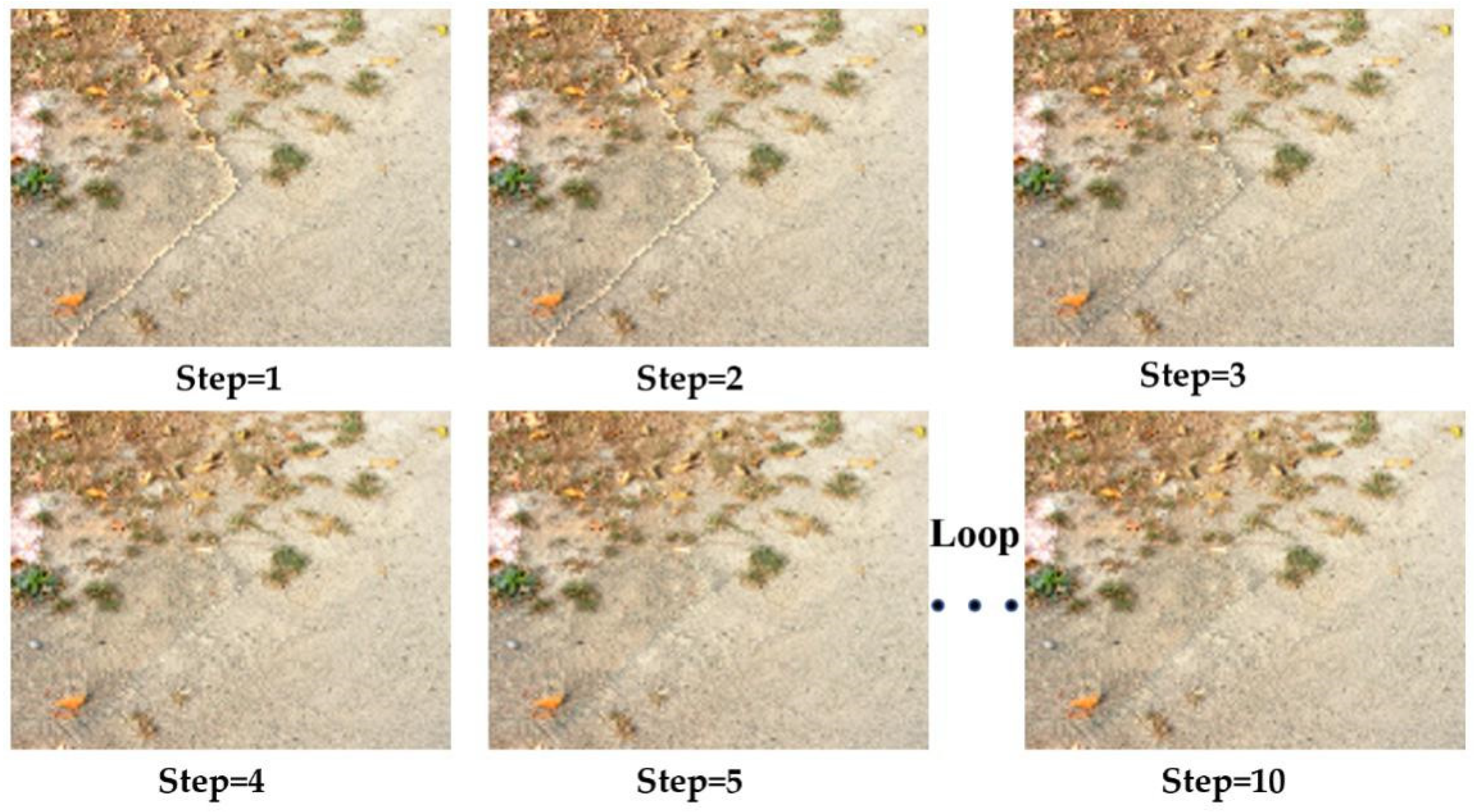
- Loop Steps 2 to 7, until , then the shadow compensation process is complete.
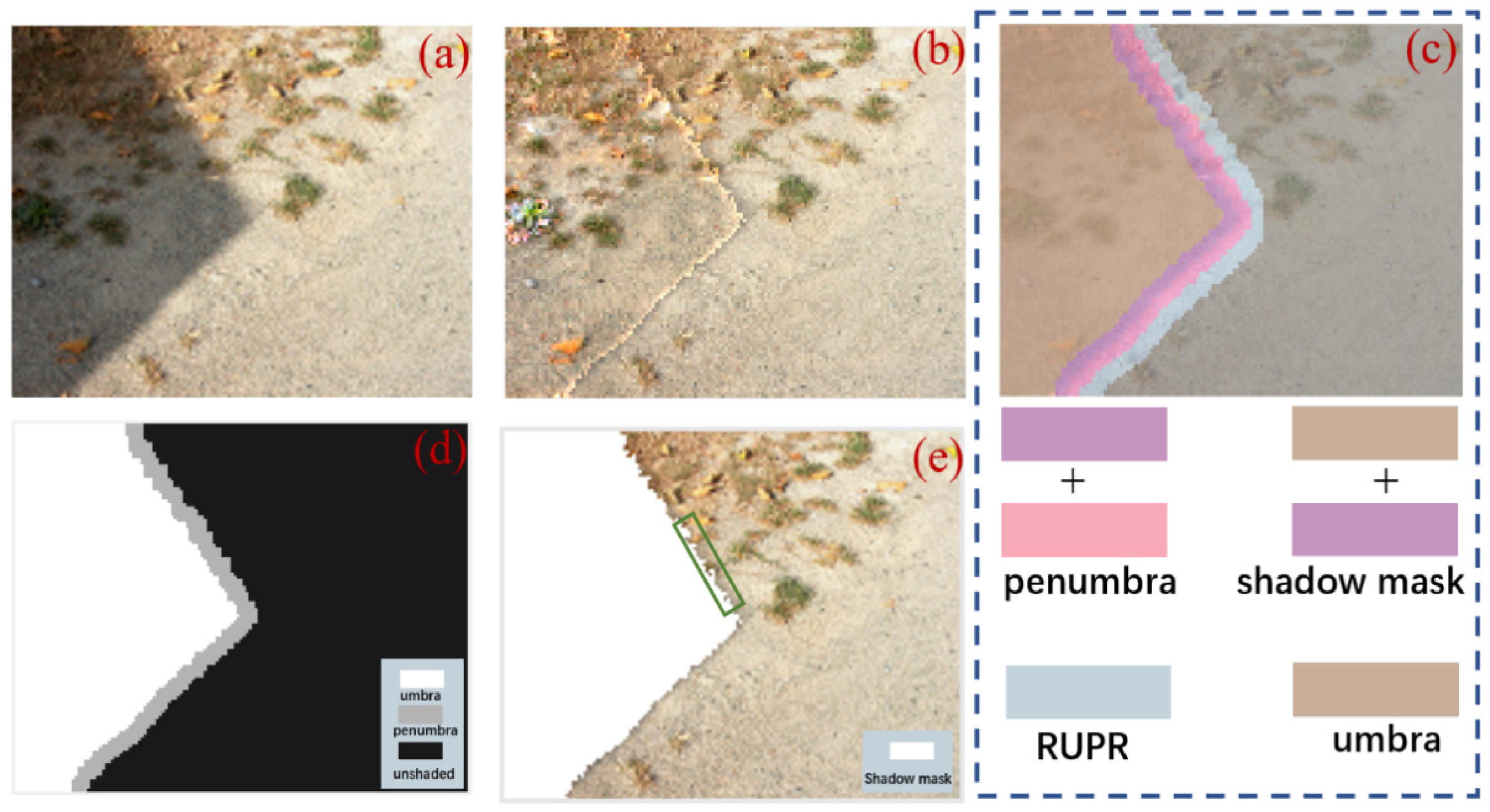
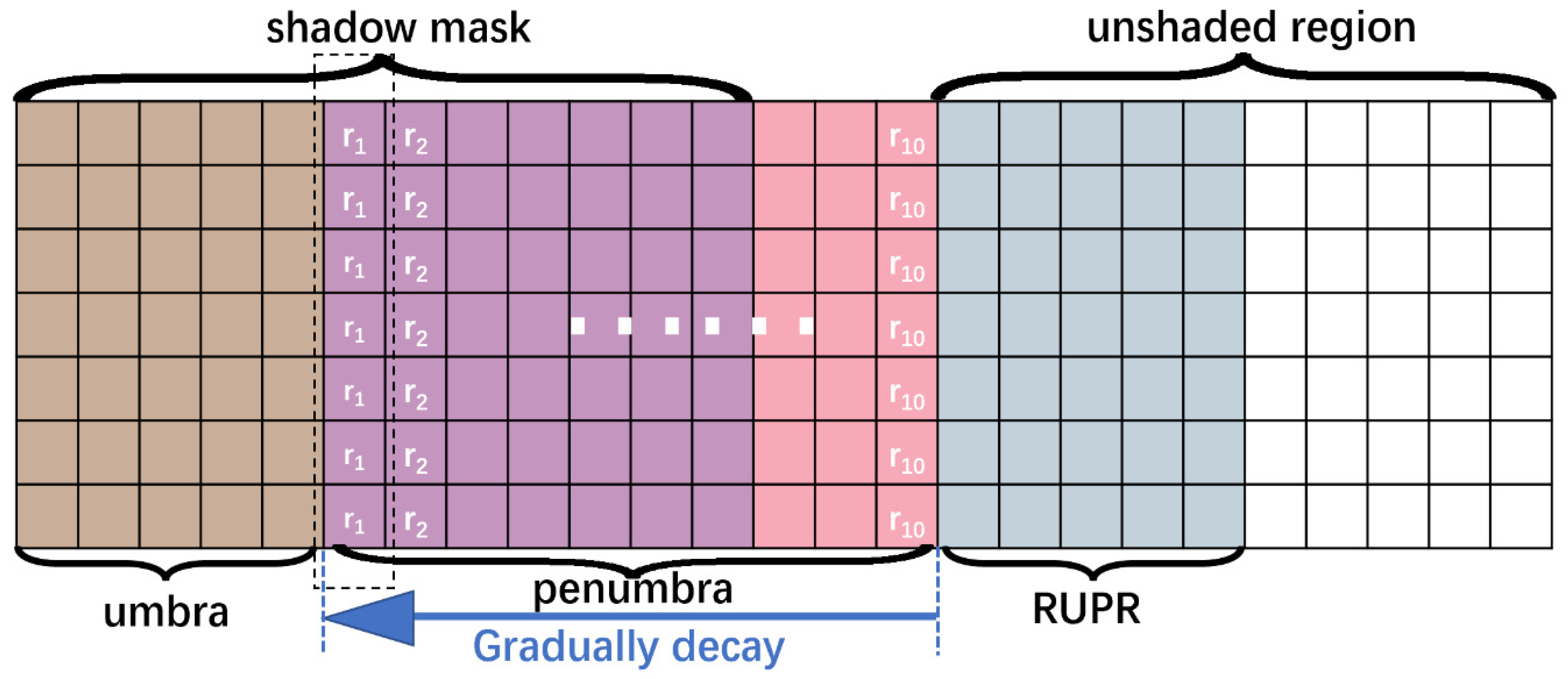
3.2. Dynamic Penumbra Compensation Method (DPCM)
4. Results
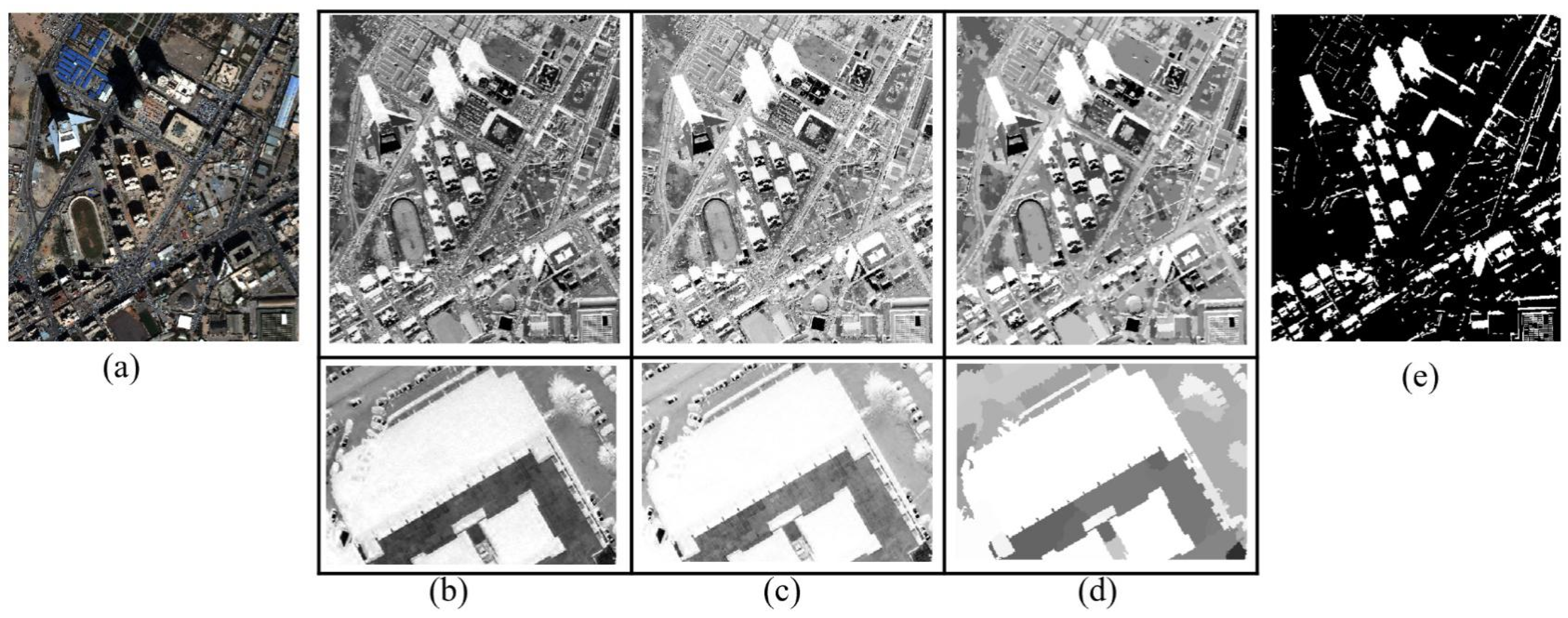
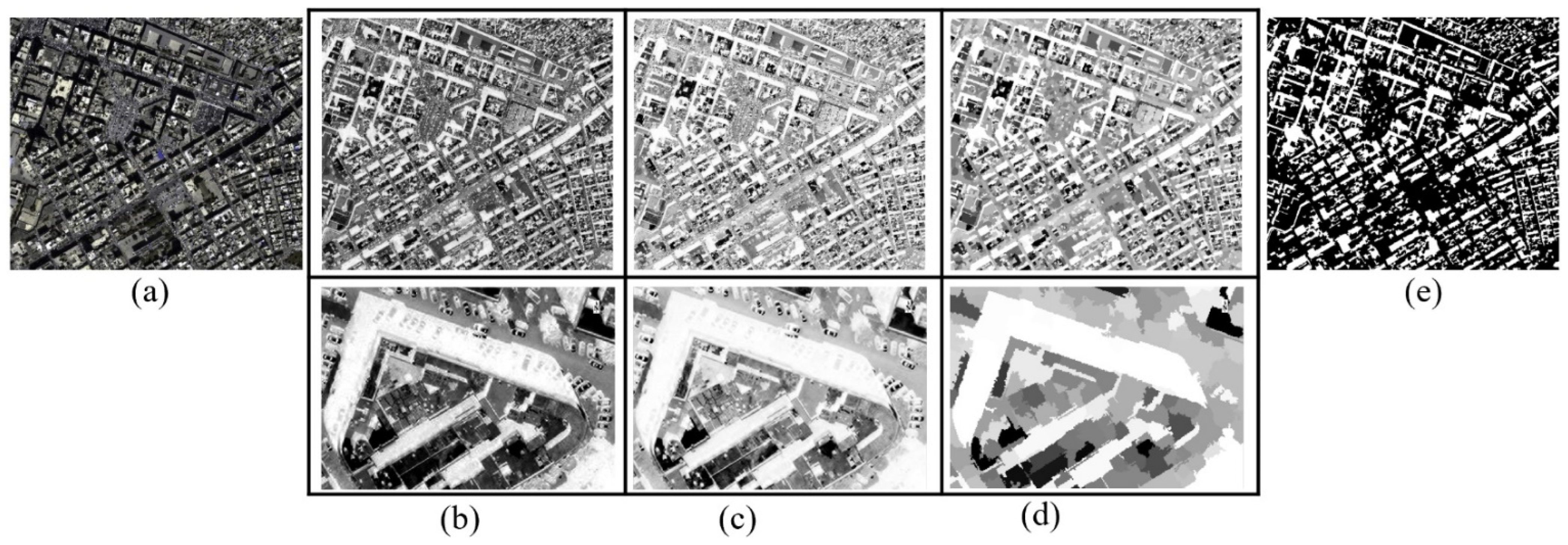
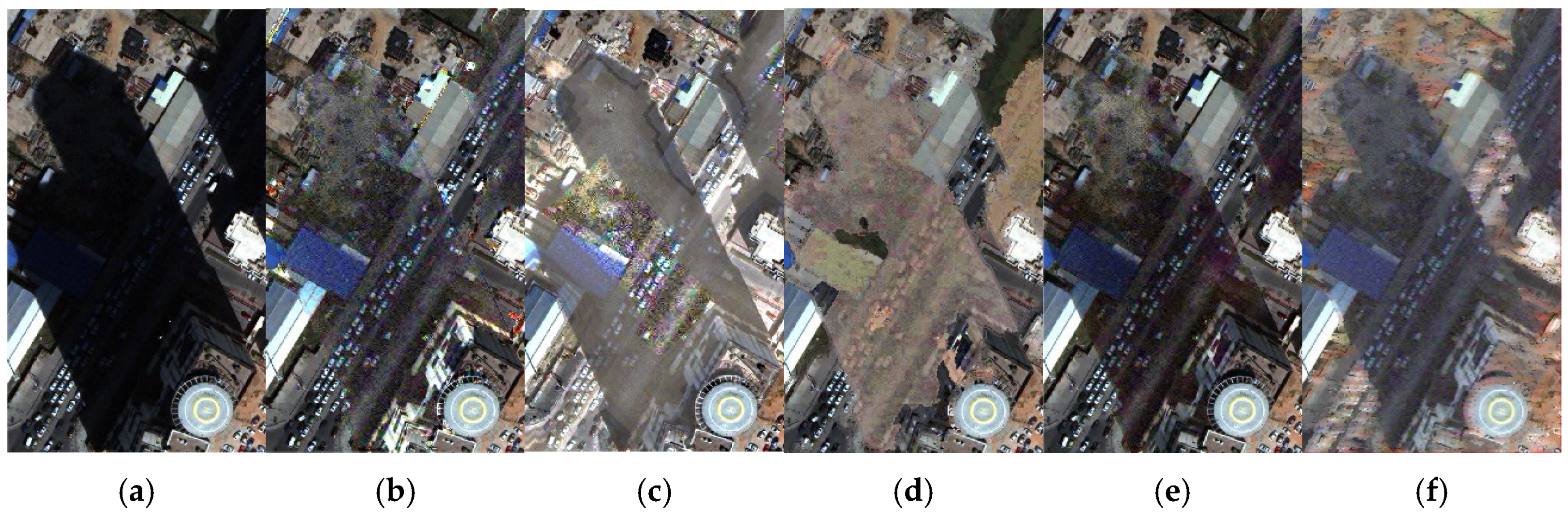
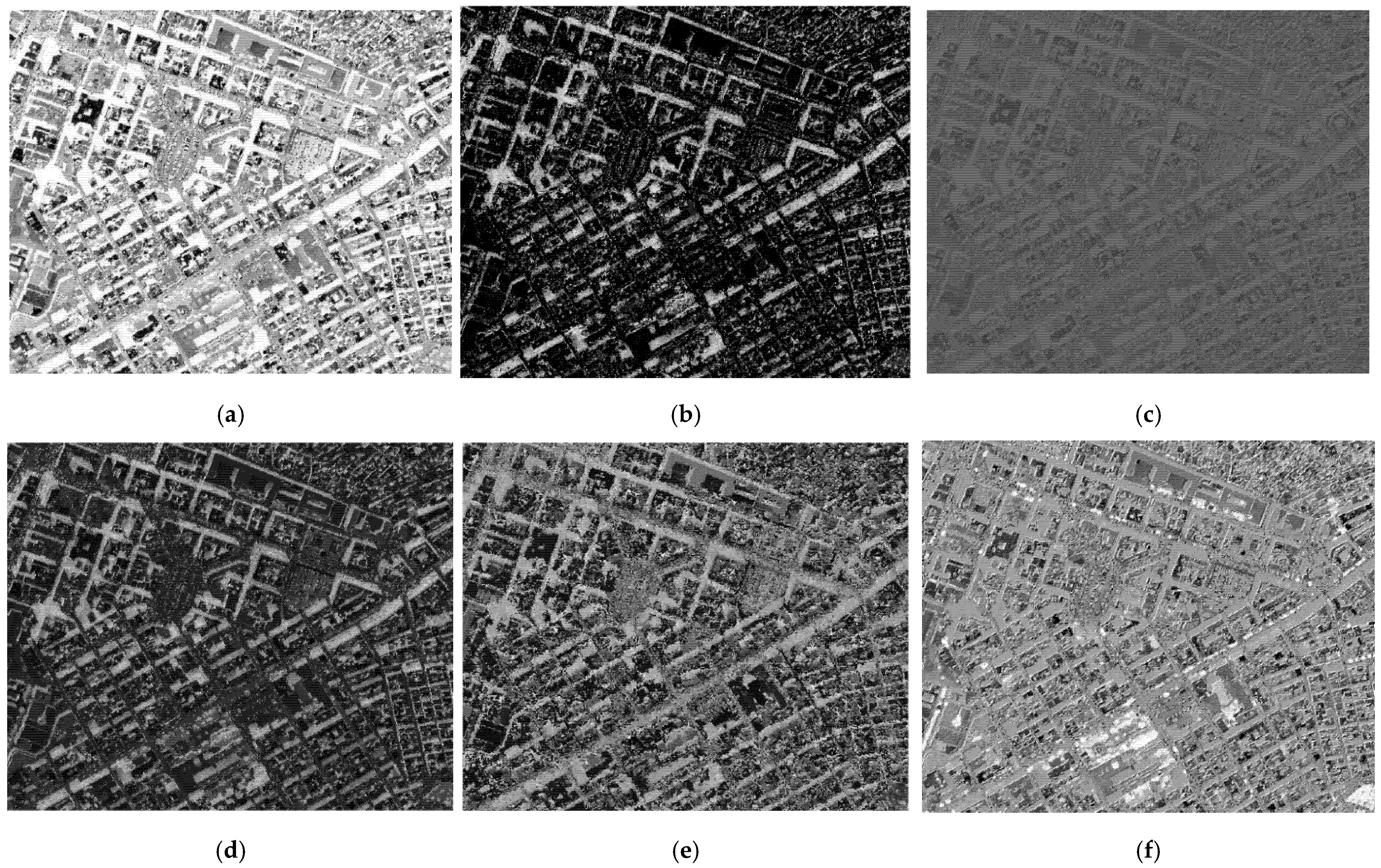
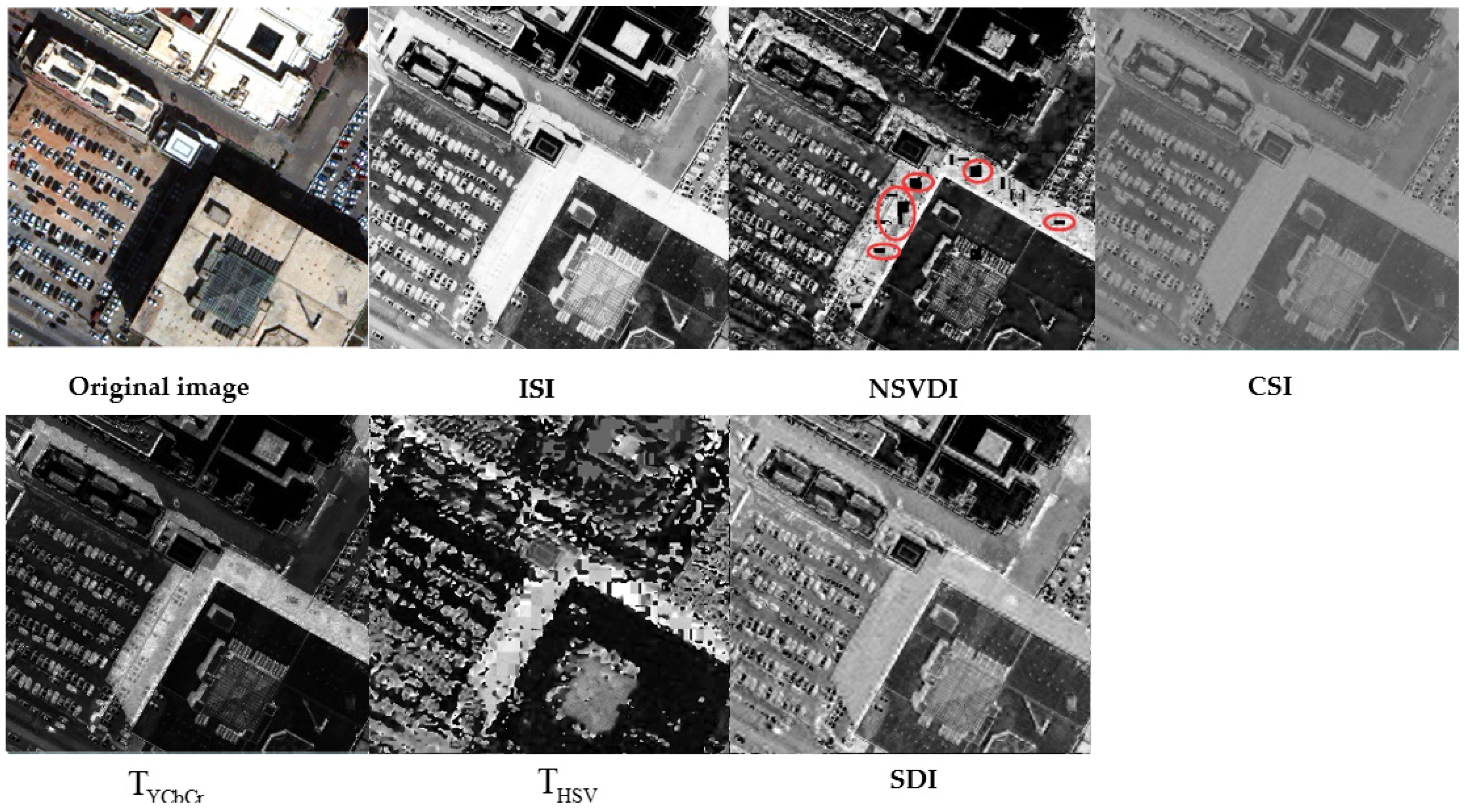
4.1. Preference and Comparative Analysis of Shadow Detection
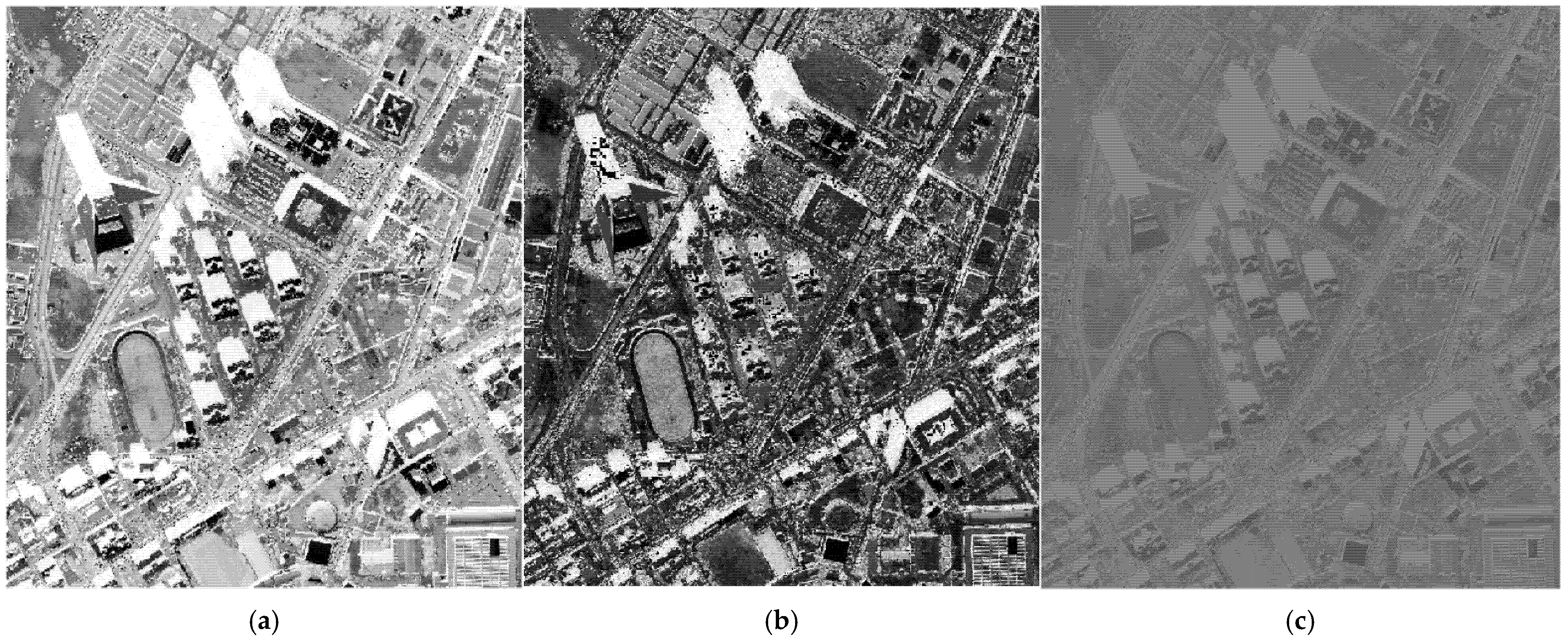
4.1.1. Qualitative Analysis of Shadow Detection
4.1.2. Comparative Analysis of Shadow Detection and Accuracy Evaluation
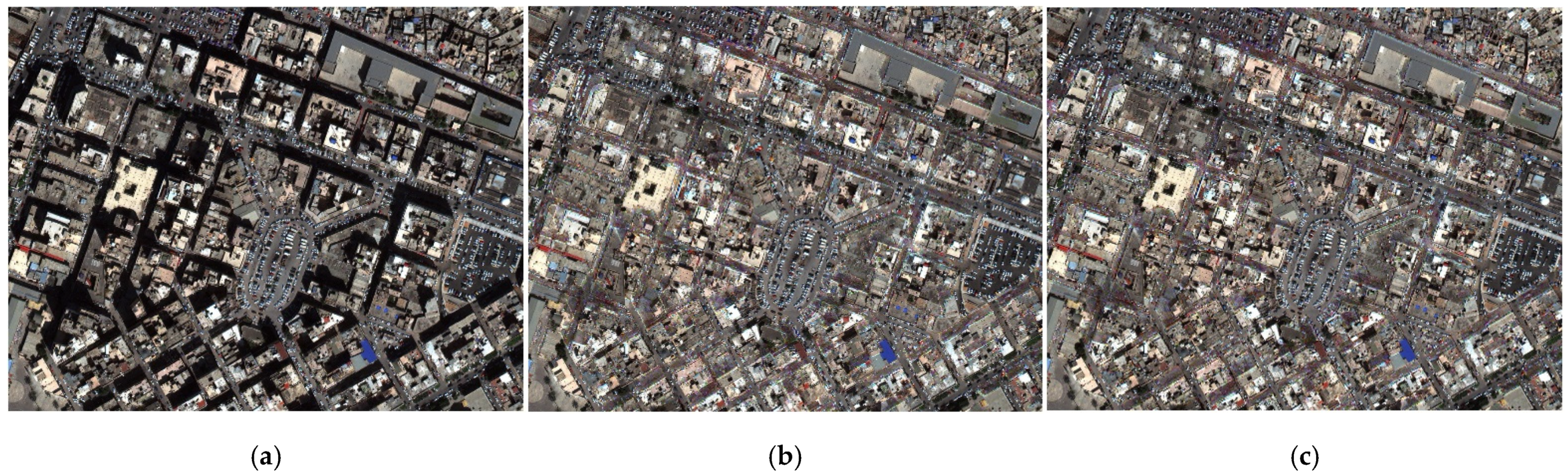
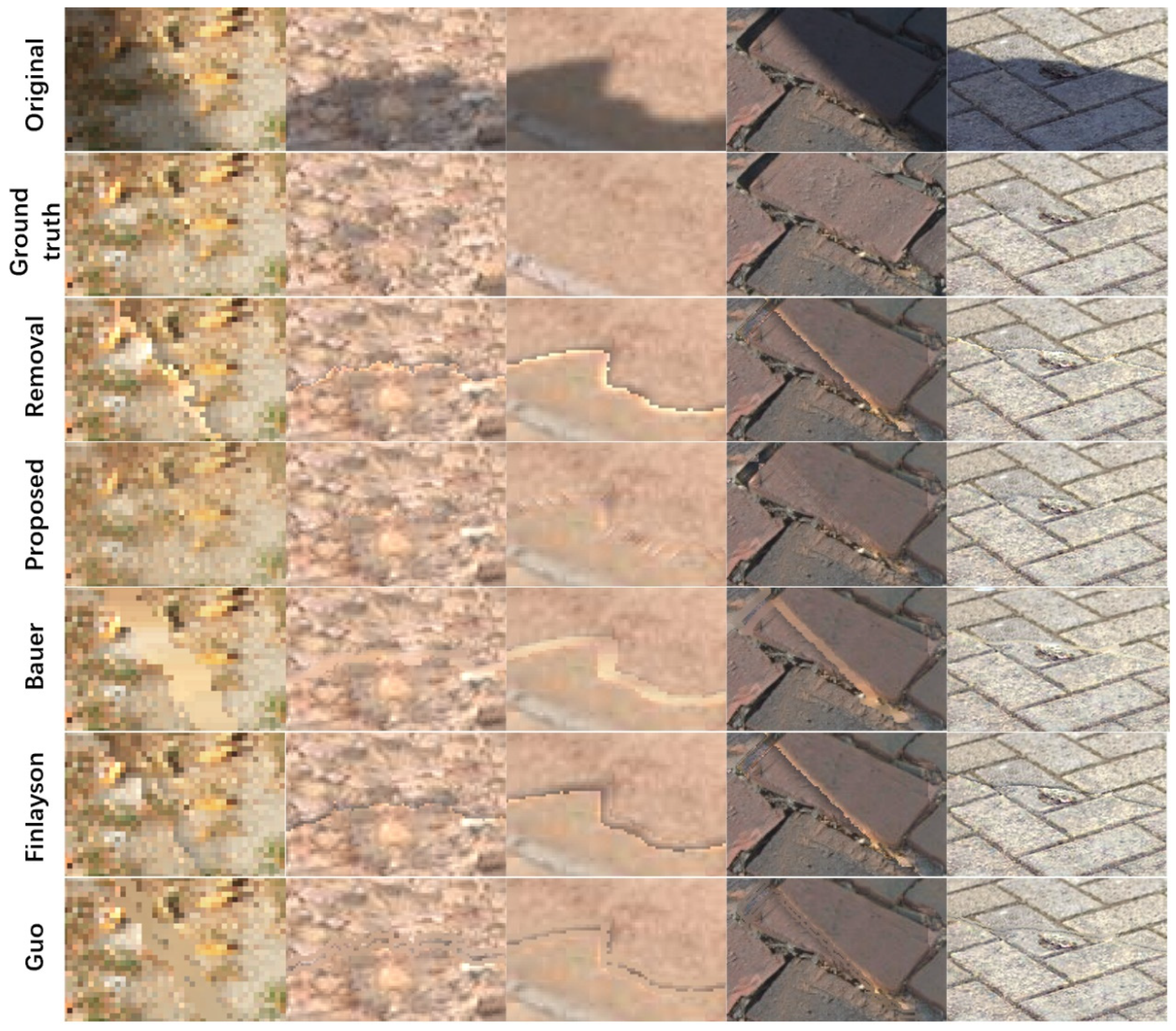
4.2. Assessment Shadow Compensation and Penumbra Removal
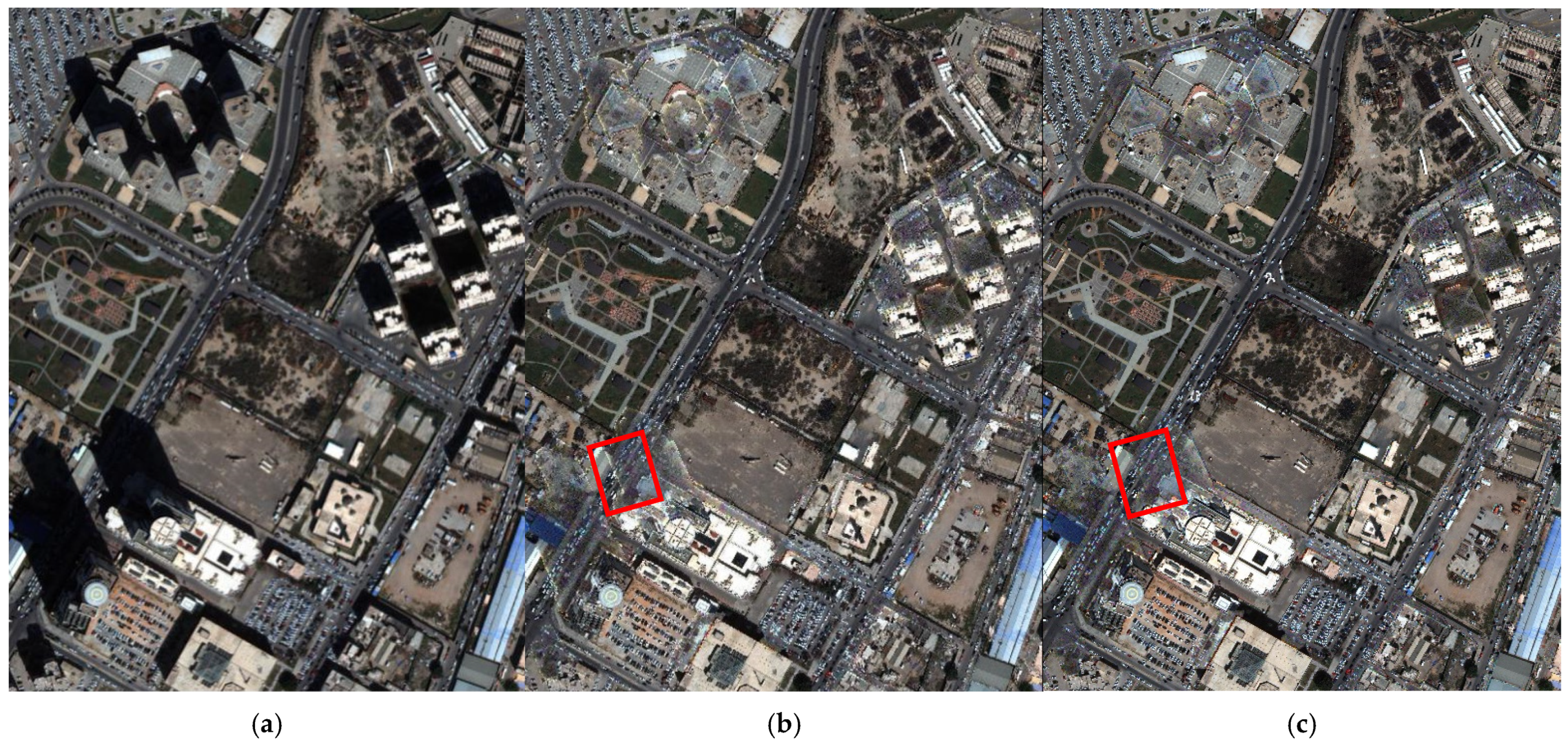
4.2.1. Preference of Shadow Compensation and Penumbra Removal
4.2.2. Comparative Analysis of Shadow Compensation
4.2.3. Comparative Analysis of Penumbra Removal
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashed, T.; Jürgens, C. Remote Sensing of Urban and Suburban Areas; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2010; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q.; Quattrochi, D.A. Urban Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 78–130. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Wang, L.; Shao, Z.; Li, D. Development of a multi-scale object-based shadow detection method for high spatial resolution image. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 6, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzi, L.; Melgani, F.; Mercier, G. A complete processing chain for shadow detection and reconstruction in VHR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 50, 3440–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Huang, G.; Troy, A.; Cadenasso, M. Object-based land cover classification of shaded areas in high spatial resolution imagery of urban areas: A comparison study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1769–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, M.A.; Aqel, S.; Aarab, A. A multiscale based approach for automatic shadow detection and removal in natural images. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2019, 78, 11263–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeline, K.; Chen, M.; Briottet, X.; Pang, S.K.; Paparoditis, N. Shadow detection in very high spatial resolution aerial images: A comparative study. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 80, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, A.O. Automated detection of buildings from single VHR multispectral images using shadow information and graph cuts. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Lett. 2013, 86, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, E.; Raettig, R.; Mack, J.; Valancius, S.; Unal, B.; Akoglu, A. Accelerated Shadow Detection and Removal Method. In Proceedings of the ACS/IEEE International Conference on Computer Systems and Applications, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 3–7 November 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, B.; Riaz, M.M.; Ghafoor, A. Automatic shadow detection and removal using image matting. Signal Process. 2020, 170, 107415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chen, J.; Rahardja, S. Hyperspectral Shadow Removal via Nonlinear Unmixing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, K.; Li, W. Object-Oriented Shadow Detection and Removal From Urban High-Resolution Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 52, 6972–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolt, G.; Shimoni, M.; Ahlberg, J. A shadow detection method for remote sensing images using VHR hyperspectral and LIDAR data. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2011; pp. 4423–4426. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Hou, Z.; Shi, Z.; Bo, Y.; Cheng, J. A shadow identification method using vegetation indices derived from hyperspectral data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 5357–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Huang, H.; Weng, Q.; Zhang, A.; Jia, X.; Ren, J.; Sun, L.; Chen, X. Combinational shadow index for building shadow extraction in urban areas from Sentinel-2A MSI imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 78, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xie, W.; Tang, L. Detection of and compensation for shadows in colored urban aerial images. In Proceedings of the World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, Hangzhou, China, 15–19 June 2004; pp. 3098–3100. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, V.J.D. A comparative study on shadow compensation of color aerial images in invariant color models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2006, 44, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.F.; Carneiro, G.B.; Doth, R.; Amaral, L.A.; De Azevedo, D.F.G. Near real-time shadow detection and removal in aerial motion imagery application. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 140, 104–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Qin, Q.; Shen, X. Shadow Segmentation and Compensation in High Resolution Satellite Images. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008; pp. 1036–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Tao, S.; Dai, Q.; Wang, W.; Wu, M. Object-oriented detection of building shadow in TripleSat-2 remote sensing imagery. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2020, 14, 036508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wen, D.; Jing, L.; Shi, P. Shadow information recovery in urban areas from very high resolution satellite imagery. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, K.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Taherzadeh, E. A Novel Spectral Index for Automatic Shadow Detection in Urban Mapping Based On WorldView-2 Satellite Imagery. Int. J. Comput. Electr. Autom. Control Inf. Eng. 2014, 8, 1774–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, L.; Tian, J.; He, S.; Tang, Y.; Lau, R.W.H. DeshadowNet: A Multi-context Embedding Deep Network for Shadow Removal. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2308–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, G.; Huamán, S.G.; Telles, J. Shadow Removal in High-Resolution Satellite Images Using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 Annual International Symposium on Information Management and Big Data, Lima, Peru, 3–5 September 2018; pp. 328–340. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, X.; Yang, J. Stacked Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks for Jointly Learning Shadow Detection and Shadow Removal. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 1788–1797. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, G.; Huang, W.; Smith, W.A.; Ren, P. A shadow constrained conditional generative adversarial net for SRTM data restoration. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Long, C.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, C. ARGAN: Attentive Recurrent Generative Adversarial Network for Shadow Detection and Removal. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Zhou, T.; Sun, C. Object-Based Shadow Index via Illumination Intensity from High Resolution Satellite Images over Urban Areas. Sensors 2020, 20, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dare, P.M. Shadow Analysis in High-Resolution Satellite Imagery of Urban Areas. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 71, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highnam, R.; Brady, M. Model-based image enhancement of far infrared images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1997, 19, 410–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabandi, P.; Yamazaki, F.; Matsuoka, M.; Kiremidjian, A.S. Shadow detection and radiometric restoration in satellite high resolution images. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004; pp. 3744–3747. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, T.F.Y.; Hoai, M.; Samaras, D. Leave-One-Out Kernel Optimization for Shadow Detection and Removal. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 40, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Xiao, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L. Efficient shadow removal using subregion matching illumination transfer. Comput. Graph. Forum 2013, 32, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yamazaki, F. Object-based shadow extraction and correction of high-resolution optical satellite images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 5, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Dai, Q.; Hoiem, D. Paired Regions for Shadow Detection and Removal. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 2956–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.D.; Drew, M.S.; Lu, C. Entropy Minimization for Shadow Removal. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2009, 85, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, G.D.; Hordley, S.D.; Lu, C.; Drew, M.S. On the removal of shadows from images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.; Busta, E.; Johnson, E. Shadow Terminator. Available online: https://sites.google.com/a/wisc.edu/shadow-terminator/ (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xiao, C. Shadow Remover: Image Shadow Removal Based on Illumination Recovering Optimization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 4623–4636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.digitalglobe.com/samples (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Comaniciu, D.; Meer, P. Mean shift: A robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polidorio, A.M.; Flores, F.C.; Imai, N.N.; Tommaselli, A.M.G.; Franco, C. Automatic shadow segmentation in aerial color images. In Proceedings of the Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image Processing, Sao Carlos, Brazil, 12–15 October 2003; pp. 270–277. [Google Scholar]
- Fredembach, C.; Süsstrunk, S. Automatic and Accurate Shadow Detection from (Potentially) a Single Image Using Near-Infrared Information. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/43981878_Automatic_and_accurate_shadow_detection_from_potentially_a_single_image_using_near-infrared_information (accessed on 9 December 2020).
- Barrow, H.; Tenenbaum, J.; Hanson, A.; Riseman, E. Recovering intrinsic scene characteristics. Comput. Vis. Syst. 1978, 2, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Z. Systematic static shadow detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Cambridge, UK, 26–26 August 2004; pp. 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Shor, Y.; Lischinski, D. The Shadow Meets the Mask: Pyramid-Based Shadow Removal. Comput. Graph. Forum 2008, 27, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, G.; Ying, Z.; Guo, X. A New Shadow Removal Method Using Color-Lines. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns, Ystad, Sweden, 22–24 August 2017; pp. 307–319. [Google Scholar]










| CoastalBlue | Blue | Green | Yellow | Red | RedEdge | NIR1 | NIR2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central wavelength (nm) | 425 | 480 | 545 | 605 | 660 | 725 | 832.5 | 950 |
| Resolution | Multi-spectral resolution: 1.24 m | |||||||
| Panchromatic resolution: 0.31 m | ||||||||
| Short-wavelength infrared: 3.7 m | ||||||||
| Location | Tripoli, Libya | |||||||
| Local time | 8 March 2016, 12:12 | |||||||
| Index | Data | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| CSI | Sentinel-2A | |
| SDI | WorldView-2 | |
| NSVDI | IKONOS | executed in HSV space |
| , | RGB data | Executed in HSV and YCbCr models separately |
| Accuracies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | PA (%) | UA (%) | OA (%) | Kappa |
| ISI | 99 | 97 | 99 | 0.97 |
| NSVDI | 83 | 77 | 87 | 0.70 |
| CSI | 99 | 71 | 88 | 0.74 |
| 96 | 90 | 95 | 0.89 | |
| 89 | 66 | 83 | 0.63 | |
| SDI | 83 | 47 | 67 | 0.35 |
| Accuracies | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index | PA (%) | UA (%) | OA (%) | Kappa |
| ISI | 96 | 97 | 98 | 0.95 |
| NSVDI | 87 | 95 | 91 | 0.82 |
| SCSI | 86 | 95 | 90 | 0.81 |
| 90 | 97 | 93 | 0.87 | |
| 75 | 89 | 81 | 0.63 | |
| SDI | 69 | 80 | 74 | 0.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Fu, H.; Sun, C.; Wang, S. Shadow Detection and Compensation from Remote Sensing Images under Complex Urban Conditions. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040699
Zhou T, Fu H, Sun C, Wang S. Shadow Detection and Compensation from Remote Sensing Images under Complex Urban Conditions. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040699
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tingting, Haoyang Fu, Chenglin Sun, and Shenghan Wang. 2021. "Shadow Detection and Compensation from Remote Sensing Images under Complex Urban Conditions" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040699
APA StyleZhou, T., Fu, H., Sun, C., & Wang, S. (2021). Shadow Detection and Compensation from Remote Sensing Images under Complex Urban Conditions. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040699






