Using Sentinel-2 to Track Field-Level Tillage Practices at Regional Scales in Smallholder Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
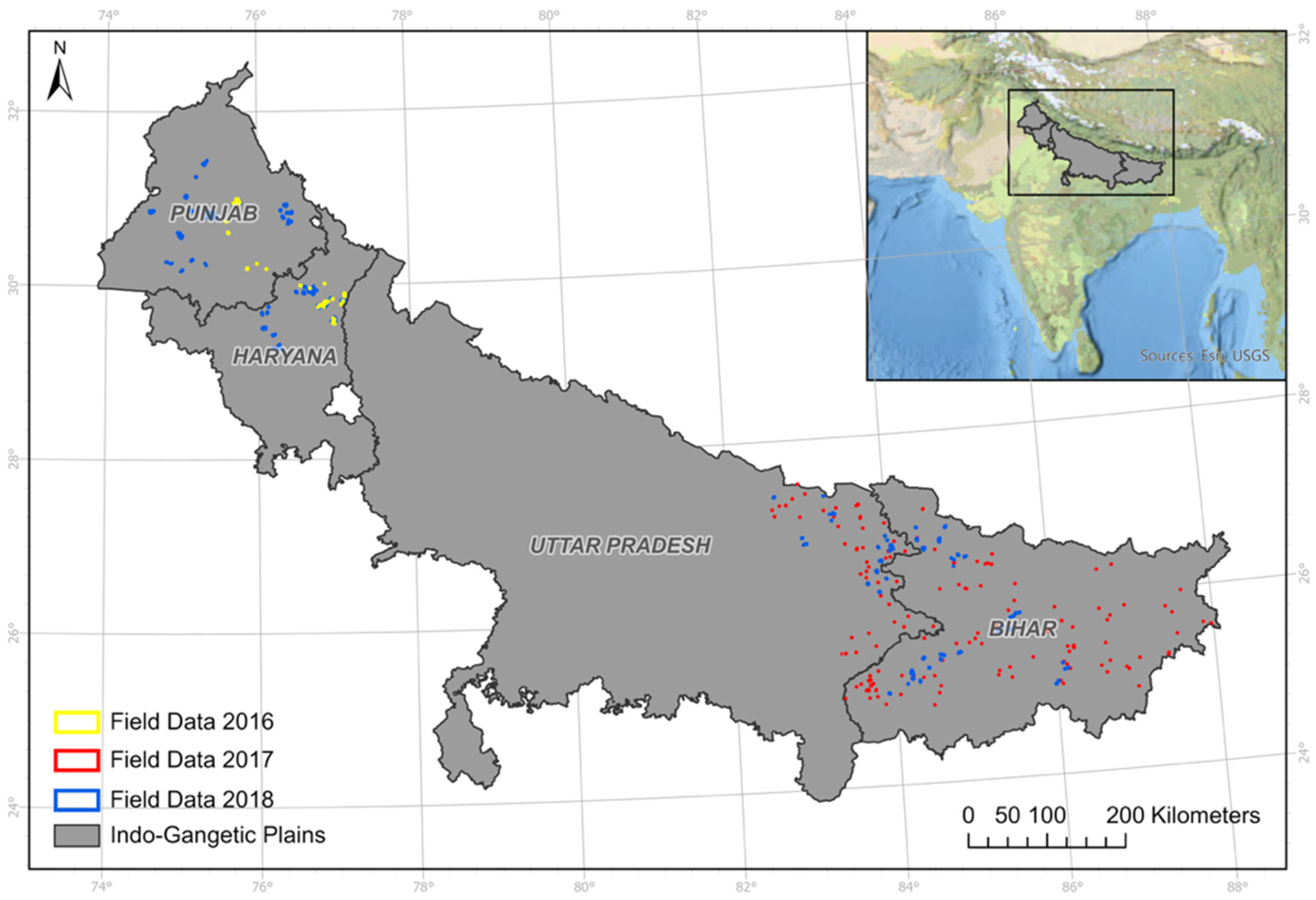
2.1. Study Area
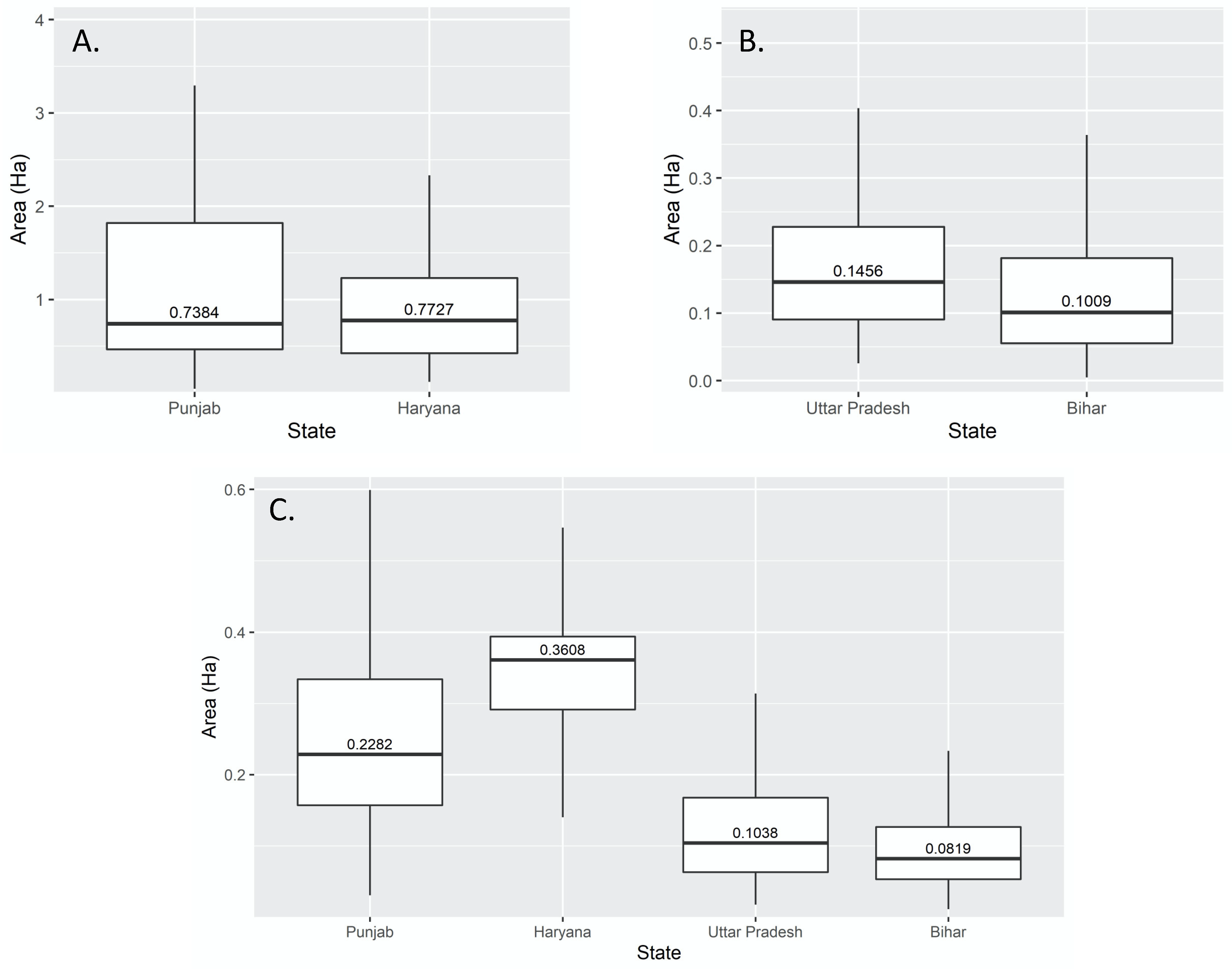
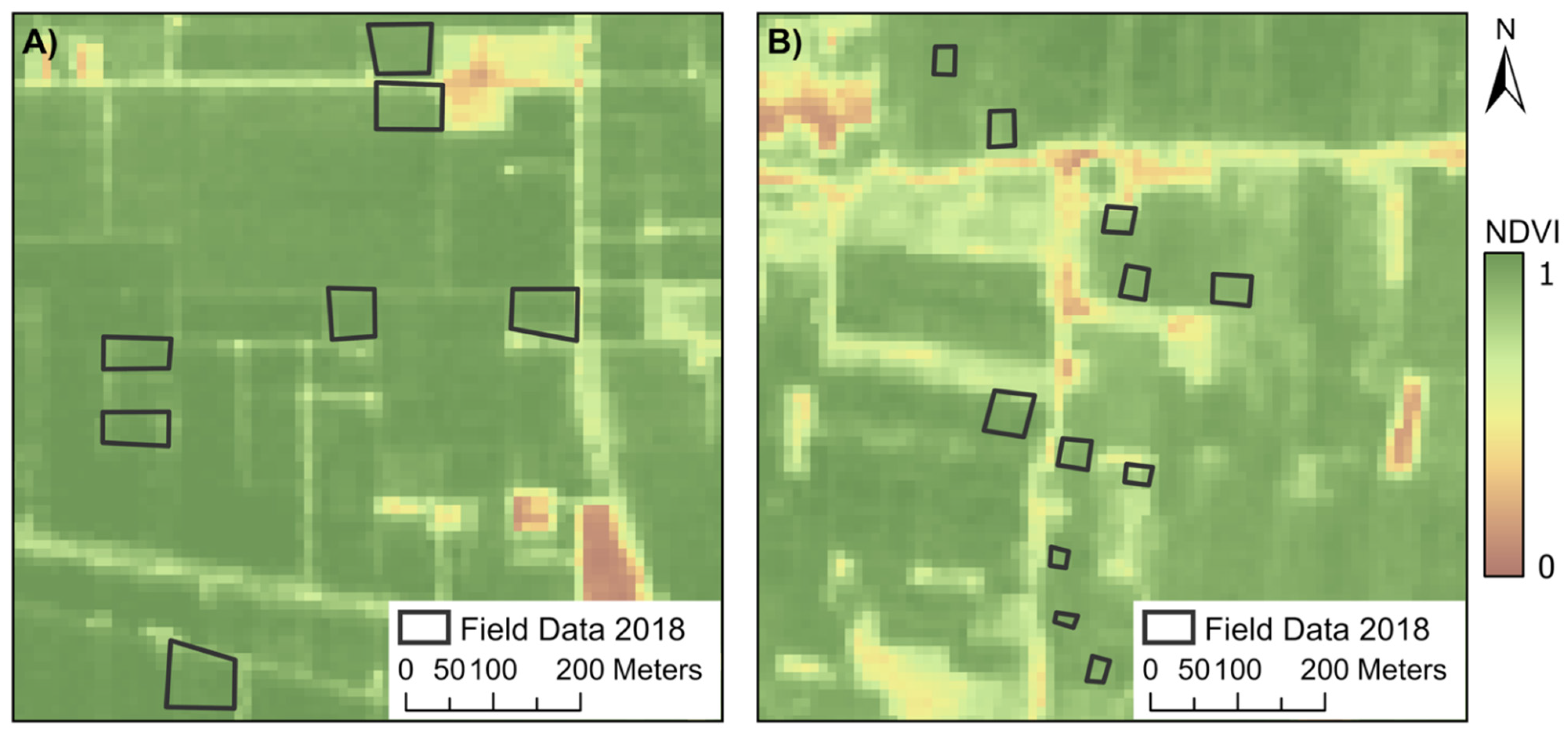
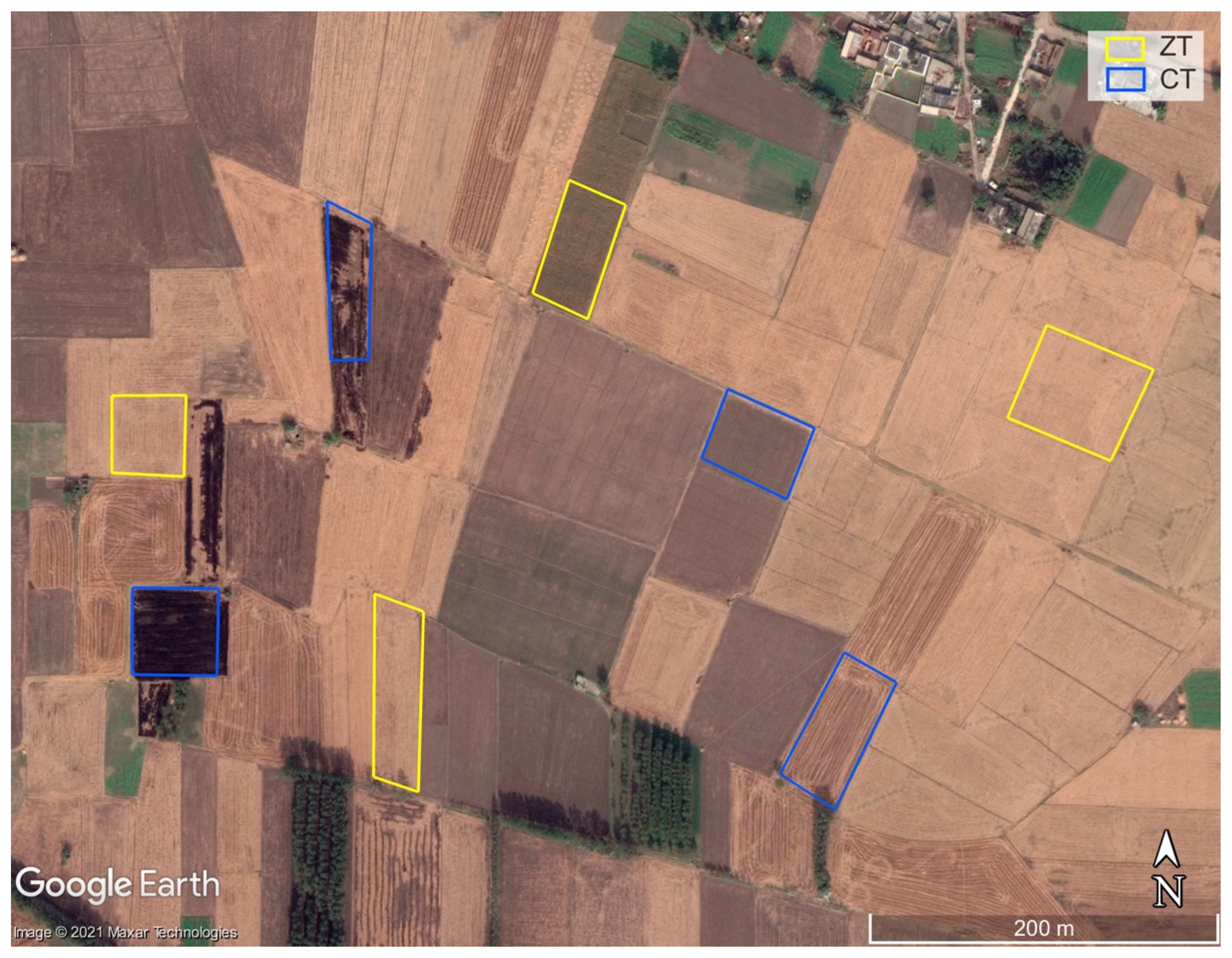
2.2. Field Data
2.3. Satellite Data and Image Preprocessing
2.4. Random Forest Models and Validation
3. Results
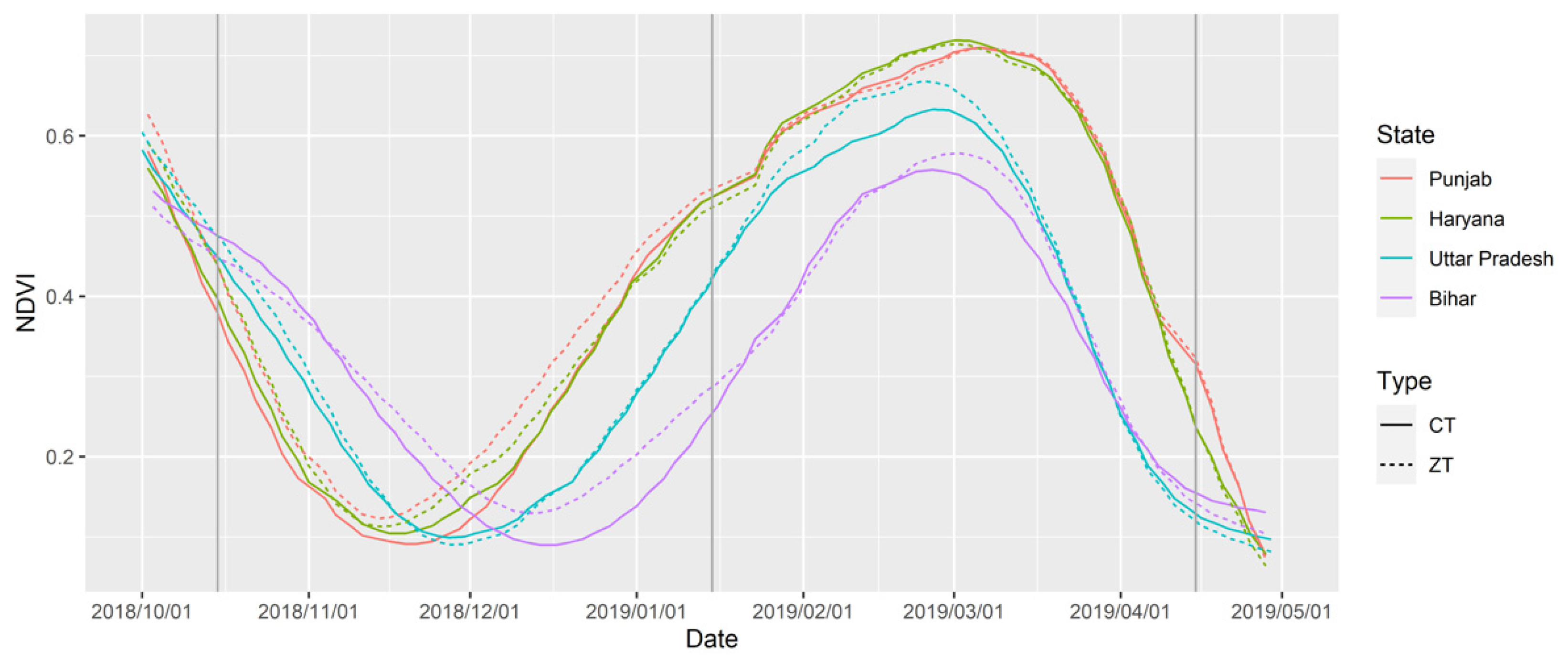
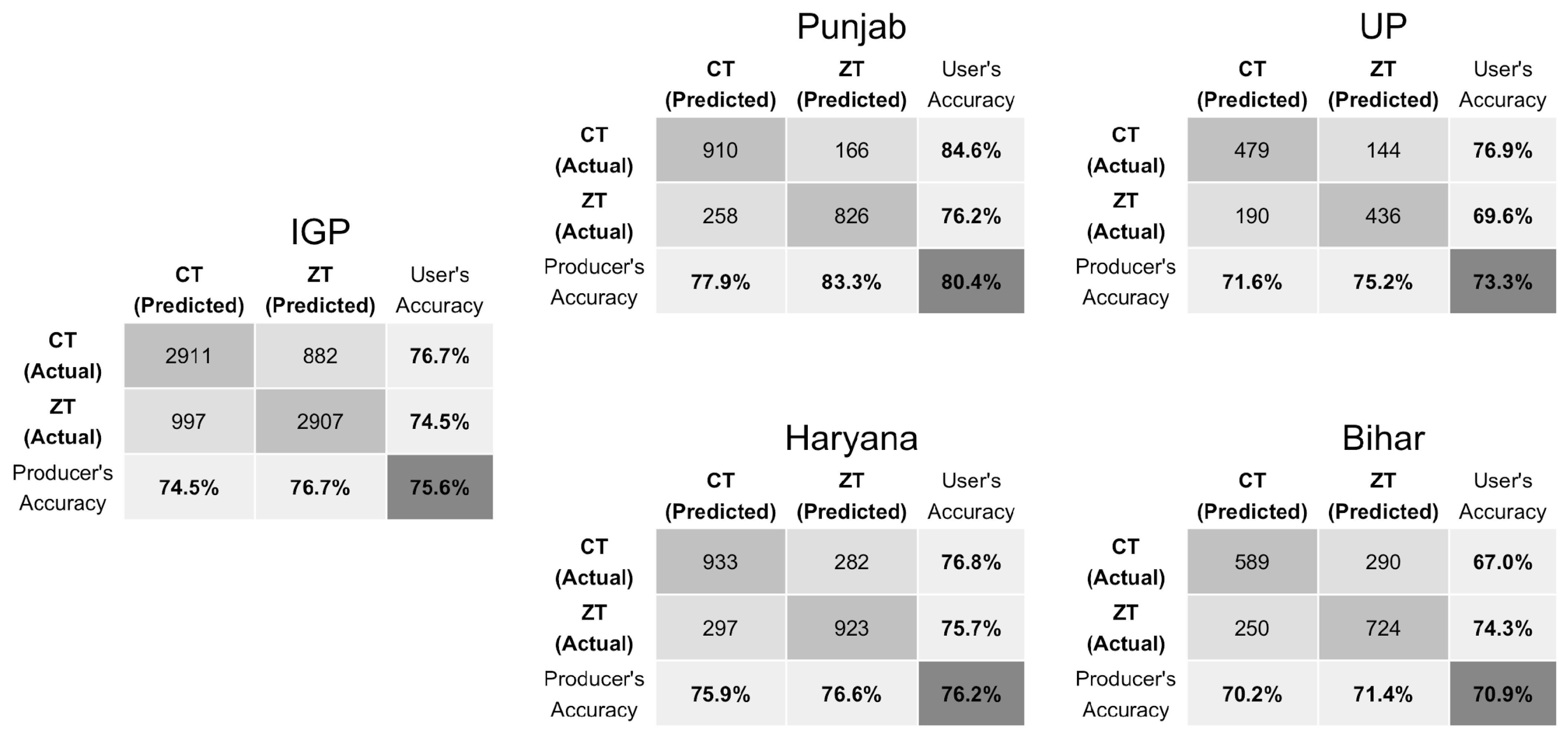
3.1. Full Season Tillage Classification
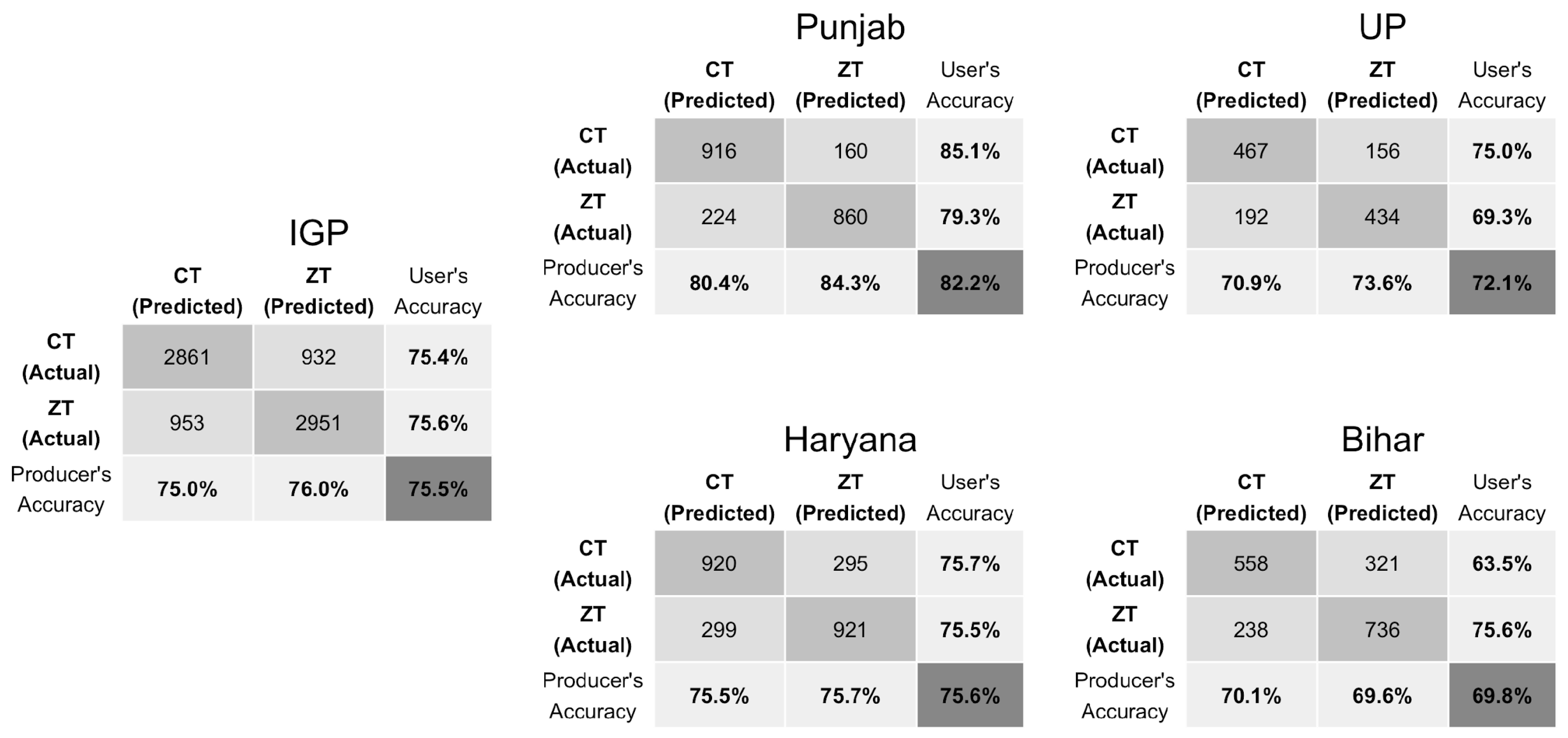
3.2. Early Season Tillage Classification
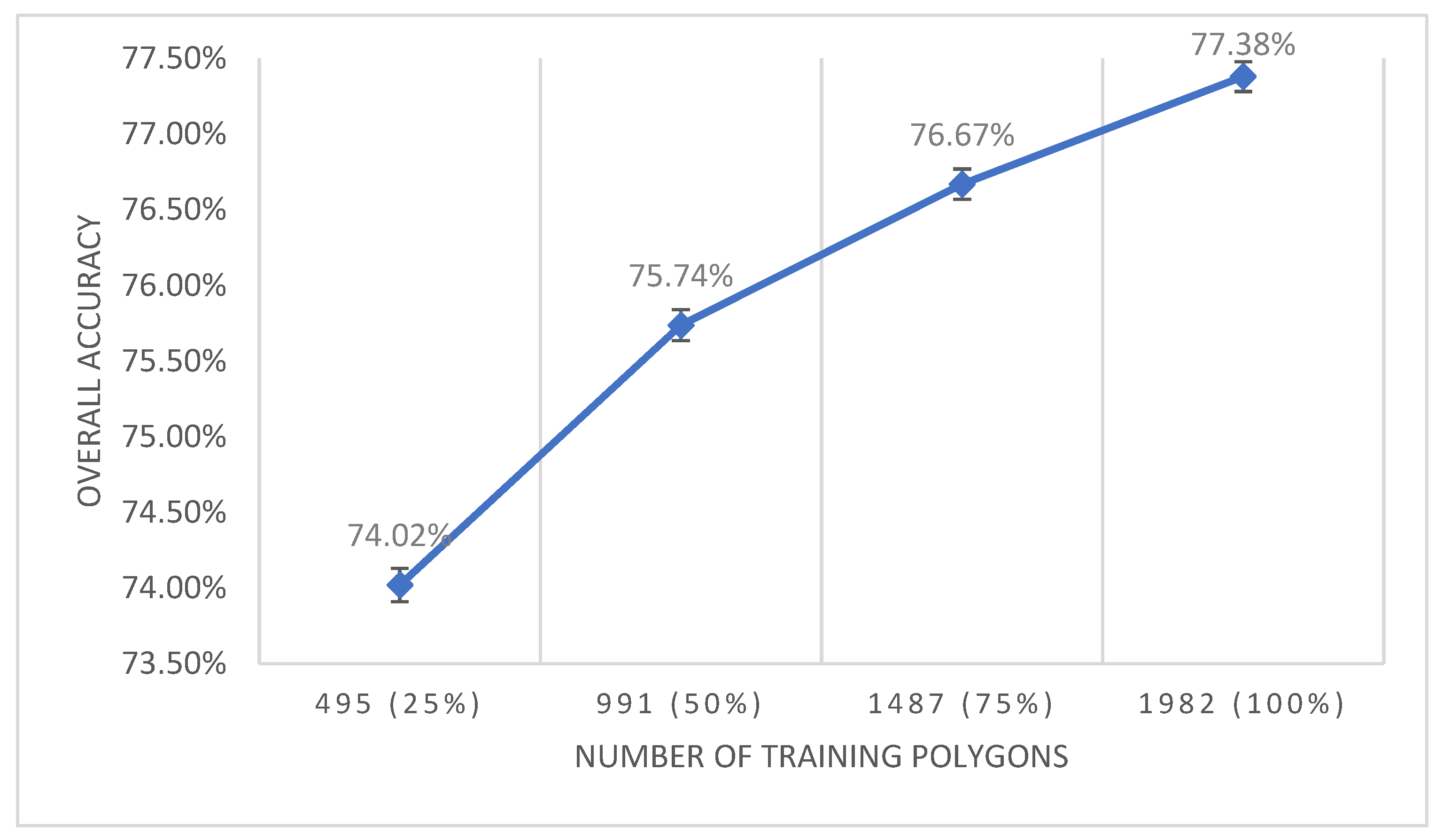
3.3. Training Sample Size versus Model Accuracy
3.4. Back in Time Classification
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Brouder, S.M.; Gomez-Macpherson, H. The Impact of Conservation Agriculture on Smallholder Agric. Yields: A Scoping Review of the Evidence. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 187, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shater, T.; Yigezu, Y.A.; Mugera, A.; Piggin, C.; Haddad, A.; Khalil, Y.; Loss, S.; Aw-Hassan, A. Does Zero Tillage Improve the Livelihoods of Smallholder Cropping Farmers? J. Agric. Econ. 2016, 67, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erenstein, O.; Laxmi, V. Zero Tillage Impacts in India’s Rice–Wheat Systems: A Review. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 100, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Aggarwal, P.; Rana, D.S. A Global Analysis of the Impact of Zero-Tillage on Soil Physical Condition, Organic Carbon Content, and Plant Root Response. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jat, M.L.; Chakraborty, D.; Ladha, J.K.; Rana, D.S.; Gathala, M.K.; McDonald, A.; Gerard, B. Conservation Agriculture for Sustainable Intensification in South Asia. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Singh, B. Toward an Evergreen Revolution sustainable intensification in smallholder farming. In A Better Planet: Forty Big Ideas for a Sustainable Future; Etsy, D., Burke, I., Eds.; Yale University Press: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-0-300-24889-0. [Google Scholar]
- Azzari, G.; Grassini, P.; Edreira, J.I.R.; Conley, S.; Mourtzinis, S.; Lobell, D.B. Satellite Mapping of Tillage Practices in the North Central US Region from 2005 to 2016. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 221, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Campbell, J.B.; Shao, Y.; Wynne, R.H. Broad-Scale Monitoring of Tillage Practices Using Sequential Landsat Imagery. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2013, 77, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steckel, J.C.; Dorband, I.I.; Montrone, L.; Ward, H.; Missbach, L.; Hafner, F.; Jakob, M.; Renner, S. Distributional Impacts of Carbon Pricing in Developing Asia. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricklemyer, R.S.; Lawrence, R.L.; Miller, P.R.; Battogtokh, N. Predicting Tillage Practices and Agric. Soil Disturbance in North Central Montana with Landsat Imagery. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 114, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Dhakal, K.; Wagle, P.; Kilic, A. Retrospective Tillage Differentiation Using the Landsat-5 TM Archive with Discriminant Analysis. Agrosyst. Geosci. Environ. 2020, 3, e20000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, M.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, B.; McDonald, A.; Malik, R.K.; Lobell, D.B. Mapping Smallholder Wheat Yields and Sowing Dates Using Micro-Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watts, J.D.; Powell, S.L.; Lawrence, R.L.; Hilker, T. Improved Classification of Conservation Tillage Adoption Using High Temporal and Synthetic Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. First Experience with Sentinel-2 Data for Crop and Tree Species Classifications in Central Europe. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Dash, J.; Huete, A.; Jiang, A.; Yin, G.; Ding, Y.; Peng, D.; Hall, C.C.; Brown, L.; Shi, Y.; et al. Retrieval of Crop Biophysical Parameters from Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 80, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Hall, C.C. A Comparison of Estimating Crop Residue Cover from Sentinel-2 Data Using Empirical Regressions and Machine Learning Methods. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, P.; Navid, H.; Feizizadeh, B.; Eskandari, I.; Blaschke, T. Fuzzy Object-Based Image Analysis Methods Using Sentinel-2A and Landsat-8 Data to Map and Characterize Soil Surface Residue. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, M.; Singh, B.; Srivastava, A.A.K.; Malik, R.K.; McDonald, A.J.; Lobell, D.B. Using Satellite Data to Identify the Causes of and Potential Solutions for Yield Gaps in India’s Wheat Belt. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 094011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Zhou, W.; Bhattarai, N.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, B.; Poonia, S.; Lobell, D.B.; Jain, M. Using Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2, and Planet Imagery to Map Crop Type of Smallholder Farms. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Campbell, J.B.; de Beurs, K.M. Remote Sensing of Crop Residue Cover Using Multi-Temporal Landsat Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.; McCarthy, G.; Mellor, A.; Newell, G.; Smith, L. Training Data Requirements for Fire Severity Mapping Using Landsat Imagery and Random Forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 245, 111839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millard, K.; Richardson, M. On the Importance of Training Data Sample Selection in Random Forest Image Classification: A Case Study in Peatland Ecosystem Mapping. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8489–8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, R.; Lin, Z.; Xu, J.; Jiang, H.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Lin, T. DeepCropMapping: A Multi-Temporal Deep Learning Approach with Improved Spatial Generalizability for Dynamic Corn and Soybean Mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 247, 111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newport, D.; Lobell, D.B.; Balwinder-Singh; Srivastava, A.K.; Rao, P.; Umashaanker, M.; Malik, R.K.; McDonald, A.; Jain, M. Factors Constraining Timely Sowing of Wheat as an Adaptation to Climate Change in Eastern India. Weather Clim. Soc. 2020, 12, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittonell, P.; Vanlauwe, B.; Leffelaar, P.A.; Rowe, E.C.; Giller, K.E. Exploring Diversity in Soil Fertility Management of Smallholder Farms in Western Kenya: I. Heterogeneity at Region and Farm Scale. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 110, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Mondal, P.; Galford, G.; Fiske, G.; DeFries, R. An Automated Approach to Map Winter Cropped Area of Smallholder Farms across Large Scales Using MODIS Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keil, A.; D’Souza, A.; McDonald, A. Growing the Service Economy for Sustainable Wheat Intensification in the Eastern Indo-Gangetic Plains: Lessons from Custom Hiring Services for Zero-Tillage. Food Secur. 2016, 18, 1011–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S. Atmospherically Corrected Time Series Using Google Earth Engine. 2018. Available online: https://github.com/samsammurphy/ee-atmcorr-timeseries (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Wilson, R.T. Py6S: A Python Interface to the 6S Radiative Transfer Model. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 51, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remote Estimation of Leaf Area Index and Green Leaf Biomass in Maize Canopies-Gitelson-2003-Geophysical Research Letters-Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://agupubs-onlinelibrary-wiley-com.proxy.lib.umich.edu/doi/full/10.1029/2002GL016450 (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the Relation between NDVI, Fractional Vegetation Cover, and Leaf Area Index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Deventer, A.P.; Ward, A.D.; Gowda, P.H.; Lyon, J.G. Using Thematic Mapper Data to Identify Contrasting Soil Plains and Tillage Practices. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1997, 63, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- McNairn, H.; Protz, R. Mapping Corn Residue Cover on Agricultural Fields in Oxford County, Ontario, Using Thematic Mapper. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 19, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, D.G.; Truman, C.C.; Schomberg, H.H.; Endale, D.M.; Strickland, T.C. Evaluating Techniques for Determining Tillage Regime in the Southeastern Coastal Plain and Piedmont. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M. Caret: Classification and Regression Training. R Package Version 6.0-88. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=caret (accessed on 1 November 2021).
- Liawm, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.J. An Introduction to the Bootstrap, 1st ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, R.; MacKinnon, J.G. Bootstrap Tests: How Many Bootstraps? Econom. Rev. 2000, 19, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paliwal, A.; Jain, M. The Accuracy of Self-Reported Crop Yield Estimates and Their Ability to Train Remote Sensing Algorithms. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merry, K.; Bettinger, P. Smartphone GPS Accuracy Study in an Urban Environment. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| State | Total Polygons 2018–2019 | Total Polygons 2017–2018 | Total Polygons 2016–2017 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Punjab | 736 | 0 | 238 |
| Haryana | 814 | 0 | 134 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 502 | 72 | 0 |
| Bihar | 778 | 120 | 0 |
| Bands | Description | Index | Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| B2 | Blue | GCVI | (NIR/Green) |
| B3 | Green | NDVI | (NIR − Red)/(NIR + Red) |
| B4 | Red | NDTI | (SWIR1 − SWIR2)/(SWIR1 + SWIR2) |
| B5 | Red Edge 1 | NDI5 | (NIR − SWIR1)/(NIR + SWIR1) |
| B6 | Red Edge 2 | NDI7 | (NIR − SWIR2)/(NIR + SWIR2) |
| B7 | Red Edge 3 | CRC | (SWIR1 − Green)/(SWIR1 + Green) |
| B8 | Near-Infrared (NIR) | STI | SWIR1/SWIR2 |
| B8A | Red Edge 4 | ||
| B11 | Short-Wave Infrared 1 (SWIR1) | ||
| B12 | Short-Wave Infrared 1 (SWIR1) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, W.; Rao, P.; Jat, M.L.; Singh, B.; Poonia, S.; Bijarniya, D.; Kumar, M.; Singh, L.K.; Schulthess, U.; Singh, R.; et al. Using Sentinel-2 to Track Field-Level Tillage Practices at Regional Scales in Smallholder Systems. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245108
Zhou W, Rao P, Jat ML, Singh B, Poonia S, Bijarniya D, Kumar M, Singh LK, Schulthess U, Singh R, et al. Using Sentinel-2 to Track Field-Level Tillage Practices at Regional Scales in Smallholder Systems. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(24):5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245108
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Weiqi, Preeti Rao, Mangi L. Jat, Balwinder Singh, Shishpal Poonia, Deepak Bijarniya, Manish Kumar, Love Kumar Singh, Urs Schulthess, Rajbir Singh, and et al. 2021. "Using Sentinel-2 to Track Field-Level Tillage Practices at Regional Scales in Smallholder Systems" Remote Sensing 13, no. 24: 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245108
APA StyleZhou, W., Rao, P., Jat, M. L., Singh, B., Poonia, S., Bijarniya, D., Kumar, M., Singh, L. K., Schulthess, U., Singh, R., & Jain, M. (2021). Using Sentinel-2 to Track Field-Level Tillage Practices at Regional Scales in Smallholder Systems. Remote Sensing, 13(24), 5108. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13245108






