Abstract
Subtidal natural hard substrates (SNHS) promote occupancy by rich benthic communities that provide irreplaceable and fundamental ecosystem functions, representing a global priority target for nature conservation and recognised in most European environmental legislation. However, scientifically validated methodologies for their quantitative spatial demarcation, including information on species occupancy and fine-scale environmental drivers (e.g., the effect of stone size on colonisation) are rare. This is, however, crucial information for sound ecological management. In this investigation, high-resolution (1 m) multibeam echosounder (MBES) depth and backscatter data and derivates, underwater imagery (UI) by video drop-frame, and grab sediment samples, all acquired within 32 km2 of seafloor in offshore Belgian waters, were integrated to produce a random forest (RF) spatial model, predicting the continuous distribution of the seafloor areal cover/m2 of the stones’ grain sizes promoting colonisation by sessile epilithic organisms. A semi-automated UI acquisition, processing, and analytical workflow was set up to quantitatively study the colonisation proportion of different grain sizes, identifying the colonisation potential to begin at stones with grain sizes Ø ≥ 2 cm. This parameter (i.e., % areal cover of stones Ø ≥ 2 cm/m2) was selected as the response variable for spatial predictive modelling. The model output is presented along with a protocol of error and uncertainty estimation. RF is confirmed as an accurate, versatile, and transferable mapping methodology, applicable to area-wide mapping of SNHS. UI is confirmed as an essential aid to acoustic seafloor classification, providing spatially representative numerical observations needed to carry out quantitative seafloor modelling of ecologically relevant parameters. This contribution sheds innovative insights into the ecologically relevant delineation of subtidal natural reef habitat, exploiting state-of-the-art underwater remote sensing and acoustic seafloor classification approaches.
1. Introduction
Subtidal natural hard substrates (SNHS), whether of geogenic or biogenic origin, represent an important ecological habitat and cover essential functions in marine ecosystems [1], making them a worldwide priority target for environmental management, conservation, and restoration. Structural complexity at various scales enhances bentho-pelagic coupling, and subsequently, the associated ecological succession phases by acting as settling, shelter, feeding, and nursery grounds for a variety of marine organisms at multiple trophic levels [1,2]. In an anthropogenically threatened and rapidly changing marine environment [3,4], the heterogeneous and scattered distribution of SNHS represents keystone patches that promote larvae dispersal and colonisation by epibenthic organisms, giving rise to subtidal natural reef habitats (e.g., “stony reefs”, see [5]). SNHS-associated biological communities are regarded as particularly rich (in terms of diversity, biomass, and species rarity) yet fragile environments, with low resistance and resilience to anthropogenic disturbance. As a result of historical and modern anthropogenic pressures, mainly those that directly physically affect the seafloor, these underwater environments are deemed significantly depauperated to the point of being deemed extinct, and/or at the brink of extinction (e.g., in the North Sea region, [4,6,7,8,9]). While all European legislation, e.g., [10,11] and policy-related documents [5,12] mention SNHS and associated biological communities in some way, scientifically validated methodologies for the quantitative and ecologically relevant spatial demarcation of SNHS habitats are rare. Revolutionising seafloor cartography and the production of detailed benthic habitat maps (BHM) [13], acoustic seafloor classification (ASC) [14,15,16] is a highly multidisciplinary branch of marine sciences that focuses on accurate and objective predictions of seafloor surficial material properties. ASC, compared to terrestrial land-cover-land-use mapping, is based on multiple and concurrently developing technologies and data-integration approaches, today achieved by: (1) seafloor mapping by hydroacoustic remote sensing; (2) ground truthing by grab, core, and underwater imaging (UI) sampling; and (3) predictive modelling using spatial prediction algorithms.
Seafloor mapping by hydroacoustic remote sensing enables acquisition of continuous and high-resolution (metric/decametric resolution for shallow-water high-frequency systems) seafloor topographic and textural information (see [17] for a review). Owing to their specific design, multibeam echosounder (MBES) systems drastically promoted the development of ASC, enabling the co-registration of coincident seafloor measurements of bathymetry (i.e., equivalent to topography) and backscatter strength (BS), recognised as a unique physical proxy of the seafloor nature and texture [18,19,20]. Supplementing the spatial mapping by hydroacoustic data, point-based measurements acquired in the form of traditional sampling instruments such as cores and/or grabs are used to ground truth (i.e., confirm/validate) the seafloor’s composition as hypothesised/inferred from the hydroacoustic observations. Nonetheless, due to a number of practical reasons (e.g., cost, time, and labour) traditional sampling techniques generally produce a too sparse sampling effort (i.e., distance between sampled points) as well as being limited to a very limited portion of the seafloor surface (typically ~0.25 m2), preventing a sound correlative analysis with the high-resolution measurements achieved by hydroacoustic sensors. Moreover, for the specific case of studying fragile SNHS habitats, traditional sampling proves to be highly destructive, conflicting with environmental conservation efforts [21]. More recently, the advent of underwater imaging (UI; i.e., underwater photography using benthic sledges and drop-down video frames; see, e.g., [22,23,24,25,26]) is providing the means to fill the investigation gap between hydroacoustic and ground truth data resolutions [27]; i.e., the spatial coverage is considerably higher, revealing the heterogeneous spatial distribution of SNHS at meter scale, as well as providing the means to sample SNHS habitat in a minimally invasive manner. Finally, predictive modelling algorithms (e.g., machine learning, clustering) are dedicated to data integration and map-making [16,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. In particular, decision-tree-based machine learning algorithms (e.g., random forest; [34]) have gained widespread popularity in the habitat mapping realm, e.g., [27,35,36,37] due to their ability to integrate the information from disparate and large datasets, detecting complex relationships between the predictor (explanatory hydroacoustic and/or modelled spatial variables) variables and the targeted response (ground truth observations) variable, without relying on any a priori assumptions about the kind of relation, nor their underlying value distributions.
This investigation is based on these recent technological and analytical advances and aims to present a data-analysis workflow interlinking high-resolution UI and MBES using a machine learning predictive modelling approach, specifically setting up a quantitative mapping methodology for SNHS habitat. Besides the innovative use of machine learning for continuous (i.e., numerical) data prediction, a key character of this habitat mapping investigation is the exploitation of the UI in favour of a quantitative (i.e., continuous; numerical) as well as ecologically informed formulation of the criterion used to spatially delineate the targeted habitat.
Study Site
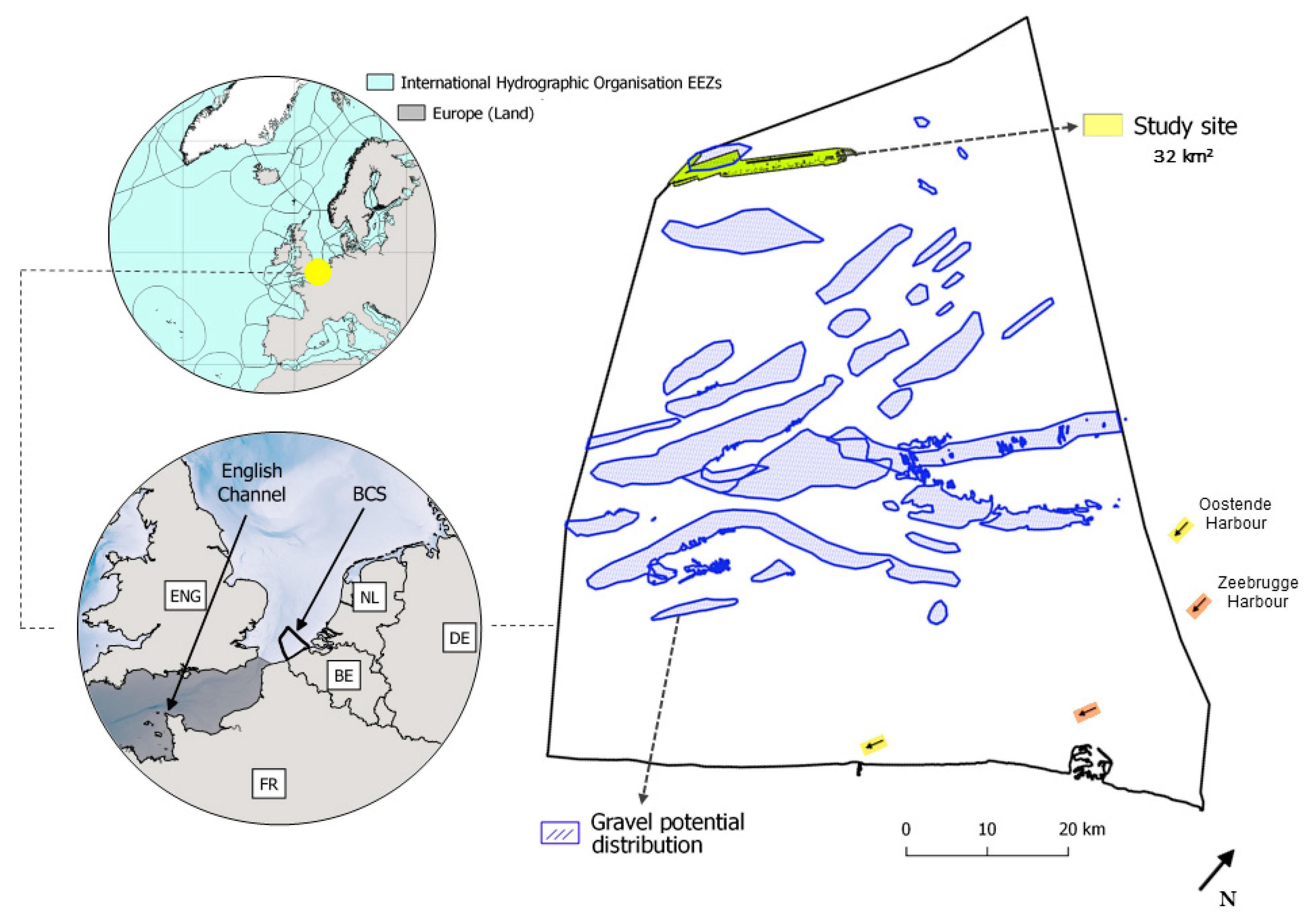
In Belgian waters, the existence of SNHS is relatively well documented, both historically ([38] and references therein) and recently. Currently, maps of potential SNHS distribution, based on a combination of geological, geophysical, sedimentological, and visual observations, have been produced [39,40,41]. As exemplified by the “gravel bed potential distribution” map (Figure 1), ~16% of the Belgian seafloor relates to variable [42] SNHS, with a potential of stone occurrences. However, the spatial resolution of such maps remains too coarse for adequate ecological management of SNHS communities, requiring the accurate pinpointing of spatial units down to the level of meso- to fine-scale patches [43,44] and/or single stones [24]. With the advent of high-resolution seafloor mapping technologies and advanced seafloor modelling approaches [16], high-resolution research can now also be addressed towards the regional scale benefitting environmental monitoring obligations. In this scenario, the Belgian continental shelf (BCS) serves as an excellent case study to select a study area overlapping with the potential distribution map and test advancing ASC-based BHM methodologies. The study site is located beyond the 24 nautical miles, in offshore waters, at the northwesternmost delimitation of the BCS (Figure 1) and covers ~32 km2 of MBES and ground truth survey area (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Here, water depth range is 37–43 mLAT and is influenced by a semi-diurnal tidal regime, with mean ranges of ~4.3 mLAT and ~2.8 mLAT during spring and neap tides, respectively (referenced in Zeebrugge [45]). The tidal ellipse is mainly oriented in SW-NE direction, and the residual current transport is mainly oriented towards the NE [46]. The water mass is well mixed year-round with salinity values around 34 practical salinity units [47], and with a relatively clear water mass characterised by sediment transport estimated at <0.5 tonnes/m per day [48]. During spring tide, peak surface and bottom current velocities can exceed 1 m/s and 0.7 m/s, respectively [48]. In this region, the maximum significant offshore wave height can reach >4 m [49].
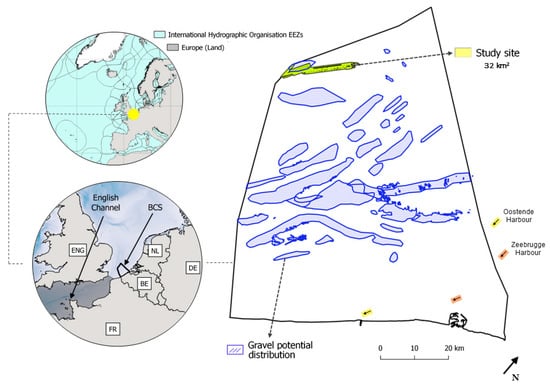
Figure 1.
Geographical setting (left; circular maps) of the BCS (right; geographically tilted, see north arrow) displaying the gravel potential distribution map [39] and the surveyed study area. Universal Transverse Mercator Zone 31 North, World Geodetic System 84 (UTM 31N, WGS84).
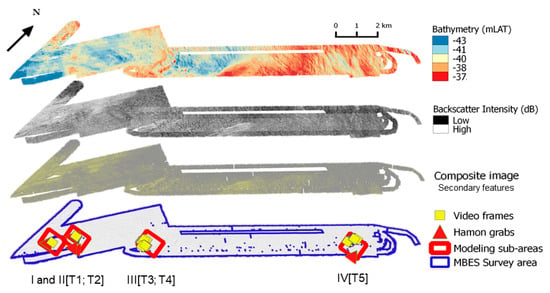
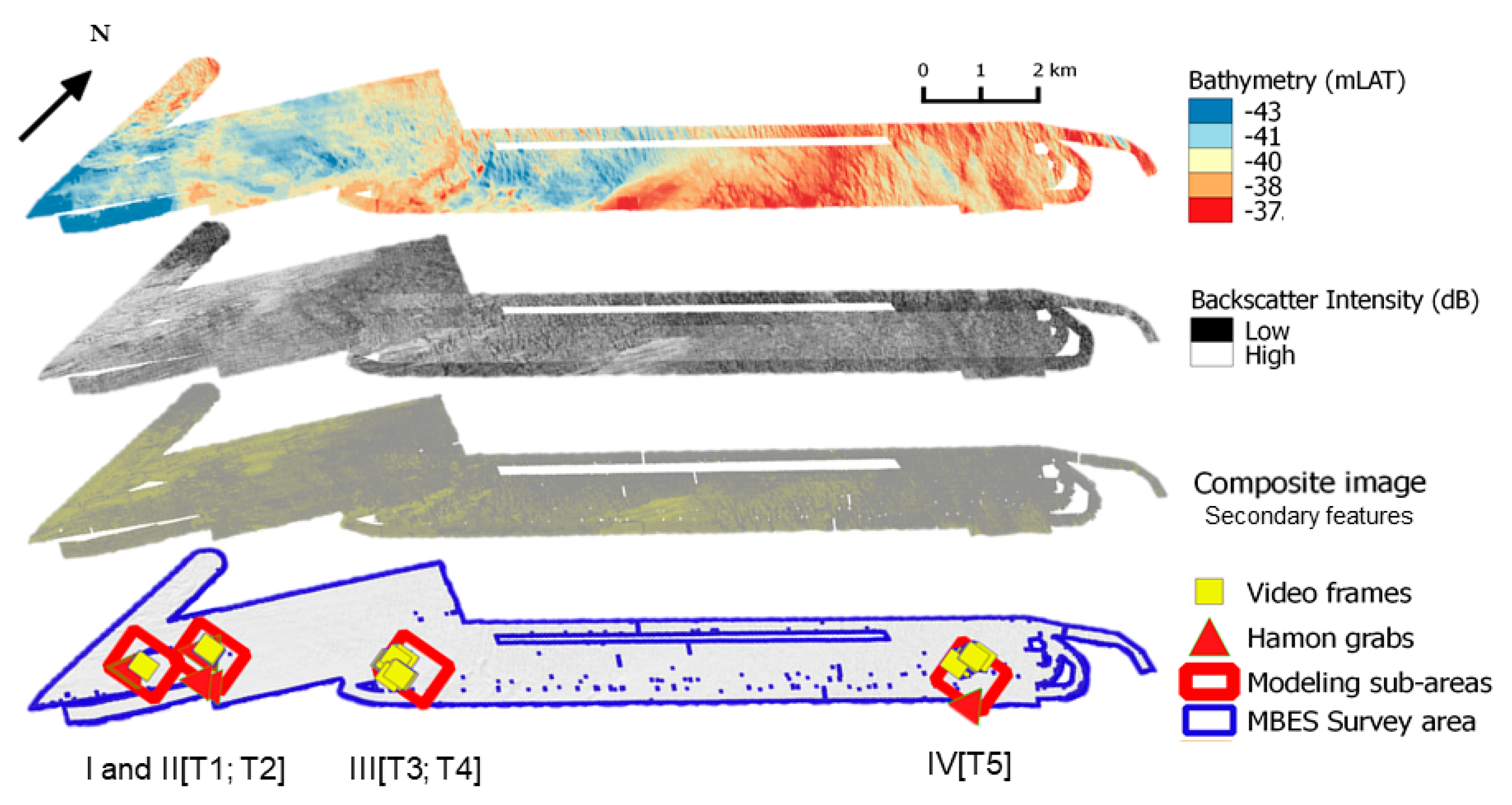
Figure 2.
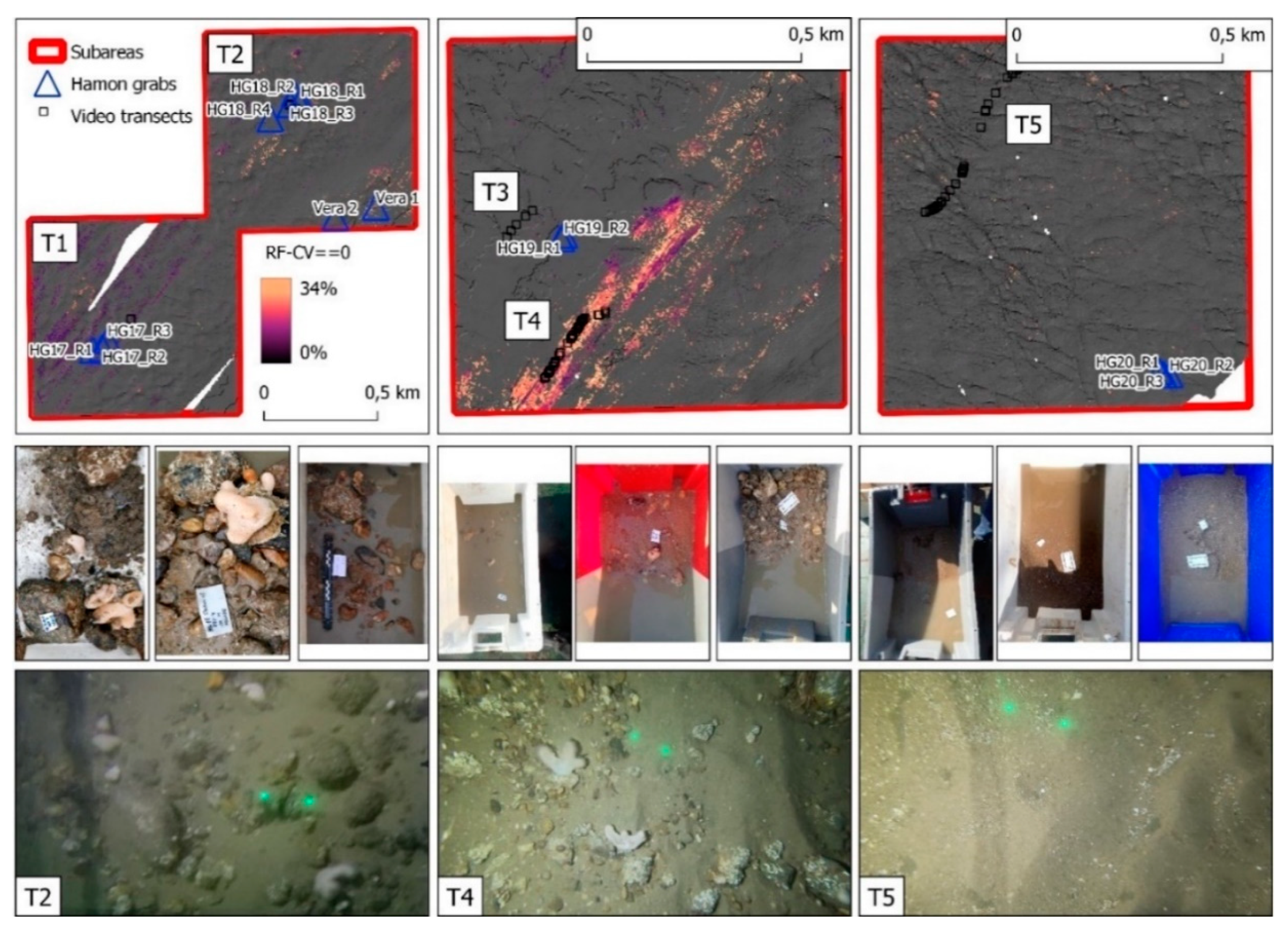
Overview of the MBES and ground truth surveys. Top to bottom: MBES bathymetry; compensated backscatter imagery; composite image of secondary features derived from the MBES primary data (see after, section “Spatial modelling by RF”); survey extent with ground truth locations and areas of interest selected for modelling. Areas of interest selected for modelling (Roman characters) and corresponding video transects (e.g., T1) are labelled accordingly in Figure 5 (see “Results” section).
In this study, the term “stones” (also referred to as “lag deposit” and “subtidal natural hard substrate” or SNHS throughout the manuscript) is in alignment with the research conducted by Michaelis and co-workers [24,25], based on the international standard ISO14688-1:2017 [50] and it is defined as solid geogenic material with a diameter larger than 2 cm. This grain size classification system was preferred over, e.g., the Wentworth [51] scale as it distinguishes between boulders and large boulders. The specific terms refer to: “coarse gravel” (Ø 2–6 cm), hereafter referred to as “gravel”, “cobble” (Ø 6–20 cm), “boulder” (Ø 20–63 cm), and “large boulder” (Ø > 63 cm). The grain size class “fine gravel” (Ø < 2 cm) was added to this standard, enhancing the grain size discrimination potential. This standard was used to derive a quantitative estimation of stone sizes from the underwater imagery.
2. Materials and Methods
Multibeam hydroacoustic surveys and ground truth data: multibeam hydroacoustic and ground truth surveys were conducted with RV A9602 Belgica during 2018 and 2019 (Table 1). Bathymetry and backscatter data were logged using a hull-mounted Kongsberg (https://www.kongsberg.com/maritime/) EM3002 Dual System operating at a nominal frequency of 300 kHz (Table 1). The echosounder emits 508 soundings per ping cycle. Transmit and receive units produce small (Tx and Rx) beams with widths of 1.5° × 1.5°. The Rx beam spacing was set in high-density equidistant geometry, and sound emitted at pulse length of 150 µs in MBES normal mode. The quality of a part of the bathymetry acquired during campaign 2018-17 was suboptimal due to a poor real-time kinetic (RTK) positioning signal and post hoc tidal-level corrections were needed. Low quality in bathymetry implies poor geometric corrections of backscatter data; [52,53] for details. Furthermore, artefacts represent a severe source of error in image analysis and predictive modelling [54,55]. Due to this, bathymetry data acquired and processed by the Agency for Maritime Services and Coast, Coastal Division, Flemish Hydrography, and acquired by a Kongsberg EM3002 dual system installed on HV Ter Streep during 2013 (Table 1), were used instead to substitute a small portion of the study area. All other surveys benefitted from RTK tidal corrections. Specific details of the MBES backscatter data processing software and pipelines can be found in [56] and [57], chapter 3. Standardised procedures were followed for backscatter data acquisition and processing, including implementing an operational routine to ensure the echosounder measurements’ stability (or drift, see [19,57,58]), enabling merging backscatter data acquired at different moments in time, hence enabling efficient image analysis, e.g., [59,60,61,62]. The backscatter processing nomenclature proposed by [20] was used, and the backscatter product used in this investigation refers to fully compensated backscatter imagery (CBI), with code: “A4 B0 C0 D0 E5 F0”. For further analysis, the MBES data were gridded into raster format (floating point 32-bit) files with a 1 m horizontal resolution.

Table 1.
Timeframe ID of the oceanographic campaigns, geophysical data type, ground truth data, and number of selected frames used for further analysis. RV = research vessel; MBES = multibeam echosounder (seafloor depth and backscatter); GT = ground truth; HG = Hamon grab; UV = underwater video; n.a. = not applicable; Rep. = replicate sample. Link to oceanographic campaign reports and course of actions available at RV Belgica web site: https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/belgica/en/(re: campaign ID).
Underwater imagery acquisition, processing, and analysis. Underwater imagery (UI) was acquired by means of a video drop-frame system; a robust steel metal, winch-operated frame (http://www.vliz.be/en/videoframe-en) equipped with a medium-resolution ROS inspector colour camera (https://www.rosys.com/), linked to a MacArtney (www.macartney.com) multimedia controller unit (pan, tilt, zoom), and set up to acquire a 1 m2 optical field of view. In this investigation, the latter camera system provided only a video live feed solution during the data acquisition phase. The UI used in this study was acquired by means of a GoPro 5 video camera (GoPro, Inc., San Mateo, CA, USA—https://gopro.com/) installed on the metal frame, downward looking (i.e., orthogonally to the seafloor ideal plane), at a height of ~75 cm from the bottom, achieving on average a field of view of ~0.47 m2 (about half the footprint size of the gridded MBES data). The GoPro camera was operated in FOV-linear mode, acquiring 60 frames per second (FPS), with a resolution of 1920 × 1440 pixels. GoPro’s focal length measures 16.5 mm. Using these settings, the underwater imagery acquired by the GoPro camera is able to resolve sub-centimetre objects. Two HUGYFOT (https://www.hugyfot.com/) Arius 1500 lumen underwater lights were installed on the frame and mounted orthogonally to the seafloor, reducing backscattering of light from the seston, otherwise reducing image quality. Two green laser pointers were also installed on the frame to provide a metric reference scale (10 cm apart). Positions were corrected for antenna layback adjusted to the cable breakpoint on the winch’s frame. Positional uncertainty of the drop-camera system was minimised by acquiring data exclusively during slack-water windows when the current velocity reaches <0.5 knot and by ensuring minimal slack of the cable. During the acquisition of videos, the frame was kept as close as possible to the bottom (i.e., ≤ 1 m, achievable by controlling the altitude from the on-board monitor control unit). To improve the quality of the videos (and subsequently extracted frames), where possible, the frame was often lowered onto the ground and left recording for several seconds.
A total of five video transects were acquired during the two oceanographic campaigns. Positioning was achieved by coupling the image timestamp to the vessel position provided by the On-Board Data Acquisition System (ODAS—https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/belgica/en/odas), with a chosen acquisition rate of 1 s to have a more precise logging of the heading and geographical coordinates. For each video transect, frames were extracted every 10 s using VLC media player, resulting in a UI sample (still frame) of the seafloor every ~2.5 m of drift/navigation. A total of 426 still frames were extracted from the five videos. From this initial set, blurred scenes (i.e., due to sediment plumes upon landing and/or a too high concentration of seston) and/or scenes that did not relate to the seafloor (i.e., down- and up-casting phases) were removed from the dataset, reducing it to n = 265 seafloor observations measuring on average 0.64 m2 (median = 0.57 m2) and exploitable for the extraction of quantitative parameters, as summarised and illustrated by Table 2 and Figure 3. Still frames were further processed using software ImageJ. Image contrast and illumination were manually enhanced. The pixel-to-cm scale was set against the laser pointers (10 cm apart), calibrating the images in terms of metric scale, and enabling further data analysis.

Table 2.
Investigated parameters form the dataset of calibrated underwater still frames obtained from underwater videos. Interpretation; ◊ = colonised/uncolonised. * = not explicitly used in this investigation. Count and areal measurements were standardised to an identical sample size of 1 m2.
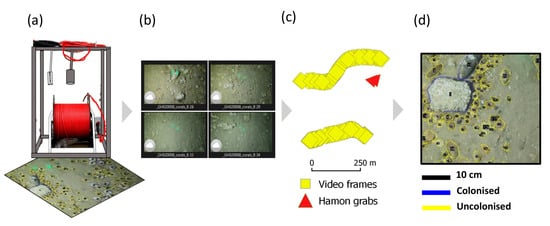
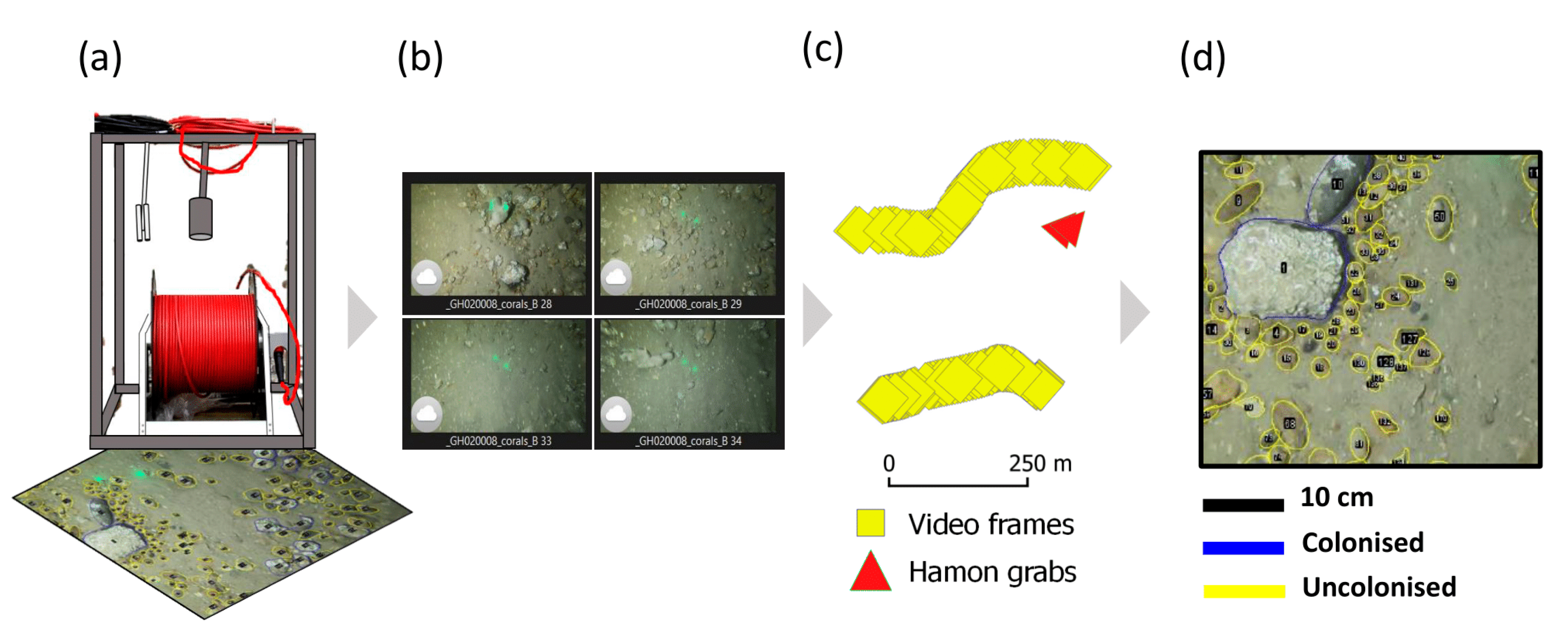
Figure 3.
Schematic overview of the key UI acquisition and processing steps. (a) Video frame gear. (b) Video segmentation, selection of still frames; and (c) georeferencing (displayed in a geographical information system (GIS) as point locations along a transect). (d) Extraction of numerical parameters from still frames; a detail (to scale) is shown wherein stones ROIs are digitised and labelled as colonised/uncolonised, allowing the derivation of Ø and the surface area of each individual ROI for each still frame.
Based on the calibrated still frames, an image-annotation protocol was set up to extract numerical parameters in order to: (A) study geo-bio relations, i.e., identify the grain size fraction of interest with respect to colonisation by epilithic organisms; and (B) test RF for regression to model the distribution of the percentage cover of the identified grain size fraction of interest over broader spatial scales. To address point A, calibrated images displaying stones (n = 149) were treated in ImageJ, whereas the remaining images, with no visible stones, were assigned a value of 0%. A semi-automated routine fitting elliptic and circular patterns, referred to as regions of interest (ROIs), was set up to circumscribe the visible stones in the still images. By doing so, the Feret (or calliper) diameter (Ø) of each stone could be extracted, thus related to a grain size class (as specified in the “Study site” section). Furthermore, stones’ ROIs were labelled as colonised and/or uncolonised. This selection criterion was based on the presence of at least one visible colony or individual specimen of epilithic organisms colonising the visible stone surface (e.g., Alcyonium digitatum, Alcyonidium diaphanum, Spirobranchus triqueter, Metridium senile, Flustra foliacea, Nemertesia sp.). This information was used to compute estimates of proportion of stone colonisation per grain size class and by video transect location. The ecological information obtained from point A is in turn tabulated along the X and Y coordinates of the ground truth dataset and used to address point B, with predictive spatial modelling by RF for regression.
Spatial modelling strategy. In this investigation, UI is exploited to define a quantitative and ecologically relevant target response for predictive modelling, thereby ecologically meaningfully delineating SNHS habitat in the predicted maps. The modelled target response relates to the surface area of geogenic features (i.e., stones) where biological colonisation by epilithic species occurs. To that end, the standardised prospective-mapping workflow, based on UI and MBES spatial data, is set up to: (1) numerically study the biological colonisation proportion of different stone sizes (in respect to visible epilithic species); hence, to identify the grain sizes diameter (Ø) where the colonisation potential begins. Consequently, the workflow is set up to: (2) exploit the numerical information achieved by UI (i.e., the % seafloor cover of these grain sizes/m2) for spatial predictive modelling using a state-of-the-art machine learning approach.
Spatial modelling by RF. RF (Breiman, 2001a and details therein) is a machine learning algorithm based on the fundamental unit of machine learning: the decision tree. The algorithm was chosen due to its widespread success in computer [63] and marine sciences applications, specifically relating to advanced ASC, e.g., [16,27,32,64,65]. Furthermore, the algorithm can be used to model continuous (i.e., numerical data), satisfying the map-making requirements of the habitat mapping methodology being tested in this investigation. RF modelling was implemented in R using part of the ModelMap package module [66] and user custom-made code snippets. The habitat-mapping methodology was tested on a spatial sub-selection of the surveyed study area (32 km2), hence four 1 × 1 km squared areas, surrounding the underwater imagery and Hamon grab sample locations (Figure 2). Within these locations, the modelling pipeline is composed of three steps: (1) feature derivation and selection; (2) model tuning; and (3) accuracy and uncertainty assessment. The aim of the statistical modelling is to produce a map displaying the distribution of the grain size fraction of interest with respect to colonisation by epilithic fauna. As such, the overall percentage cover of the identified grain size fractions of interest (i.e., % relativised to surface area) was selected as the response variable to be modelled over the MBES spatial data.
Feature derivation and selection. A set of geomorphometric, statistical, and textural secondary features was computed from the MBES primary data. From the CBI, statistical (mean, max. min. mode, median, and standard deviation) and textural (Sobel–Feldman filters for intensity, direction, and edge R package SpatialEco, [67], grey level co-occurrence matrix homogeneity index R package GLCM [68], and Moran’s I autocorrelation R package raster [69]) were derived, whereas from the bathymetry, rugosity and slope were computed. Overall, n = 15 secondary features were derived, using a 3 × 3-pixel neighbourhood window. The importance of multiscale analysis in predictive models is recognised [70], though only the smallest possible scale of derivation (i.e., window of 3 × 3) was used to ensure maximal exploitation of the high-resolution data. Secondary features were chosen based on their expected influence on the target response and on their reported importance in previous research [16]. A feature selection routine was applied to reduce the initial dataset to a set of relevant features only. The RF Boruta [71] wrapper function was used, including all features, even those that were highly correlated with a Spearman rank coefficient of 0.96 (as from correlations analysis, not shown here, and as from previous RF research [63]).
Model tuning: The RF algorithm has few parameters that require tuning and has been reported to be generally insensitive to alterations of the default values [34]. Recent applications of RF in marine sciences however indicated the importance of tuning two hyperparameters: (1) the number of decision trees grown in the forest (i.e., ntree = 500); and (2) the number of predictors used at the splits during the tree-building process (mtry). The ModelMap package [66] automatically accounts for this potential bias and select the optima with respect to the out-of-bag (OOB) error estimate (in mean squared residual—MSR). In terms of training data, 30% was withheld for validation, and training sample selection (n = 186) was randomly stratified per bins of 10%, balancing test and training sample sets.
Model accuracy was evaluated against a set of withheld samples (30%, n = 79). The following accuracy metrics were computed between observed and predicted values: mean absolute error (MAE), mean squared error (MSE), root mean squared error (RMSE), Pearson correlation coefficient (p), and Spearman correlation coefficient (ρ). Both MAE and RMSE are measured in the same units as the response variable. R2 and descriptive statistics (i.e., quantiles) are additionally used to assess model performance. Moreover, model uncertainty was accounted for by computing the coefficient of variation (CV). Being composed of several decision trees, the model’s CV can be obtained by dividing the standard deviation of the predictions for each pixel by their respective predicted mean value. This spatial information was used to mask the RF model output, displaying the predictions for the pixels with an equivalent CV pixel equal to 0 (i.e., the lowest uncertainty). Further corroborating the evaluation of model accuracy, a set of Hamon grab samples (see Table 1) were used to qualitatively validate model predictions. This source of ground truth data could only be used qualitatively, validating the model predictions in a binary sense (i.e., presence/absence of stones), given the incomparability of estimates of percentages of stone cover between underwater imagery and grab samples, as well as the lack of coincident video and Hamon grab sample locations that would allow quantitative comparison. Finally, RF importance metrics (from Boruta) and partial dependence plots were used to study how selected important features influenced the prediction of the target response.
3. Results
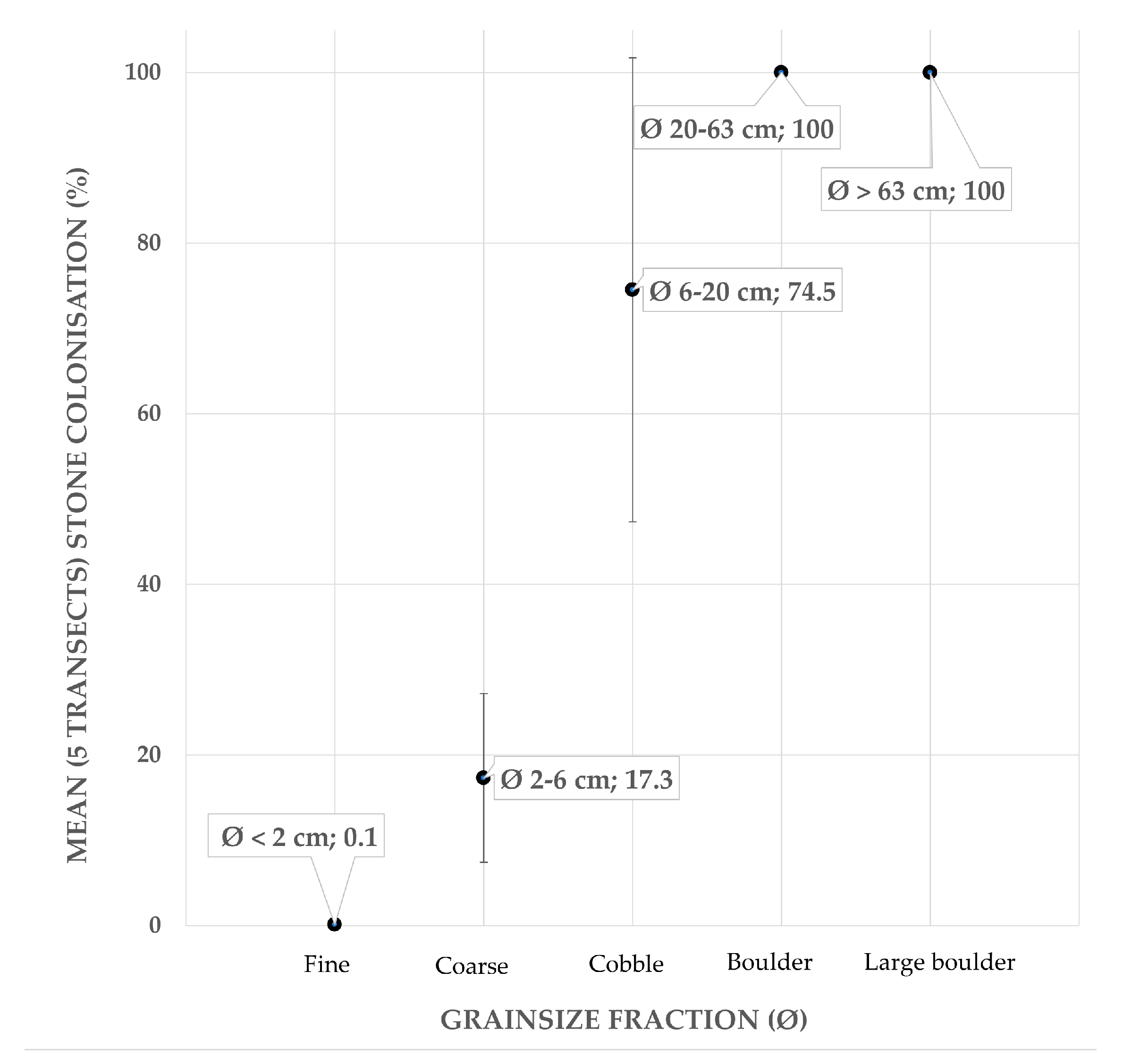
Bio-Geo relations from underwater imagery. Overall, the number of delineated stones (NDS) in the UI dataset accounts for n = 9639 stones. Except for the fine gravel (NDS = 2110) that was consistently uncolonised by epilithic fauna across the five video transects, the proportions of colonised coarse gravel (NDS = 5986), cobbles (NDS = 1492), boulders (NDS = 49), and large boulders (NDS = 2) significantly differed ( statistics; degrees of freedom (D.F.) = 4; fine gravel ; coarse gravel 22,565; cobble 39.716; boulder ; very large boulder ). Across the five transects, the proportion of colonisation ranges varies considerably across grain size classes. Besides fine gravel (i.e., 0%), colonisation of coarse gravel is considerable, ranging between 5.4 and 27.7%. Cobbles are colonised in the range 34.5–98.8%, whereas boulders and large boulders, if present, are consistently colonised (0–100%). The relationship between the average (across five video transects) proportion of colonisation with increasing stone size is reported in Figure 4. Following these observations, it was decided that for this dataset and moment in time, the grain size of interest with respect to colonisation by epilithic fauna starts at stone sizes Ø ≥ 2 cm. Thus, the areal cover cumulatively accounting for coarse gravel, cobble, boulder, and large boulder grain size classes (expressed as %/m2 and in the range 0–46%) was selected as the parameter (target response) from underwater imagery used for spatial modelling.
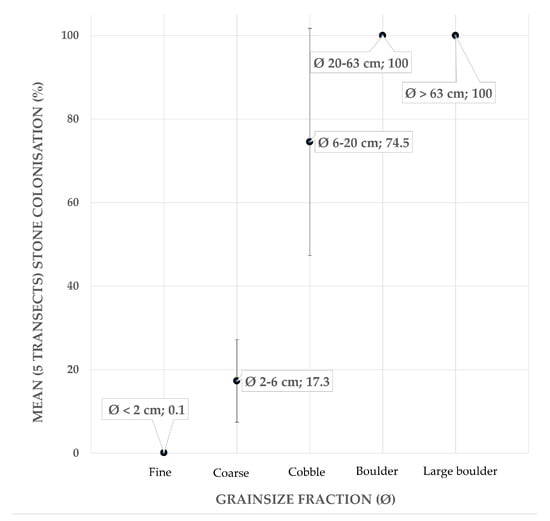
Figure 4.
Average (across 5 transects) proportion of stone colonisation (%) by ISO 14688-1:2017 grain size classes. Bars displaying the standard deviation.
RF spatial predictions, accuracy, and uncertainty. Predictive performance of the selected RF model (i.e., 70% training, 500 trees, and six features randomly selected at each node) was tested, per modelled subarea, by comparisons of observed and predicted values from the whittled test set (i.e., 30%). The modelling approach indicated a good performance, quantified by multiple accuracy metrics (Table 3). Both MAE and RMSE have very low values, the adjusted R2 has a moderately high value, and both linear and nonlinear correlation coefficients coincide with a high value, indicating the relative absence of outliers (as observed in previous studies; Gazis et al., 2018). Accordingly, the difference between observed and predicted mean and median (Q3) values is very small (0.3 and 1%, respectively). The interquartile range at intervals Q2 and Q5 reveals the inherent limitation of RF regression unable to predict out-of-training-range values [34], as well as over- and underestimating minimum and maximum values, respectively (as observed in similar investigations [27,72]).

Table 3.
Accuracy metrics computed from observed and predicted values of test samples (30%). MAE: mean absolute error; MSE: mean squared error; RMSE: root mean squared error; R2: R squared from linear regression; P: Pearson correlation coefficient; Spearman (ρ): Spearman rank correlation coefficient. Q: quantile; SD: standard deviation.
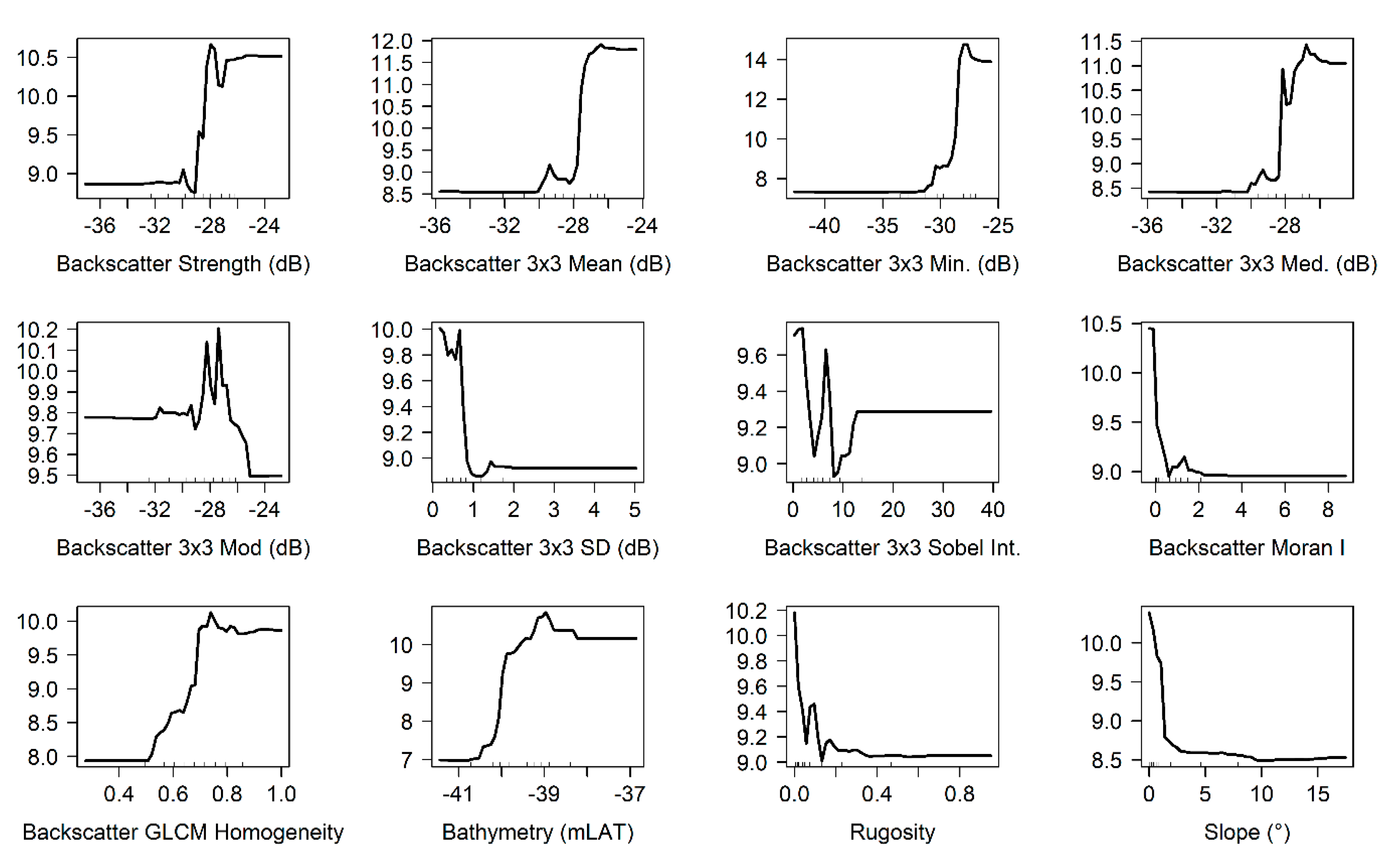
RF importance and spatial drivers. The analysis of the RF importance, by means of Boruta feature selection and partial dependence plots of selected features, revealed their ranked importance (not shown here), in respect to the prediction of the target response (i.e., those that explained most variance), as well as revealing their underlying nonlinear relations (Figure 5). Of the overall fifteen features, two were discarded (3 × 3 CBI Sobel filters for direction and edge). The remainder (n = 13) features were kept as important, scoring >5 Z-scores (i.e., all CBI statistics (min. max. median, standard deviation, and mode), bathymetry and all secondary morphometric features (rugosity and slope), CBI Moran’s I autocorrelation, and CBI Sobel intensity index). Expressed in terms of Z-scores by the Boruta analysis, the feature that most significantly contributed to the target prediction was the backscatter minimum value (high backscatter strength), followed by the bathymetry. All geomorphometric features (i.e., slope and rugosity), were retained as important. The partial dependence plots reveal that all the retained features contribute in a non-linear manner to the prediction of the response variable, as well as showing that, at this scale (i.e., 1 m horizontal resolution and 3 × 3 neighbourhood windows), there exist specific data intervals (e.g., mid-range depths, higher backscatter intensities, terrain with a slope <4°, rugosity values < 0.35) promoting higher coverage of stones with a high potential of colonisation by epilithic fauna.
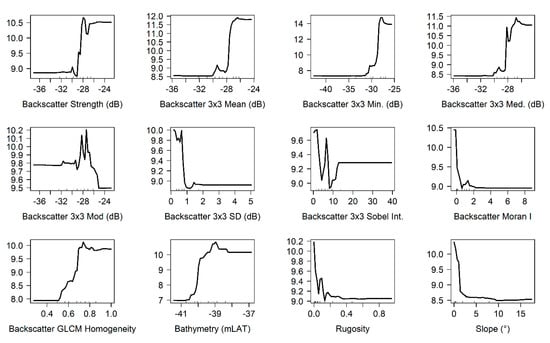
Figure 5.
Partial dependence plots. Y-axis: response variable. X-axis: feature values with deciles (tick marks).
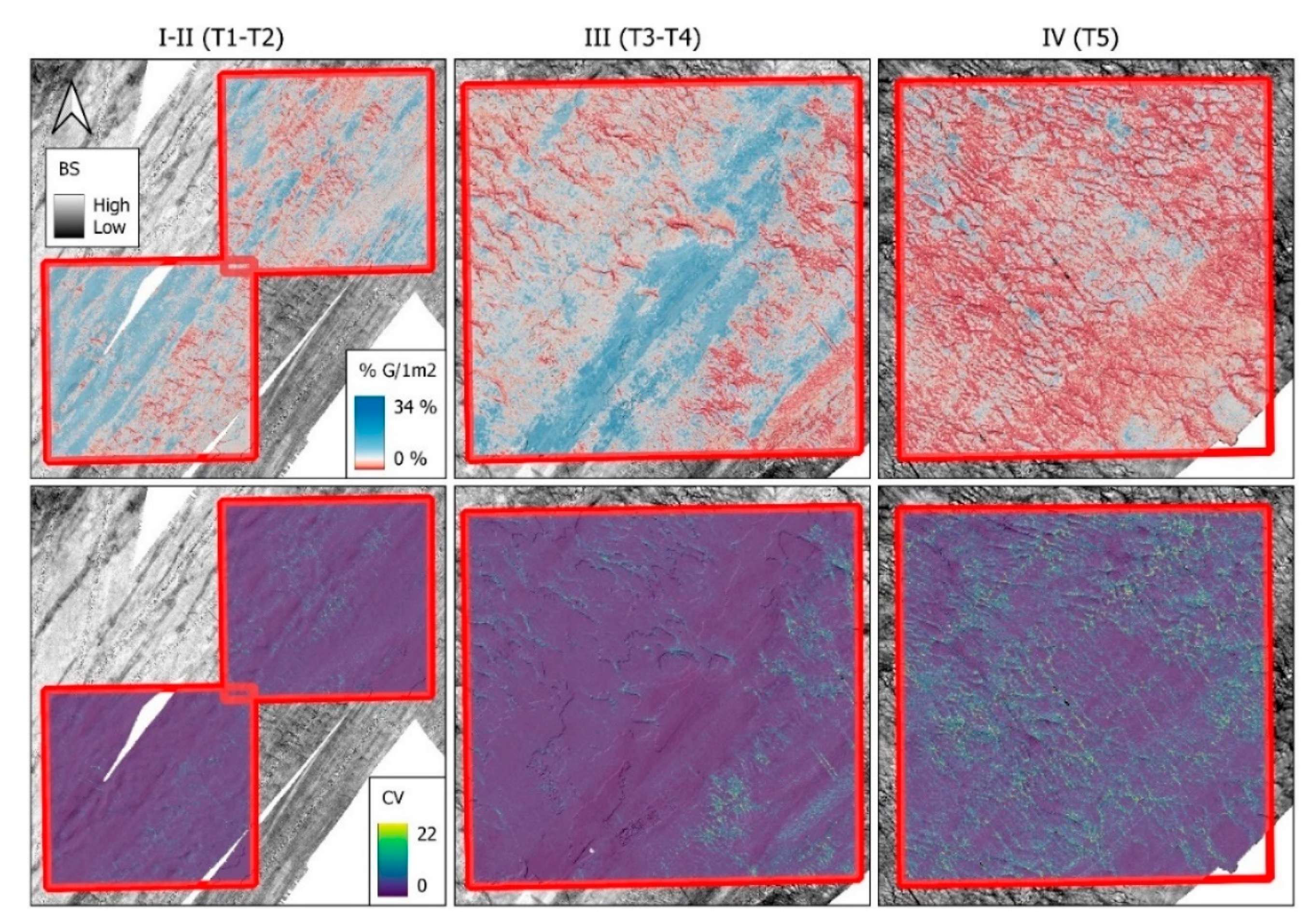
Predicted spatial distribution of subtidal natural hard substrates associated with epilithic organisms. The first row of Figure 6 displays the spatial predictions (range 0–34%) of the natural hard substrates identified as having a high potential of colonisation by epilithic fauna. These modelled predictions capture the morpho-sedimentological continuum of the seafloor/habitat and show that the distribution of hard substrates (expressed as stone coverage %/m2) coincides with two predominant spatial configurations (i.e., seascape patterns): (1) relatively large-scale striations (here aligned with the main tidal axis SW-NE and within depressions where the current channelises); and (2) small-scale elliptical shapes, observed under the form of relatively small-scale troughs/depressions. Striations develop longitudinally in the orders of kilometres, forming a stripy pattern with narrow (200–300 m) bands, alternated by sand ribbons. Small-scale elliptical shapes (patches) range in Ø 10–25 m and alternate with small to medium-sized sand ripple morphologies ranging in height 1–2 m and wavelength (λ) 10–20 m (as apparent from the hill shade semi-transparent map highlighting the geomorphology). Both spatial configurations are populated by relatively high percentages of stone cover, with values in the range 10–34% cover.
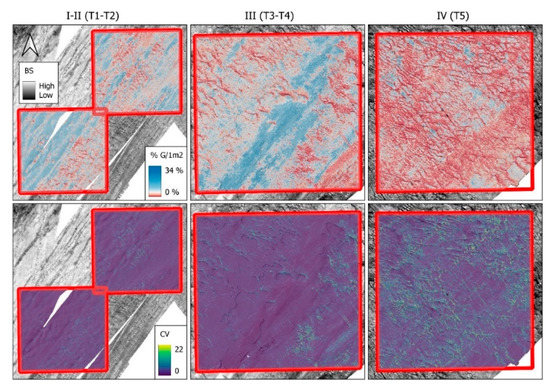

Figure 6.
RF spatial predictions within the subareas selected for modelling. Locations shown in Figure 2. First row: predicted % areal cover of stones Ø ≥ 2 cm/m2 (ISO 14688-1:2017 grain size classes) within quadrants I, II, III, and IV. The CBI is displayed beneath top and mid rows. BS: backscatter strength. Second row: coefficient of variation of the predictions. Third row: masked model predictions where the CV == 0, along with pictures of coincident Hamon grab samples and validation still frames from underwater videos (note video transect label for relative location on the maps). A semi-transparent hill shade layer is superimposed with 3 × vertical exaggeration for a prospective view of the surrounding geomorphology and the map colour palettes are displayed using quantile breaks. Fourth row: pictures of coincident Hamon grab samples. Fifth row: coincident underwater imagery. The laser points are 10 cm apart (frame randomly picked from 30% test dataset). Still frames T2 and T4 are from “dense stone lag shapes” whereas T5 is “bare sandy bottom”. Conspicuous epilithic species in the UI, noticeably colonies of A. digitatum and dense bioencrustations by S. triqueter.
Complementing the model predictions, the coefficient of variation (mid-row Figure 6) displays spatial uncertainty. This information provides a spatially explicit understanding of the modelled areas’ uncertainty, displaying the by-pixel algorithm’s consistency in allocating predicted values. This information was used to spatially constrain the model predictions (bottom row, Figure 6) where the CV was lowest, i.e., with a value of 0. The resulting map captures the spatially explicit patchy distribution of the natural hard substrate and removes the minimum overestimated values coincident with the hill shade sand signatures. Finally, the Hamon grab samples (blue outlined triangles, bottom row pictures, Figure 6), qualitatively corroborate the model predictions, in a binary sense, displaying samples with a high content of hard substrate, correctly allocated to pixels of striations and small-scale elliptical patches (blue tail of the colour palette), whereas predominantly sandy samples are correctly allocated outside these zones, thus on areas predicted in the range 0–8% (red tail of the colour palette, first row, Figure 6; dark black areas, third row, Figure 6).
4. Discussion
The investigation focused on the scientific validation of a transferrable and quantitative (i.e., continuous data prediction) habitat mapping routine, suited to the spatially explicit demarcation of subtidal natural hard substrates environments (i.e., in the offshore North Sea setting) with high potential of colonisation by epilithic fauna. The proposed methodology exploited a combination of contemporary and non-destructive (minimally invasive) remote sensing (ship-based MBES soundings) and ground truthing technologies (UI by drop frame), interlinked by a state-of-the-art machine learning predictive algorithm (i.e., using RF for regression). The innovative character of the habitat mapping approach tested in this investigation is the quantitative exploitation of the UI for the development of an ecologically informed SNHS habitat delineation criterion, aiding the spatial delineation of the realised niche of reef-associated epilithic organisms. The following paragraphs discuss the success of this investigation, focusing on the exploitation of UI for a quantitative appraisal of SNHS habitat and the potential of this data for ecologically informed habitat modelling. Lastly, shortcomings and future outlooks are highlighted.
In line with recent applications of UI for the characterisation of SNHS and associated epibenthic assemblages in the English Channel and Southern North sea marine regions setting, e.g., [21,24,25,26,37,73], seafloor imaging by drop/drift frames is confirmed as a highly time efficient (i.e., number of samples vs. sampling time) approach, providing spatially representative data of interest for the characterisation of high-frequency (in respect to the acoustical signal penetration into the seafloor; see [18,74]) and high-resolution (in respect to the sample size match between remote sensing and ground truthing data) MBES data. The UI observations revealed comprehensive details of the seafloor nature: substrate, biota, and their spatial organisation and structure (size of visible biotic and abiotic occurrences) and provided insight into sedimentary processes and geo-bio relations. Based on such data, the investigation showed how UI enables deriving an ecologically relevant spatial delineation criterion to map SNHS habitat. Firstly, the proportion of biologically colonised substrate could be related to specific grain size fractions (starting from stones Ø > 2 cm). Consequently, UI provided the quantitative information needed to set up predictive seafloor modelling, in this case producing maps capturing the percent cover (%/m2) of the grain size fractions with the highest potential of colonisation by epilithic fauna. Thus, UI satisfies both a numerical ecological appreciation of bio-geo relations and the production of a dataset enabling ecologically informed seafloor substrate modelling. Consequently, the seafloor model herein produced may not be considered as a mere substrate map (i.e., abiotic map), rather, as a benthic habitat map [13] specifically related to SNHS assemblages of epilithic fauna. Here it must be mentioned that including environmentally dynamic variables (i.e., hydrodynamics) at relevant scales in the modelling process [75] would inevitably enhance the ecological significance of the modelled map outputs, including a refined and mechanistic understanding of the fine-scale driving factors of SNHS communities. Interestingly, if such seafloor predictions are repeated in time (i.e., by repeating the data acquisition and processing workflow herein tested, on datasets acquired, e.g., during different seasons), spatiotemporal and high-resolution changes in the areas of potential epibenthic colonisation may further help elucidate environmental drivers and temporal dependencies of such benthic communities. Indeed, considerations of the fourth dimension (i.e., time) in BHM studies is fundamental for the interpretation of static maps (i.e., “snapshot-in-time”) and of the UI data and derived observations. With regard to the latter, it must be noted that mechanisms of seafloor disturbance (both natural and/or anthropogenic, e.g., periodic stone burial and/or abrasion by bottom fishing gears), may cause a bias to the biological observations (e.g., colonisation). Therefore, it is important to consider that the resulting datasets and resulting spatial models may have a strong dependence on the local seafloor spatiotemporal dynamicity over timescales ranging from seconds to years.
With regard to spatial modelling, as for other recent investigations, e.g., [27,35,36,37,63] the use of RF is confirmed as a well-performing (accurate) and versatile predictive algorithm. From a relatively limited number of loci, RF exploits the multivariate information, including highly correlated features, while avoiding overfitting [34]. RF learns complex underlying non-linear relations (e.g., Figure 5, partial dependence plots in this investigation) between explanatory features (i.e., the hydroacoustic data) and the target response (derived from UI), predicting fitted relations on the broader “unseen” surveyed area and revealing trends and patterns that may reveal casualties and even be used to formulate novel scientific hypotheses [76]. Using RF for regression produces output models that are interpretable as a seafloor morpho-sedimentological continuum. Unlike predictive modelling of habitat classification schemes [77], continuous spatial predictions provide finer ecological information (e.g., gradients [36,78]) and enable better exploitation of high-resolution hydroacoustic data, leading to a better depiction of seafloor heterogeneity, evidencing fine-scale variations that may otherwise remain unnoticed where a single categorical/thematic class is used instead. Further benefits of RF for regression and for the case of modelling spatially clustered and heterogeneous seafloor features, such as SNHS, is the randomisation of the training data points in each decision tree. This leads to a new set of training data points informing the model’s learning process, and since the spatial selection is ignored by the random selection process, the influence of spatial autocorrelation is limited, making it an appropriate modelling approach for spatially clustered data (e.g., mapping of polymetallic nodules in [27]). Furthermore, RF benefits from a relatively simple model-tuning, and does not rely on any prior transformation/standardisation of the input data, or on any a priori assumption/requirement of the data structure (e.g., normality; [34]). Finally, at the cost of increasing the computational time, a favourable characteristic of RF for regression is the potential of deriving spatially coincident measures of uncertainty for the model predictions, such as the CV herein used, providing interesting insights into the algorithm decisions consistency in allocating the learnt predicted values to the unseen data. Moreover, coincident uncertainty measures enabled spatial subselection of the model predictions, masking overestimated values (i.e., those predicted on obviously sandy areas; cfr. hill shade prospective view in Figure 5), and explicitly revealing the two main spatial distribution patterns of the modelled response: distributed as striations and elliptical geometries of hard substrate. Striations are indicative of a strong tidal stream and the presence of hard substrates [79] and were also observed by earlier studies in nearby study sites (e.g., English Channel [80]; Belgian waters, [81,82]). Holme and Wilson [80] described such striations as “longitudinal tide swept furrows” associated with rich epibenthic communities. For the study site assessed in this investigation, this observation is confirmed by the UI (e.g., Figure 5), displaying a typical SNHS fauna, including long-lived (i.e., >5 yrs.), vertically developing, and arborescent sessile epilithic species. Indeed, knowledge of the spatially explicit distribution of the stone’s coverage (i.e., by seafloor units of 1 m2) is an invaluable asset to biological data survey planning, as well as providing the baseline for environmental monitoring at ecologically relevant scales. Recent studies, including the present investigation, demonstrated that stone size is a fundamental driver of SNHS epibenthic (epilithic) species assemblages [24,25]. Furthermore, besides the size of individual stones, seascape patterns, such as the striations and elliptical shapes herein identified, can be important proxies of biological communities (describing the relation between geological and biological structure, e.g., [83,84]. Therefore, at such scales, the integration of MBES and UI by RF for regression largely improves the identification of the ecology of such seascape patterns.
Hitherto, only a few cases have been published showing the importance of geological complexity or geodiversity in marine management, e.g., [84,85], but clearly if these coincide with hotspots of biodiversity, a new era is emerging in the mapping of SNHS. This is indeed the case for the Southern North Sea region, having a complex geological history and a diverse morphosedimentary setting. For example, the results of this research (including the interpretation of the UI-derived community matrix; not shown here) may suggest that all SNHS striations and elliptical shapes in this specific environmental setting may be considered as priority areas for conservation and monitoring, hosting high-priority SNHS biological assemblages.
While the instrumentation and set-up used in the present investigation proved highly valuable for targeting the research aim, some improvements could be made at both the UI data acquisition and processing and the predictive modelling phases. Hereafter, shortcomings are flagged. Technical improvements are needed in the design of the UI acquisition platform, including increased illumination allowing one to position the recording camera higher above the seafloor to naturally achieve a viewing angle closely matching the resolution of the MBES data (i.e., 1 m). Although videos were acquired under optimal sea state conditions and tidal windows, and extracted image stills were well positioned (i.e., georeferenced to the drop-frame cable’s breakpoint), installation of a dedicated positioning system would represent a considerable positional improvement and decrease the chances of positional error propagation in the modelling phase. Analysis of underwater imagery can be highly time-consuming given the high number of data points compared to conventional sampling gears. While the extraction of parameters (i.e., such as the stone’s Ø and areal cover) from still images was mostly automated, the annotation, i.e., segmentation into ROIs and labelling into colonised and/or uncolonised, was performed manually. The success of fully automated image-annotation applications [86] is inextricably linked to the quality of the underwater imagery, in turn dictated by the specific set-up of the various components on the UI acquisition platform, by the quality and functioning of the components themselves, and by the environmental conditions at the time of UI acquisition. Thus, it is expected that considerable improvements in the use of such technology for seafloor ecological characterisation and quantitative predictive modelling will come in from R&D-oriented technical improvements of the UI acquisition platform itself, as well as from the field of computer science and big data, in the application of machine and deep learning algorithms to the automated annotation of UI [87], as well as image processing, correction, and filtering (e.g., during data acquisition, minimising a posteriori labour-intensive aspects of image analysis).
Specifically relating to relatively turbid water environment, development of “clear-water housing” underwater optical systems [88] will inevitably benefit future SNHS research. Regarding the RF predictive modelling, as reported by others [27], the most significant improvements in predictive accuracy and performance result from the use of more training data points.
The availability of more data, especially if they are better distributed (i.e., data that will include the entire range of the target response, for example from all the different topographies and acoustical facies), would inevitably reinforce the model in learning improved and wider relationships between the predictor and response variables, while also ensuring a larger number of validation data points to derive accuracy metrics from. Here, use of towed sledge systems and or/autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) represent an invaluable asset to the collection of larger volumes of UI in complement to the MBES data [89]. In this regard, an important aspect of machine learning application to habitat mapping studies will be to address the effect of the amount of training data on model performance. This aspect remains poorly explored in this domain and is at the centre of discussion of recent research, e.g., [27]. This aspect will be particularly important in view of upscaling the habitat mapping approach tested in this investigation and incorporating it into standards designed to specifically survey and characterise SNHS habitat. It will be important to define quantitatively the amount of UI groundtruth data to be collected, in respect to the extent of the hydroacoustic survey. A sufficient underlying number of observations is needed for a representative model to be constructed. In this investigation, modelling tests (not shown here) were conducted to predict the target response over the entire 32 km2 surveyed area. However, these produced poorer accuracies, evidencing the relative paucity of UI observations available for this study. While a good practice approach is to check, prior to the modelling phase, the representativeness of the training and testing groundtruth and underlying MBES datasets (i.e., by comparing the probability density functions from the primary MBES data prediction surface and sample locations; not shown), further tests are required to elucidate this aspect further, particularly in view of the large volumes of MBES data expected to become available in the coming years [90]. Finally, future tests based on this predictive modelling approach may benefit from the use of RF for quantile regression, having the potential to improve the uncertainty reporting by exploiting lower and upper quartiles as confidence around the mean predictions [66].
5. Conclusions
The results of this investigation show that the acquisition, processing, and analysis of underwater seafloor imagery data provide seafloor mappers with quantitative and ecologically relevant information on the distribution of subtidal natural hard substrates. This numerical information can be integrated with ship-based MBES data by means of RF machine learning, here used to compute high-resolution predictions of stone areal coverage (%/1 m2) at scales relevant for ecological management. Such spatial predictions provide a direct link to the distribution of SNHS epibenthic assemblages that are a priority for environmental conservation and monitoring in European seas and elsewhere. Furthermore, this investigation demonstrated how the use of underwater imagery enabled understanding of how stone size influences biological colonisation and, consequently, how this information can be quantitatively exploited to develop ecologically meaningful habitat delineation criteria.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, G.M.G.; methodology, G.M.G.; formal analysis, G.M.G.; investigation, G.M.G., D.A.K. and V.V.L.; resources, S.D. (Steven Degraer); data curation, G.M.G. and D.A.K., writing—original draft preparation, G.M.G. and D.A.K.; writing—review and editing, G.M.G., D.A.K., S.D. (Steven Degraer), V.V.L., S.D. (Samuel Deleu) and F.K.; visualisation, G.M.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Raw and processed data are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This paper is a contribution to the national Belgian Marine Strategy Framework Directive monitoring program on seafloor integrity (D6), and biodiversity and benthic habitats (D1) for natural hard substrate communities (https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/msfd/nl/monitoring/2020/ANSBE-P9-Benthos-4-hard-substrate and https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/msfd/nl/monitoring/2020/#ANSBE-P5-Seabed-physical). Moreover, this work is a contribution to the projects MOZ4 (Flemish Authorities, Agency Maritime Services and Coast, Coast, contract 211.177) and ZAGRI, a federal Belgian program for the continuous monitoring of sand and gravel extraction, paid from private revenues. Ship time RV Belgica was provided by BELSPO and RBINS–OD Nature. Lars Kint and Nathan Terseleer are thanked for their field work support. The collaboration of the vessel’s commander and crew members is highly appreciated. Flanders Marine Institute (VLIZ) is acknowledged for the use of the video frame.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wahl, M. (Ed.) Marine Hard Bottom Communities: Patterns, Dynamics, Diversity, and Change; Springer Ecological Studies: Dordrecht, The Netherlands; New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 206, pp. 1–420. [Google Scholar]
- McArthur, M.; Brooke, B.; Przeslawski, R.; Ryan, D.; Lucieer, V.; Nichol, S.; McCallum, A.; Mellin, C.; Cresswell, I.; Radke, L. On the use of abiotic surrogates to describe marine benthic biodiversity. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halpern, B.S.; Walbridge, S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Kappel, C.V.; Micheli, F.; D’Agrosa, C.; Watson, R. A global map of human impact on marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 319, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halpern, B.S.; Frazier, M.; Potapenko, J.; Casey, K.; Koenig, K.; Longo, C.; Lowndes, J.S.; Rockwood, R.C.; Selig, E.R.; Selkoe, K.A.; et al. Spatial and temporal changes in cumulative human impacts on the world’s ocean. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Irving, R. Summary Report of an Inter-Agency Workshop 26–27 March. In The Identification of the Main Characteristics of Stony Reef Habitats under the Habitats Directive; JNCC: Peterborough, UK, 2009; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Houziaux, J.-S.; Fettweis, M.; Francken, F.; van Lancker, V. Historic (1900) seafloor composition in the Belgian–Dutch part of the North Sea: A reconstruction based on calibrated visual sediment descriptions. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houziaux, J.-S.; Haelters, J.; Kerckhof, F. Facts from history: The former ecological value of gravel grounds in Belgian marine waters: Their importance for biodiversity, the relationship with fisheries. In ICES Marine Habitat Committee (2007), Report of the Study Group on Biodiversity Science (SGBIODIV), 9-11 May 2007 VLIZ, Belgium; ICES: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Houziaux, J.-S.; Kerckhof, F.; Degrendele, K.; Roche, M.; Norro, A. The Hinder Banks: Yet an Important Area for the Belgian Marine Biodiversity? Belgian Science Policy: Brussels, Belgium, 2008; p. 259. [Google Scholar]
- Foveau, A.; Desroy, N.; Dewarumez, J.-M.; Dauvin, J.-C.; Cabioch, L. Long-term changes in the sessile epifauna of the Dover Strait pebble community. J. Oceanogr. Res. Data 2008, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Council Directive 2008/56/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 June 2008 establishing a framework for community action in the field of marine environmental policy (Marine Strategy Framework Directive) (Text with EEA rele-vance). Off. J. Eur. Union 2008, 164, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. L 1992, 206, 7–50. [Google Scholar]
- Papenmeier, S.; Darr, A.; Feldens, P.; Michaelis, R. Hydroacoustic Mapping of Geogenic Hard Substrates: Challenges and Review of German Approaches. Geosciences 2020, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, C.; Smith, S.J.; Lawton, P.; Anderson, J.T. Benthic habitat mapping: A review of progress towards improved understanding of the spatial ecology of the seafloor using acoustic techniques. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 502–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.T.; Holliday, D.V.; Kloser, R.; Reid, D.; Simrad, Y.; Brown, C.; Chapman, R.; Coggan, R.; Kieser, R.; Michaels, L.W.; et al. (Eds.) Acoustic Seabed Classification of Marine Physical and Biological Landscapes; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea Conseil International pour l’Exploration de la Mer: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.T.; van Holliday, D.; Kloser, R.; Reid, D.G.; Simard, Y. Acoustic seabed classification: Current practice and future directions. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2008, 65, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesing, M.; Mitchell, P.J.; O’Keeffe, E.; Gavazzi, G.O.; Bas, T.L. Limitations of Predicting Substrate Classes on a Sedimentary Complex but Morphologically Simple Seabed. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, A.J.; Cato, I.; Desprez, M.; Fader, G.; Schüttenhelm, R.T.E.; Side, J. An overview of seabed-mapping technologies in the context of marine habitat classification. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2003, 60, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lurton, X. An Introduction to Underwater Acoustics: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Springer Praxis Books and Praxis Publishing: Berlin/Heidelnerg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lurton, X.; Lamarche, G. Backscatter Measurements by Seafloor-Mapping Sonars. Guidelines and Recommendations. Available online: http://geohab.org/wpcontent/uploads/2014/05/BSWGREPORT-MAY2015.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Lamarche, G.; Lurton, X. Recommendations for improved and coherent acquisition and processing of backscatter data from seafloor-mapping sonars. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beisiegel, K.; Darr, A.; Gogina, M.; Zettler, M.L. Benefits and shortcomings of non-destructive benthic imagery for monitoring hard-bottom habitats. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, E.; Cousens, S.; Nancollas, S.; Stauss, C.; Royle, J.; Attrill, M. Drawing lines at the sand: Evidence for functional vs. visual reef boundaries in temperate Marine Protected Areas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 76, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheehan, E.V.; Stevens, T.F.; Gall, S.C.; Cousens, S.L.; Attrill, M.J. Recovery of a Temperate Reef Assemblage in a Marine Protected Area following the Exclusion of Towed Demersal Fishing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, R.; Hass, H.C.; Mielck, F.; Papenmeier, S.; Sander, L.; Ebbe, B.; Gutow, L.; Wiltshire, K.H. Hard-substrate habitats in the German Bight (South-Eastern North Sea) observed using drift videos. J. Sea Res. 2019, 144, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, R.; Hass, H.C.; Mielck, F.; Papenmeier, S.; Sander, L.; Gutow, L.; Wiltshire, K.H. Epibenthic assemblag-es of hard-substrate habitats in the German Bight (south-eastern North Sea) described using drift videos. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Reijden, K.J.; Koop, L.; O’Flynn, S.; Garcia, S.; Bos, O.; van Sluis, C.; Maaholm, D.J.; Herman, P.M.; Simons, D.G.; Olff, H.; et al. Discovery of Sabellaria spinulosa reefs in an intensively fished area of the Dutch Continental Shelf, North Sea. J. Sea Res. 2019, 144, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gazis, I.-Z.; Schoening, T.; Alevizos, E.; Greinert, J. Quantitative mapping and predictive modeling of Mn nodules’ distribution from hydroacoustic and optical AUV data linked by random forests machine learning. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 7347–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ierodiaconou, D.; Monk, J.; Rattray, A.; Laurenson, L.; Versace, V.L. Comparison of automated classification tech-niques for predicting benthic biological communities using hydroacoustics and video observations. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, S28–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierodiaconou, D.; Schimel, A.C.G.; Kennedy, D.; Monk, J.; Gaylard, G.; Young, M.; Diesing, M.; Rattray, A. Combining pixel and object based image analysis of ultra-high resolution multibeam bathymetry and backscatter for habitat mapping in shallow marine waters. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 271–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montereale-Gavazzi, G.; Madricardo, F.; Janowski, L.; Kruss, A.; Blondel, P.; Sigovini, M.; Foglini, F. Evaluation of seabed mapping methods for fine scale classification of extremely shallow benthic habitats—Application to the Venice La-goon, Italy. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 170, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janowski, L.; Trzcinska, K.; Tegowski, J.; Kruss, A.; Rucinska-Zjadacz, M.; Pocwiardowski, P. Nearshore Benthic Habitat Mapping Based on Multi-Frequency, Multibeam Echosounder Data Using a Combined Object-Based Approach: A Case Study from the Rowy Site in the Southern Baltic Sea. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misiuk, B.; Lecours, V.; Bell, T. A multiscale approach to mapping seabed sediments. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diesing, M.; Coggan, R.; Vanstaen, K. Widespread rocky reef occurrence in the central English Channel and the implications for predictive habitat mapping. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 83, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herkül, K.; Peterson, A.; Paekivi, S. Applying multibeam sonar and mathematical modeling for mapping seabed sub-strate and biota of offshore shallows. Estuar. Coastal. Shelf. Sci. 2017, 192, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kågesten, G.; Fiorentino, D.; Baumgartner, F.; Zillén, L. How Do Continuous High-Resolution Models of Patchy Seabed Habitats Enhance Classification Schemes? Geosciences 2019, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, L.R.; Bartholomä, A.; Singer, A.; Bischof, K.; Coers, S.; Kröncke, I. Small-scale distribution modeling of ben-thic species in a protected natural hard ground area in the German North Sea (Helgoländer Steingrund). Geo-Mar. Lett. 2020, 40, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra, H. Gravels of the southern North Sea. Mar. Geol. 1969, 7, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lancker, V.; Du Four, I.; Verfaillie, E.; Deleu, S.; Schelfaut, K.; Fettweis, M.; van den Eynde, D.; Francken, F.; Monbaliu, J.; Giardino, A.; et al. Management, Research and Budgetting of Aggregates in Shelf Seas Related to End-Users (Marebasse); Belgian Science Policy: Brussel, Belgium, 2007; p. 139. [Google Scholar]
- van Lancker, V.; Francken, F.; Kapel, M.; Kint, L.; Terseleer, N.; van den Eynde, D.; Hademenos, V.; Missiaen, T.; de Mol, R.; de Tre, G.; et al. Transnational and Integrated Long-Term Marine Exploitation Strategies (TILES): Final Report (BRAIN-be-Belgian Research Action through Interdisciplinary Networks); Belgian Science Policy: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; p. 75. [Google Scholar]
- TILES Consortium 2018. TILES Voxel model subsurface Belgian and southern Netherland’s part of the North Sea. Belspo Brain-be project TILES (Transnational and Integrated Long-term Marine Exploitation Strategies, BR/121/A2/TILES). Available online: https://odnature.naturalsciences.be/downloads/tiles/tiles_information_sheet_en.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Deleu, S.; van Lancker, V.; van den Eynde, D.; Moerkerke, G. Morphodynamic evolution of the kink of an offshore tidal sandbank: The Westhinder Bank (Southern North Sea). Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1587–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostrom, C.; Pittman, S.; Simenstad, C.; Kneib, R.T. Seascape ecology of coastal biogenic habitats: Advances, gaps, and challenges. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 427, 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pittman, S.; Kneib, R.; Simenstad, C. Practicing coastal seascape ecology. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 427, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Lancker, V. Sediment and Morpho Dynamics of a Siliciclastic near Coastal Area, in Relation to Hydrodynamical and Meteorological Conditions: Belgian Continental Shelf. Ph.D. Thesis, Gent University, Ghent, Belgium, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- van den Eynde, D. Interpretation of tracer experiments with fine-grained dredging material at the Belgian Continental Shelf by the use of numerical models. J. Mar. Syst. 2004, 48, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, S.; Tett, P.; Mills, D.; van der Molen, J. Stratified and nonstratified areas in the North Sea: Long-term variability and biological and policy implications: NORTH SEA stratification regimes. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2015, 120, 4670–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lanckneus, J.; van Lancker, V.; Moerkerke, G.; van den Eynde, D.; Fettweis, M.; de Batist, M.; Jacobs, P. Investigation of the Natural Sand Transport on the Belgian Continental Shelf (BUDGET). Available online: http://www.belspo.be/belspo/organisation/Publ/pub_ostc/Mn/Abstract/Abs17.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2019).
- van den Eynde, D.; de Sutter, R.; Haerens, P. Evolution of marine storminess in the Belgian part of the North Sea. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 12, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Organization for Standardization. ISO 14688–1: 2017: Geotechnical Investigation and Testing—Identification and Classification of Soil—Part 1: Iden-tification and Description; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimel, A.C.G.; Beaudoin, J.; Parnum, I.M.; Le Bas, T.; Schmidt, V.; Keith, G.; Ierodiaconou, D. Multibeam sonar backscatter data processing. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M. Sources and impacts of Bottom Slope Uncertainty on Estimation of Seafloor Backscatter from Swath Sonars. Geosciences 2019, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecours, V.; Devillers, R.; Edinger, E.N.; Brown, C.; Lucieer, V. Influence of artefacts in marine digital terrain models on habitat maps and species distribution models: A multiscale assessment. Remote. Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 3, 232–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecours, V.; Dolan, M.F.J.; Micallef, A.; Lucieer, V.L. A review of marine geomorphometry, the quantitative study of the seafloor. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 3207–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montereale-Gavazzi, G.; Roche, M.; Degrendele, K.; Lurton, X.; Terseleer, N.; Baeye, M.; Francken, F.; van Lancker, V. Insights into the Short-Term Tidal Variability of Multibeam Backscatter from Field Experiments on Different Seafloor Types. Geosciences 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montereale-Gavazzi, G. Development of Seafloor Mapping Strategies Supporting Integrated Marine Management. Application of Seafloor Backscatter by Multibeam Echosounders. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Roche, M.; Degrendele, K.; Vrignaud, C.; Loyer, S.; Le Bas, T.; Augustin, J.-M.; Lurton, X. Control of the repeatability of high frequency multibeam echosounder backscatter by using natural reference areas. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urgeles, R.; Locat, J.; Schmitt, T.; Clarke, J.H. The July 1996 flood deposit in the Saguenay Fjord, Quebec, Canada: Implications for sources of spatial and temporal backscatter variations. Mar. Geol. 2002, 184, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Clarke, J.E.; Iwanowska, K.K.; Parrott, R.; Duffy, G.; Lamplugh, M.; Griffin, J. Inter-calibrating multi-source, multi-platform backscatter data sets to assist in compiling regional sediment type maps: Bay of Fundy. In Proceedings of the Canadian Hydrographic Conference and National Surveyors Conference, Victoria, Canada, 5–8 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lacharité, M.; Brown, C.; Gazzola, V. Multisource multibeam backscatter data: Developing a strategy for the production of benthic habitat maps using semi-automated seafloor classification methods. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiuk, B.; Brown, C.; Robert, K.; Lacharité, M. Harmonizing Multi-Source Sonar Backscatter Datasets for Seabed Mapping Using Bulk Shift Approaches. Remote. Sens. 2020, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Tran, M.; Siwabessy, J. Selecting Optimal Random Forest Predictive Models: A Case Study on Predicting the Spatial Distribution of Seabed Hardness. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesing, M.; Green, S.L.; Stephens, D.; Lark, R.; Stewart, H.A.; Dove, D. Mapping seabed sediments: Comparison of manual, geostatistical, object-based image analysis and machine learning approaches. Cont. Shelf Res. 2014, 84, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diesing, M.; Stephens, D. A multi-model ensemble approach to seabed mapping. J. Sea Res. 2015, 100, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, E.; Frescino, T. ModelMap: Modeling and Map Production Using Random Forest and Stochastic Gradient Boosting. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ModelMap (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Evans, J.S. spatialEco. R package version 1.3. 2021. Available online: https://github.com/jeffreyevans/spatialEco (accessed on 10 September 2021).
- Zvoleff, A. GLCM: Calculate Textures from Grey-Level Co-Occurrence Matrices (GLCMs). R Package Version 1. Available online: https://search.r-project.org/CRAN/refmans/glcm/html/glcm-package.html (accessed on 11 November 2021).
- Hijmans, R.J.; van Etten, J.; Cheng, J.; Mattiuzzi, M.; Sumner, M.; Greenberg, J.A. Raster: Geographic Data Analysis and Modeling, R package version 2.1-16; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, M.F.J.; O’Connell, B.; Brown, C.; Guinan, J.C.; Grehan, A. Multiscale Terrain Analysis of Multibeam Bathymetry Data for Habitat Mapping on the Continental Slope. Mar. Geodesy 2007, 30, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kursa, M.; Rudnicki, W. Feature Selection with theBorutaPackage. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horning, N. RandomForests: An algorithm for image classification and generation of continuous fields data sets. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics for Spatial Infrastructure Development in Earth and Allied Sciences (GIS-IDEAS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 9–11 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Foveau, A.; Dauvin, J.-C. Surprisingly diversified macrofauna in mobile gravels and pebbles from high-energy hy-drodynamic environment of the ‘Raz Blanchard’ (English Channel). Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2017, 16, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huff, L.C. Acoustic Remote Sensing as a Tool for Habitat Mapping in Alaska Waters. In Marine Habitat Mapping Technology for Alaska; Reynolds, J.R., Greene, H.G., Eds.; Alaska Sea Grant, University of Alaska Fairbanks: Fairbanks, AK, USA, 2008; pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Rattray, A.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Womersley, T. Wave exposure as a predictor of benthic habitat distribution on high energy temperate reefs. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breiman, L. Statistical Modeling: The Two Cultures (with comments and a rejoinder by the author). Stat. Sci. 2001, 16, 199–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, J.A.; Clements, A.; Lillis, H.; Galparsoro, I.; Bildstein, T.; Pesch, R. A review of the influence of marine habitat classification schemes on mapping studies: Inherent assumptions, influence on end products, and suggestions for future developments. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2019, 76, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, P.J.; Aldridge, J.; Diesing, M. Legacy data: How decades of seabed sampling can produce robust predic-tions and versatile products. Geosciences 2019, 9, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, F.E.; Stride, A.A. Offshore Tidal Sands-Processes and Deposits. Estuaries 1984, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holme, N.A.; Wilson, J.B. Faunas Associated with Longitudinal Furrows and Sand Ribbons in a Tide-Swept Area in the English Channel. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 1985, 65, 1051–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleu, S.; van Lancker, V. Geological setting of gravel occurrences on the Belgian part of the North Sea. In Management, Research and Budgeting of Aggregates in Shelf Seas Related to End-Users (Marebasse); Final Scientific Report; Belgian Science Policy Office: Brussels, Belgium, 2007; pp. 101–115. [Google Scholar]
- Montereale-Gavazzi, G.; Roche, M.; Lurton, X.; Degrendele, K.; Terseleer, N.; van Lancker, V. Seafloor change detection using multibeam echosounder backscatter: Case study on the Belgian part of the North Sea. Mar. Geophys. Res. 2018, 39, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proudfoot, B.; Devillers, R.; Brown, C.J. Integrating fine-scale seafloor mapping and spatial pattern metrics into marine conservation prioritization. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2020, 30, 1613–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, M.; von Rönn, G.A.; Barboza, F.R.; Karez, R.; Reimers, H.-C.; Schwarzer, K.; Wahl, M. How Do Geological Structure and Biological Diversity Relate? Benthic Communities in Boulder Fields of the Southwestern Baltic Sea. Chesap. Sci. 2021, 44, 1994–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucatelli, D.; Goes, E.R.; Brown, C.J.; Souza-Filho, J.F.; Guedes-Silva, E.; Araújo, T.C.M. Geodiversity as an in-dicator to benthic habitat distribution: An integrative approach in a tropical continental shelf. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2019, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Schoening, T.; Jones, D.O.B.; Greinert, J. Compact-Morphology-based poly-metallic Nodule Delineation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šiaulys, A.; Vaičiukynas, E.; Medelytė, S.; Olenin, S.; Šaškov, A.; Buškus, K.; Verikas, A. A fully annotated imagery dataset of sublittoral benthic species in Svalbard, Arctic. Data Brief 2021, 35, 106823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.E.; Griffin, R.A.; Rees, S.C.; Unsworth, R.K. Improving visual biodiversity assessments of motile fauna in turbid aquatic environments. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2019, 17, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sture, Ø.; Ludvigsen, M.; Aas, L.M.S. Autonomous underwater vehicles as a platform for underwater hyper-spectral imaging. In OCEANS 2017-Aberdeen, Proceedings of the IEEE OCEANS 2017 ABERDEEN, 19th, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mayer, L.; Jakobsson, M.; Allen, G.; Dorschel, B.; Falconer, R.; Ferrini, V.; Lamarche, G.; Snaith, H.; Weatherall, P. The Nippon Foundation—GEBCO Seabed 2030 Project: The Quest to See the World’s Oceans Completely Mapped by 2030. Geosciences 2018, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).