1D Stochastic Inversion of Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data with Realistic Prior and Accounting for the Forward Modeling Error
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- we do not restrict ourselves to the Gaussian assumption for the model parameters distribution as we are going to consider quite general prior distributions defined through the realizations of those distributions and that will be generated via a geologically informed procedure;
- the will not consist uniquely of the component attributable to the noise in the observations, but it will also include a term incorporating the modeling error. In particular, the modeling error will be assumed to be consistent with a Gaussian probability density defined by the mean and the covariance . Hence, the in Equation (1) will have now the following expression [47]with .
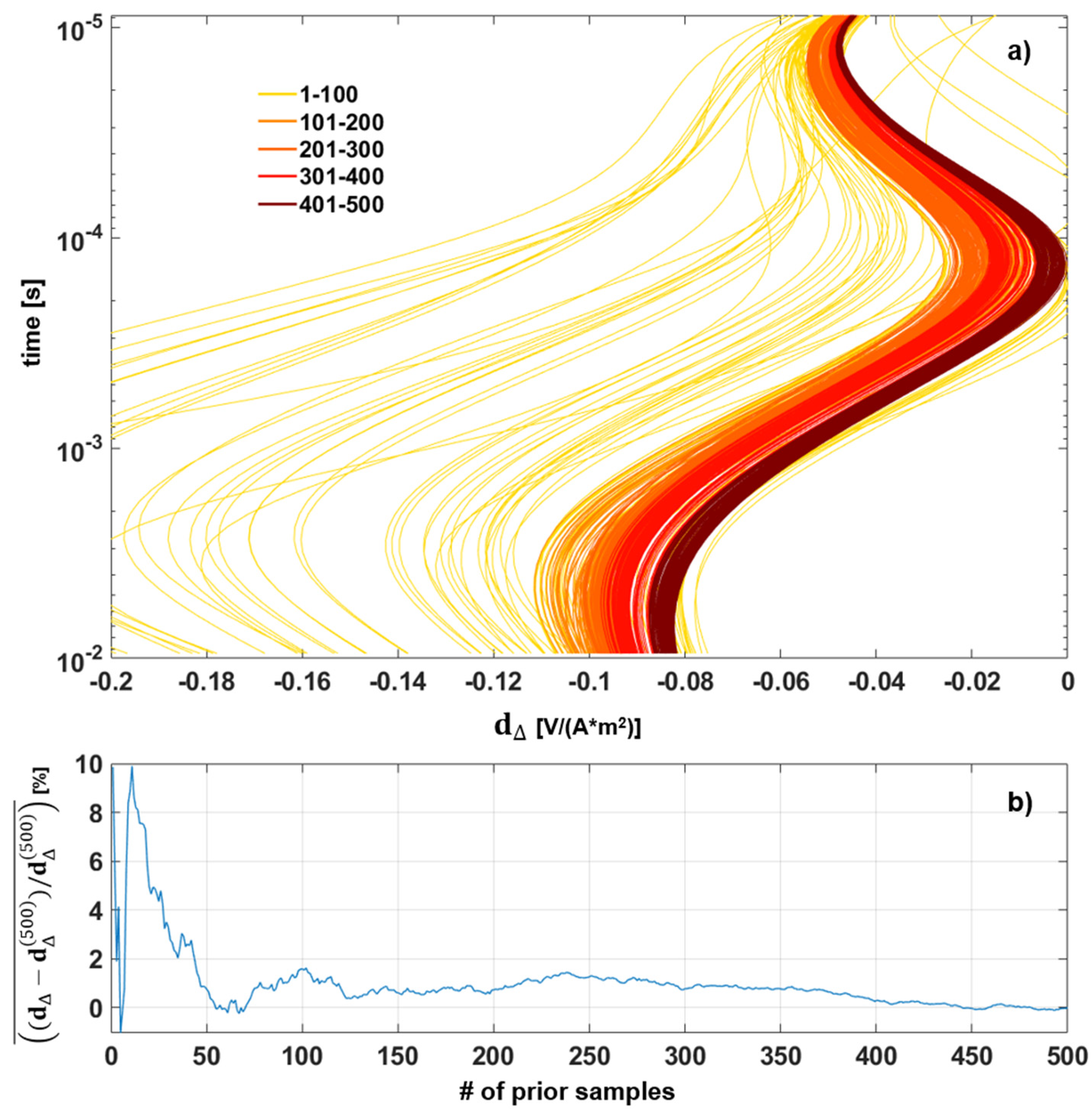
2.1. Estimation of Gaussian Correlated Modeling Errors
2.2. Inversion Strategies
3. Results
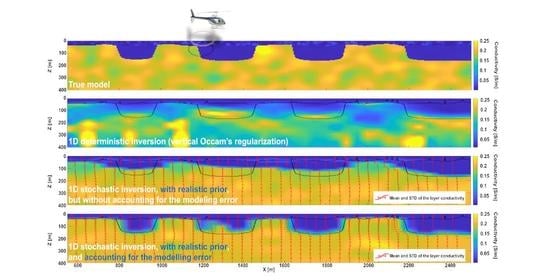
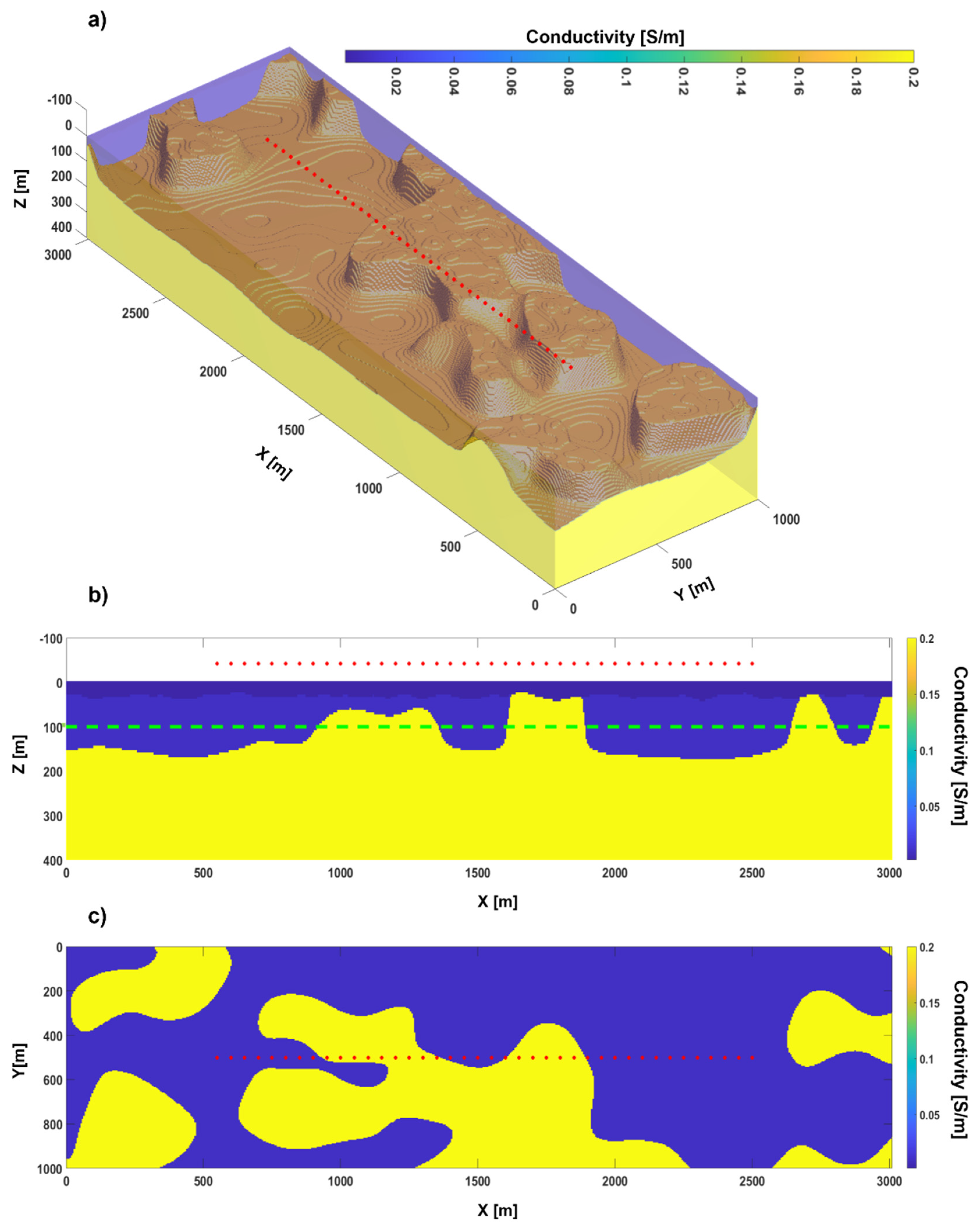
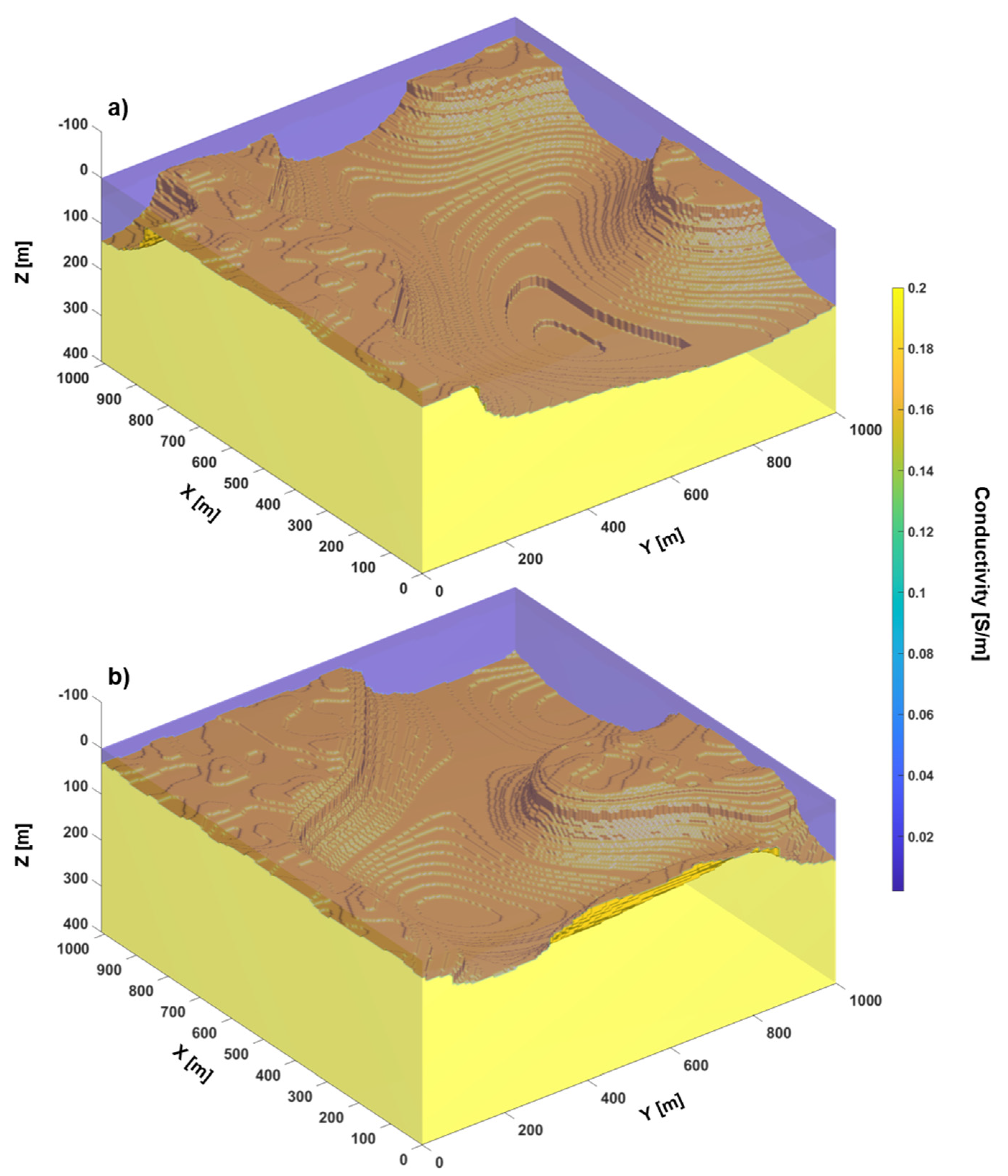
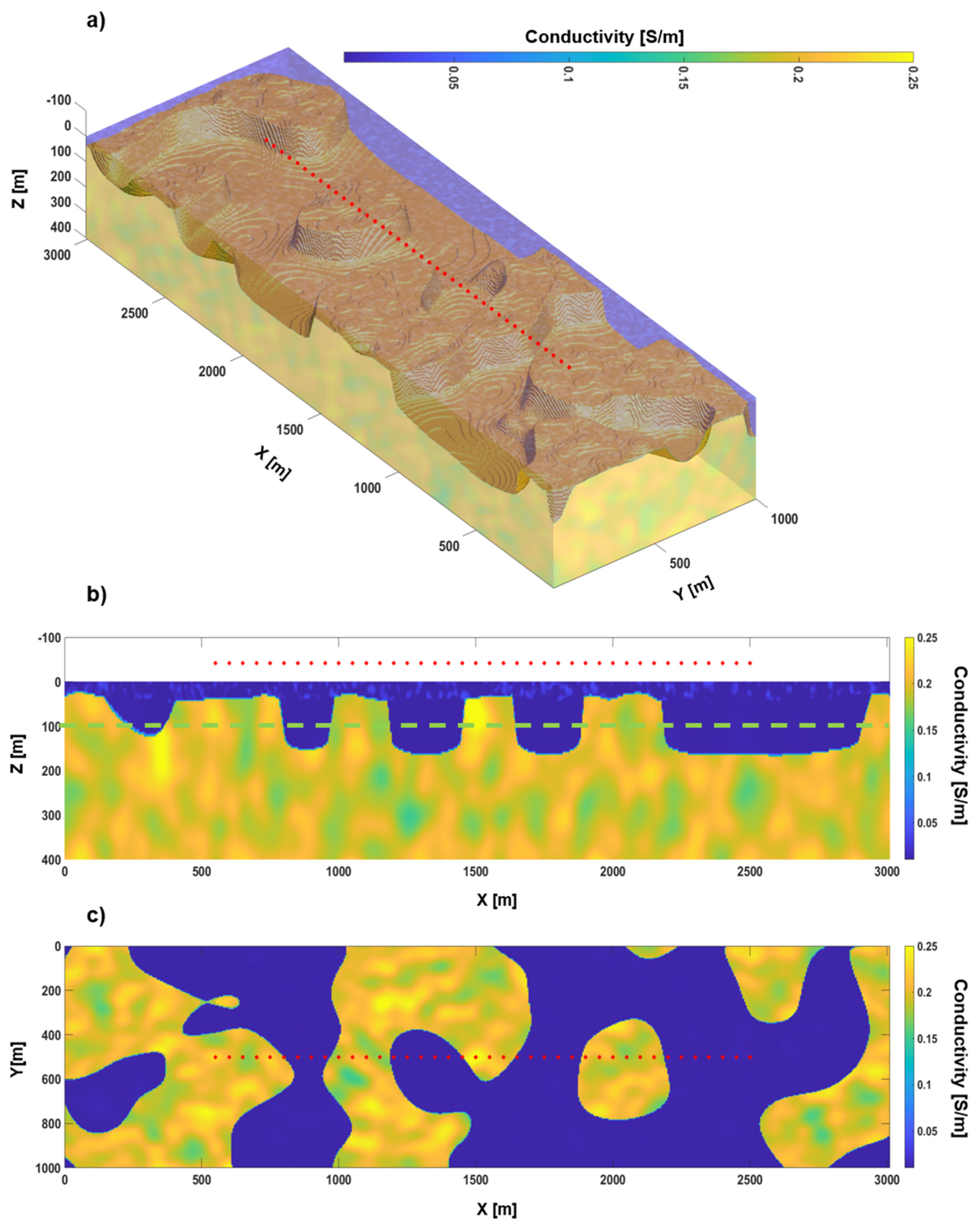
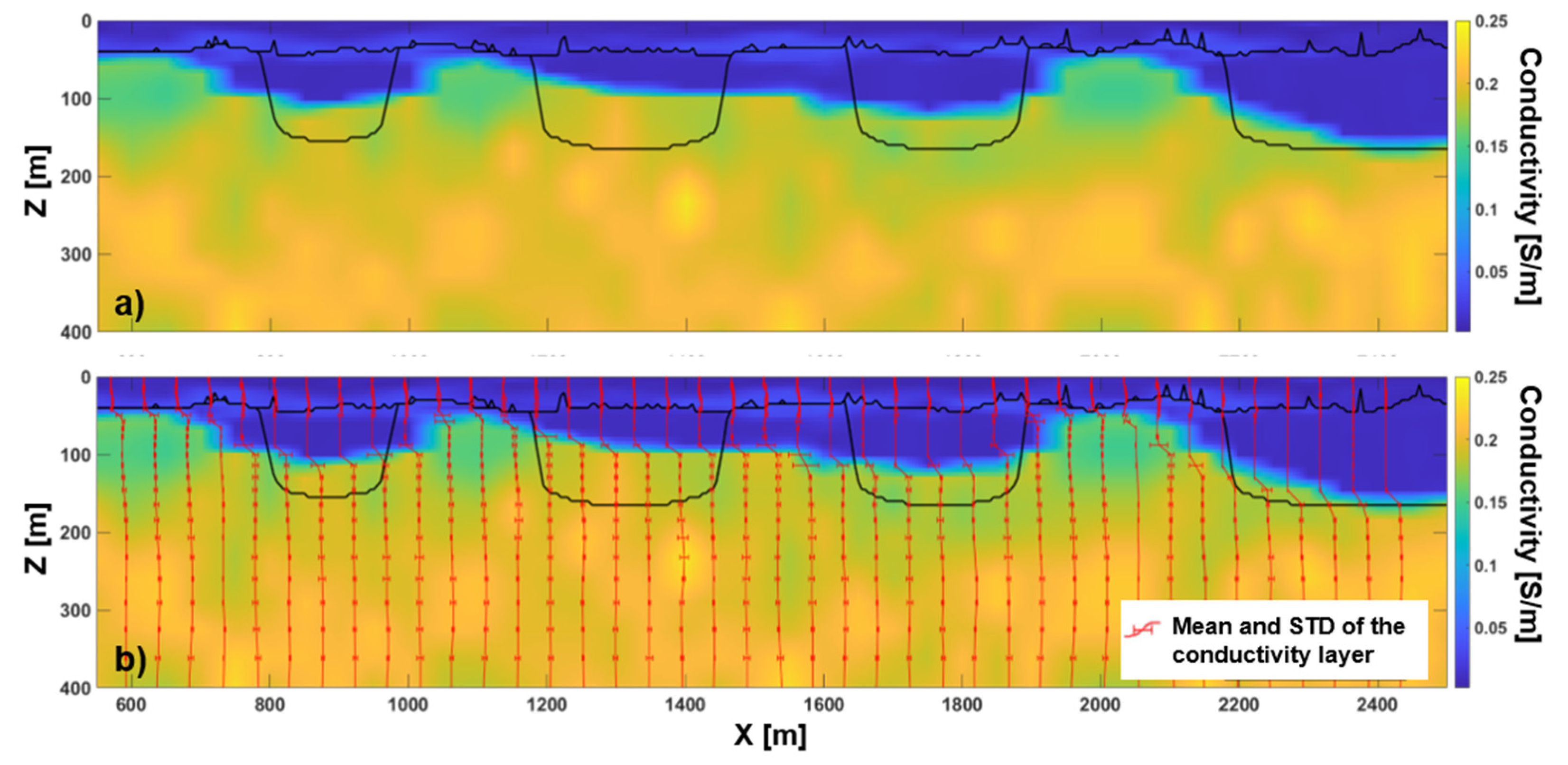
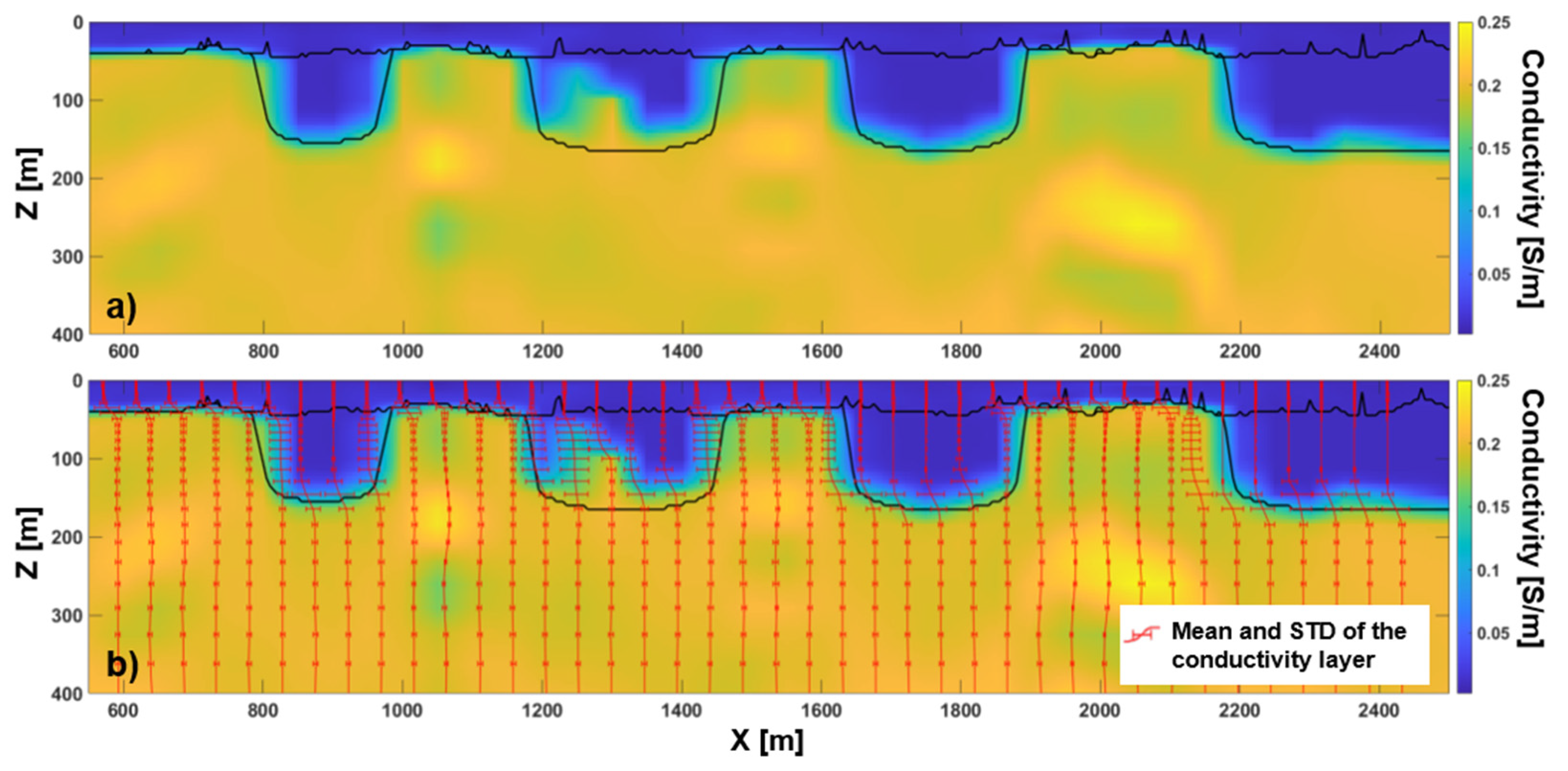
3.1. Test 1: 3D Conductivity Distribution with Homogeneous Layers
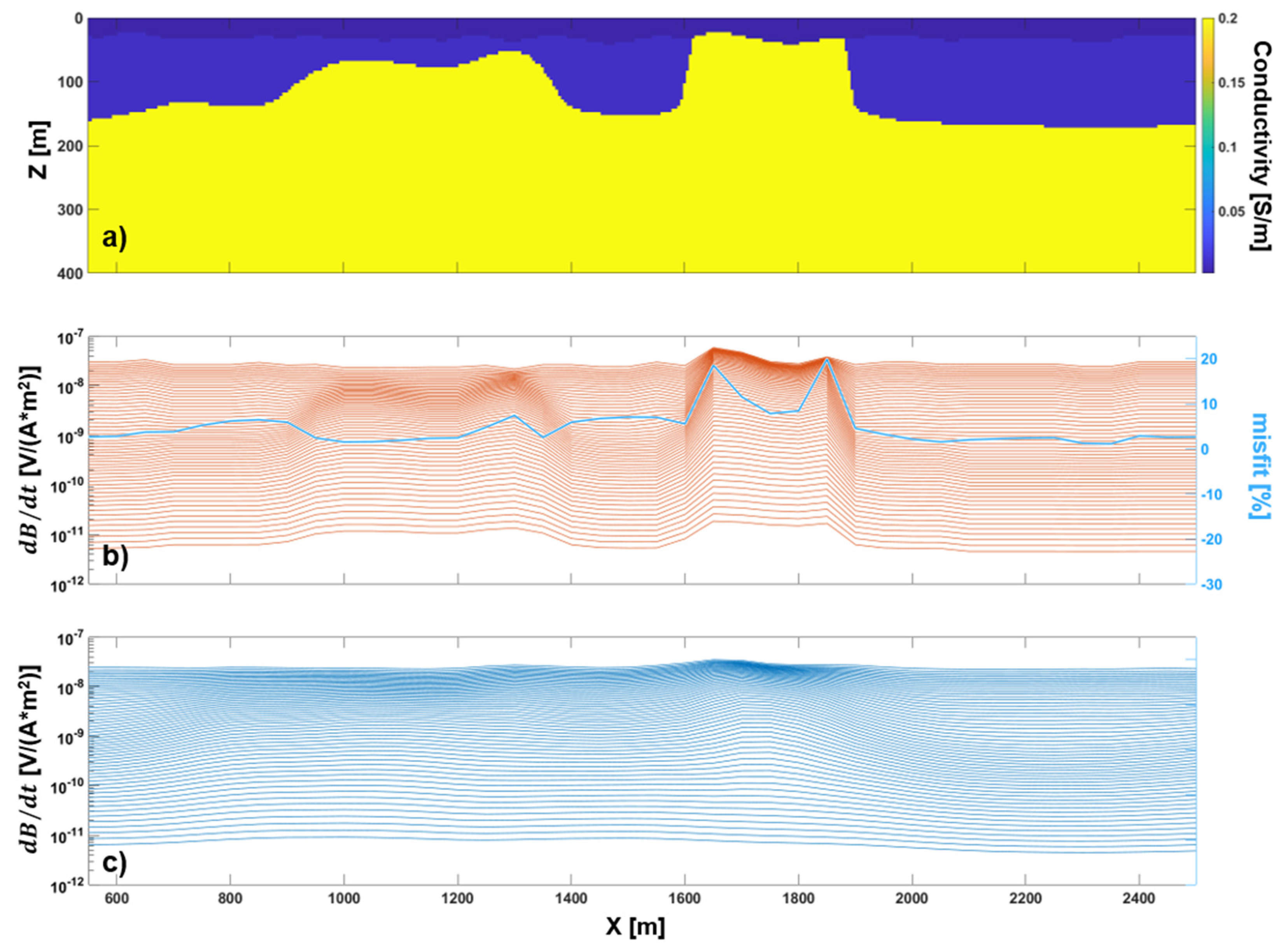
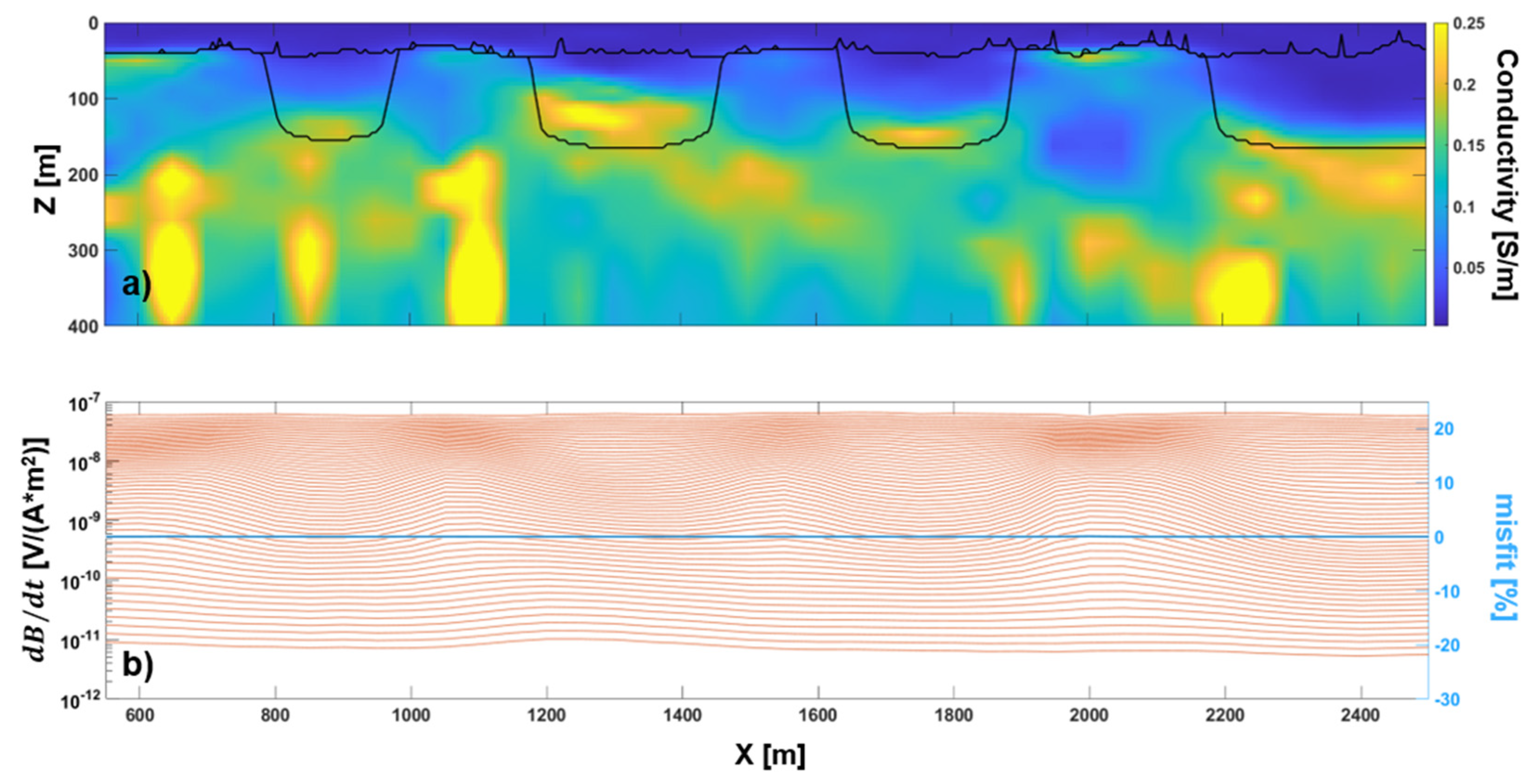
3.1.1. Deterministic Occam’s Inversion
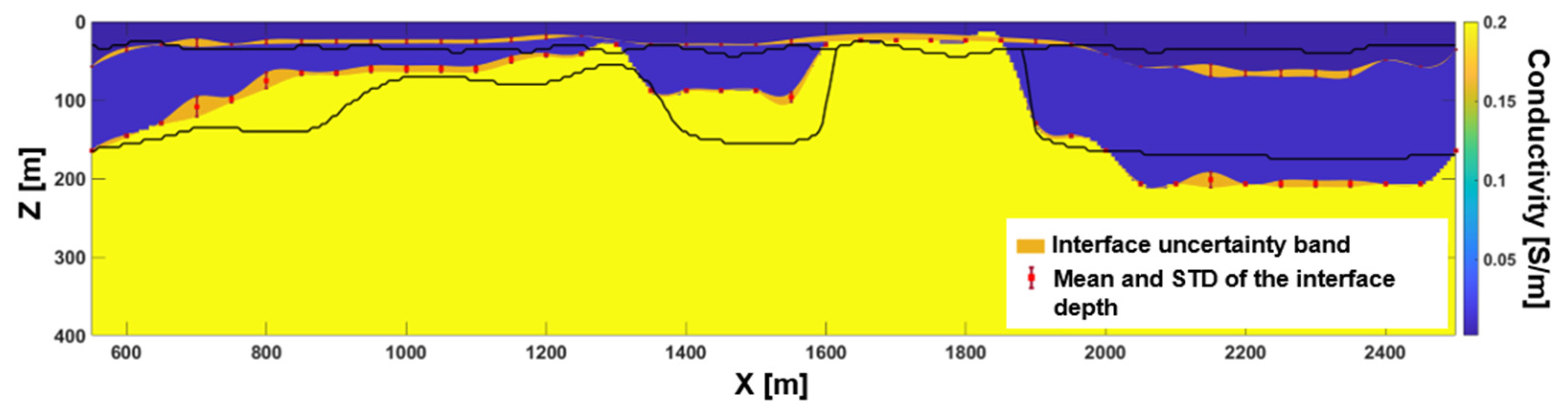
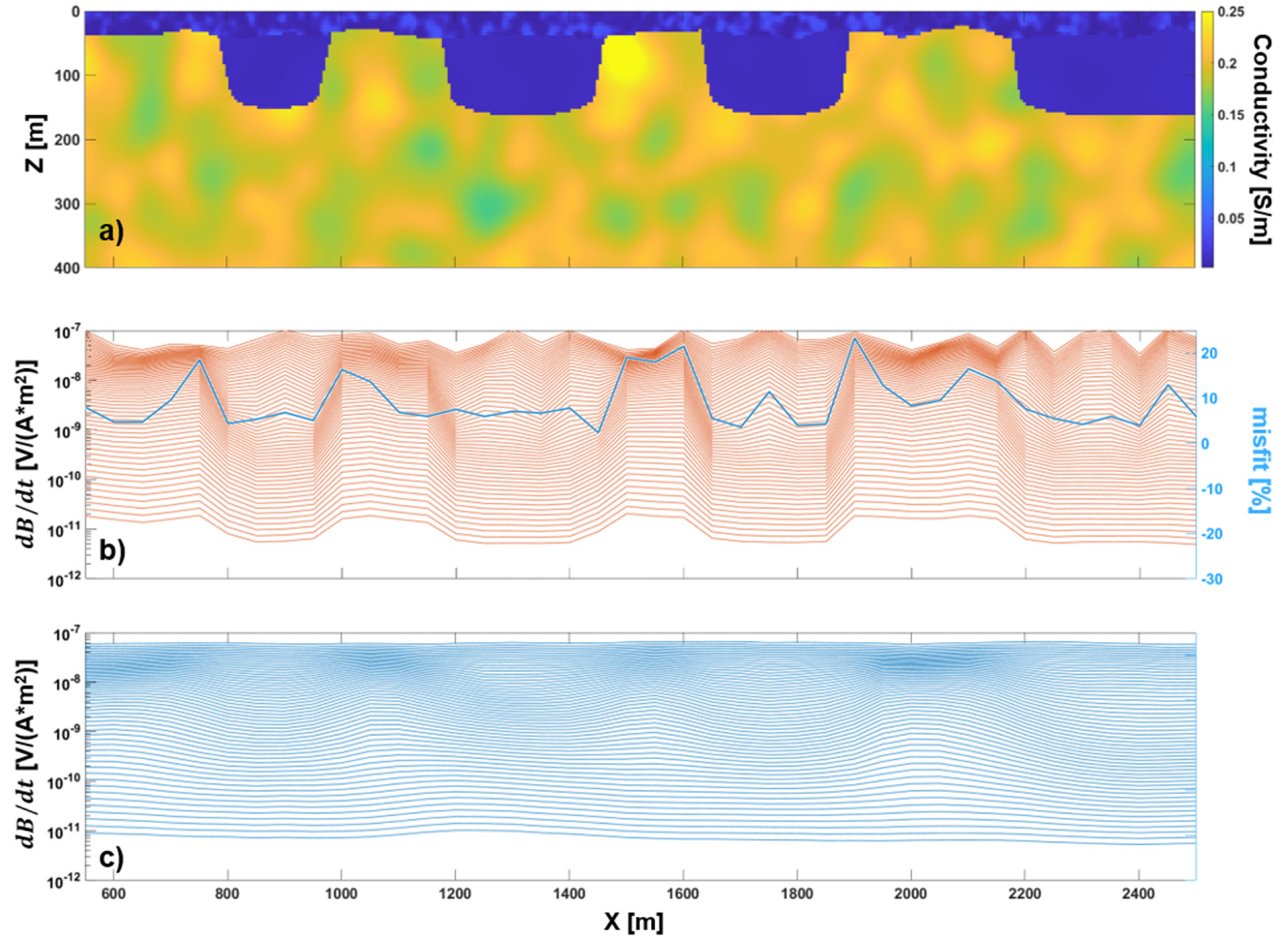
3.1.2. Stochastic Inversion without Modeling Error Assessment
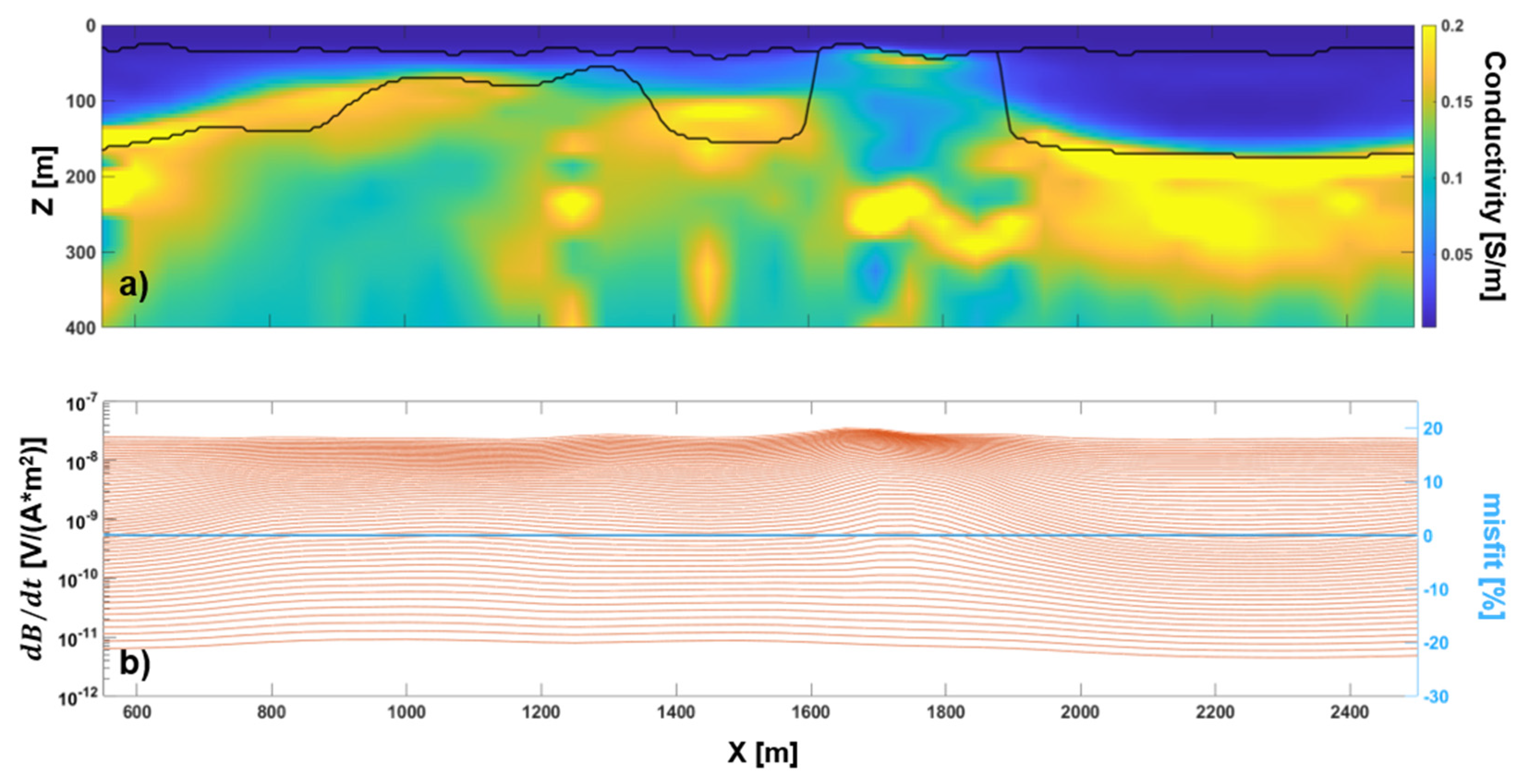
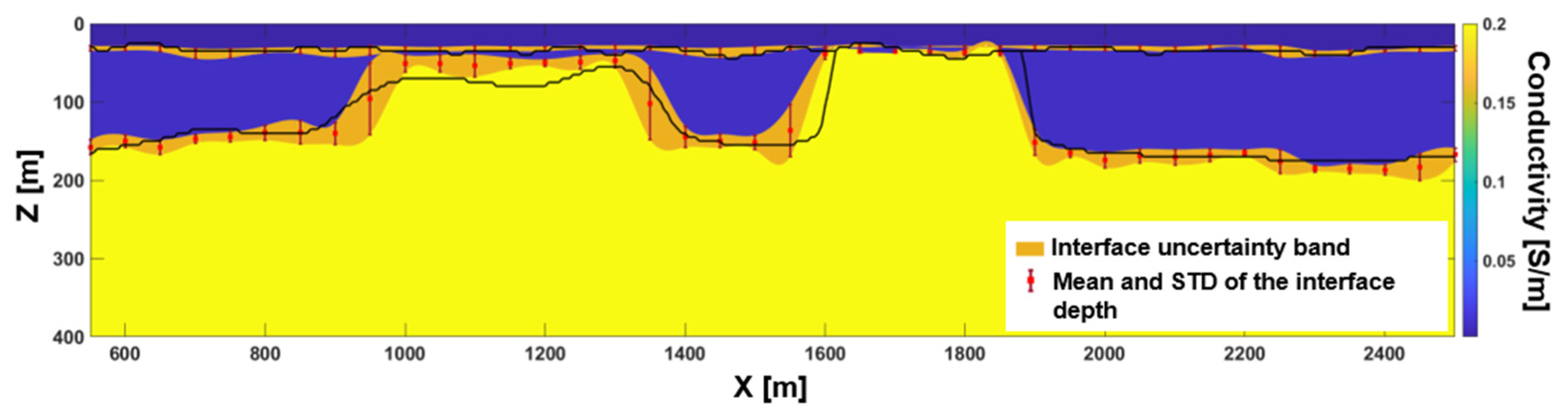
3.1.3. Stochastic Inversion Incorporating the 1D Modeling Error
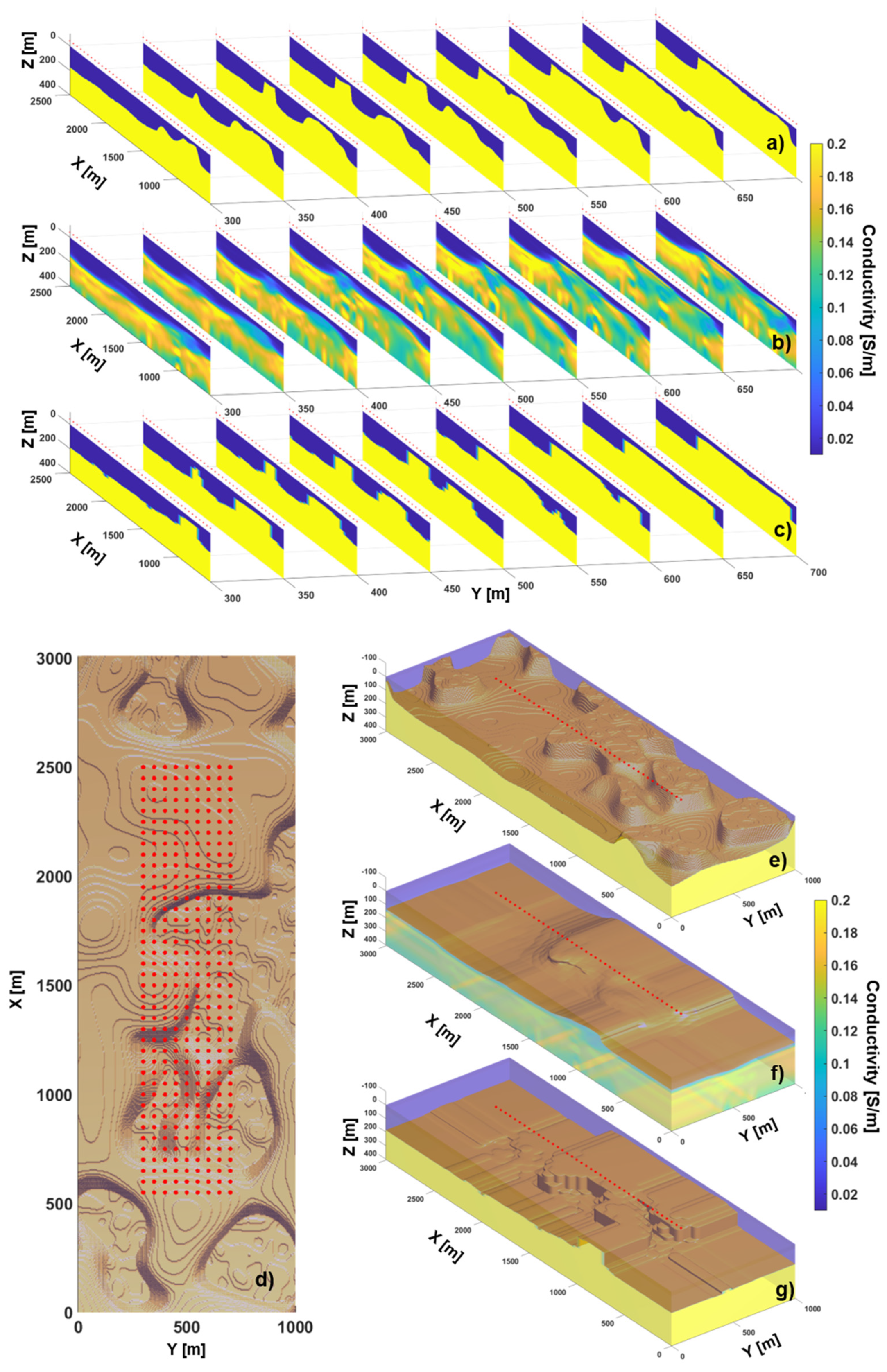
3.2. Test 2: 3D Conductivity Distribution with Heterogeneous Layers
4. Discussion
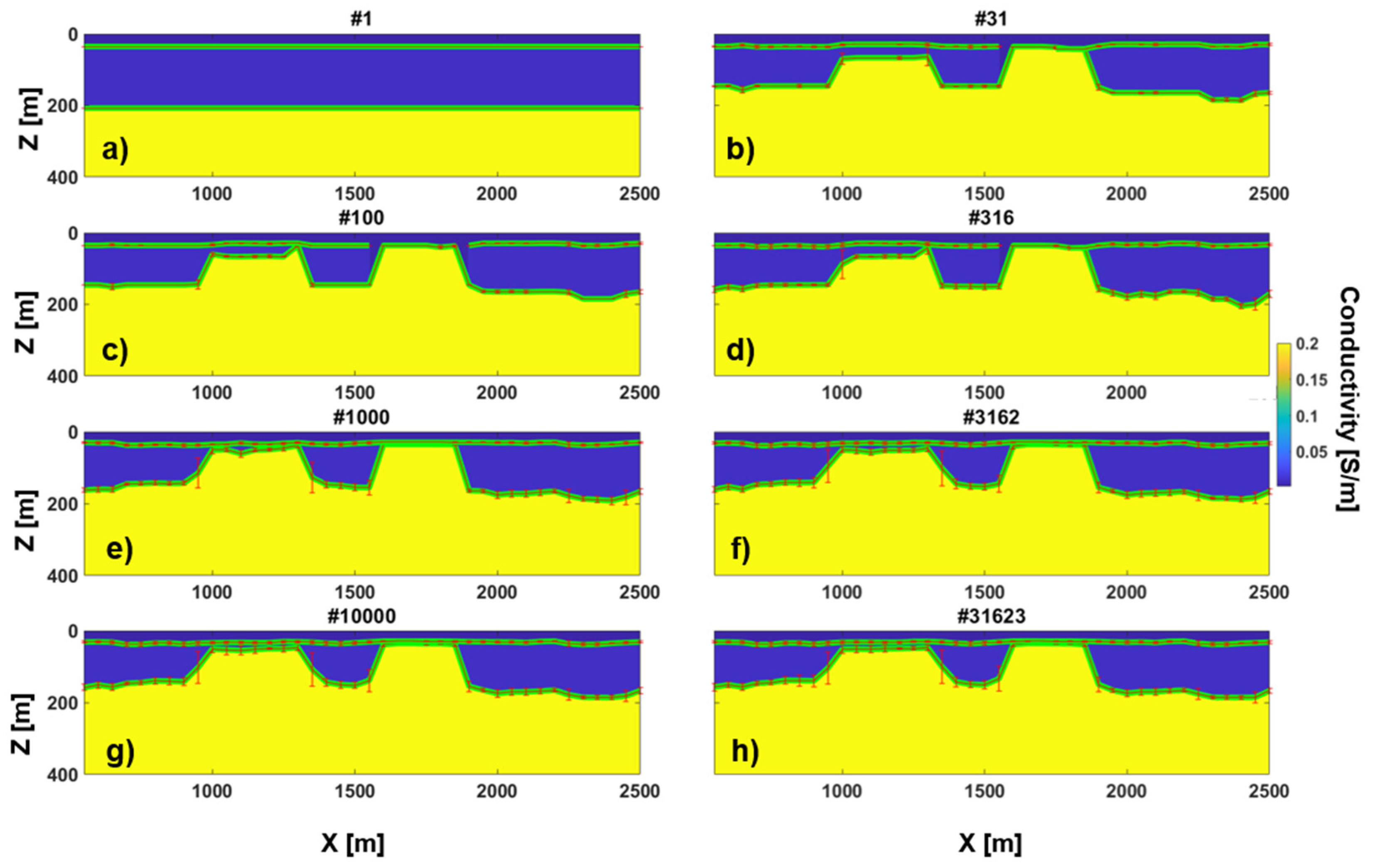
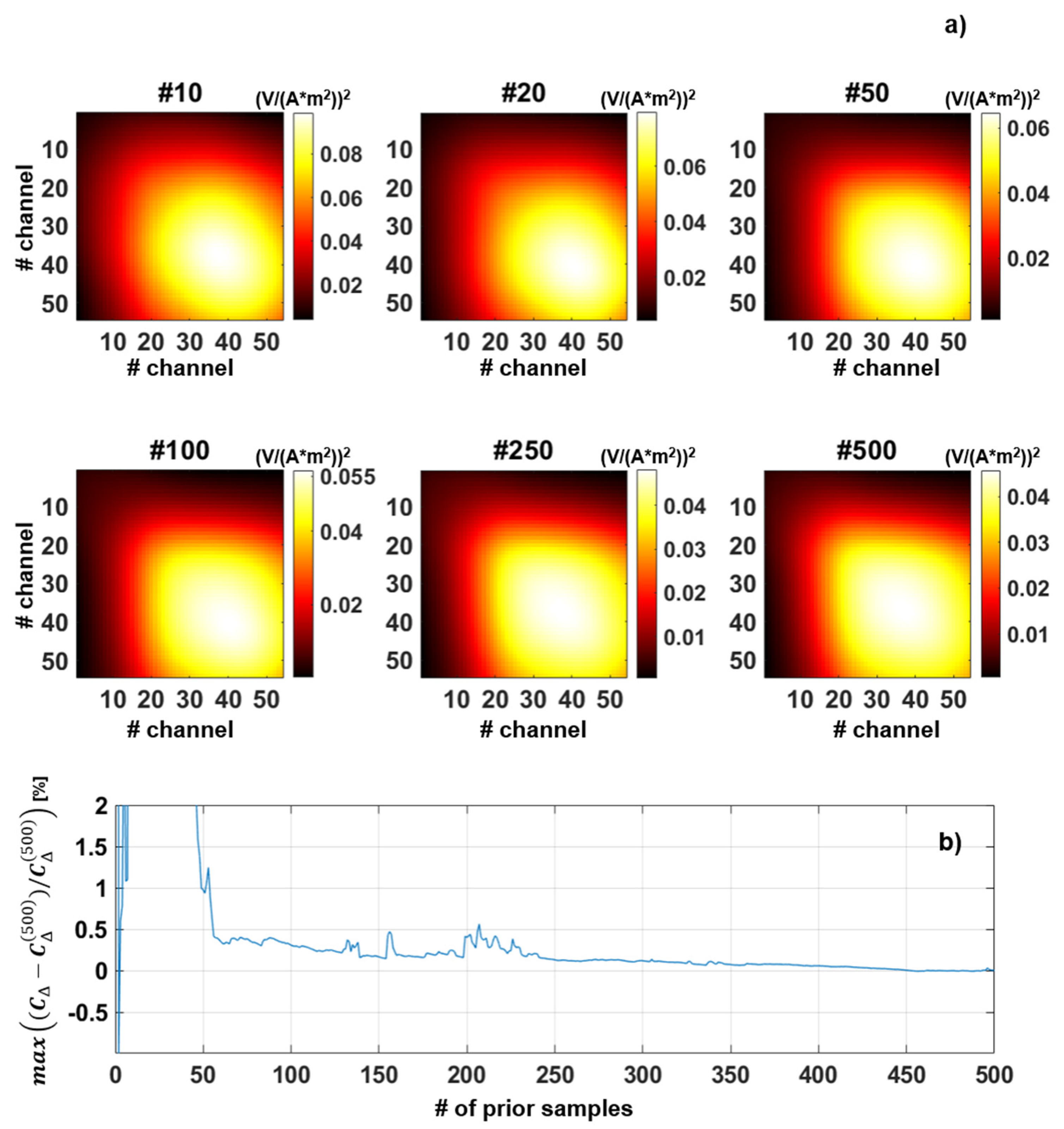
4.1. About the Numerosity of the Prior Samples for the Convergency of the Stochastic Inversion
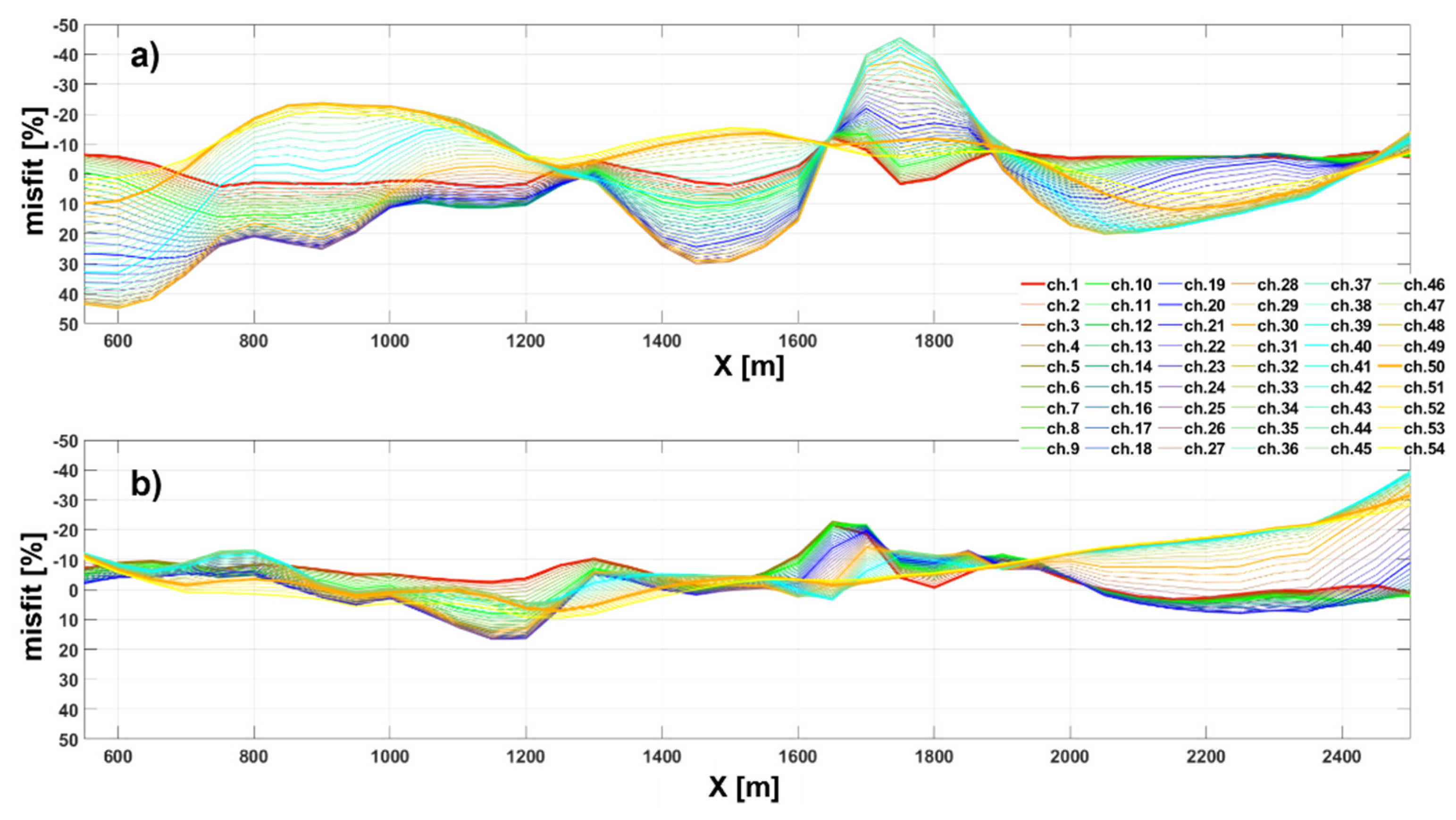
4.2. About the Numerosity of the Prior’s Samples for the Estimation of the Modeling Error
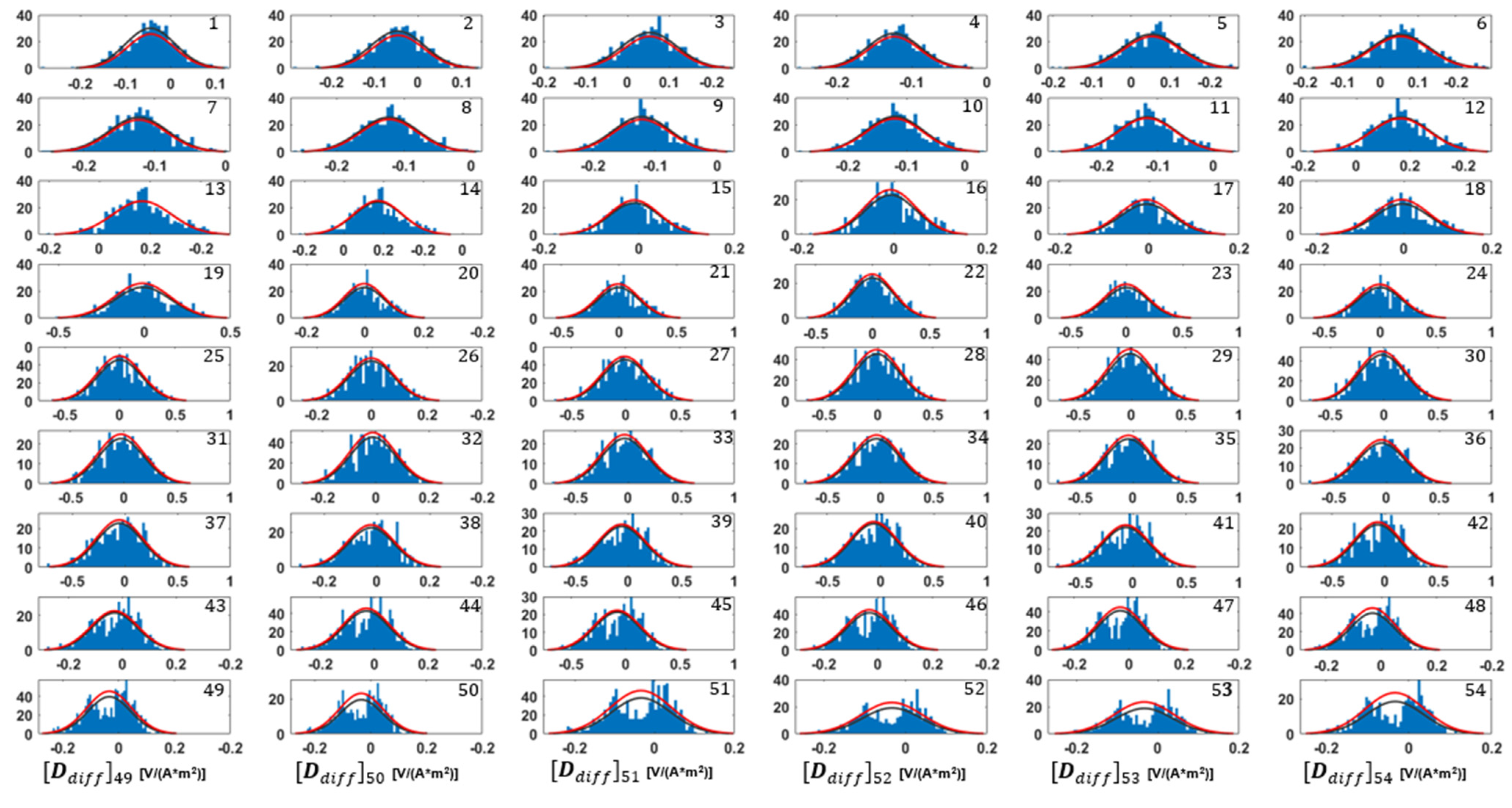
4.3. About the Gaussianity of the Modeling Error
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhdanov, M.S.; Alfouzan, F.A.; Cox, L.; Alotaibi, A.; Alyousif, M.; Sunwall, D.; Endo, M. Large-scale 3D modeling and in-version of multiphysics airborne geophysical data: A case study from the Arabian Shield, Saudi Arabia. Minerals 2018, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witherly, K. The quest for the Holy Grail in mining geophysics: A review of the development and application of airborne EM systems over the last 50 years. Geophysics 2000, 19, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfouzan, F.A.; Alotaibi, A.M.; Cox, L.H.; Zhdanov, M.S. Spectral induced polarization survey with distributed array system for mineral exploration: Case study in Saudi Arabia. Minerals 2020, 10, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cudahy, T. Mineral mapping for exploration: An australian journey of evolving spectral sensing technologies and industry collaboration. Geosciences 2016, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountain, D. Airborne electromagnetic systems—50 years of development. Explor. Geophys. 1998, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karshakov, E.V.; Podmogov, Y.G.; Kertsman, V.M.; Moilanen, J. Combined frequency domain and time domain airborne data for environmental and engineering challenges. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2017, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moilanen, E.; Karshakov, E.; Volkovitsky, A. Time domain helicopter EM system Equator: Resolution, sensitivity, universality. In 6th International AEM Conference & Exhibition; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Houten, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Volkovitsky, A.; Karshakov, E. Airborne EM systems variety: What is the difference? In 6th International AEM Conference & Exhibition; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Houten, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Combrinck, M.; Wright, R. Achieving accurate interpretation results from full-waveform streamed data AEM surveys. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezzoli, A.; Dauti, F.; Wijns, C. Robust scanning of AEM data for IP effects. Explor. Geophys. 2021, 52, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legault, J.M.; Izarra, C.; Prikhodko, A.; Zhao, S.; Saadawi, E.M. Helicopter EM (ZTEM–VTEM) survey results over the Nuqrah copper–lead–zinc–gold SEDEX massive sulphide deposit in the Western Arabian Shield, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, K.; Prikhodko, A.; Legault, J.M.; Plastow, G.C.; Kapetas, J.; Druecker, M. VTEM airborne EM, aeromagnetic and gamma-ray spectrometric data over the Cerro Quema high sulphidation epithermal gold deposits, Panama. Explor. Geophys. 2016, 47, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, K.I.; Auken, E. SkyTEM-A new high-resolution helicopter transient electromagnetic system. Explor. Geophys. 2004, 35, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, W.; Paterson, N.R.; Kwan, K. AeroTEM characteristics and field results. Geophysics 2001, 20, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Hodges, G.; Miles, P. MULTIPULSE–high resolution and high power in one TDEM system. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Lee, T.J. The moments of the impulse response: A new paradigm for the interpretation of transient electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2002, 67, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annan, A.P.; Lookwood, R. An application of airborne geotem in australian conditions. Explor. Geophys. 1991, 22, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macnae, J. Improving the accuracy of shallow depth determinations in AEM sounding. Explor. Geophys. 2004, 35, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, G.; Street, G.; Kahimise, I.; Hutchins, D. Regional TEMPEST survey in north-east Namibia. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggatt, P.B.; Klinkert, P.S.; Hage, T.B. The Spectrem airborne electromagnetic system—Further developments. Geophysics 2000, 65, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapia, V.; Viezzoli, A.; Jørgensen, F.; Oldenborger, A.G.; Marchetti, M. The impact on geological and hydrogeological mapping results of moving from ground to airborne TEM. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2014, 19, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Siemon, B.; Christiansen, A.V.; Auken, E. A review of helicopter-borne electromagnetic methods for groundwater exploration. Near Surf. Geophys. 2009, 7, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siemon, B.; Seht, M.I.-V.; Frank, S. Airborne electromagnetic and radiometric peat thickness mapping of a bog in Northwest Germany (Ahlen-Falkenberger Moor). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høyer, A.-S.; Jørgensen, F.; Sandersen, P.B.; Viezzoli, A.; Møller, I. 3D geological modelling of a complex buried-valley network delineated from borehole and AEM data. J. Appl. Geophys. 2015, 122, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, G.; Gervasio, I.; Brancatelli, G.; Boaga, J.; Della Vedova, B.; Cassiani, G. Frequency-dependent multi-offset phase analysis of surface waves: An example of high-resolution characterization of a riparian aquifer. Geophys. Prospect. 2015, 64, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Guo, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z. An efficient footprint-guided compact finite element algorithm for 3-D airborne electro-magnetic modeling. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1809–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reninger, P.-A.; Martelet, G.; Perrin, J.; Dumont, M. Processing methodology for regional AEM surveys and local implications. Explor. Geophys. 2019, 51, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikunoo, E.A.; Vignoli, G.; Jørgensen, F.; Yidana, S.M.; Banoeng-Yakubo, B. New regional stratigraphic insights from a 3D geological model of the Nasia sub-basin, Ghana, developed for hydrogeological purposes and based on reprocessed B-field data originally collected for mineral exploration. Solid Earth 2020, 11, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, V.A.; Auken, E. Optimizing a layered and laterally constrained 2D inversion of resistivity data using Broyden’s update and 1D derivatives. J. Appl. Geophys. 2004, 56, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, G.; Fiandaca, G.; Christiansen, A.V.; Kirkegaard, C.; Auken, E. Sharp spatially constrained inversion with applications to transient electromagnetic data. Geophys. Prospect. 2014, 63, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, R.; Sambridge, M. A holistic approach to inversion of frequency-domain airborne EM data. Geophysics 2006, 71, G301–G312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, R.; Sambridge, M. A holistic approach to inversion of time-domain airborne EM. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2006, 2006, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socco, L.V.; Boiero, D.; Foti, S.; Wisén, R. Laterally constrained inversion of ground roll from seismic reflection records. Geophysics 2009, 74, G35–G45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, G.; Deiana, R.; Cassiani, G. Focused inversion of vertical radar profile (VRP) traveltime data. Geophysics 2012, 77, H9–H18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot-Hedlin, C.; Constable, S. Occam’s inversion to generate smooth, two-dimensional models from magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 1990, 55, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignoli, G.; Guillemoteau, J.; Barreto, J.; Rossi, M. Reconstruction, with tunable sparsity levels, of shear wave velocity profiles from surface wave data. Geophys. J. Int. 2021, 225, 1935–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.; Vignoli, G.; Ueda, T. Sharp boundary inversion in crosswell travel-time tomography. J. Geophys. Eng. 2006, 3, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Viezzoli, A.; Auken, E.; Munday, T. Spatially constrained inversion for quasi 3D modelling of airborne electromagnetic data–an application for environmental assessment in the Lower Murray Region of South Australia. Explor. Geophys. 2009, 40, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley-Cooper, A.Y.; Viezzoli, A.; Guillemoteau, J.; Vignoli, G.; Macnae, J.; Cox, L.; Munday, T. Airborne electromagnetic mod-elling options and their consequences in target definition. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansen, A.V.; Auken, E.; Kirkegaard, C.; Schamper, C.; Vignoli, G. An efficient hybrid scheme for fast and accurate inversion of airborne transient electromagnetic data. Explor. Geophys. 2016, 47, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Vignoli, G.; Viezzoli, A.; Nevalainen, J.; Vacca, G. (Quasi-) real-time inversion of airborne time-domain electro-magnetic data via artificial neural network. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M. Probabilistic inverse problems using machine learning-applied to inversion of airborne EM data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021. submitted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V.; Kirkegaard, C.; Fiandaca, G.; Schamper, C.; Behroozmand, A.A.; Binley, A.; Nielsen, E.; Effersø, F.; Christensen, N.B.; et al. An overview of a highly versatile forward and stable inverse algorithm for airborne, ground-based and borehole electromagnetic and electric data. Explor. Geophys. 2015, 46, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vest Christiansen, A.V.; Auken, E.; Viezzoli, A. Quantification of modeling errors in airborne TEM caused by inac-curate system description. Geophysics 2011, 76, F43–F52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, D.W.; Heagy, L.J.; Kang, S.; Cockett, R. 3D electromagnetic modelling and inversion: A case for open source. Explor. Geophys. 2019, 51, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auken, E.; Foged, N.; Larsen, J.J.; Lassen, K.V.T.; Maurya, P.K.; Dath, S.M.; Eiskjær, T.T. tTEM—A towed transient electro-magnetic system for detailed 3D imaging of the top 70 m of, the subsurface. Geophysics 2019, 84, E13–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M.; Cordua, K.S.; Jacobsen, B.H.; Mosegaard, K. Accounting for imperfect forward modeling in geophysical inverse problems—Exemplified for crosshole tomography. Geophysics 2014, 79, H1–H21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuma, M.; Cox, L.; Zhdanov, M. Paradigm change in interpretation of AEM data by using a large-scale parallel 3D inversion. In Near Surface Geoscience—First Conference on Geophysics for Mineral Exploration and Mining; European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers: Houten, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Oldenburg, D.W. Three-dimensional inversion of airborne time-domain electromagnetic data with applications to a porphyry deposit. Geophysics 2012, 77, B23–B34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yin, C. 3D inversion for multipulse airborne transient electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2016, 81, E401–E408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, E.; Ascher, U.M.; Oldenburg, D.W. Inversion of 3D electromagnetic data in frequency and time domain using an inexact all-at-once approach. Geophysics 2004, 69, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, M.S.; Schwarzbach, C.; Haber, E.; Oldenburg, D.W. 3D parametric hybrid inversion of time-domain airborne electromagnetic data. Geophysics 2015, 80, K25–K36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, L.H.; Wilson, G.A.; Zhdanov, M. 3D inversion of airborne electromagnetic data using a moving footprint. Explor. Geophys. 2010, 41, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M. Foundations of Geophysical Electromagnetic Theory and Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezzoli, A.; Munday, T.; Auken, E.; Christiansen, A.V. Accurate quasi 3D versus practical full 3D inversion of AEM data–the Bookpurnong case study. Preview 2010, 149, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, J.; Gunning, J.; Annetts, D. Probabilistic inversion of airborne electromagnetic data under spatial constraints. Geophysics 2015, 80, E135–E146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, A. Inverse Problem Theory and Methods for Model Parameter Estimation; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhdanov, M.S. Geophysical Inverse Theory and Regularization Problems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tarantola, A.; Valette, B. Generalized nonlinear inverse problems solved using the least squares criterion. Rev. Geophys. 1982, 20, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, S.; Parker, R.L.; Constable, C. Occam’s inversion: A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data. Geophysics 1987, 52, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høyer, A.S.; Vignoli, G.; Hansen, T.M.; Vu, L.T.; Keefer, D.A.; Jørgensen, F. Multiple-point statistical simulation for hydrogeological models: 3-D training image development and conditioning strategies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 6069–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, E. Computational Methods in Geophysical Electromagnetics; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallée, M.A.; Smith, R.S. Application of Occam’s inversion to airborne time-domain electromagnetics. Lead. Edge 2009, 28, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosegaard, K.; Tarantola, A. Monte Carlo sampling of solutions to inverse problems. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1995, 100, 12431–12447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M.; Cordua, K.S.; Looms, M.C.; Mosegaard, K. SIPPI: A Matlab toolbox for sampling the solution to inverse problems with complex prior information: Part 1—Methodology. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M.; Cordua, K.S.; Looms, M.C.; Mosegaard, K. SIPPI: A Matlab toolbox for sampling the solution to inverse problems with complex prior information: Part 2—Application to crosshole GPR tomography. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, F.; Sandersen, P.B. Buried and open tunnel valleys in Denmark—Erosion beneath multiple ice sheets. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2006, 25, 1339–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kehew, A.E.; Piotrowski, J.A.; Jørgensen, F. Tunnel valleys: Concepts and controversies—A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 113, 33–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ravalec, M.; Noetinger, B.; Hu, L.Y. The FFT Moving Average (FFT-MA) Generator: An efficient numerical method for generating and conditioning gaussian simulations. Math. Geol. 2000, 32, 701–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.M.; Minsley, B.J. Inversion of airborne EM data with an explicit choice of prior model. Geophys. J. Int. 2019, 218, 1348–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, P.; Vignoli, G.; Hansen, T.M. 1D Stochastic Inversion of Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data with Realistic Prior and Accounting for the Forward Modeling Error. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193881
Bai P, Vignoli G, Hansen TM. 1D Stochastic Inversion of Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data with Realistic Prior and Accounting for the Forward Modeling Error. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(19):3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193881
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Peng, Giulio Vignoli, and Thomas Mejer Hansen. 2021. "1D Stochastic Inversion of Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data with Realistic Prior and Accounting for the Forward Modeling Error" Remote Sensing 13, no. 19: 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193881
APA StyleBai, P., Vignoli, G., & Hansen, T. M. (2021). 1D Stochastic Inversion of Airborne Time-Domain Electromagnetic Data with Realistic Prior and Accounting for the Forward Modeling Error. Remote Sensing, 13(19), 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193881