Full Lifecycle Monitoring on Drought-Converted Catastrophic Flood Using Sentinel-1 SAR: A Case Study of Poyang Lake Region during Summer 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
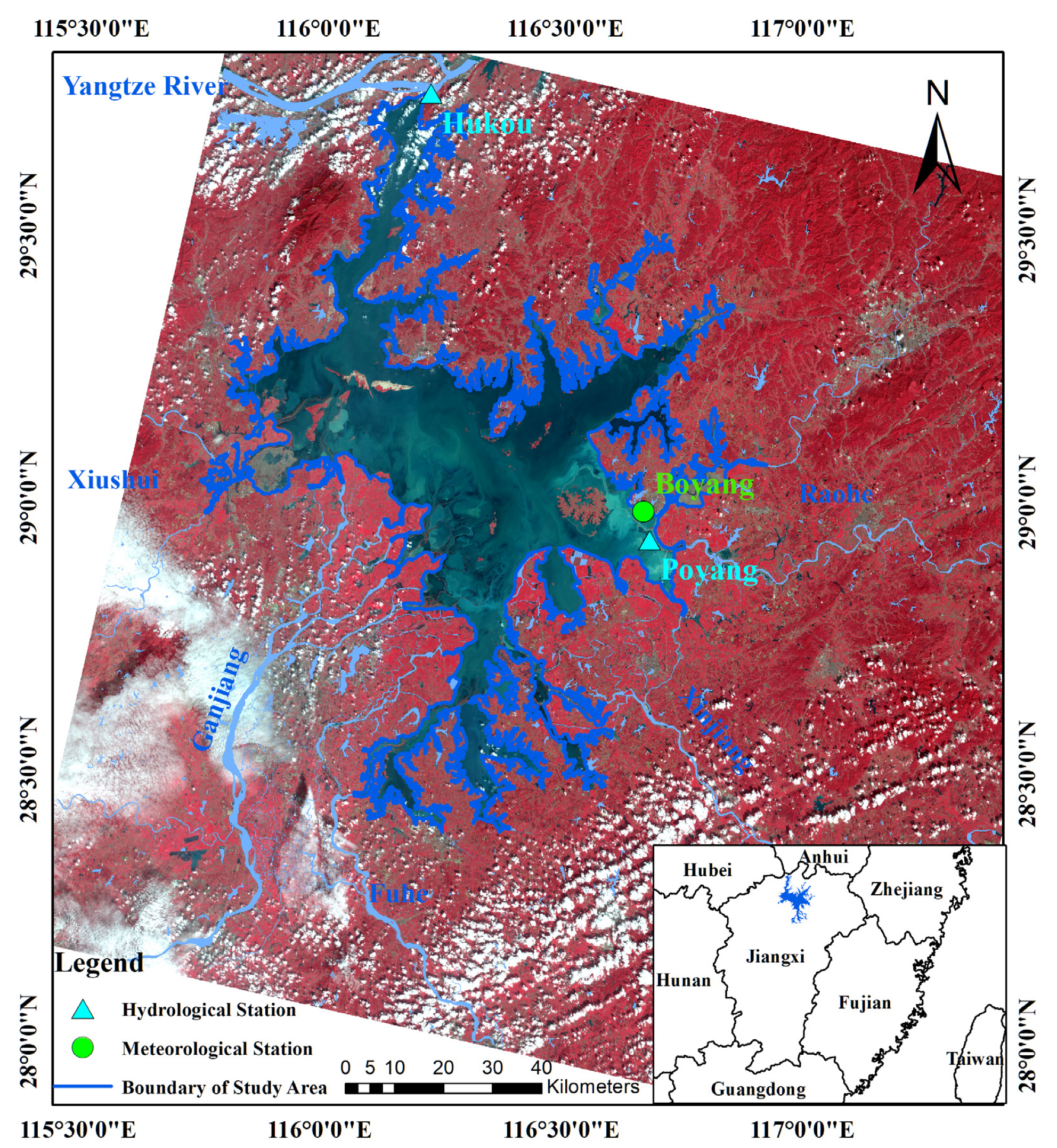
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
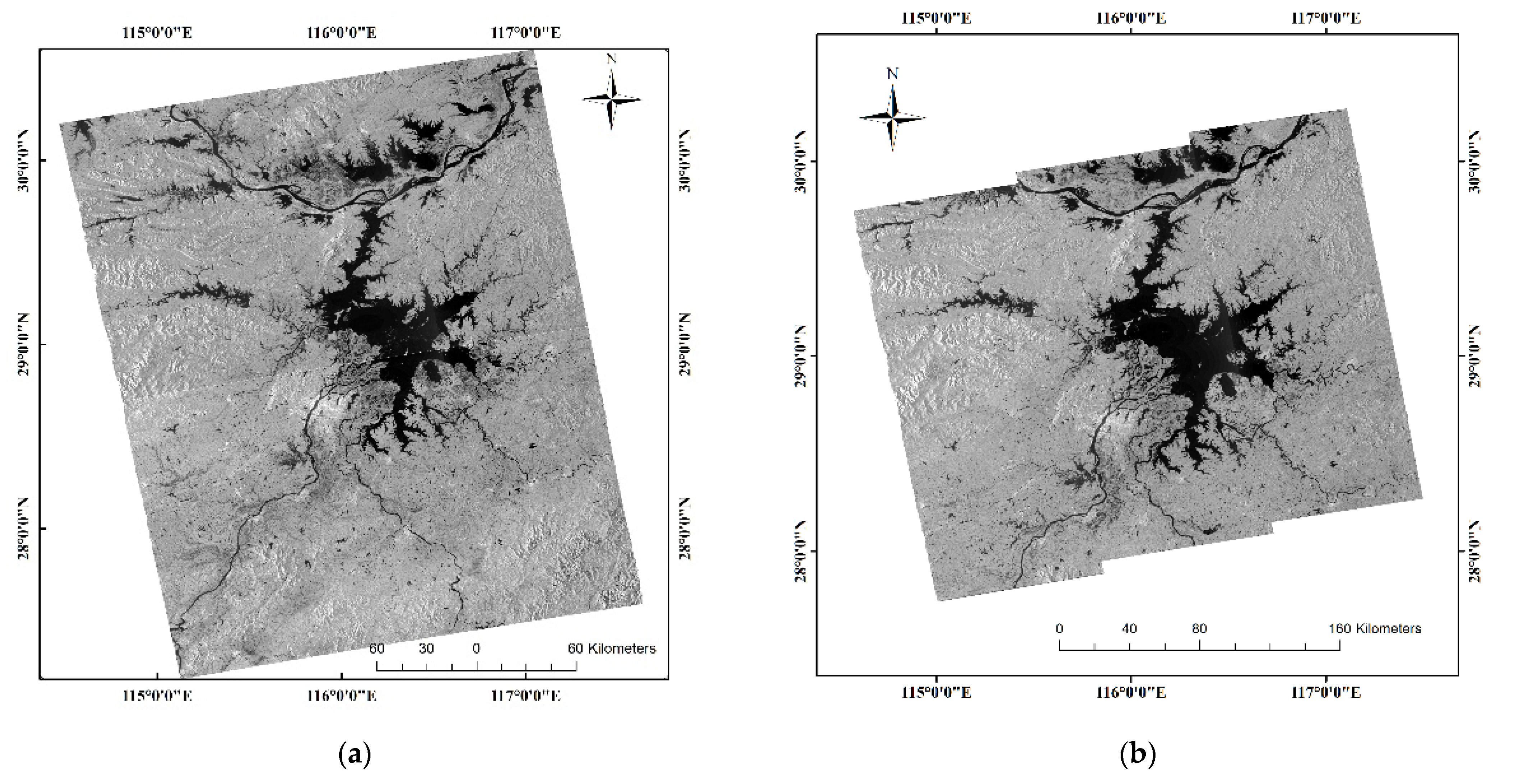
2.2.1. Sentinel-1 SAR Images
2.2.2. Auxiliary Data
2.3. Methods
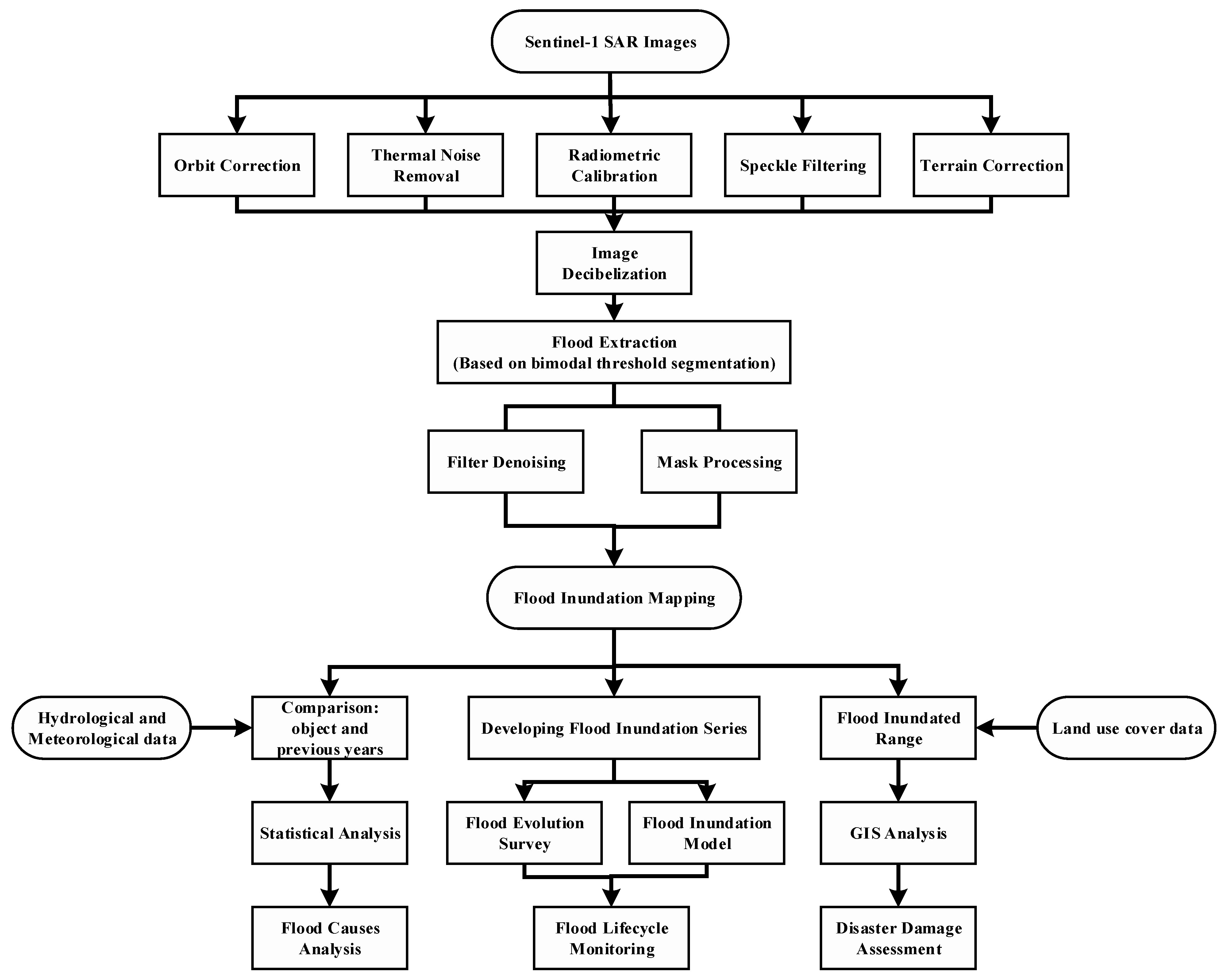
2.3.1. Flood Extraction and Monitoring Using Sentinel-1 SAR Images
2.3.2. Hydro-Meteorological Analysis of Flood Causes
2.3.3. Damage Assessment Using GIS Techniques
3. Results
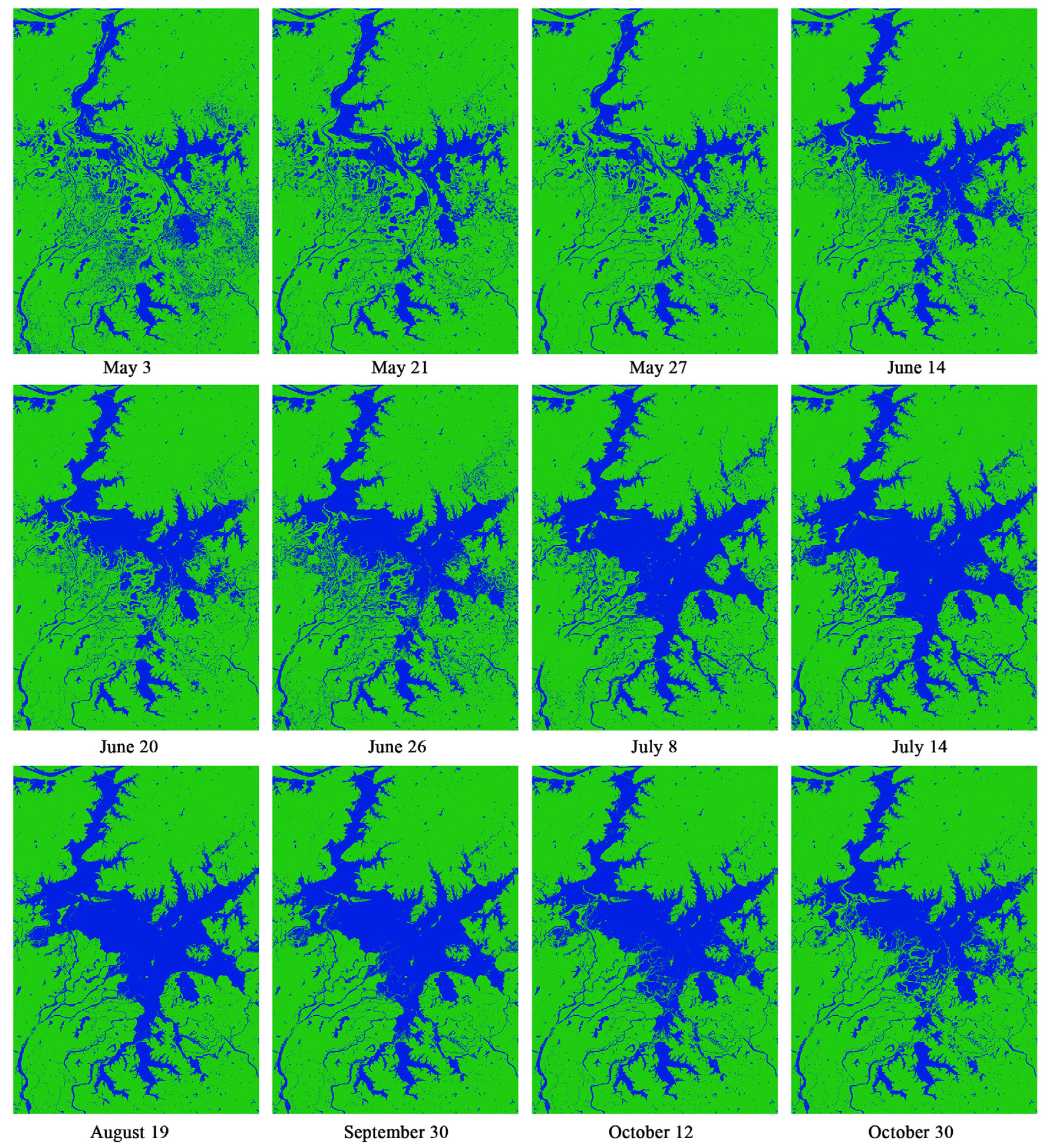
3.1. Flood Full Lifecycle Monitoring Using Sentinel-1 SAR and Inundation Models
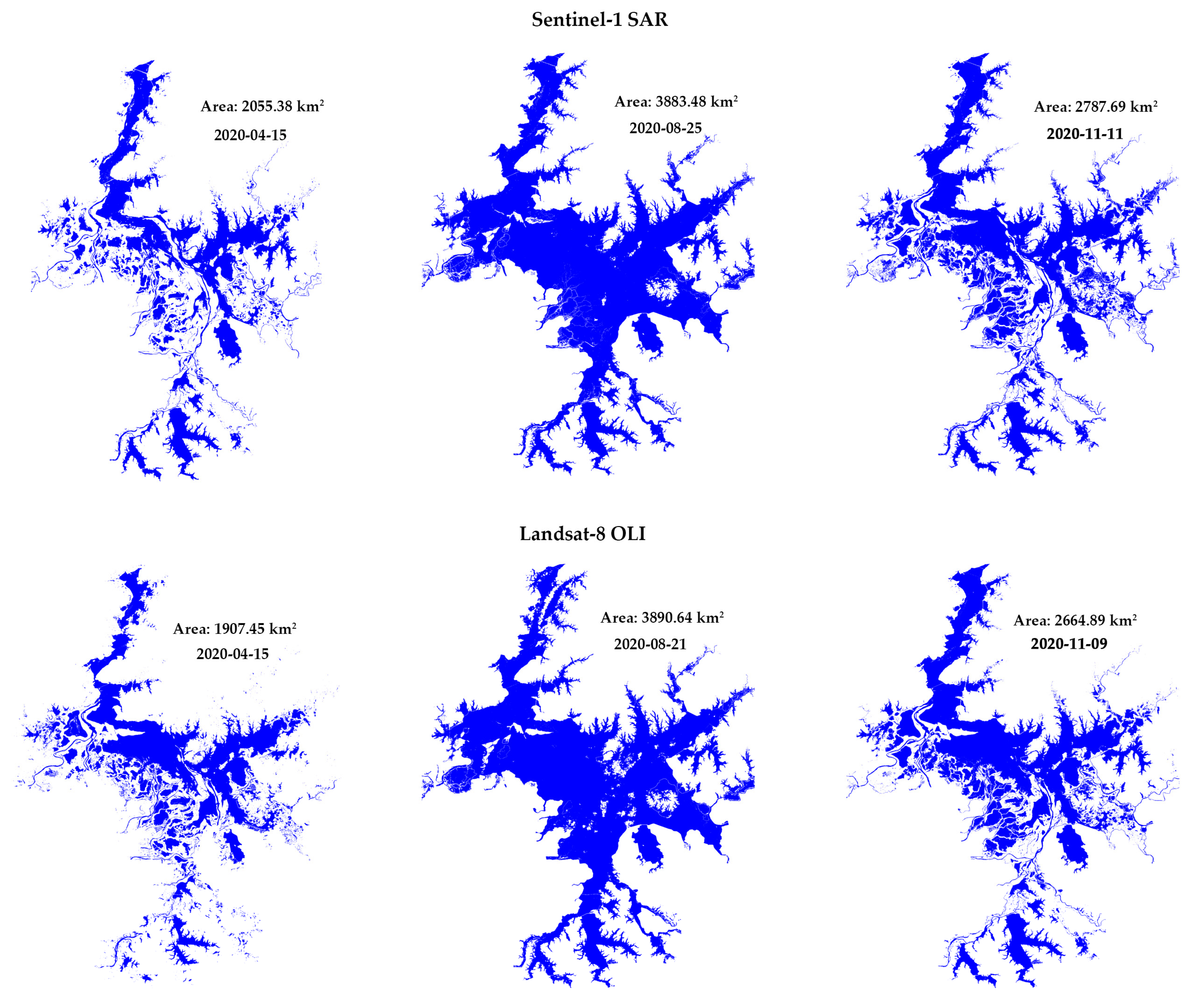
3.1.1. Validation of Flood Area Extraction
3.1.2. Full Lifecycle Monitoring of Flood Using Sentinel-1 SAR
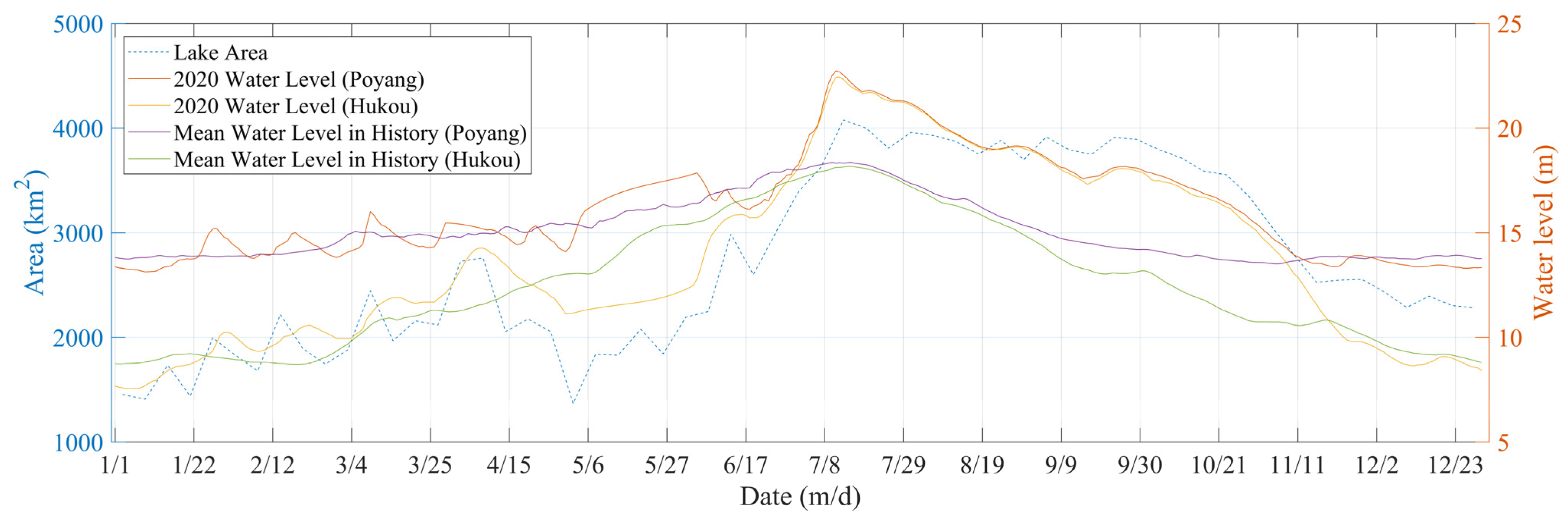
3.1.3. Using Inundation Models to Near-Real-Time Monitor
3.2. Potential Causes of Drought-Converted Flood Hazard
3.2.1. Hydrological Analysis
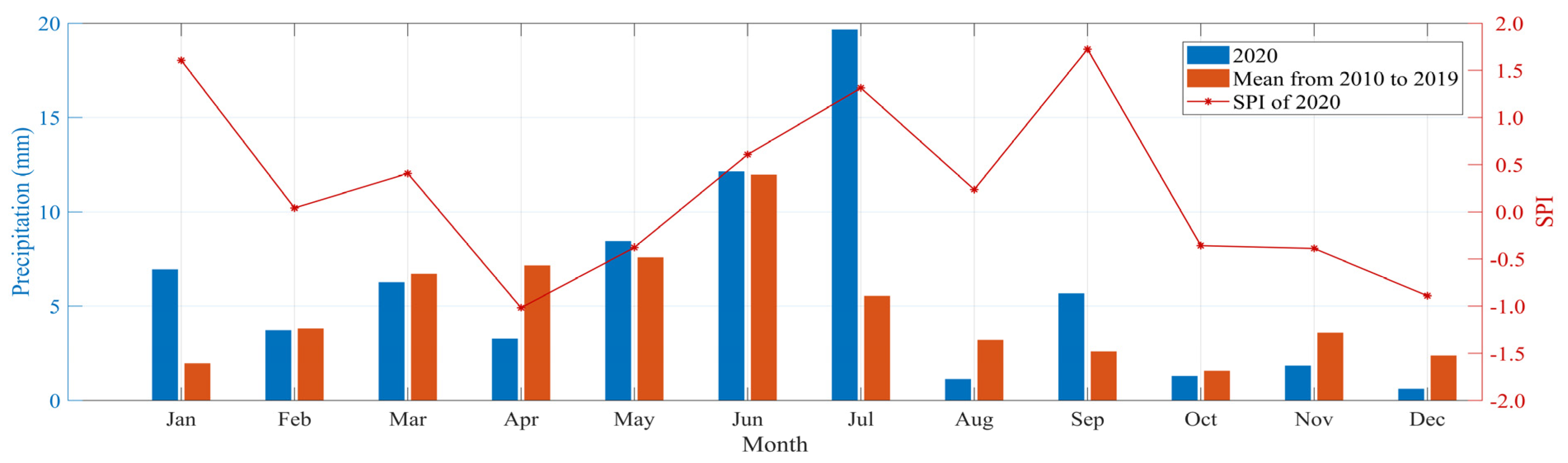
3.2.2. Meteorological Analysis
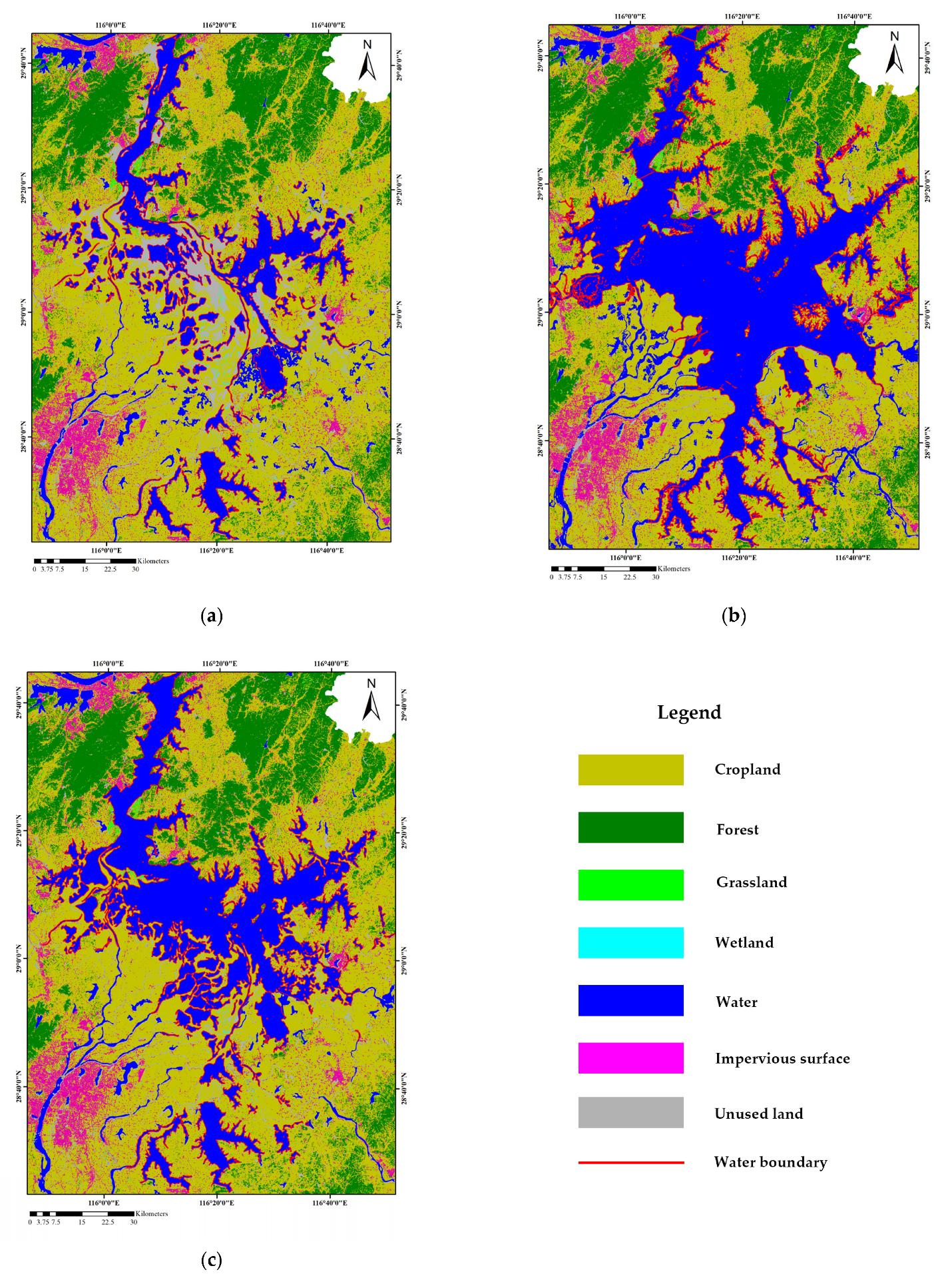
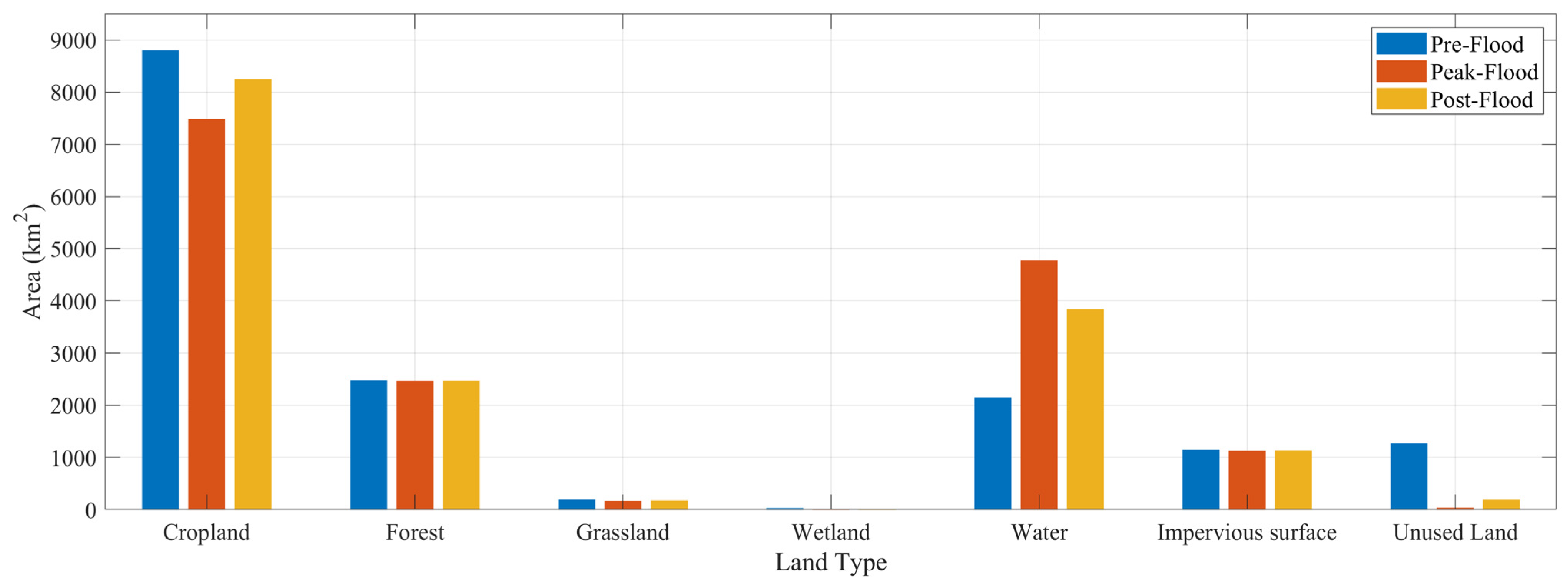
3.3. Flood Damage Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
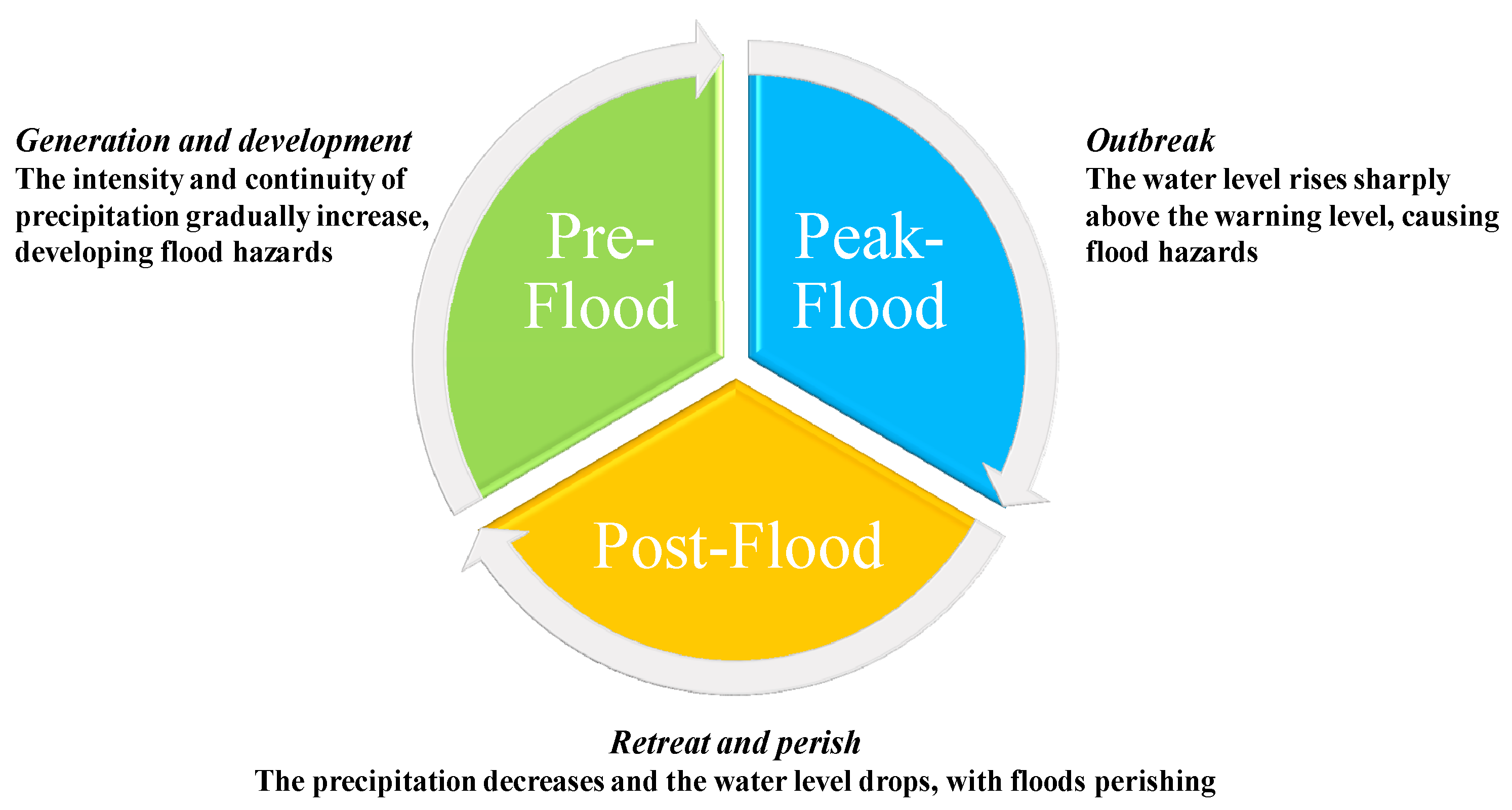
4.2. Flood Full Lifecycle Model
4.3. Drought-Converted Flood with Its Prevention and Mitigation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Chisenga, C.; Mahmood, S. The Riverine Flood Catastrophe in August 2010 in South Punjab, Pakistan: Potential Causes, Extent and Damage Assessment. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 14121–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.J.; Jongman, B.; Weiland, F.S.; Bouwman, A.; Van Beek, R.; Bierkens, M.F.; Ligtvoet, W.; Winsemius, H.C. Assessing flood risk at the global scale: Model setup, results, and sensitivity. Environ. Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 044019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, M.; Chen, A.; Djordjević, S.; Butler, D.; Mark, O. Urban flood impact assessment: A state-of-the-art review. Urban Water J. 2015, 12, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tate, E.; Strong, A.; Kraus, T.; Xiong, H. Flood recovery and property acquisition in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 2055–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J.; Cao, B.; Park, E.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W.; Tarolli, P. Flood Monitoring in Rural Areas of the Pearl River Basin (China) Using Sentinel-1 SAR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Lin, J. An investigation of the hydrological influence on the distribution and transition of wetland cover in a complex lake–floodplain system using time-series remote sensing and hydrodynamic simulation. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 125038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refice, A.; D’Addabbo, A.; Capolongo, D. Methods, Techniques and Sensors for Precision Flood Monitoring Through Remote Sensing. In Flood Monitoring through Remote Sensing; Refice, A., D’Addabbo, A., Capolongo, D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sanyal, J.; Lu, X.X. Application of Remote Sensing in Flood Management with Special Reference to Monsoon Asia: A Review. Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Akhtar, M.; Muhammad, S.; Paras, S.; Rahmatullah, J. Techniques of Remote Sensing and GIS for flood monitoring and damage assessment: A case study of Sindh province, Pakistan. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci. 2012, 15, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psomiadis, E.; Soulis, K.X.; Zoka, M.; Dercas, N. Synergistic Approach of Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques for Flash-Flood Monitoring and Damage Assessment in Thessaly Plain Area, Greece. Water 2019, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajjad, A.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; Chisenga, C.; Saleem, N.; Hassan, H. Operational Monitoring and Damage Assessment of Riverine Flood-2014 in the Lower Chenab Plain, Punjab, Pakistan, Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faisal, A.; Kafy, A.; Roy, S. Integration of remote sensing and GIS techniques for flood monitoring and damage assessment: A case study of naogaon district. Bangladesh J. Remote Sens. GIS 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Di, L.; Yu, E.G.; Kang, L.; Shrestha, R.; Rahman, S.; Tang, J.; Deng, M.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, C.; et al. A review of remote sensing in flood assessment. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fifth International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-Geoinformatics), Tianjin, China, 18–20 July 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, T.; Van Nguyen, N.; Kotera, A.; Ohno, H.; Ishitsuka, N.; Yokozawa, M. Detecting temporal changes in the extent of annual flooding within the Cambodia and the Vietnamese Mekong Delta from MODIS time-series imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 109, 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetti, M.; Nutini, F.; Manfron, G.; Brivio, P.A.; Nelson, A. Comparative Analysis of Normalised Difference Spectral Indices Derived from MODIS for Detecting Surface Water in Flooded Rice Cropping Systems. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sianturi, R.; Jetten, V.; Sartohadi, J. Mapping cropping patterns in irrigated rice fields in West Java: Towards mapping vulnerability to flooding using time-series MODIS imageries. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2018, 66, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.D.; Liou, Y.-A. Object-Based Flood Mapping and Affected Rice Field Estimation with Landsat 8 OLI and MODIS Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 5077–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, X.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Xie, H.; Chao, W.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Makhinov, A.; Makhinova, A.; Jiang, Y. An approach for flood monitoring by the combined use of Landsat 8 optical imagery and COSMO-SkyMed radar imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 136, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Du, C.; Mu, M.; Xu, J.; et al. Remote sensing monitoring of the suspended particle size in Hongze Lake based on GF-1 data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 3179–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Li, J.; Mo, W.; Luo, W.; Wu, D.; Gao, W.; Sun, C. Water depth retrieval models of East Dongting Lake, China, using GF-1 multi-spectral remote sensing images. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e01004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; He, H.; Chen, W.; Wang, L. Direct tangible damage assessment for regional snowmelt flood disasters with HJ-1 and HR satellite images: A case study of the Altay region, northern Xinjiang, China. Nat. Hazards 2018, 94, 1099–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, L.; Liao, M. Forty-year water body changes in Poyang Lake and the ecological impacts based on Landsat and HJ-1 A/B observations. J. Hydrol. 2020, 589, 125161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, E.; Lu, Z.; Suzuoki, Y.; Rangoonwala, A.; Werle, D. Monitoring Duration and Extent of Storm-Surge and Flooding in Western Coastal Louisiana Marshes With Envisat ASAR Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, Y.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Rahmoune, R. Flood monitoring using microwave passive remote sensing (AMSR-E) in part of the Brahmaputra basin, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4967–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Schmitt, M.; Li, L.; Zhu, X.X. Analysing changes of the Poyang Lake water area using Sentinel-1 synthetic aperture radar imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 7041–7069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yesou, H.; Huber, C.; Haouet, S.; Lai, X.; Huang, S.; De Fraipont, P.; Desnos, Y.L. Exploiting Sentinel 1 time series to monitor the largest fresh water bodies in PR China, the Poyang Lake. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 3882–3885. [Google Scholar]
- Yesou, H.; Pottier, E.; Mercier, G.; Grizonnet, M.; Haouet, S.; Giros, A.; Faivre, R.; Huber, C.; Michel, J. Synergy of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 imagery for wetland monitoring information extraction from continuous flow of sentinel images applied to water bodies and vegetation mapping and monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Beijing, China, 10–15 July 2016; pp. 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, B. Multitemporal Water Extraction of Dongting Lake and Poyang Lake Based on an Automatic Water Extraction and Dynamic Monitoring Framework. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, M.; Dong, J.; Sarmah, S.; You, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Doughty, R.; Xiao, X. Identifying floods and flood-affected paddy rice fields in Bangladesh based on Sentinel-1 imagery and Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 166, 278–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chan, N.W.; Pan, B.; Ge, X.; Yang, H. Mapping flood by the object-based method using backscattering coefficient and interference coherence of Sentinel-1 time series. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, X.; Di, L.; Guo, L.; Lin, L. An efficient classification method of fully polarimetric SAR image based on polarimetric features and spatial features. In Proceedings of the 2015 Fourth International Conference on Agro-Geoinformatics (Agro-geoinformatics), Istanbul, Turkey, 20–24 July 2015; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Toté, C.; Patricio, D.; Boogaard, H.; Van Der Wijngaart, R.; Tarnavsky, E.; Funk, C. Evaluation of Satellite Rainfall Estimates for Drought and Flood Monitoring in Mozambique. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1758–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, G.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Shen, B. A Preliminary Research on the Reason of a Sharp Turn from Drought to Flood in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River in Late Spring and Early Summer of 2011. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 1009–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.; Xue, C.; Zhang, D. Spatio-temporal variations of the drought-flood abrupt alternation events in the Lake Poyang Basin from 1960 to 2012. J. Lake Sci. 2020, 32, 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Q.; Xu, C.; Chen, J. A method to identify the drought-flood transition based on the meteorological drought index. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2019, 74, 2358–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.-B.; Wang, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.-J.; Hao, Y.-W.; Chen, Z.; Lin, D.-D.; Xu, J.; Xia, S.; Li, S.-Z. Potential impact of flooding on schistosomiasis in Poyang Lake regions based on multi-source remote sensing images. Parasites Vect. 2021, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Zhang, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; She, D.; Xia, J. Characteristics of dry-wet abrupt alternation events in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River Basin and the relationship with ENSO. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1039–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Lu, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, X.; Liu, H. Hydrodynamic and Inundation Modeling of China’s Largest Freshwater Lake Aided by Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4858–4879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Luo, Z.; Tangdamrongsub, N.; Zhou, Z.; He, L.; Xu, C.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y. Identifying Flood Events over the Poyang Lake Basin Using Multiple Satellite Remote Sensing Observations, Hydrological Models and In Situ Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Gong, J.; Sun, K.; Yin, J.; Chen, X. Estimation of Soil Moisture Index Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 Images over Poyang Lake Ungauged Zone. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.-C.; Werner, A.; Li, Y.-L.; Yao, J.; Li, X.; Xu, C.-Y. An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang Lake: Comparison of Yangtze River and local catchment impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Chunyu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qian, B.; Zhao, D.; Xia, Z. Impacts of Streamflow and Topographic Changes on Water Level during the Dry Season of Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2020, 25, 05020001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Keim, B.D.; Song, J. Flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region: Trends and teleconnections. Int. J. Clim. 2006, 26, 1255–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shankman, D.; Liang, Q. Landscape Changes and Increasing Flood Frequency in China’s Poyang Lake Region. Prof. Geogr. 2003, 55, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geudtner, D.; Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Davidson, M.; Rommen, B. Sentinel-1 System capabilities and applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 13–18 July 2014; pp. 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Snoeij, P.; Geudtner, D.; Bibby, D.; Davidson, M.; Attema, E.; Potin, P.; Rommen, B.; Floury, N.; Brown, M.; et al. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-based flood mapping: A fully automated processing chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, F.C.; Muñoz, M.D.M. Flood Monitoring Based on the Study of Sentinel-1 SAR Images: The Ebro River Case Study. Water 2019, 11, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, B. Operational Flood Detection Using Sentinel-1 SAR Data over Large Areas. Water 2019, 11, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, S.; Ruan, R.; Yan, M.; She, Y. Extraction of Hongze Lake Reclamation Area Based on RADARSAT SAR and LANDSAT ETM. In 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology Esiat 2011; Wu, Y., Ed.; Procedia Environmental Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 10, Pt C; pp. 2294–2300. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Jang, H.; Kim, N.; Sohn, H.-G. Water Area Extraction Using RADARSAT SAR Imagery Combined with Landsat Imagery and Terrain Information. Sensors 2015, 15, 6652–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, J. Image Segmentation Based on 2D Otsu Method with Histogram Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering, Wuhan, China, 12–14 December 2008; Volume 6, pp. 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, R.; Tormos, T.; Danis, P. Geographic object based image analysis using very high spatial and temporal resolution radar and optical imagery in tracking water level fluctuations in a freshwater reservoir. South-East. Eur. J. Earth Obs. Geomat. 2014, 3, 287–291. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Wang, G.; Amankwah, S.O.Y.; Wei, X.; Hu, Y.; Feng, A. Monitoring the summer flooding in the Poyang Lake area of China in 2020 based on Sentinel-1 data and multiple convolutional neural networks. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 102, 102400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.V.; Kling, H. On typical range, sensitivity, and normalization of Mean Squared Error and Nash-Sutcliffe Efficiency type metrics. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Boston, MA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; Volume 17, pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sudheer, K.P.; Bhallamudi, S.M.; Narasimhan, B.; Thomas, J.; Bindhu, V.M.; Vema, V.K.; Kurian, C. Role of Dams on the Floods of August 2018 in Periyar River Basin, Kerala. Curr. Sci. 2019, 116, 780–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortajada, C. Dams: An Essential Component of Development. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Satellite | Product Level | Product Type | Instrument Mode | Polarization | Start Relative Orbit | Stop Relative Orbit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 A | Level-1 | GRD | IW | VV, VH | 40 | 40 |
| Sentinel-1 B | Level-1 | GRD | IW | VV, VH | 40 | 40 |
| Month | Maximum | Minimum | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previous | 2020 | Previous | 2020 | |
| May | 17.76 | 12.15 | 8.42 | 11.12 |
| June | 19.91 | 17.65 | 9.90 | 12.22 |
| July | 21.30 | 22.43 | 13.59 | 17.85 |
| August | 20.02 | 21.09 | 12.88 | 18.94 |
| September | 17.00 | 18.95 | 9.79 | 17.30 |
| October | 15.83 | 17.91 | 8.00 | 15.23 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, Q.; Wu, Y. Full Lifecycle Monitoring on Drought-Converted Catastrophic Flood Using Sentinel-1 SAR: A Case Study of Poyang Lake Region during Summer 2020. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173485
Yang H, Wang H, Lu J, Zhou Z, Feng Q, Wu Y. Full Lifecycle Monitoring on Drought-Converted Catastrophic Flood Using Sentinel-1 SAR: A Case Study of Poyang Lake Region during Summer 2020. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(17):3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173485
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Haoxiao, Hongxian Wang, Jianzhong Lu, Zhenzhong Zhou, Qi Feng, and Yue Wu. 2021. "Full Lifecycle Monitoring on Drought-Converted Catastrophic Flood Using Sentinel-1 SAR: A Case Study of Poyang Lake Region during Summer 2020" Remote Sensing 13, no. 17: 3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173485
APA StyleYang, H., Wang, H., Lu, J., Zhou, Z., Feng, Q., & Wu, Y. (2021). Full Lifecycle Monitoring on Drought-Converted Catastrophic Flood Using Sentinel-1 SAR: A Case Study of Poyang Lake Region during Summer 2020. Remote Sensing, 13(17), 3485. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13173485







