Vegetation Dynamics and Climatological Drivers in Ethiopia at the Turn of the Century
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
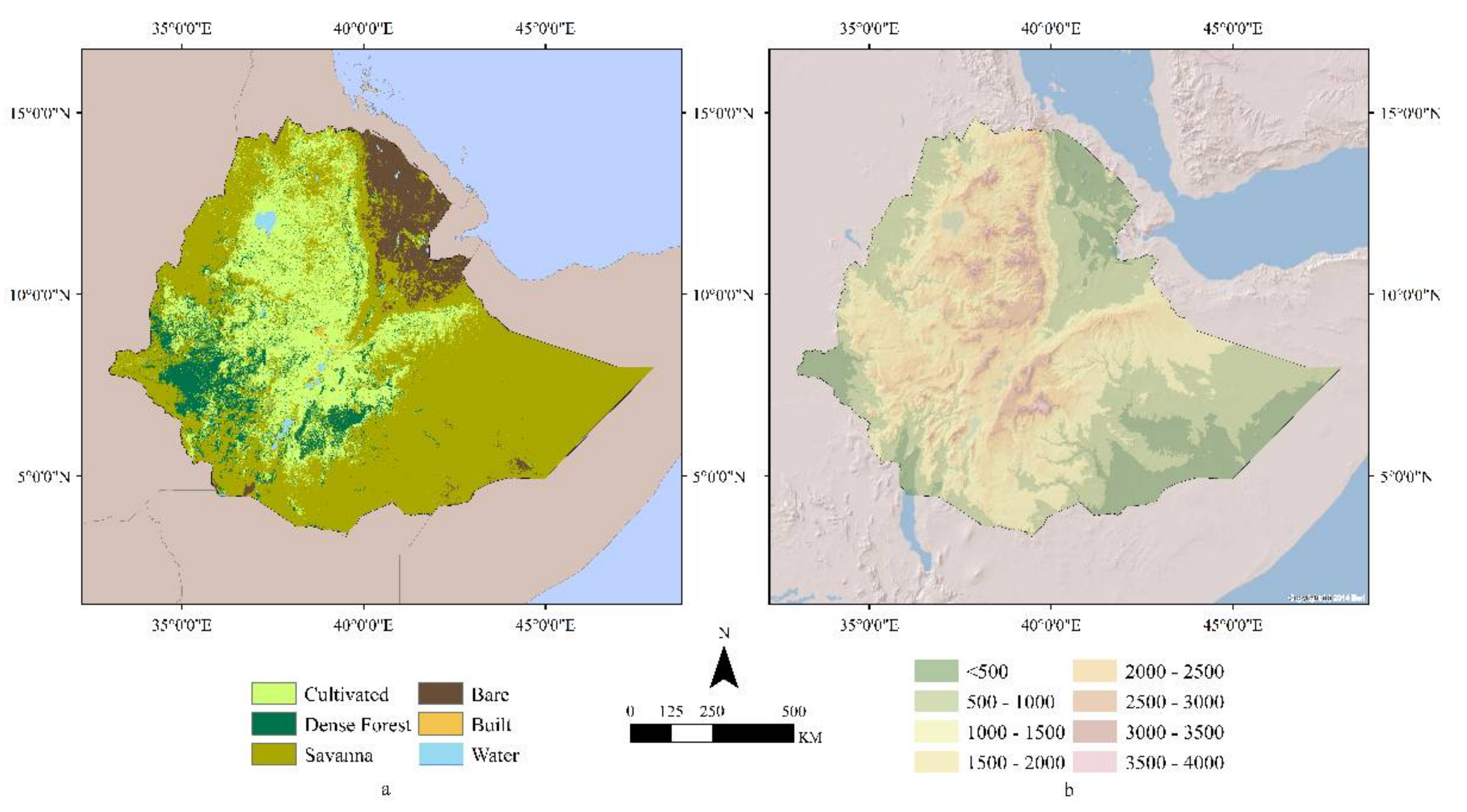
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Methodological Approach
2.2.1. NDVI Data and Directional Persistence Calculation
2.2.2. Climatic Data and Spatial Panel Regression Models
3. Results
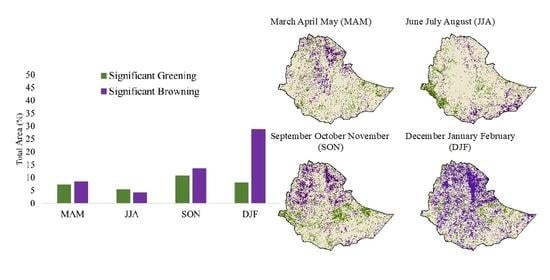
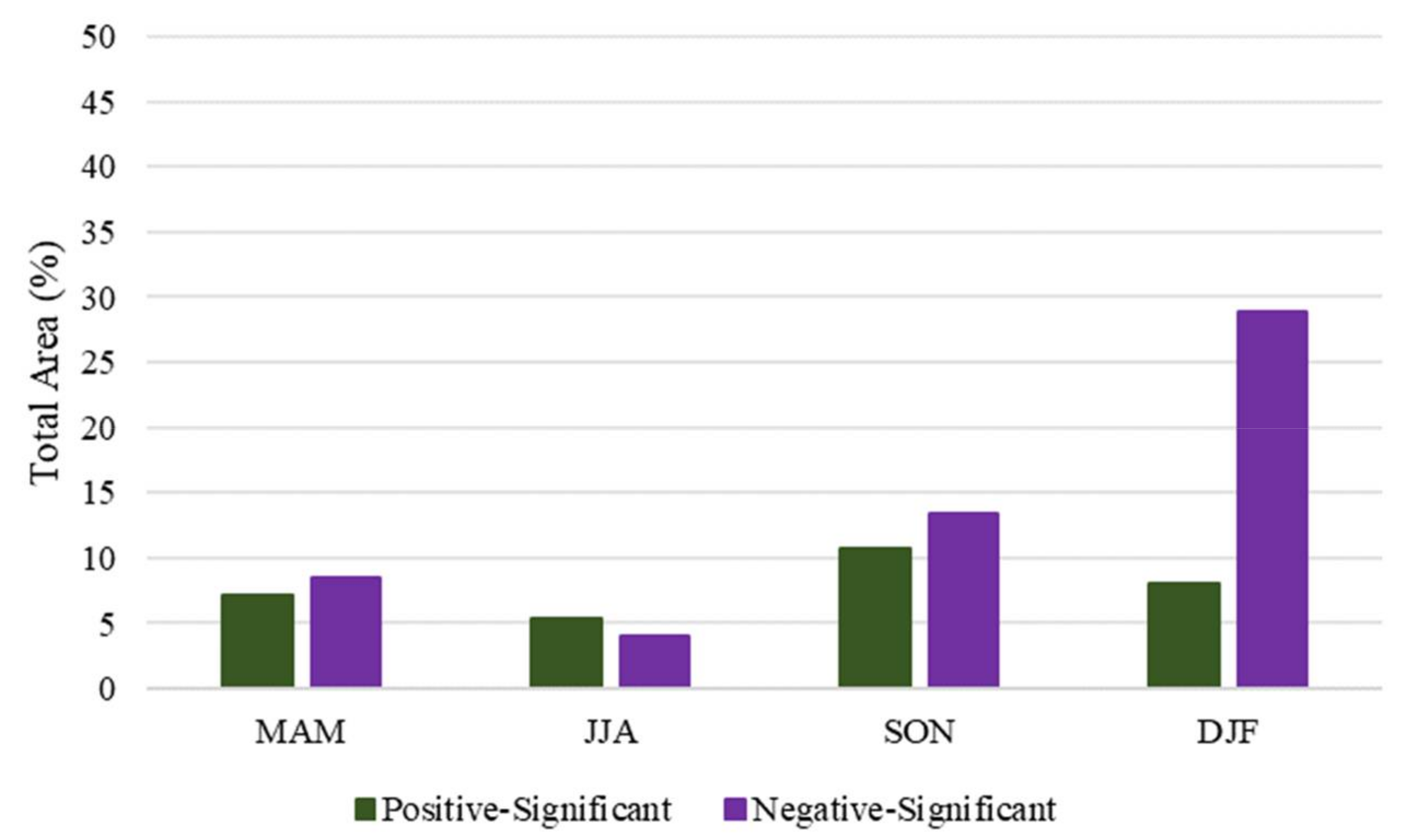
3.1. Directional Persistence Analysis
3.2. Spatial Panel Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roerink, G.J.; Menenti, M.; Soepboer, W.; Su, Z. Assessment of climate impact on vegetation dynamics by using remote sensing. Appl. Quant. Remote Sens. Hydrol. 2003, 28, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Pan, N.; Feng, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, C. Vegetation dynamic trends and the main drivers detected using the ensemble empirical mode decomposition method in East Africa. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2542–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiter, S.; Higgins, S.I. Impacts of climate change on the vegetation of Africa: An adaptive dynamic vegetation modelling approach. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2224–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdeczny, O.; Adams, S.; Baarsch, F.; Coumou, D.; Robinson, A.; Hare, W.; Schaeffer, M.; Perrette, M.; Reinhardt, J. Climate change impacts in Sub-Saharan Africa: From physical changes to their social repercussions. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2017, 17, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, P.; Neilson, R.P.; Lenihan, J.M.; Drapek, R.J. Global patterns in the vulnerability of ecosystems to vegetation shifts due to climate change. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwendwa, M.; Begashaw, B. Drylands of Africa Pose Unique Challenge to Achieving MDGs; Columbia Cimate School: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin, J.; Jayne, T.S.; Headey, D. Scarcity amidst abundance? Reassessing the potential for cropland expansion in Africa. Food Policy 2014, 48, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zewdie, W.; Csaplovics, E.; Inostroza, L. Monitoring ecosystem dynamics in northwestern Ethiopia using NDVI and climate variables to assess long term trends in dryland vegetation variability. Appl. Geogr. 2017, 79, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerretelli, S.; Poggio, L.; Gimona, A.; Yakob, G.; Boke, S.; Habte, M.; Coull, M.; Peressotti, A.; Black, H. Spatial assessment of land degradation through key ecosystem services: The role of globally available data. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628, 539–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dardel, C.; Kergoat, L.; Hiernaux, P.; Mougin, E.; Grippa, M.; Tucker, C.J. Re-greening Sahel: 30 years of remote sensing data and field observations (Mali, Niger). Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Anyamba, A.; Tucker, C.J. Recent trends in vegetation dynamics in the African Sahel and their relationship to climate. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2005, 15, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickler, T.; Eklundh, L.; Seaquist, J.W.; Smith, B.; Ardö, J.; Olsson, L.; Sykes, M.T.; Sjöström, M. Precipitation controls Sahel greening trend. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, N.; Feng, X.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Ji, F.; Pan, S. Increasing global vegetation browning hidden in overall vegetation greening: Insights from time-varying trends. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Bai, X.; Tan, Q.; Li, Q.; Wu, L.; Tian, S.; Hu, Z.; Li, C.; Deng, Y. Factors Affecting Long-Term Trends in Global NDVI. Forests 2019, 10, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalisa, W.; Igbawua, T.; Henchiri, M.; Ali, S.; Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J. Assessment of climate impact on vegetation dynamics over East Africa from 1982 to 2015. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camberlin, P.; Martiny, N.; Philippon, N.; Richard, Y. Determinants of the interannual relationships between remote sensed photosynthetic activity and rainfall in tropical Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Motesharrei, S. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Global NDVI Trends: Correlations with Climate and Human Factors. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13233–13250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamali, S.; Seaquist, J.; Ardö, J.; Eklundh, L. Investigating temporal relationships between rainfall, soil moisture and MODIS-derived NDVI and EVI for six sites in Africa. In Proceedings of the 34th International Symposium on Remote Sensing of Environment, Sydney, Australia, 10–15 April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mucheye, T.; Tebkew, M.; Mariam, Y.G.; Abich, A. Long-term dynamics of woodland vegetation with response of climate variability in the lowlands of north western part of Ethiopia. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 23, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyum, Z.; Ayoade, L.O.; Onilude, M.A.; Feyissa, M. Analysis of Vegetation Dynamics and Responses to Inter-annual Changes of Climatic Variables in Dry Afromontane Forest Fragments, Northern Ethiopia. Am. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 2018, 7, 133–144. [Google Scholar]
- Chamaille-Jammes, S.; Fritz, H.; Murindagomo, F. Spatial patterns of the NDVI-rainfall relationship at the seasonal and interannual time scales in an African savanna. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5185–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, M.L.; Nicholson, S.E. On the Relation between Rainfall and the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index for Diverse Vegetation Types in East-Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 2369–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoungrana, B.J.-B.; Conrad, C.; Amekudzi, L.K.; Thiel, M.; Da, E.D. Land Use/Cover Response to Rainfall Variability: A Comparing Analysis between NDVI and EVI in the Southwest of Burkina Faso. Climate 2015, 3, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Workie, T.G.; Debella, H.J. Climate change and its effects on vegetation phenology across ecoregions of Ethiopia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2018, 13, e00366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xie, Y.; Brown, D.G.; Bai, Y.; Hua, J.; Judd, K. Spatial variability of the adaptation of grassland vegetation to climatic change in Inner Mongolia of China. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M. Geographical weighting as a further refinement to regression modelling: An example focused on the NDVI-rainfall relationship. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 88, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georganos, S.; Abdi, A.M.; Tenenbaum, D.E.; Kalogirou, S. Examining the NDVI-rainfall relationship in the semi-arid Sahel using geographically weighted regression. J. Arid. Environ. 2017, 146, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Peters, A.J. A spatial regression procedure for evaluating the relationship between AVHRR-NDVI and climate in the northern Great Plains. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, W. A spatial panel data analysis of China’s urban land expansion, 2004–2014. Pap. Reg. Sci. 2019, 98, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller-Rushing, A.J.; Inouye, D.W.; Primack, R.B. How well do first flowering dates measure plant responses to climate change? The effects of population size and sampling frequency. J. Ecol. 2008, 96, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Kaufmann, R.K. Modeling the drivers of urban land use change in the Pearl River Delta, China: Integrating remote sensing with socioeconomic data. Land Econ. 2003, 79, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Byerlee, D.; Spielman, D.; Alemu, D.; Gautam, M. Policies to Promote Cereal Intensification in Ethiopia: A Review of Evidence and Experience; International Food and Policy Research Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Simane, B.; Beyene, H.; Deressa, W.; Kumie, A.; Berhane, K.; Samet, J. Review of Climate Change and Health in Ethiopia: Status and Gap Analysis. Ethiop. J. Health Dev. 2016, 30, 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, Y.-A.; Mulualem, G.M. Spatio-temporal Assessment of Drought in Ethiopia and the Impact of Recent Intense Droughts. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunting, E.L.; Southworth, J.; Herrero, H.; Ryan, S.J.; Waylen, P. Understanding Long-Term Savanna Vegetation Persistence across Three Drainage Basins in Southern Africa. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, H.; Waylen, P.; Southworth, J.; Khatami, R.; Yang, D.; Child, B. A Healthy Park Needs Healthy Vegetation: The Story of Gorongosa National Park in the 21st Century. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Southworth, J.; Zhu, L.; Bunting, E.; Ryan, S.J.; Herrero, H.; Waylen, P.R.; Hill, M.J. Changes in vegetation persistence across global savanna landscapes, 1982–2010. J. Land Use Sci. 2016, 11, 7–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.; Southworth, J.; Waylen, P. Spatial persistence and temporal patterns in vegetation cover across Florida, 1982–2006. Phys. Geogr. 2014, 35, 151–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Michaelsen, J.; Marshall, M. Mapping Recent Decadal Climate Variations in Precipitation and Temperature across Eastern Africa and the Sahel; Wardlow, B., Anderson, M., Verdin, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Small Family Farms; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nationas: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ayele, E.G.; Tebeje, A.; Demissie, S.; Belete, M.; Jemberrie, M.; Teshome, W.; Megistu, D.; Teshale, E. Time Series Land Cover Mapping and Change Detection Analysis Using Geographic Information System and Remote Sensing, Northern Ethiopia. Air Soil Water Res. 2018, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tolessa, T.; Senbeta, F.; Kidane, M. The impact of land use/land cover change on ecosystem services in the central highlands of Ethiopia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 23, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaw, T.; Bantider, A.; Silassie, H.G. Land degradation in Ethiopia: Causes, impacts and rehabilitation techniques. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Tesfahunegn, G.B. Farmers’ perception on land degradation in northern Ethiopia: Implication for developing sustainable land management. Soc. Sci. J. 2019, 56, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazin, B.; Sterk, G. Drought vulnerability drives land-use and land cover changes in the Rift Valley dry lands of Ethiopia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. Arable Land (% of Land Area)–Ethiopia|Data; World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Khatami, R.; Southworth, J.; Muir, C.; Caughlin, T.; Ayana, A.N.; Brown, D.G.; Liao, C.; Agrawal, A. Operational Large-Area Land-Cover Mapping: An Ethiopia Case Study. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebru, T. Deforestation in Ethiopia: Causes, impacts, and remedy. Int. J. Eng. Dev. Res. 2016, 4, 204. [Google Scholar]
- Shekuru, A.H.; Berlie, A.B.; Bizuneh, Y.K. Variability and Trends of Temperature and Rainfall over Three Agro-Ecological Zones in North Shewa, Central Ethiopia. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-53268/v1 (accessed on 25 June 2021).
- Diro, G.T.; Black, E.; Grimes, D.I.F. Seasonal forecasting of Ethiopian spring rains. Meteorol. Appl. 2008, 15, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagesho, N.; Goel, N.K.; Jain, M.K. Temporal and spatial variability of annual and seasonal rainfall over Ethiopia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 354–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleshi, Y.; Zanke, U. Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int. J. Climatol. 2004, 24, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, B. Seasonal Drought in the Greater Horn of Africa and Its Recent Increase during the March May Long Rains. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 7953–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, D.; Schipper, E.L.F. Adaptation to climate change in Africa: Challenges and opportunities identified from Ethiopia. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2011, 21, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, I.; Ruppel, O.C.; Abdrabo, M.A.; Essel, A.; Lennard, C.; Padgham, J.; Urquhart, P. Climate Change 2014: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Part B: Regional Aspects. Contribution of Working Group II to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Waylen, P.; Southworth, J.; Gibbes, C.; Tsai, H. Time Series Analysis of Land Cover Change: Developing Statistical Tools to Determine Significance of Land Cover Changes in Persistence Analyses. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4473–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero, H.; Southworth, J.; Muir, C.; Khatami, R.; Bunting, E.; Child, B. An Evaluation of Vegetation Health in and around Southern African National Parks during the 21st Century (2000–2016). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forkel, M.; Carvalhais, N.; Verbesselt, J.; Mahecha, M.D.; Neigh, C.S.R.; Reichstein, M. Trend Change Detection in NDVI Time Series: Effects of Inter-Annual Variability and Methodology. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 2113–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibbes, C.; Southworth, J.; Waylen, P.; Child, B. Climate variability as a dominant driver of post-disturbance savanna dynamics. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 53, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, D.O.; Prince, S.D. Rainfall and foliar dynamics in tropical southern Africa: Potential impacts of global climatic change on savanna vegetation. Clim. Chang. 1996, 33, 69–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E. Climatic and environmental change in Africa during the last two centuries. Clim. Res. 2001, 17, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dinku, T.; Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Maidment, R.; Tadesse, T.; Gadain, H.; Ceccato, P. Validation of the CHIRPS satellite rainfall estimates over eastern Africa. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018, 144, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousvel, S.; Armand, N.; Andre, L.; Tengeleng, S.; Alain, T.S.; Armel, K. Comparison between Vegetation and Rainfall of Bioclimatic Ecoregions in Central Africa. Atmosphere 2013, 4, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Peterson, S.; Shukla, S.; Davenport, F.; Michaelsen, J.; Knapp, K.R.; Landsfeld, M.; Husak, G.; Harrison, L.; et al. A High-Resolution 1983-2016 T-max Climate Data Record Based on Infrared Temperatures and Stations by the Climate Hazard Center. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 5639–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhorst, J.P. Specification and estimation of spatial panel data models. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 2003, 26, 244–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debarsy, N.; Ertur, C. Testing for spatial autocorrelation in a fixed effects panel data model. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2010, 40, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeSage, J.P.; Pace, R.K. Spatial Econometric Models; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Belotti, F.; Hughes, G.; Mortari, A.P. Spatial panel-data models using Stata. Stata J. 2017, 17, 139–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golgher, A.B.; Voss, P.R. How to Interpret the Coefficients of Spatial Models: Spillovers, Direct and Indirect Effects. Spat. Demogr. 2016, 4, 175–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiemela, S.N.; Noulekoun, F.; Zenebe, A.; Abadi, N.; Birhane, E. Transformation of degraded farmlands to agroforestry in Zongi Village, Ethiopia. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 1317–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emiru, H.; Mohammed, A. Anthropogenic impact on land use land cover: Influence on weather and vegetation in Bambasi Wereda, Ethiopia. Spat. Inf. Res. 2018, 26, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefa, G.; Frankl, A.; Lanckriet, S.; Biadgilgn, D.; Gebreyohannes, Z.; Amanuel, Z.; Poesen, J.; Nyssen, J. Changes in land use/cover mapped over 80 years in the Highlands of Northern Ethiopia. J. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 1538–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, X.-P.; Hansen, M.C.; Stehman, S.V.; Potapov, P.V.; Tyukavina, A.; Vermote, E.F.; Townshend, J.R. Global land change from 1982 to 2016. Nature 2018, 560, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassawmar, T.; Zeleke, G.; Bantider, A.; Gessesse, G.D.; Abraha, L. A synoptic land change assessment of Ethiopia’s Rainfed Agricultural Area for evidence-based agricultural ecosystem management. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Connor, T.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Climate variability and trends at a national scale. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawinkel, P.; Thiery, W.; Lhermitte, S.; Swinnen, E.; Verbist, B.; van Orshoven, J.; Muys, B. Vegetation response to precipitation variability in East Africa controlled by biogeographical factors. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 121, 2422–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campo-Bescós, M.A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Kaplan, D.A.; Southworth, J.; Zhu, L.; Waylen, P.R. Beyond Precipitation: Physiographic Gradients Dictate the Relative Importance of Environmental Drivers on Savanna Vegetation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedallu, C.; Chéret, V.; Denux, J.P.; Perez, V.; Azcona, J.S.; Seynave, I.; Gégout, J.C. Soil and climate differently impact NDVI patterns according to the season and the stand type. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2874–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, L.; Barbosa, H.; Bhadwal, S.; Cowie, A.; Delusca, K.; Flores-Renteria, D.; Hermans, K.; Jobbagy, E.; Kurz, W.; Li, D.; et al. Climate Change and Land: An IPCC Special Report on Climate Change, Desertification, Land Degradation, Sustainable Land Management, Food Security, and Greenhouse Gas Fluxes in Terrestrial Ecosystems. 2019. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/srccl/ (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- World Bank. Ethiopia–A Country Study on the Economic Impacts of Climate Change; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sessions, D.N.; Stevans, L.K. Investigating omitted variable bias in regression parameter estimation: A genetic algorithm approach. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2006, 50, 2835–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, M.; Cao, M.; He, Y.; Mekonnen, E.; Song, X.; Yang, J. Ethiopian vegetation types, climate and topography. Plant Divers. 2020, 42, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNFCCC. Ethiopia’s Second National Communication to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change; Ministry of Environment and Forest: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, D.A.; Chun, Y. Spatial Autocorrelation and Uncertainty Associated with Remotely-Sensed Data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Nonspatial Model | Quasi-Spatial Model | Spatial Panel Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | |
| Precipitation | 0.0630 *** (0.0019) | 0.0893 *** (0.0014) | 0.0049 *** (0.0015) | 0.0070 *** (0.0005) | 0.0050 *** (0.0012) | 0.0071 *** (0.0005) |
| Temperature | −0.0614 *** (0.0094) | −0.1732 *** (0.0057) | −0.2827 *** (0.0341) | −0.2426 *** (0.0158) | −0.2900 *** (0.0355) | −0.2504 *** (0.0155) |
| 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.94 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.19 | |
| Precipitation θ | - | - | - | - | 0.0002 (0.0010) | −0.0019 (0.0009) |
| Temperature θ | - | - | - | - | 0.0426 (0.0278) | 0.0611 * (0.0241) |
| NDVI ρ | - | - | - | - | 0.0495 *** (0.0081) | 0.1823 *** (0.0098) |
| N | 6919 | 25,806 | 6919 | 25,806 | 6919 | 25,806 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muir, C.; Southworth, J.; Khatami, R.; Herrero, H.; Akyapı, B. Vegetation Dynamics and Climatological Drivers in Ethiopia at the Turn of the Century. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163267
Muir C, Southworth J, Khatami R, Herrero H, Akyapı B. Vegetation Dynamics and Climatological Drivers in Ethiopia at the Turn of the Century. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(16):3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163267
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuir, Carly, Jane Southworth, Reza Khatami, Hannah Herrero, and Berkay Akyapı. 2021. "Vegetation Dynamics and Climatological Drivers in Ethiopia at the Turn of the Century" Remote Sensing 13, no. 16: 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163267
APA StyleMuir, C., Southworth, J., Khatami, R., Herrero, H., & Akyapı, B. (2021). Vegetation Dynamics and Climatological Drivers in Ethiopia at the Turn of the Century. Remote Sensing, 13(16), 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13163267