Soil Salinization Level Monitoring and Classifying by Mixed Chaotic Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
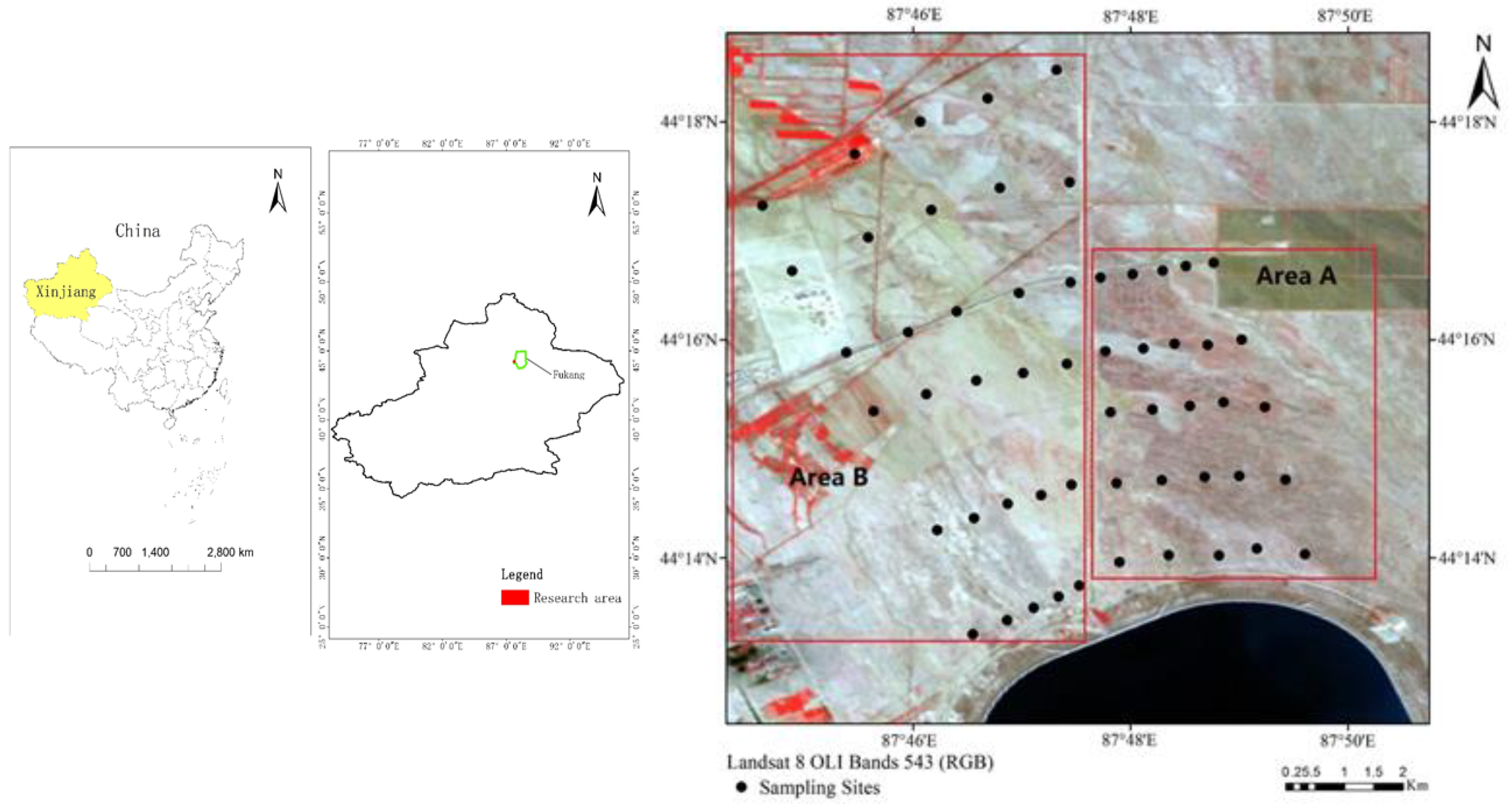
2.1. Soil Sample Collection
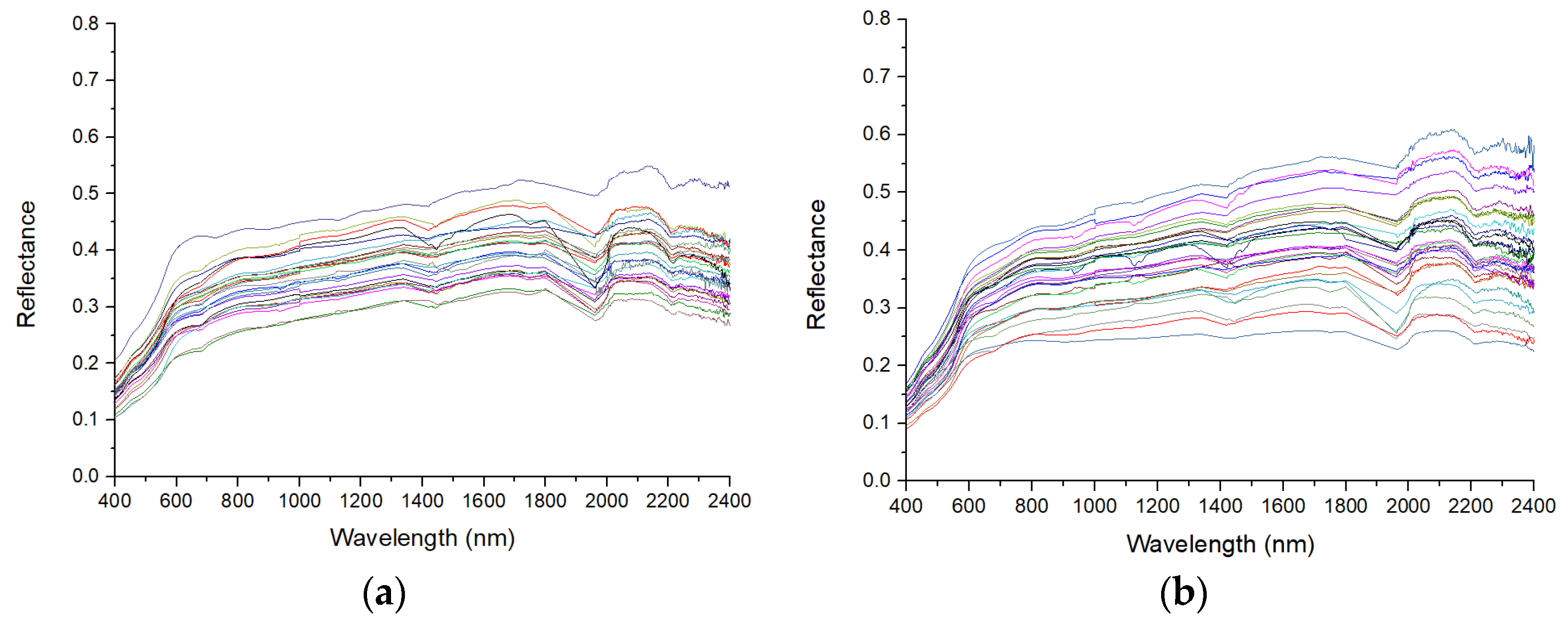
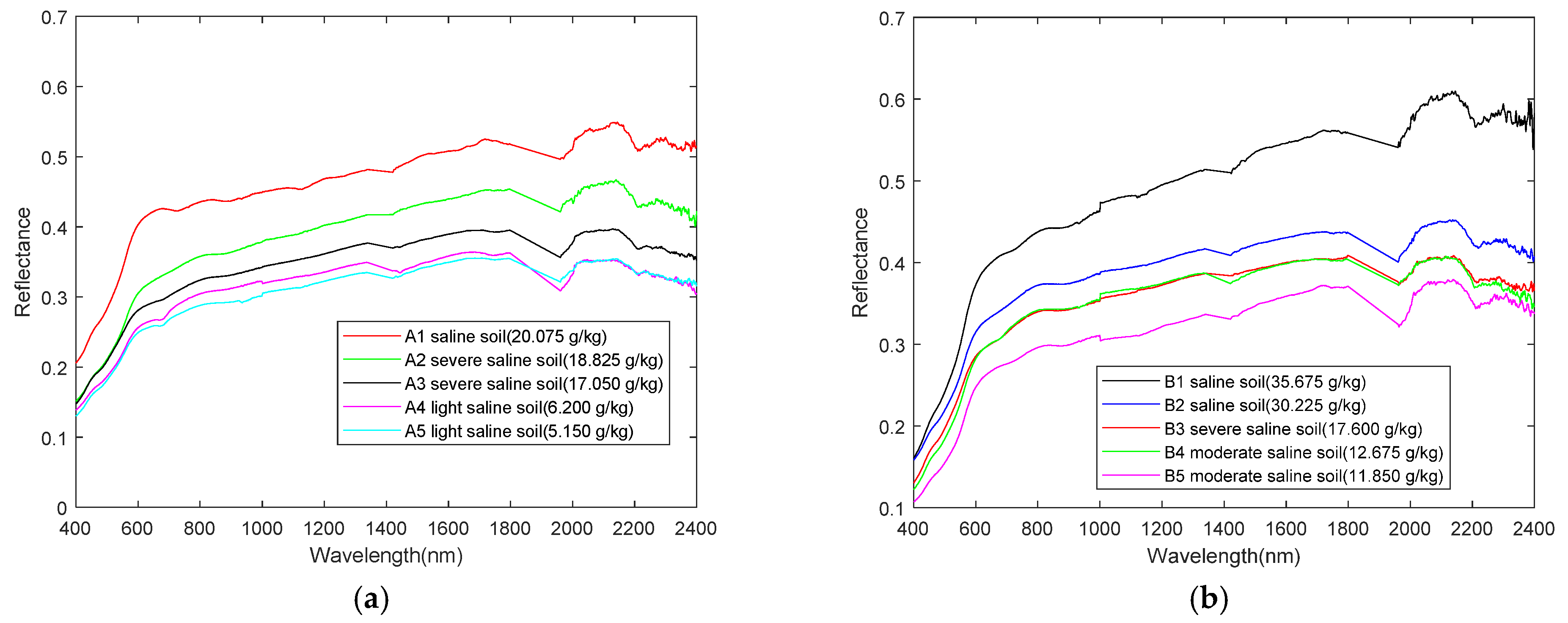
2.2. Soil Hyperspectral Measurement
2.3. Spectrum Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Classification of Soil Salinization Level
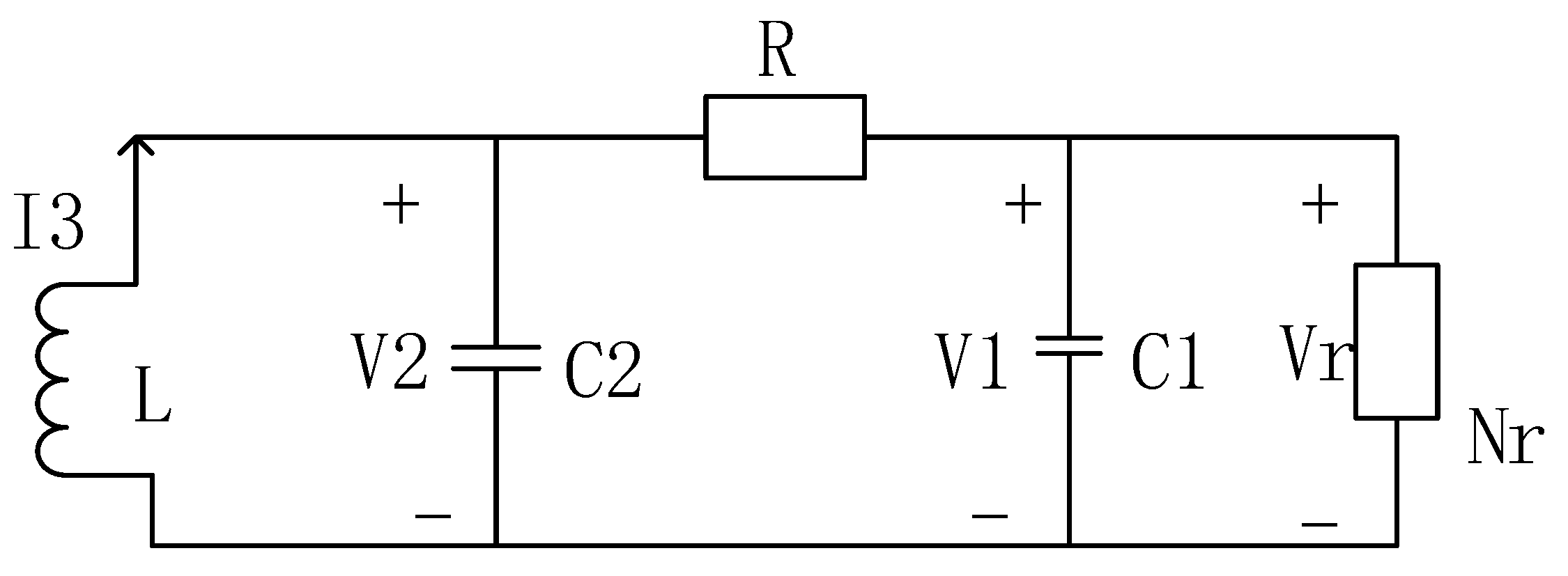
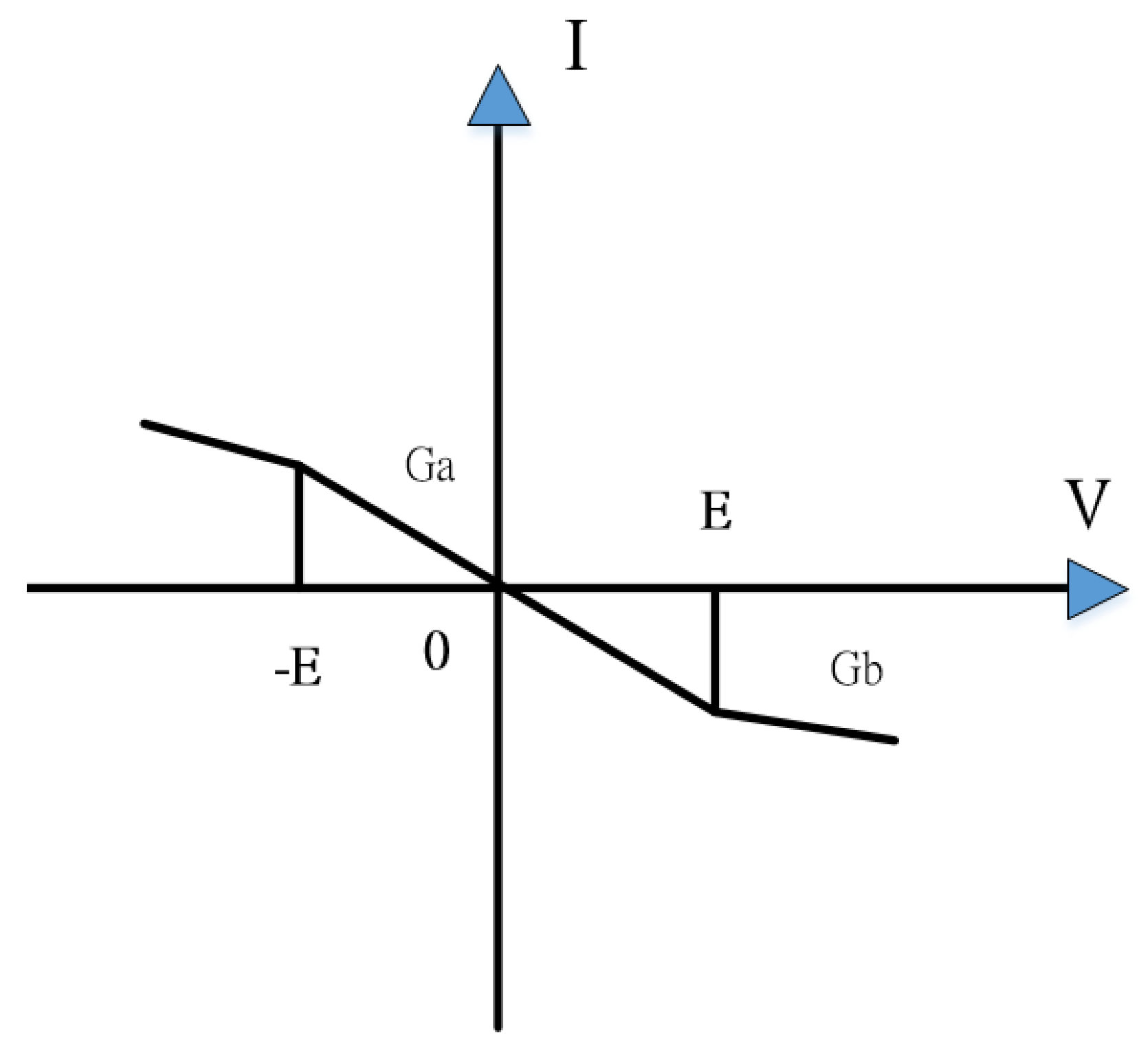
2.5. Chua’s Circuit
2.6. Chen-Lee Chaotic System
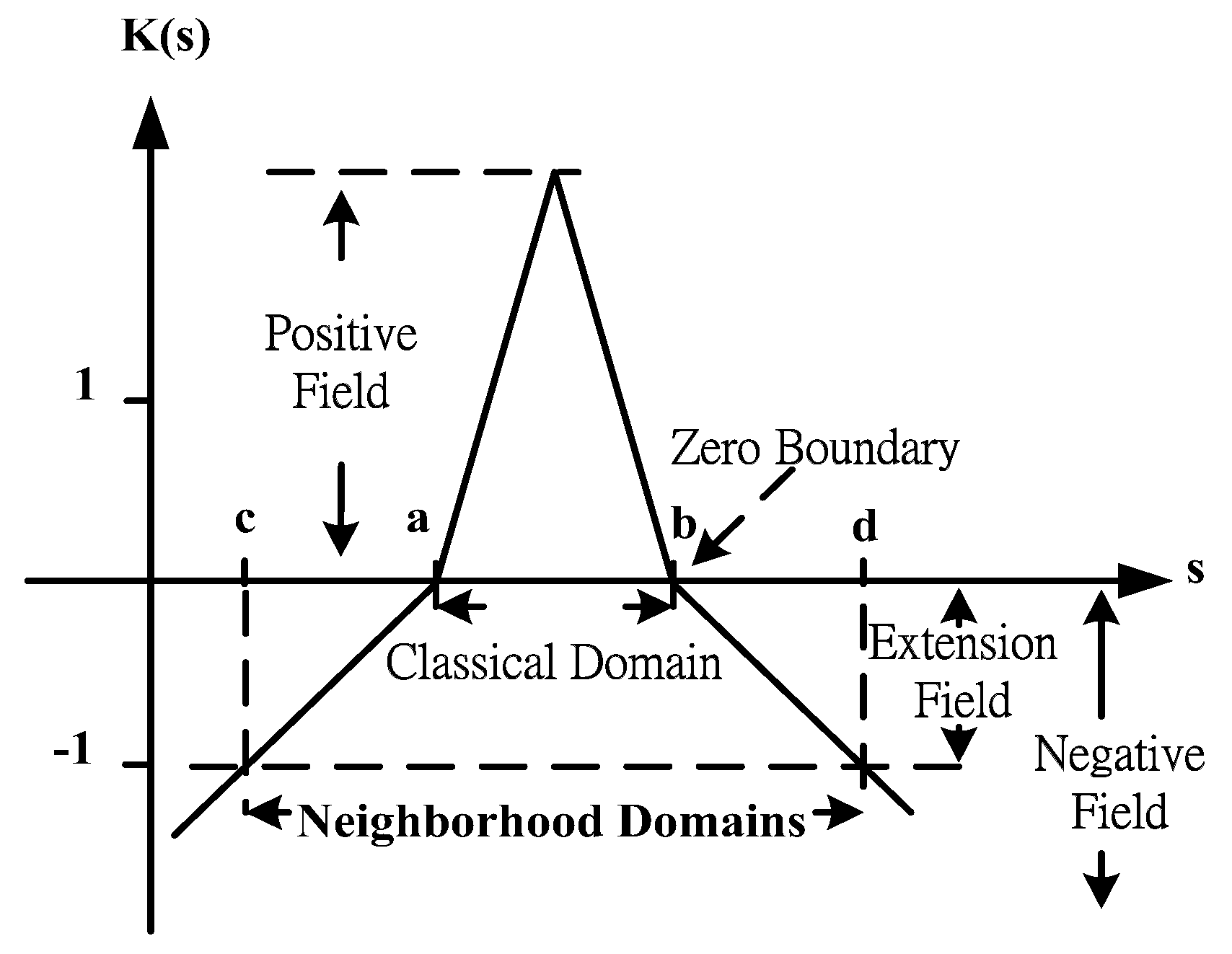
2.7. Extension Theory
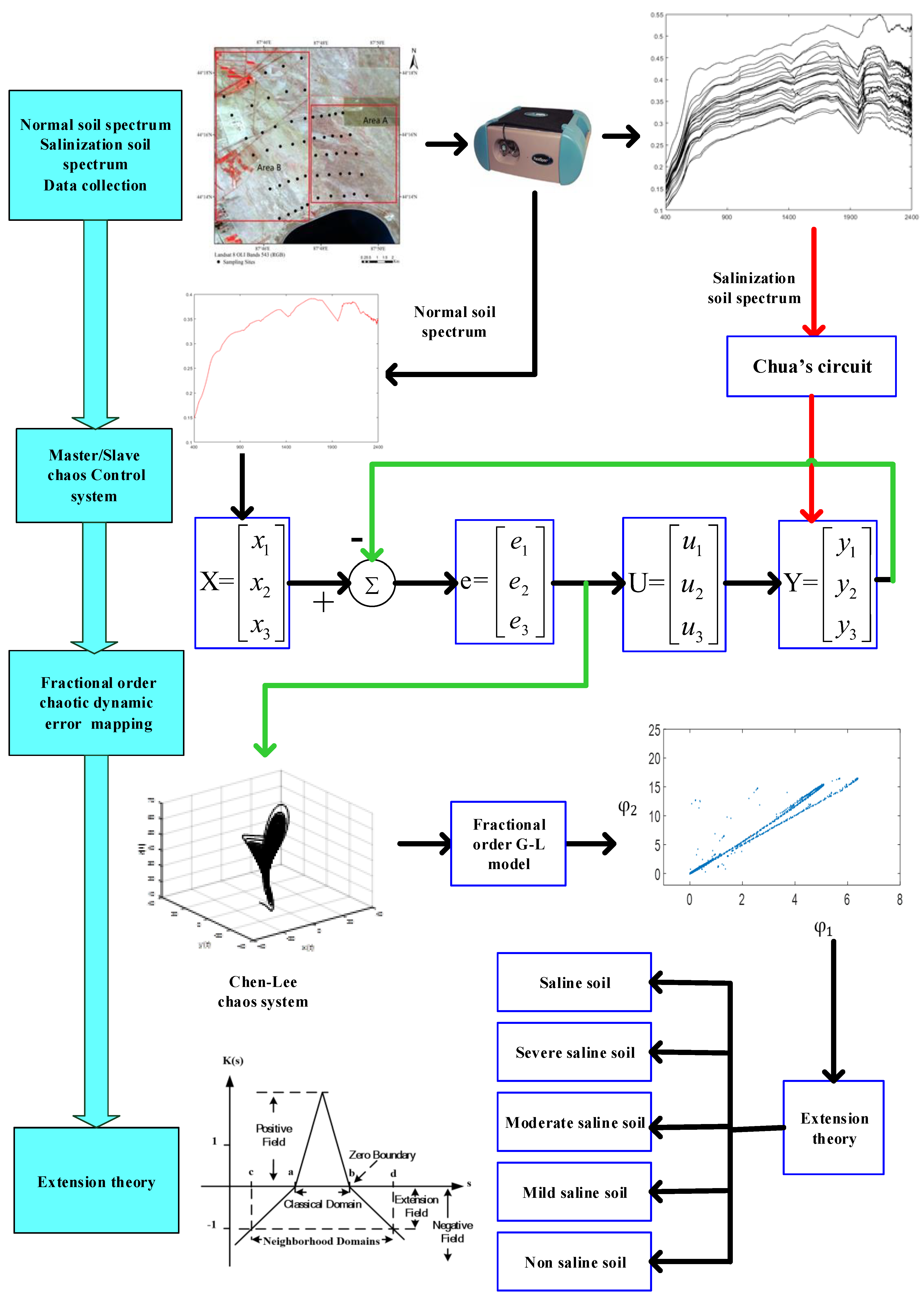
2.8. Intelligent Classification System Architecture
3. Simulation results
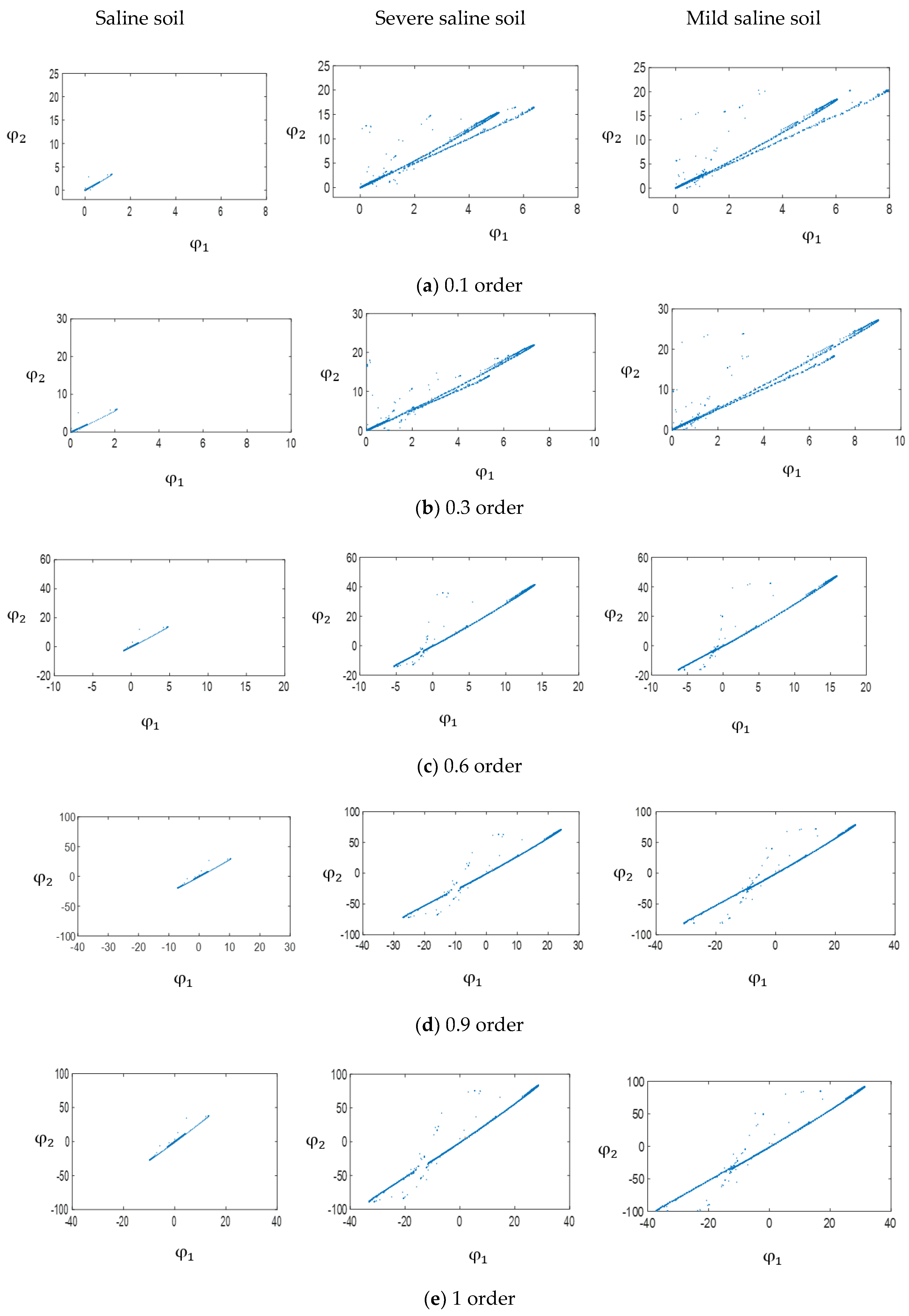
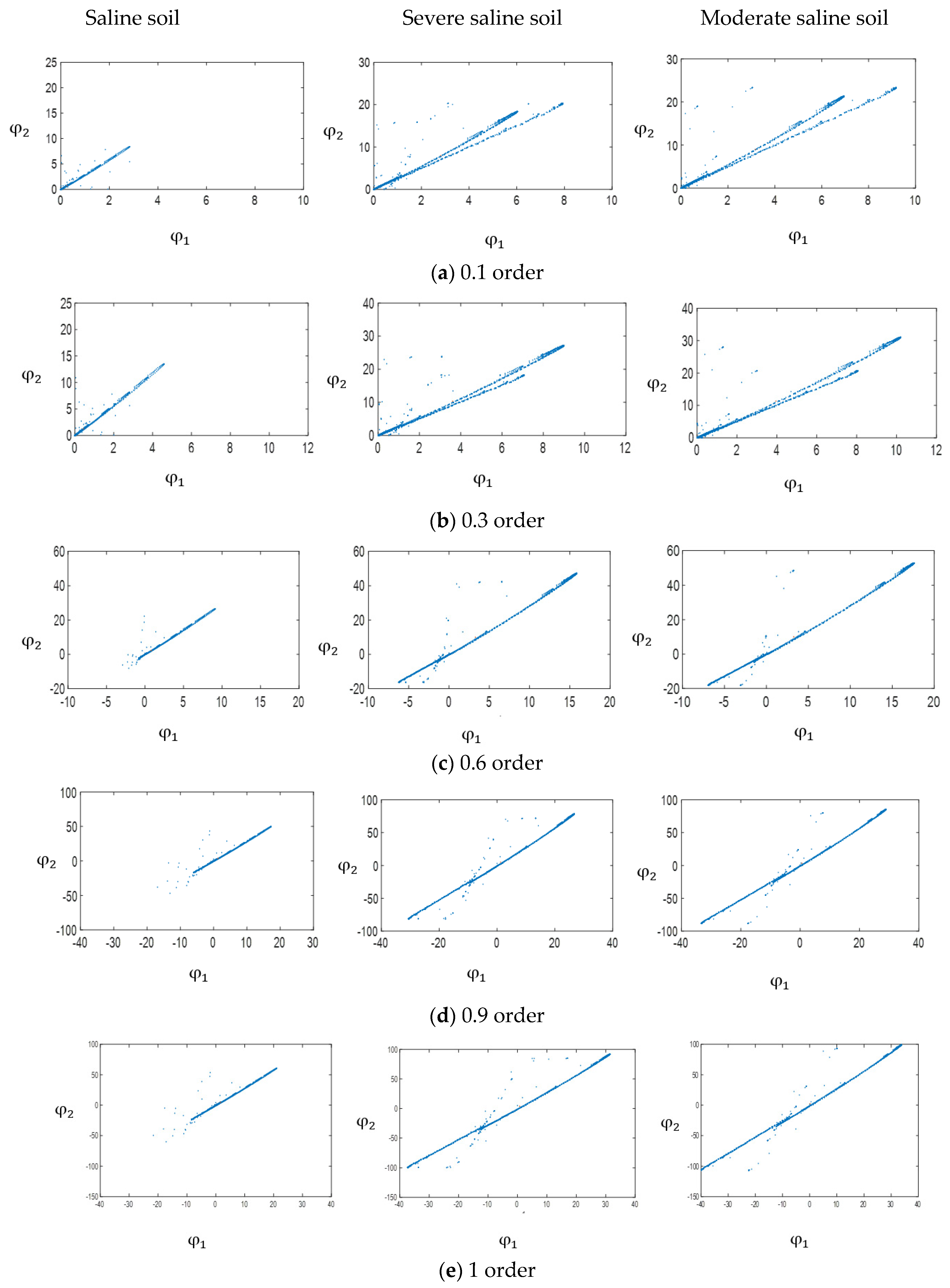
3.1. Mixed Fractional Order Master/Slave Chaotic System Dynamic Error Distribution
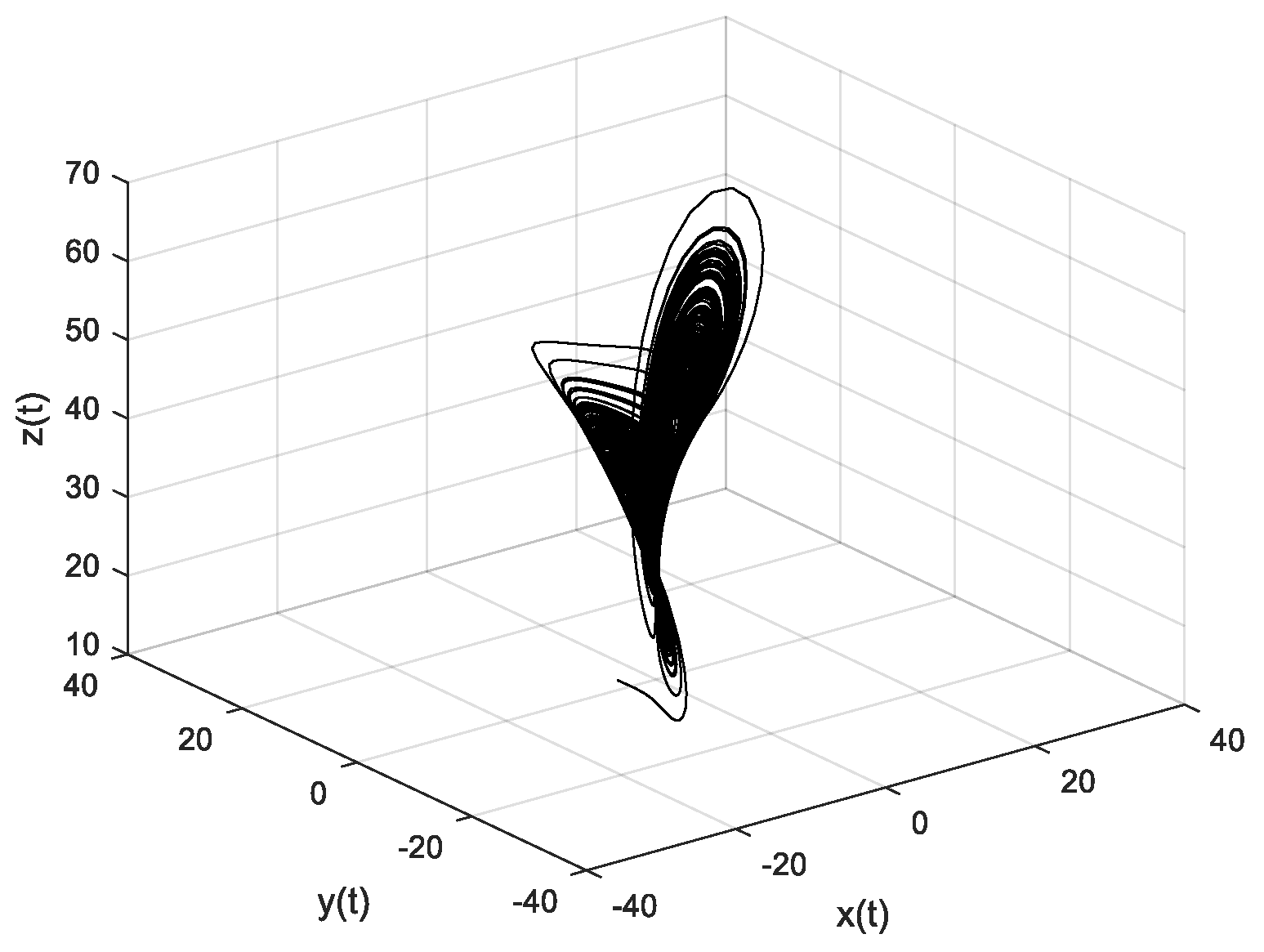
3.2. Mixed Fractional Order Master/Slave Chaotic Attractor
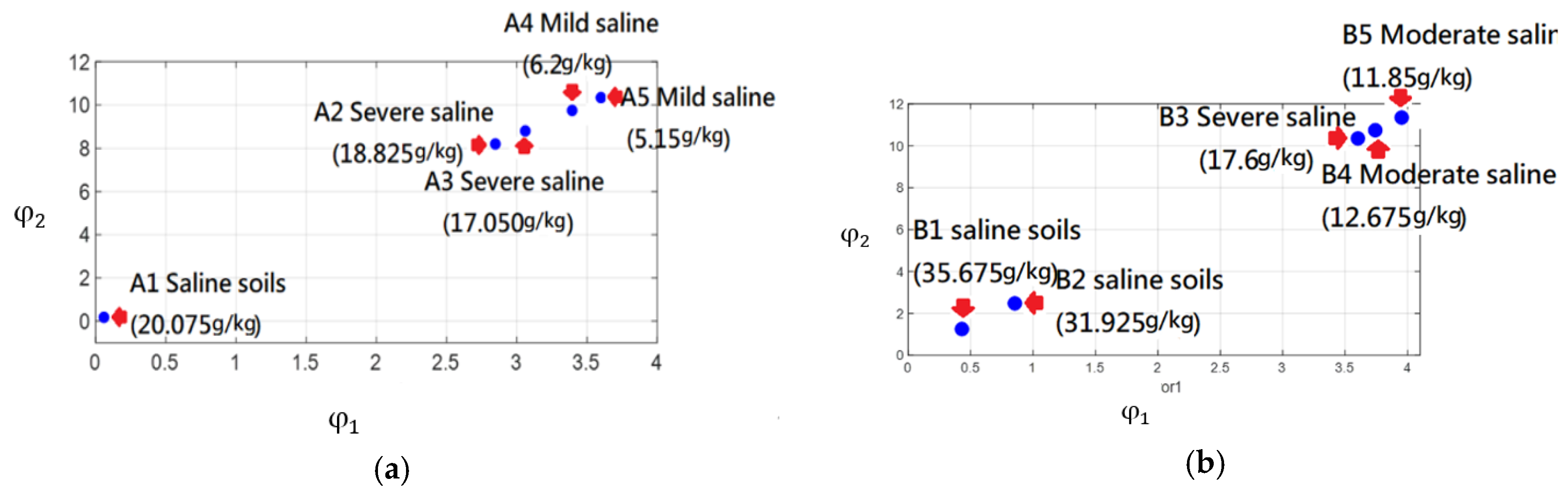
3.3. Building an Extension Matter-Element Model and Extension Classic Domain
3.4. Calculating Correlation Level
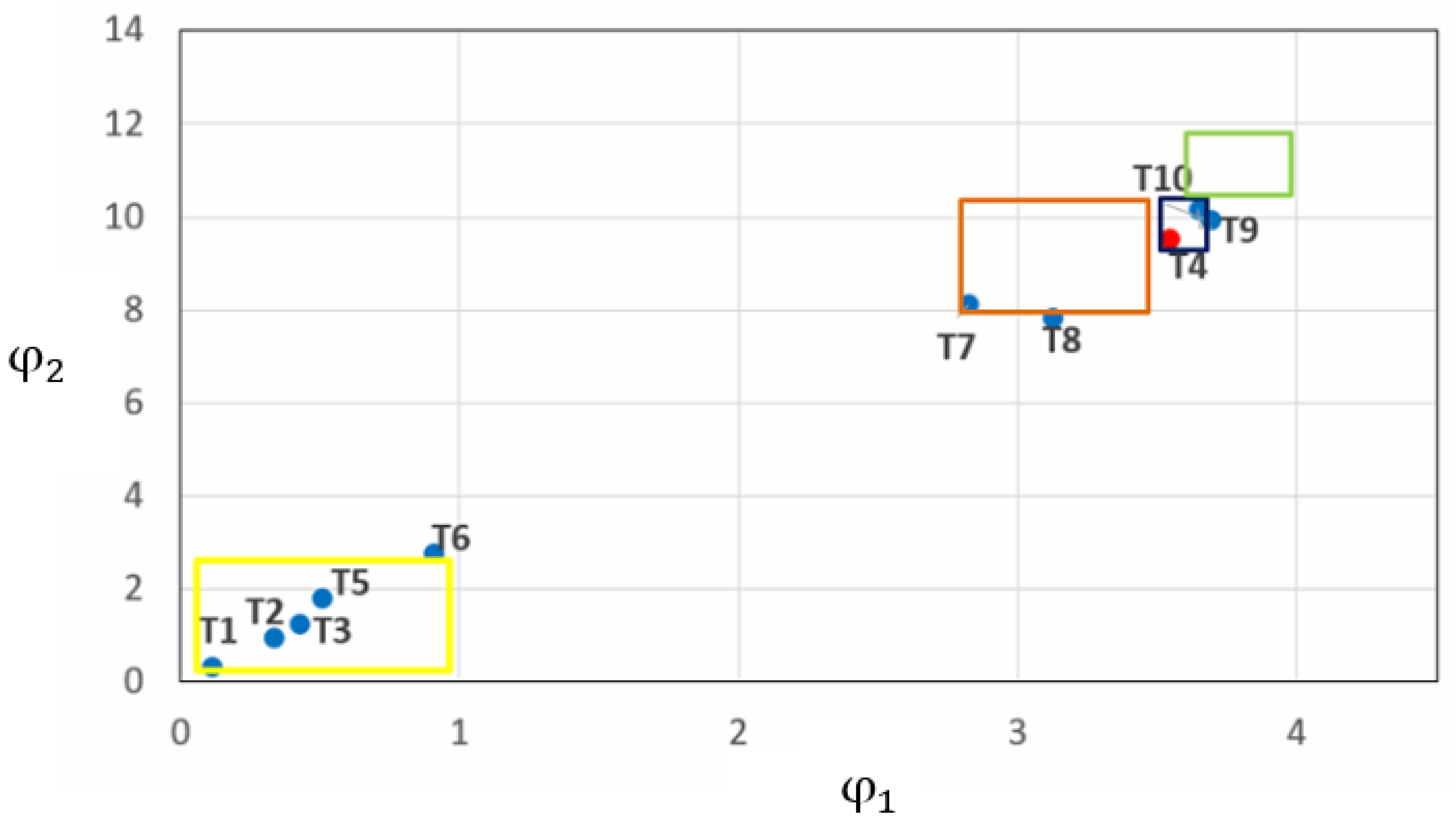
3.5. Extension Classification Results
3.6. Classification Result of Validation Set
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, J.; Roberts, D.; Dennison, P.; Stow, D. Spectral-radiometric differentiation of non-photosynthetic vegetation and soil within Landsat and Sentinel 2 wavebands. Remote Sens. Lett. 2018, 9, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Dong, D.M.; Li, Z.W.; Wang, X.K. A novel soil nutrient detection method based on combined ATR and DRIFT mid-infrared spectra. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.H.; Xiong, H.G.; Zhao, J.Z.; Fu, C.B. Mechanism improvement for pretreatment accuracy of field spectra if saline soil using fractional differential algorithm. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2019, 39, 2495–2500. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Xue, J.; Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; He, Y.; Shi, Z. Integrating remote sensing and landscape characteristics to estimate soil salinity using machine learning methods: A case study from southern xinjiang, China. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.H.; Zhan, C.; Li, Z.L.; Wu, H.; Tang, R.L. Estimation of land surface temperature from MODIS data for the atmosphere with air temperature inversion profile. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 2976–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Shi, Z.W.; Xu, X. Analysis for the Weakly Pareto Optimum in Multiobjective-Based Hyperspectral Band Selection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Gautam, G.; Saha, S.K. Hyperspectral remote sensing data derived spectral indices in characterizing salt-affected soils: A case study of Indo-Gangetic plains of India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 3299–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Shen, R.L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wan, Q.J.; Shi, T.Z.; Wang, J.J.; Wan, Y.; Hong, Y.S.; Li, X.C. Estimating heavy metal concentrations in suburban soils with reflectance Spectroscopy. Geoderma 2019, 336, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, N.; Abduwasit, G.; Tashpolat, T.; Racha, E.; Ding, J.L.; Matthew, M.; Abdulla, A.; Mamat, S.; Zhang, F.; Abdugheni, A.; et al. Monitoring soil salinization in Keriya River Basin, Northwestern China using passive reflective and active microwave remote sensing data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8803–8829. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Tiyip, T.; Ding, J.L.; Kung, H.; Johnson, V.C.; Sawut, M.; Tashpolat, N.; Gui, D.W. Studies on the reflectance spectral features of saline soil along the middle reaches of Tarim River: A case study in Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2743–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Ran, Q.Y.; He, G.X.; Tiyip, T. A soil quality assessment under different land use types in Keriya river basin, Southern Xinjiang, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidike, A.; Zhao, S.H.; Wen, Y.M. Estimating soil salinity in Pingluo County of China using QuickBird data and soil reflectance spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutmemet, I.; Tiyip, T.; Ding, J.L.; Sawut, M.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Q. Monitoring soil salinization in arid area using PolSAR data and polarimetric decomposition method. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- IMetternicht, G.; AZinck, J. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shen, G.R.; Wang, Z.J.; Lu, S.M.; Zhi, T.; Xiang, Q.Q. Soil salt content and its spectral characteristics during microbial remediation processes. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2017, 37, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Han, J.C.; Li, J. Research on Hyperspectral Inversion of Soil Salinity in Typical Semiarid Area. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2014, 34, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, F.L.; Wu, M.C.; Tiyip, T. Study on soil salinization information in Arid Region using remote sensing technique. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Pu, L.J.; Han, M.F.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.S.; Xiang, Y.Z. Soil salinization research in China: Advances and prospects. J. Geogr. Sci. 2014, 24, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.D.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.R.; Liu, L.Y.; Zhang, R. Improved multi-level fuzzy evaluation model based on cloud theory for evaluation of soil salinization degree. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 88–95. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.L.; Liu, Q.M. Regional soil salinity monitoring based on multi-source collaborative remote sensing data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Farifteh, J.; Meer, F.V.D.; Meijde, M.V.D.; Atzberger, C. Spectral characteristics of salt-affected soils: A laboratory experiment. Geoderma 2008, 145, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.; Sethi, M.; Yadav, R.K.; Bundela, D.S.; Singh, M.; Chattaraj, S.; Singh, S.K.; Nasre, R.A.; Bishnoi, S.R.; Dhale, S.; et al. Visible-near infrared reflectance spectroscopy for rapid characterization of salt-affected soil in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of Haryana, India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2017, 45, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. A Spectral Index for Estimating Soil Salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China Using EO-1 Hyperion Data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouazen, A.M.; Kuang, B.; Baerdemaeker, J.D.; Ramonb, H. Comparison among principal component, partial least squares and back propagation neural network analyses for accuracy of measurement of selected soil properties with visible and near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 2010, 158, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Jiang, T.C.; Yunger, J.A.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, J.G. Hyperspectral Inverse Model for Soil Salt Ions Based on Support Vector Machine. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2018, 49, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Madhok, V.; Dogra, S.; Lakshminarayan, A. Quantum correlations as probes of chaos and ergodicity. Opt. Commun. 2018, 420, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Zhang, Q.L.; Bao, B.C.; Hu, Y.H. Non-Autonomous Second-Order Memristive Chaotic Circuit. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 21039–21045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhassan, R.; Delfim, F.M.T. Control of a novel chaotic fractional order system using a state feedback technique. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 755–763. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.; Norihan, M.A. Synchronization of two different fractional-order chaotic systems with unknown parameters using a robust adaptive nonlinear controller. Nonlinear Dyn. 2016, 85, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Pham, V.T.; Jafari, S.; Volos, C.; Jesus, M.M.P.; Esteban, T.C. A New Chaotic System with Stable Equilibrium from Theoretical Model to Circuit Implementation. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 8851–8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, A.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, H.; Fu, C. Application of Fractional Differential Calculation in Pretreatment of Saline Soil Hyperspectral Reflectance Data. J. Sens. 2018, 2018, 8017614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.F.; Xi, M.; Wang, Q.G.; Kong, F.L.; Li, Y. Characterization of soil salinization in typical estuarine area of the Jiaozhou Bay, China. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2018, 103, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harti, A.; Lhissou, R.; Chokmani, K.; Ouzemou, J.E.; Hassouna, M.; Bachaoui, E.M.; El Ghmari, A. Spatiotemporal monitoring of soil salinization in irrigated Tadla Plain (Morocco) using satellite spectral indices. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 50, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.Z.; Zhang, B. A Novel Weak Signal Detection Method via Chaotic Synchronization Using Chua’s Circuit. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaci, F.A.; Yilmaz, S. Bayesian Stable Mixture Model of State Densities of Generalized Chua’s Circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2015, 25, 1550038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Chen, H.K. Chaos and hybrid projective synchronization of commensurate and incommensurate fractional-order Chen-Lee systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2010, 62, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.K.; Sheu, L.J.; Tam, L.M.; Lao, S.K. A new finding of the existence of Feigenbaum’s constants in the fractional-order Chen-Lee system. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 68, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.X.; Guo, R.W. Control problems of Chen-Lee system by adaptive control method. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 87, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, B. Chaos Control and Projective Synchronization of a Chaotic Chen-Lee System. Chin. J. Phys. 2009, 47, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.K.; I Lee, C.I. Anti-control of chaos in rigid body motion. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2004, 21, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, H.T.; Wu, S.Y.; Chen, C.L.; Li, Y.C. Fractional-Order Chaotic Self-Synchronization-Based Tracking Faults Diagnosis of Ball Bearing Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.C.; Chen, W.L.; Lin, C.H.; Kan, C.D.; Wu, M.J. Residual Stenosis Estimation of Arteriovenous Grafts Using a Dual-Channel Phonoangiography with Fractional-Order Features. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2015, 19, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.W.; Li, S.C.; Meng, F.Q. Application of extenics theory for evaluating effect degree of damaged mountains based on analytic hierarchy process. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4463–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.W.; Han, J.M.; Xu, X.Q. Susceptibility area regionalization of land subsidence based on extenics theory. Clust. Comput.—J. Netw. Softw. Tools Appl. 2017, 20, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhu, Z.X.; Xiang, Z.B.; Chen, Z.X.; Shi, Y. An Intelligent Transformation Knowledge Mining Method Based on Extenics. J. Internet Technol. 2013, 14, 315–325. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.T.; Yau, H.T.; Li, Y.C. Research and Development of a Chaotic Signal Synchronization Error Dynamics-Based Ball Bearing Fault Diagnostor. Entropy 2014, 16, 5358–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.J.; Su, X.Y.; Yu, K.T.; Jian, B.L.; Yau, H.T. Inspection on Ball Bearing Malfunction by Chen-Lee Chaos System. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 28267–28275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Hsieh, C.T.; Yau, H.T.; Li, Y.C. Study on Unified Chaotic System-Based Wind Turbine Blade Fault Diagnostic System. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2015, 25, 1550042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Spectrometer Model | FieldSpec® 3Hi-Res |
|---|---|
| Spectral range | 350–2500 nm |
| Spectral resolution | 3 nm@700 nm |
| 8 nm@1400/2100 nm | |
| sampling interval | 1.4 nm@350–1000 nm |
| 1.1 nm@1001–2500 nm | |
| Equivalent noise radiation | VNIR 1.0 × 10−9 W/cm2/sr@700 nm |
| SWIR 1.4 × 10−9 W/cm2/nm/sr/@1400 nm | |
| SWIR 2.2 × 10−9 W/cm2/nm/sr@2100 nm | |
| Band accuracy | 0.5 nm |
| Number of output bands | 2151 |
| Detector | 350–1100 nm, Low-noise 512-element PDA 1000–1800 nm and 1700–2500 nm, two InGaAs detector units |
| In | 1.5 m optical fiber (25° field of view) |
| Degree of Soil Salinization | Soil Salt Content (g/kg) |
|---|---|
| Non-saline soil | <5.0 |
| Mild saline soil | 5.0–10.0 |
| Moderate saline soil | 10.0–15.0 |
| Severe saline soil | 15.0–20.0 |
| Saline soil | >20.0 |
| Sample A | Saline Soils | Severe Saline | Mild Saline |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| A2 | −1 | 1 | −0.06729 |
| A3 | −1 | 1 | 0.099209 |
| A4 | −1 | −0.31168 | 1 |
| A5 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| Sample B | Saline Soils | Severe Saline | Moderate Saline |
|---|---|---|---|
| B1 | 1 | −1 | −1 |
| B2 | 1 | −0.9872 | −1 |
| B3 | −1 | 1 | 0.3628 |
| B4 | −1 | 0.1769 | 1 |
| B5 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| Sample A | Salt Content (g/kg) | State |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 20.075 | Saline soils |
| A2 | 18.825 | Severe saline |
| A3 | 17.050 | Severe saline |
| A4 | 6.200 | Mild saline |
| A5 | 5.150 | Mild saline |
| Sample A | Salt Content (g/kg) | State |
|---|---|---|
| A1 | 35.675 | Saline soils |
| A2 | 31.925 | Saline soils |
| A3 | 17.600 | Severe saline |
| A4 | 12.675 | Moderate saline |
| A5 | 11.850 | Moderate saline |
| Sample T | Salt Content (g/kg) | Saline Soils | Severe Saline | Moderate Saline | Mild Saline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 21.625 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| T2 | 21.15 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| T3 | 35.675 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| T4 | 20.4 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 |
| T5 | 47.85 | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 |
| T6 | 28.275 | 0.985 | −0.015 | −1 | −1 |
| T7 | 19 | −1 | 1 | −1 | −0.0448 |
| T8 | 16.625 | −1 | 0.973 | −1 | −0.027 |
| T9 | 7.125 | −1 | −1 | 0.1256 | 0.9875 |
| T10 | 8.425 | −1 | 0.036 | −1 | 0.964 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, A.; Fu, C.; Yau, H.-T.; Su, X.-Y.; Xiong, H. Soil Salinization Level Monitoring and Classifying by Mixed Chaotic Systems. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193819
Tian A, Fu C, Yau H-T, Su X-Y, Xiong H. Soil Salinization Level Monitoring and Classifying by Mixed Chaotic Systems. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(19):3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193819
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Anhong, Chengbiao Fu, Her-Terng Yau, Xiao-Yi Su, and Heigang Xiong. 2021. "Soil Salinization Level Monitoring and Classifying by Mixed Chaotic Systems" Remote Sensing 13, no. 19: 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193819
APA StyleTian, A., Fu, C., Yau, H.-T., Su, X.-Y., & Xiong, H. (2021). Soil Salinization Level Monitoring and Classifying by Mixed Chaotic Systems. Remote Sensing, 13(19), 3819. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13193819







