Influence of Indian Summer Monsoon on Tropopause, Trace Gases and Aerosols in Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone Observed by COSMIC, MLS and CALIPSO
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data Base
2.1. COSMIC GPSRO Observations
2.2. Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) Measurements
2.3. Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Satellite Observations (CALIPSO) Stratospheric Aerosol Data
3. Results and Discussion
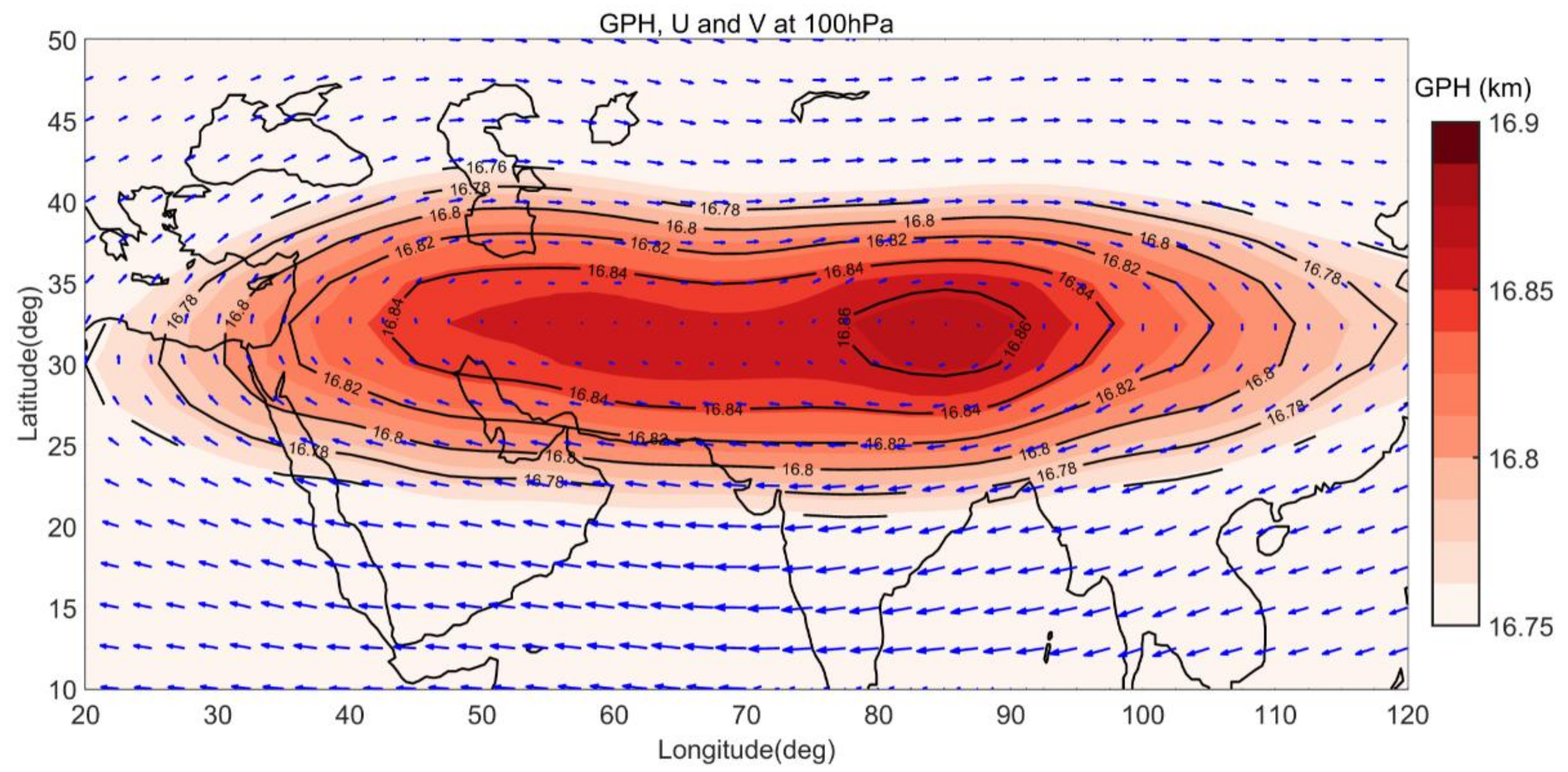
3.1. Climatological State of ASMA during Summer Monsoon
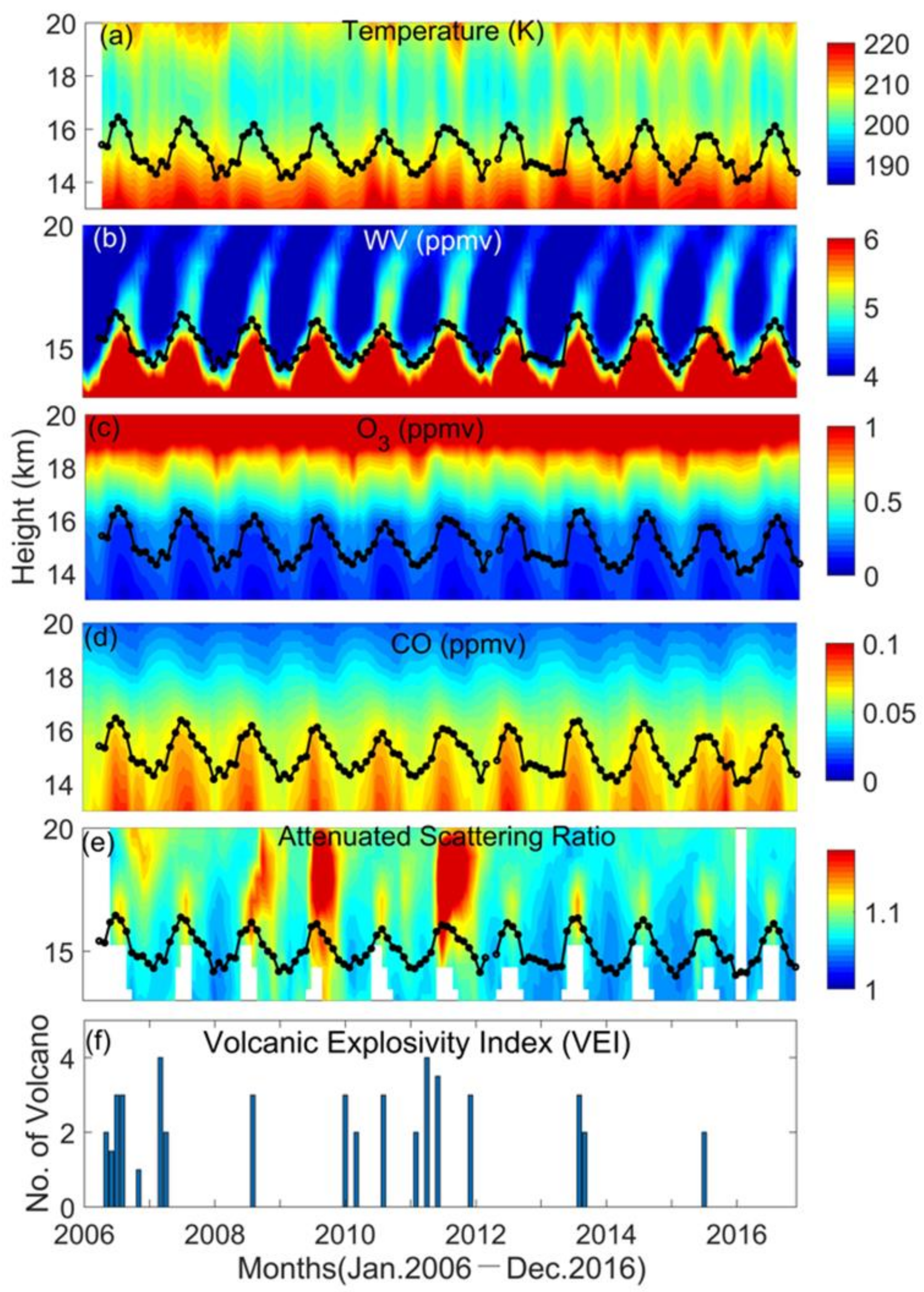
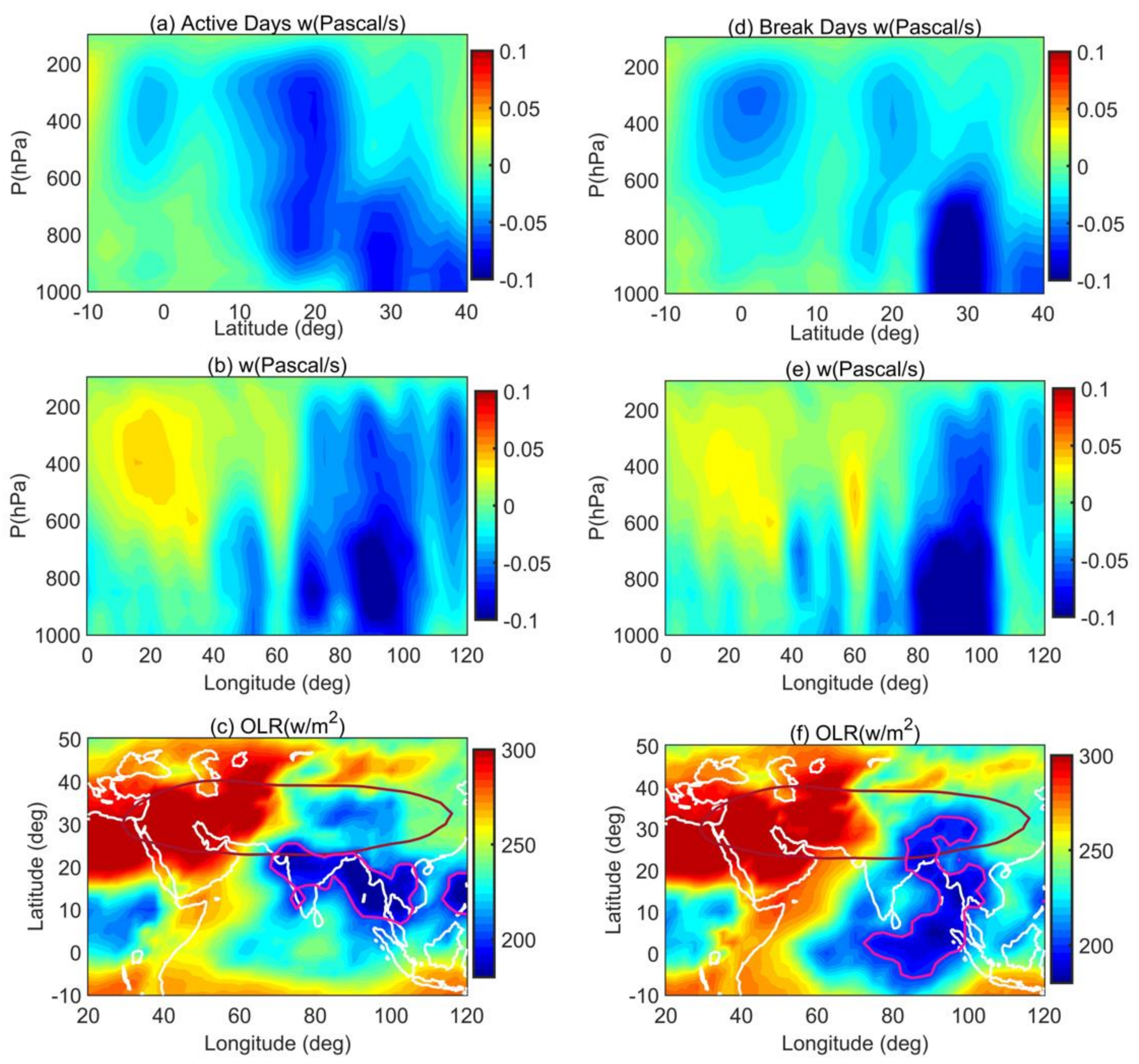
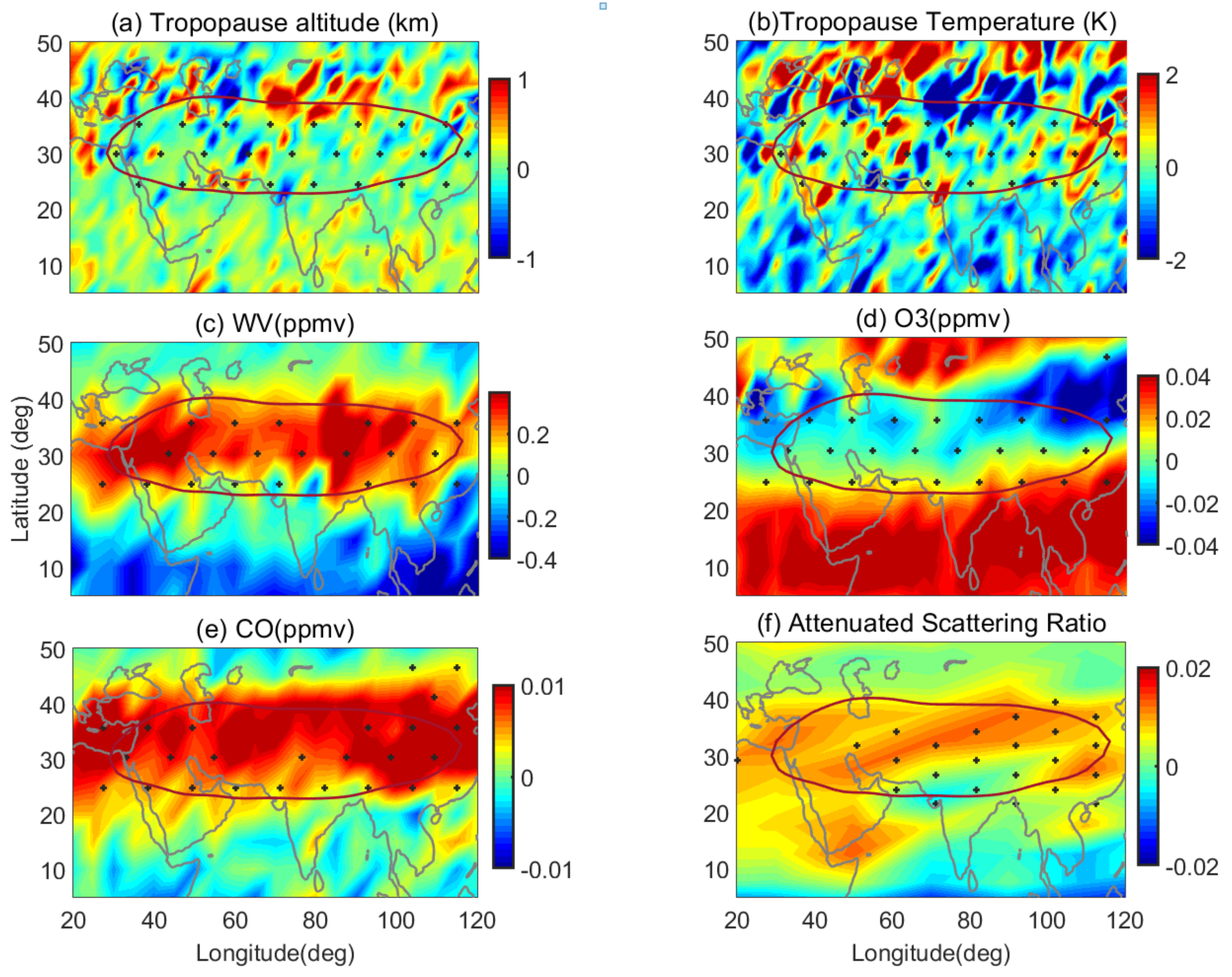
3.2. Influence of Asian Summer Monsoon Activity
4. Summary and Conclusions
- Strong seasonal variability is observed in all the parameters in the ASMA. Enhancement in the WV, CO and ASR and decrease in the tropopause temperature and O3 are found exactly below the tropopause altitude. During 2008, 2009 and 2011, higher ASR values are present above the tropopause altitude, which corresponds to moderate volcanic eruptions.
- The tropopause altitude and tropopause temperature in the ASMA during the monsoon season show an increasing and decreasing pattern, respectively. This increase and decrease are not observed clearly during active spells and in strong monsoon years, whereas, during La Niña years, a clear increase (decrease) in the tropopause altitude (temperature) is observed.
- The convection during active spells, strong monsoon years and during strong La Niña years is dominant, and spatially homogenized over land region compared to the ocean with strong updrafts that transport large amounts of rich moisture air and ozone poor air to the upper troposphere. Irrespective of the monsoon activity, deep convection is noticed over the BoB. Thus, vertical transport is possible throughout the monsoon season through strong updrafts (deep convection) from this region. During the pre-monsoon season, burning of agricultural waste and forest clearing is common in major places of Southeast Asia, which releases huge CO emissions. The CO can be easily transported to higher altitudes with the existence of ascending motion over the monsoon region.
- The ASR is large during the strong monsoon years and during strong La Niña years in the ASMA region. During strong La Niña and strong monsoon years, the aerosol layer that existed at top of the tropopause altitude provides evidence that boundary air enters into the stratosphere within the ASMA. It is noticed that aerosols are confined to the NH in the latitude band of 30–40°N.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Randel, W.J.; Jensen, E.J. Physical processes in the tropical tropopause layer and their roles in a changing climate. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Kishore, P. Asian summer monsoon anticyclone: Trends and variability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 6789–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkerton, T.J. Evidence of meridional motion in the summer lower stratosphere adjacent to monsoon regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1995, 100, 16675–16688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.R.; Ratnam, M.V.; Basha, G.; Pani, S.K.; Lin, N.H. Structure, dy-namics, and trace gases variability within the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone in extreme El Niño of 2015–16. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 2020, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, B.; Mujumdar, M.; Kripalani, R.H.; Prabhu, A.; Krishnan, R. Recent trends and tele-connections among South and East Asian summer monsoons in a warming environment. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 48, 2489–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Pan, L.L.; Honomichl, S.; Bergman, J.W.; Randel, W.J.; Francis, G.; Clerbaux, C.; George, M.; Liu, X.; Tian, W. Space–time variability in UTLS chemical distribution in the Asian summer monsoon viewed by limb and nadir satellite sensors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2018, 18, 12511–12530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Wu, G.; Qian, Y. The Bimodality of the 100 hPa South Asia High and its Relationship to the Climate Anomaly over East Asia in Summer. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 80, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Dong, B.; Liang, X.; Duan, A.; Bao, Q.; Yu, J. Revisiting Asian monsoon formation and change associated with Tibetan Plateau forcing: I. Formation. Clim. Dyn. 2012, 39, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nützel, M.; Dameris, M.; Garny, H. Movement, drivers and bimodality of the South Asian High. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 14755–14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, R.; Bonazzola, M.; Legras, B.; Surbled, K.; Fueglistaler, S. Water vapour transport and dehydration above convective outflow during Asian monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, J.S.; Fu, R.; Fueglistaler, S.; Liu, Y.S.; Zhang, Y. The influence of summertime convection over Southeast Asia on water vapor in the tropical stratosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.; Günther, G.; Müller, R.; Grooß, J.-U.; Hoor, P.; Krämer, M.; Müller, S.; Zahn, A.; Riese, M. Fast transport from Southeast Asia boundary layer sources to northern Europe: Rapid uplift in typhoons and eastward eddy shedding of the Asian monsoon anticyclone. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2014, 14, 12745–12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vogel, B.; Günther, G.; Müller, R.; Grooß, J.-U.; Afchine, A.; Bozem, H.; Hoor, P.; Krämer, M.; Müller, S.; Riese, M.; et al. Long-range transport pathways of tropospheric source gases originating in Asia into the northern lower stratosphere during the Asian monsoon season 2012. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 15301–15325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ploeger, F.; Konopka, P.; Walker, K.; Riese, M. Quantifying pollution transport from the Asian monsoon anticyclone into the lower stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2017, 17, 7055–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergman, J.W.; Jensen, E.J.; Pfister, L.; Yang, Q. Seasonal differences of vertical-transport efficiency in the tropical tropopause layer: On the interplay between tropical deep convection, large-scale vertical ascent, and horizontal circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, 05302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Hu, Y.; Wright, J.S.; Jiang, J.H.; Dickinson, R.E.; Chen, M.; Wu, D.L. Short circuit of water vapor and polluted air to the global stratosphere by convective transport over the Tibetan Plateau. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 5664–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernier, J.-P.; Thomason, L.; Kar, J. CALIPSO detection of an Asian tropopause aerosol layer. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernier, J.-P.; Fairlie, T.D.; Deshler, T.; Ratnam, M.V.; Gadhavi, H.; Kumar, B.S.; Natarajan, M.; Pandit, A.K.; Raj, S.T.A.; Kumar, A.H.; et al. BATAL: The Balloon Measurement Campaigns of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 99, 955–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, W.K.M.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z. Origin, Maintenance and Variability of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL): The Roles of Monsoon Dynamics. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kloss, C.; Berthet, G.; Sellitto, P.; Ploeger, F.; Bucci, S.; Khaykin, S.; Jégou, F.; Taha, G.; Thomason, L.W.; Barret, B.; et al. Transport of the 2017 Canadian wildfire plume to the tropics via the Asian monsoon circulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 13547–13567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albritton, D.L.; Derwent, R.G.; Isaksen, I.S.A.; Lal, M.; Wuebbles, D.J. Trace gas radiative forcing indices. Clim. Chang. 1994, 994, 163–203. [Google Scholar]
- Hanumanthu, S.; Vogel, B.; Müller, R.; Brunamonti, S.; Fadnavis, S.; Li, D.; Ölsner, P.; Naja, M.; Singh, B.B.; Kumar, K.R.; et al. Strong day-to-day variability of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL) in August 2016 at the Himalayan foothills. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2020, 20, 14273–14302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A.; Bernhardt, P.A.; Chen, Y.; Cucurull, L.; Dymond, K.F.; Ector, D.; Healy, S.B.; Ho, S.-P.; Hunt, D.C.; Kuo, Y.; et al. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 Mission: Early Results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovskiy, S.; Röcken, C.; Hunt, D.; Schreiner, W.; Johnson, J.; Masters, D.; Esterhuizen, S. GPS profiling of the lower troposphere from space: Inversion and demodulation of the open-loop radio occultation signals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kursinski, E.R.; Hajj, G.A.; Schofield, J.T.; Linfield, R.P.; Hardy, K.R. Observing Earth’s atmosphere with radio occultation measurements using the Global Positioning System. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 1997, 102, 23429–23465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.N.; Ratnam, M.V.; Mehta, S.; Nath, D.; Basha, S.G.; Rao, V.V.M.J.; Murthy, B.V.K.; Tsuda, T.; Nakamura, K. Validation of the COSMIC Radio Occultation Data over Gadanki (13.48°N, 79.2°E): A Tropical Region. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2009, 20, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kishore, P.; Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Velicogna, I.; Ouarda, T.B.; Rao, D.N. Evaluating CMIP5 models using GPS radio occultation COSMIC temperature in UTLS region during 2006–2013: Twenty-first century projection and trends. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 3253–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnam, M.V.; Sunilkumar, S.V.; Parameswaran, K.; Murthy, B.K.; Ramkumar, G.; Rajeev, K.; Pramitha, M. Tropical tropopause dynamics (TTD) campaigns over Indian region: An overview. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2014, 121, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.R.; Ratnam, M.V.; Basha, G.; Krishnamurthy, B.V.; Venkateswararao, B. Effect of tropical cyclones on the tropical tropopause parameters observed using COSMIC GPS RO data. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2015, 15, 10239–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babu, R.; Ratnam, M.V.; Basha, G.; Krishnamurthy, B. Indian summer monsoon onset signatures on the tropical tropopause layer. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2019, 20, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.; Raj, S.A.; Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V. Recent trends in the UTLS temperature and tropical tropopause parameters over tropical South Indian region. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2020, 197, 105164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.J.; Read, W.G.; Santee, M.L.; Livesey, N.J.; Froidevaux, L.; Lambert, A.; Manney, G.L. Convectively injected water vapor in the North American summer lowermost stratosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 2316–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livesey, N.J. Aura Microwave Limb Sounder (MLS) Version 4.2× Level 2 Data Quality and Description Document; NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2018.
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leetmaa, A.; Reynolds, R.; Jenne, R.; Josepht, D. The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1996, 77, 437–471. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeevan, M.; Gadgil, S.; Bhate, J. Active and break spells of the Indian summer monsoon. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 119, 229–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoskins, B.J.; Rodwell, M.J. A Model of the Asian Summer Monsoon. Part I: The Global Scale. J. Atmos. Sci. 1995, 52, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.L.; Honomichl, S.B.; Kinnison, D.E.; Abalos, M.; Randel, W.J.; Bergman, J.W.; Bian, J. Transport of chemical tracers from the boundary layer to stratosphere associated with the dynamics of the Asian summer monsoon. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 14159–14174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Pan, L.L.; Paulik, L.; Vömel, H.; Chen, H.; Lu, D. In situ water vapor and ozone measurements in Lhasa and Kunming during the Asian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mote, P.W.; Rosenlof, K.H.; McIntyre, M.E.; Carr, E.S.; Gille, J.C.; Holton, J.R.; Waters, J.W. An atmospheric tape recorder: The imprint of tropical tropopause temperatures on stratospheric water vapor. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 3989–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Lau, W.K.M.; Li, Z.; Cribb, M. Relationship between Asian monsoon strength and transport of surface aerosols to the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer (ATAL): Interannual variability and decadal changes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2019, 19, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ravindrababu, S.; Ratnam, M.V.; Basha, G.; Liou, Y.-A.; Reddy, N.N. Large Anomalies in the Tropical Upper Troposphere Lower Stratosphere (UTLS) Trace Gases Observed during the Extreme 2015–16 El Niño Event by Using Satellite Measurements. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bossolasco, A.; Jegou, F.; Sellitto, P.; Berthet, G.; Kloss, C.; Legras, B. Global modeling studies of composition and decadal trends of the Asian Tropopause Aerosol Layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2021, 21, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Randel, W.J.; Emmons, L.K.; Livesey, N.J. Transport pathways of carbon monoxide in the Asian summer monsoon diagnosed from Model of Ozone and Related Tracers (MOZART). J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2009, 114, 08303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergman, J.W.; Fierli, F.; Jensen, E.J.; Honomichl, S.; Pan, L.L. Boundary layer sources for the Asian anticyclone: Regional contributions to a vertical conduit. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 2560–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadnavis, S.; Semeniuk, K.; Pozzoli, L.; Schultz, M.G.; Ghude, S.D.; Das, S.K.; Kakatkar, R. Transport of aerosols into the UTLS and their impact on the Asian monsoon region as seen in a global model simulation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2013, 13, 8771–8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, P.; Rosenlof, K.H.; Liu, S.; Telg, H.; Thornberry, T.D.; Rollins, A.W.; Portmann, R.; Bai, Z.; Ray, E.A.; Duan, Y.; et al. Efficient transport of tropospheric aerosol into the stratosphere via the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6972–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fadnavis, S.; Roy, C.; Chattopadhyay, R.; Sioris, C.E.; Rap, A.; Müller, R.; Krishnan, R. Transport of trace gases via eddy shedding from the Asian summer monsoon anticyclone and associated impacts on ozone heating rates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11493–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Basha, G.; Ratnam, M.V.; Jiang, J.H.; Kishore, P.; Ravindra Babu, S. Influence of Indian Summer Monsoon on Tropopause, Trace Gases and Aerosols in Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone Observed by COSMIC, MLS and CALIPSO. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173486
Basha G, Ratnam MV, Jiang JH, Kishore P, Ravindra Babu S. Influence of Indian Summer Monsoon on Tropopause, Trace Gases and Aerosols in Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone Observed by COSMIC, MLS and CALIPSO. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(17):3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173486
Chicago/Turabian StyleBasha, Ghouse, Madineni Venkat Ratnam, Jonathan H. Jiang, Pangaluru Kishore, and Saginela Ravindra Babu. 2021. "Influence of Indian Summer Monsoon on Tropopause, Trace Gases and Aerosols in Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone Observed by COSMIC, MLS and CALIPSO" Remote Sensing 13, no. 17: 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173486
APA StyleBasha, G., Ratnam, M. V., Jiang, J. H., Kishore, P., & Ravindra Babu, S. (2021). Influence of Indian Summer Monsoon on Tropopause, Trace Gases and Aerosols in Asian Summer Monsoon Anticyclone Observed by COSMIC, MLS and CALIPSO. Remote Sensing, 13(17), 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173486






