High Accuracy Interpolation of DEM Using Generative Adversarial Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Generative Adversarial Networks
2.2. CEDGAN
2.3. Model Architecture
2.3.1. Gated Convolution
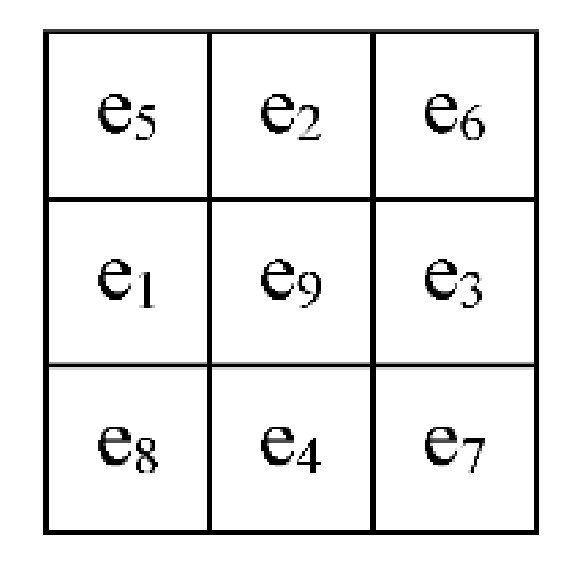
2.3.2. Dilated Convolution Structure
2.3.3. SN-PatchGAN and its Discriminative Loss
2.3.4. The Proposed Generator’s Structure and its Loss
2.4. Data Description
2.5. Evaluation Metrics
2.5.1. Quantitative Evaluation
2.5.2. Visual Evaluation
3. Results
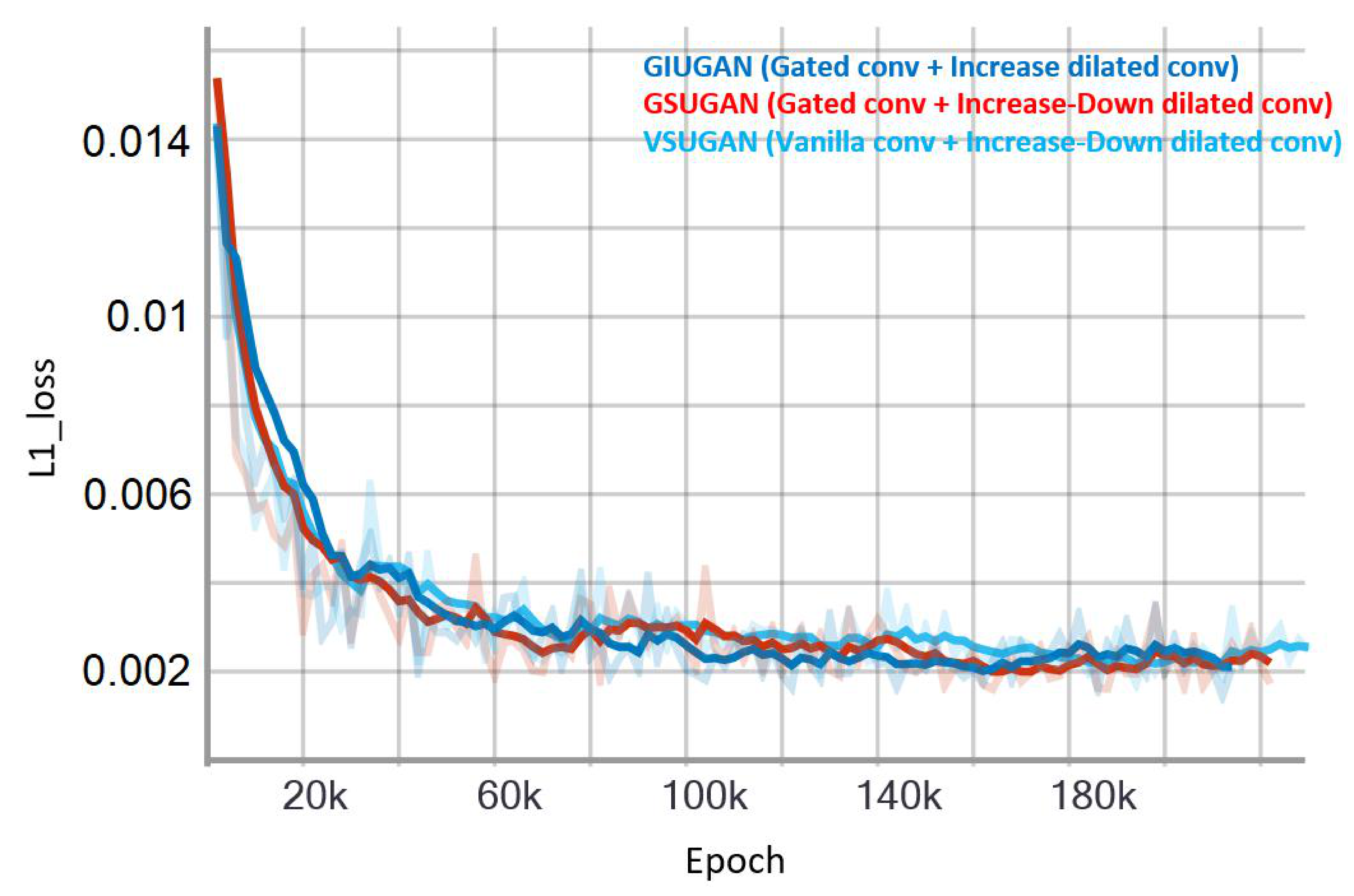
3.1. Training and Validation
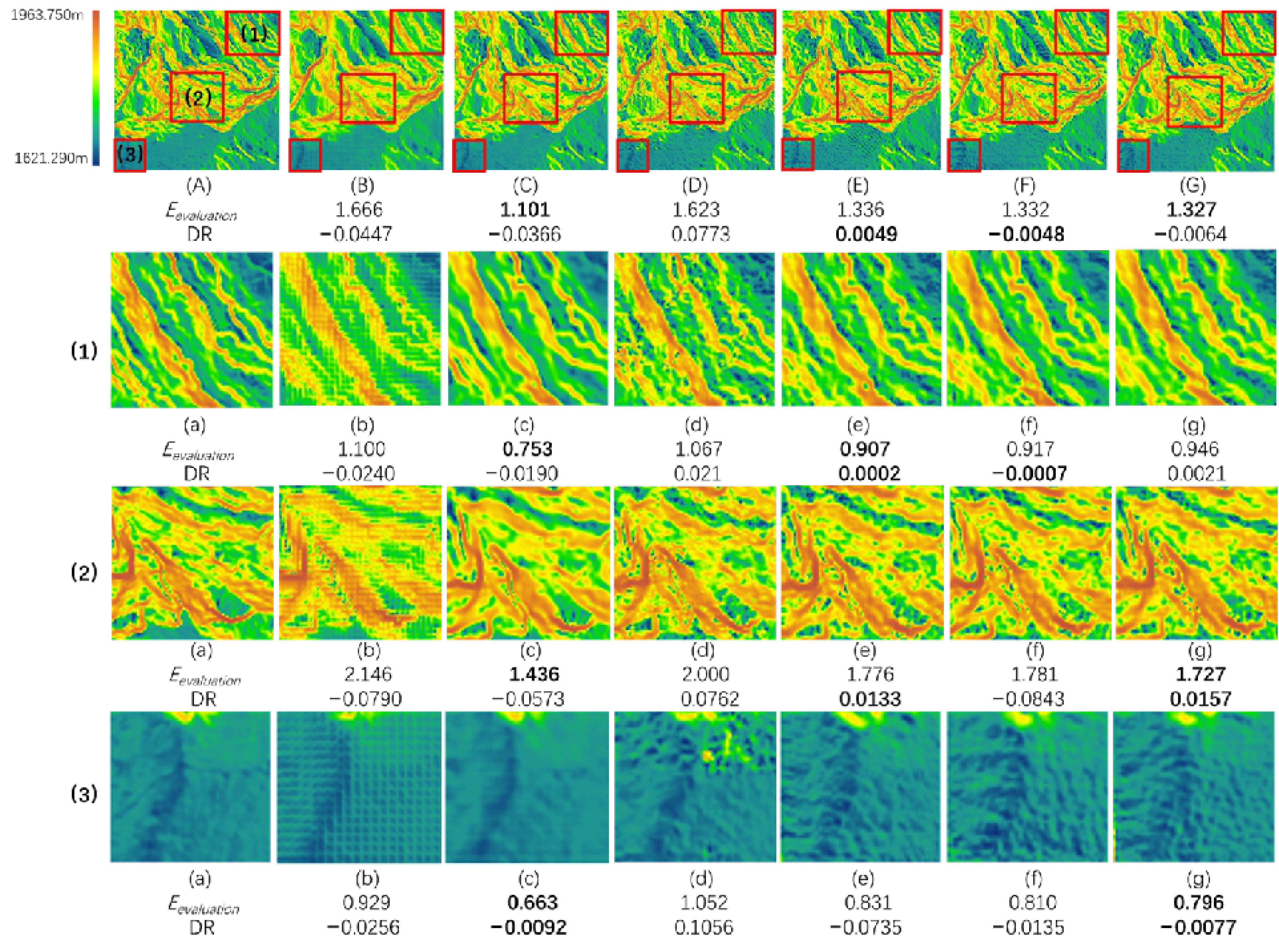
3.2. Potentials
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peralvo, M.; Maidment, D. Influence of DEM interpolation methods in drainage analysis. Gis Hydro 2004, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, A.; Reuter, H.; Gessler, P. DEM production methods and sources. Dev. Soil Sci. 2009, 33, 65–85. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, P.V. A comparative analysis of different DEM interpolation methods. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2013, 16, 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, C.; Gold, C. Digital Terrain Modeling: Principles and Methodology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mitas, L.; Mitasova, H. Spatial interpolation. Geogr. Inf. Syst. Princ. Tech. Manag. Appl. 1999, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Erdogan, S. A comparision of interpolation methods for producing digital elevation models at the field scale. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2009, 34, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M. Evaluation of DEM interpolation techniques for characterizing terrain roughness. CATENA 2021, 198, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizor, P.J. Principles of Geographical Information Systems for Land Resources Assessment. Soil Sci. 1987, 144, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, F.J.; Agüera, F.; Aguilar, M.A.; Carvajal, F. Effects of Terrain Morphology, Sampling Density, and Interpolation Methods on Grid DEM Accuracy. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2005, 71, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J. Effects of Interpolation Errors on the Analysis of DEMs. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1997, 22, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N. The origins of kriging. Math. Geol. 1990, 22, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Sui, H.; Zhou, Y. Effects of various factors on the accuracy of DEMs: An intensive experimental investigation. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplot, V.; Darboux, F.d.r.; Bourennane, H.; Leguédois, S.; Silvera, N.; Phachomphon, K. Accuracy of interpolation techniques for the derivation of digital elevation models in relation to landform types and data density. Geomorphology 2006, 77, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Khoshelham, K.; Akdim, N.; El Ghandour, F.-e.; Labbassi, K.; Menenti, M. Impact of spatial resolution, interpolation and filtering algorithms on DEM accuracy for geomorphometric research: A case study from Sahel-Doukkala, Morocco. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2018, 4, 1537–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Huang, Z.; Shi, L.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y. Inferring spatial interaction patterns from sequential snapshots of spatial distributions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2018, 32, 783–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Loy, C.C.; He, K.; Tang, X. Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 38, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kwon Lee, J.; Mu Lee, K. Accurate Image Super-resolution Using Very Deep Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1646–1654. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, W.; Caballero, J.; Huszár, F.; Totz, J.; Aitken, A.P.; Bishop, R.; Rueckert, D.; Wang, Z. Real-time Single Image and Video Super-resolution Using an Efficient Sub-pixel Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1874–1883. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.; Son, S.; Kim, H.; Nah, S.; Mu Lee, K. Enhanced Deep Residual Networks for Single Image Super-resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z. Convolutional Neural Network Based Dem Super Resolution. In Proceedings of the The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 2016 XXIII ISPRS Congress, Prague, Czech Republic, 12–19 July 2016; Volume XLI-B3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yi, W.; Gui, Q.; Hou, W.; Ding, M. Deep gradient prior network for DEM super-resolution: Transfer learning from image to DEM. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 150, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 2, pp. 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, M.; Osindero, S. Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1784. [Google Scholar]
- Ledig, C.; Theis, L.; Huszar, F.; Caballero, J.; Cunningham, A.; Acosta, A.; Aitken, A.; Tejani, A.; Totz, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Photo-Realistic Single Image Super-Resolution Using a Generative Adversarial Network. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.04802. [Google Scholar]
- Guérin, É.; Digne, J.; Galin, É.; Peytavie, A.; Wolf, C.; Benes, B.; Martinez, B.t. Interactive example-based terrain authoring with conditional generative adversarial networks. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, F.; Yao, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y. Spatial interpolation using conditional generative adversarial neural networks. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 735–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriil, K.; Muntingh, G.; Barrowclough, O.J.D. Void Filling of Digital Elevation Models With Deep Generative Models. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T. Free-Form Image Inpainting with Gated Convolution. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.03589. [Google Scholar]
- Arjovsky, M.; Chintala, S.; Bottou, L.o. Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–11 August 2017; Volume 70, pp. 214–223. [Google Scholar]
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.05957. [Google Scholar]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-Image Translation with Conditional Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.07004. [Google Scholar]
- Jo, Y.; Park, J. SC-FEGAN: Face Editing Generative Adversarial Network with User’s Sketch and Color. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1902.06838. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi, R.; Fujita, A.; Nemoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Hikosaka, S. Effective Use of Dilated Convolutions for Segmenting Small Object Instances in Remote Sensing Imagery. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.00179. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, B.K.P. Hill shading and the reflectance map. Proc. IEEE 1981, 69, 14–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, M.K.; Campbell, B.A.; Bulmer, M.H.; Farr, T.G.; Gaddis, L.R.; Plaut, J.J. The roughness of natural terrain: A planetary and remote sensing perspective. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 2001, 106, 32777–32795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.W. Roughness in the Earth Sciences. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2014, 136, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.; Degloria, S.; Elliot, S.D. A Terrain Ruggedness Index that Quantifies Topographic Heterogeneity. Int. J. Sci. 1999, 5, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, V.K.; Ren, J.-C.; Xu, X.-Y.; Zhao, S.; Xie, G.; Masero, V.; Hussain, A. Deep Learning Based Single Image Super-resolution: A Survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2019, 16, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Methods | Eelevation | Eslope | DR |
|---|---|---|---|
| IDW | 0.186 | 3.389 | −0.0025 |
| EDSR [19] | 0.088 | 1.842 | −0.0032 |
| CEDGAN [26] | 0.168 | 3.345 | 0.0058 |
| VSUGAN (Vanilla conv + Increase-Down dilated conv) | 0.176 | 2.825 | 0.0030 |
| GIUGAN (Gated conv + Increase dilated conv) | 0.165 | 2.877 | 0.0018 |
| GSUGAN (Gated conv + Increase-Down dilated conv) | 0.153 | 2.710 | 0.0005 |
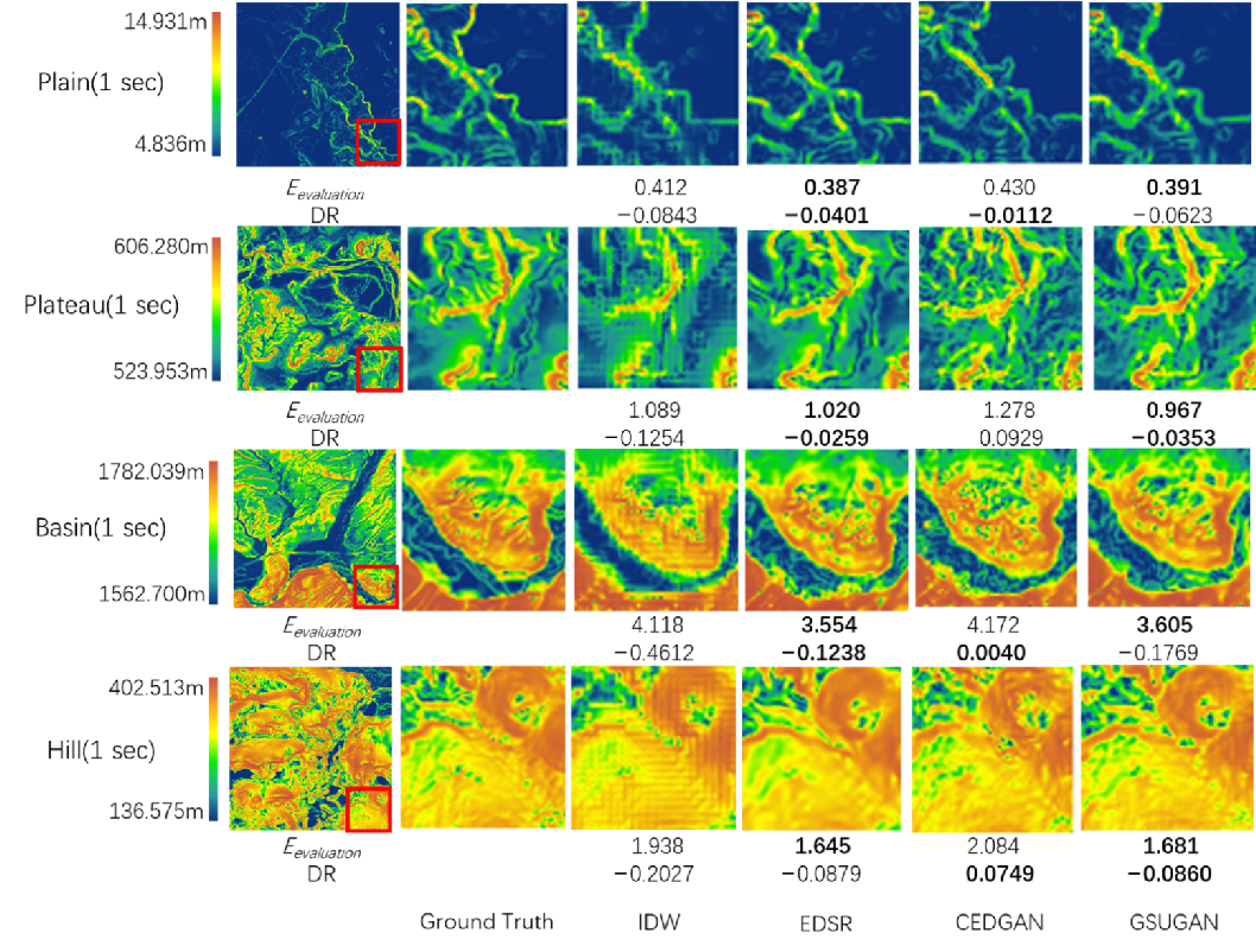
| Terrain | Resolution | Meanh | Eelevation | Slope | Eslope | DR | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IDW | ESDR | CEDGAN | GSUGAN | IDW | ESDR | CEDGAN | GSUGAN | IDW | ESDR | CEDGAN | GSUGAN | |||||
| Plain | 1 m | 2.283 | 0.055 | 0.055 | 0.070 | 0.052 | 3.1844 | 1.888 | 1.567 | 1.795 | 1.598 | 0.0342 | −0.0160 | −0.0068 | 0.0015 | −0.0105 |
| 1/3 s | 9.260 | 0.135 | 0.125 | 0.160 | 0.134 | 0.954 | 0.436 | 0.386 | 0.466 | 0.421 | 0.0812 | −0.0234 | −0.0094 | 0.0025 | −0.0111 | |
| 1 s | 15.034 | 0.298 | 0.268 | 0.338 | 0.275 | 0.563 | 0.328 | 0.279 | 0.328 | 0.295 | 0.1607 | −0.0507 | −0.0176 | 0.0044 | −0.0260 | |
| Plateau | 1 m | 6.469 | 0.021 | 0.023 | 0.028 | 0.024 | 3.031 | 0.634 | 0.641 | 0.763 | 0.675 | 0.0199 | −0.0049 | −0.0039 | −0.0009 | −0.0038 |
| 1/3 s | 49.056 | 0.286 | 0.150 | 0.253 | 0.220 | 3.488 | 0.797 | 0.487 | 0.762 | 0.671 | 0.2290 | −0.0152 | −0.0051 | 0.0107 | −0.0020 | |
| 1sec | 92.474 | 0.986 | 0.599 | 0.892 | 0.783 | 3.234 | 0.933 | 0.630 | 0.867 | 0.786 | 0.6289 | −0.0838 | −0.0122 | 0.0383 | −0.0020 | |
| Basin | 1 m | 139.351 | 0.202 | 0.093 | 0.196 | 0.174 | 25.626 | 2.910 | 1.460 | 3.174 | 2.472 | 0.2816 | 0.0009 | −0.0017 | 0.0086 | 0.0031 |
| 1/3 s | 224.816 | 0.722 | 0.305 | 0.607 | 0.519 | 8.571 | 1.614 | 0.813 | 1.562 | 1.265 | 0.8115 | −0.0330 | −0.0096 | 0.0237 | 0.0029 | |
| 1 s | 520.604 | 2.964 | 1.660 | 2.783 | 2.466 | 8.407 | 2.379 | 1.464 | 2.347 | 2.057 | 2.4317 | −0.3054 | −0.0895 | 0.0794 | −0.0168 | |
| Hill | 1 m | 39.995 | 0.092 | 0.054 | 0.093 | 0.075 | 11.071 | 2.420 | 1.631 | 2.571 | 1.694 | 0.1031 | −0.0061 | −0.0044 | 0.0028 | −0.0025 |
| 1/3 s | 178.745 | 0.737 | 0.446 | 0.719 | 0.6000 | 7.655 | 2.017 | 1.356 | 2.044 | 1.694 | 0.7182 | −0.0609 | −0.0322 | 0.0181 | −0.0192 | |
| 1 s | 344.718 | 2.358 | 1.581 | 2.291 | 2.000 | 6.946 | 2.123 | 1.568 | 2.155 | 1.879 | 2.0041 | −0.2610 | −0.1228 | 0.0363 | −0.0820 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, L.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y. High Accuracy Interpolation of DEM Using Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040676
Yan L, Tang X, Zhang Y. High Accuracy Interpolation of DEM Using Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040676
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Li, Xingfen Tang, and Yi Zhang. 2021. "High Accuracy Interpolation of DEM Using Generative Adversarial Network" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040676
APA StyleYan, L., Tang, X., & Zhang, Y. (2021). High Accuracy Interpolation of DEM Using Generative Adversarial Network. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040676







