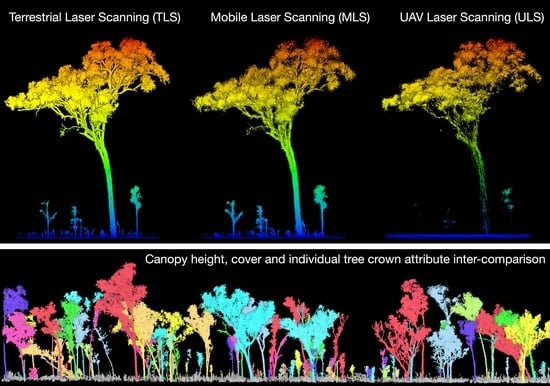
Leveraging TLS as a Calibration and Validation Tool for MLS and ULS Mapping of Savanna Structure and Biomass at Landscape-Scales
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Are there significant differences in the representation of woody canopy height and cover captured by TLS, MLS and ULS?
- How reliably can tree stem DBH and above-ground woody biomass be mapped from TLS, MLS and ULS?
2. Materials and Methods
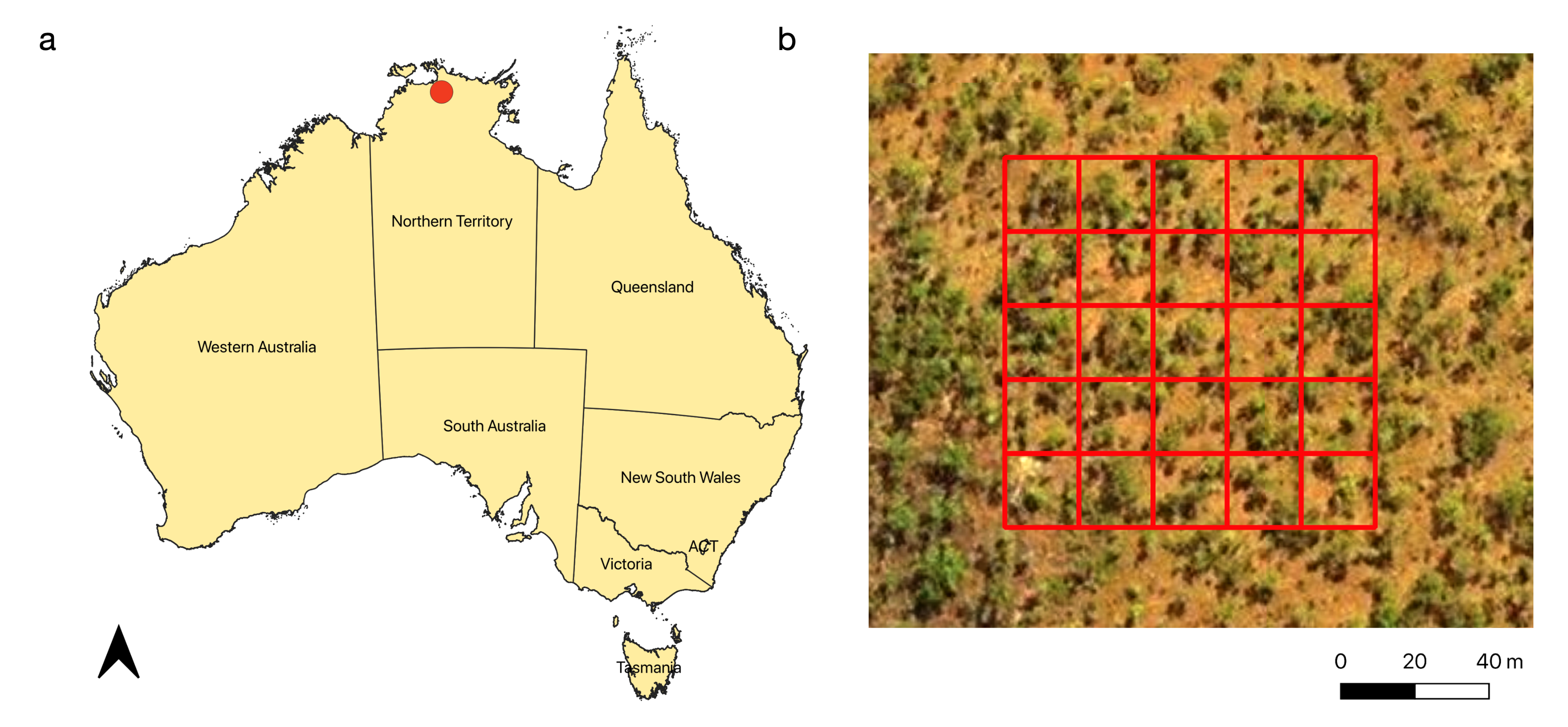
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Field Inventory
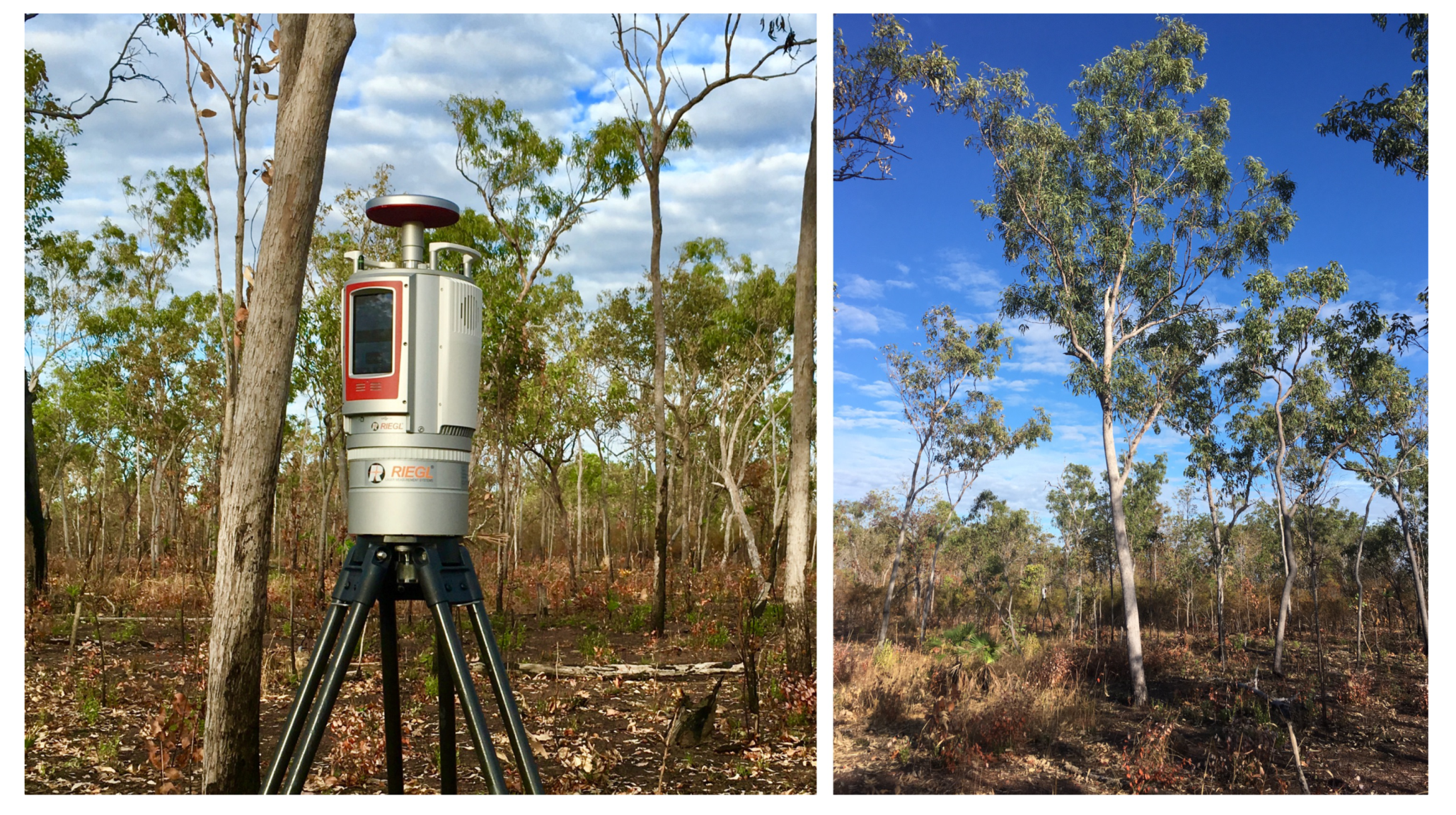
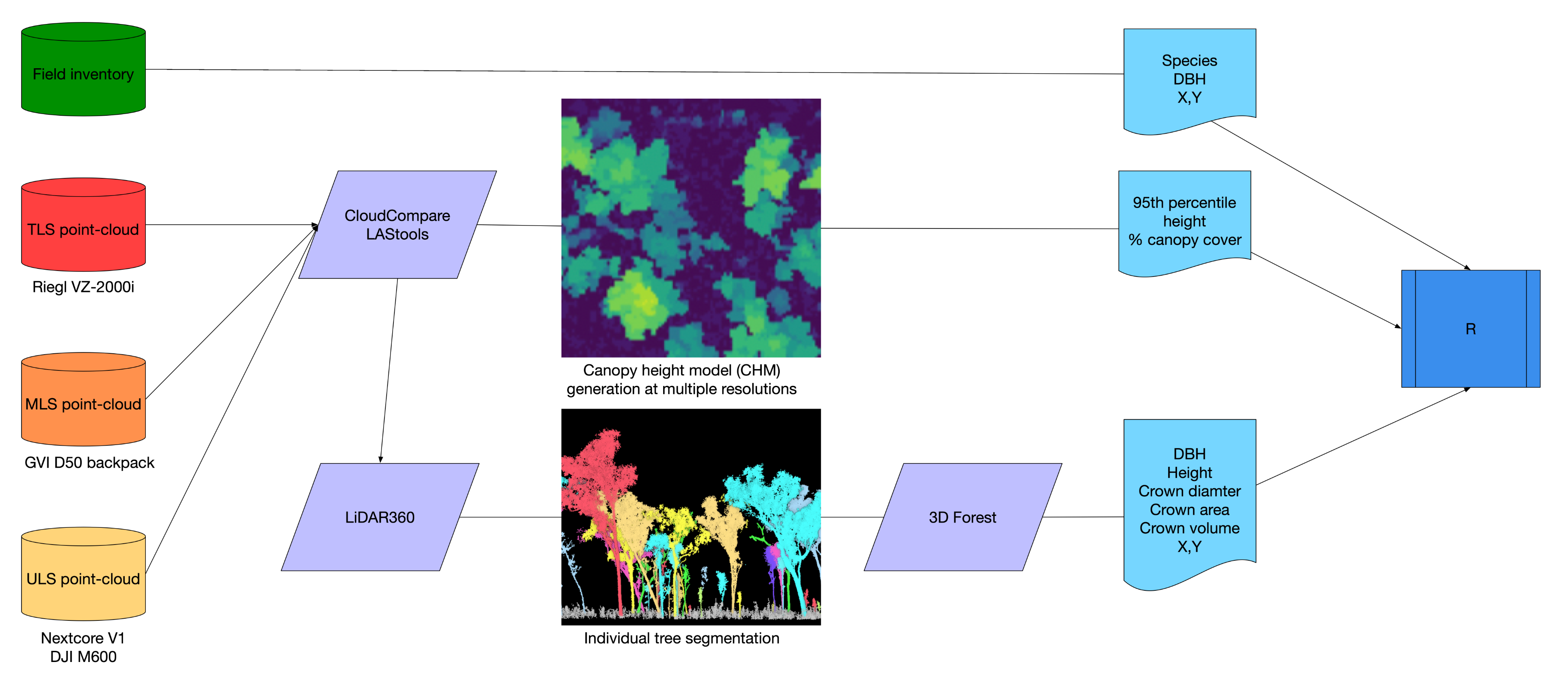
2.3. Laser Scanning
2.4. Point-Cloud Processing
2.5. Structural Analysis
2.5.1. Canopy Characterization
2.5.2. Individual Tree Delineation and Measurement
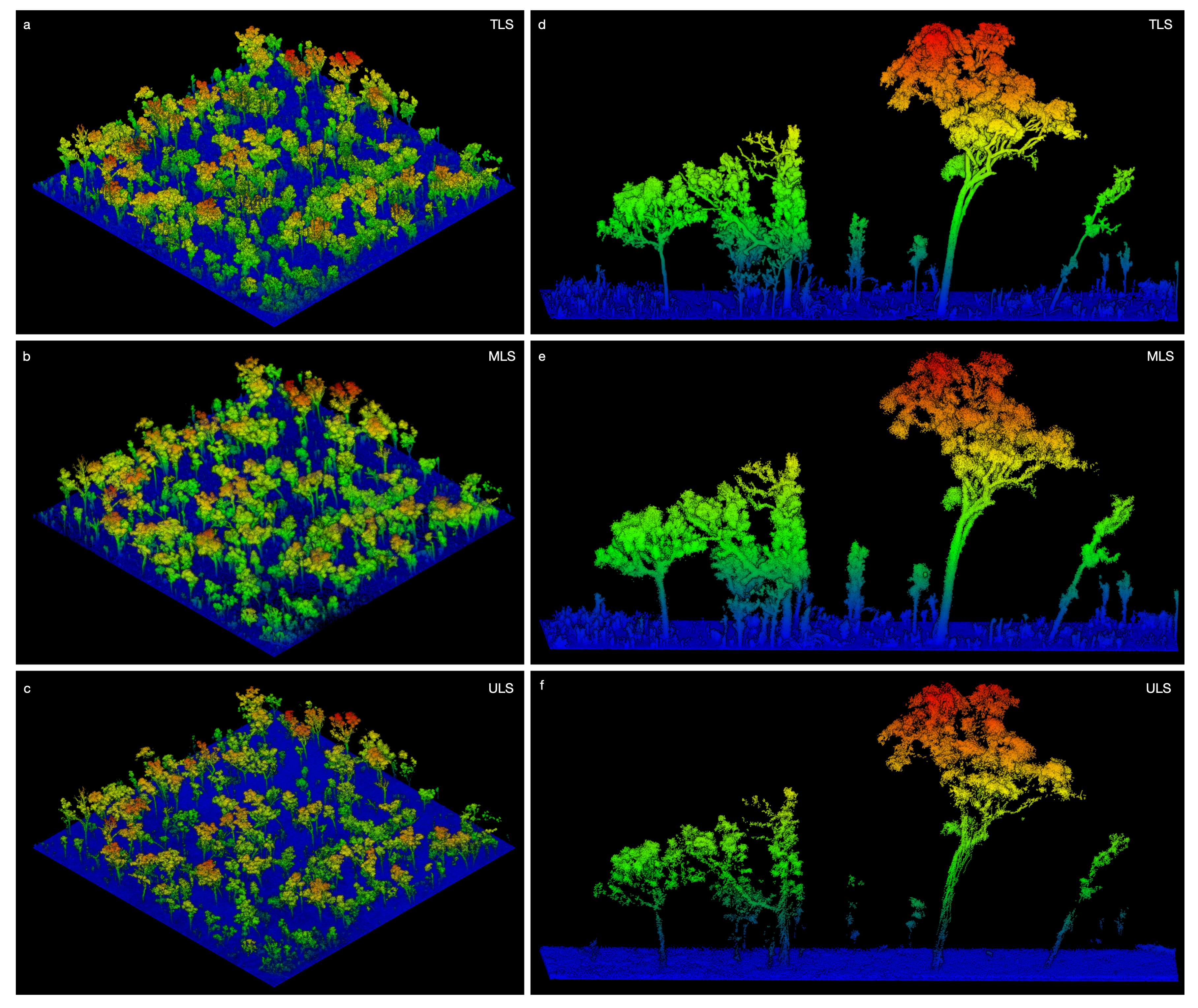
3. Results
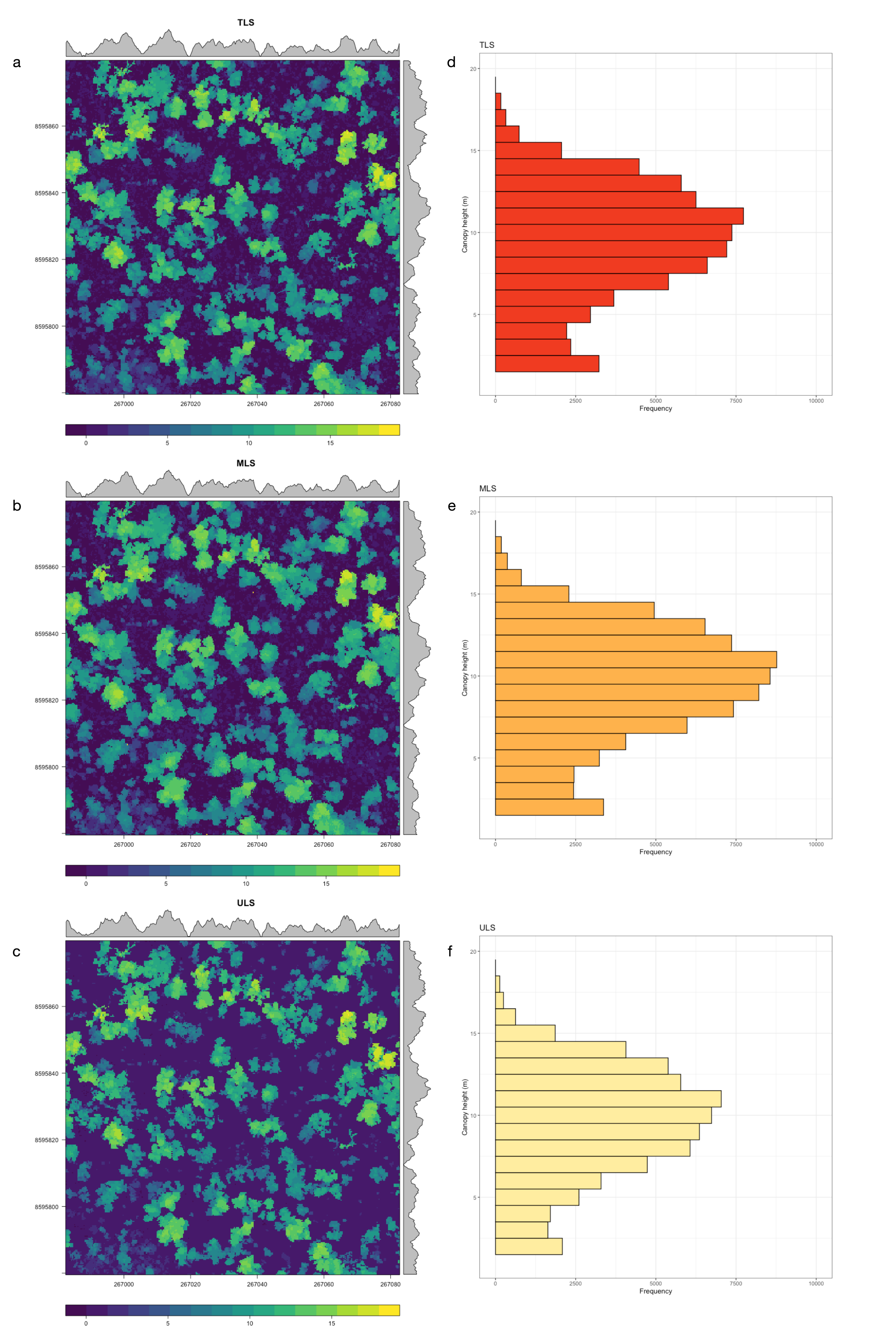
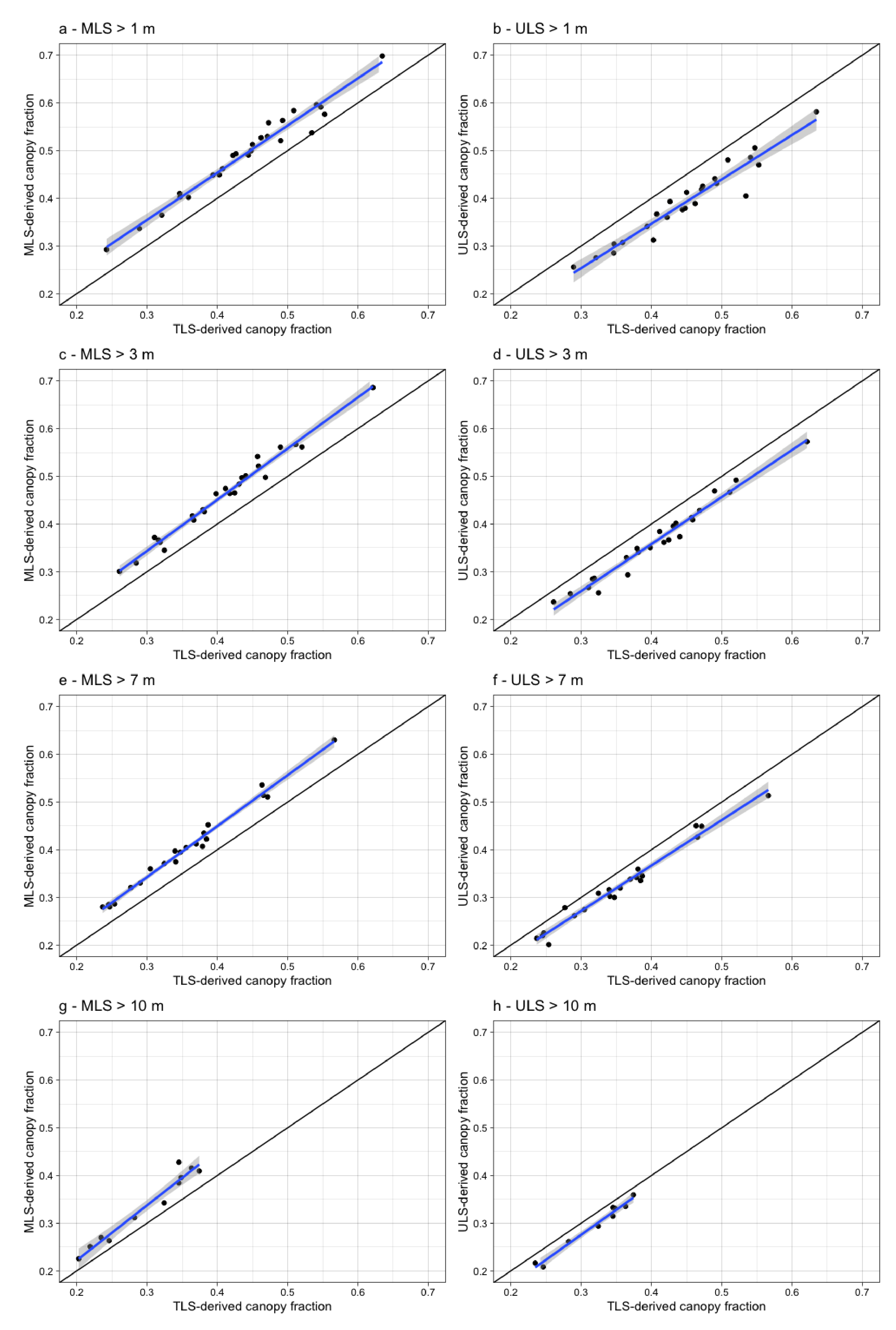
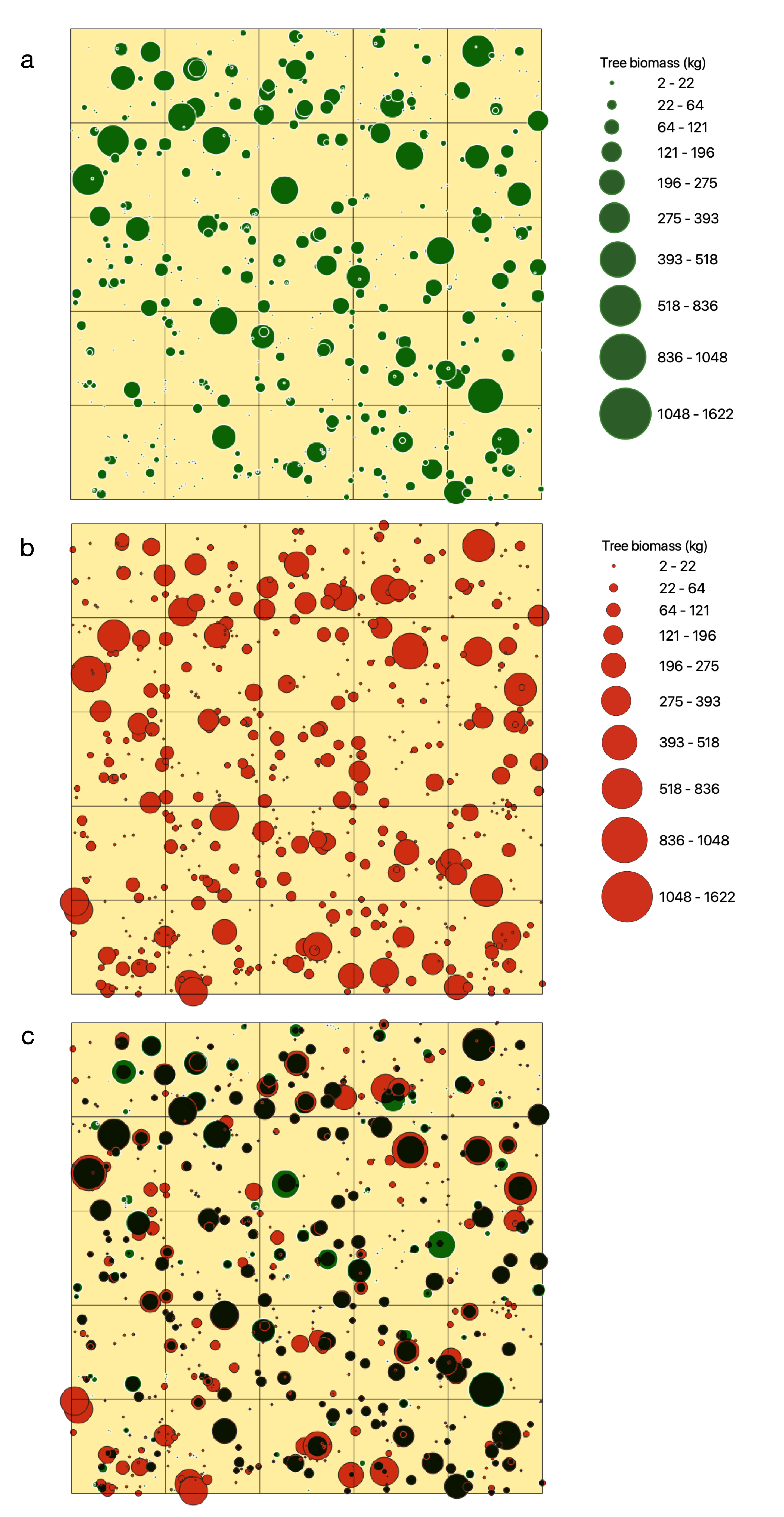
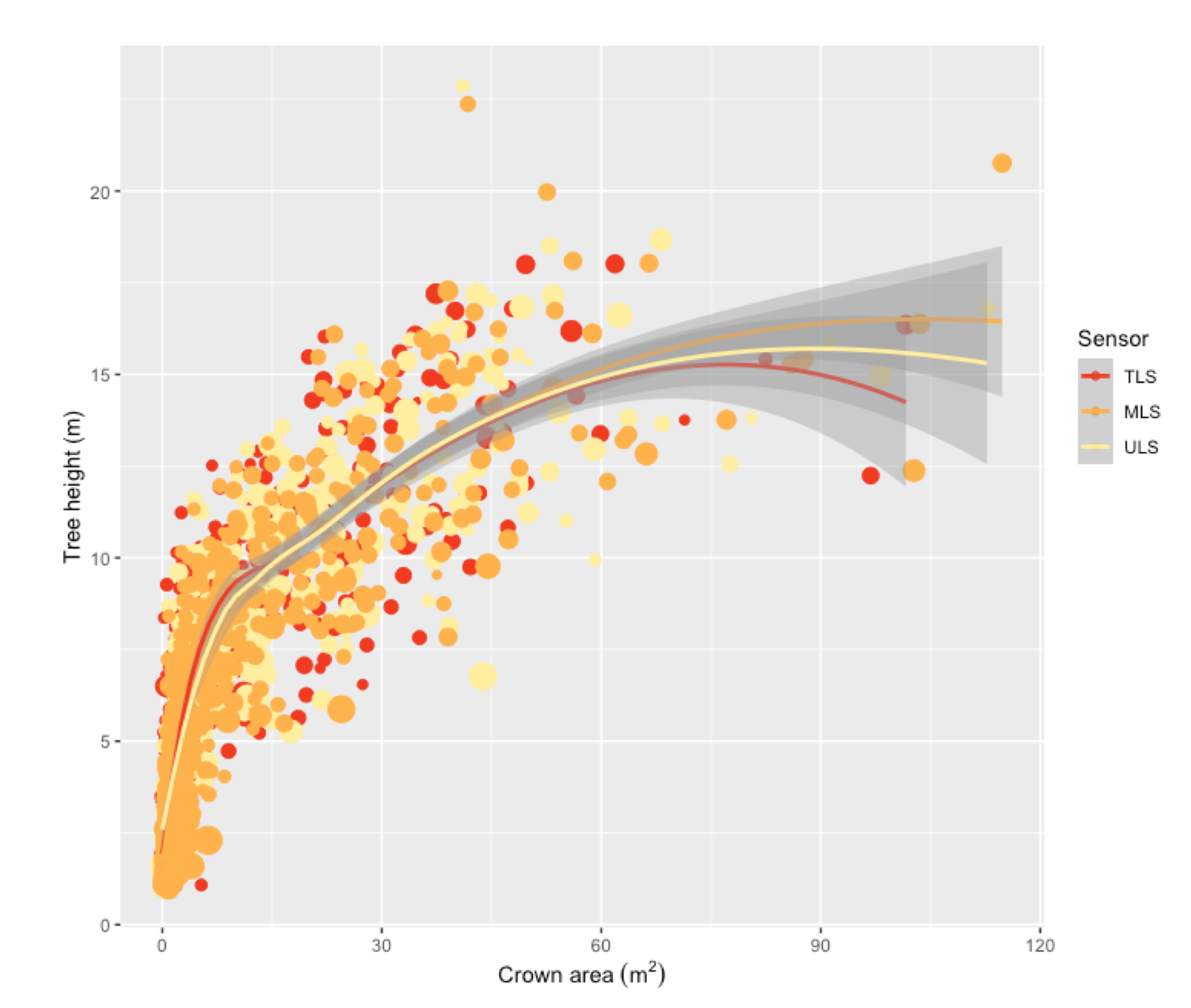
3.1. Woody Canopy Characterization
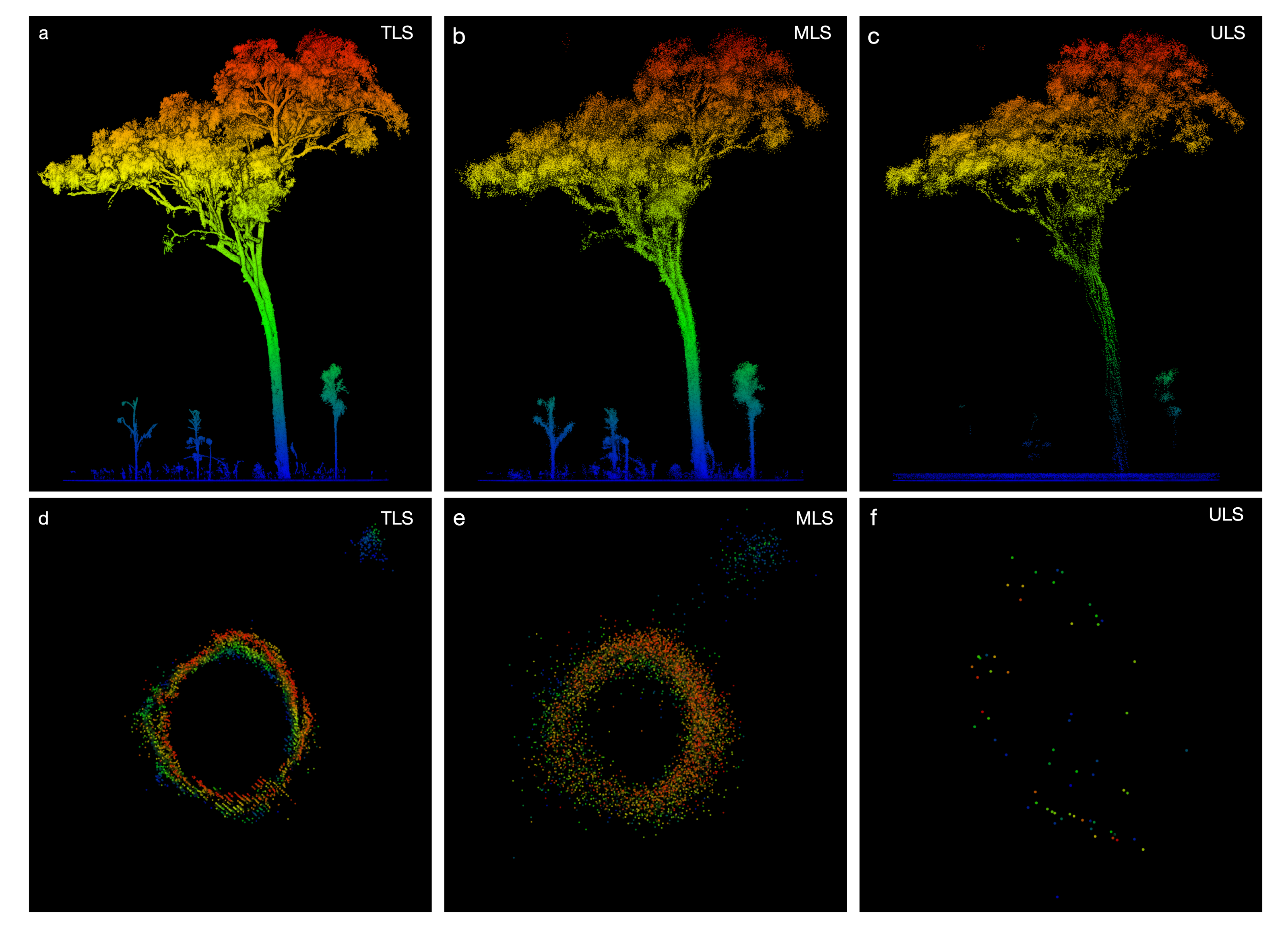
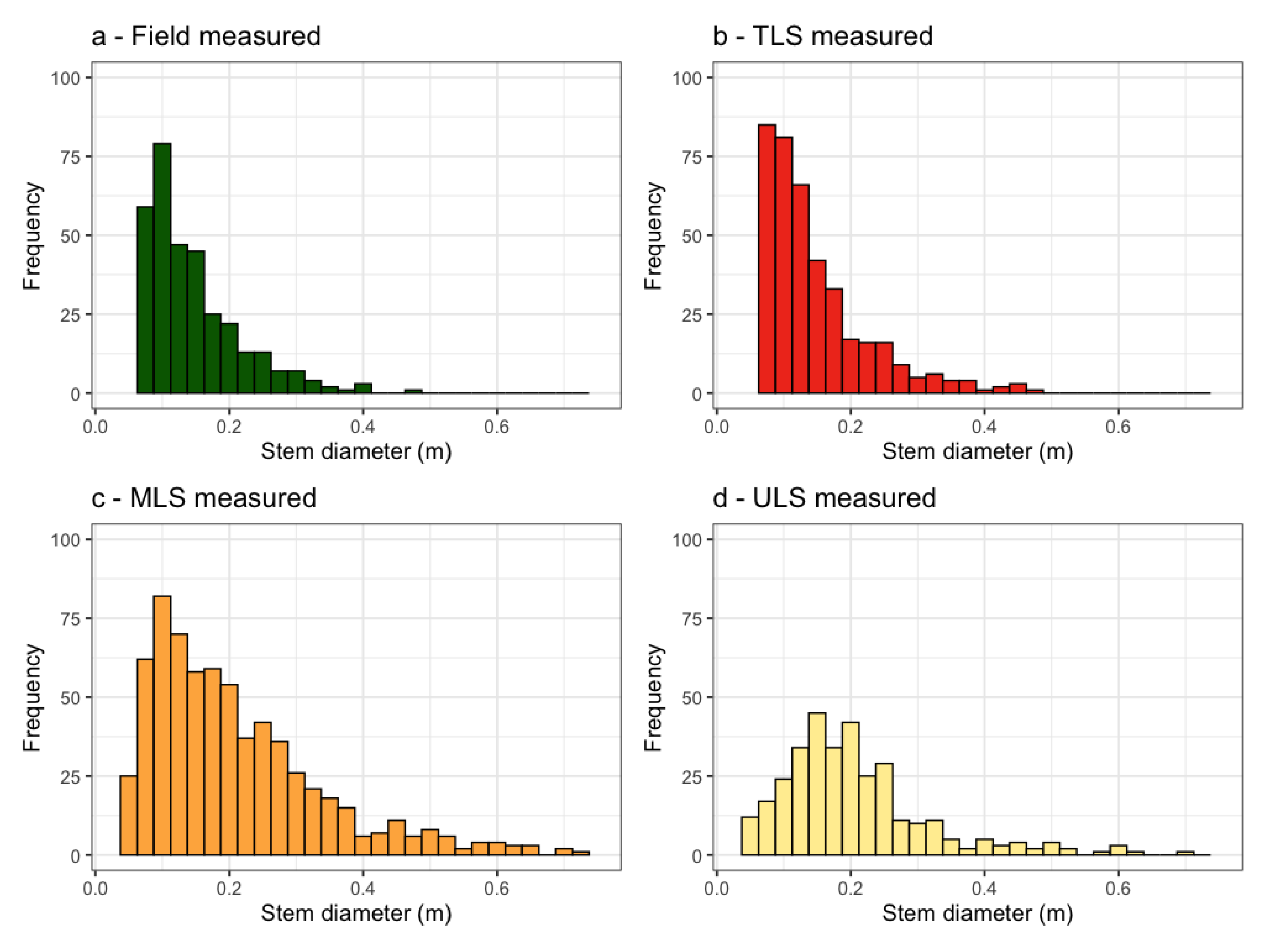
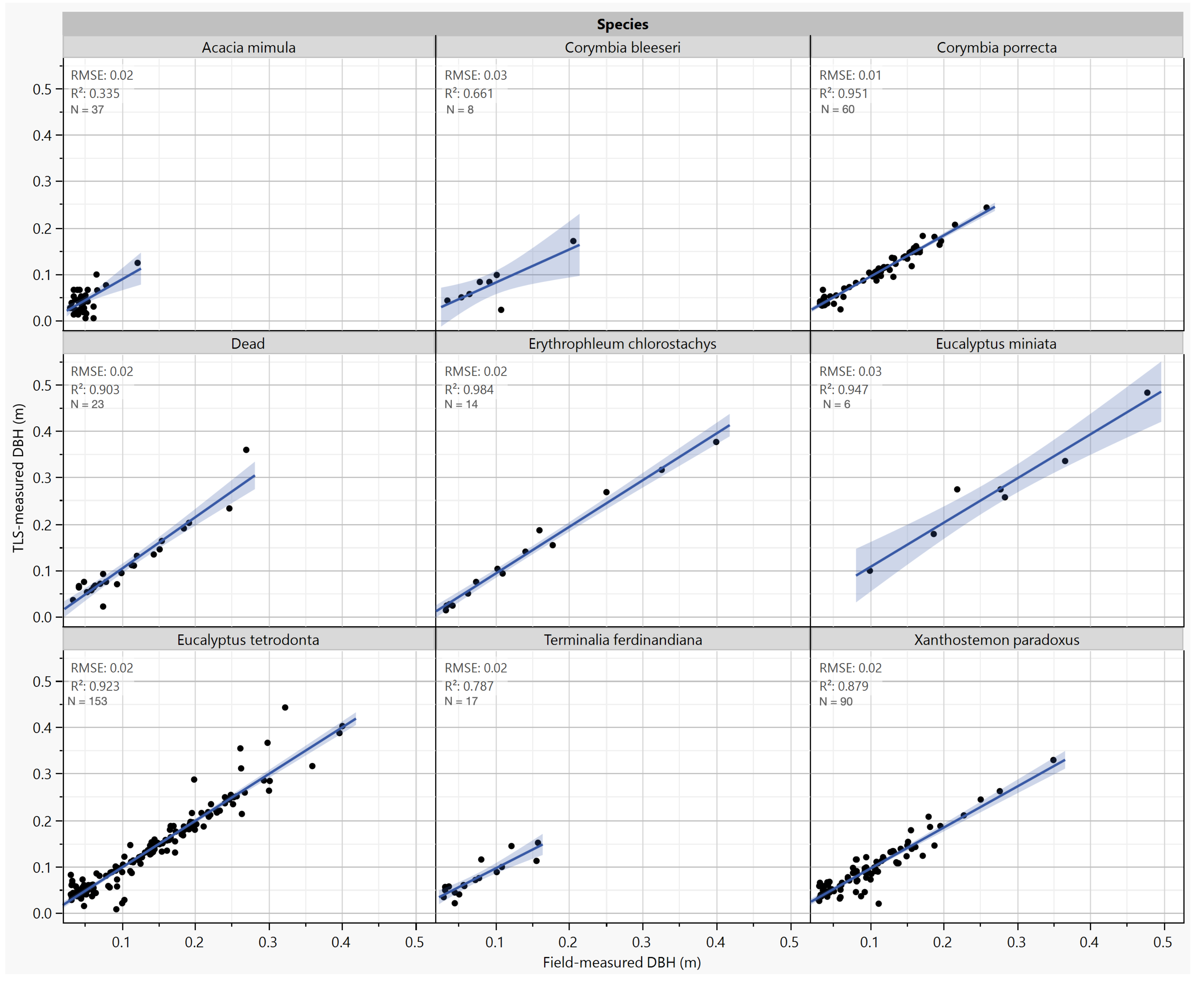
3.2. Individual Tree Characterization
3.3. Allometric Scaling
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficient Monitoring of Habitat Structure
4.2. Individual Trees and Biomass Scaling
4.3. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGB | Above-ground biomass |
| DBH | Diameter at breast height |
| CHM | Canopy height model |
| GEDI | Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigator |
| GPS | Global Positioning System |
| LiDAR | Light-detection-and-ranging |
| MLS | Mobile Laser Scanning |
| RTK | Real-time Kinematic |
| SAR | Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| SLAM | Simultaneous Location and Mapping |
| TLS | Terrestrial Laser Scanning |
| ULS | UAV Laser Scanning |
| UAV | Unmanned Aerial Vehicle |
References
- Gillson, L. Evidence of Hierarchical Patch Dynamics in an east African savanna? Landsc. Ecol. 2005, 19, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, S.R.; Rogers, K.H. Context-dependent vegetation dynamics in an African savanna. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 515–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, S.R.S.; Asner, G.G.P.; Kennedy-Bowdoin, T.T.; Knapp, D.D.E. The relative influence of fire and herbivory on savanna three-dimensional vegetation structure. Biol. Conserv. 2009, 142, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncrieff, G.R.; Chamaillé-Jammes, S.; Higgins, S.I.; O’Hara, R.B.; Bond, W.J. Tree allometries reflect a lifetime of herbivory in an African savanna. Ecology 2011, 92, 2310–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolley, L.A.; Murphy, B.P.; Radford, I.J.; Westaway, J.; Woinarski, J.C. Cyclones, fire, and termites: The drivers of tree hollow abundance in northern Australia’s mesic tropical savanna. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 419–420, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, L.; Hutley, L.B.; Calders, K.; Levick, S.R. Exploring the Variability of Tropical Savanna Tree Structural Allometry with Terrestrial Laser Scanning. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.I.; Larmour, J.S.; Roxburgh, S.H.; England, J.R.; Davies, M.J.; Luck, H.D. Measurements of stem diameter: Implications for individual- and stand-level errors. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Coops, N.C.; Roy, D.P.; White, J.C.; Hermosilla, T. Land Cover 2.0. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 4254–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, G.N.; Halpin, P.N.; Helmuth, B.; Hestir, E.L.; Skidmore, A.; Abrams, M.J.; Aguirre, N.; Blair, M.; Botha, E.; Colloff, M.; et al. Remote Sensing for Biodiversity. In The GEO Handbook on Biodiversity Observation Networks; Walters, M., Scholes, R.J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 187–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, M.J.; Hanan, N.P. Ecosystem Function in Savannas: Measurement and Modeling at Landscape to Global Scales; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefsky, M.A.; Cohen, W.B.; Parker, G.; Harding, D.J. Lidar Remote Sensing for Ecosystem Studies. BioScience 2002, 52, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, S.; Rogers, K. Structural biodiversity monitoring in savanna ecosystems: Integrating LiDAR and high resolution imagery through object-based image analysis. In Object-Based Image Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgan, M.S.; Asner, G.P.; Levick, S.R.; Martin, R.E.; Chadwick, O.A. Topo-edaphic controls over woody plant biomass in South African savannas. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levick, S.R.; Richards, A.E.; Cook, G.D.; Schatz, J.; Guderle, M.; Williams, R.J.; Subedi, P.; Trumbore, S.E.; Andersen, A.N. Rapid response of habitat structure and above-ground carbon storage to altered fire regimes in tropical savanna. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1493–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.B.; Asner, G.P. Advances in animal ecology from 3D-LiDAR ecosystem mapping. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2014, 29, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobo-Wilson, A.M.; Murphy, B.P.; Cremona, T.; Carthew, S.M.; Levick, S.R. Illuminating den-tree selection by an arboreal mammal using terrestrial laser scanning in northern Australia. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calders, K.; Adams, J.; Armston, J.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bauwens, S.; Bentley, L.P.; Chave, J.; Danson, F.M.; Demol, M.; Disney, M.; et al. Terrestrial laser scanning in forest ecology: Expanding the horizon. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 251, 112102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Hyyppä, J.; Kaartinen, H.; Lehtomäki, M.; Pyörälä, J.; Pfeifer, N.; Holopainen, M.; Brolly, G.; Francesco, P.; Hackenberg, J.; et al. International benchmarking of terrestrial laser scanning approaches for forest inventories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 144, 137–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newnham, G.J.; Armston, J.D.; Calders, K.; Disney, M.I.; Lovell, J.L.; Schaaf, C.B.; Strahler, A.H.; Mark Danson, F. Terrestrial laser scanning for plot-scale forest measurement. Curr. For. Rep. 2015, 1, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Levick, S.R.; Guderle, M.; Schmullius, C. Moving from plot-based to hillslope-scale assessments of savanna vegetation structure with long-range terrestrial laser scanning (LR-TLS). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 90, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauwens, S.; Bartholomeus, H.; Calders, K.; Lejeune, P. Forest inventory with terrestrial LiDAR: A comparison of static and hand-held mobile laser scanning. Forests 2016, 7, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte, A.P.D.; Rex, F.E.; de Almeida, D.R.A.; Sanquetta, C.R.; Silva, C.A.; Moura, M.M.; Wilkinson, B.; Zambrano, A.M.A.; da Cunha Neto, E.M.; Veras, H.F.; et al. Measuring individual tree diameter and height using gatoreye high-density UAV-lidar in an integrated crop-livestock-forest system. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, J.R.; Armston, J.; Birrer, M.; Cushman, K.C.; Duncanson, L.; Eck, C.; Falleger, C.; Imbach, B.; Král, K.; Krůček, M.; et al. New Opportunities for Forest Remote Sensing Through Ultra-High-Density Drone Lidar. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 959–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, C.; Schaefer, M.; Jovanovic, T.; Crawford, D. Comparing terrestrial laser scanners’ ability to measure tree height and diameter in a managed forest environment. Aust. For. 2020, 83, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velas, M.; Spanel, M.; Sleziak, T.; Habrovec, J.; Herout, A. Indoor and outdoor backpack mapping with calibrated pair of velodyne lidars. Sensors 2019, 19, 3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stal, C.; Verbeurgt, J.; De Sloover, L.; De Wulf, A. Assessment of handheld mobile terrestrial laser scanning for estimating tree parameters. J. For. Res. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, L.D.; Whiteside, T.G.; Williamson, G.J.; Bartolo, R.E.; Bowman, D.M. Multi-decadal stability of woody cover in a mesic eucalypt savanna in the Australian monsoon tropics. Austral Ecol. 2020, 45, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beringer, J.; Hutley, L.B.; Abramson, D.; Arndt, S.K.; Briggs, P.; Bristow, M.; Canadell, J.G.; Cernusak, L.A.; Eamus, D.; Edwards, A.C.; et al. Fire in Australian savannas: From leaf to landscape. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Santin, L.; Rudge, M.L.; Bartolo, R.E.; Whiteside, T.G.; Erskine, P.D. Reference site selection protocols for mine site ecosystem restoration. Restor. Ecol. 2021, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardeau-Montaut, D. CloudCompare—Open Source Project. Available online: http://www.cloudcompare.org/ (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Rapidlasso GmbH. LAStools—Efficient LiDAR Processing Software. 2020. Available online: https://rapidlasso.com/lastools/ (accessed on 12 January 2020).
- Massey, F.J. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for Goodness of Fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wu, F.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Xue, B.; Hu, X.; Li, P.; Tian, D.; Li, C.; et al. Segmenting tree crowns from terrestrial and mobile LiDAR data by exploring ecological theories. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 110, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trochta, J.; Kruček, M.; Vrška, T.; Kraâl, K. 3D Forest: An application for descriptions of three-dimensional forest structures using terrestrial LiDAR. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.J.; Zerihun, A.; Montagu, K.D.; Hoffman, M.; Hutley, L.B.; Chen, X. Allometry for estimating aboveground tree biomass in tropical and subtropical eucalypt woodlands: Towards general predictive equations. Aust. J. Bot. 2005, 53, 607–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, P.; Lau, A.; Disney, M.; Calders, K.; Burt, A.; Gonzalez de Tanago, J.; Bartholomeus, H.; Brede, B.; Herold, M. Data acquisition considerations for Terrestrial Laser Scanning of forest plots. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 196, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillman, S.; Wallace, L.; Lucieer, A.; Reinke, K.; Turner, D.; Jones, S. A comparison of terrestrial and UAS sensors for measuring fuel hazard in a dry sclerophyll forest. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 95, 102261. [Google Scholar]
- Bienert, A.; Georgi, L.; Kunz, M.; Maas, H.G.; von Oheimb, G. Comparison and combination of mobile and terrestrial laser scanning for natural forest inventories. Forests 2018, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollob, C.; Ritter, T.; Nothdurft, A. Comparison of 3D point clouds obtained by terrestrial laser scanning and personal laser scanning on forest inventory sample plots. Data 2020, 5, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jucker, T.; Caspersen, J.; Chave, J.; Antin, C.; Barbier, N.; Bongers, F.; Dalponte, M.; van Ewijk, K.Y.; Forrester, D.I.; Haeni, M.; et al. Allometric equations for integrating remote sensing imagery into forest monitoring programmes. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, G.D.; Goyens, C.M. The impact of wind on trees in Australian tropical savannas: Lessons from Cyclone Monica. Austral Ecol. 2008, 33, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.I.; Boni Vicari, M.; Burt, A.; Calders, K.; Lewis, S.L.; Raumonen, P.; Wilkes, P. Weighing trees with lasers: Advances, challenges and opportunities. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20170048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disney, M.; Burt, A.; Wilkes, P.; Armston, J.; Duncanson, L. New 3D measurements of large redwood trees for biomass and structure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raumonen, P.; Kaasalainen, M.; Åkerblom, M.; Kaasalainen, S.; Kaartinen, H.; Vastaranta, M.; Holopainen, M.; Disney, M.; Lewis, P. Fast Automatic Precision Tree Models from Terrestrial Laser Scanner Data. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 491–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TLS | MLS | ULS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Instrument | Riegl VZ-2000i | LiBackPack D50 | Nextcore Version 1 |
| Manufacturer | Riegl | Green Valley International | Nextcore |
| Sensor | Riegl | Velodyne | Quanergy M8 |
| Platform | Tripod | Backpack | Drone (DJI M600) |
| Acquisition time | 120 min | 20 min | 15 min |
| Co-registration processing time | 60 min | 20 min | 20 min |
| Filtered point density (m) | 7340 | 2401 | 2015 |
| Attribute | TLS | MLS | ULS |
|---|---|---|---|
| CHM max height (m) | 18.02 | 18.65 | 18.05 |
| Woody canopy cover (%) | 51.5 | 55.3 | 39.8 |
| Woody canopy cover > 3 m (%) | 42.4 | 46.1 | 36.9 |
| Woody canopy cover > 5 m (%) | 39.9 | 44.7 | 34.8 |
| Woody canopy cover > 10 m (%) | 18.9 | 22.1 | 17.9 |
| Attribute | TLS | MLS | ULS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crown volume max (m) | 428.37 | 475.29 | 406.37 |
| Crown volume mean (m) | 19.94 | 23.49 | 41.67 |
| Crown volume CV (m) | 2.33 | 2.29 | 1.6 |
| Woody biomass (Mg ha) | 44.21 | - | - |
| Woody biomass (Mg C ha) | 22.10 | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levick, S.R.; Whiteside, T.; Loewensteiner, D.A.; Rudge, M.; Bartolo, R. Leveraging TLS as a Calibration and Validation Tool for MLS and ULS Mapping of Savanna Structure and Biomass at Landscape-Scales. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020257
Levick SR, Whiteside T, Loewensteiner DA, Rudge M, Bartolo R. Leveraging TLS as a Calibration and Validation Tool for MLS and ULS Mapping of Savanna Structure and Biomass at Landscape-Scales. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020257
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevick, Shaun R., Tim Whiteside, David A. Loewensteiner, Mitchel Rudge, and Renee Bartolo. 2021. "Leveraging TLS as a Calibration and Validation Tool for MLS and ULS Mapping of Savanna Structure and Biomass at Landscape-Scales" Remote Sensing 13, no. 2: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020257
APA StyleLevick, S. R., Whiteside, T., Loewensteiner, D. A., Rudge, M., & Bartolo, R. (2021). Leveraging TLS as a Calibration and Validation Tool for MLS and ULS Mapping of Savanna Structure and Biomass at Landscape-Scales. Remote Sensing, 13(2), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020257