Study of Persistent Haze Pollution in Winter over Jinan (China) Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Stations and Data
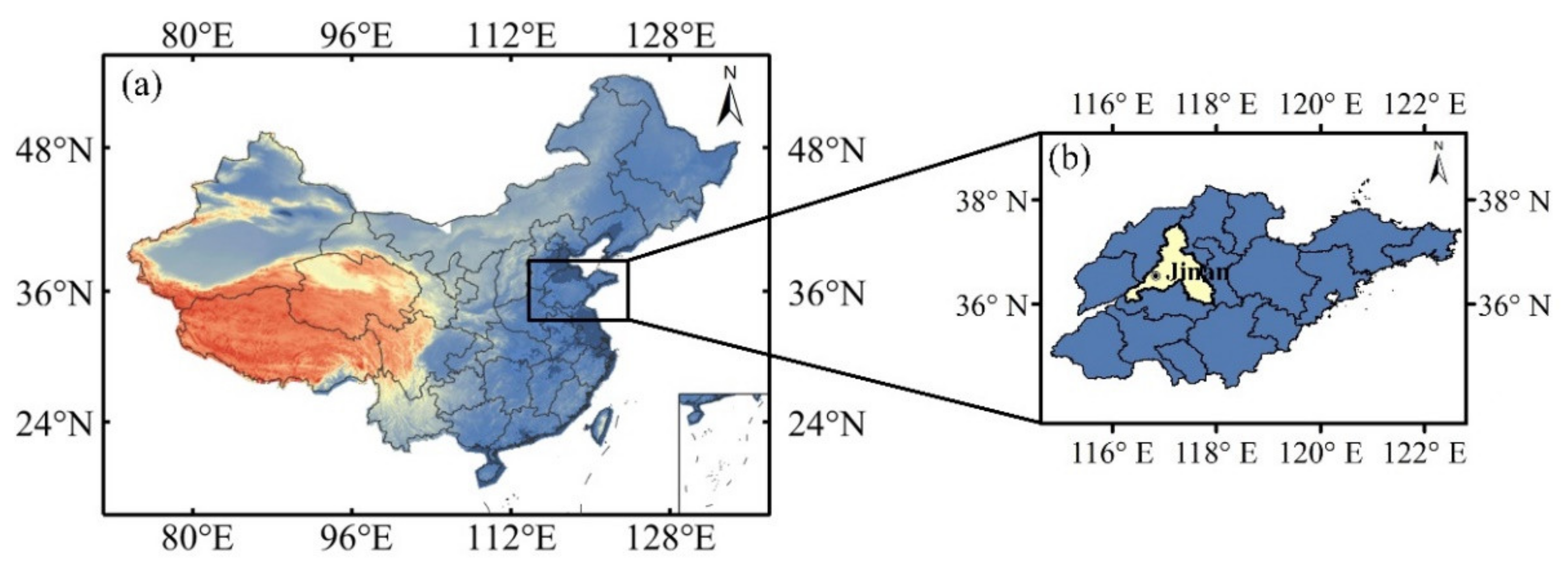
2.1. Observation Site
2.2. Ground-Based Data
2.3. Satellite Observations
2.4. Other Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Overview of Winter Haze Pollution in Jinan
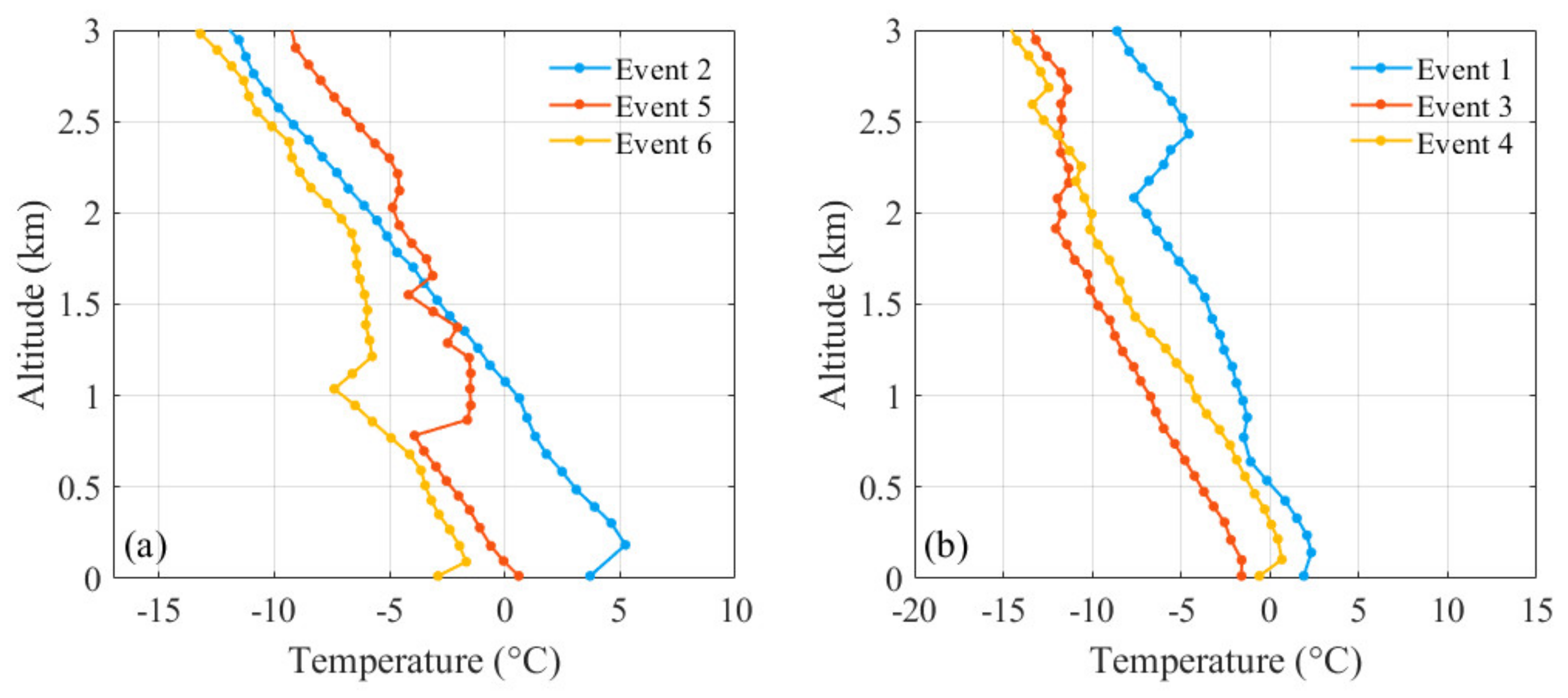
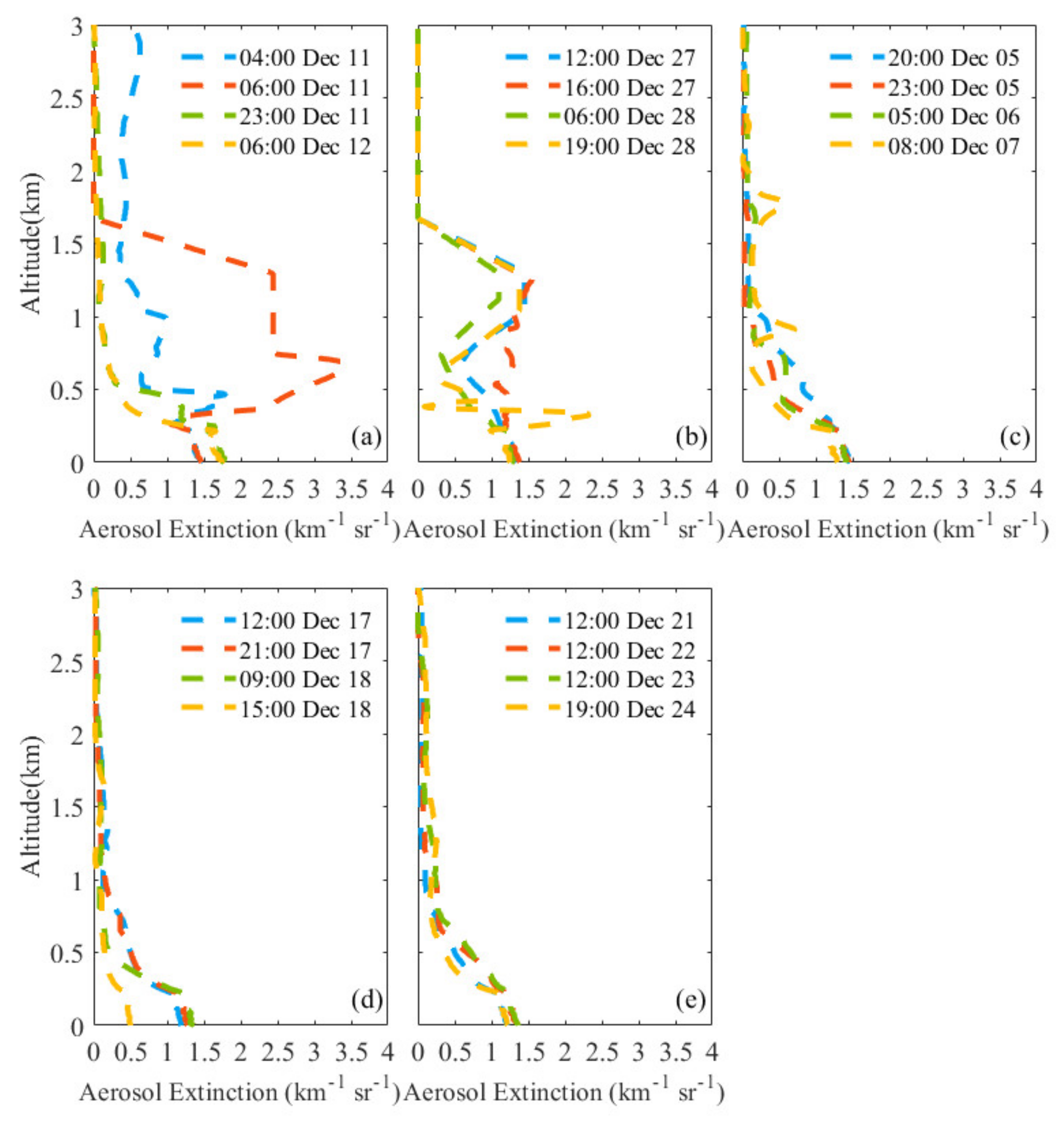
3.2. Vertical Characteristics during Haze Pollution
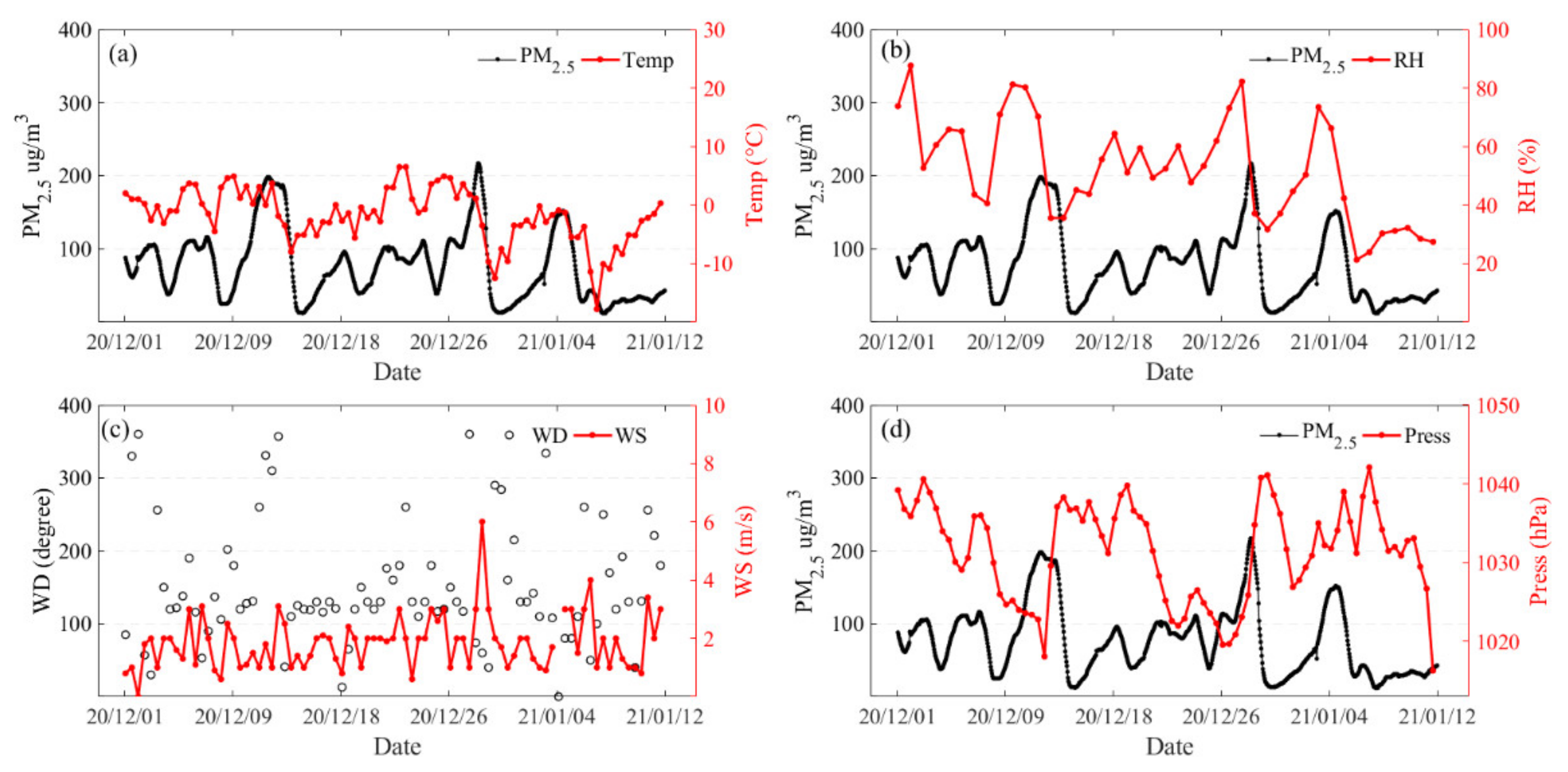
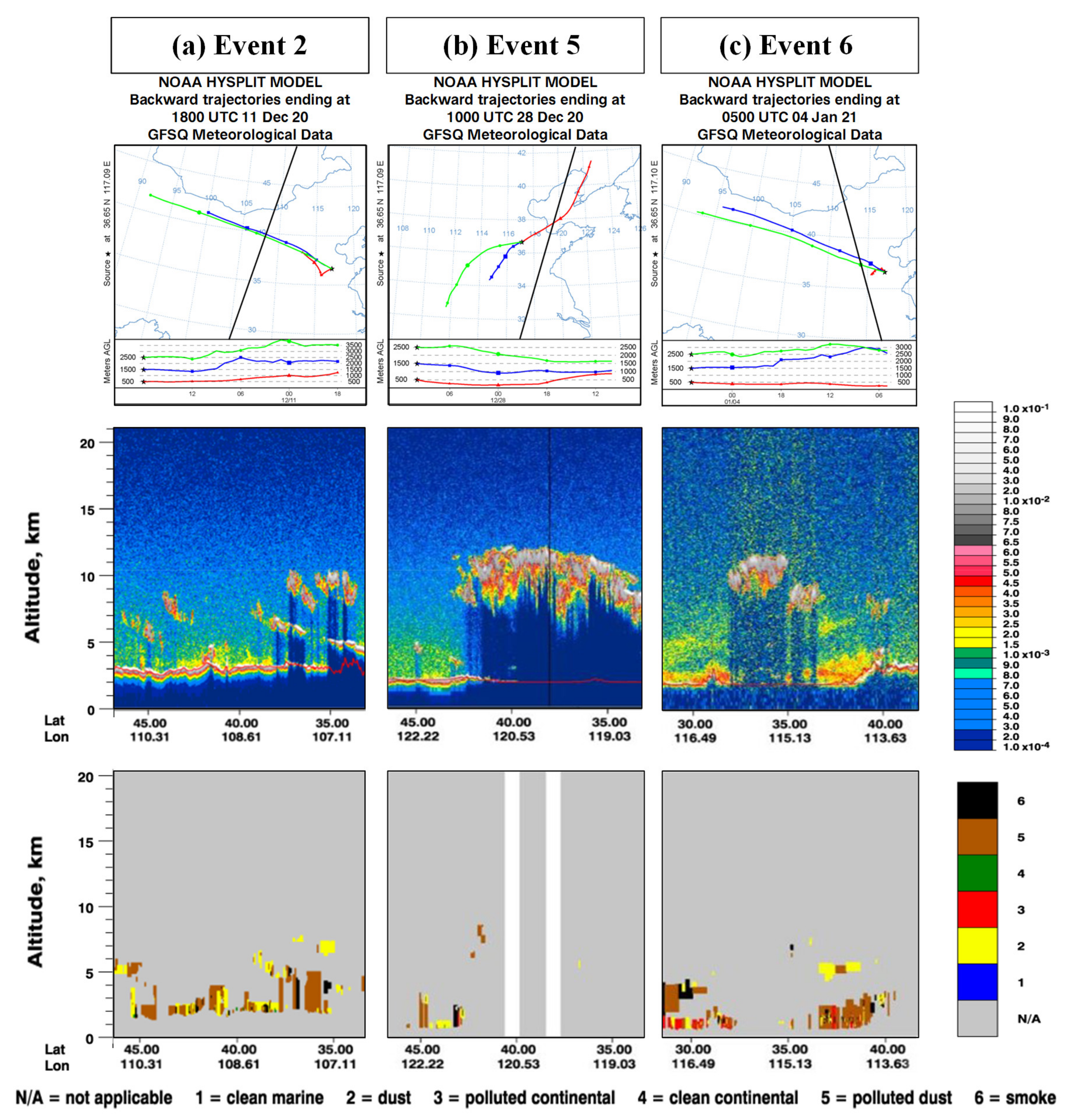
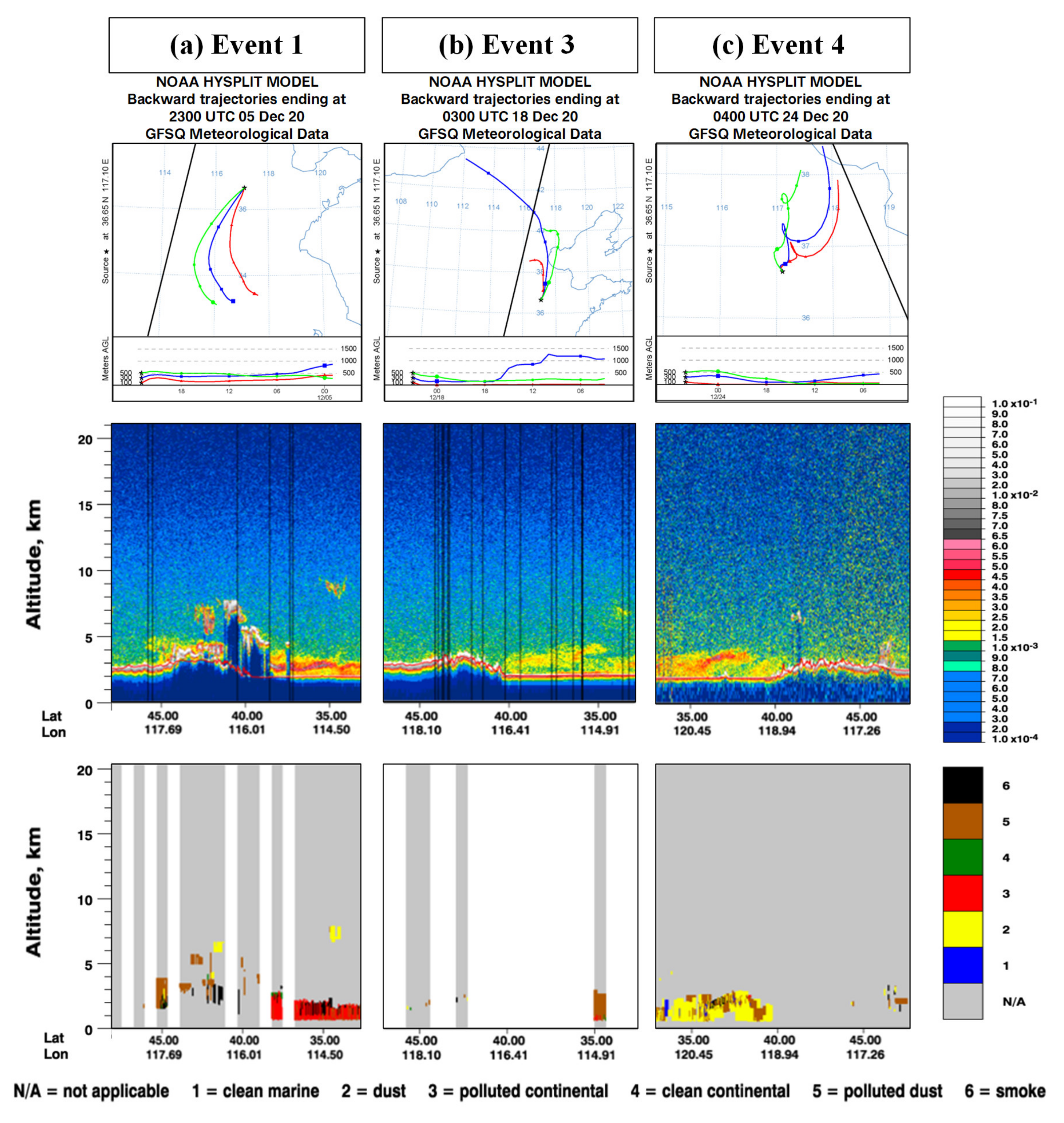
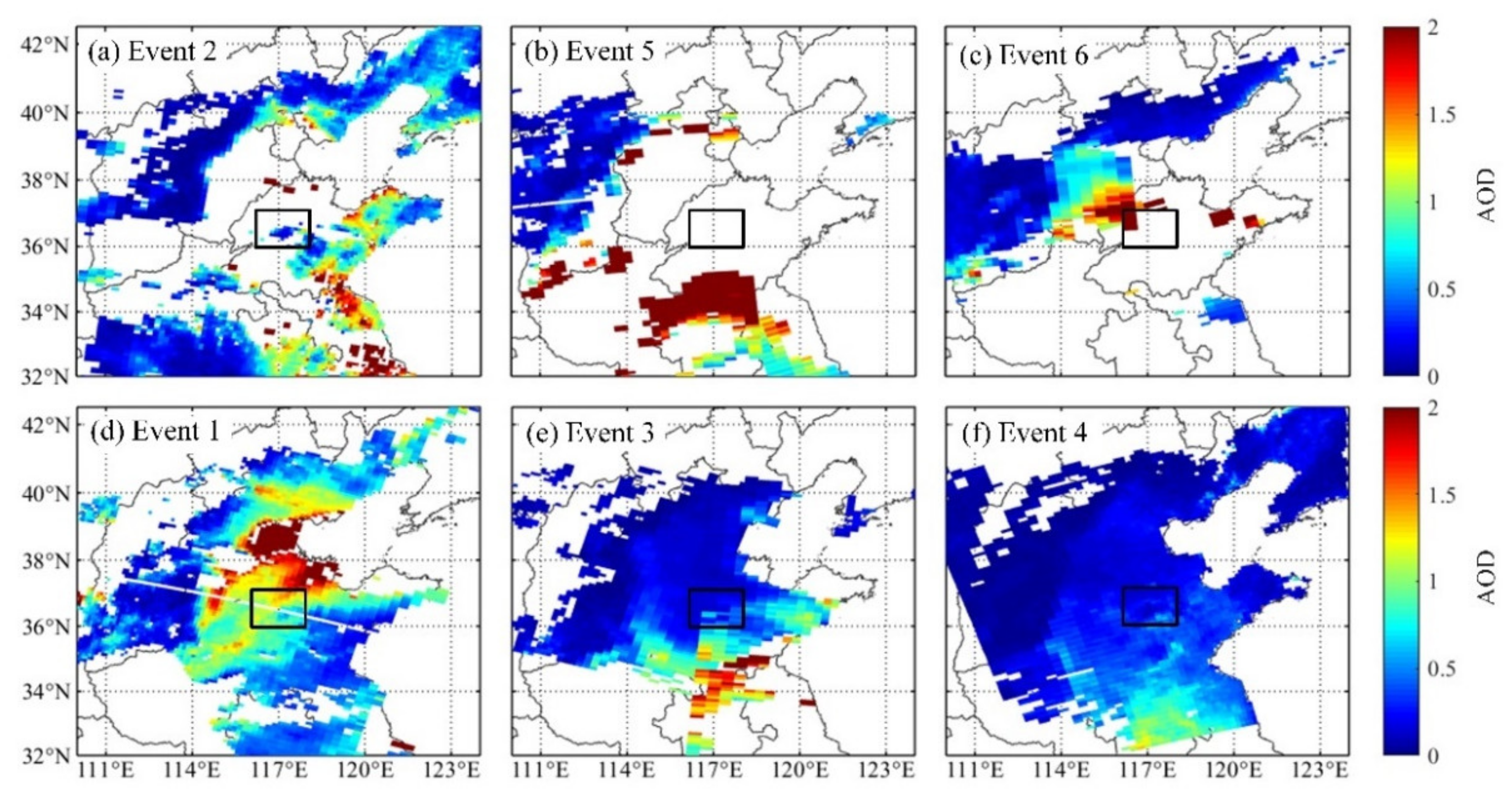
3.3. Formation Process of Haze Pollution in Jinan Area
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Z.; Wan, B.; Su, F.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Hong, Z.; Hu, F.; Cheng, S. Several characteristics of atmospheric environmental quality in China at present. Res. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; He, J.; Miao, Z.; Du, L. Space–Time Linear Mixed-Effects (STLME) model for mapping hourly fine particulate loadings in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 292, 125993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, X. The assessment of emission-source contributions to air quality by using a coupled MM5-ARPS-CMAQ modeling system: A case study in the Beijing metropolitan region, China. Environ. Model. Softw. 2007, 22, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Jia, S. A study of urban pollution and haze clouds over northern China during the dusty season based on satellite and surface observations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Ji, D.; Tang, G.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Xin, J. Mechanism for the formation of the January 2013 heavy haze pollution episode over central and eastern China. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Liu, B.; Gong, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Bai, K.; Stoffelen, A. Technical note: First comparison of wind observations from ESA’s satellite mission Aeolus and ground-based radar wind profiler network of China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2945–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Schauer, J.J.; Yu, W.; Hu, Y. Seasonal and spatial differences in source contributions to PM2. 5 in Wuhan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 577, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, R.; Hsu, N.C.; Kafatos, M.; Tsay, S.C. Influences of winter haze on fog/low cloud over the Indo-Gangetic plains. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, D05207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gautam, R.; Singh, M.K. Urban heat island over Delhi punches holes in widespread fog in the Indo—Gangetic Plains. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.; Chourey, R.; Rizvi, S.; Singh, M.; Gautam, R. An automated fog monitoring system for the Indo-Gangetic Plains based on satellite measurements. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing and Modeling of the Atmosphere, Oceans, and Interactions VI, New Delhi, India, 3 May 2016; p. 988226. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo, N.; Gil-Molto, J.; Varea, M.; Chofre, C.; Yubero, E. Seasonal and interannual trends in PM levels and associated inorganic ions in southeastern Spain. Microchem. J. 2013, 110, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Su, L.; Tao, J. Satellite observation of regional haze pollution over the North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréon, F.-M.; Tanré, D.; Generoso, S. Aerosol effect on cloud droplet size monitored from satellite. Science 2002, 295, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, T.; Chen, J. A climatology of aerosol optical depth over China from recent 10 years of MODIS remote sensing data. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Han, G.; Ma, X.; Gong, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Pei, Z.; Gou, H.; Bu, L. Quantifying CO2 uptakes over oceans using LIDAR: A tentative experiment in Bohai bay. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL091160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P.; Yang, T.; Jiang, Q.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Jia, J. Aerosol composition, sources and processes during wintertime in Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 4577–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M. Observations of aerosol color ratio and depolarization ratio over Wuhan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jin, S.; Jin, Y. Characteristics of aerosol within the nocturnal residual layer and its effects on surface PM2. 5 over China. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J. Study of continuous air pollution in winter over Wuhan based on ground-based and satellite observations. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Su, L. Satellite observation of abnormal yellow haze clouds over East China during summer agricultural burning season. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Han, S.; Yao, Q.; Cai, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Feng, J. Analysis of a Severe Regional Haze-fog-dust Episode over North China in Autumn by Using Multiple Observation Data. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Yi, F. Dust aerosols detected using a ground-based polarization lidar and CALIPSO over Wuhan (30.5 N, 114.4 E), China. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 536762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X. Weather condition dominates regional PM2. 5 pollutions in the eastern coastal provinces of China during winter. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, Y.; Che, H.; Liu, S. On the heavy aerosol pollution and its meteorological dependence in Shandong province, China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 256, 105572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-F.; Lyu, H.-M.; Shen, J.S.; Lu, L.-H.; Li, G.; Arulrajah, A. Evaluation of environmental risk due to metro system construction in Jinan, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Jin, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gong, W. Evaluation of retrieval methods for planetary boundary layer height based on radiosonde data. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2021, 14, 5977–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wang, W.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, R.; Wang, X.; Nie, W.; Gao, X. Aerosol size distributions in urban Jinan: Seasonal characteristics and variations between weekdays and weekends in a heavily polluted atmosphere. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 179, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M.; Shi, Y. The relationship between black carbon and atmospheric boundary layer height. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.M.; Yin, J. Particulate matter in the atmosphere: Which particle properties are important for its effects on health? Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, W.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Powell, K.A.; Lucker, P.L.; Weimer, C. CALIPSO lidar description and performance assessment. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Vaughan, M.; Uno, I.; Sugimoto, N.; Kittaka, C.; Trepte, C.; Wang, Z.; Hostetler, C. Airborne dust distributions over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas derived from the first year of CALIPSO lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5045–5060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.-P.; Hostetler, C.A.; Kittaka, C.; Rogers, R.R. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.; Townshend, J.; Vermote, E.; Masuoka, E.; Wolfe, R.; Saleous, N.; Roy, D.; Morisette, J. An overview of MODIS Land data processing and product status. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.-R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.; Kleidman, R. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, S.; Mao, J.; Liu, Y. Validation of MODIS and Deep Blue aerosol optical depth retrievals in an arid/semi-arid region of northwest China. Particuology 2012, 10, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, A.; Draxler, R.R.; Rolph, G.D.; Stunder, B.J.; Cohen, M.; Ngan, F. NOAA’s HYSPLIT atmospheric transport and dispersion modeling system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 2059–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HYSPLIT Trajectory Model—WEB. Available online: https://www.ready.noaa.gov/HYSPLIT.php (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Ambient Air Quality Standards. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/t20120302_224165.shtml (accessed on 29 September 2021).
- Gao, J.; Tian, H.; Cheng, K.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Wang, S.; Hao, J.; Wang, K.; Hua, S.; Zhu, C. The variation of chemical characteristics of PM2. 5 and PM10 and formation causes during two haze pollution events in urban Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 107, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindra, K.; Singh, T.; Sinha, V.; Sinha, B.; Paul, S.; Attri, S.; Mor, S. Appraisal of regional haze event and its relationship with PM2. 5 concentration, crop residue burning and meteorology in Chandigarh, India. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 128562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, P.; Xu, J.; Meng, W.; Pu, W.; Dong, F.; He, D.; Shi, Q. Analysis of a winter regional haze event and its formation mechanism in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; Han, G.; Xu, H.; Shi, T.; Zhong, W.; Gong, W. Study on Collaborative Emission Reduction in Green-House and Pollutant Gas Due to COVID-19 Lockdown in China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.; Du, L. Improving characteristic band selection in leaf biochemical property estimation considering interrelations among biochemical parameters based on the PROSPECT-D model. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 400–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, Y.; Wang, J.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Formation mechanism of continuous extreme haze episodes in the megacity Beijing, China, in January 2013. Atmos. Res. 2015, 155, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, K.; Che, H.; Chen, Q.; An, L.; Zeng, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J. Aerosol optical properties based on ground and satellite retrievals during a serious haze episode in December 2015 over Beijing. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, Y.; An, J.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Xu, W. Characteristics and formation mechanism of continuous hazes in China: A case study during the autumn of 2014 in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 8165–8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pachauri, T.; Singla, V.; Satsangi, A.; Lakhani, A.; Kumari, K.M. Characterization of major pollution events (dust, haze, and two festival events) at Agra, India. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5737–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z. Formation process of the widespread extreme haze pollution over northern China in January 2013: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M. Surface aerosol optical properties during high and low pollution periods at an urban site in central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 3035–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Xie, C.; Zhuang, P.; Tian, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. Study of persistent foggy-hazy composite pollution in winter over Huainan through ground-based and satellite measurements. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, B.; Hu, D.; Che, H.; Du, R.; Wu, Y.; Xia, X.; Zha, B.; Liu, J.; Niu, Y.; Wang, H. Seasonal variation of aerosol optical properties in an urban site of the Yangtze Delta Region of China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2884–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Che, H.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, X.; Hong, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Aerosol vertical distribution and typical air pollution episodes over northeastern China during 2016 analyzed by ground-based lidar. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 918–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Hu, Q.; Dong, Y.; Liu, H.; Xing, C.; Tan, W. Quantify the Contribution of Dust and Anthropogenic Sources to Aerosols in North China by Lidar and Validated with CALIPSO. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Liu, B.; Shi, Y.; Chen, Z. Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects: Assessment of urban aerosols in central China using 10-year observations. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 182, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, L.; Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Gui, K.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, T.; Li, X. Aerosol optical properties over an urban site in Central China determined using ground-based sun photometer measurements. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 620–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Gong, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, J.; Fu, X.; Zhang, G. Ionic composition of submicron particles (PM1. 0) during the long-lasting haze period in January 2013 in Wuhan, central China. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Tang, A.; Wang, Y.; An, Z. Chemical characteristics of PM2. 5 and PM10 in haze− fog episodes in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3148–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
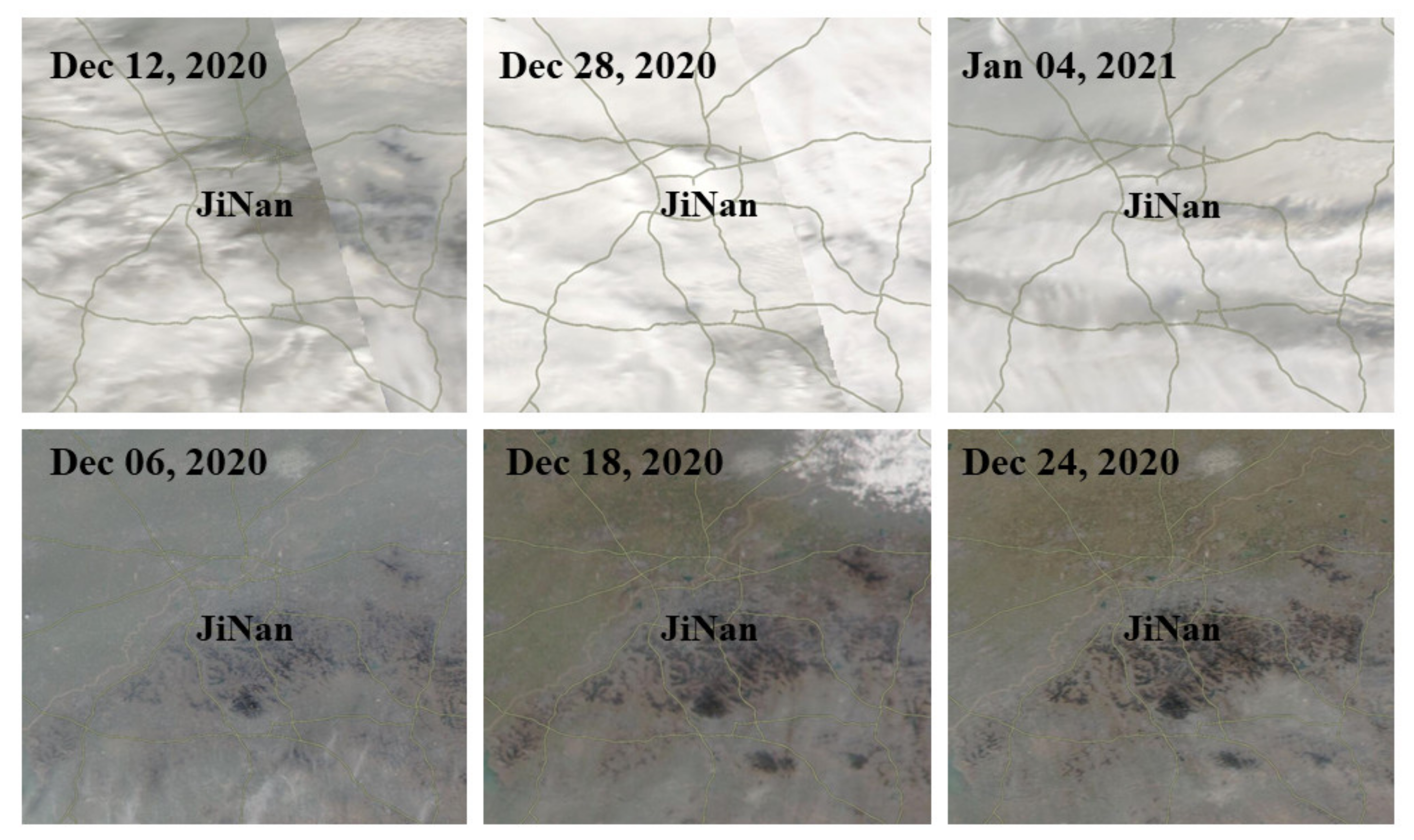

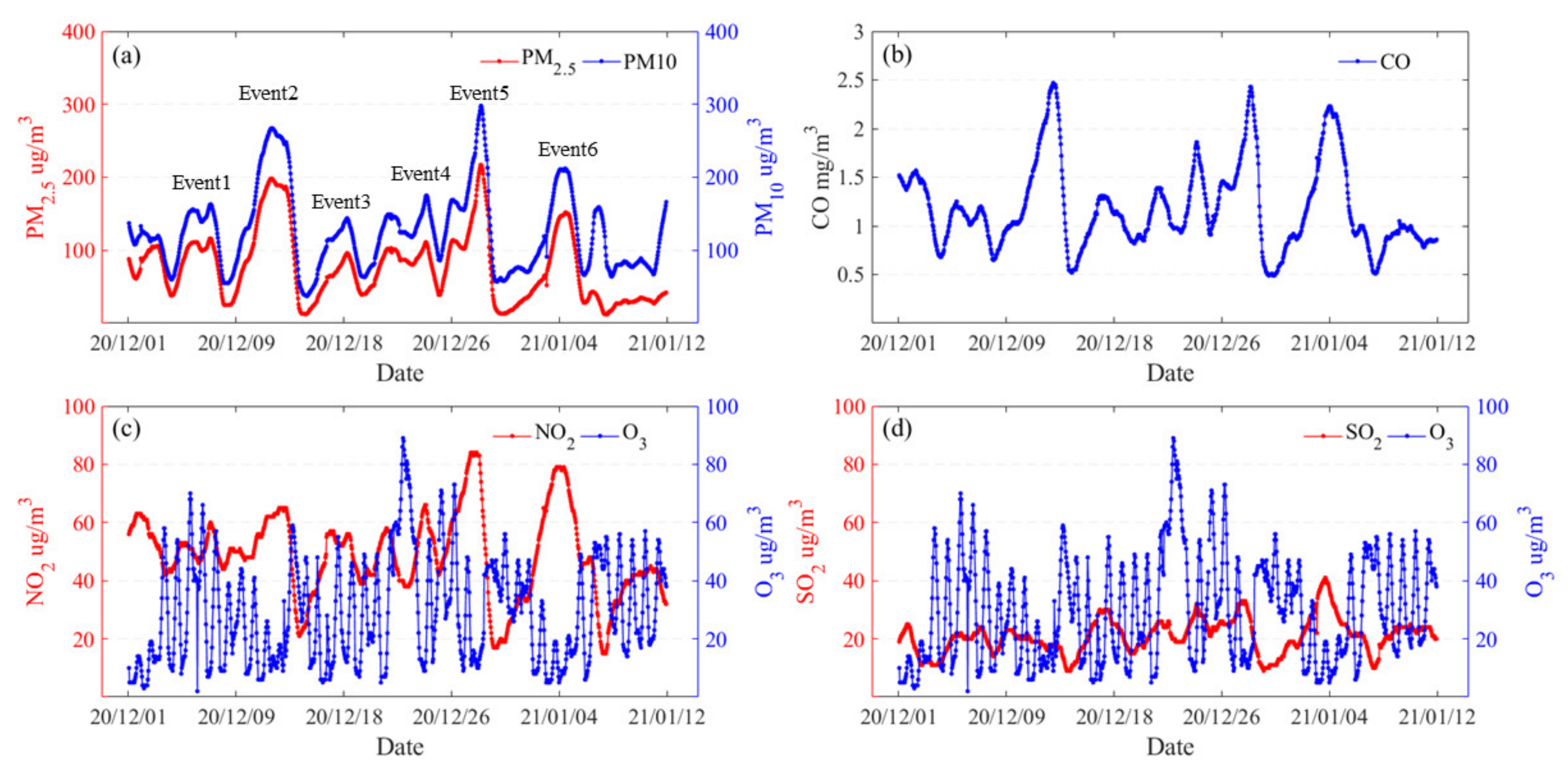
| Event Type | Event Number | Duration (LT) | Max PM2.5 (μgm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type 1 | Event 1 | 01:00 5 December 2020–21:00 7 December 2020 | 111 |
| Event 3 | 18:00 17 December 2020–21:00 18 December 2020 | 103 | |
| Event 4 | 22:00 20 December 2020–00:00 25 December 2020 | 111 | |
| Type 2 | Event 2 | 20:00 9 December 2020–21:00 13 December 2020 | 198 |
| Event 5 | 03:00 26 December 2020–15:00 29 December 2020 | 217 | |
| Event 6 | 05:00 3 January 2021–11:00 5 January 2021 | 152 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Shi, R.; Jin, S.; Wang, W.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, P.; Gong, W.; Zhao, Y. Study of Persistent Haze Pollution in Winter over Jinan (China) Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234862
Li H, Shi R, Jin S, Wang W, Fan R, Zhang Y, Liu B, Zhao P, Gong W, Zhao Y. Study of Persistent Haze Pollution in Winter over Jinan (China) Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(23):4862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234862
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hui, Rui Shi, Shikuan Jin, Weiyan Wang, Ruonan Fan, Yiqun Zhang, Boming Liu, Peitao Zhao, Wei Gong, and Yuefeng Zhao. 2021. "Study of Persistent Haze Pollution in Winter over Jinan (China) Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations" Remote Sensing 13, no. 23: 4862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234862
APA StyleLi, H., Shi, R., Jin, S., Wang, W., Fan, R., Zhang, Y., Liu, B., Zhao, P., Gong, W., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Study of Persistent Haze Pollution in Winter over Jinan (China) Based on Ground-Based and Satellite Observations. Remote Sensing, 13(23), 4862. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13234862








