Machine Learning Based Algorithms for Global Dust Aerosol Detection from Satellite Images: Inter-Comparisons and Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Description
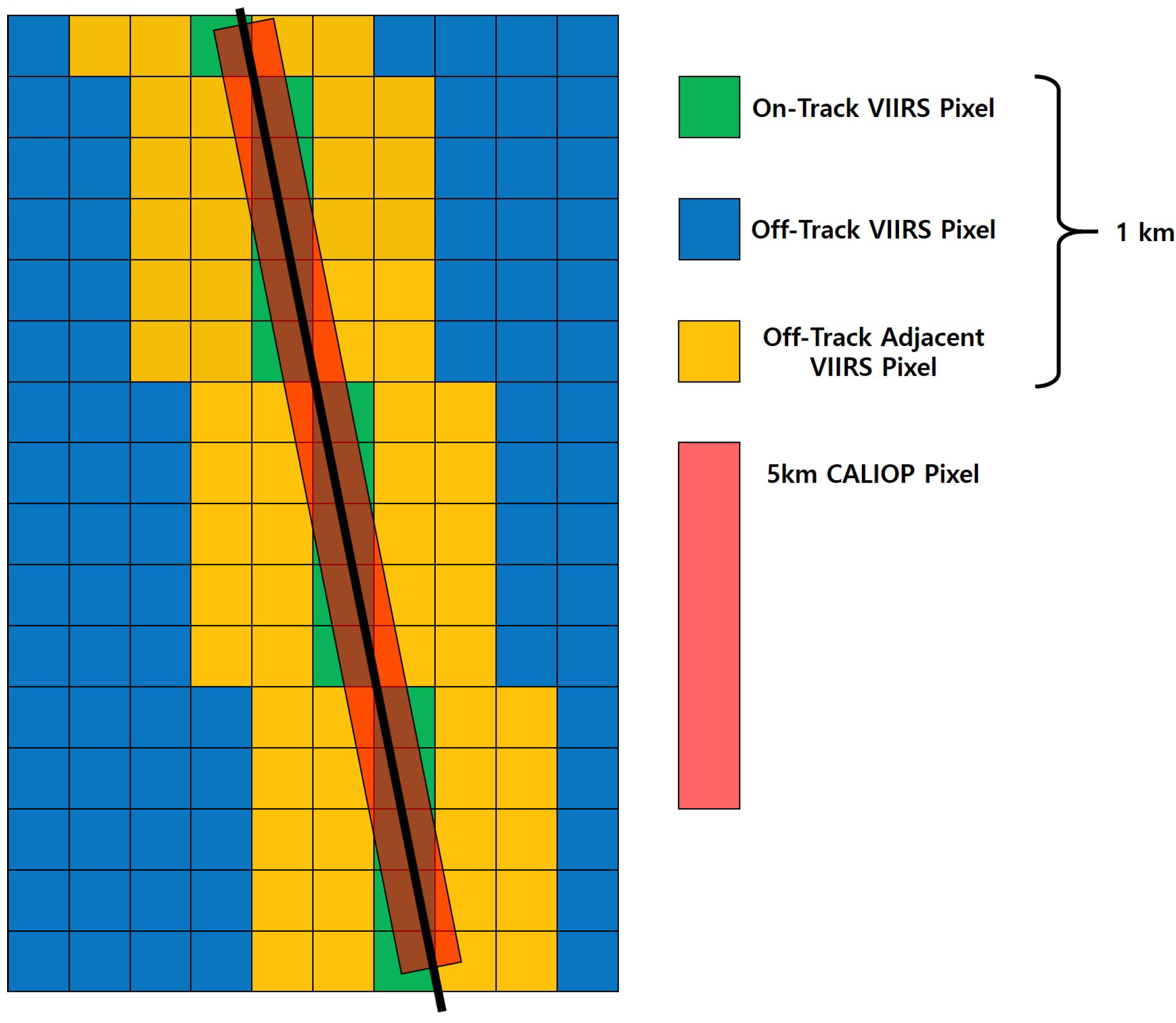
2.1. CALIOP and VIIRS Products and Collocation
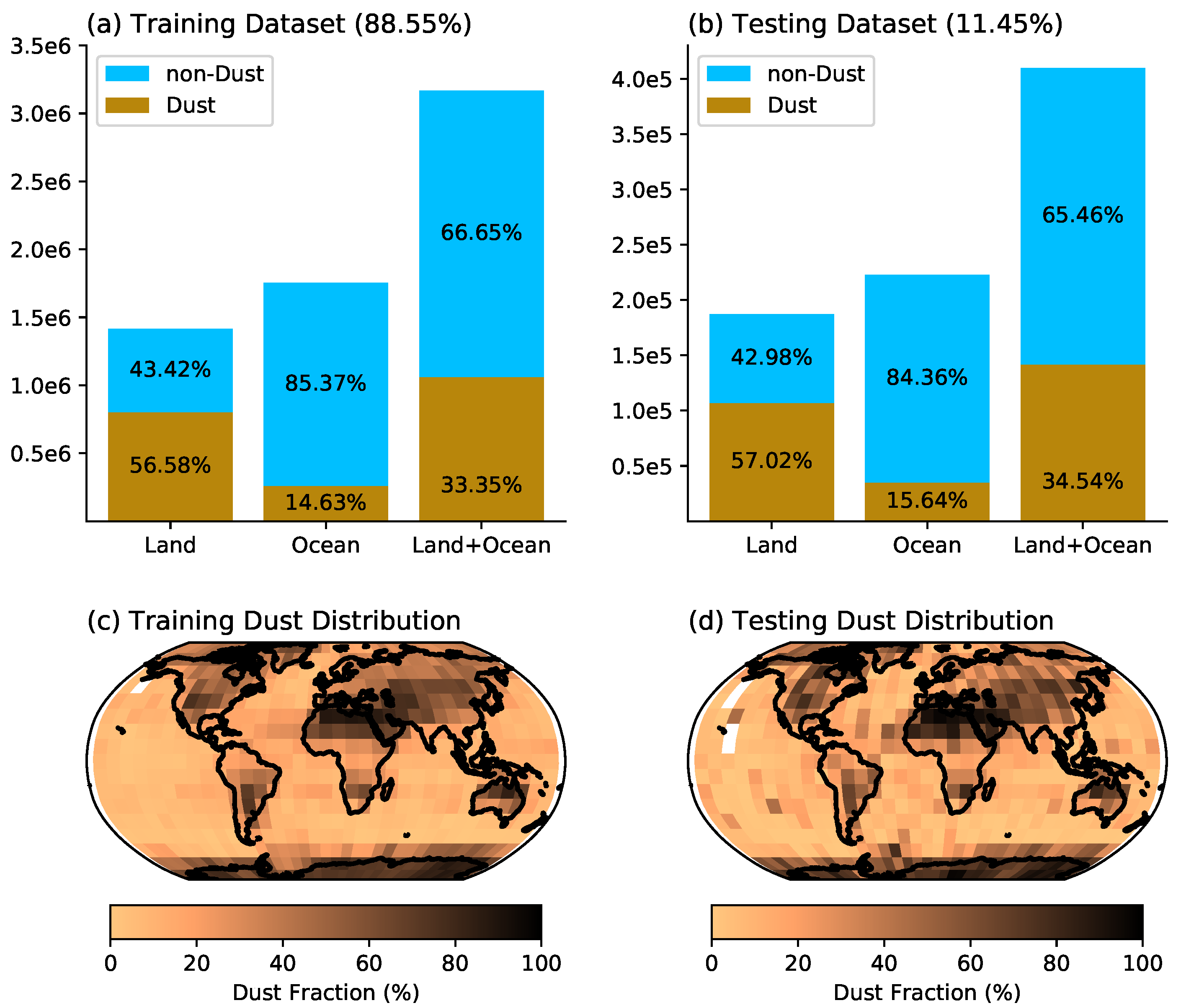
2.2. Training and Testing Data
2.3. Physics-Based Model (PHYS) from NOAA for Off-Track Comparison
3. ML Model Development
3.1. Logistic Regression (LR)
3.2. K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN)
3.3. Random Forests (RF)
3.4. Feedforward Neural Networks (FFNN)
3.5. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)
3.6. Input Data Selection
4. Model Evaluation
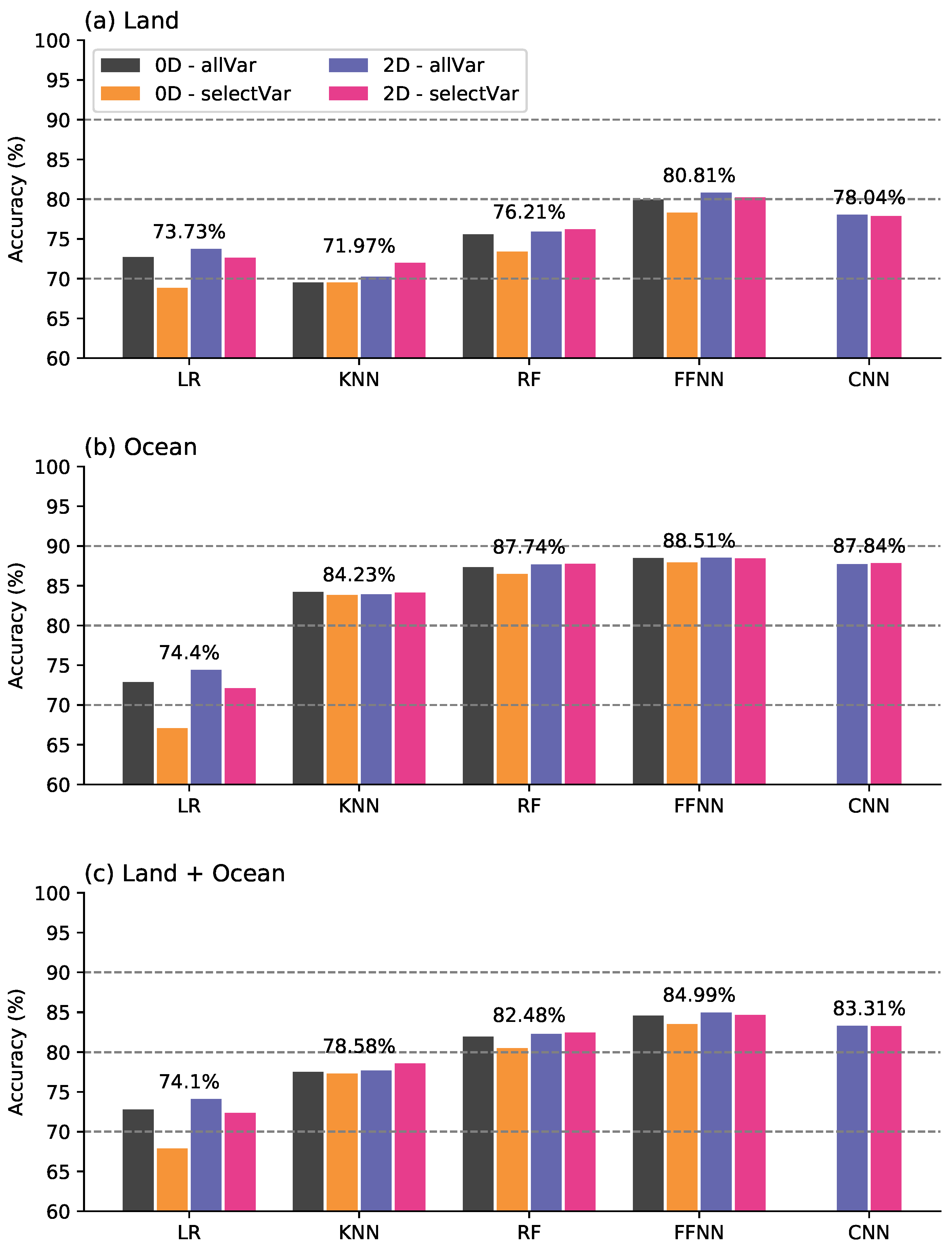
4.1. On-Track Validation and Comparison of ML Based Models
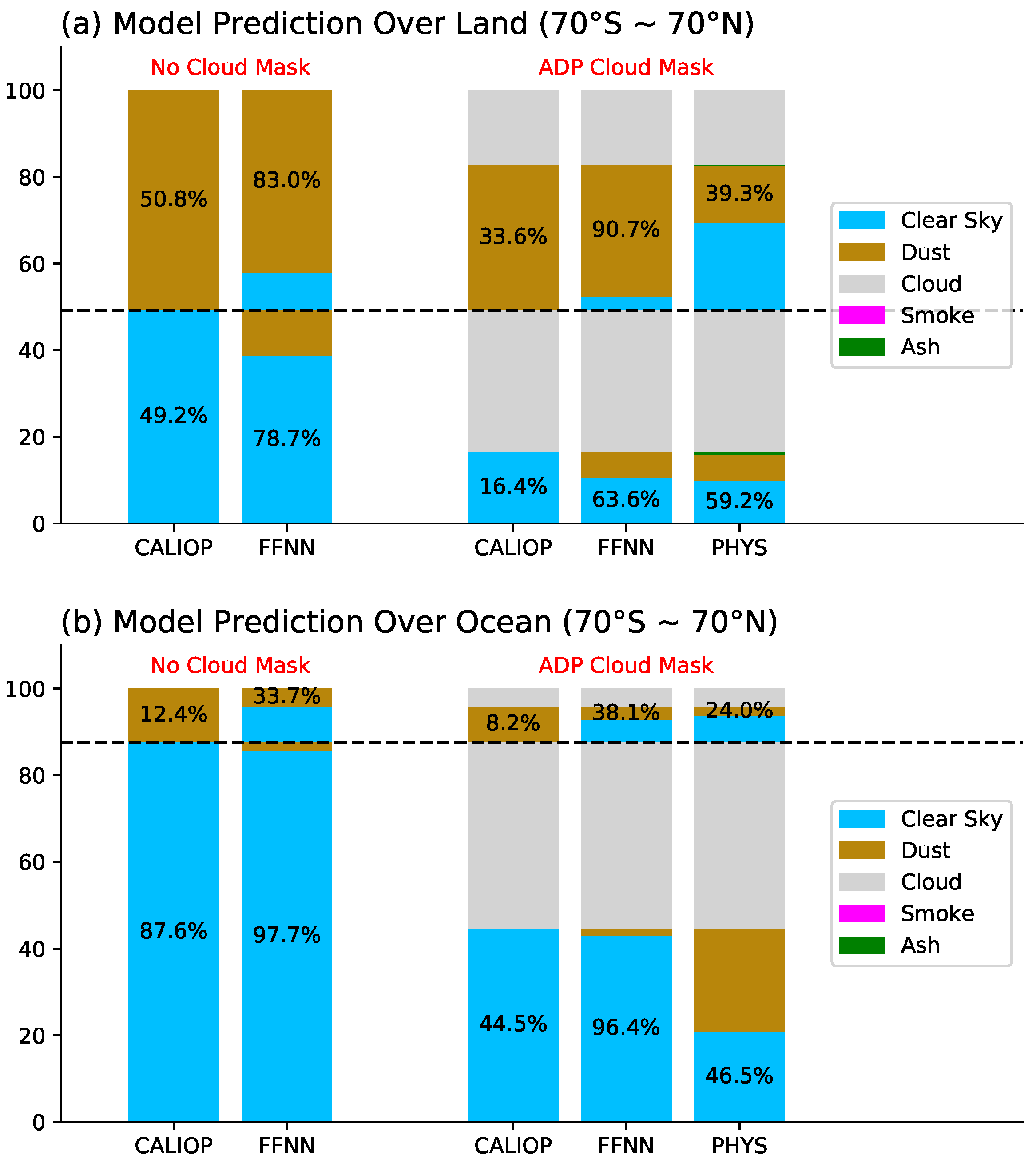
4.2. On-Track Comparison of FFNN with the CALIOP and PHYS Model
5. Evaluation of FFNN-Based VIIRS Dust Detection off CALIOP Track
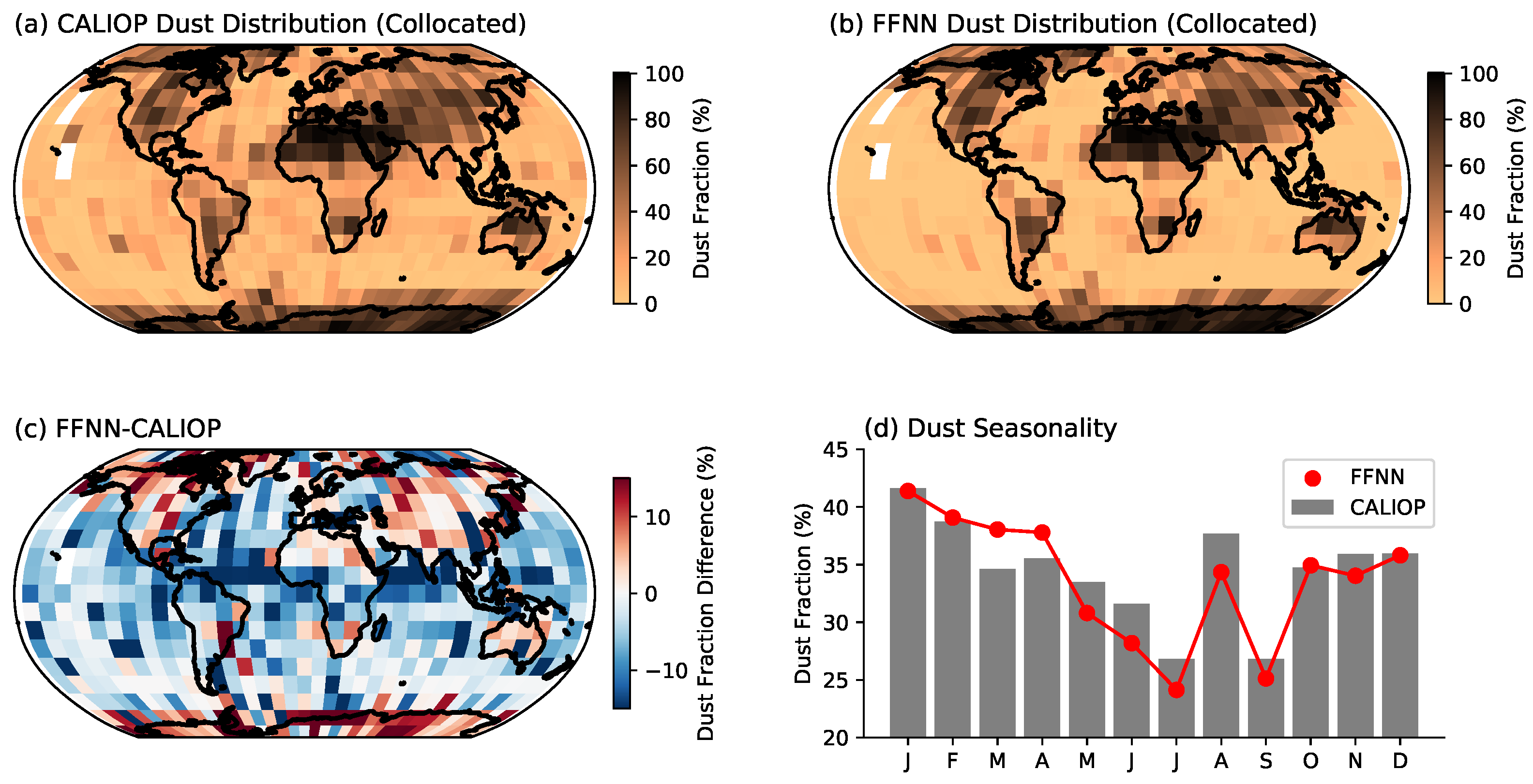
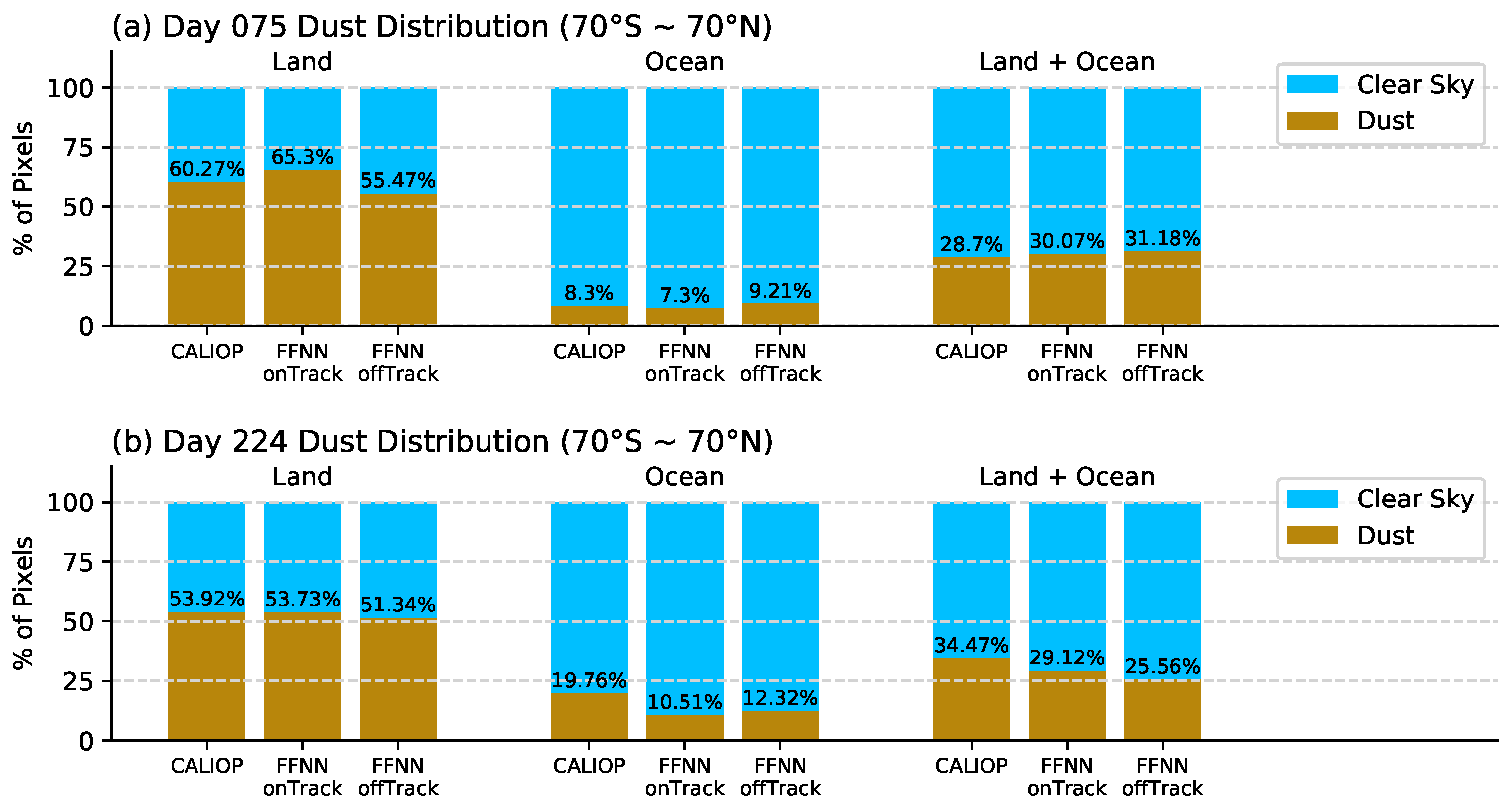
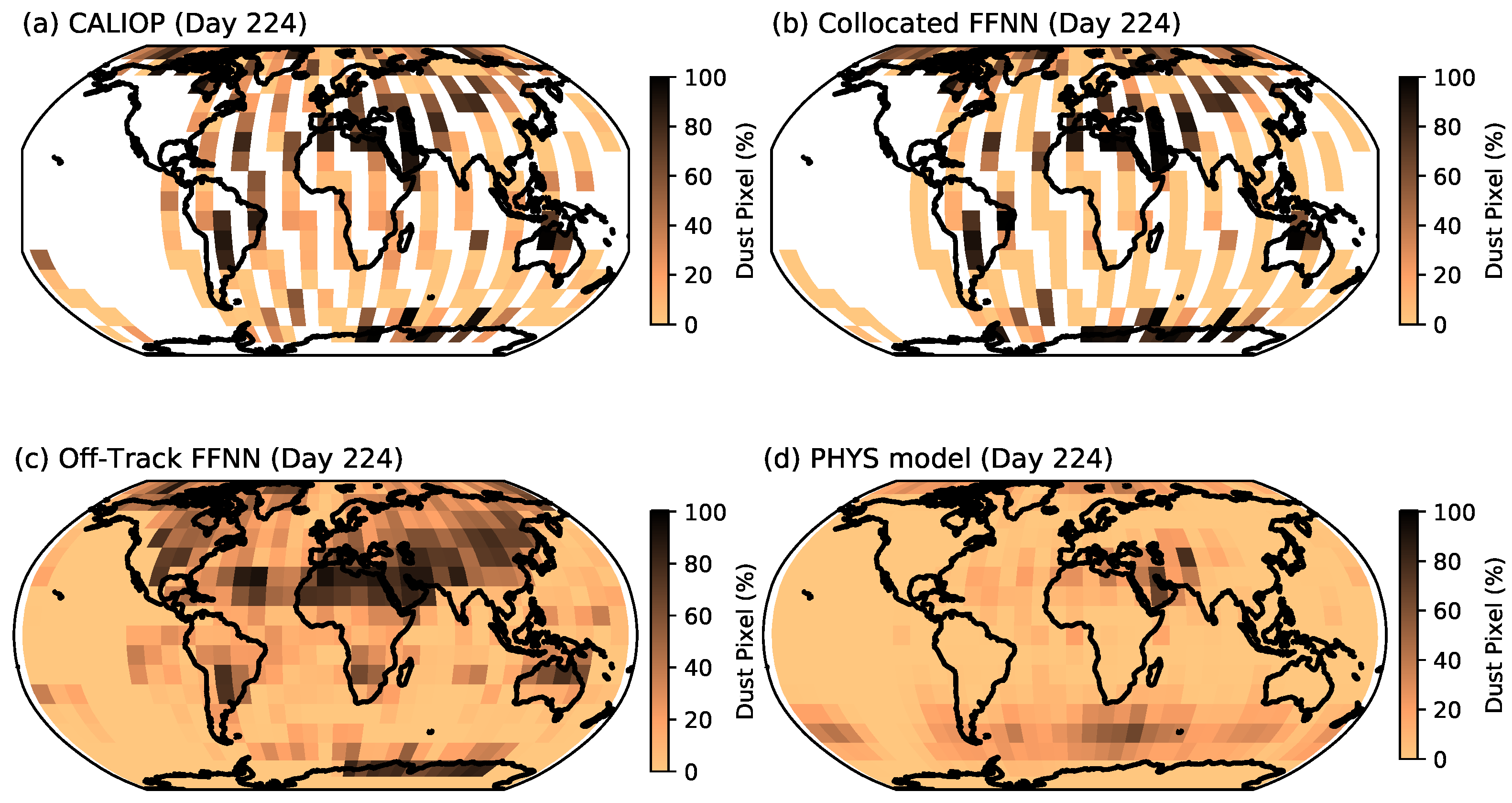
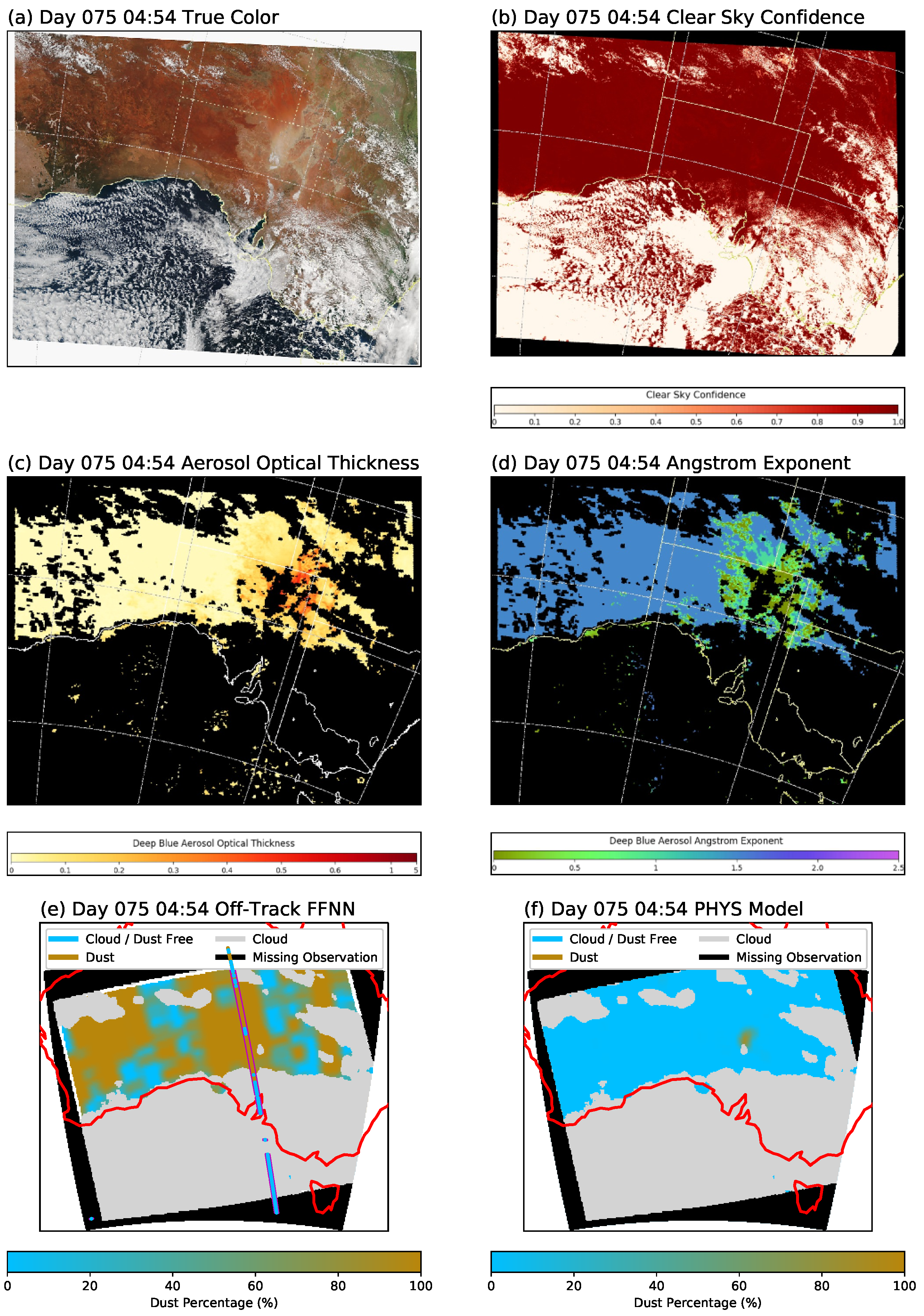
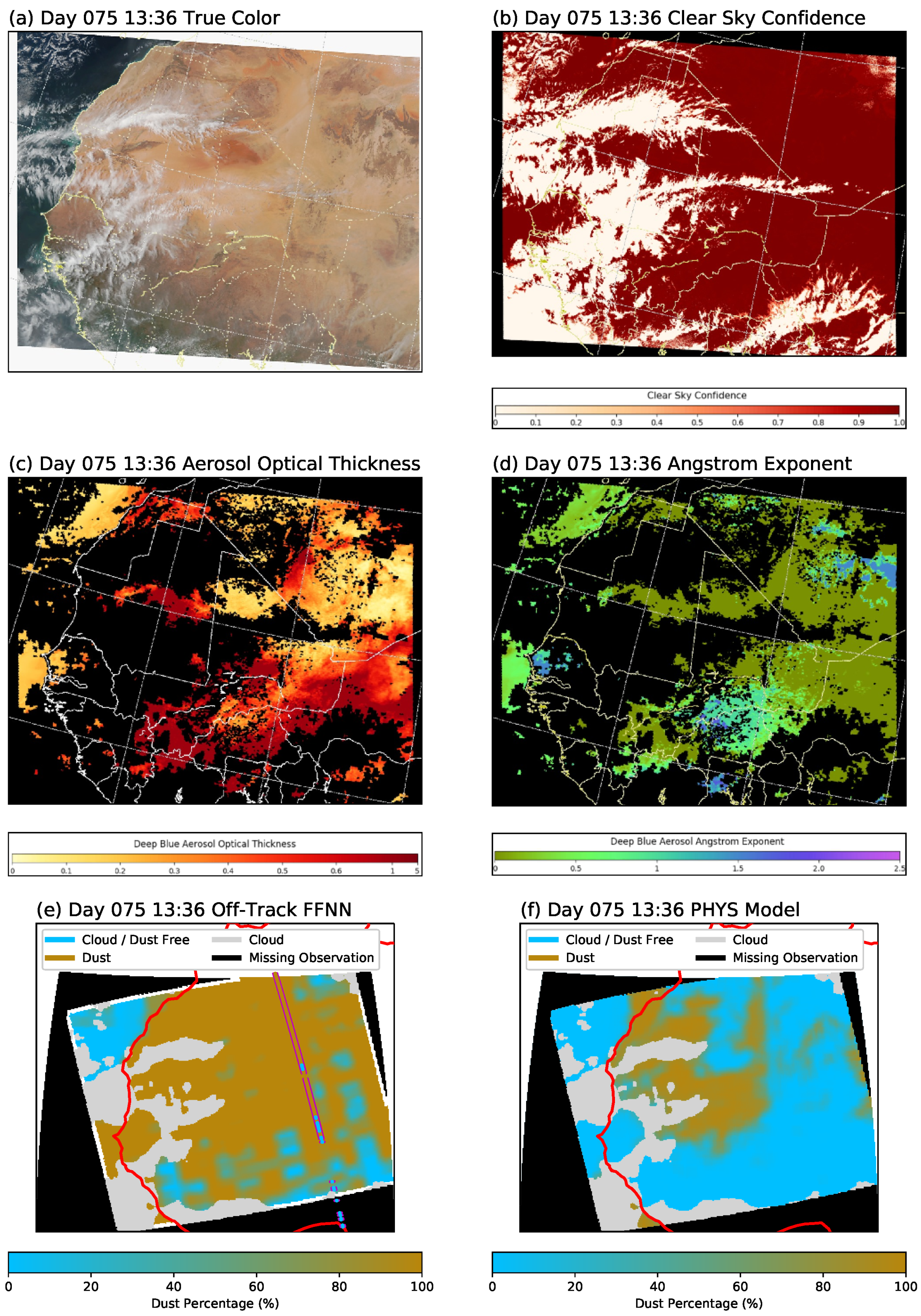
5.1. Entire VIIRS Granule Run for Days 75 and 224
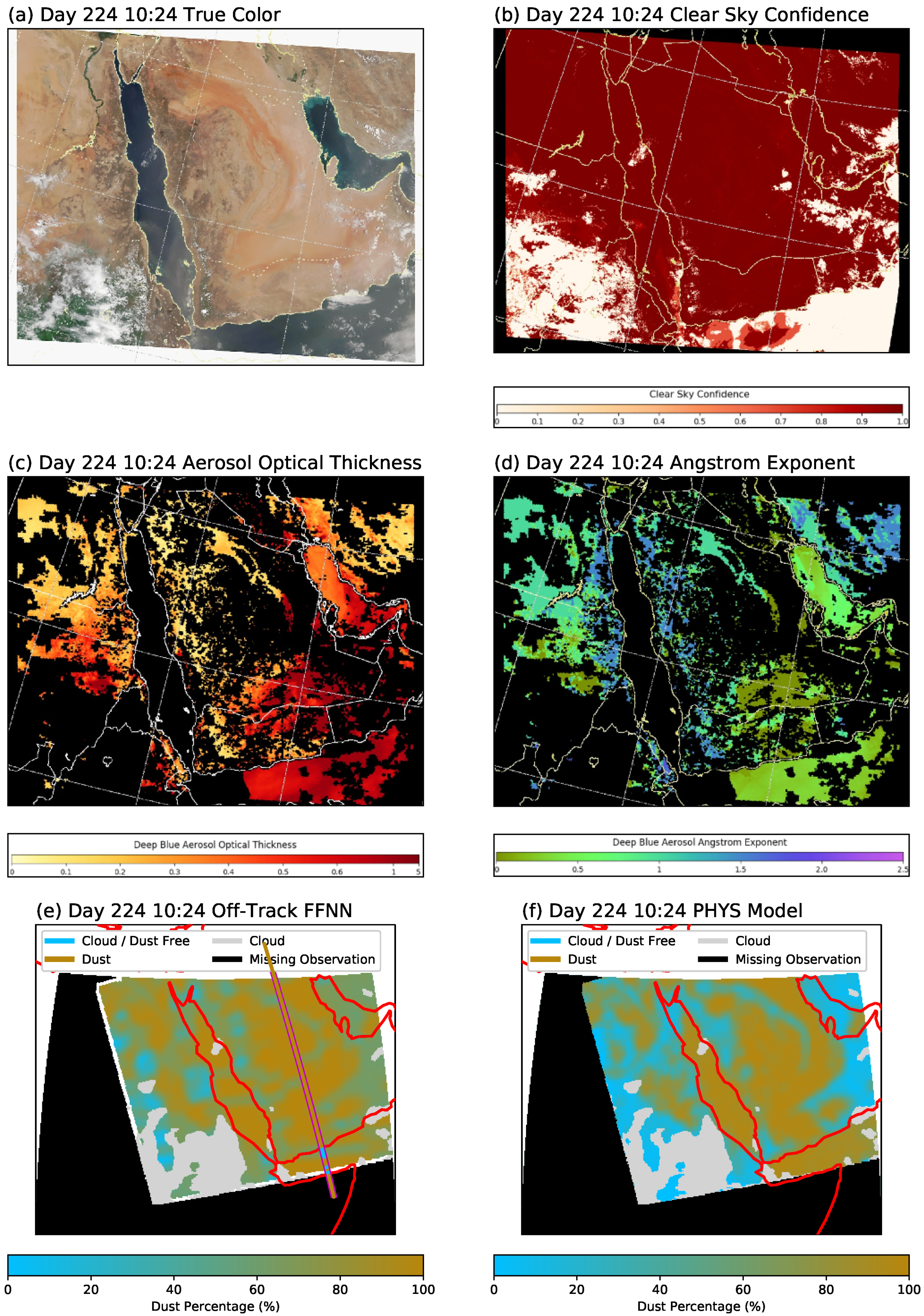
5.2. Off-Track Case Studies
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sugden, D.E.; McCulloch, R.D.; Bory, A.J.M.; Hein, A.S. Influence of Patagonian glaciers on Antarctic dust deposition during the last glacial period. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Eguchi, K.; Yumimoto, K.; Takemura, T.; Shimizu, A.; Uematsu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Hara, Y.; Sugimoto, N. Asian dust transported one full circuit around the globe. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, J.M. Long-range transport of mineral dust in the global atmosphere: Impact of African dust on the environment of the southeastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 3396–3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, D.W.; Kellogg, C.A. Dust storms and their impact on ocean and human health: Dust in Earth’s atmosphere. EcoHealth 2004, 1, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalib, L.; Al-Taiar, A. Dust storms and the risk of asthma admissions to hospitals in Kuwait. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 433, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B.H.; Takahashi, H.; Stephens, G.L.; Yue, Q.; Delanoë, J.; Manipon, G.; Manning, E.; Heymsfield, A.J. Ice cloud microphysical trends observed by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 10715–10739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Bhartia, P.K.; Herman, J.R.; Ahmad, Z.; Gleason, J. Derivation of aerosol properties from satellite measurements of backscattered ultraviolet radiation: Theoretical basis. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 17099–17110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpert, P.; Kishcha, P.; Shtivelman, A.; Krichak, S.O.; Joseph, J.H. Vertical distribution of Saharan dust based on 2.5-year model predictions. Atmos. Res. 2004, 70, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorthy, K.K.; Babu, S.S.; Satheesh, S.K.; Srinivasan, J.; Dutt, C.B.S. Dust absorption over the “Great Indian Desert” inferred using ground-based and satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evan, A.T.; Heidinger, A.K.; Pavolonis, M.J. Development of a new over-water Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer dust detection algorithm. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3903–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Ramanathan, V.; Li, F.; Kim, D. Dust plumes over the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic oceans: Climatology and radiative impact. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKinnon, D.J.; Chavez, P.S., Jr.; Fraser, R.S.; Niemeyer, T.C.; Gillette, D.A. Calibration of GOES-VISSR, visible-band satellite data and its application to the analysis of a dust storm at Owens Lake, California. Geomorphology 1996, 17, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and surface UV products from Ozone Monitoring Instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Reid, J.S.; Hyer, E.J.; Hsu, N.C. Critical evaluation of the MODIS Deep Blue aerosol optical depth product for data assimilation over North Africa. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X. Asian dust detection from the satellite observations of moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS). Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souri, A.H.; Vajedian, S. Dust storm detection using random forests and physical-based approaches over the Middle East. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 124, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.M.; Nasiri, S.L.; Yang, P.; Laszlo, I.; Zhao, X.T. Detection of optically thin mineral dust aerosol layers over the ocean using MODIS. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2013, 30, 896–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Karnieli, A.; Tanré, D. Detection of dust over deserts using satellite data in the solar wavelengths. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, M.; Desbois, M.; Vovor, K. Satellite detection of Saharan dust: Optimized imaging during nighttime. J. Clim. 1988, 1, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.X.P.; Ackerman, S.; Guo, W. Dust and smoke detection for multi-channel imagers. Remote Sens. 2010, 2, 2347–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Pelon, J.; Coakley, J.A., Jr.; Ackerman, S.A.; Charlson, R.J.; Colarco, P.R.; Flamant, P.; Fu, Q.; Hoff, R.M.; Kittaka, C.; et al. The CALIPSO mission: A global 3D view of aerosols and clouds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91.9, 1211–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyridieu, S.; Chédin, A.; Tanré, D.; Capelle, V.; Pierangelo, C.; Lamquin, N.; Armante, R. Saharan dust infrared optical depth and altitude retrieved from AIRS: A focus over North Atlantic–comparison to MODIS and CALIPSO. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 1953–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciren, P.; Kondragunta, S. Dust aerosol index (DAI) algorithm for MODIS. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4770–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, C. Dust Aerosol Retrieval over the Oceans with the MODIS/VIIRS Dark Target algorithm. Part I: Dust Detection. Earth Space Sci. 2020, 7, e2020EA001221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Song, Q.; Patwardhan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Gangopadhyay, A. A hybrid algorithm for mineral dust detection using satellite data. In Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on eScience (eScience), San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 September 2019; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroughani, M.; Pourhashemi, S.; Hashemi, H.; Salehi, M.; Amirahmadi, A.; Asadi, M.A.Z.; Berndtsson, R. Application of remote sensing techniques and machine learning algorithms in dust source detection and dust source susceptibility mapping. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 56, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Guo, P.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Zhang, Z. A Deep Learning Model for Detecting Dust in Earth’s Atmosphere from Satellite Remote Sensing Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP), Bologna, Italy, 14–17 September 2020; pp. 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Igbawua, T.; Liu, Y. Developing a dust storm detection method combining Support Vector Machine and satellite data in typical dust regions of Asia. Adv. Space Res. 2020, 65, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Perea, P.; Rosiles, J.G.; Cota-Ruiz, J. Statistical and neural pattern recognition methods for dust aerosol detection. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 7648–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, Á.; Seethala, C.; Deneke, H. View angle dependence of MODIS liquid water path retrievals in warm oceanic clouds. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 8304–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddux, B.C.; Ackerman, S.A.; Platnick, S. Viewing geometry dependencies in MODIS cloud products. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2010, 27, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.M.; Zhang, Z.; Meyer, K.; Lebsock, M.; Platnick, S.; Ackerman, A.S.; Di Girolamo, L.; Labonnote, L.C.; Cornet, C.; Riedi, J.; et al. Frequency and causes of failed MODIS cloud property retrievals for liquid phase clouds over global oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 4132–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Platnick, S.; Meyer, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y. A machine-learning-based cloud detection and thermodynamic-phase classification algorithm using passive spectral observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 2257–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.; Winker, D.; Kittaka, C.; Getzewich, B.; Kuehn, R.; Omar, A.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Hostetler, C. The CALIPSOLidar Cloud and Aerosol Discrimination: Version 2 Algorithm and Initial Assessment of Performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1198–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Kar, J.; Zeng, S.; Tackett, J.; Vaughan, M.; Avery, M.; Pelon, J.; Getzewich, B.; Lee, K.P.; Magill, B.; et al. Discriminating between clouds and aerosols in the CALIOP version 4.1 data products. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 703–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Winker, D.M.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kuehn, R.E.; Hunt, W.H.; Getzewich, B.J.; Young, S.A.; Liu, Z.; McGill, J.M. Fully Automated Detection of Cloud and Aerosol Layers in the CALIPSO Lidar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2034–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holz, R.E.; Ackerman, S.A.; Nagle, F.W.; Frey, R.; Dutcher, S.; Kuehn, R.E. Global Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) cloud detection and height evaluation using CALIOP. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2008, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Meyer, K.; Yu, H.; Platnick, S.; Colarco, P.; Liu, Z.; Oreopoulos, L. Shortwave direct radiative effects of above-cloud aerosols over global oceans derived from 8 years of CALIOP and MODIS observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2877–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciren, P.; Kondragunta, S. NOAA/NESDIS/STAR Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: JPSS Aerosol Detection Product. Available online: https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/smcd/spb/aq/AerosolWatch/docs/JPSS_VIIRS_EPS_ADP_ATBD_V1.3_20180606.pdf (accessed on 6 December 2020).
- Dreiseitl, S.; Ohno-Machado, L. Logistic regression and artificial neural network classification models: A methodology review. J. Biomed. Inform. 2002, 35, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRoberts, R.E. Satellite image-based maps: Scientific inference or pretty pictures? Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, R.H.; Latifovic, R. Mapping insect-induced tree defoliation and mortality using coarse spatial resolution satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Xu, X.; Du, H.; Ge, H.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, Y. Estimating aboveground carbon of Moso bamboo forests using the k nearest neighbors technique and satellite imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2011, 77, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M. Random forest classifier for remote sensing classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.V. Advantages and disadvantages of using artificial neural networks versus logistic regression for predicting medical outcomes. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1996, 49, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Fei, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Jiao, H.; Zhang, L. SatCNN: Satellite image dataset classification using agile convolutional neural networks. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, K.; Wang, H. Cloud classification of satellite image based on convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 8th IEEE International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science, Beijing, China, 24–26 November 2017; pp. 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, H.; Botambekov, D.; Walther, A. NOAA/NESDIS/STAR Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: A Naïve Bayesian Cloud Mask Delivered to NOAA Enterprise. Available online: https://www.star.nesdis.noaa.gov/jpss/documents/ATBD/ATBD_EPS_Cloud_Mask_v1.2.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2016).
- Shi, Y.R.; Levy, R.C.; Eck, T.F.; Fisher, B.; Mattoo, S.; Remer, L.A.; Slutsker, I.; Zhang, J. Characterizing the 2015 Indonesia fire event using modified MODIS aerosol retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Variables | |
|---|---|
| Non-Dust | No aerosol detected, |
| Other types of Aerosols | |
| Dust | Pure Dust, |
| Dust mixtures, | |
| Dust above or below other types of aerosols | |
| Predictor Variables | |
|---|---|
| Radiances from VIIRS M-bands (16) | |
| (band center in µm) | M01 (0.412 µm), M02 (0.445 µm), M03 (0.488 µm), M04 (0.555 µm), |
| M05 (0.672 µm), M06 (0.746 µm), M07 (0.865 µm), M08 (1.240 µm), | |
| M09 (1.378 µm), M10 (1.61 µm), M11 (2.25 µm), M12 (3.7 µm), | |
| M13 (4.05 µm), M14 (8.55 µm), M15 (10.763 µm), M16 (12.01 µm) | |
| Geometric Variables (4) | Solar Azimuth Angle (SAA), |
| Solar Zenith Angle (SZA), | |
| Viewing Azimuth Angle (VAA), | |
| Viewing Zenith Angle (VZA) | |
| Observation Information (3) | Day of Year (1–365), |
| Latitude, | |
| Longitude | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Shi, Y.R.; Cai, C.; Ciren, P.; Wang, J.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Zhang, Z. Machine Learning Based Algorithms for Global Dust Aerosol Detection from Satellite Images: Inter-Comparisons and Evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030456
Lee J, Shi YR, Cai C, Ciren P, Wang J, Gangopadhyay A, Zhang Z. Machine Learning Based Algorithms for Global Dust Aerosol Detection from Satellite Images: Inter-Comparisons and Evaluation. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(3):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030456
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jangho, Yingxi Rona Shi, Changjie Cai, Pubu Ciren, Jianwu Wang, Aryya Gangopadhyay, and Zhibo Zhang. 2021. "Machine Learning Based Algorithms for Global Dust Aerosol Detection from Satellite Images: Inter-Comparisons and Evaluation" Remote Sensing 13, no. 3: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030456
APA StyleLee, J., Shi, Y. R., Cai, C., Ciren, P., Wang, J., Gangopadhyay, A., & Zhang, Z. (2021). Machine Learning Based Algorithms for Global Dust Aerosol Detection from Satellite Images: Inter-Comparisons and Evaluation. Remote Sensing, 13(3), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13030456








