Efficient Hybrid Supervision for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The proposed method can well balance performance and labeling cost for instance segmentation in aerial images.
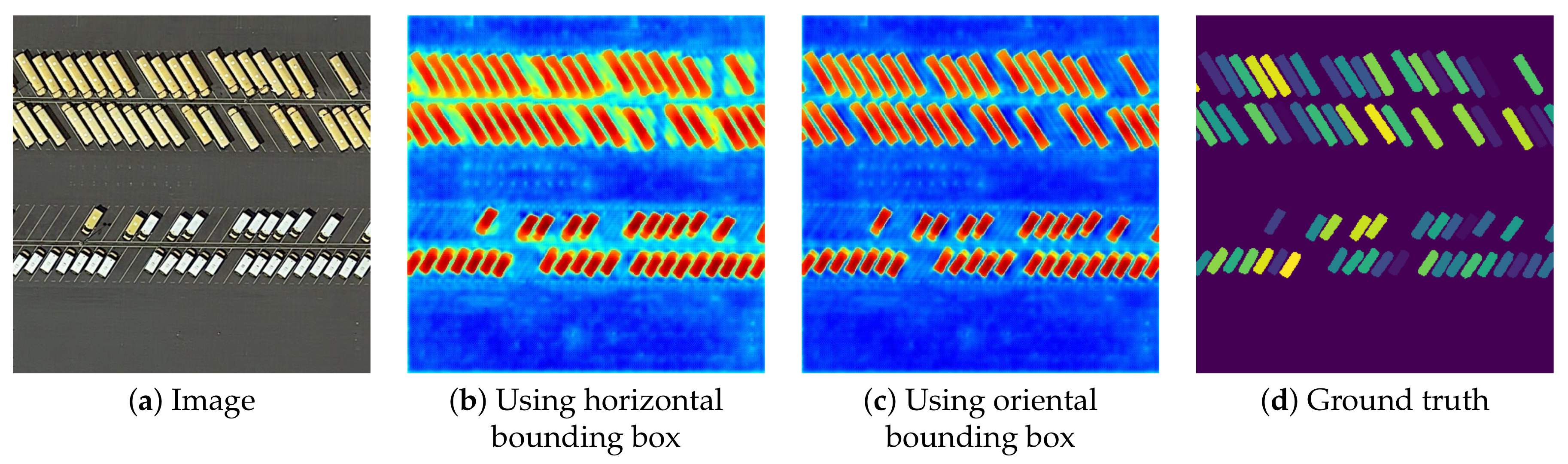
- We propose a pipeline that consists of an ancillary segmentation model and a primary instance segmentation model. The ancillary segmentation model with bounding box attention module, bounding box filter module and oriented bounding box labels can effectively address the specific challenges in aerial images, i.e., cluttered background, extremely dense and small objects, and objects with arbitrary orientations.
- We evaluate our method and achieve 32.1 AP on challenging iSAID dataset [11] using 10% pixel-wise labels, which is comparable to fully supervised method 33.9 AP and much better than weakly supervised setting 26.5 AP.
2. Related Work
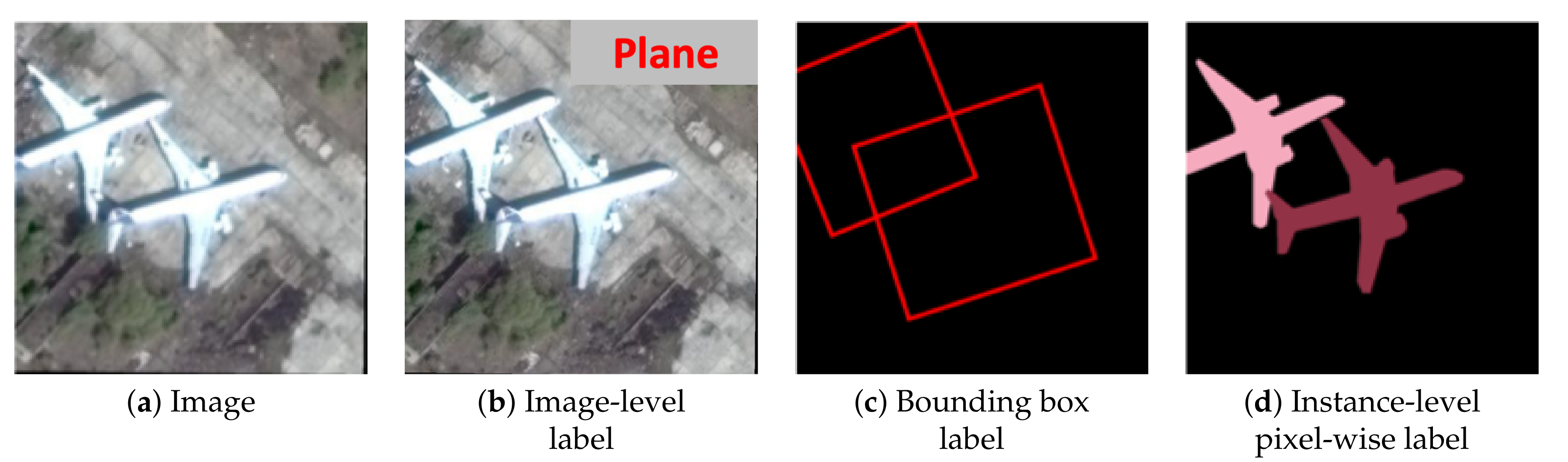
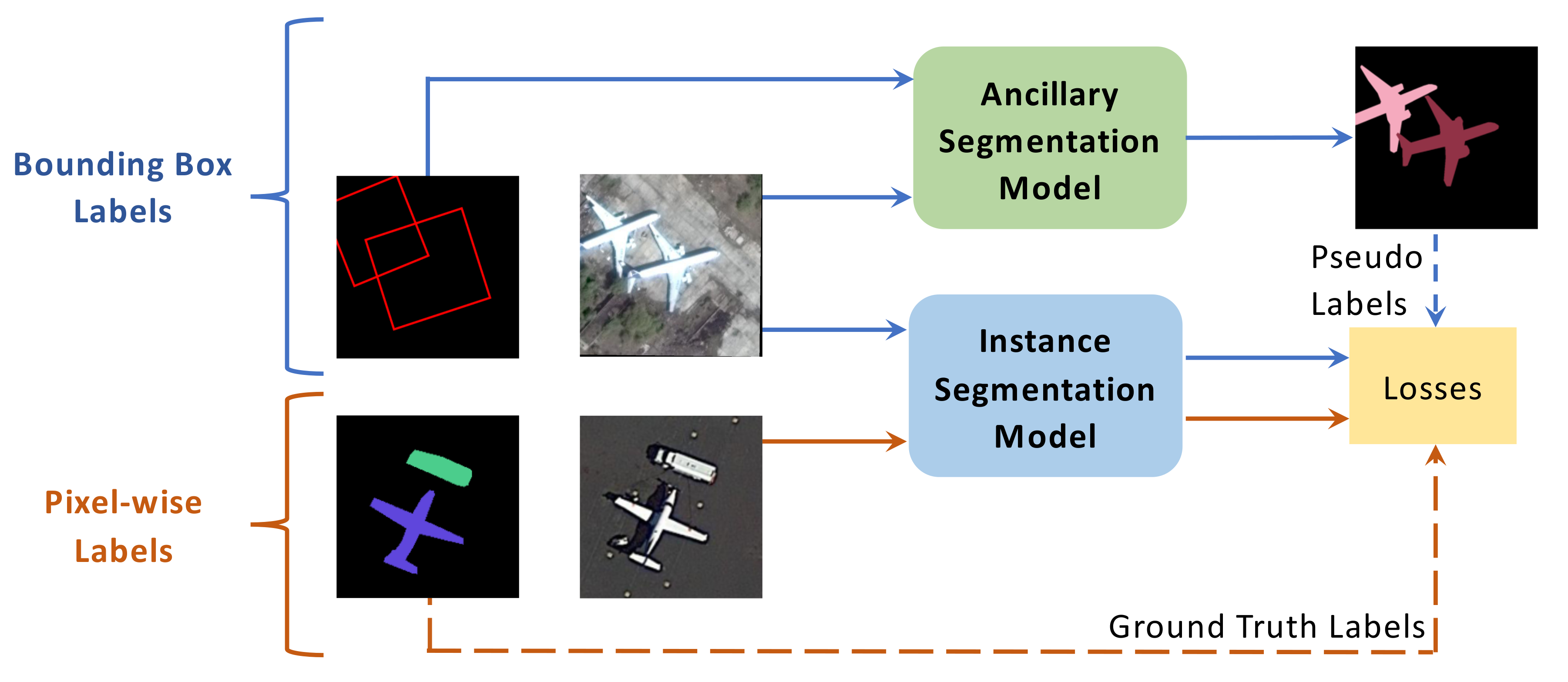
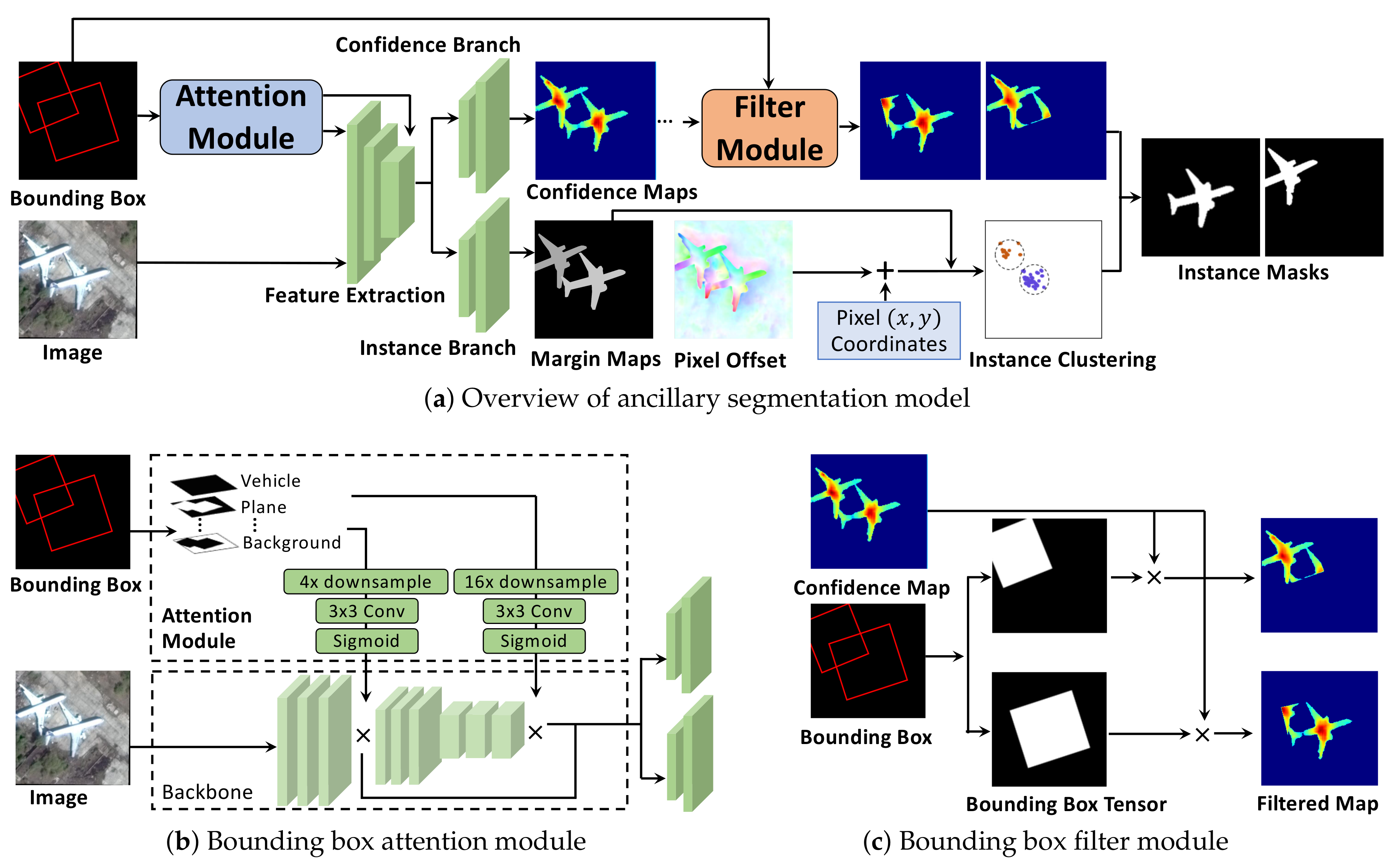
3. Hybrid Supervision for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images
3.1. Motivation
- Image-level labels only provide the information about categories of objects in images and cannot indicate specific location of each object. They are usually used for image classification [52] but can be hardly used for instance segmentation task in aerial images especially when objects of interest are small and densely distributed.
- Bounding box labels can provide the information about categories, and locations of objects. They are usually used for object detection [12]. Nonetheless, they do not contain the information about shapes of objects, which are important for instance segmentation task.
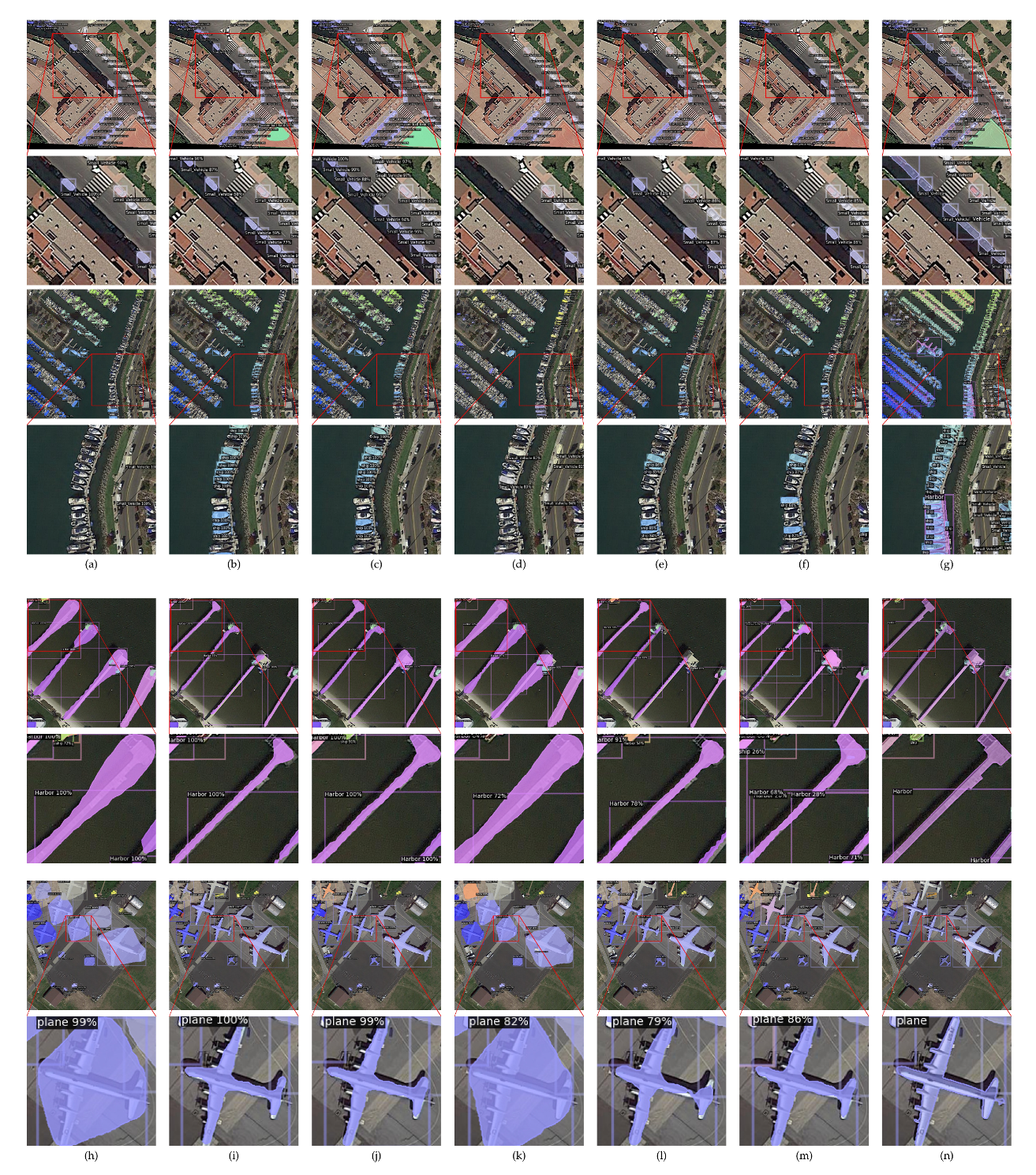
- Cluttered background. Aerial images can cover various scenes rather than specific scenes, e.g., cities, oceans and field. Furthermore, other factors like trees and shadows of buildings can also disturb the detection and segmentation. Therefore, the background (area without interested objects) can be highly diverse and cause false positives easily. Taking Figure 1a as an example, a line of cars in the shadow of the buildings are easy to ignore, and the shape of white cars surrounded by zebra crossings are difficult to obtain accurately.
- Extremely dense and small objects. Aerial images are taken from a much longer distance than natural images, which results in an extremely dense distribution of small objects. For example, as shown in Figure 1b, many small vehicles are concentrated in specific area, sizes of these objects are smaller than 10 pixels in the aerial image. At the same time, there also exists extremely large objects, as shown in Figure 1c, making object detection more complex and challenging.
3.2. Formulation
3.3. Design and Learning Details
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metric
4.2. Implementation Details
- Weak supervision. Considering there exists no weakly supervised method for instance segmentation in aerial images, we use bounding box labels as pseudo instance-level pixel-wise labels for training, so as to serve as weakly supervised results.
- Full supervision. With all pixel-wise labels available, the full supervision can easily reach the best result. For a comprehensive comparison, we provide the fully supervised results with different percentage of pixel-wise labels available (i.e., 5%, 10%, 20% and 100%).
- Weak and full supervision. For a fair comparison, we provide the results of weak and full supervision. Under this setting, the instance segmentation model is trained with both instance-level pixel-wise labels and bounding box labels, notice that bounding box labels are utilized to train the bounding box branch and classification branch only.
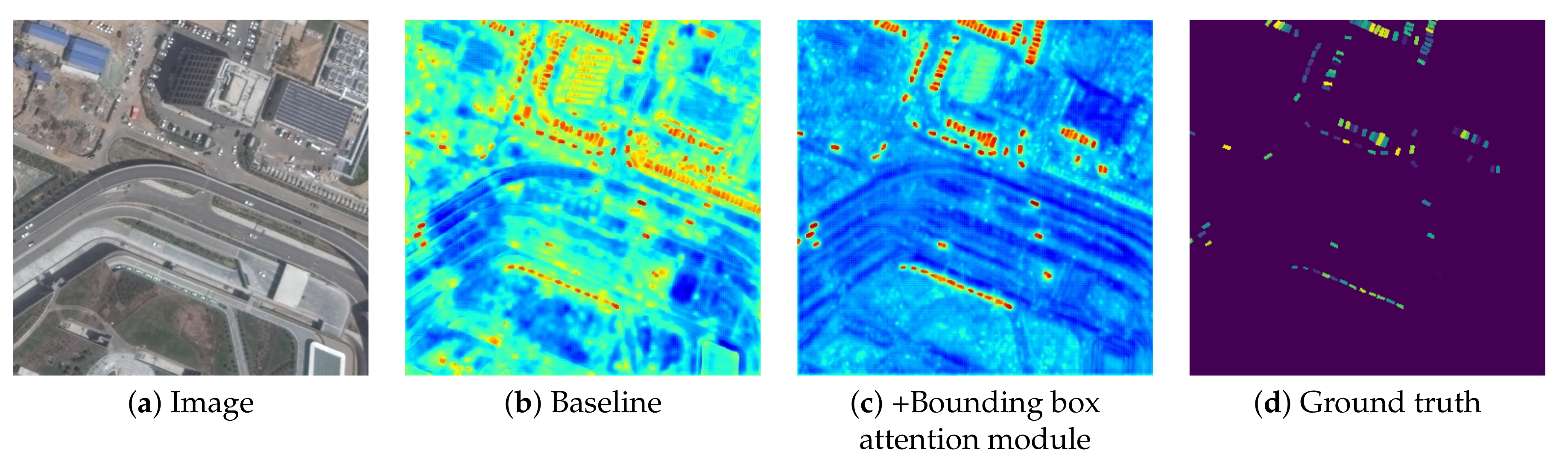
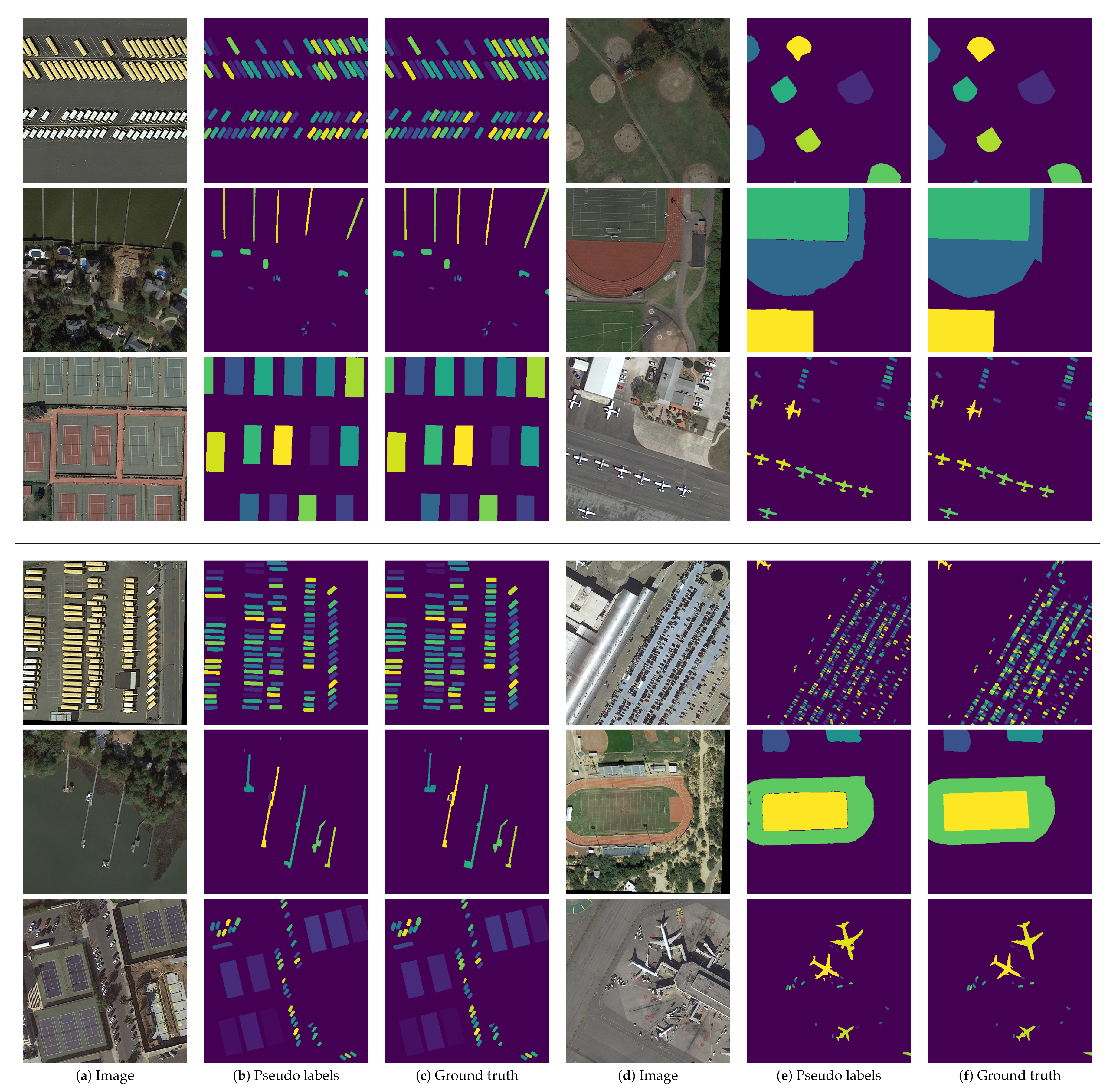
4.3. Qualitative Evaluation
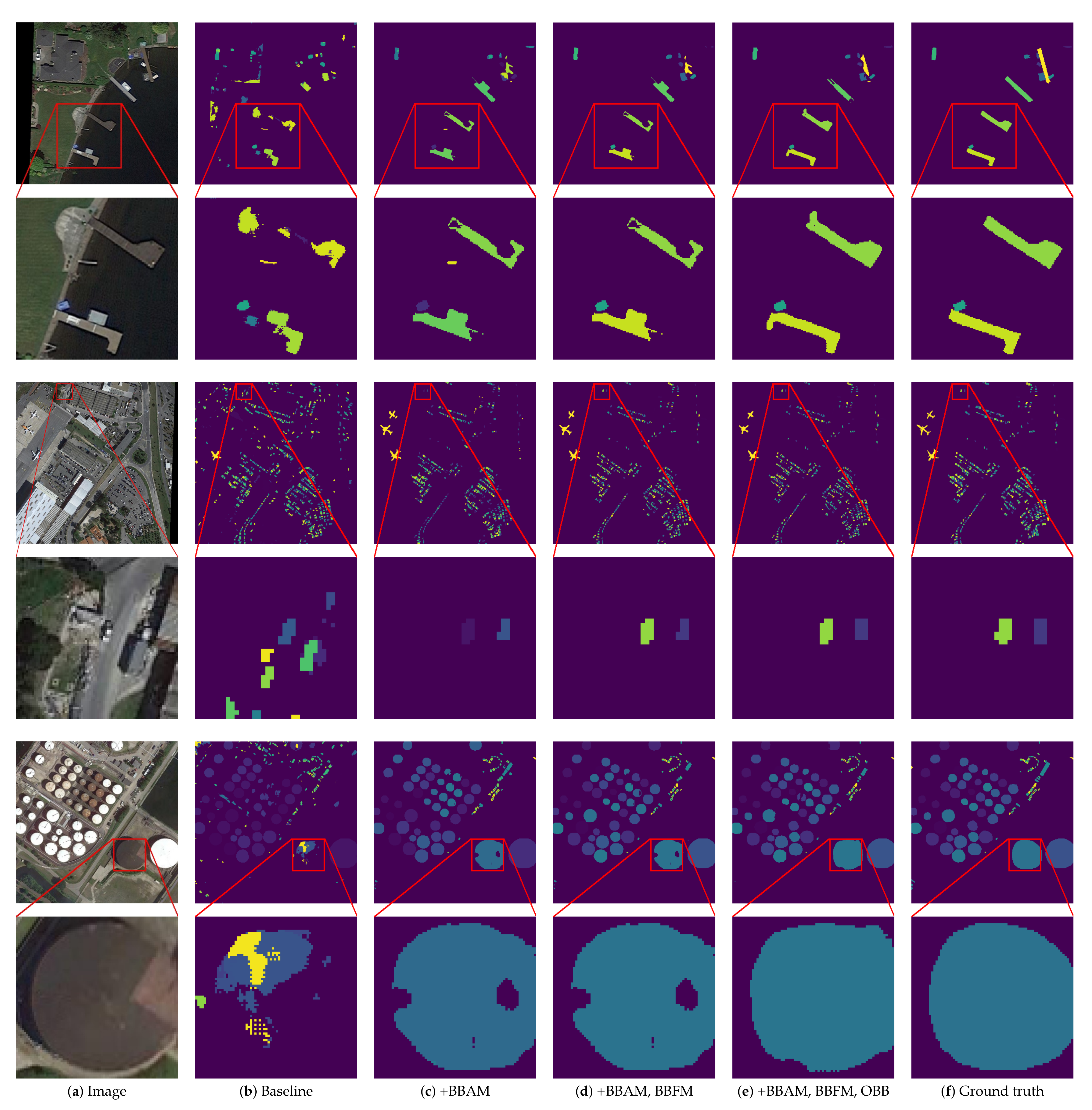
4.4. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wen, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, L.; Benediktsson, J.A. A novel automatic change detection method for urban high-resolution remotely sensed imagery based on multiindex scene representation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 54, 609–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, M.; Tuia, D. Dense semantic labeling of subdecimeter resolution images with convolutional neural networks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 55, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopsiaftis, G.; Karantzalos, K. Vehicle detection and traffic density monitoring from very high resolution satellite video data. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 1881–1884. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Pang, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Shi, J.; Ouyang, W.; et al. Hybrid task cascade for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 4974–4983. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Zhou, C.; Xiao, F.; Lee, Y.J. YOLACT: Real-time instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 9157–9166. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Park, J. CenterMask: Real-Time Anchor-Free Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 13906–13915. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Sun, K.; Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Huang, Y.; Yan, Y. BlendMask: Top-down meets bottom-up for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 8573–8581. [Google Scholar]
- Bearman, A.; Russakovsky, O.; Ferrari, V.; Li, F.-F. What’s the point: Semantic segmentation with point supervision. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 549–565. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas Zamir, S.; Arora, A.; Gupta, A.; Khan, S.; Sun, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Zhu, F.; Shao, L.; Xia, G.S.; Bai, X. iSAID: A Large-scale Dataset for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes (voc) challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2010, 88, 303–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, Q.; Qiu, Q.; Jiao, J. Weakly supervised instance segmentation using class peak response. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3791–3800. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, J.; Cho, S.; Kwak, S. Weakly Supervised Learning of Instance Segmentation with Inter-pixel Relations. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 2209–2218. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, W.; Guo, S.; Huang, W.; Scott, M.R. Label-PEnet: Sequential Label Propagation and Enhancement Networks for Weakly Supervised Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 3345–3354. [Google Scholar]
- Khoreva, A.; Benenson, R.; Hosang, J.; Hein, M.; Schiele, B. Simple does it: Weakly supervised instance and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 876–885. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Arnab, A.; Torr, P.H. Weakly-and semi-supervised panoptic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 102–118. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C.C.; Hsu, K.J.; Tsai, C.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chuang, Y.Y. Weakly Supervised Instance Segmentation using the Bounding Box Tightness Prior. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 6586–6597. [Google Scholar]
- Rother, C.; Kolmogorov, V.; Blake, A. “GrabCut” interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts. ACM Trans. Graph. 2004, 23, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeláez, P.; Pont-Tuset, J.; Barron, J.T.; Marques, F.; Malik, J. Multiscale combinatorial grouping. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 328–335. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Yang, K. Denseaspp for semantic segmentation in street scenes. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3684–3692. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Tang, S.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Li, J. Tree-structured kronecker convolutional network for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Shanghai, China, 8–12 July 2019; pp. 940–945. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid scene parsing network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2881–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, G.; Milan, A.; Shen, C.; Reid, I. Refinenet: Multi-path refinement networks for high-resolution semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1925–1934. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 3146–3154. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, W.C.; Tsai, Y.H.; Shen, X.; Lin, Z.; Sunkavalli, K.; Lu, X.; Yang, M.H. Scene parsing with global context embedding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2631–2639. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Dana, K.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Tyagi, A.; Agrawal, A. Context encoding for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7151–7160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Xue, X.; Sun, J. Exfuse: Enhancing feature fusion for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, L.; Gong, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, X. Mask scoring R-CNN. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 6409–6418. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, H.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Shao, T.; Zhou, K. EmbedMask: Embedding Coupling for One-stage Instance Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1912.01954. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Shen, C.; Chen, H.; He, T. Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 9627–9636. [Google Scholar]
- Sherrah, J. Fully convolutional networks for dense semantic labelling of high-resolution aerial imagery. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.02585. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.; Ehrlich, M.; Shah, S.; Davis, L.S.; Chellappa, R. Stacked U-Nets for Ground Material Segmentation in Remote Sensing Imagery. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi, R.; Fujita, A.; Nemoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Hikosaka, S. Effective use of dilated convolutions for segmenting small object instances in remote sensing imagery. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Lake Tahoe, CA, USA, 12–15 March 2018; pp. 1442–1450. [Google Scholar]
- Mou, L.; Zhu, X.X. Vehicle instance segmentation from aerial image and video using a multitask learning residual fully convolutional network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 6699–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Diao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Chang, Z.; Yan, M.; Sun, X.; Gao, X. Ship Instance Segmentation from Remote Sensing Images Using Sequence Local Context Module. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019; pp. 1025–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, D.; Kuzma, R.; McGee, K.; Dooley, S.; Laielli, M.; Klaric, M.; Bulatov, Y.; McCord, B. xview: Objects in context in overhead imagery. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.07856. [Google Scholar]
- Maggiori, E.; Tarabalka, Y.; Charpiat, G.; Alliez, P. Can semantic labeling methods generalize to any city? The inria aerial image labeling benchmark. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Fort Worth, TX, USA, 23–28 July 2017; pp. 3226–3229. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, H.; Brown, M.; Wang, S. A benchmark for building footprint classification using orthorectified rgb imagery and digital surface models from commercial satellites. In Proceedings of the IEEE Applied Imagery Pattern Recognition Workshop, Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, N.; Lindenbaum, D.; Bastidas, A.; Van Etten, A.; McPherson, S.; Shermeyer, J.; Kumar, V.; Tang, H. SpaceNet MVOI: A Multi-View Overhead Imagery Dataset Supplementary Material. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.12239. [Google Scholar]
- Everingham, M.; Eslami, S.A.; Van Gool, L.; Williams, C.K.; Winn, J.; Zisserman, A. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2015, 111, 98–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellver, M.; Salvador, A.; Torres, J.; Giro-i-Nieto, X. Budget-aware Semi-Supervised Semantic and Instance Segmentation. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.05880. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Xiao, H.; Shi, H.; Jie, Z.; Feng, J.; Huang, T.S. Revisiting dilated convolution: A simple approach for weakly-and semi-supervised semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7268–7277. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, M.S.; Vahdat, A.; Macready, W.G. Semi-Supervised Semantic Image Segmentation with Self-correcting Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 12715–12725. [Google Scholar]
- Neven, D.; Brabandere, B.D.; Proesmans, M.; Gool, L.V. Instance segmentation by jointly optimizing spatial embeddings and clustering bandwidth. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 8837–8845. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Fu, P.; Luo, Z. R2CNN: Rotational region cnn for orientation robust scene text detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.09579. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Z.; Sun, X.; Fu, K. SCRDet: Towards more robust detection for small, cluttered and rotated objects. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–3 November 2019; pp. 8232–8241. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, M.; Rannen Triki, A.; Blaschko, M.B. The Lovász-Softmax loss: A tractable surrogate for the optimization of the intersection-over-union measure in neural networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4413–4421. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the PInternational Conference on Learning Representations, Banff, AB, Canada, 14–16 April 2014; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Girshick, R.; Dollár, P.; Tu, Z.; He, K. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1492–1500. [Google Scholar]




| Supervision | Instance Segmentation Model | Number of Pixel-Wise Labels | Number of Horizontal Bounding Box Labels | Number of Oriented Bounding Box Labels | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weak | Mask R-CNN [4] | - | 1411 (100%) | - | 13.3 | 34.7 | 7.2 | 8.5 | 14.8 | 18.5 |
| - | - | 1411 (100%) | 26.5 | 47.0 | 26.2 | 14.8 | 32.1 | 36.0 | ||
| CenterMask [8] | - | 1411 (100%) | - | 12.6 | 33.0 | 7.2 | 7.4 | 14.5 | 18.4 | |
| - | - | 1411 (100%) | 26.1 | 45.8 | 25.6 | 12.5 | 31.9 | 39.6 | ||
| Full | Mask R-CNN [4] | 70 (5%) | - | - | 15.7 | 25.3 | 17.0 | 5.9 | 19.9 | 22.6 |
| 141 (10%) | - | - | 22.5 | 38.8 | 22.5 | 10.6 | 28.7 | 30.2 | ||
| 282 (20%) | - | - | 26.5 | 43.8 | 33.6 | 13.0 | 33.6 | 34.8 | ||
| 1411 (100%) | - | - | 33.9 | 56.4 | 35.7 | 18.8 | 41.1 | 50.1 | ||
| CenterMask [8] | 70 (5%) | - | - | 15.2 | 24.9 | 16.1 | 5.2 | 20.5 | 22.8 | |
| 141 (10%) | - | - | 23.3 | 39.2 | 23.9 | 10.3 | 30.4 | 28.9 | ||
| 282 (20%) | - | - | 26.8 | 44.5 | 28.0 | 11.7 | 35.1 | 37.3 | ||
| 1411 (100%) | - | - | 34.0 | 56.3 | 35.8 | 18.0 | 42.8 | 53.8 | ||
| Weak+Full | Mask R-CNN [4] | 141 (10%) | 1270 (90%) | - | 28.6 | 49.1 | 28.9 | 15.5 | 34.2 | 40.7 |
| CenterMask [8] | 141 (10%) | 1270 (90%) | - | 28.3 | 48.8 | 28.1 | 14.5 | 33.9 | 40.5 | |
| Hybrid(Ours) | Mask R-CNN [4] | 70 (5%) | - | 1341 (95%) | 28.7 | 51.1 | 27.8 | 16.4 | 34.1 | 35.2 |
| 141 (10%) | 1270 (90%) | - | 31.2 | 53.6 | 31.9 | 17.5 | 37.5 | 38.9 | ||
| 141 (10%) | - | 1270 (90%) | 32.1 | 55.0 | 32.4 | 18.5 | 39.0 | 42.2 | ||
| 242 (20%) | - | 1169 (80%) | 33.3 | 55.5 | 34.6 | 18.7 | 40.5 | 47.4 | ||
| CenterMask [8] | 70 (5%) | - | 1341 (95%) | 29.3 | 51.4 | 28.8 | 15.2 | 36.5 | 45.6 | |
| 141 (10%) | 1270 (90%) | - | 31.0 | 52.9 | 31.1 | 16.2 | 38.6 | 47.9 | ||
| 141 (10%) | - | 1270 (90%) | 31.5 | 54.0 | 31.2 | 17.0 | 39.2 | 48.0 | ||
| 242 (20%) | - | 1169 (80%) | 32.2 | 54.2 | 32.1 | 17.2 | 40.1 | 49.1 |
| Method | Ship | Storage Tank | Baseball Diamond | Tennis Court | Basketball Court | Ground Field Track | Bridge | Large Vehicle | Small Vehicle | Heli- Copter | Swimming Pool | Round- about | Soccer- Ball Field | Plane | Harbor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN [4] | ||||||||||||||||
| Weak * | 7.23 | 26.37 | 30.41 | 24.08 | 17.52 | 14.73 | 3.24 | 4.59 | 6.27 | 0.20 | 10.72 | 29.35 | 23.37 | 0.12 | 0.99 | 13.28 |
| Weak | 31.08 | 30.93 | 43.59 | 74.02 | 33.20 | 22.11 | 18.98 | 33.31 | 12.60 | 0.43 | 24.51 | 30.20 | 38.46 | 0.43 | 4.27 | 26.54 |
| Full (5%) | 11.68 | 21.80 | 32.09 | 54.81 | 4.16 | 10.21 | 2.01 | 23.23 | 7.70 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 15.88 | 19.18 | 31.29 | 0.75 | 15.67 |
| Full (10%) | 28.10 | 21.86 | 36.32 | 65.88 | 10.55 | 13.17 | 12.19 | 26.33 | 8.07 | 4.32 | 18.20 | 15.68 | 22.31 | 39.95 | 13.91 | 22.46 |
| Full (20%) | 33.38 | 25.75 | 40.13 | 68.82 | 17.96 | 16.46 | 14.52 | 30.33 | 12.25 | 5.65 | 24.14 | 18.22 | 29.75 | 42.84 | 17.77 | 26.53 |
| Full (100%) | 39.70 | 34.64 | 46.73 | 75.46 | 34.61 | 29.83 | 17.34 | 34.81 | 13.10 | 6.09 | 29.33 | 28.07 | 42.24 | 49.68 | 26.84 | 33.90 |
| Weak+Full * (10%) | 30.32 | 31.98 | 41.87 | 69.29 | 31.12 | 23.79 | 17.45 | 31.39 | 11.61 | 2.33 | 24.81 | 25.06 | 34.54 | 38.57 | 14.10 | 28.55 |
| Ours (5%) | 33.39 | 32.71 | 49.37 | 73.72 | 24.36 | 19.82 | 14.68 | 30.87 | 12.14 | 3.00 | 29.97 | 24.25 | 35.62 | 32.79 | 13.15 | 28.67 |
| Ours * (10%) | 36.58 | 34.16 | 49.40 | 72.64 | 26.01 | 22.85 | 18.55 | 31.66 | 12.49 | 2.37 | 28.87 | 25.60 | 37.24 | 45.99 | 23.55 | 31.20 |
| Ours (10%) | 37.66 | 34.77 | 49.71 | 73.53 | 29.18 | 23.88 | 19.01 | 32.01 | 12.93 | 4.17 | 29.13 | 27.05 | 40.63 | 44.66 | 23.59 | 32.13 |
| Ours (20%) | 38.05 | 35.51 | 48.12 | 76.82 | 31.59 | 25.36 | 19.36 | 35.20 | 13.36 | 5.08 | 30.10 | 31.38 | 42.87 | 43.23 | 23.21 | 33.28 |
| CenterMask [8] | ||||||||||||||||
| Weak * | 5.15 | 25.84 | 31.95 | 24.32 | 18.66 | 12.09 | 2.70 | 3.44 | 3.74 | 0.27 | 10.20 | 26.51 | 23.63 | 0.09 | 0.80 | 12.63 |
| Weak | 23.41 | 29.50 | 44.53 | 75.41 | 42.79 | 18.82 | 18.25 | 29.68 | 9.28 | 0.69 | 24.58 | 29.66 | 40.14 | 0.43 | 4.18 | 26.09 |
| Full (5%) | 9.87 | 24.69 | 27.09 | 57.13 | 8.03 | 9.50 | 2.45 | 17.40 | 5.83 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 18.18 | 16.49 | 30.73 | 0.72 | 15.22 |
| Full (10%) | 22.83 | 25.86 | 38.53 | 68.82 | 16.49 | 13.33 | 13.87 | 23.22 | 6.87 | 3.44 | 20.08 | 17.83 | 21.50 | 40.56 | 16.55 | 23.32 |
| Full (20%) | 24.80 | 28.42 | 42.48 | 69.81 | 24.77 | 17.39 | 16.02 | 27.20 | 8.17 | 3.69 | 24.27 | 23.01 | 31.02 | 42.71 | 18.13 | 26.79 |
| Full (100%) | 30.23 | 35.19 | 51.53 | 77.16 | 42.36 | 24.50 | 19.97 | 32.01 | 10.06 | 5.29 | 30.34 | 32.61 | 44.89 | 47.93 | 26.30 | 34.02 |
| Weak+Full * (10%) | 23.66 | 28.45 | 45.63 | 71.95 | 34.47 | 19.39 | 18.76 | 27.64 | 8.23 | 2.25 | 25.20 | 26.17 | 38.06 | 38.28 | 17.57 | 28.38 |
| Ours (5%) | 26.73 | 33.24 | 49.34 | 74.52 | 38.13 | 18.87 | 16.68 | 30.31 | 9.11 | 3.23 | 27.02 | 33.50 | 40.71 | 27.98 | 10.52 | 29.33 |
| Ours * (10%) | 27.90 | 33.36 | 49.58 | 76.02 | 39.26 | 18.27 | 17.69 | 30.76 | 9.28 | 4.64 | 27.87 | 32.45 | 40.08 | 37.97 | 19.15 | 30.95 |
| Ours (10%) | 28.32 | 33.80 | 49.52 | 76.51 | 40.19 | 20.10 | 18.64 | 31.26 | 9.68 | 4.32 | 28.10 | 33.63 | 42.04 | 36.97 | 19.57 | 31.51 |
| Ours (20%) | 28.48 | 33.97 | 50.10 | 76.67 | 42.11 | 21.47 | 18.74 | 31.61 | 9.72 | 4.87 | 29.62 | 34.18 | 43.93 | 37.58 | 20.61 | 32.22 |
| Bounding Box Attention Module | Bounding Box Filter Module | Oriented Bounding Box | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | 12.9 | 23.9 | 11.8 | 6.3 | 15.4 | 14.2 |
| √ | × | × | 38.1 | 70.4 | 36.6 | 32.9 | 41.3 | 36.3 |
| √ | √ | × | 41.2 | 77.2 | 38.8 | 34.5 | 47.3 | 42.6 |
| √ | √ | √ | 44.2 | 79.1 | 44.5 | 35.1 | 51.7 | 44.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Fu, Y.; You, S.; Liu, H. Efficient Hybrid Supervision for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020252
Chen L, Fu Y, You S, Liu H. Efficient Hybrid Supervision for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(2):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020252
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Linwei, Ying Fu, Shaodi You, and Hongzhe Liu. 2021. "Efficient Hybrid Supervision for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images" Remote Sensing 13, no. 2: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020252
APA StyleChen, L., Fu, Y., You, S., & Liu, H. (2021). Efficient Hybrid Supervision for Instance Segmentation in Aerial Images. Remote Sensing, 13(2), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13020252






