Synergy of Remote Sensing Data for Exploring Hydrothermal Mineral Resources Using GIS-Based Fuzzy Logic Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
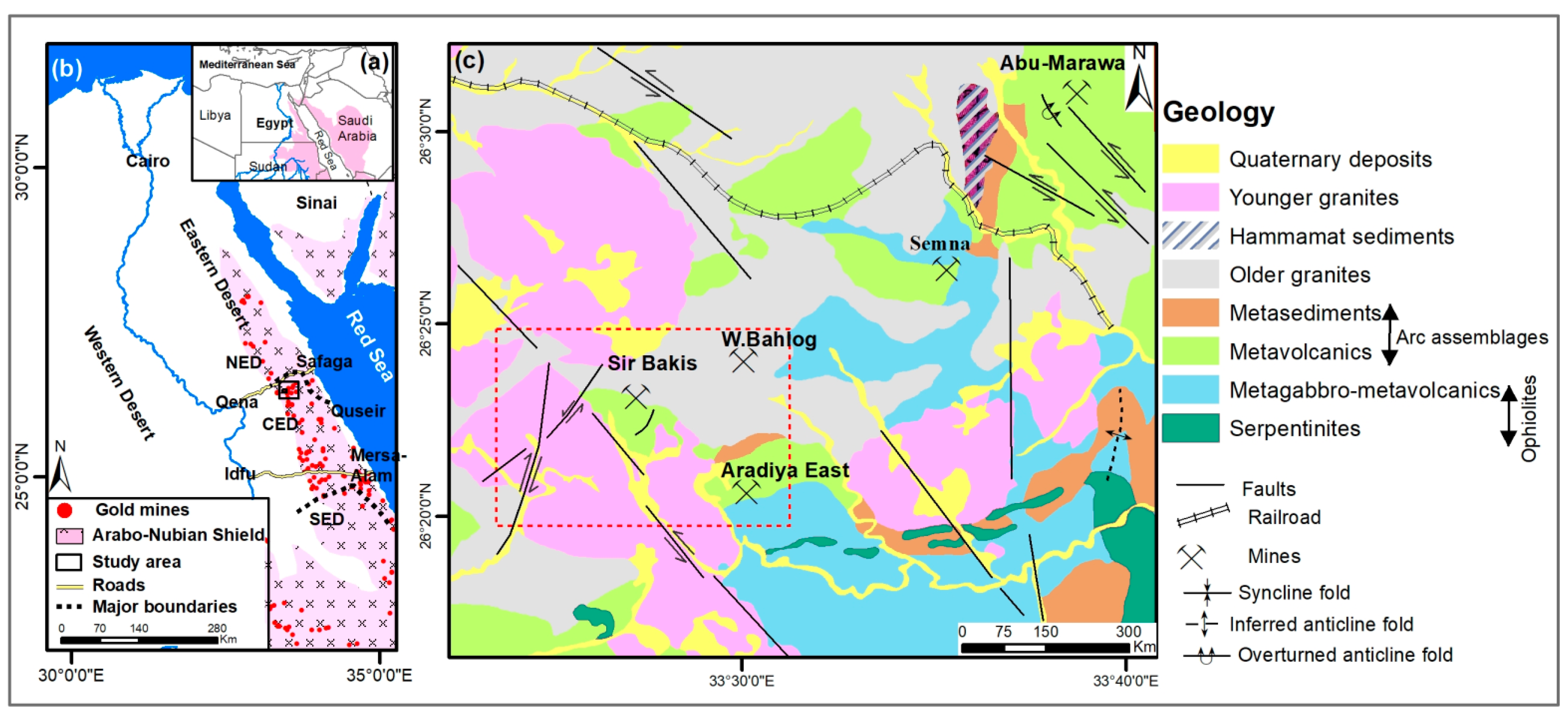
2. Study Area
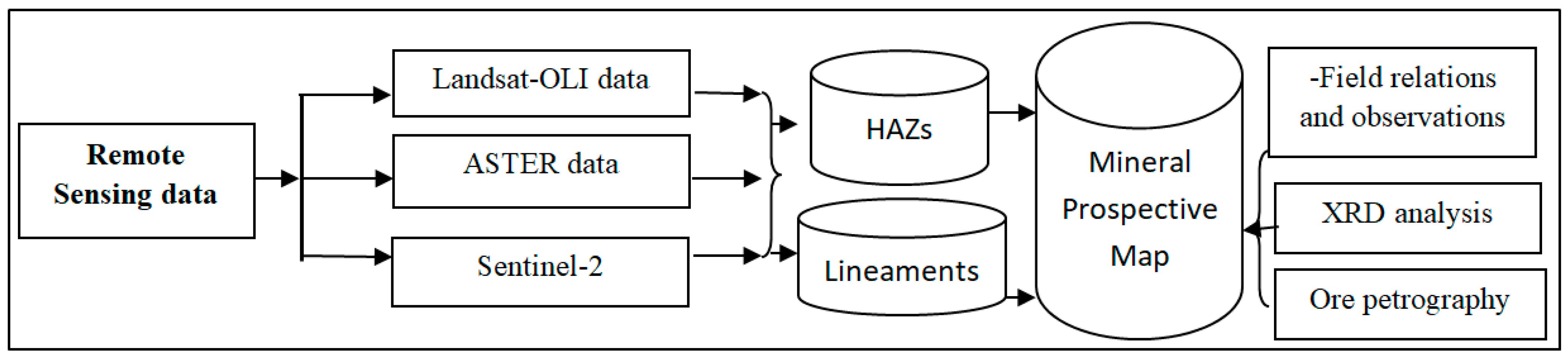
3. Analytical Techniques
3.1. Remote Sensing Techniques
3.2. Field and Lab Analysis
4. Results
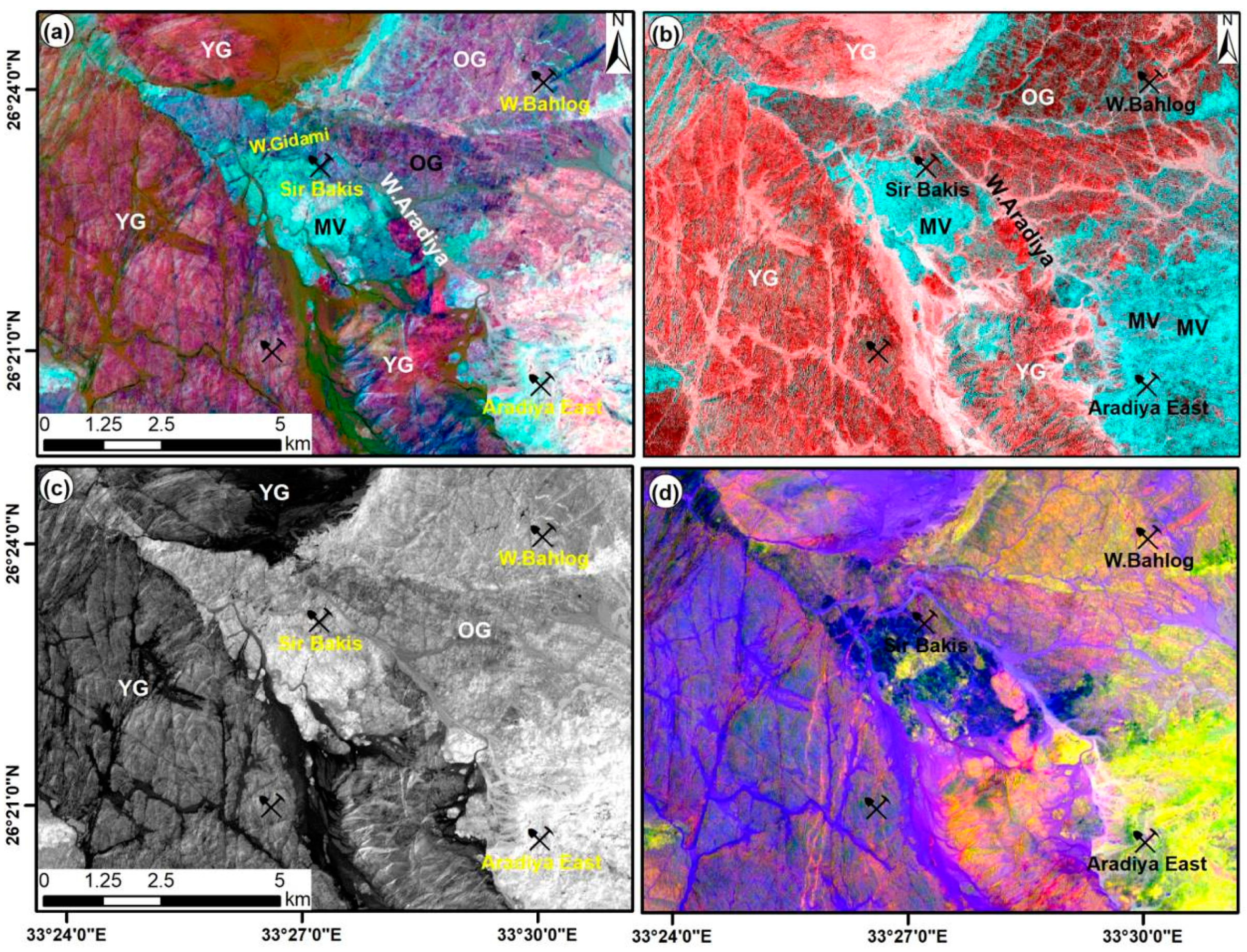
4.1. Lithologic Characteristics
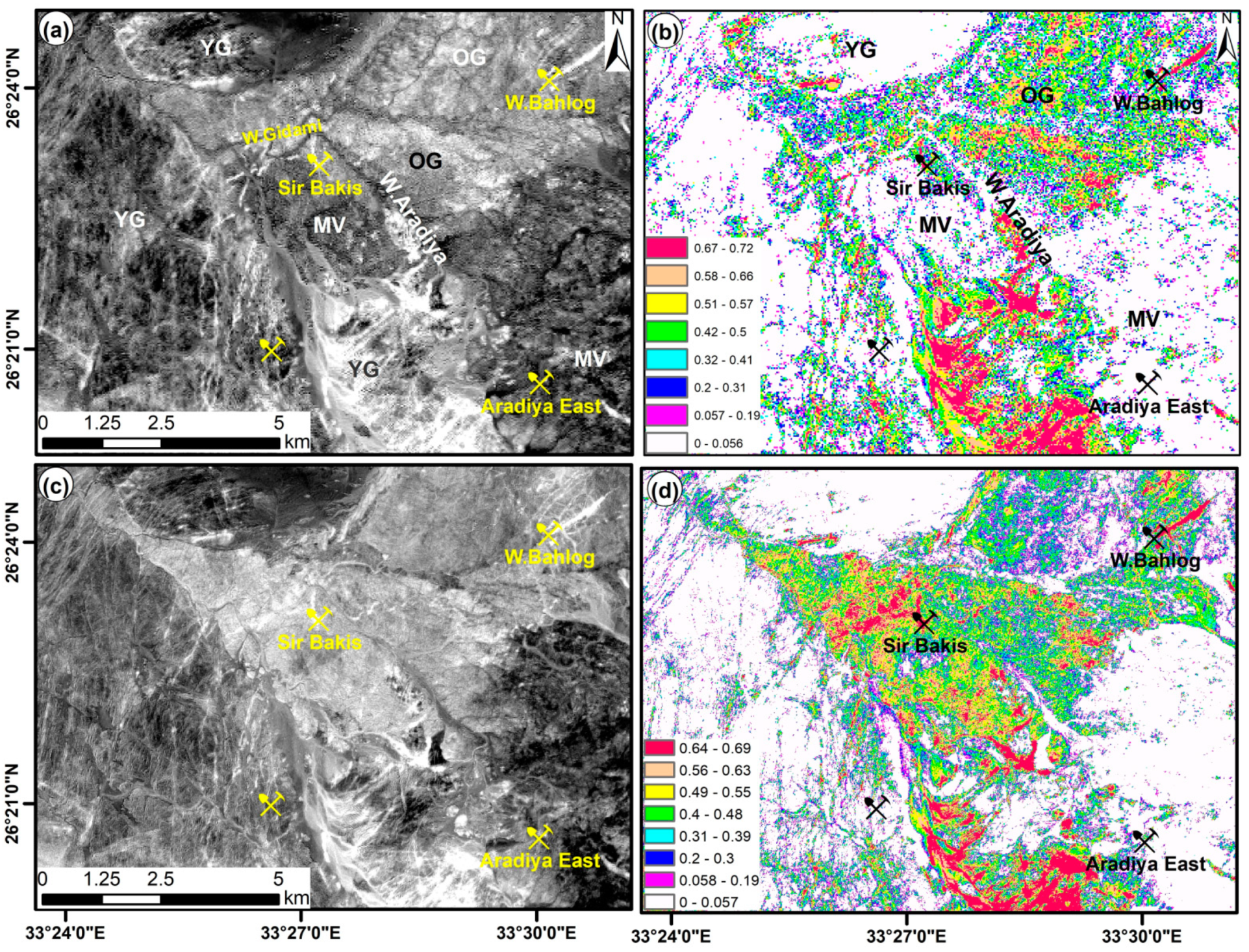
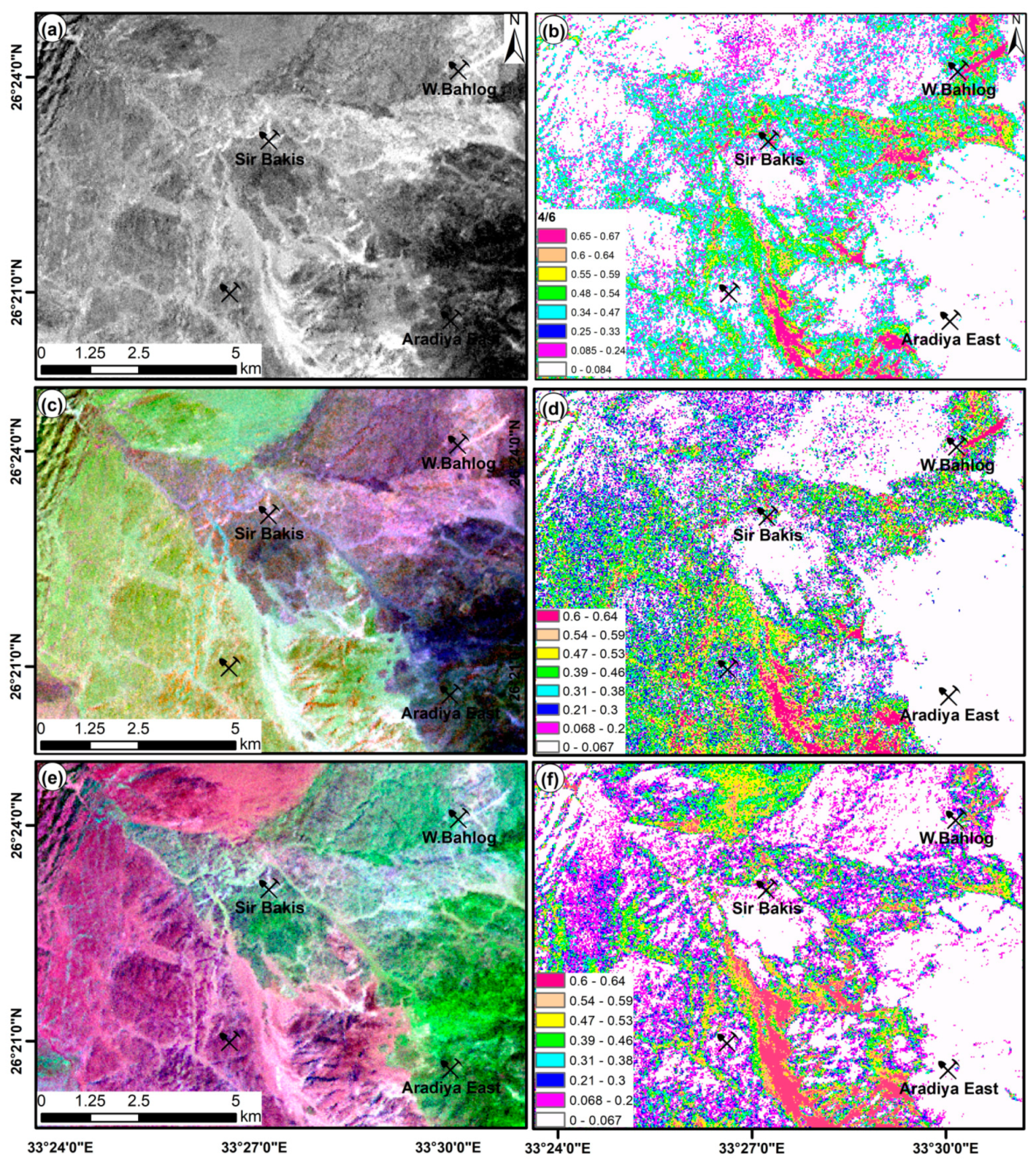
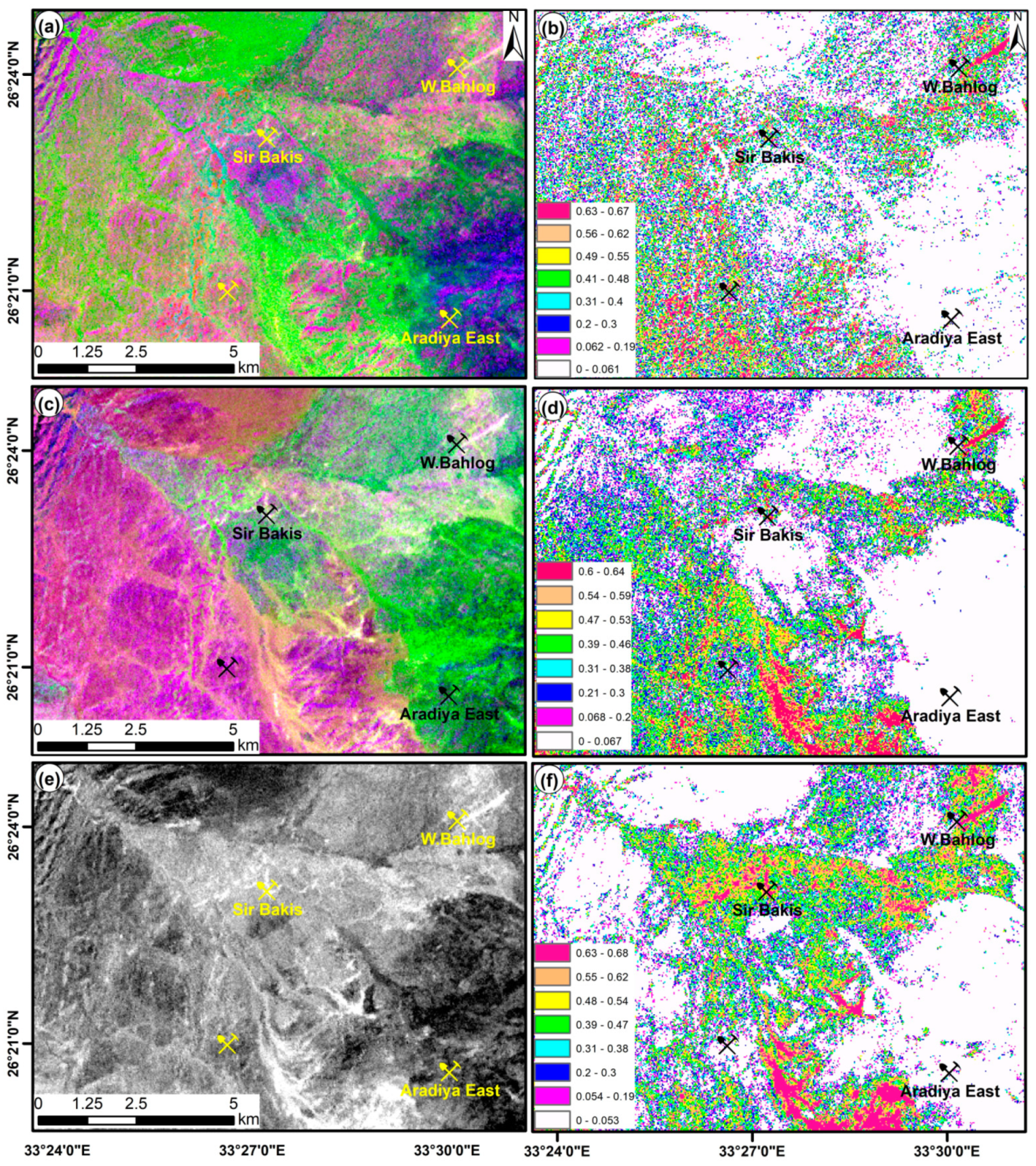
4.2. Hydrothermal Alteration Maps and Mineralization
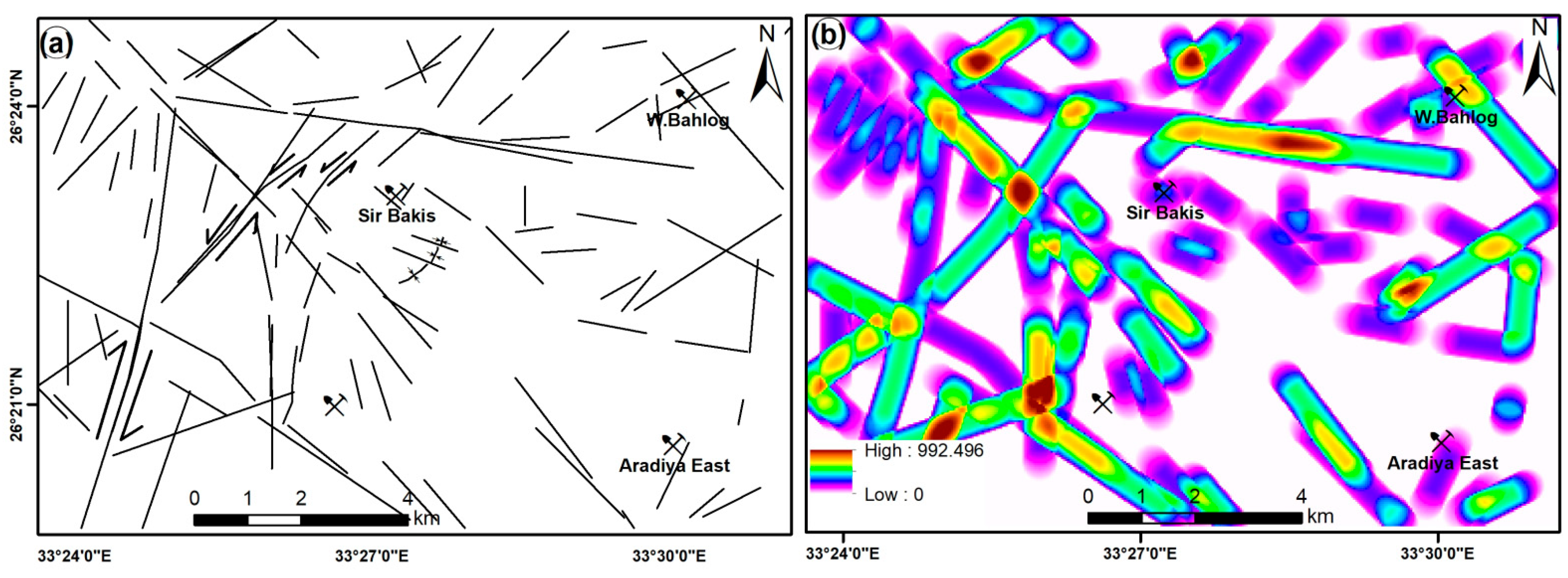
4.3. Lineaments
4.4. Mineral Prospective Map (MPM)
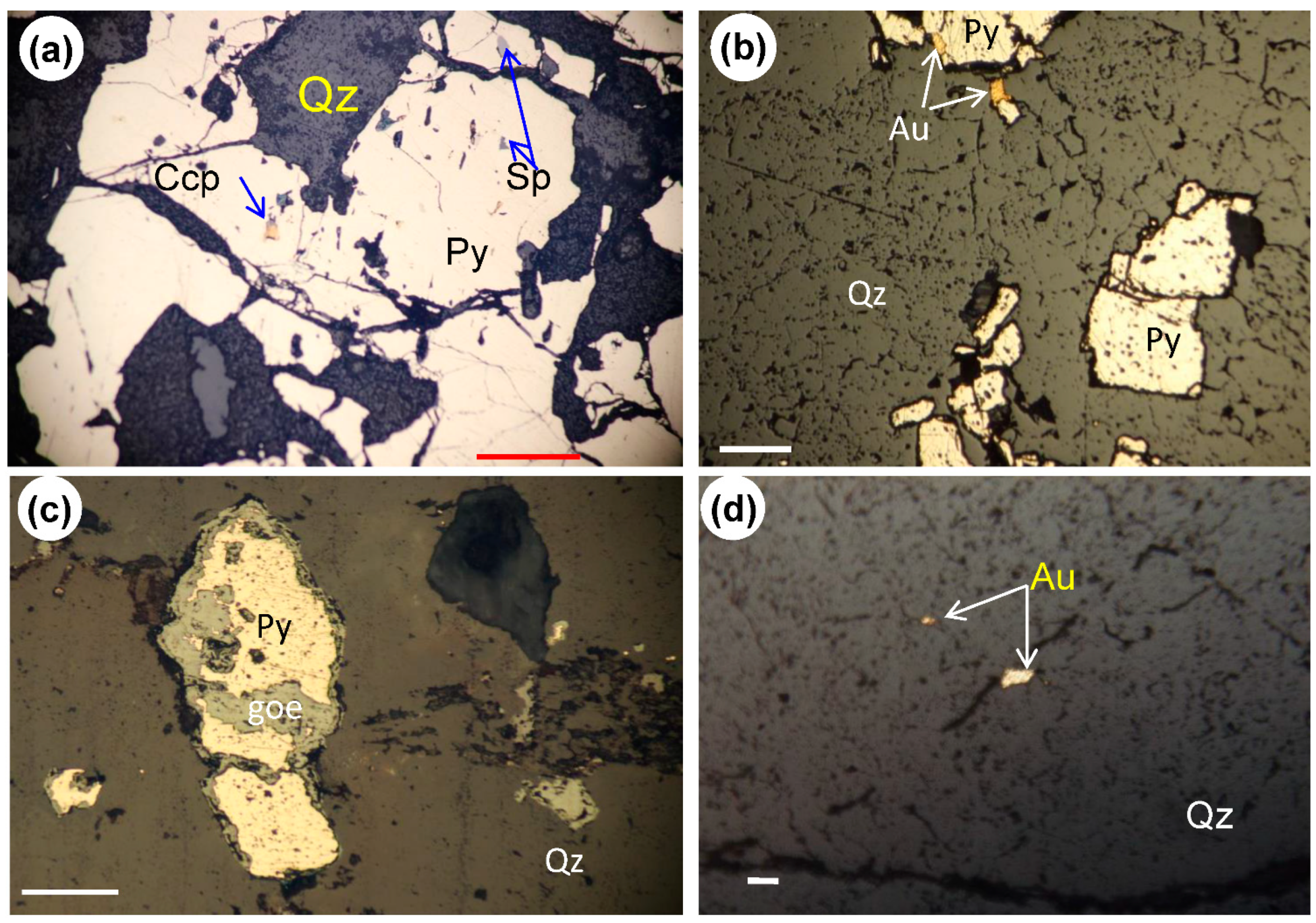
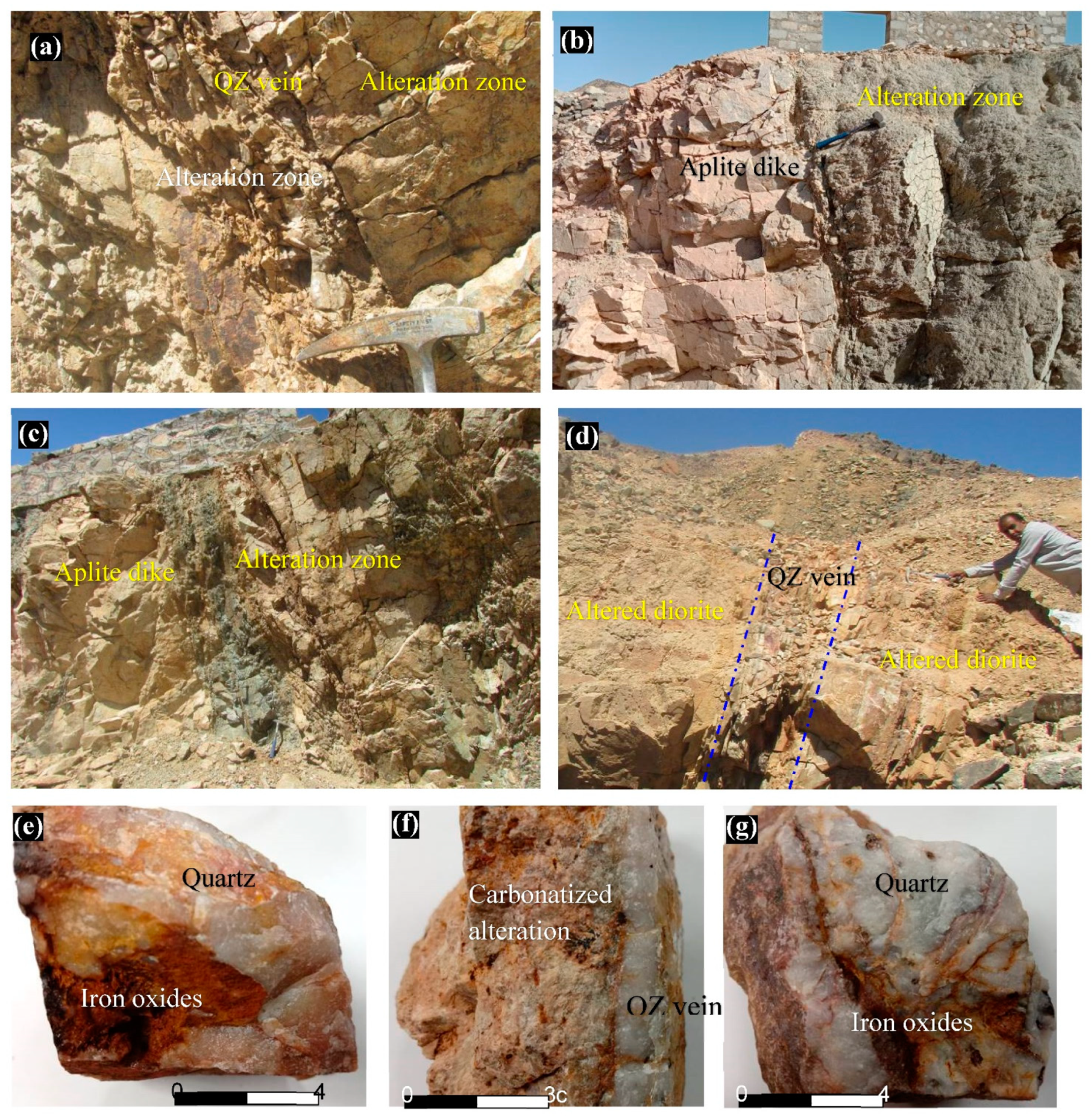
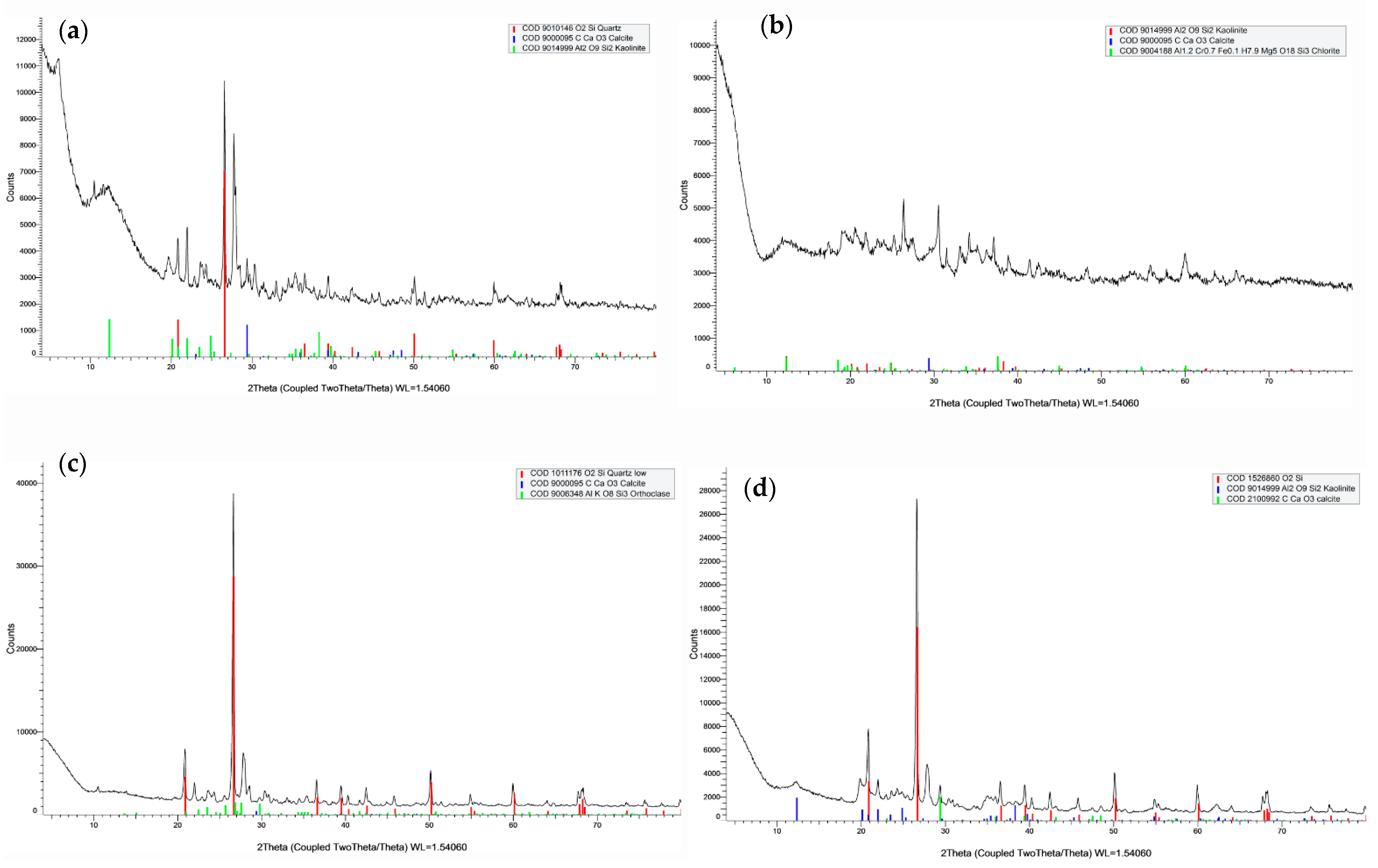
4.5. Field Validation and Laboratory Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdelkareem, M.; Kamal El-Din, G.M.; Osman, I. An integrated approach for mapping mineral resources in the Eastern Desert of Egypt. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 73, 682–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Al-Arifi, N.; Abdelkareem, M.; Abdalla, F. Application of remote sensing and GIS techniques for exploring potential areas of hydrothermal mineralization in the central Eastern Desert of Egypt. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowan, L.C.; Hook, S.J.; Abrams, M.J.; Mars, J.C. Mapping Hydrothermally Altered Rocks at Cuprite, Nevada, Using the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), a New Satellite-Imaging System. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazand, K.; Sarvestani, J.F.; Ravasan, M.R.S. Hydrothermal Alteration Mapping Using ASTER Data for Reconnaissance Porphyry Copper Mineralization in the Ahar Area, NW Iran. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2013, 41, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Hashim, M. The application of ASTER remote sensing data to porphyry copper and epithermal gold deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, M.; Maghsoudi, A.; Pour, A.B. Application of Landsat-8 and ASTER satellite remote sensing data for porphyry copper exploration: A case study from Shahr-e-Babak, Kerman, south of Iran. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 1186–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, S.; Khakzad, A.; Afzal, P. Application of stepwise weight assessment ratio analysis (SWARA) for copper prospectivity mapping in the Anarak region, central Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zhou, K. Mineral prospectivity mapping with weights of evidence and fuzzy logic methods. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 29, 2639–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkareem, M.; El-Baz, F. Characterizing hydrothermal alteration zones in Hamama area in the central Eastern Desert of Egypt by remotely sensed data. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 1307–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockwell, B.W.; Hofstra, A.H. Identification of quartz and carbonate minerals across northern Nevada using ASTER thermal infrared emissivity data—Implications for geologic mapping and mineral resource investigations in well-studied and frontier areas. Geosphere 2008, 4, 218–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, A.B.; Park, T.Y.S.; Park, Y.; Hong, J.K.; Zoheir, B.; Pradhan, B.; Ayoobi, I.; Hashim, M. Application of Multi-Sensor Satellite Data for Exploration of Zn–Pb Sulfide Mineralization in the Franklinian Basin, North Greenland. Remote. Sens. 2018, 10, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, S.; Nasir, S. Characterization of ASTER spectral bands for mapping of alteration zones of volcanogenic massive sulphide deposits. Ore Geol. Rev. 2017, 88, 317–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurata, K.; Yamaguchi, Y. Integration and Visualization of Mineralogical and Topographical Information Derived from ASTER and DEM Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, H.; Rasouli, A.A.; Babaei, K. Using SWIR bands From ASTER for discrimination of hydrothermal alterated mineral in the northwest of Iran (SE Sanadaj city); a key for exploration of copper and gold mineralization. Res. J. Appl. Sci. 2007, 2, 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Azizi, H.; Tarverdi, M.A.; Akbarpour, A. Extraction of hydrothermal alterations from ASTER SWIR data from east Zanjan, northern Iran. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pazner, M.; Duke, N. Lithologic and mineral information extraction for gold exploration using ASTER data in the south Chocolate Mountains (California). ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2007, 62, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrino, T.A.; Crósta, A.P.; Toledo, C.L.B.; Silva, A.M. Hyperspectral remote sensing applied to mineral exploration in southern Peru: A multiple data integration approach in the Chapi Chiara gold prospect. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 64, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yi, G.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Zhong, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bie, X. Integrating Data of ASTER and Landsat-8 OLI (AO) for Hydrothermal Alteration Mineral Mapping in Duolong Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit, Tibetan Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouki, S.M.; Ramazi, H.R.; Maghsoudi, A.; Pour, A.B.; Sohrabi, G. A Remote Sensing-Based Application of Bayesian Networks for Epithermal Gold Potential Mapping in Ahar-Arasbaran Area, NW Iran. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crósta, A.P.; De Souza Filho, C.R.; Azevedo, F.; Brodie, C. Targeting key alteration minerals in epithermal deposits in Patagonia, Argentina, using ASTER imagery and principal component analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4233–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, Y. A stabilized vegetation index and several mineralogic indices defined for ASTER VNIR and SWIR data. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 1552–1554. [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya, Y. Advanced remote lithologic mapping in ophiolite zone with ASTER multispectral thermal infrared data. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 1561–1563. [Google Scholar]
- Son, Y.S.; Kim, K.E.; Yoon, W.J.; Cho, S.J. Regional mineral mapping of island arc terranes in southeastern Mongolia using multi-spectral remote sensing data. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 113, 103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.R.; Wilkinson, L.; Heather, K.; Fumerton, S.; Bernier, M.A.; Ayer, J.; Dahn, R. Application of GIS Processing Techniques for Producing Mineral Prospectivity Maps—A Case Study: Mesothermal Au in the Swayze Greenstone Belt, Ontario, Canada. Nat. Resour. Res. 2001, 10, 91–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, A.; Porwal, A.; McCuaig, T.C.; Chudasama, B.; Dentith, M.C.; Aitken, A.R.A. Mineral systems approach applied to GIS-based 2D-prospectivity modelling of geological regions: Insights from Western Australia. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 673–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Chen, F.; Zhong, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y. GIS-based mineral prospectivity mapping using machine learning methods: A case study from Tongling ore district, eastern China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2019, 109, 26–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.D.; Souza, S.M.d.; Sordi, D.A.d.; Tavares, F.M.; Klein, E.; Lopes, E.C.d.S. Predictive Mapping of Prospectivity in the Gurupi Orogenic Gold Belt, Nort–Northeast Brazil: An Example of District-Scale Mineral System Approach to Exploration Targeting. Nat. Resour. Res. 2017, 26, 509–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Klemm, R.; Murr, A. Gold of the Pharaohs—6000 years of gold mining in Egypt and Nubia. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2001, 33, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, A. Genesis of gold mineralization of Fatria, Gidami, Atalla and Hangaliya, Eastern Desert of Egypt. Münchner Geol. Hefte 1999, 27, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Conoco. Geological Map of Egypt, Scale 1:500,000; The Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation: Cairo, Egypt, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werff, H.; Van der Meer, F. Sentinel-2A MSI and Landsat 8 OLI Provide Data Continuity for Geological Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, M.J.; Brown, D.; Lepley, L.; Sadowski, R. Remote sensing for porphyry copper deposits in southern Arizona. Econ. Geol. 1983, 78, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estornell, J.; Martí-Gavilá, J.M.; Sebastiá, M.T.; Mengual, J. Principal component analysis applied to remote sensing. Model. Sci. Educ. Learn. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.A. Remote Sensing Digital Image Analysis: An Introduction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1986; p. 297. [Google Scholar]
- Kashani, S.B.M.; Abedi, M.; Norouzi, G.H. Fuzzy logic mineral potential mapping for copper exploration using multi-disciplinary geo-datasets, a case study in seridune deposit, Iran. Earth Sci. Inform. 2016, 9, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, J.; Tsoukalas, L.H.; Uhrig, R.E. MATLAB Supplement to Fuzzy and Neural Approaches in Engineering; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Zhao, J.; Sui, Y.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Z. Application of Knowledge-Driven Methods for Mineral Prospectivity Mapping of Polymetallic Sulfide Deposits in the Southwest Indian Ridge between 46° and 52°E. Minerals 2020, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.; Cheng, Q.; Jing, L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, M.; Ding, H. Assessment of the Capability of Sentinel-2 Imagery for Iron-Bearing Minerals Mapping: A Case Study in the Cuprite Area, Nevada. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosta, A.P.; Moore, J.M. Enhancement of Landsat Themetic Mapper Imagery for Residual Soil Mapping in SW Minas Gerais State, Brazil: A Prospecting Case History in Greenstone Belt Terrain. In Proceedings of the 7th Thematic Conference on Remote Sensing for Exploration Geology, Calgary, AL, Canada, 1 October 1989; pp. 1173–1187. [Google Scholar]
- Crosta, A.P.; Rabelo, A. Assessing of Landsat TM for hydrothermal alteration mapping in central western Brazil. In Proceedings of the Ninth Thematic Conference Geologic Remote Sensing, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–11 February 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Amuda, O.S.; Adebisi, S.; Jimoda, L.; Alade, A. Challenges and Possible Panacea to 349 the Municipal Solid Wastes Management in Nigeria. J. Sust. Dev. Stud. 2014, 6, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Poormirzaee, R.; Oskouei, M.M. Use of spectral analysis for detection of alterations in ETM data, Yazd, Iran. Appl. Geomat. 2010, 2, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Testa, F.J.; Villanueva, C.; Cooke, D.R.; Zhang, L. Lithological and Hydrothermal Alteration Mapping of Epithermal, Porphyry and Tourmaline Breccia Districts in the Argentine Andes Using ASTER Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedini, E. Mineral mapping in the Kap Simpson complex, central East Greenland, using HyMap and ASTER remote sensing data. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 60–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrich, R.; La Tour, T.E.; Willmore, L. Fluid participation in deep fault zones: Evidence from geological, geochemical, and 18O/16O relations. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 1984, 89, 4331–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, R.H. Fluid Flow Accompanying Faulting: Field Evidence and Models. Earthq. Predictionpp. 1981, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerrich, R.; Watson, J.V.; Reading, H.G.; Watterson, J.; White, S.J.; Reading, H.G.; Watterson, J.; White, S.H. Fluid transport in lineaments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1986, 317, 219–251. [Google Scholar]
- Arribas, J.A. Characteristics of high-sulfidation epithermal deposits, and their relation to magmatic fluid. In Magma, Fluid, and Ore Deposits; Jambor, J.L., Ed.; Mineral Assoc Canada Short Course: Quebec, QC, Canada, 1995; pp. 419–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldon, H.A.; Ord, A. Evolution of porosity, permeability and fluid pressure in dilatant faults pos” failure: Implications for fluid flow and mineralization. Geofluids 2005, 5, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabins, F.F. Remote sensing for mineral exploration. Ore Geol. Rev. 1999, 14, 157–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Arifi, N.; El-Din, G.K.; Abdelkareem, M.; Abdalla, F. Integration of remote-sensing, structural, and geochemical data for characterizing granitoid rocks in Um Naggat pluton, Central Eastern Desert, Egypt. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekandari, M.; Masoumi, I.; Pour, A.B.; Muslim, A.M.; Rahmani, O.; Hashim, M.; Zoheir, B.; Pradhan, B.; Misra, A.; Aminpour, S.M. Application of Landsat-8, Sentinel-2, ASTER and WorldView-3 Spectral Imagery for Exploration of Carbonate-Hosted Pb-Zn Deposits in the Central Iranian Terrane (CIT). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yajima, T. ASTER Data Analysis Applied to Mineral Resource Exploration and Geological Mapping; Nagoya University: Nagoya, Japan, 2014; p. 77. [Google Scholar]
- Cudahy, T.J.; Jones, M.; Thomas, M.; Laukamp, C.; Caccetta, M.; Hewson, R.D.; Rodger, A.D.; Verrall, M. Next Generation Mineral Mapping: Queensland Airborne HyMap and Satellite ASTER Surveys, 2006-2008; CSIRO Exploration and Mining: Canberra, Australia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cudahy, T.J. Satellite ASTER Geoscience Product Notes South Australia. Res. Publ. Repos. 2012, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, R.; Robson, D.; Mauger, A.; Cudahy, T.; Thomas, M.; Jones, S. Using the Geoscience Australia-CSIRO ASTER maps and airborne geophysics to explore Australian geoscience. J. Spat. Sci. 2015, 60, 207–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdevar, M.R.; Ketabi, P.; Saadatkhah, N.; Rahnamarad, J.; Mohammadi, S.S. Application of ASTER SWIR data on detection of alteration zone in the Sheikhabad area, eastern Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 5909–5919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Carranza, E.J.M.; Wang, H. Evaluation of uncertainty in mineral prospectivity mapping due to missing evidence: A case study with skarn-type Fe deposits in Southwestern Fujian Province, China. Ore Geol. Rev. 2015, 71, 502–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, P.; Khakzad, A.; Moarefvand, P.; Omran, N.R.; Esfandiari, B.; Alghalandis, Y.F. Geochemical anomaly separation by multifractal modeling in Kahang (Gor Gor) porphyry system, Central Iran. J. Geochem. Explor. 2010, 104, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, L. Quantifying Hydrothermal Alteration: A Review of Methods. Geosciences 2018, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Eigenvector | Band 2 | Band 5 | Band 6 | Band 7 | Eigenvalue % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.143 | 0.552 | 0.627 | 0.532 | 96.540 |
| PC2 | 0.178 | 0.737 | −0.151 | −0.635 | 2.560 |
| PC3 | 0.417 | 0.203 | −0.716 | 0.522 | 0.592 |
| PC4 | 0.880 | −0.334 | 0.268 | −0.206 | 0.308 |
| Eigenvector | Band 2 | Band 3 | Band 4 | Band 8 | Band 11 | Band 12 | Eigenvalue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | −0.434 | −0.433 | −0.430 | −0.429 | −0.356 | −0.358 | 91.698 |
| PC2 | 0.259 | 0.256 | 0.249 | 0.245 | −0.611 | −0.610 | 8.220 |
| PC3 | 0.586 | 0.324 | −0.308 | −0.620 | −0.184 | 0.195 | 0.076 |
| PC4 | 0.167 | 0.103 | −0.136 | −0.136 | 0.681 | −0.678 | 0.004 |
| PC5 | 0.470 | −0.424 | −0.569 | 0.523 | −0.030 | 0.030 | 0.001 |
| PC6 | 0.390 | −0.672 | 0.562 | −0.281 | 0.032 | −0.031 | 0.000 |
| Eigenvector | Band 4 | Band 5 | Band 6 | Eigenvalue % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | 0.943 | 0.226 | 0.242 | 99.34 |
| PC2 | 0.330 | −0.568 | −0.754 | 0.59 |
| PC3 | 0.033 | −0.791 | 0.611 | 0.07 |
| Prospective Zone | Rank | Area % |
|---|---|---|
| Very low | 0 to 0.086 | 95.32 |
| Low | 0.087 to 0.24 | 1.20 |
| Moderate | 0.25 to 0.36 | 0.82 |
| Good | 0.37 to 0.46 | 1.05 |
| Very good | 0.47 to 0.55 | 1.02 |
| Excellent | 0.56 to 0.71 | 0.59 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelkareem, M.; Al-Arifi, N. Synergy of Remote Sensing Data for Exploring Hydrothermal Mineral Resources Using GIS-Based Fuzzy Logic Approach. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224492
Abdelkareem M, Al-Arifi N. Synergy of Remote Sensing Data for Exploring Hydrothermal Mineral Resources Using GIS-Based Fuzzy Logic Approach. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(22):4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224492
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelkareem, Mohamed, and Nassir Al-Arifi. 2021. "Synergy of Remote Sensing Data for Exploring Hydrothermal Mineral Resources Using GIS-Based Fuzzy Logic Approach" Remote Sensing 13, no. 22: 4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224492
APA StyleAbdelkareem, M., & Al-Arifi, N. (2021). Synergy of Remote Sensing Data for Exploring Hydrothermal Mineral Resources Using GIS-Based Fuzzy Logic Approach. Remote Sensing, 13(22), 4492. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13224492





